Structural Integrity of Nucleolin Is Required to Suppress TDP-43-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Yeast and Human Cell Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. FTLD-Related TDP-43 Mutants Are Toxic to Yeast Cells, but Cured by NCL Expression
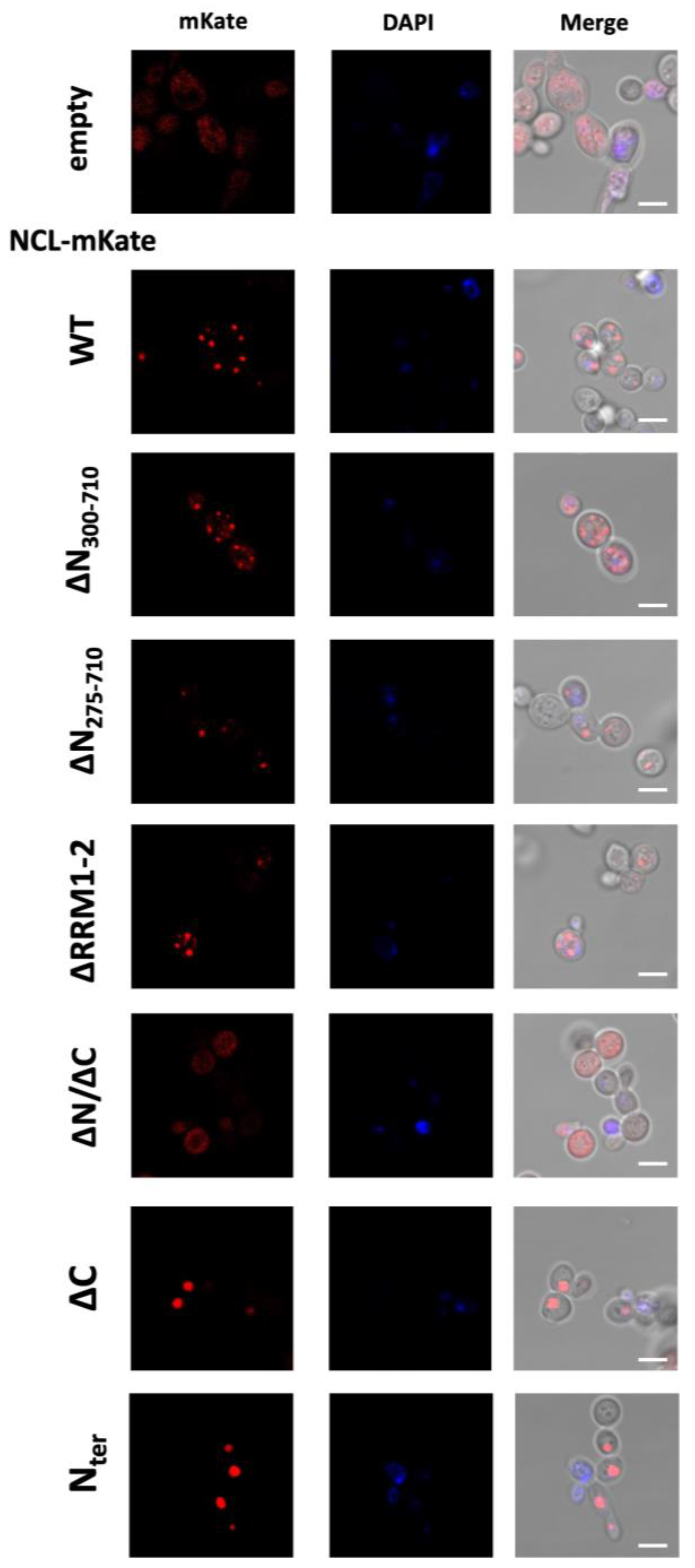
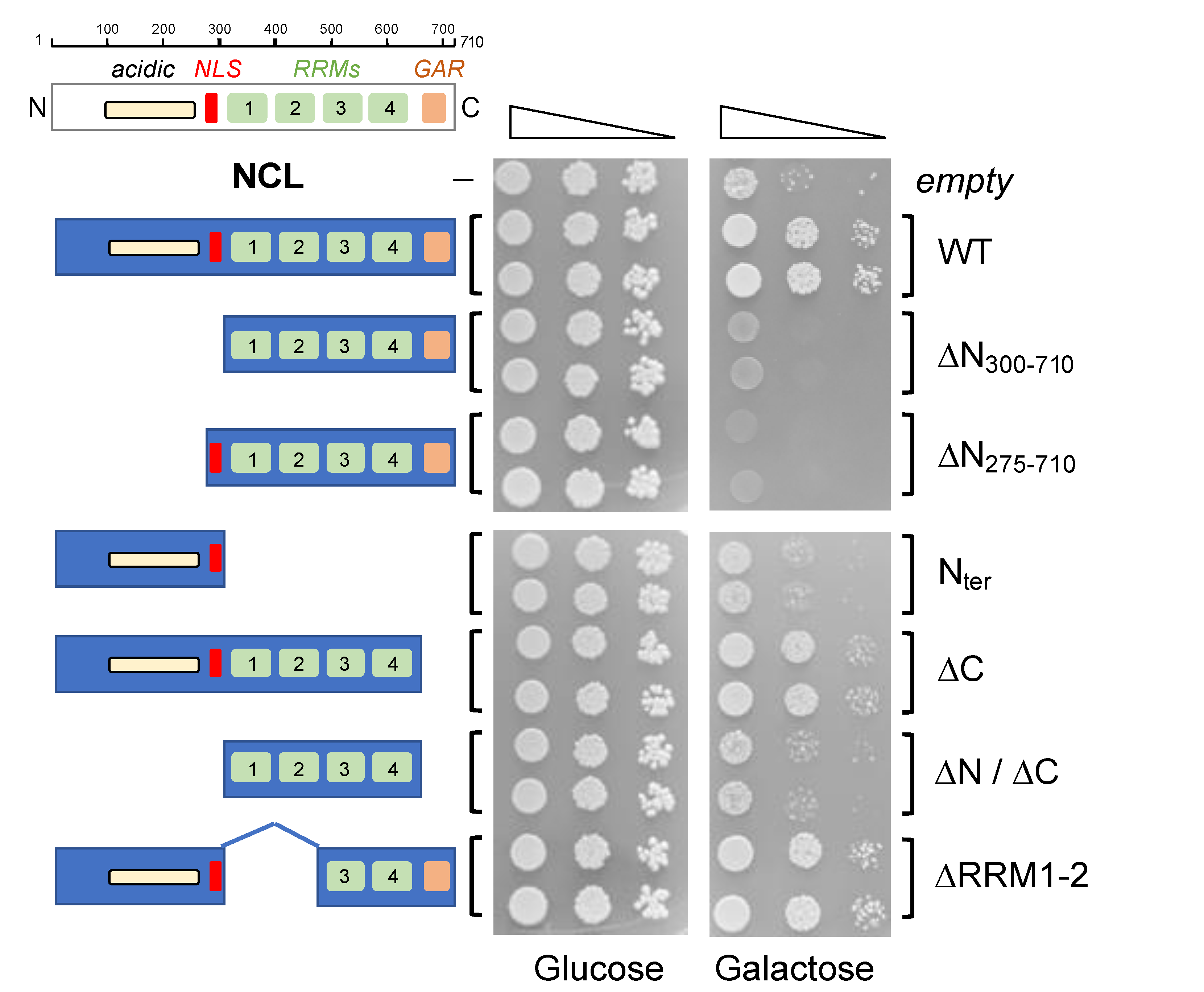
2.2. Analysis of NCL Mutants in S. cerevisiae Yeast Cells
| NCL | Coordinates (aa) | MW (Theoretical) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | WT (full-length) | 1–710 | 76.5 |
| 2 | ΔN300–710 | 300–710 | 44.7 |
| 3 | ΔN275–710 | 275–710 | 47.5 |
| 4 | Nter | 1–300 | 32.2 |
| 5 | ΔC | 1–650 | 70.7 |
| 6 | ΔN/ΔC | 300–650 | 38.9 |
| 7 | ΔRRM1–2 | 1–300//471–710 | 57.8 |
2.3. Effects of NCL Mutations on Its Ability to Suppress TDP-43-Dependent Toxicity in Yeast Cells
2.4. Evaluation of Toxicity of FTLD-Related TDP-43 G295S Mutation in a Human Cell Model
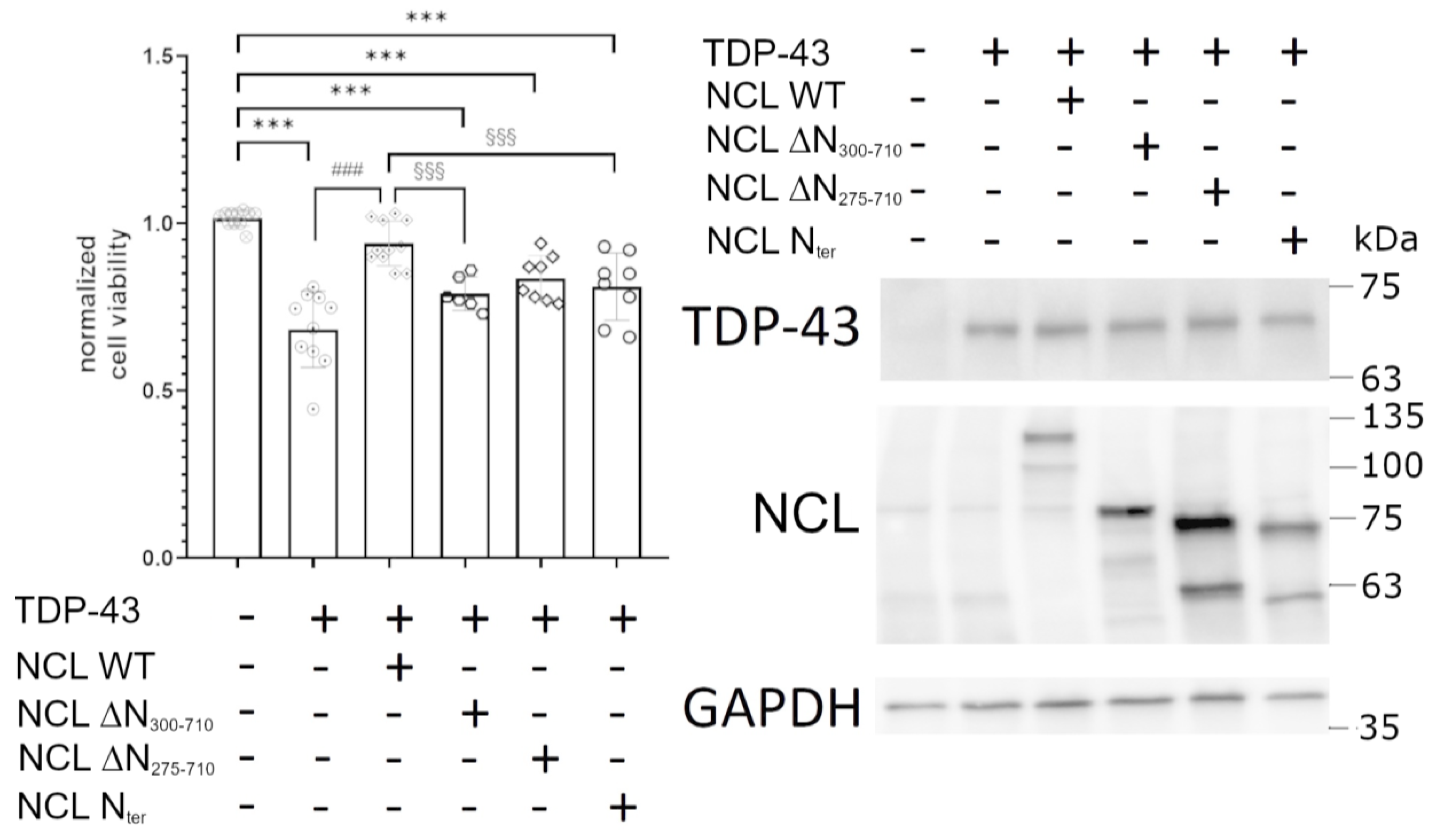
2.5. NCL Mutations Perturbed Its Ability to Alleviate TDP-43 Cytotoxicity in HEK293T Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, Plasmids and Primers
4.2. Yeast Manipulation and Cell Viability Assay
4.3. HEK293T Cell Culture, Transfection and Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Confocal Microscopy
4.5. Cell Lysis and Protein Extraction
4.6. Western Blot and Antibodies
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.E. Characterization and Functional Implications of the RNA Binding Properties of Nuclear Factor TDP-43, a Novel Splicing Regulator OfCFTR Exon 9. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 36337–36343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, Y.M.; Zago, P.; D’Ambrogio, A.; Xu, Y.-F.; Petrucelli, L.; Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.E. Structural Determinants of the Cellular Localization and Shuttling of TDP-43. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3778–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.H.; Wu, F.; Harrich, D.; García-Martínez, L.F.; Gaynor, R.B. Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Cellular Protein, TDP-43, That Binds to Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 TAR DNA Sequence Motifs. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3584–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.-C.; Polymenidou, M.; Cleveland, D.W. Converging Mechanisms in ALS and FTD: Disrupted RNA and Protein Homeostasis. Neuron 2013, 79, 416–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.; Bharathi, V.; Sivalingam, V.; Girdhar, A.; Patel, B.K. Molecular Mechanisms of TDP-43 Misfolding and Pathology in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.E. TDP-43: Gumming up Neurons through Protein-Protein and Protein-RNA Interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, Y.M.; De Conti, L.; Avendaño-Vázquez, S.E.; Dhir, A.; Romano, M.; D’Ambrogio, A.; Tollervey, J.; Ule, J.; Baralle, M.; Buratti, E.; et al. TDP-43 Regulates Its MRNA Levels through a Negative Feedback Loop. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroz, T.; Hock, E.-M.; Ernst, P.; Foglieni, C.; Jambeau, M.; Gilhespy, L.A.B.; Laferriere, F.; Maniecka, Z.; Plückthun, A.; Mittl, P.; et al. Functional and Dynamic Polymerization of the ALS-Linked Protein TDP-43 Antagonizes Its Pathologic Aggregation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, M.; Johnson, B.S.; King, O.D.; Gitler, A.D.; Shorter, J. Prion-like Disorders: Blurring the Divide between Transmissibility and Infectivity. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentealba, R.A.; Udan, M.; Bell, S.; Wegorzewska, I.; Shao, J.; Diamond, M.I.; Weihl, C.C.; Baloh, R.H. Interaction with Polyglutamine Aggregates Reveals a Q/N-Rich Domain in TDP-43. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 26304–26314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, Y.M.; Pantano, S.; D’Ambrogio, A.; Buratti, E.; Brindisi, A.; Marchetti, C.; Romano, M.; Baralle, F.E. Human, Drosophila, and C. Elegans TDP43: Nucleic Acid Binding Properties and Splicing Regulatory Function. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratti, E.; Brindisi, A.; Giombi, M.; Tisminetzky, S.; Ayala, Y.M.; Baralle, F.E. TDP-43 Binds Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A/B through Its C-Terminal Tail. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37572–37584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freibaum, B.D.; Chitta, R.K.; High, A.A.; Taylor, J.P. Global Analysis of TDP-43 Interacting Proteins Reveals Strong Association with RNA Splicing and Translation Machinery. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1104–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conicella, A.E.; Zerze, G.H.; Mittal, J.; Fawzi, N.L. ALS Mutations Disrupt Phase Separation Mediated by α-Helical Structure in the TDP-43 Low-Complexity C-Terminal Domain. Structure 2016, 24, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Kar, A.; Ray, P.; Chen, X.; Rao, E.J.; Yang, M.; Ye, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. An ALS-Associated Mutation Affecting TDP-43 Enhances Protein Aggregation, Fibril Formation and Neurotoxicity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budini, M.; Romano, V.; Quadri, Z.; Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.E. TDP-43 Loss of Cellular Function through Aggregation Requires Additional Structural Determinants beyond Its C-Terminal Q/N Prion-like Domain. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mompeán, M.; Buratti, E.; Guarnaccia, C.; Brito, R.M.M.; Chakrabartty, A.; Baralle, F.E.; Laurents, D.V. Structural Characterization of the Minimal Segment of TDP-43 Competent for Aggregation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 545, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-L.; Che, M.-X.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, C.-J.; Xie, M.-Y.; Li, H.-Y.; He, J.-H.; Hu, H.-Y. Structural Transformation of the Amyloidogenic Core Region of TDP-43 Protein Initiates Its Aggregation and Cytoplasmic Inclusion. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19614–19624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, M.; Sampathu, D.M.; Kwong, L.K.; Truax, A.C.; Micsenyi, M.C.; Chou, T.T.; Bruce, J.; Schuck, T.; Grossman, M.; Clark, C.M.; et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Science 2006, 314, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotter, E.L.; Chen, H.J.; Shaw, C.E. TDP-43 Proteinopathy and ALS: Insights into Disease Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Akiyama, H.; Ikeda, K.; Nonaka, T.; Mori, H.; Mann, D.; Tsuchiya, K.; Yoshida, M.; Hashizume, Y.; et al. TDP-43 Is a Component of Ubiquitin-Positive Tau-Negative Inclusions in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeve, B.F.; Boxer, A.L.; Kumfor, F.; Pijnenburg, Y.; Rohrer, J.D. Advances and Controversies in Frontotemporal Dementia: Diagnosis, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Considerations. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador-Ortiz, C.; Lin, W.-L.; Ahmed, Z.; Personett, D.; Davies, P.; Duara, R.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Hutton, M.L.; Dickson, D.W. TDP-43 Immunoreactivity in Hippocampal Sclerosis and Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreedharan, J.; Blair, I.P.; Tripathi, V.B.; Hu, X.; Vance, C.; Rogelj, B.; Ackerley, S.; Durnall, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Buratti, E.; et al. TDP-43 Mutations in Familial and Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Science 2008, 319, 1668–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.S.; Snead, D.; Lee, J.J.; McCaffery, J.M.; Shorter, J.; Gitler, A.D. TDP-43 Is Intrinsically Aggregation-Prone, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Linked Mutations Accelerate Aggregation and Increase Toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 20329–20339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armakola, M.; Hart, M.P.; Gitler, A.D. TDP-43 Toxicity in Yeast. Methods 2011, 53, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.S.; McCaffery, J.M.; Lindquist, S.; Gitler, A.D. A Yeast TDP-43 Proteinopathy Model: Exploring the Molecular Determinants of TDP-43 Aggregation and Cellular Toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6439–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryndushkin, D.; Wickner, R.B.; Shewmaker, F. FUS/TLS Forms Cytoplasmic Aggregates, Inhibits Cell Growth and Interacts with TDP-43 in a Yeast Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.S.; Park, S.K.S.; Liebman, S.W. Respiration Enhances TDP-43 Toxicity, but TDP-43 Retains Some Toxicity in the Absence of Respiration. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-K.; Hong, J.Y.; Arslan, F.; Kanneganti, V.; Patel, B.; Tietsort, A.; Tank, E.M.H.; Li, X.; Barmada, S.J.; Liebman, S.W. Overexpression of the Essential Sis1 Chaperone Reduces TDP-43 Effects on Toxicity and Proteolysis. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-K.; Park, S.; Liebman, S.W. TDP-43 Toxicity in Yeast Is Associated with a Reduction in Autophagy, and Deletions of TIP41 and PBP1 Counteract These Effects. Viruses 2022, 14, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peggion, C.; Massimino, M.L.; Stella, R.; Bortolotto, R.; Agostini, J.; Maldi, A.; Sartori, G.; Tonello, F.; Bertoli, A.; Lopreiato, R. Nucleolin Rescues TDP-43 Toxicity in Yeast and Human Cell Models. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelard, F.; Bouvet, P. Nucleolin: A MultiFACeTed Protein. Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajrishi, M.M.; Tuteja, R.; Tuteja, N. Nucleolin. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginisty, H.; Sicard, H.; Roger, B.; Bouvet, P. Structure and Functions of Nucleolin. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Guan, Q.; Gao, L. New Perspectives of Physiological and Pathological Functions of Nucleolin (NCL). Life Sci. 2017, 186, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonello, F.; Massimino, M.L.; Peggion, C. Nucleolin: A Cell Portal for Viruses, Bacteria, and Toxins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storck, S.; Thiry, M.; Bouvet, P. Conditional Knockout of Nucleolin in DT40 Cells Reveals the Functional Redundancy of Its RNA-Binding Domains. Biol. Cell 2009, 101, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creancier, L.; Prats, H.; Zanibellato, C.; Amalric, F.; Bugler, B. Determination of the Functional Domains Involved in Nucleolar Targeting of Nucleolin. Mol. Biol. Cell 1993, 4, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Zachmann, M.S.; Nigg, E.A. Protein Localization to the Nucleolus: A Search for Targeting Domains in Nucleolin. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 105, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellar, G.J.; DiMario, P.J. Deletion and Site-Specific Mutagenesis of Nucleolin’s Carboxy GAR Domain. Chromosoma 2003, 111, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron-Mandel, E.; Koppel, I.; Abraham, O.; Rishal, I.; Smith, T.P.; Buchanan, C.N.; Sahoo, P.K.; Kadlec, J.; Oses-Prieto, J.A.; Kawaguchi, R.; et al. The Glycine Arginine-rich Domain of the RNA-binding Protein Nucleolin Regulates Its Subcellular Localization. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e107158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroni, B.; Archetti, S.; Del Bo, R.; Papetti, A.; Buratti, E.; Bonvicini, C.; Agosti, C.; Cosseddu, M.; Turla, M.; Di Lorenzo, D.; et al. TARDBP Mutations in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: Frequency, Clinical Features, and Disease Course. Rejuvenation Res. 2010, 13, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, P.; Camuzat, A.; Guillot-Noel, L.; Thomas-Antérion, C.; Couratier, P.; Wong, T.H.; Teichmann, M.; Golfier, V.; Auriacombe, S.; Belliard, S.; et al. Defining the Spectrum of Frontotemporal Dementias Associated with TARDBP Mutations. Neurol. Genet. 2016, 2, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winton, M.J.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Kwong, L.K.; Yuan, W.; Wood, E.M.; Yu, C.-E.; Schellenberg, G.D.; Rademakers, R.; Caselli, R.; Karydas, A.; et al. A90V TDP-43 Variant Results in the Aberrant Localization of TDP-43 in Vitro. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2252–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, M.; Morelle, W.; Coddeville, B.; Pons, A.; Masson, M.; Mazurier, J.; Legrand, D. Nucleolin Undergoes Partial N- and O-Glycosylations in the Extranuclear Cell Compartment. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 5804–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoja-Łukowicz, D.; Kedracka-Krok, S.; Duda, W.; Lityńska, A. The Lectin-Binding Pattern of Nucleolin and Its Interaction with Endogenous Galectin-3. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2014, 19, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelnovo, V.; Canu, E.; De Mattei, F.; Filippi, M.; Agosta, F. Basal Ganglia Alterations in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1133758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machts, J.; Loewe, K.; Kaufmann, J.; Jakubiczka, S.; Abdulla, S.; Petri, S.; Dengler, R.; Heinze, H.-J.; Vielhaber, S.; Schoenfeld, M.A.; et al. Basal Ganglia Pathology in ALS Is Associated with Neuropsychological Deficits. Neurology 2015, 85, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bede, P.; Iyer, P.M.; Finegan, E.; Omer, T.; Hardiman, O. Virtual Brain Biopsies in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Diagnostic Classification Based on in Vivo Pathological Patterns. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 15, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riancho, J.; Paz-Fajardo, L.; López de Munaín, A. Clinical and Preclinical Evidence of Somatosensory Involvement in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, M.; Seeley, W.W.; Boxer, A.L.; Hillis, A.E.; Knopman, D.S.; Ljubenov, P.A.; Miller, B.; Piguet, O.; Rademakers, R.; Whitwell, J.L.; et al. Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, K.; Miller, B.L. Frontotemporal Dementia: Neuropathology, Genetics, Neuroimaging, and Treatments. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 43, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Spina, S.; Miller, B.L. Frontotemporal Dementia. Lancet 2015, 386, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couratier, P.; Corcia, P.; Lautrette, G.; Nicol, M.; Marin, B. ALS and Frontotemporal Dementia Belong to a Common Disease Spectrum. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 173, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirola, L.; Mukherjee, A.; Mutsuddi, M. Recent Updates on the Genetics of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 5673–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-Z.; Ma, J.; Dou, J.-Z. The Role of TDP-43 in Neurodegenerative Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 4223–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, T.J.; Lee, V.M.Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q. TDP-43 Functions and Pathogenic Mechanisms Implicated in TDP-43 Proteinopathies. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, T.F.; Rademakers, R.; Petrucelli, L. TARDBP Mutation Analysis in TDP-43 Proteinopathies and Deciphering the Toxicity of Mutant TDP-43. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 33, S35–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, E. Chapter One—Functional Significance of TDP-43 Mutations in Disease; Friedmann, T., Dunlap, J.C., Goodwin, S.F.B.T.-A.G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 91, pp. 1–53. ISBN 0065-2660. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Goda, N.; Iwaya, N.; Tenno, T.; Shirakawa, M.; Hiroaki, H. Structure and Function of the N-Terminal Nucleolin Binding Domain of Nuclear Valosin-Containing Protein-like 2 (NVL2) Harboring a Nucleolar Localization Signal. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21732–21741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, J.F.; Berkova, Z.; Mathur, R.; Zhu, H.; Braun, F.K.; Tao, R.-H.; Sabichi, A.L.; Ao, X.; Maeng, H.; Samaniego, F. Nucleolin Inhibits Fas Ligand Binding and Suppresses Fas-Mediated Apoptosis in Vivo via a Surface Nucleolin-Fas Complex. Blood 2013, 121, 4729–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberg, D.C.; Burke, D.; Strathern, J.N.; Burke, D.; Laboratory, C.S.H. Methods in Yeast Genetics: A Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Course Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 0879697288. [Google Scholar]
- Vokes, M.; Carpenter, A. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., David, D., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., Struhl, K., Eds.; Chapter 14, Unit 14.17; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gietz, R.D.; Woods, R.A. Yeast Transformation by the LiAc/SS Carrier DNA/PEG Method. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 313, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirisola, M.G.; Braun, R.J.; Petranovic, D. Approaches to Study Yeast Cell Aging and Death. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014, 14, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noree, C.; Sirinonthanawech, N. Nuclear Targeted Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Asparagine Synthetases Associate with the Mitotic Spindle Regardless of Their Enzymatic Activity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.P.H.; Bruns, M.; Hartley, B.S. Extraction and Rapid Inactivation of Proteins FromSaccharomyces Cerevisiae by Trichloroacetic Acid Precipitation. Yeast 1989, 5, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peggion, C.; Massimino, M.L.; Pereira, D.; Granuzzo, S.; Righetto, F.; Bortolotto, R.; Agostini, J.; Sartori, G.; Bertoli, A.; Lopreiato, R. Structural Integrity of Nucleolin Is Required to Suppress TDP-43-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Yeast and Human Cell Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417466
Peggion C, Massimino ML, Pereira D, Granuzzo S, Righetto F, Bortolotto R, Agostini J, Sartori G, Bertoli A, Lopreiato R. Structural Integrity of Nucleolin Is Required to Suppress TDP-43-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Yeast and Human Cell Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417466
Chicago/Turabian StylePeggion, Caterina, Maria Lina Massimino, Daniel Pereira, Sara Granuzzo, Francesca Righetto, Raissa Bortolotto, Jessica Agostini, Geppo Sartori, Alessandro Bertoli, and Raffaele Lopreiato. 2023. "Structural Integrity of Nucleolin Is Required to Suppress TDP-43-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Yeast and Human Cell Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417466
APA StylePeggion, C., Massimino, M. L., Pereira, D., Granuzzo, S., Righetto, F., Bortolotto, R., Agostini, J., Sartori, G., Bertoli, A., & Lopreiato, R. (2023). Structural Integrity of Nucleolin Is Required to Suppress TDP-43-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Yeast and Human Cell Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417466





