Abstract
In spite of its variety of biological activities, the clinical exploitation of human NGF (hNGF) is currently limited to ocular pathologies. It is therefore interesting to test the effects of hNGF in preclinical models that may predict their efficacy and safety in the clinical setting of ocular disorders and compare the effects of hNGF with those of its analogs. We used a human retinal pigment cell line, ARPE-19 cells, to investigate the effects of hNGF and its analogs, mouse NGF (mNGF) and painless NGF (pNGF), on cell viability under basal conditions and after exposure to oxidative stimuli, i.e., hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and ultraviolet (UV)-A rays. The effects of hNGF and pNGF were also tested on the gene expression and protein synthesis of the two NGF receptor subtypes, p75 neurotrophic receptors (p75NTR) and tyrosine kinase A (TrkA) receptors. We drew the following conclusions: (i) the exposure of ARPE-19 cells to H2O2 or UV-A causes a dose-dependent decrease in the number of viable cells; (ii) under baseline conditions, hNGF, but not pNGF, causes a concentration-dependent decrease in cell viability in the range of doses 1–100 ng/mL; (iii) hNGF, but not pNGF, significantly potentiates the toxic effects of H2O2 or of UV-A on ARPE-19 cells in the range of doses 1–100 ng/mL, while mNGF at the same doses presents an intermediate behavior; (iv) 100 ng/mL of hNGF triggers an increase in p75NTR expression in H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells, while pNGF at the same dose does not; (v) pNGF, but not hNGF (both given at 100 ng/mL), increases the total cell fluorescence intensity for TrkA receptors in H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells. The present findings suggest a vicious positive feedback loop through which NGF-mediated upregulation of p75NTR contributes to worsening the toxic effects of oxidative damage in the human retinal epithelial cell line ARPE-19. Looking at the possible clinical relevance of these findings, one can postulate that pNGF might show a better benefit/risk ratio than hNGF in the treatment of ocular disorders.
Keywords:
human NGF; mouse NGF; painless NGF; ARPE-19 cells; H2O2; UV-A; p75NTR receptors; TrkA receptors 1. Introduction
Nerve growth factor (NGF) was originally defined as a neurotrophic factor acting primarily on sympathetic and sensory neuronal cells [1]. At the time, it was found to exert regulatory activity in a large array of human cell types expressing NGF receptors, including skin fibroblasts, epidermal keratinocytes, umbilical vein endothelial cells and mast cells [2,3].
More recently, our group reported that NGF also exerts modulatory activities on mouse microglia [4], as well as on human microglial cells [5]. In spite of such a rapidly expanding profile as a pleiotropic regulatory agent, due to its potent pain-sensitizing activity [6,7], so far, hNGF has only been approved in human therapy for the topical treatment of moderate (persistent epithelial defect) or severe (corneal ulcer) neurotrophic keratitis in adults [8]. Apart from the approved indication, hNGF topical eyedrops are currently under clinical development for severe Sjogren dry eye disease [9,10], for moderate-to-severe dry eye syndrome [11,12] and for glaucoma [13].
Looking at hNGF from a pharmacological viewpoint, this agent should be considered in all respects as the first-in-class of a new class of medicines, namely the NGF analogs. Another member of this class, mNGF, shows an amino acid sequence very similar to that of hNGF (89.2%) and has been used in humans to test efficacy in skin wound healing in diabetic patients, in corneal lesions and in childhood optic gliomas [14,15,16]. Although it showed a promising benefit/risk ratio in these pilot studies (also because the lower affinity of mNGF for human TrkA and p75NTR receptors might have limited the pain-sensitizing effects [17]), mNGF did not undergo further clinical development, being potentially more immunogenic than NGF as a heterologous protein, and it should only be considered as a useful pharmacological tool.
In order to overcome the liabilities of human NGF-based drug candidates and fully exploit their potential, an optimized recombinant mutated form of hNGF, the so-called pNGF, was developed and characterized [4,18]. Painless NGF harbors two amino acid changes compared to wild type hNGF: glutamic acid replacing arginine in position 100 and serine replacing proline in position 61. The former change (R100E) was inspired by the congenital painlessness disease HSAN V [19] and is aimed at reducing pain sensitization activity while preserving neurotrophic potency. The latter amino acid change (P61S) allows pNGF detection and discrimination from the endogenous NGF in biological fluids without changing its pharmacological properties. Pharmacologically, the R100E mutation reduces the binding affinity to p75NTR (mainly involved in apoptosis) by two orders of magnitude compared to that of wild type NGF, with no affinity change for TrkA receptors (mediating neuronal survival [4,18]). Therefore, pNGF presents the same TrkA-mediated neurotrophic and neuroprotective properties of hNGF but shows very limited p75NTR signaling, together with a markedly lower algogenic activity in in vivo animal models [20]. Painless NGF has completed a full set of preclinical studies and is currently under clinical development for vision loss in pediatric patients affected by optic nerve gliomas [21], following on the positive results of a double-blind placebo-controlled study with mNGF eyedrops [16].
Thus, as a common feature of the whole class of NGF analogs, their clinical exploitation as therapeutic agents focuses on the area of ocular pathologies, in spite of a vast array of biological activities. Because of such organ-specific use, it is interesting to compare the effects of hNGF and its analogs in preclinical models that may be predictive of the efficacy and safety of these agents in the clinical setting of ocular disorders. We have previously characterized a human retinal pigment cell line, ARPE-19 cells, looking in particular at their sensitivity to oxidative damage, and used this model to investigate the putative protective effects of antioxidant agents [22]. In the present study, we used ARPE-19 cells to compare the effects of hNGF, mNGF and pNGF on cell viability, both under basal conditions and after cell damage induced by exposure to standard oxidative stimuli. The expression of NGF receptors in ARPE-19 cells and their possible changes associated with oxidative damage were also investigated.
2. Results
Under the experimental conditions described in Section 4, human retinal pigment ARPE-19 cells are sensitive to oxidative damage. Figure 1 shows the effects of standard oxidative agents, i.e., a 24 h exposure to 300 µM H2O2 (Figure 1B) and a 2 h exposure to UV-A (Figure 1C), compared to unchallenged control cells (Figure 1A). In this experimental paradigm, the quantification of oxidative damage, expressed as cell viability after the exposure to standardized oxidative challenge, is reported in Figure 1D, showing that the exposure to increasing doses of H2O2 for 24 h causes concentration-dependent lethality in ARPE-19. The estimated EC50 of H2O2 is between 350 and 400 µM. Likewise, the exposure to a physical oxidative stimulus, i.e., ultraviolet-A (UV-A) light, induces a time-dependent increase in ARPE-19 lethality, with an estimated EC50 achieved after an exposure to UV-A between 90 and 120 min (Figure 1E).
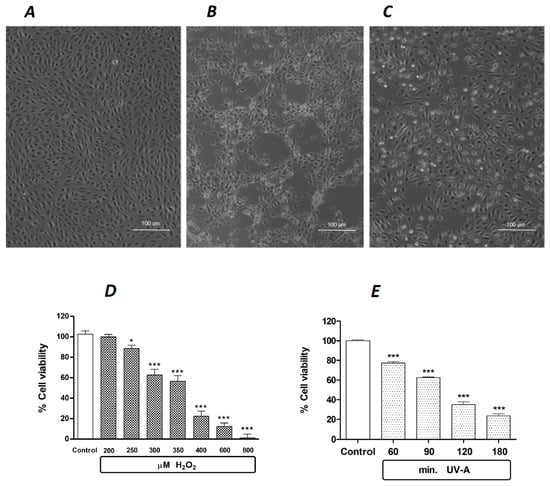
Figure 1.
The effects of standard oxidative stimuli, H2O2 and UV-A on human ARPE-19 cells in vitro. Representative phase contrast microscopies (×10 magnification) of human ARPE-19 cells under baseline control conditions (A), after a 24 h exposure to 300 µM H2O2 (B) and after a 2 h exposure to UV-A (C). (D): H2O2 decreases ARPE-19 cell viability in a concentration-dependent manner after a 24 h exposure. (E): UV-A decreases ARPE-19 cell viability in a time-dependent manner. Data from (D,E) are expressed as percentage cell viability, with the means ± 1 SEM of 6 replicates per experimental group. *: p < 0.05 and ***: p < 0.001 vs. controls.
Under basal conditions, the exposure of ARPE-19 cells to hNGF for 24 h produces a concentration-dependent decrease in cell viability, with a significant reduction (about 24.4%) observed at 100 ng/mL (Figure 2A), whereas no effect whatsoever was observed after the exposure to pNGF up to 100 ng/mL (Figure 2B).
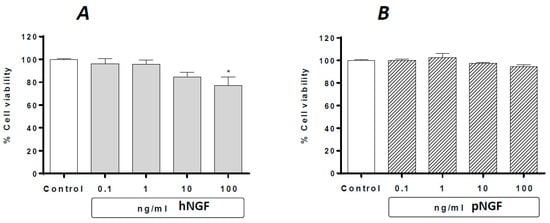
Figure 2.
The effects of hNGF (A) and pNGF (B) on cultured human ARPE-19 under baseline conditions. Data are expressed as percentage cell viability, with the means ± 1 SEM of 6 replicates per experimental group. *: p < 0.05 vs. controls.
Such a tendency to a cytotoxic effect associated with the exposure to hNGF, but not to pNGF, is markedly potentiated by a 24 h pre-treatment with submaximal toxic concentrations of H2O2 (Figure 3A,B). The same distinct results for hNGF and pNGF, respectively, are obtained after a 1 h pre-exposure to UV-A (Figure 3C,D). The pictures in Figure 4 are representative images showing the effects of the exposure to 100 ng/mL pNGF (Figure 4C) and 100 ng/mL hNGF (Figure 4D), both given after a 24 h pretreatment with 300 µM H2O2, compared to untreated control cells (Figure 4A) or cells pre-treated with 300 µM H2O2 only (Figure 4B). The reduced number of viable cells in the hNGF-treated cultures (Figure 4D), with respect to pNGF-incubated cells (Figure 4C), can be clearly observed. Likewise, Figure 5 shows representative images of the effects of 100 ng/mL pNGF (Figure 5C) and 100 ng/mL hNGF (Figure 5D) exposure, both given after a 1 h pre-exposure to UV-A, compared to untreated control cells (Figure 5A) or cells pre-exposed to UV-A only (Figure 5B). In this case, the distinct cytotoxic effect of hNGF versus that of pNGF (Figure 5C,D, respectively) is also clearly visible. This distinct cytotoxic effect of hNGF, with respect to pNGF, is most likely mediated by p75NTR due to the greatly reduced affinity of pNGF for p75NTR with respect to hNGF [4,18].
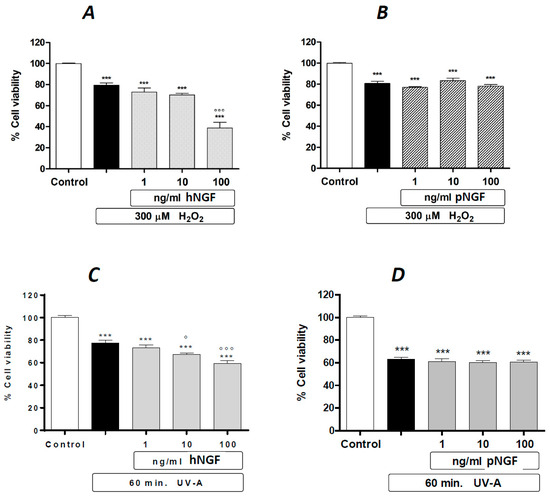
Figure 3.
The effects of hNGF and pNGF on cultured human ARPE-19 after a 24 h exposure to 300 µM H2O2 (A,B) or a 2 h exposure to UV-A (C,D). Black bars: H2O2 (A,B) or UV-A (C,D) given alone. Data are expressed as percentage cell viability, with the means ± 1 SEM of 6 replicates per experimental group. ***: p < 0.001 vs. controls. ° and °°°: p < 0.05 and p < 0.001 vs. the oxidative stimulus given alone, respectively.
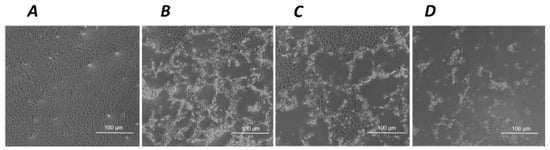
Figure 4.
The effects of hNGF and pNGF on cultured human ARPE-19 after a 24 h exposure to 300 µM H2O2. Representative phase contrast microscopies (×10 magnification) showing human ARPE-19 cells under baseline control conditions (A) and after a 24 h exposure to 300 µM H2O2 alone (B) or in the presence of 100 ng/mL pNGF (C) or 100 ng/mL hNGF (D).
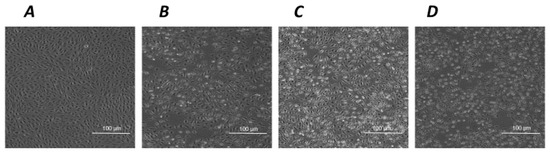
Figure 5.
The effects of hNGF and pNGF on cultured human ARPE-19 after a 2 h exposure to UV-A. Representative phase contrast microscopies (×10 magnification) showing human ARPE-19 cells under baseline control conditions (A) and after a 2 h exposure to UV-A alone (B) or in the presence of 100 ng/mL pNGF (C) or 100 ng/mL hNGF (D).
In a further set of experiments, we tested the effects of mNGF in the same experimental paradigm as described above. Mouse NGF appears to exert an intermediate effect compared to hNGF and pNGF, with a trend of potentiating the damage induced by H2O2 or UV-A, although to a lesser extent than hNGF (compare the result in Figure 6A,B to those in Figure 3A,C). Such ‘in-between’ behavior of mNGF is directly evident in experiments carried out with hNGF and pNGF taken as controls (Figure 6C) and is likely related to the lower binding affinity of mNGF for human p75NTR than that of hNGF [17].
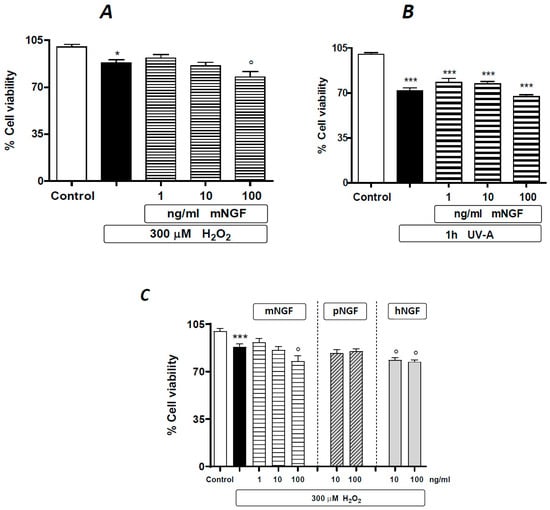
Figure 6.
The effects of mNGF on human ARPE-19 cells under baseline conditions and after oxidative stimuli. The effects of graded doses of mNGF on ARPE-19 cells pre-exposed to 300 µM H2O2 (A) or to UV-A (B). (C) Comparative effects of mNGF, pNGP and hNGF on ARPE-19 cells pre-exposed to 300 µM H2O2. Black bars: H2O2 (A,C) or UV-A (B) given alone. Data are expressed as percentage cell viability, with the means ± 1 SEM of 6 replicates per experimental group. * and ***: p < 0.05 and p < 0.001 vs. controls, respectively. °: p < 0.05 vs. the oxidative stimulus given alone.
To clarify the mechanisms underlying the toxic effects of hNGF on ARPE19 cells, we investigated the expression and localization of the receptors mediating the biological actions of NGF, namely TrkA and p75NTR [23,24,25,26]. In a first series of experiments carried out using RT-PCR, we found that TrkA mRNA is below the detection threshold, both in baseline conditions and after exposure to 300 µM H2O2 alone or in combination with 100 ng/mL hNGF or pNGF. In contrast, p75NTR mRNA expression can be measured under baseline conditions, as well as after the exposure to 300 µM H2O2 alone. Notably, p75 mRNA expression is strongly increased after exposure to H2O2 in the presence of hNGF (Figure 7), while p75NTR is not induced when H2O2 treatment is performed in the presence of pNGF (Figure 7). Given that pNGF, unlike hNGF, does not signal via p75NTR, this result suggests a p75-dependent positive feedback loop, whereby a p75-dependent signal increases the expression of p75NTR.
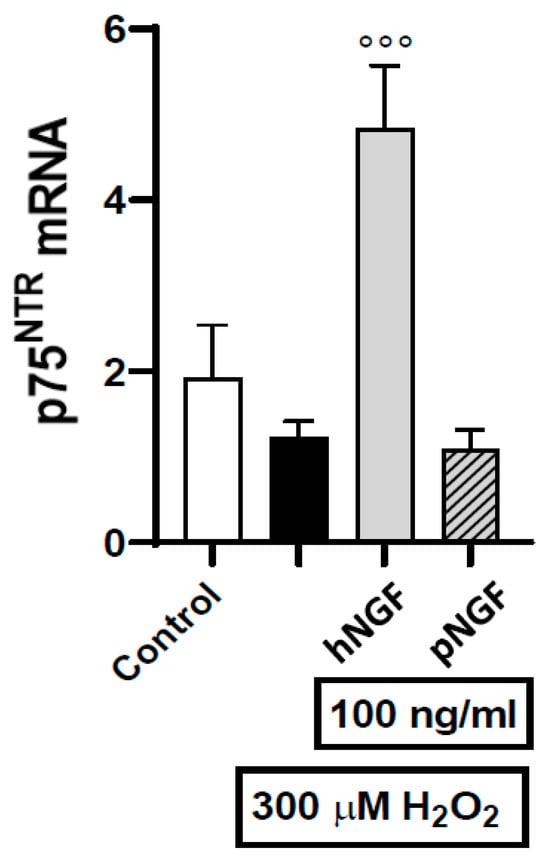
Figure 7.
The effects of 100 ng/mL hNGF and pNGF on p75NTR gene expression in ARPE-19 cells pre-exposed to 300 µM H2O2. Black bar: H2O2 given alone. Data are the means ± 1 SEM of the results from 3 different experiments with similar results. °°°: p < 0.001 vs. the oxidative stimulus given alone.
In order to provide complementary results to the bio-molecular experiments described above, immunofluorescence assays were performed in a separate set of experiments to assess the expression and localization of TrkA and p75NTR proteins in ARPE-19 cells treated with H2O2, hNGF and pNGF. First, the immunofluorescence experiments showed that ARPE-19 cells express TrkA receptors (visualized with the mouse monoclonal antibody MNAC13 directed against the native human receptor) and p75NTR receptors (Figure 8B,C). The negative controls omitting the primary antibodies are shown in Supplementary Figure S1. With regard to the subcellular localization of the two receptors, in physiological/control conditions, p75NTR was detected mostly in the perinuclear zone and the nuclear zone (Figure 8B), with the latter associated with the presence of p75+ clusters of puncta in the nuclear portion (red dots, Figure 8B), whereas we observed a cytosolic or nuclear localization for TrkA receptors associated with small dots in the cytoplasmic compartment (small green dots, Figure 8C).
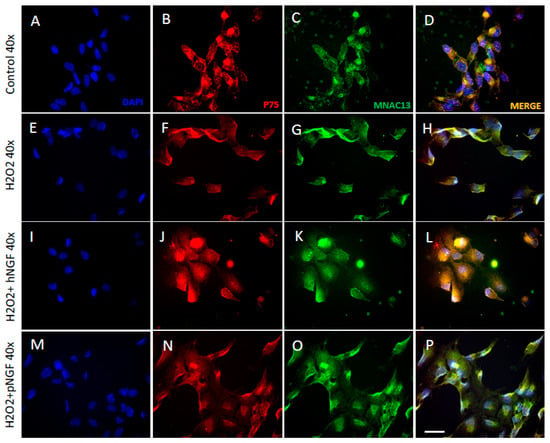
Figure 8.
Expression of NGF receptors in human ARPE-19 cells under baseline conditions (A–D) and after exposure to 300 µM H2O2 alone (E–H) or in the presence of hNGF (I–L) or pNGF (M–P). Blue fluorescence indicates DAPI staining of cell nuclei, red and green fluorescence indicate p75NRT and TrkA expression, respectively. Magnification ×40.
In cells treated with H2O2 (Figure 8E–H), the nuclear p75NTR clusters of puncta disappeared and were replaced by a more diffuse localization in the nucleus, with a stronger accumulation in the perinuclear membrane (Figure 8F). With regard to TrkA receptor labeling, following oxidative stress induction, the TrkA receptor labeling appeared more intense than that of p75NTR, compared to the control condition (Figure 8A–H). This observation was confirmed through the quantitative analysis of immunofluorescence (Figure 9A,B). Besides being more intense, the subcellular localization of TrkA receptors after H2O2 treatment was also mostly nuclear and cytosolic, with a greater increase in the perinuclear zone (green dots, Figure 8G).
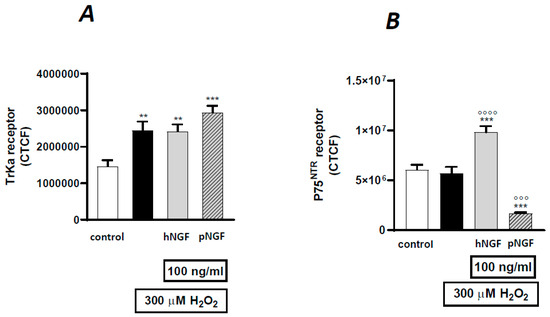
Figure 9.
The correct total cell fluorescence (CTCF) of TrkA (A) and p75NRT (B) receptor expression in ARPE-19 cells under baseline conditions or after exposure to 300 µM H2O2, alone or in the presence of 100 mg/mL hNGF or pNGF. Black bars: H2O2 given alone. Data are the means ± 1 SEM of the results from 3 different experiments with similar results. ** and ***: p < 0.01 and p < 0.001 vs. controls; °°° and °°°°: p < 0.001 and p < 0.0001 vs. the oxidative stimulus given alone.
The distinct effects of hNGF and pNGF on H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells were then compared. The addition of hNGF to H202-treated cells significantly increased the p75NTR expression compared to H2O2 exposure alone (p < 0.001, Figure 8F,J and Figure 9B), while pNGF-H2O2 treated cells showed a strong reduction in the p75 labeling (p < 0.001, Figure 8N and Figure 9B). Conversely, in H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells incubated with pNGF, the intensity of TrkA receptor expression was higher than that in the cells incubated with hNGF (p < 0.001 vs. p < 0.01; Figure 8K,O and Figure 9A). Moreover, the p75/TrkA co-localization was reduced by pNGF after H2O2 treatment (Figure 8D vs. Figure 8H).
We conclude that pNGF induces a marked decrease in p75NTR expression in H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells, whereas in the same cells, hNGF increases p75NTR expression. These data corroborate the above RT-PCR results, pointing to an increase in both p75NTR mRNA and protein driven by hNGF treatment (Figure 7).
3. Discussion
The main findings of this study are the following: (i) the human retinal pigment cell line ARPE-19 is sensitive to oxidative damage since exposure to H2O2 or UV-A causes a concentration- or time-dependent decrease in the number of viable cells in vitro; (ii) under baseline control conditions, hNGF, but not its mutant optimized form pNGF, causes a concentration-dependent decrease in cell viability in the 1–100 ng/mL range; (iii) hNGF significantly potentiates the toxic effects of H2O2 or UV-A on ARPE-19 cells, whereas pNGF has no influence whatsoever on the damaging effects of oxidative agents, while mNGF presents an intermediate behavior in this experimental setting; (iv) hNGF triggers an increase in p75NTR expression in H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells, while pNGF does not; (v) pNGF, more so than hNGF, increases the total cell fluorescence intensity for TrkA receptors in H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells.
Oxidative damage to the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is highly relevant to inherited retinal degenerations (IRDs) and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The RPE is a crucial cellular layer providing essential support and maintenance functions for the photoreceptors. It plays a vital role in the visual cycle, nutrient transport, waste disposal and protection against oxidative stress [27]. Diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa, Stargardt disease and AMD often involve dysfunction or loss of RPE cells [28,29]. Oxidative damage significantly contributes to the degenerative process in these diseases. Several factors may underlie oxidative stress in the RPE, such as light exposure, retinal metabolism and impaired antioxidant defense mechanisms. Oxidative damage to the RPE can lead to various detrimental effects, including lipofuscin accumulation, mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments and inflammation. These processes contribute to the progressive degeneration of photoreceptors and vision loss [27,28,29].
Given the broad neuroprotective properties of NGF and NGF-related proteins, exerted on target neurons and on glial cells, and the availability of clinically approved hNGF eyedrops [30], there is interest in evaluating both the neuroprotective effects of NGF and also its potential safety pitfalls and liabilities in human retinal cell models. In turn, this may help with designing and exploiting optimized NGF-related molecules.
In the present study, we found that hNGF worsened the H2O2-mediated (as well as the UV-mediated) oxidative damage of human RPE cells in a dose-dependent manner. We surmise that this exacerbation may be linked to the enhanced expression of the proapoptotic receptor p75NTR induced by hNGF, for the following reasons: (i) pNGF, which is a TrkA-biased variant of NGF with a 200-fold lower binding affinity for p75NTR, does not exacerbate the oxidative damage effect; (ii) hNGF, but not the p75-less pNGF, is a potent inducer of p75NTR mRNA and protein in the human retinal ARPE-19 cell line. Based on the data presented, this suggestion is in line with the established fact that the expression of p75NTR is upregulated by different forms of injuries and insults in different cells and tissues [31,32]. Moreover, oxidative stress induces p75NTR-mediated neurite neurodegeneration and apoptosis [33]. Notably pNGF, a TrkA-biased mutant NGF agonist devoid of p75NTR signaling ability, affected neither the H2O2-treated RPE cell viability nor the p75NTR expression level. On the other hand, as far as neuroprotection against oxidative stress is concerned, we observed that pNGF, while showing no additional toxic effect, did not ameliorate the reduced cell viability, as might have been expected. This lack of neuroprotection could arise due to the low expression of TrkA receptors in these cells. Compelling evidence showed that NGF and its mutated form exert neuroprotection by acting on glial cells [4,18]. Hence, a diverse cellular landscape, in its full complexity as found in vivo, is essential in order to obtain effective non-cell-autonomous neuroprotection of human retinal epithelial target cell(s) by pNGF. Future experiments on the effects of pNGF on H2O2-treated ARPE-19 cells co-cultured with different types of retinal glial cells will allow testing whether neuroprotection by pNGF, against oxidative stress toxicity of human epithelial cells, can be observed in these conditions.
Both NGF and its precursor proNGF are expressed in the rat RPE [34] and NGF mRNA, and p75NTR expression was also demonstrated in both human iris epithelial cells and RPE cells [35]. While the expression of the NGF and its p75NTR receptor in RPE cells has been previously observed, little is known about the functional significance of NGF-p75NTR signaling in RPE physiology and its potential role in retinal diseases. Our results provide a significant functional contribution to the understanding of NGF-p75 receptor signaling in a human retinal epithelial cell line. Some studies suggested that NGF may exert direct neuroprotective action on retinal photoreceptors [36,37]. A recent study in a zebrafish model of retinal degeneration [38] showed that intravitreally injected NGF has a pro-regenerative effect on photoreceptors. Depending on the hNGF dose, all these effects may be dampened by the p75-mediated pro-apoptotic effect. The use of pNGF, without influence on RPE cell death, could exert full efficacy in its neuroprotection of photoreceptors. The use of pNGF could potentiate the effect of antioxidants currently under evaluation to treat cone degeneration in IRD, i.e., n-acetylcysteine [39], which has been shown to protect RPE cells from oxidative damage [40].
It is important to take into account the limitations of this study. We consider that all data presented here have intrinsic validity, since different analogs are compared with each other in a system showing consistent responses to standardized stimuli. However, the system is limited to a single cell line, namely ARPE-19 cells. These cells have been extensively used since their first description in 1996, and more than 2000 reports have been published so far based on this cell line. A recent review has been published that analyzed the pitfalls of ARPE-19 cells used as a model of retinal pigmented epithelium [41], suggesting that a confirmation of the present results in a model of primary, non-transformed RPE cells is advisable.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
Human recombinant NGF was purchased from the Alomone laboratory (Jerusalem BioPark, Jerusalem, Israel). Painless NGF was kindly provided by Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A. (Parma, Italy). Hydrogen peroxide solution 30% (w/w) in H2O, 100 mL vials, and mouse NGF were purchased from Merck Life Science S.r.L. (Milan, Italy).
4.2. Cell Cultures and Treatments
ARPE-19 cells were obtained from the American Type Cell Culture (ATCC-CRL-2302, Manassas, VA, USA) and cultured according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The cells were raised in a DMEM/F12 medium (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 10% FBS (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), 2mM L-Glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and 100 U/mL penicillin–streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 environment. When cells reached 80% of confluence, they were split and sub-cultured at a concentration of 30,000 cells/cm2 at first, and later at a density of 15,000 cells/well in 96-well plates for experimental procedures.
On the day of the experiment, the cells were pre-treated for 24 h, in starvation conditions (0% FBS), with hNGF, pNGF or mNGF (treated groups) or medium alone (control group). The pre-treatment was followed by a second incubation period of 24 h, during which cells were exposed to oxidative stress in the presence of the neurotrophic factor added again.
The cells were exposed to two different agents inducing oxidative stress: H2O2 and UV-A rays, a chemical and physical oxidative stimulus, respectively. Specifically, after pretreatment with the neurotrophic factor (hNGF, pNGF or mNGF), the cells were exposed to H2O2 for 24 h or UV-A rays for 1 h. Irradiation was performed using a UV lamp (Vilber Lourmat VL-62C Power 6W; Vilber Lourmat Deutschland GmbH, Eberhardzell, Germany) with wavelength at 365 nm, placed at 10 cm from the cells for 1 h at an intensity of approximately 0.06 J/cm2/s. Immediately after exposure to the UV-A rays, the cells were put in an incubator until the end of the 24 h incubation period.
4.3. Assessment of Cell Viability
Twenty-four hours after inducing oxidative stress, with or without the neurotrophic factor, the cell viability was evaluated using the MTS assay (Promega, Waltham, MA, USA), according to the manufacturer’s procedure. The MTS reagent (20 µL) was added to cells, where it was converted to formazan. The quantity of formazan released into the culture supernatant, directly proportional to the number of living cells, was determined by measuring the absorbance at 490 nm with a microplate photometer (Victor 4, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The results are expressed as the percentage of cell viability relative to the untreated control.
Furthermore, the morphological features of the ARPE-19 cells, exposed to oxidative damage and/or in the presence of neurotrophic factors, were analyzed and photographed using phase-contrast microscopy (TE300-Eclipse-microscope; Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) at a magnification of ×10.
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
Total RNA from ARPE-19 was extracted using the Trizol reagent protocol. A Qubit™ RNA HS Assay Kit was used to measure RNA concentration (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and 40 ng aliquots of RNA were converted to cDNA using random hexamer primers. Quantitative changes in mRNA levels were measured through qRT-PCR using the following conditions: 35 cycles of denaturation (95 °C for 20 s), annealing and extension (60 °C for 20 s). The qRT PCR was carried out using the Brilliant III Ultra-Fast SYBR® Green QPCR Master Mix (Stratagene, San Diego, CA, USA). PCR reactions were conducted in a 20 µL reaction volume using an AriaMX real-time PCR machine (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The following primer sequences were used: P75NTR forward primers CCTACGGCTACTACCAGGATG, reverse primers CACACGGTGTTCTGCTTGT; human TrkA receptor forward primers TCAATGGCTCCGTGCTCAAT, reverse primers TGCTGTTAGTGTCAGGGATGG and β-actin forward primers ACGTTGCTATCCAGGCTGTGCTAT, reverse primers TTAATGTCACGCACGATTTCCCGC. Relative mRNA concentrations were calculated from the take-off point of reactions (threshold cycle, Ct comparative quantitation) using AriaMX software (Agilent Aria v1.5) and based upon the −∆∆Ct method. Ct values for β-actin expression worked as a normalizing signal.
4.5. Immunofluorescence
Cells were plated on ibidi chambers at a density of 45,000 cells/cm2. After the treatment, the seeding medium was removed, and cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde-PBS for 20 min at room temperature. After three washes in PBS 1X (10 min each), cells were permeabilized in PBS-Triton X-100 (Fluka) 0.5% for 10 min at room temperature and then washed three times with PBS 1X (10 min each). Cells were incubated for 1 h at room temperature with blocking solutions containing 0.3% Triton X-100 plus 2% bovine serum albumin (BSA) and 0.1 M Glycine, then overnight at 4 °C with the following primary antibodies: polyclonal rabbit anti-p75 (1:500, Promega cod. G3231) and mouse monoclonal anti-TrkA, MNAC13 (1:500 from 93 γ/λ stock concentration). The fluorescence was detected using secondary antibodies conjugated with Alexa-Fluor 488 (Green) and Alexa-Fluor 546 (Red) (1:500; Invitrogen-Thermo Fisher, Segrate, MI, Italy, cod. A32723 and A31572) in PBS for 1 h at RT. Each well was then incubated in Dapi (1:500; Invitrogen-Thermo Fisher) in PBS to make the cell nuclei visible. Coverslips were mounted using Fluoromount mounting medium (Sigma, cod. F4680). Confocal images were acquired with an Olympus microscope equipped with an Olympus Confocal scan unit (microscope BX61 and Confocal system FV500) managed using AnalySIS Fluoview software with 3 laser lines, a UV diode laser (405 nm), Ar–Kr (488 nm) and He–Ne (546 nm), respectively, used to detect Dapi staining and secondary antibodies. Double staining was revealed with a scanning sequential mode to eliminate possible bleed-through effect. For the negative control, only secondary antibodies were incubated in PBS for 1 h at RT. Quantitative data from images were obtained keeping the following image acquisition criteria: 40× objective, 1024 × 1024 frame.
The intensity of p75NTR and MNAC13 immunofluorescence was quantified following the protocol described by L. Hammond, QBI, The University of Queensland, Australia. The corrected total cell fluorescence (CTCF) was calculated by subtracting the value corresponding to the integrated density from the cell’s area for the mean fluorescence of background readings. A total of 10 cells were counted in each field, and 5 fields were examined for each experimental condition (control, H2O2, hNGF and pNGF), yielding a total of 50 cells analyzed for each group (n = 50).
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was repeated a minimum of two times, in sextuplicate. Data were analyzed through one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by the post hoc Dunnet or Newman–Keuls tests for comparisons between group means. Immunofluorescence quantification was analyzed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. Data were analyzed using a PrismTM computer program (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). All data are expressed as means ± 1 standard error of the mean (SEM), and differences were considered statistically significant if p < 0.05.
5. Conclusions
NGF and its analogs display a vast array of biological activities; nevertheless, the clinical exploitation of hNGF is currently limited to the setting of ocular disorders. In this study, we showed that hNGF, but not the optimized variant ‘painless NGF’, exacerbates oxidative damage in human epithelial retinal pigment cells; hNGF toxicity appears to be associated with a vicious cycle of NGF-induced over-expression of p75NTR receptors. We conclude that painless NGF might show a better benefit/risk ratio than NGF in the treatment of ocular disorders.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms242216237/s1.
Author Contributions
G.T. conceived and carried out the viability experiments. M.P. carried out the viability and RT-PCR experiments. L.L. carried out the RT-PCR experiments. S.M. carried out the immunofluorescence experiments and drafted the paper. L.B. carried out the immunofluorescence experiments. B.F. drafted the paper. A.C. drafted the paper. P.N. conceived the study and drafted the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by internal funding from UCSC (Fondi di Ateneo D1: 2021–2022) to GT. The contribution of financial support in the form of “Ricerca Corrente 2023” from Fondazione Policlinico Universitario “A. Gemelli” IRCCS to G.T. is acknowledged. This work was also supported by the “Fondo Ordinario Enti” (FOE D.M 865/2019) in the framework of a collaboration agreement between the Italian National Research Council and EBRI. We thank the EBRI’s Facility NGF Lab for providing the anti-TrkA antibody, MNAC13.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
The individual themselves provided information.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AMD | Age-related macular degeneration |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| ARPE-19 | Adult retinal pigment epithelial-19 (cell line) |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| EC50 | Effective concentration 50 (half-maximal) |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| hNGF | Human nerve growth factor |
| HSAN V | Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type V |
| IRD | Inherited retinal degeneration |
| mNGF | Mouse nerve growth factor |
| MTS | (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium) inner salt |
| NGF | Nerve growth factor |
| p75NTR | p75 neurotrophin receptor |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| RPE | Retinal pigment epithelium |
| RT-PCR | Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| TrkA | Tyrosine kinase A |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Levi-Montalcini, R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science 1987, 237, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi-Montalcini, R.; Skaper, S.D.; Dal Toso, R.; Petrelli, L.; Leon, A. Nerve growth factor: From neurotrophin to neurokine. Trends Neurosci. 1996, 19, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gostynska, N.; Pannella, M.; Rocco, M.L.; Giardino, L.; Aloe, L.; Calzà, L. The pleiotropic molecule NGF regulates the in vitro properties of fibroblasts; keratinocytes; and endothelial cells: Implications for wound healing. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C360–C371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.; Capsoni, S. Painless nerve growth factor: A TrkA biased agonist mediating a broad neuroprotection via its actions on microglia cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, L.; Marinelli, S.; Ciotti, G.M.P.; Pizzoferrato, M.; Palmerio, F.; Chiavari, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Navarra, P. The effects of painless nerve growth factor on human microglia polarization. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 969058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apfel, S.C. Nerve growth factor for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy: What went wrong; what went right; and what does the future hold? Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2002, 50, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pezet, S.; McMahon, S.B. Neurotrophins: Mediators and modulators of pain. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 507–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/oxervate-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05133180. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05136170. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03019627. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03982368. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02855450. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Lambiase, A.; Rama, P.; Bonini, S.; Caprioglio, G.; Aloe, L. Topical treatment with nerve growth factor for corneal neurotrophic ulcers. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generini, S.; Tuveri, M.A.; Matucci Cerinic, M.; Mastinu, F.; Manni, L.; Aloe, L. Topical application of nerve growth factor in human diabetic foot ulcers. A study of three cases. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2004, 112, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsini, B.; Chiaretti, A.; Rizzo, D.; Piccardi, M.; Ruggiero, A.; Manni, L.; Soligo, M.; Dickmann, A.; Federici, M.; Salerni, A.; et al. Nerve growth factor improves visual loss in childhood optic gliomas: A randomized; double-blind; phase II clinical trial. Brain 2016, 139, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, F.; Malerba, F.; Bruni Ercole, B.; Lamba, D.; Cattaneo, A. A comparative analysis of the structural; functional and biological differences between Mouse and Human Nerve Growth Factor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1854, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covaceuszach, S.; Capsoni, S.; Marinelli, S.; Pavone, F.; Ceci, M.; Ugolini, G.; Vignone, D.; Amato, G.; Paoletti, F.; Lamba, D.; et al. In vitro receptor binding properties of a “painless” NGF mutein; linked to hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy type V. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capsoni, S. From genes to pain: Nerve growth factor and hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type V. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 39, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capsoni, S.; Covaceuszach, S.; Marinelli, S.; Ceci, M.; Bernardo, A.; Minghetti, L.; Ugolini, G.; Pavone, F.; Cattaneo, A. Taking pain out of NGF: A “painless” NGF mutant; linked to hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy type V; with full neurotrophic activity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05733572. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 15 September 2023).
- Clementi, M.E.; Pizzoferrato, M.; Bianchetti, G.; Brancato, A.; Sampaolese, B.; Maulucci, G.; Tringali, G. Cytoprotective Effect of Idebenone through Modulation of the Intrinsic Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Exposed to Oxidative Stress Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.V.; Hempstead, B.L. p75 and Trk: A two-receptor system. Trends Neurosci. 1995, 18, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.R.; Miller, F.D. Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2000, 10, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechant, G.; Barde, Y.A. The neurotrophin receptor p75(NTR): Novel functions and implications for diseases of the nervous system. Nat. Neurosci. 2002, 5, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.V. Neurotrophins and their receptors: A convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Lytvynchuk, L.; Ardan, T.; Studenovska, H.; Faura, G.; Eide, L.; Znaor, L.; Erceg, S.; Stieger, K.; Motlik, J.; et al. Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell Development: Extrapolating Basic Biology to Stem Cell Research. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, A.; Meshkat, B.I.; Jablonski, M.M.; Hollingsworth, T.J. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Pathogenesis Underlying Inherited Retinal Dystrophies. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, M.; Bora, K.; Blomfield, A.K.; Pavlovich, M.C.; Huang, S.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, J. Oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelium degeneration: From pathogenesis to therapeutic targets in dry age-related macular degeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pedrotti, E.; Bonacci, E.; Chierego, C.; De Gregorio, A.; Cozzini, T.; Brighenti, T.; Caldarella, G.; Pastore, G.; Fasolo, A.; Marchini, G. Eight months follow-up of corneal nerves and sensitivity after treatment with cenegermin for neurotrophic keratopathy. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coassin, M.; Lambiase, A.; Sposato, V.; Micera, A.; Bonini, S.; Aloe, L. Retinal p75 and bax overexpression is associated with retinal ganglion cells apoptosis in a rat model of glaucoma. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 246, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Dergham, P.; Nedev, H.; Xu, J.; Galan, A.; Rivera, J.C.; Zhi Hua, S.; Mehta, H.M.; Woo, S.B.; Sarunic, M.V.; et al. Chronic and acute models of retinal neurodegeneration TrkA activity are neuroprotective whereas p75NTR activity is neurotoxic through a paracrine mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 39392–39400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, B.R.; Snow, J.P.; Vollbrecht, P.; Pathak, A.; Valentine, W.M.; Deutch, A.Y.; Carter, B.D. A role for the p75 neurotrophin receptor in axonal degeneration and apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 21205–21216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Sima, A.; Lee, J.; Brachet, P.; Dicou, E. Nerve growth factor (NGF); proNGF and NGF receptor-like immunoreactivity in BB rat retina. Brain Res. 1990, 523, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kociok, N.; Heppekausen, H.; Schraermeyer, U.; Esser, P.; Thumann, G.; Grisanti, S.; Heimann, K. The mRNA expression of cytokines and their receptors in cultured iris pigment epithelial cells: A comparison with retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 1998, 67, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchetti, M.; Mantelli, F.; Rocco, M.L.; Micera, A.; Brandolini, L.; Focareta, L.; Pisano, C.; Aloe, L.; Lambiase, A. Recombinant Human Nerve Growth Factor Treatment Promotes Photoreceptor Survival in the Retinas of Rats with Retinitis Pigmentosa. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, M.L.; Balzamino, B.O.; Petrocchi Passeri, P.; Micera, A.; Aloe, L. Effect of Purified Murine NGF on Isolated Photoreceptors of a Rodent Developing Retinitis Pigmentosa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocchiaro, P.; Di Donato, V.; Rubbini, D.; Mastropasqua, R.; Allegretti, M.; Mantelli, F.; Aramini, A.; Brandolini, L. Intravitreal Administration of rhNGF Enhances Regenerative Processes in a Zebrafish Model of Retinal Degeneration. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 822359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, P.A.; Iftikhar, M.; Hafiz, G.; Akhlaq, A.; Tsai, G.; Wehling, D.; Lu, L.; Wall, G.M.; Singh, M.S.; Kong, X. Oral N-acetylcysteine improves cone function in retinitis pigmentosa patients in phase I trial. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1527–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kularatne, R.N.; Bulumulla, C.; Catchpole, T.; Takacs, A.; Christie, A.; Stefan, M.C.; Csaky, K.G. Protection of human retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative damage using cysteine prodrugs. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, B.A.; Fliesler, S.J. Reassessing the suitability of ARPE-19 cells as a valid model of native RPE biology. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 219, 109046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).