A 4D Proteome Investigation of the Potential Mechanisms of SA in Triggering Resistance in Kiwifruit to Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Foliar Symptoms and Colonization Dynamics in Psa Treatment and SA + Psa Treatment
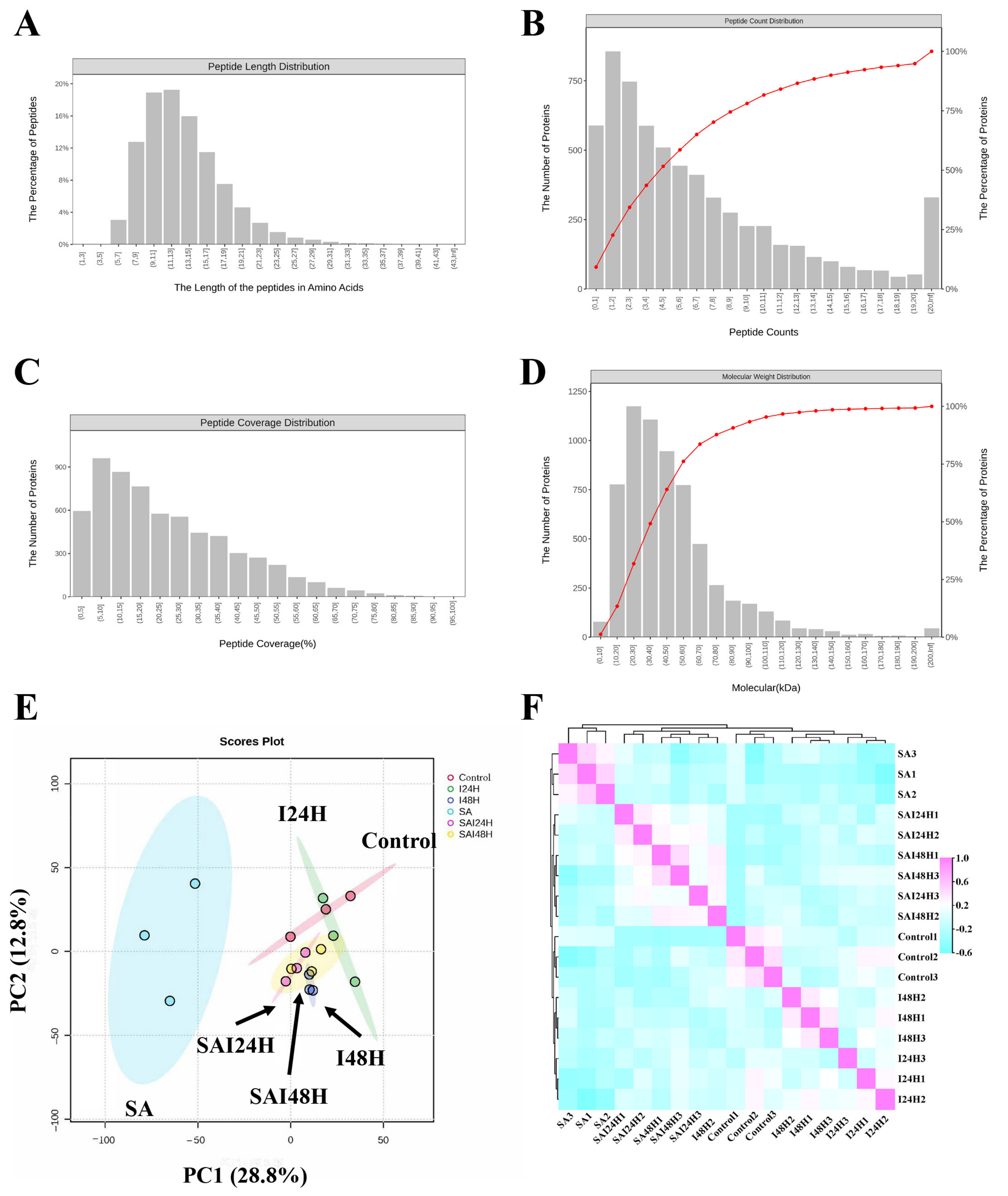
2.2. Proteome Analysis of Kiwifruit Following SA and Psa Treatment
2.3. Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae (Psa) Infection Induced Dramatic Variations in Proteome of Kiwifruit
2.4. Exogenous SA Treatment Altered the Proteomic Pattern of Kiwifruit
2.5. SA Promoted the Activation of Resistance Responses in Kiwifruit in Responses to Psa Infection
2.6. SA Promoted Multi-Responses Relevant to Resistance to Protect Kiwifruit from Psa Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation and Collection
4.2. Protein Extraction and Digestion
4.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.4. Identification and Quantitation of Proteins
4.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niu, Q.; Shen, J.; Liu, Y.; Nie, C.Y.; Skrypchenko, N.V.; Liu, D.J. Research progress on main active constituents and pharmacological activities of Actinidia arguta. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2019, 40, 344. [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Takikawa, Y.; Tsuyumu, S.; Goto, M. Occurrence of bacterial canker of kiwifruit in Japan: Description of symptoms, isolation of the pathogen and screening of bactericides. Jpn. J. Phytopathol. 1989, 55, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.; Sarojini, V. Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae: Chemical control, resistance mechanisms and possible alternatives. Plant Pathol. 2014, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scortichini, M. Occurrence of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae on kiwifruit in Italy. Plant Pathol. 1994, 43, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanneste, J.L.; Poliakoff, F.; Audusseau, C.; Cornish, D.A.; Paillard, S.; Rivoal, C.; Yu, J. First report of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae the causal agent of bacterial canker of kiwifruit on Actinidia deliciosa in France. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanneste, J.L.; Yu, J.; Cornish, D.A. Identification, virulence and distribution of two biovars of Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae in New Zealand. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Kim, K.H.; Son, K.I.; Ckoi, E.D. Outbreak and spread of bacterial canker of kiwifruit caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae biovar 3 in Korea. Korean J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 32, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.Z.; Zhu, X.X.; Wang, Y.D. Preliminary studies on kiwifruit diseases in Hunan province. Sichuan Fruit Tree Technol. 1990, 18, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.S.; Tang, X.F.; Liu, S.J. Identification of the pathogenic bacteria of Actinidia bacterial canker. J. Southwest Univ. 1992, 14, 500–503. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Li, Y.; Wan, S.; Zhang, J.; Pang, Q.; Li, G.; Xing, J.H. Pathogen identification of kiwifruit canker in Anhui province. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 1995, 22, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.J.; Gao, R.X. Survey and identification of Actinidia spp. diseases in Fujian, China. J. Fujian Agric. Univ. 1995, 24, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, G.H.; Koh, Y.J.; Jung, J.S. Identification of strA-strB genes in streptomycin-resistant Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae biovar 2 strains isolated in Korea. Plant Pathol. J. 2021, 37, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConn, M.; Creelman, R.A.; Bell, E.; Mullet, J.E.; Browse, J. Jasmonate is essential for insect defense in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5473–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngou, B.P.M.; Jones, J.D.G.; Ding, P.T. Plant immune networks. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomma, B.P.; Penninckx, I.A.; Cammue, B. The complexity of disease signaling in Arabidopsis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2001, 13, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Zuo, K.; Zhao, J.; Ling, H.; Cao, Y.F.; Qiu, C.X.; Li, F.P.; Sun, X.F.; Tang, K.X. Overexpression of GbERF confers alteration of ethylene-responsive gene expression and enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas syringae in transgenic tobacco. J. Biosci. 2006, 31, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Torres-Zabala, M.; Truman, W.; Bennett, M.H.; Lafforgue, G.; Mansfield, J.W.; Egea, P.R.; Bogre, L.; Grant, M. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato hijacks the Arabidopsis abscisic acid signalling pathway to cause disease. EMBO J. 2007, 6, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.R.; Dong, Q.Y.; Yu, D.Q. Arabidopsis WRKY46 coordinates with WRKY70 and WRKY53 in basal resistance against pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Sci. 2012, 185–186, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryals, J.; Lawton, K.A.; Delaney, T.P.; Friedrich, L.; Kessmann, H.; Neuenschwander, U.; Uknes, S.; Vernooij, B.; Weymann, K. Signal transduction in systemic acquired resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4202–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endah, R.; Beyene, G.; Kiggundu, A.; van den Berg, N.; Schlüter, U.; Kunert, K.; Chikwamba, R. Elicitor and Fusarium-induces expression of NPR1-like genes in banana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Hu, H.; Fan, B.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Z. Biosynthesis and roles of salicylic acid in balancing stress response and growth in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Ma, Y.; Sui, Y.; Xing, H.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Q.; Jiang, Y. Molecular mechanism of miR160d in regulating kiwifruit resistance to botrytis cinerea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10304–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gfeller, A.; Liechti, R.; Farmer, E.E. Arabidopsis jasmonate signaling pathway. Sci. Stke Signal Transduct. Knowl. Environ. 2006, 3, cm4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, A.; Baldwin, I.T. Plant responses to insect herbivory: The emerging molecular analysis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 299–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klessing, D.I.; Durner, J.; Noad, R.; Navarre, D.A.; Wendehennem, D.; Kumar, D.; Zhou, J.M.; Shah, J.; Zhang, S.; Kachroo, P.; et al. Nitric oxide and salicylic acid signaling in plant defense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8849–8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukasik, E.; Takken, F.L. Standing strong, resistance proteins instigators of plant defense. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogel, K.H.; Langen, G. Induced discase resistance and gene expression in cereals. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eszter, H.; Gabriella, S. Induction of abiotic stress tolerance by salicylic acid signaling. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2007, 26, 290–300. [Google Scholar]
- Alvaerz, M.E. Salicylic acid in the machinery of hypersensitive cell death and disease resistance. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 44, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsani, O.; Vaipuesta, V.; Motella, M.A. Evidence for a role of salicylic acid in the oxidative damage generated by NaCl and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis seedings. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.; Boden, E.; Arias, J. Salicylic acid and NPR1 induce the recruitment of trans-activating TGA factors to a defense gene promoter in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, K.A.; Friedrich, L.; Hunt, M.; Weymann, K.; Delaney, T.; Kessmann, H.; Staub, T.; Ryals, J. Benzothiadiazole induces disease resistance in Arabidopsis by activation of the systemic acquired resistance signal transduction pathway. Plant J. 1996, 10, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.R.; Ryals, J.A. Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 1991, 3, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Bowling, S.A.; Gordon, A.S. Characterization of an Arabidopsis mutant that is non-responsive to inducers of systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X. Generation of broad-spectrum disease resistance by overexpression of an essential regulatory gene in systemic acquired resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6531–6536. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Long, Y.H.; Yin, X.H.; Yang, S. Sulfur-induced resistance against Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae via triggering salicylic acid signaling pathway in kiwifruit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro-Villanueva, F.; Mao, X.; Chapple, C. Linking phenylpropanoid metabolism, lignin deposition, and plant growth inhibition. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 56, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, S. MAPK cascades in plant disease resistance signaling. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwalya, J.; Alazem, M.; Kim, K.H. Photosynthesis-related genes induce resistance against soybean mosaic virus: Evidence for involvement of the RNA silencing pathway. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 23, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Seilaniantz, A.; Navarro, L.; Bari, R.; Jones, J.D. Pathological hormone imbalances. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.C.; Fan, B.F.; Chen, Z.X. Pathogen-induced Arabidopsis WRKY7 is a transcriptional repressor and enhances plant susceptibility to Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Y.; Mosher, S.L.; Fan, B.F.; Klessig, D.; Chen, Z.X. Functional analysis of Arabidopsis WRKY25 transcription factor in plant defense against Pseudomonas syringae. BMC Plant Biol. 2007, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluchamy, S.; Panthee, D.R. Differential expression analysis of a select list of genes in susceptible and resistant heirloom tomatoes with respect to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2015, 142, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Wang, M.M.; Yin, Y.L.; Onan, E.; Zhou, G.F.; Peng, S.; Xia, X.J.; Shi, K.; Yu, J.Q.; Zhou, Y.H. RNA-seq analysis reveals the role of red light in resistance against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 in tomato plants. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.; Fariduddin, Q.; Castroverde, C.D.M. Salicylic acid: A key regulator of redox signaling and plant immunity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 168, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van der Ent, S.; Van Wees, S.C.M. Networking by small-molecule hormones in plant immunity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.; Mou, Z. Salicylic acid and its function in plant immunity. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.M.; Zhu, S.; Kachroo, P.; Kachroo, A. Signal regulators of systemic acquired resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shine, M.B.; Xiao, X.; Kachroo, P.; Kachroo, A. Signaling mechanisms underlying systemic acquired resistance to microbial pathogens. Plant Sci. 2019, 279, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Salicylic acid: Biosynthesis, perception, and contributions to plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2019, 50, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, T.; Friedrich, L.; Vernooij, B.; Negrotto, D.; Nye, G.; Uknes, S.; Ward, E.; Kessmann, H.; Ryals, J. Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 1993, 261, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, T.P.; Uknes, S.; Vernooij, B.; Friedrich, L.; Weymann, K.; Negrotto, D.; Gaffney, T.; Gut-Rella, M.; Kessmann, H.; Ward, E.; et al. A central role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance. Science 1994, 266, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlot, A.C.; Dempsey, D.A.; Klessig, D.F. Salicylic acid, a multifaceted hormone to combat disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chu, J.Y.; Boyle, P.; Wang, Y.; Brindle, I.D.; Luca, V.D.; Despres, C. The Arabidopsis NPR1 protein is a receptor for the plant defense hormone salicylic acid. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes da Silva, M.; Vasconcelos, M.W.; Pinto, V.; Balestra, G.M.; Mazzaglia, A.; Gomez-Cadenas, A.; Carvalho, S.M.P.l. Role of methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid in kiwifruit plants further subjected to Psa infection: Biochemical and genetic responses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Fang, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Li, R.; Bolund, L. WEGO: A web tool for plotting GO annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W293–W297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, D.; Yan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L. A 4D Proteome Investigation of the Potential Mechanisms of SA in Triggering Resistance in Kiwifruit to Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417448
Qu D, Yan F, Zhang Y, Huang L. A 4D Proteome Investigation of the Potential Mechanisms of SA in Triggering Resistance in Kiwifruit to Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(24):17448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417448
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Dong, Fei Yan, Yu Zhang, and Lili Huang. 2023. "A 4D Proteome Investigation of the Potential Mechanisms of SA in Triggering Resistance in Kiwifruit to Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 24: 17448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417448
APA StyleQu, D., Yan, F., Zhang, Y., & Huang, L. (2023). A 4D Proteome Investigation of the Potential Mechanisms of SA in Triggering Resistance in Kiwifruit to Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(24), 17448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242417448





