CD6 and Its Interacting Partners: Newcomers to the Block of Cancer Immunotherapies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
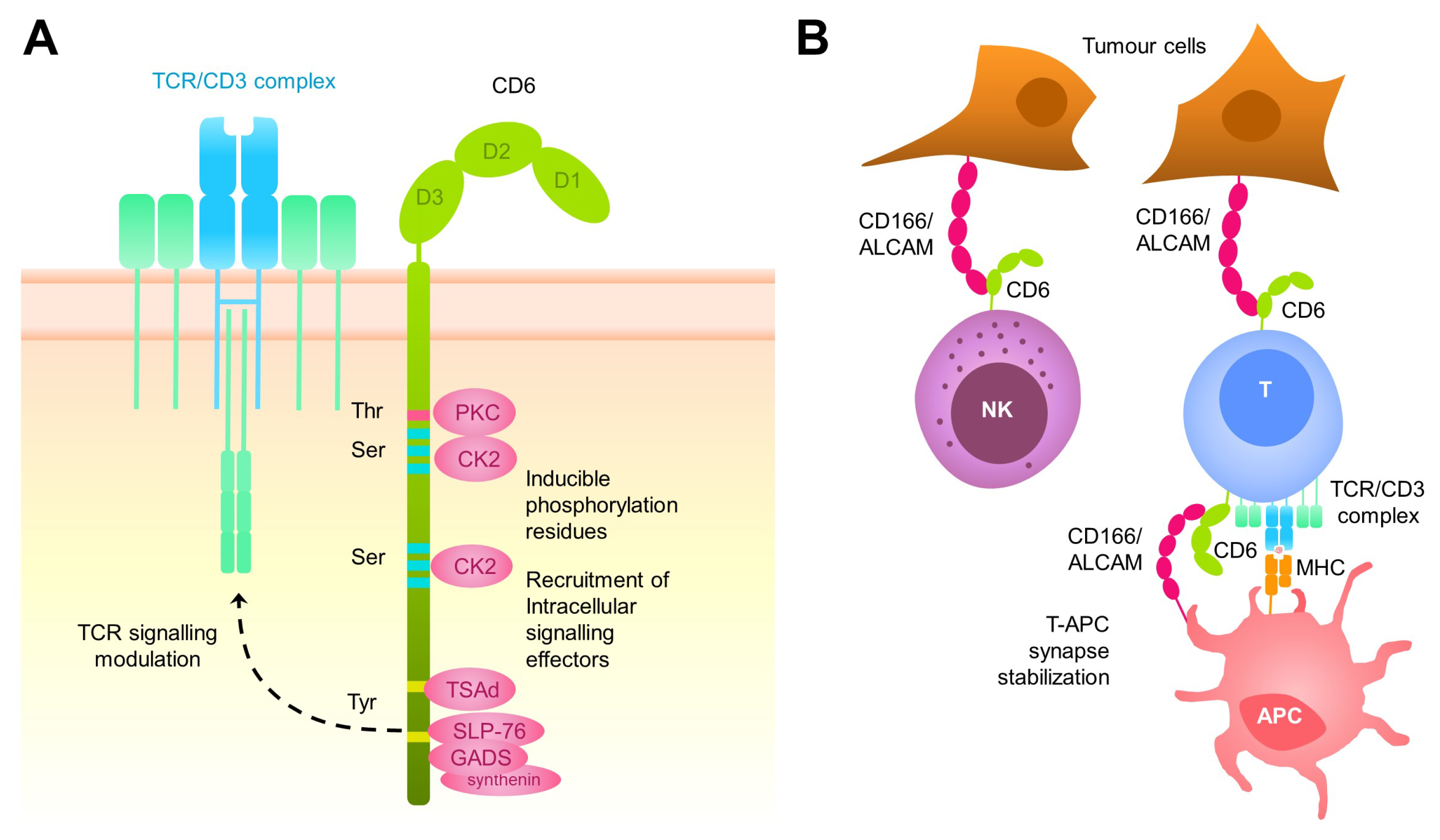
2. The CD6 Receptor: Structure, Function, Tissue Distribution, and Ligands
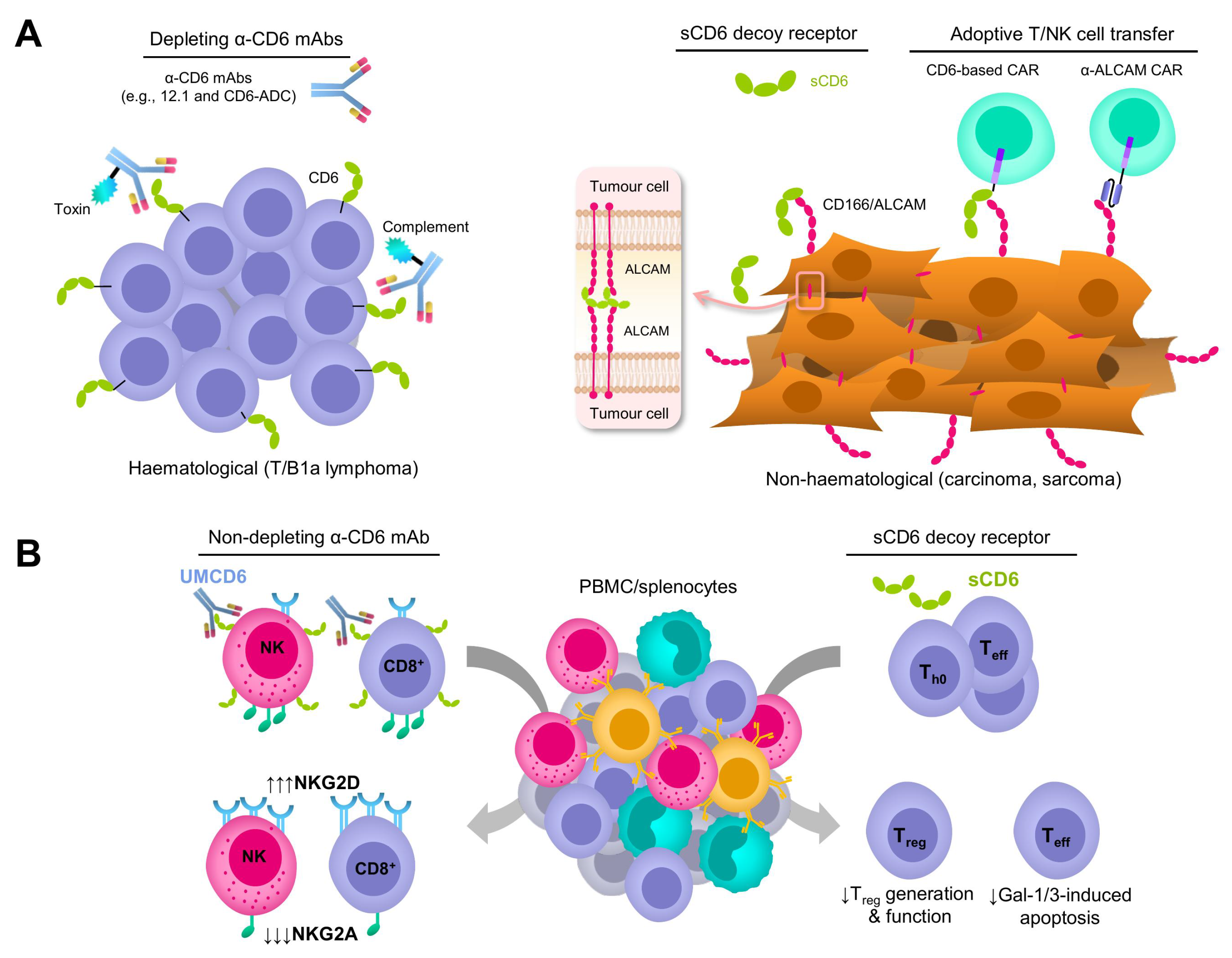
3. Depleting and Non-Depleting Anti-CD6 mAb-Based Strategies
4. CD6 Decoy Receptor-Based Strategies
5. Adoptive Immune Cell Transfer-Based Strategies
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | Adeno-Associated Virus |
| ADC | Antibody Drug Conjugate |
| ADCC | Antibody-Dependent Cell Cytotoxicity |
| ADCP | Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis |
| ALCAM | Activated Leukocyte Cell Adhesion Molecule |
| APC | Antigen Presenting Cells |
| B-CLL | B-type Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia |
| BCMA | B-Cell Maturation Antigen |
| CEA | CarcinoEmbryonic Antigen |
| CARs | Chimeric Antigen-specific Receptors |
| CDCP1 | CUB Domain-Containing Protein 1 |
| CIA | Collagen-Induced Arthritis |
| CRC | Colorectal Cancer cells |
| CRS | Cytokine Release Syndrome |
| CTCL | Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma |
| EAE | Experimental Autoimmune Encephalitis |
| EAU | Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GPC3 | Glypican-3 |
| ICI | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors |
| IgSF | Immunoglobulin SuperFamily |
| IL-1RII | Interleukin-1 Type II Receptor |
| INF- | Interferon gamma |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| MMAE | MonoMethyl Auristatin E |
| PBMCs | Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells |
| PMA | Phormol-Myrisate Acetate |
| PSA | Prostate-Specific Antigen |
| sCD6 | Soluble CD6 |
| shCD6 | Soluble human CD6 |
| smCD6 | Soluble mouse CD6 |
| scFv | Single-chain variable fragment |
| SRCR | Scavenger Receptor Cisteine-Rich |
| TAAs | Tumour-Associated Antigens |
| TCL | T-Cell Lymphoma |
| TNF | Tumour Necrosis Factor |
| TNF- | Tumour Necrosis Factor alpha |
| TRAIL | TNF-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand |
| TSAs | Tumour-Specific Antigens |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Majidpoor, J.; Toolee, H.; Mortezaee, K. The current knowledge concerning solid cancer and therapy. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, A.; Sato, E.; Fujii, H.; Sun, B.; Nishioka, H.; Aruoma, O.I. The influence of active hexose correlated compound (AHCC) on cisplatin-evoked chemotherapeutic and side effects in tumor-bearing mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 222, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolleman, E.J.; Melis, M.; Valkema, R.; Boerman, O.C.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M. Kidney protection during peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with somatostatin analogues. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 1018–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debela, D.T.; Muzazu, S.G.; Heraro, K.D.; Ndalama, M.T.; Mesele, B.W.; Haile, D.C.; Kitui, S.K.; Manyazewal, T. New approaches and procedures for cancer treatment: Current perspectives. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 20503121211034366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwood, M.M.; Jonsson, J.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schiöth, H.B. Soluble ligands as drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.D.; Park, S.H. Immunological and clinical implications of immune checkpoint blockade in human cancer. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2019, 42, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1–positive non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Eng. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N. Eng. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- June, C.H.; O’Connor, R.S.; Kawalekar, O.U.; Ghassemi, S.; Milone, M.C. CAR T cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Science 2018, 359, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Li, D.; Zhu, X. Cancer immunotherapy: Pros, cons and beyond. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consuegra-Fernandez, M.; Lin, F.; Fox, D.A.; Lozano, F. Clinical and experimental evidence for targeting CD6 in immune-based disorders. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, V.G.; Moestrup, S.K.; Holmskov, U.; Mollenhauer, J.; Lozano, F. The conserved scavenger receptor cysteine-rich superfamily in therapy and diagnosis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 967–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoun, M.; Kadin, M.; Martin, P.; Nettleton, J.; Hansen, J. A novel human T cell antigen preferentially expressed on mature T cells and shared by both well and poorly differentiated B cell leukemias and lymphomas. J. Immunol. 1981, 127, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, M.; Müller, B.; Ter Meer, D.; Raffegerst, S.; Simm, B.; Wilde, S.; Spranger, S.; Ellwart, J.; Mosetter, B.; Umansky, L.; et al. The CD6 scavenger receptor is differentially expressed on a CD56dim natural killer cell subpopulation and contributes to natural killer-derived cytokine and chemokine secretion. J. Innate. Immun. 2011, 3, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, B.; Funke, I.; Seed, B.; Riethmüller, G.; Weiss, E. Expression of the CD6 T lymphocyte differentiation antigen in normal human brain. J. Neuroimmunol. 1990, 29, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruffo, A.; Melnick, M.; Linsley, P.; Seed, B. The lymphocyte glycoprotein CD6 contains a repeated domain structure characteristic of a new family of cell surface and secreted proteins. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, L.; Farnós, M.; Martínez-Florensa, M.; Martínez, V.G.; Lozano, F. Identification of functionally relevant phoshorylatable serine clusters in the cytoplasmic region of the human CD6 lymphocyte surface receptor. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, W.H.; de Vegvar, H.E.N.; Prohaska, S.S.; Rhee, J.W.; Parnes, J.R. Human CD6 possesses a large, alternatively spliced cytoplasmic domain. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 2765–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.M.; Henriques, S.N.; Santos, R.F.; Carmo, A.M. CD6, a rheostat-type signalosome that tunes T cell activation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, E.; Escoda-Ferran, C.; Climent, N.; Miró-Julià, C.; Simões, I.T.; Martínez-Florensa, M.; Sarukhan, A.; Carreras, E.; Lozano, F. Human CD6 down-modulation following T-cell activation compromises lymphocyte survival and proliferative responses. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrias, M.R.; Farnós, M.; Mota, R.; Sánchez-Barbero, F.; Ibáñez, A.; Gimferrer, I.; Vera, J.; Fenutría, R.; Casals, C.; Yélamos, J.; et al. CD6 binds to pathogen-associated molecular patterns and protects from LPS-induced septic shock. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11724–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimferrer, I.; Calvo, M.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Farnós, M.; Sarrias, M.R.; Enrich, C.; Vives, J.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Lozano, F. Relevance of CD6-mediated interactions in T cell activation and proliferation. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.W.; Joosten, B.; Torensma, R.; Parnes, J.R.; van Leeuwen, F.N.; Figdor, C.G. Long-term engagement of CD6 and ALCAM is essential for T-cell proliferation induced by dendritic cells. Blood 2006, 107, 3212–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.J.; Barclay, A.N.; Brown, M.H. Frontline: Optimal T cell activation requires the engagement of CD6 and CD166. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangemi, R.; Swack, J.A.; Gaviria, D.M.; Romain, P.L. Anti-T12, an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, can activate human T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, L.M.; Garcia, C.A.; Jondal, M.; Chow, S.C. The anti-CD6 mAb, IOR-T1, defined a new epitope on the human CD6 molecule that induces greater responsiveness in T cell receptor/CD3-mediated T cell proliferation. Cell. Immunol. 1994, 154, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.I.; Gonçalves, C.M.; Pinto, M.; Fabre, S.; Santos, A.M.; Lee, S.F.; Castro, M.A.; Nunes, R.J.; Barbosa, R.R.; Parnes, J.R.; et al. CD6 attenuates early and late signaling events, setting thresholds for T-cell activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orta-Mascaró, M.; Consuegra-Fernández, M.; Carreras, E.; Roncagalli, R.; Carreras-Sureda, A.; Alvarez, P.; Girard, L.; Simões, I.; Martínez-Florensa, M.; Aranda, F.; et al. CD6 modulates thymocyte selection and peripheral T cell homeostasis. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Singer, N.G.; Whitbred, J.; Bowen, M.A.; Fox, D.A.; Lin, F. CD6 as a potential target for treating multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2687–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consuegra-Fernández, M.; Martínez-Florensa, M.; Aranda, F.; de Salort, J.; Armiger-Borràs, N.; Lozano, T.; Casares, N.; Lasarte, J.J.; Engel, P.; Lozano, F. Relevance of CD6-mediated interactions in the regulation of peripheral T-cell responses and tolerance. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Qiu, W.; Bell, B.A.; Dvorina, N.; Baldwin, W.M., III; Singer, N.; Kern, T.; Caspi, R.R.; Fox, D.A.; et al. Targeting CD6 for the treatment of experimental autoimmune uveitis. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 90, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consuegra-Fernández, M.; Julià, M.; Martínez-Florensa, M.; Aranda, F.; Català, C.; Armiger-Borràs, N.; Arias, M.T.; Santiago, F.; Guilabert, A.; Esteve, A.; et al. Genetic and experimental evidence for the involvement of the CD6 lymphocyte receptor in psoriasis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, D.; Grégoire, C.; Voisinne, G.; Celis-Gutierrez, J.; Aussel, R.; Girard, L.; Camus, M.; Marcellin, M.; Argenty, J.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; et al. The T cell CD6 receptor operates a multitask signalosome with opposite functions in T cell activation. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Wee, S.F.; Whichard, L.; Bowen, M.; Pesando, J.; Aruffo, A.; Haynes, B. Identification and characterization of a 100-kD ligand for CD6 on human thymic epithelial cells. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, M.A.; Patel, D.D.; Li, X.; Modrell, B.; Malacko, A.R.; Wang, W.C.; Marquardt, H.; Neubauer, M.; Pesando, J.M.; Francke, U. Cloning, mapping, and characterization of activated leukocyte-cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM), a CD6 ligand. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 181, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferragut, F.; Vachetta, V.S.; Troncoso, M.F.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Elola, M.T. ALCAM/CD166: A pleiotropic mediator of cell adhesion, stemness and cancer progression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 61, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, M.A.; Bajorath, J.; Siadak, A.W.; Modrell, B.; Malacko, A.R.; Marquardt, H.; Nadler, S.G.; Aruffo, A. The amino-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule binds specifically to the membrane-proximal scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain of CD6 with a 1:1 stoichiometry. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 17390–17396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Riet, J.; Zimmerman, A.W.; Cambi, A.; Joosten, B.; Speller, S.; Torensma, R.; van Leeuwen, F.N.; Figdor, C.G.; de Lange, F. Distinct kinetic and mechanical properties govern ALCAM-mediated interactions as shown by single-molecule force spectroscopy. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 3965–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, N.G.; Fox, D.A.; Haqqi, T.M.; Beretta, L.; Endres, J.S.; Prohaska, S.; Parnes, J.R.; Bromberg, J.; Sramkoski, R.M. CD6: Expression during development, apoptosis and selection of human and mouse thymocytes. Int. Immunol. 2002, 14, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, R.; Wosik, K.; Berard, J.L.; Dodelet-Devillers, A.; Ifergan, I.; Kebir, H.; Haqqani, A.S.; Kreymborg, K.; Krug, S.; Moumdjian, R.; et al. Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule promotes leukocyte trafficking into the central nervous system. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, M.C.; Heinly, C.S.; Whichard, L.P.; Patel, D.D. Cytokine-regulated expression of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (CD166) on monocyte-lineage cells and in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borjini, N.; Lun, Y.; Jang, G.F.; Crabb, J.; Chen, Y.; Crabb, J.; Fox, D.A.; Ivanov, A.I.; Lin, F. CD6 triggers actomyosin cytoskeleton remodeling after binding to its receptor complex. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2023, qiad124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoda-Ferran, C.; Carrasco, E.; Caballero-Baños, M.; Miró-Julià, C.; Martínez-Florensa, M.; Consuegra-Fernández, M.; Martínez, V.G.; Liu, F.T.; Lozano, F. Modulation of CD6 function through interaction with Galectin-1 and-3. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 2805–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyindah-Asonye, G.; Li, Y.; Ruth, J.H.; Spassov, D.S.; Hebron, K.E.; Zijlstra, A.; Moasser, M.M.; Wang, B.; Singer, N.G.; Cui, H.; et al. CD318 is a ligand for CD6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6912–E6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiariotti, L.; Salvatore, P.; Frunzio, R.; Bruni, C.B. Galectin genes: Regulation of expression. Glycoconj. J. 2002, 19, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.T.; Rabinovich, G.A. Galectins as modulators of tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio, L.M.; De Santiago, A.; Aguilar-SantelisesHa, M.; Mellstedt, K.; Jondal, M. CD6 ligation modulates the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and protects chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from apoptosis induced by anti-IgM. Blood 1997, 89, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrea-Rubio, M.; Fox, D.A. The dual role of CD6 as a therapeutic target in cancer and autoimmune disease. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1026521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassn Mesrati, M.; Syafruddin, S.E.; Mohtar, M.A.; Syahir, A. CD44: A multifunctional mediator of cancer progression. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahavi, D.; Weiner, L. Monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Antibodies 2020, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinherz, E.L.; Geha, R.; Rappeport, J.M.; Wilson, M.; Penta, A.C.; Hussey, R.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Daley, J.F.; Levine, H.; Rosen, F.S.; et al. Reconstitution after transplantation with T-lymphocyte-depleted HLA haplotype-mismatched bone marrow for severe combined immunodeficiency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 6047–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, C.; Milford, E.; Reinherz, E.; Schlossman, S.; Tilney, N.; Strom, T.; Kirkman, R.; Busch, G.; Araujo, J. Monoclonal anti-T12 antibody as therapy for renal allograft rejection. Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1983, 96, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Budamakuntla, L.; Shree-Lakshmi, H.; Bansal, A.; Venkatarayaraju, S.K. Spotlight on itolizumab in the treatment of psoriasis–current perspectives from India. Psoriasis 2019, 9, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, P.; Moreno, E.; E Aira, L.; C Rodríguez, P. Therapeutic targeting of CD6 in autoimmune diseases: A review of cuban clinical studies with the antibodies IOR-T1 and itolizumab. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruth, J.H.; Gurrea-Rubio, M.; Athukorala, K.S.; Rasmussen, S.M.; Weber, D.P.; Randon, P.M.; Gedert, R.J.; Lind, M.E.; Amin, M.A.; Campbell, P.L.; et al. CD6 is a target for cancer immunotherapy. JCI Insight. 2021, 6, e145662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, N.; Luo, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; DiFilippo, F.P.; Androjna, C.; Fox, D.A.; Ondrejka, S.L.; Hsi, E.D.; Jagadeesh, D.; et al. CD6-targeted antibody-drug conjugate as a new therapeutic agent for T cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2023, 17, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, S.; Guo, J.; Zeng, X.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhao, X. CD166-specific CAR-T cells potently target colorectal cancer cells. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 27, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Xia, K.; Liang, C.; Tao, H. Anti-CD166/4-1BB chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy for the treatment of osteosarcoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, I.T.; Aranda, F.; Casadó-Llombart, S.; Velasco-de Andrés, M.; Català, C.; Álvarez, P.; Consuegra-Fernández, M.; Orta-Mascaró, M.; Merino, R.; Merino, J.; et al. Multifaceted effects of soluble human CD6 in experimental cancer models. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2020, 8, e000172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Assudani, D.; Nair, P.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Deodhar, S.; Arumugam, M.; Iyer, H.; Melarkode, R. Safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of T1h, a humanized anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, in moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis-results from a randomized phase II trial. (96.13). J. Immunol. 2010, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, S.; Krupashankar, D.; Budamakuntla, L.; Srinivas, C.; Khopkar, U.; Gupta, S.; Shetty, N.; Pratap, D.V.S.; Gopal, M.; Rao, T.N.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of itolizumab in patients with moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis: A double-blind, randomized-withdrawal, placebo-controlled study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupashankar, D.; Dogra, S.; Kura, M.; Saraswat, A.; Budamakuntla, L.; Sumathy, T.; Shah, R.; Gopal, M.; Rao, T.N.; Srinivas, C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of itolizumab, a novel anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis: Results of a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase-III study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, P.C.; Torres-Moya, R.; Reyes, G.; Molinero, C.; Prada, D.; Lopez, A.M.; Hernandez, I.M.; Hernandez, M.V.; Martinez, J.P.; Hernandez, X.; et al. A clinical exploratory study with itolizumab, an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results Immunol. 2012, 2, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.C.; Prada, D.M.; Moreno, E.; Aira, L.; Molinero, C.; López, A.; Gómez, J.; Hernández, I.; Martínez, J.; Reyes, Y.; et al. The anti-CD6 antibody itolizumab provides clinical benefit without lymphopenia in rheumatoid arthritis patients: Results from a 6-month, open-label Phase I clinical trial. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 191, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ruth, J.H.; Rasmussen, S.M.; Athukorala, K.S.; Weber, D.P.; Amin, M.A.; Campbell, P.L.; Singer, N.G.; Fox, D.A.; Lin, F. Targeting CD6 attenuates murine collagen induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahjoubin-Tehran, M.; Rezaei, S.; Jalili, A.; Aghaee-Bakhtiari, S.H.; Orafai, H.M.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Peptide decoys: A new technology offering therapeutic opportunities for breast cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, J.; Savvides, S.N. Mechanisms of immunomodulation by mammalian and viral decoy receptors: Insights from structures. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Font, J.; García-Carrasco, M.; Calvo, J.; Places, L.; Padilla, O.; Cervera, R.; Bowen, M.; Lozano, F.; Ingelmo, M. High circulating levels of soluble scavenger receptors (sCD5 and sCD6) in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology 2001, 40, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibar, J.; Martínez-Florensa, M.; Castro, P.; Carrasco, E.; Escoda-Ferran, C.; Fernández, S.; Butjosa, M.; Hernández, C.; Rinaudo, M.; Lozano, F.; et al. Pattern of soluble CD5 and CD6 lymphocyte receptors in critically ill patients with septic syndromes. J. Crit. Care 2015, 30, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, S.F.; Wang, W.C.; Farr, A.G.; Nelson, A.J.; Patel, D.D.; Haynes, B.F.; Linsley, P.S.; Aruffo, A. Characterization of a CD6 ligand (s) expressed on human-and murine-derived cell lines and murine lymphoid tissues. Cell. Immunol. 1994, 158, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.J.; Mittal, S.K.; Chauhan, S.K. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Suppress T-Cell-Mediated Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity via ALCAM-CD6 Interaction. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2023, 12, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-de Andrés, M.; Muñoz-Sánchez, G.; Carrillo-Serradell, L.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, M.d.M.; Català, C.; Isamat, M.; Lozano, F. Chimeric antigen receptor–based therapies beyond cancer. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, 2250184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Abila, B.; Mostafa Kamel, Y. CAR-T: What Is Next? Cancers 2023, 15, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.C.; Selitsky, S.R.; Chai, S.; Armistead, P.M.; Vincent, B.G.; Serody, J.S. Alternative tumour-specific antigens. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, M.; Qin, Y.; Gao, W.; Tao, L.; Su, W.; Zhong, J. Neoantigen: A new breakthrough in tumor immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 672356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marofi, F.; Al-Awad, A.S.; Sulaiman Rahman, H.; Markov, A.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Ivanovna Enina, Y.; Mahmoodi, M.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Yazdanifar, M.; Stanley Chartrand, M.; et al. CAR-NK cell: A new paradigm in tumor immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 673276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Molecule | Type | Study Type | Disease | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UMCD6 | Humanised mouse anti-human CD6 mAb | Pre-clinical | CD166/ALCAM-expressing human tumours | [56] |
| CD6-ADC | Humanised mouse anti-human CD6 mAb (UMCD6) toxin-conjugated | Pre-clinical | Human T-cell lymphomas | [57] |
| CD6-CAR | CD6-based CAR-T cells | Pre-clinical | Human Colon adeno-carcinoma | [58] |
| CD166-CAR | Anti-human CD166 CAR-T cells | Pre-clinical | Human Osteosarcoma | [59] |
| IOR-T1 | Mouse anti-human CD6 mAb | Clinical | Human cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) | [55] |
| shCD6 | Soluble human CD6 protein | Pre-clinical | Mouse tumours of different lineages | [60] |
| Anti-T12 (12.1) | Mouse anti-human CD6 mAb | Clinical | Human kidney transplant rejection | [53] |
| Human bone marrow transplant rejection | [52] | |||
| Itolizumab | Humanised mouse anti-human CD6 (IOR-T1) mAb | Clinical (CTRI/2009/091/ 001009) | Psoriasis | [61,62,63] |
| (RPCEC00000007 and RPCEC00000035, Cuban Registry of Clinical Trials) | Rheumatoid arthritis | [64,65] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aragón-Serrano, L.; Carrillo-Serradell, L.; Planells-Romeo, V.; Isamat, M.; Velasco-de Andrés, M.; Lozano, F. CD6 and Its Interacting Partners: Newcomers to the Block of Cancer Immunotherapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417510
Aragón-Serrano L, Carrillo-Serradell L, Planells-Romeo V, Isamat M, Velasco-de Andrés M, Lozano F. CD6 and Its Interacting Partners: Newcomers to the Block of Cancer Immunotherapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417510
Chicago/Turabian StyleAragón-Serrano, Lucía, Laura Carrillo-Serradell, Violeta Planells-Romeo, Marcos Isamat, María Velasco-de Andrés, and Francisco Lozano. 2023. "CD6 and Its Interacting Partners: Newcomers to the Block of Cancer Immunotherapies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417510
APA StyleAragón-Serrano, L., Carrillo-Serradell, L., Planells-Romeo, V., Isamat, M., Velasco-de Andrés, M., & Lozano, F. (2023). CD6 and Its Interacting Partners: Newcomers to the Block of Cancer Immunotherapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17510. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417510






