CD14+-Monocytes Exposed to Apolipoprotein CIII Express Tissue Factor
Abstract
1. Introduction
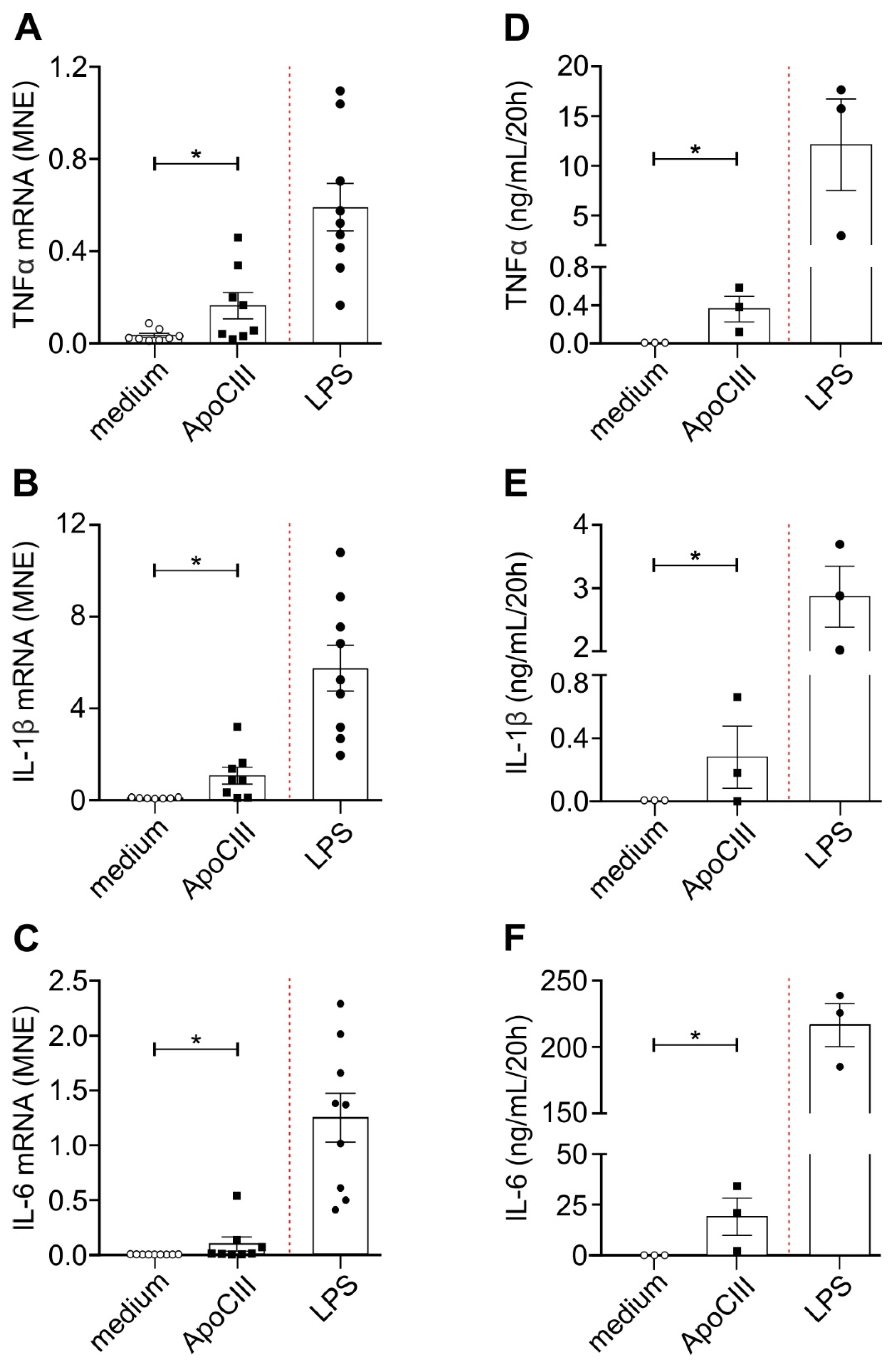
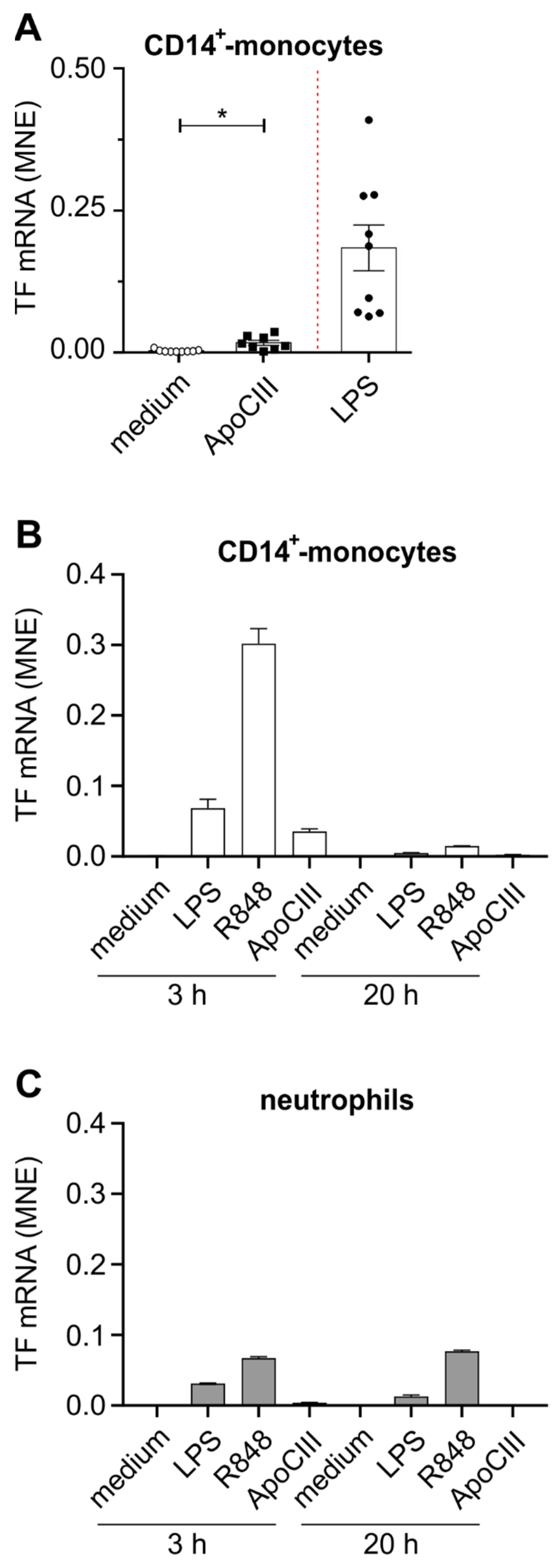
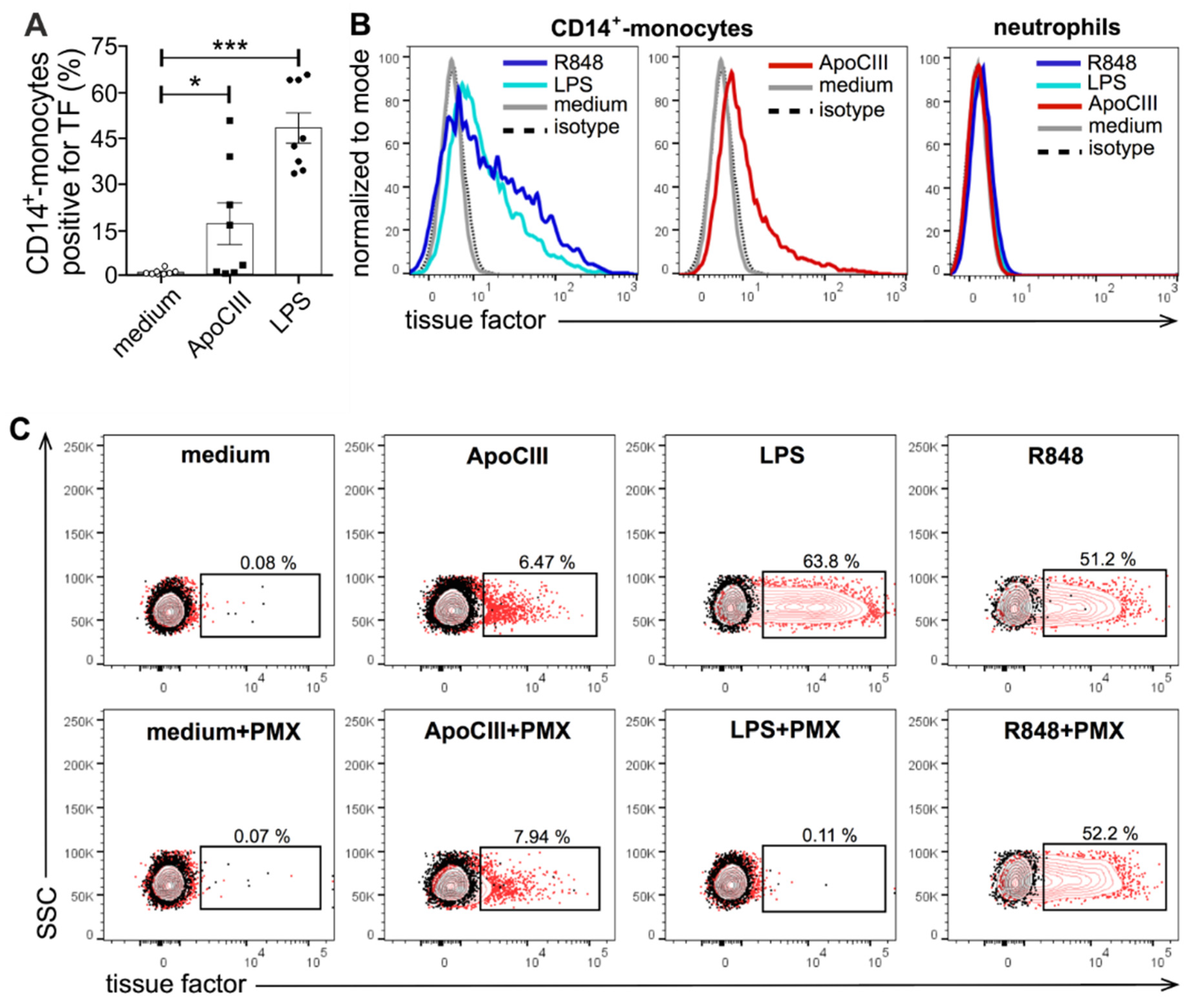
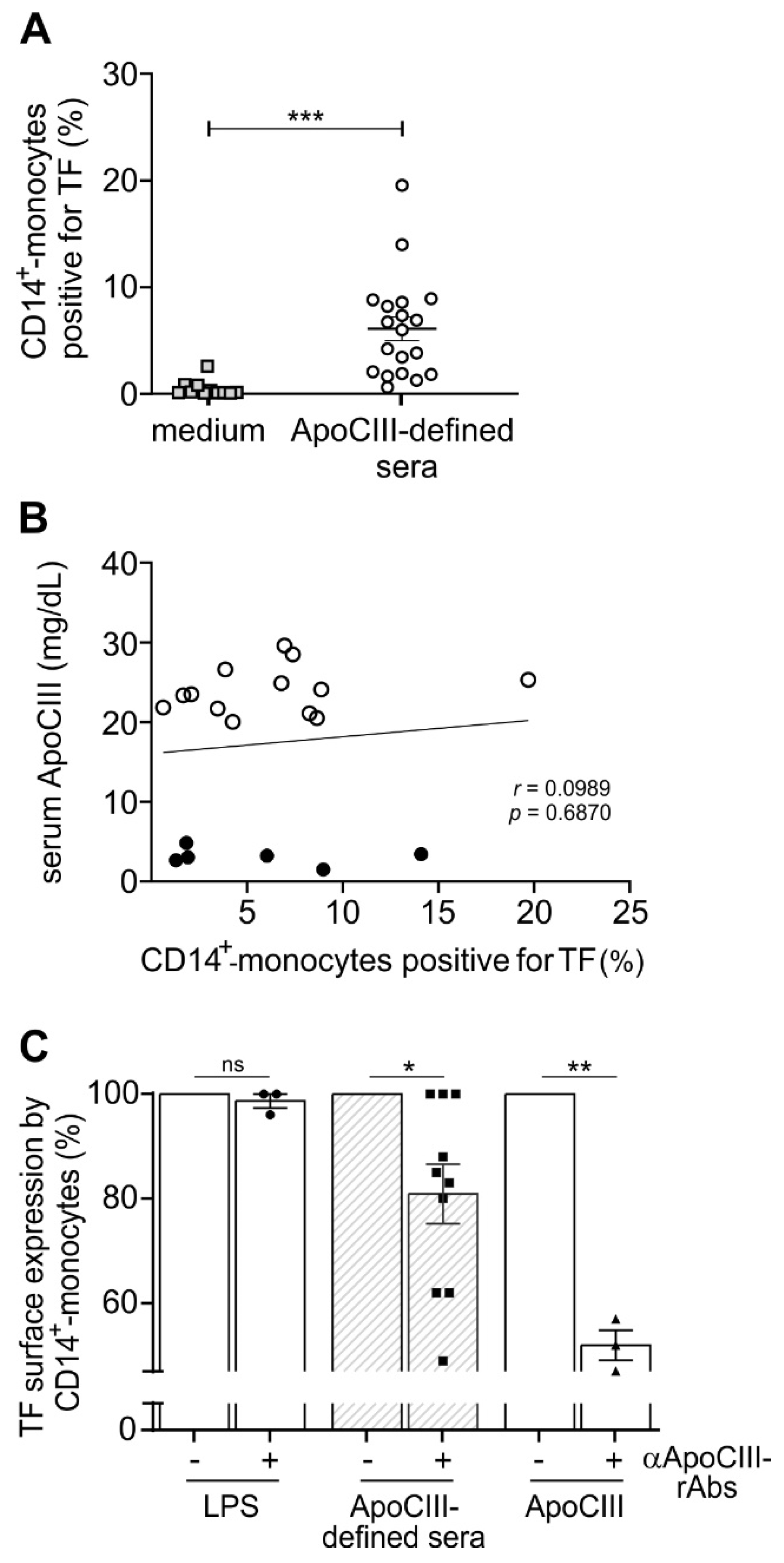
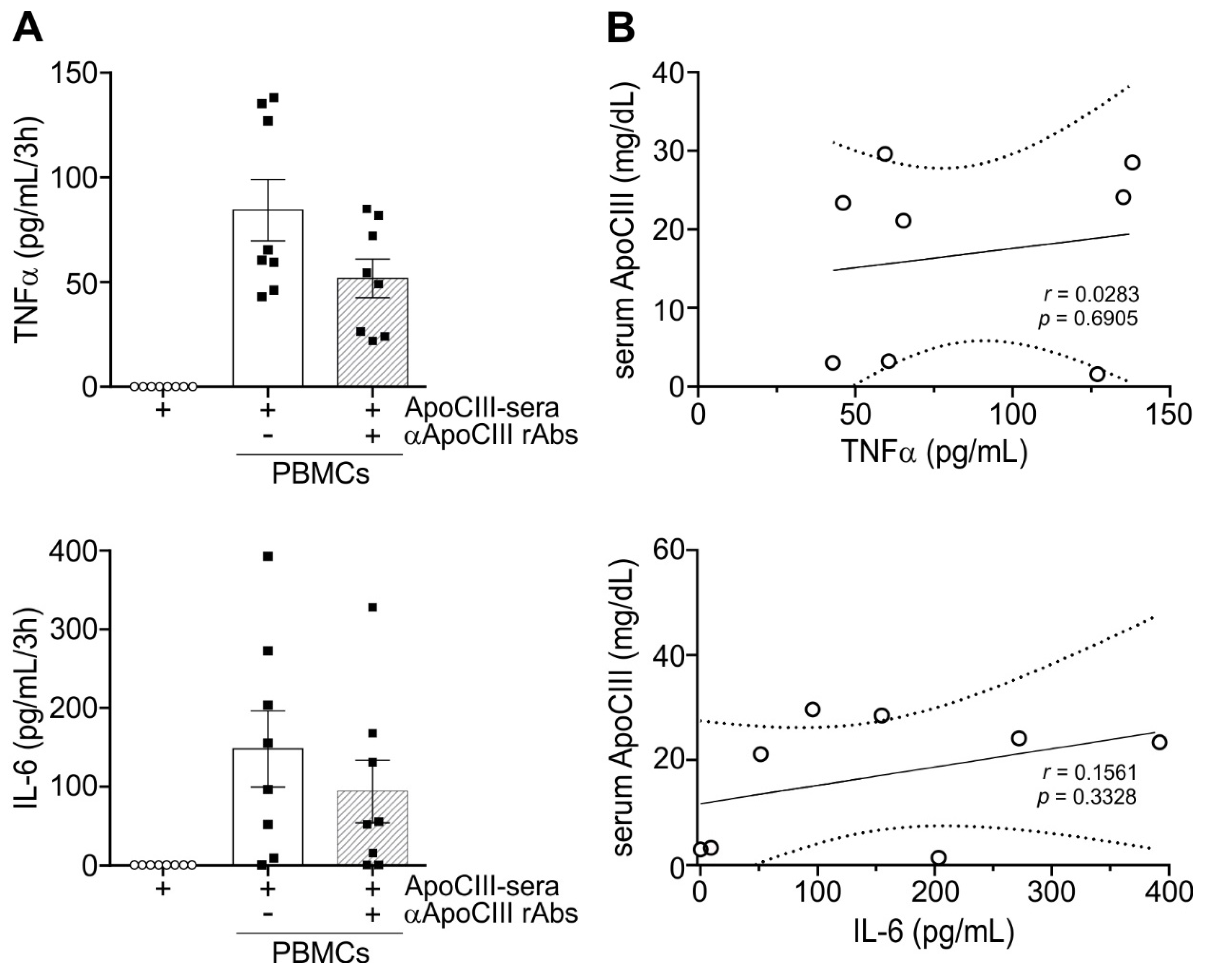
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Purification and Culture
4.3. RNA Purification and RT-Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.5. Detection of Extracellular Cytokines
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ooi, E.M.M.; Barrett, P.H.R.; Chan, D.C.; Watts, G.F. Apolipoprotein C-III: Understanding an emerging cardiovascular risk factor. Clin. Sci. 2008, 114, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dib, I.; Khalil, A.; Chouaib, R.; El-Makhour, Y.; Noureddine, H. Apolipoprotein C-III and cardiovascular diseases: When genetics meet molecular pathologies. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Ballmoos, M.C.W.; Haring, B.; Sacks, F.M. The risk of cardiovascular events with increased apolipoprotein CIII: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2015, 9, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, A.; Aikawa, M.; Alcaide, P.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Libby, P.; Sacks, F.M. Apolipoprotein CIII Induces Expression of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 in Vascular Endothelial Cells and Increases Adhesion of Monocytic Cells. Circulation 2006, 114, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, A.; Osaka, M.; Tani, M.; Azuma, H.; Sacks, F.M.; Shimokado, K.; Yoshida, M. Apolipoprotein CIII Links Hyperlipidemia With Vascular Endothelial Cell Dysfunction. Circulation 2008, 118, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, H.; Chu, S.; Zhong, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Ren, X.; Yu, J. APOC3 induces endothelial dysfunction through TNF-α and JAM-1. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2016, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewinger, S.; Reiser, J.; Jankowski, V.; AlAnsary, D.; Hahm, E.; Triem, S.; Klug, M.; Schunk, S.J.; Schmit, D.; Kramann, R.; et al. Apolipoprotein C3 induces inflammation and organ damage by alternative inflammasome activation. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 21, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, D.M.; Key, N.S. The tissue factor-factor VIIa complex: Procoagulant activity, regulation, and multitasking. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, P.; Nilsson, L.; Karpe, F.; Hamsten, A. Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Response Element in the Promoter Region of the Human Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Gene Implicated in the Impaired Fibrinolysis of Hypertriglyceridemia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Kaneko, T.; Wakita, Y.; Minamikawa, K.; Nagaya, S.; Tamaki, S.; Deguchi, K.; Shirakawa, S. Effect of lipoproteins on tissue factor activity and PAI-II antigen in human monocytes and macrophages. Int. J. Cardiol. 1994, 47, S21–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, O.; Martinelli, N.; Girelli, D.; Pizzolo, F.; Friso, S.; Beltrame, F.; Lotto, V.; Annarumma, L.; Corrocher, R. Apolipoprotein C-III predicts cardiovascular mortality in severe coronary artery disease and is associated with an enhanced plasma thrombin generation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 8, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, O.; Martinelli, N.; Baroni, M.; Branchini, A.; Girelli, D.; Friso, S.; Pizzolo, F.; Bernardi, F. Factor II Activity is Similarly Increased in Patients With Elevated Apolipoprotein CIII and in Carriers of the Factor II 20210A Allele. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2013, 2, e000440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, O.; Turcato, G.; Moruzzi, S.; Castagna, A.; Girelli, D.; Pizzolo, F.; Friso, S.; Sandri, M.; Bassi, A.; Martinelli, N. Not Just Arterial Damage: Increased Incidence of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Cardiovascular Patients With Elevated Plasma Levels of Apolipoprotein CIII. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e010973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, N.; Baroni, M.; Castagna, A.; Lunghi, B.; Stefanoni, F.; Tosi, F.; Croce, J.; Udali, S.; Woodhams, B.; Girelli, D.; et al. Apolipoprotein C-III Strongly Correlates with Activated Factor VII–Anti-Thrombin Complex: An Additional Link between Plasma Lipids and Coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M. ApoC3 fires up monocytes to promote tissue damage. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 16, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperstock, M.S. Inactivation of Endotoxin by Polymyxin B. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1974, 6, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Erasmo, L.; Di Costanzo, A.; Gallo, A.; Bruckert, E.; Arca, M. ApoCIII: A multifaceted protein in cardiometabolic disease. Metabolism 2020, 113, 154395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Azcutia, V.; Aikawa, E.; Figueiredo, J.-L.; Croce, K.; Sonoki, H.; Sacks, F.M.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Aikawa, M. Statins suppress apolipoprotein CIII-induced vascular endothelial cell activation and monocyte adhesion. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 34, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauersberger, C.; Hinterdobler, J.; Schunkert, H.; Kessler, T.; Sager, H.B. Where the Action Is—Leukocyte Recruitment in Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I. 2016 Russell Ross Memorial Lecture in Vascular Biology. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.; Landmesser, U.; Rauch, U. Tissue factor as a link between inflammation and coagulation. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 26, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.P.; Mackman, N. Tissue Factor. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterud, B. Tissue factor in blood cells and endothelial cells. Front. Biosci. 2012, E4, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Seidu, S.; Khunti, K. Statins and primary prevention of venous thromboembolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e83–e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, F.A.; Lijfering, W.M.; Van der Laarse, A.; Ruhaak, L.R.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Cannegieter, S.C.; Cobbaert, C. Association of apolipoproteins C-I, C-II, C-III and E with coagulation markers and venous thromboembolism risk. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, W.; Edom, R.W.; Wang, D.; Weng, N.; Zhang, S.W. Relative Quantitation of Glycoisoforms of Intact Apolipoprotein C3 in Human Plasma by Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2867–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, M.; Chiariello, C.; Conte, E.; Castagna, A.; Robotti, E.; Gosetti, F.; Patrone, M.; Martinelli, N.; Bassi, A.; Cecconi, D.; et al. Plasma Proteome Profiles of Stable CAD Patients Stratified According to Total Apo C-III Levels. Proteom.—Clin. Appl. 2018, 13, e1800023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamassia, N.; Bianchetto-Aguilera, F.; Gasperini, S.; Polletti, S.; Gardiman, E.; Ostuni, R.; Natoli, G.; Cassatella, M.A. Induction of OCT2 contributes to regulate the gene expression program in human neutrophils activated via TLR8. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzetti, F.; Tamassia, N.; Arruda-Silva, F.; Gasperini, S.; Cassatella, M.A. The importance of being “pure” neutrophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 139, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Aguilera, F.B.; Castellucci, M.; Rossato, M.; Costa, S.; Lunardi, C.; Ostuni, R.; Girolomoni, G.; Natoli, G.; Bazzoni, F.; et al. Chromatin remodelling and autocrine TNFα are required for optimal interleukin-6 expression in activated human neutrophils. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Tomai, M.; Miller, R.L.; E Lipson, K.; Kieper, W.C.; E Zarraga, I.; Vasilakos, J.P. Resiquimod and other immune response modifiers as vaccine adjuvants. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2007, 6, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzetti, F.; Finotti, G.; Tamassia, N.; Bianchetto-Aguilera, F.; Castellucci, M.; Canè, S.; Lonardi, S.; Cavallini, C.; Matte, A.; Gasperini, S.; et al. CD66b−CD64dimCD115− cells in the human bone marrow represent neutrophil-committed progenitors. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olivieri, O.; Gasperini, S.; Calzetti, F.; Gardiman, E.; Castagna, A.; Martinelli, N.; Tamassia, N.; Cassatella, M.A. CD14+-Monocytes Exposed to Apolipoprotein CIII Express Tissue Factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032223
Olivieri O, Gasperini S, Calzetti F, Gardiman E, Castagna A, Martinelli N, Tamassia N, Cassatella MA. CD14+-Monocytes Exposed to Apolipoprotein CIII Express Tissue Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(3):2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032223
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlivieri, Oliviero, Sara Gasperini, Federica Calzetti, Elisa Gardiman, Annalisa Castagna, Nicola Martinelli, Nicola Tamassia, and Marco A. Cassatella. 2023. "CD14+-Monocytes Exposed to Apolipoprotein CIII Express Tissue Factor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 3: 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032223
APA StyleOlivieri, O., Gasperini, S., Calzetti, F., Gardiman, E., Castagna, A., Martinelli, N., Tamassia, N., & Cassatella, M. A. (2023). CD14+-Monocytes Exposed to Apolipoprotein CIII Express Tissue Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(3), 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032223





