Elevated Fecal Calprotectin Accompanied by Intestinal Neutrophil Infiltration and Goblet Cell Hyperplasia in a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
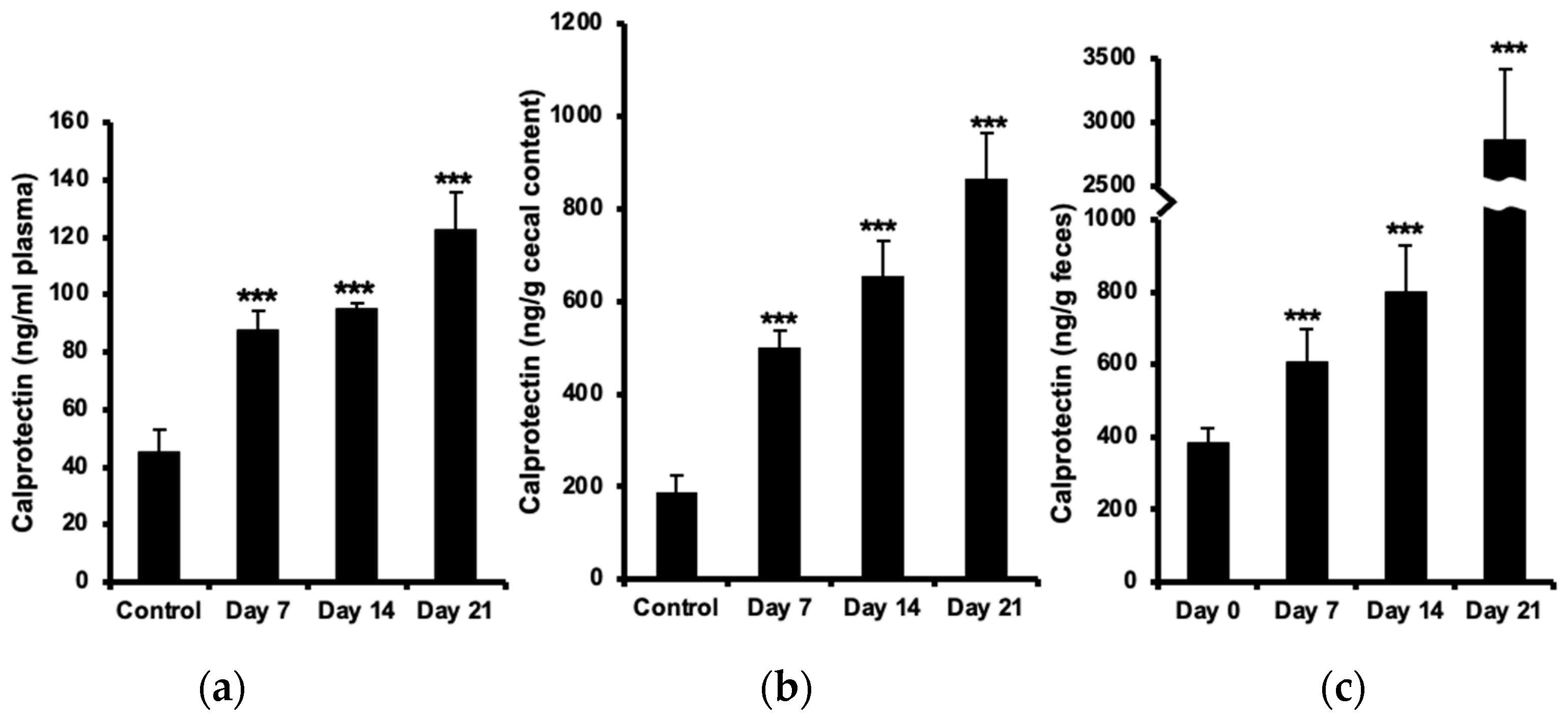
2.1. Increased Calprotectin in Plasma, Cecal Content, and Feces
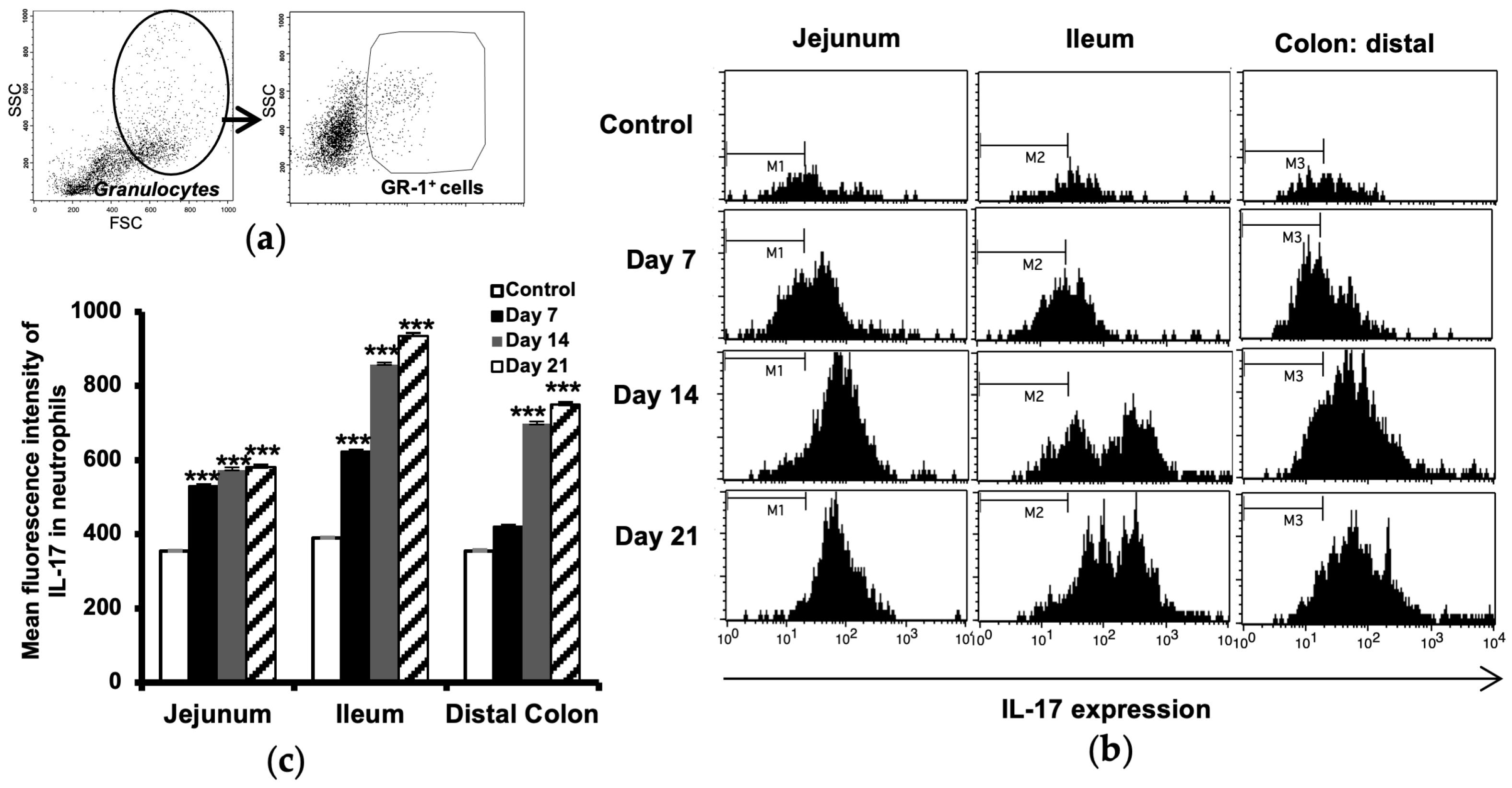
2.2. Increased Number of Neutrophils in the Intestine
2.3. Increased IL-17 Expression in Intestinal Neutrophils
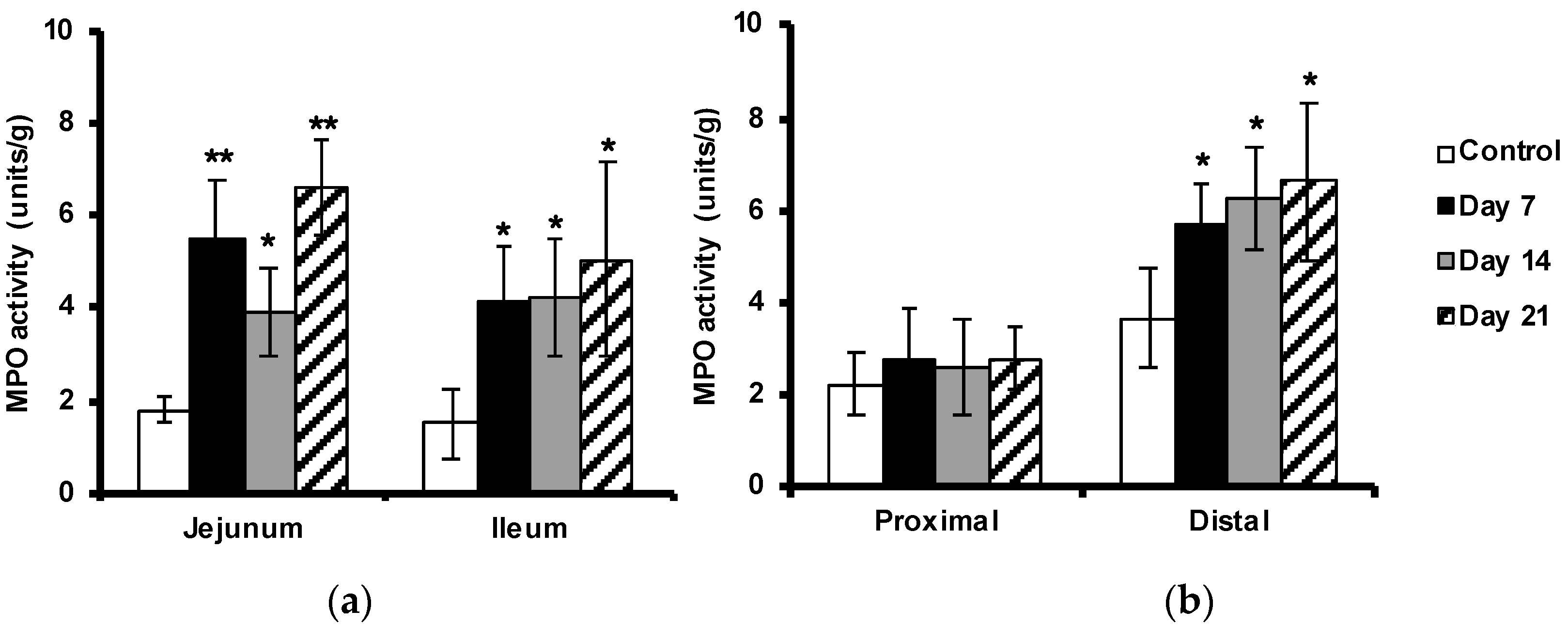
2.4. Enhanced Myeloperoxidase Activity in the Intestine
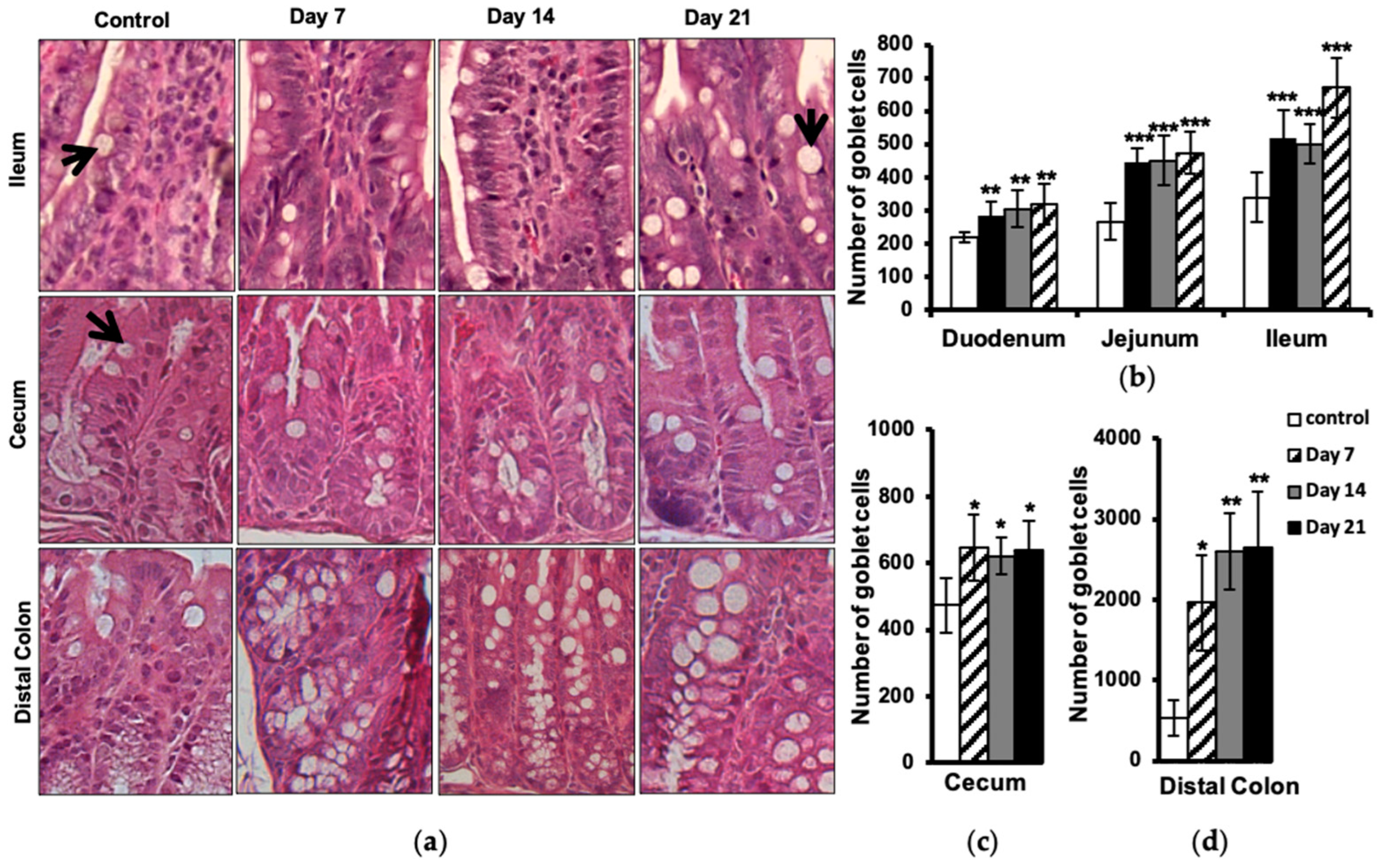
2.5. Increased Number of Intestinal Goblet Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Induction and Assessment of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE)
4.3. Calprotectin Measurement
4.4. Microscopic Analysis of Neutrophils and Goblet Cells
4.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Neutrophils
4.6. Myeloperoxidase Activity
4.7. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marrie, R.A.; Leung, S.; Tyry, T.; Cutter, G.R.; Fox, R.; Salter, A. Functional gastrointestinal disorders negatively affect health-related quality of life in MS. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2019, 9, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhawajah, M.M.; Caminero, A.B.; Freeman, H.J.; Oger, J.J.F. Multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel diseases: What we know and what we would need to know! Mult. Scler. 2013, 19, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, C.; Chelvanayagam, S. Bowel problems and coping strategies in people with multiple sclerosis. Br. J. Nurs. 2010, 19, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouri, M.; Bredberg, A.; Weström, B.; Lavasani, S. Intestinal barrier dysfunction develops at the onset of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, and can be induced by adoptive transfer of auto-reactive T cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 3, e106335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöström, B.; Bredberg, A.; Mandl, T.; Alonso-Magdalena, L.; Ohlsson, B.; Lavasani, S.; Nouri, M.; Henriksson, G. Increased intestinal permeability in primary Sjögren’s syndrome and multiple sclerosis. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bert, S.; Nadkarni, S.; Perretti, M. Neutrophil-T cell crosstalk and the control of the host inflammatory response. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 314, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, M.; Maggi, L.; Micheletti, A.; Lazzeri, E.; Tamassia, N.; Costantini, C.; Cosmi, L.; Lunardi, C.; Annunziato, F.; Romagnani, S.; et al. Evidence for a cross-talk between human neutrophils and Th17 cells. Blood 2010, 115, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, B.M.; Parkos, C.A. The role of neutrophils during intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2012, 5, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojkowska, D.W.; Szpakowski, P.; Ksiazek-Winiarek, D.; Leszczynski, M.; Glabinski, A. Interactions between neutrophils, Th17 Cells, and chemokines during the initiation of experimental model of multiple sclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 590409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xue, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Du, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, M.J. Mast cell deficiency exacerbates inflammatory bowel symptoms in interleukin-10-deficient mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9106–9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Ogawa, A.; Mizoguchi, E.; Shimomura, Y.; Andoh, A.; Bhan, A.K.; Blumberg, R.S.; Xavier, R.J.; Mizoguchi, A. IL-22 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volin, M.V.; Shahrara, S. Role of TH-17 Cells in Rheumatic and Other Autoimmune Diseases. Rheumatology 2011, 20, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbakk, M.; Naess-Andresen, C.F.; Fagerhol, M.K.; Lingaas, E.; Dale, I.; Brandtzaeg, P. Antimicrobial actions of calcium binding leucocyte L1 protein, calprotectin. Lancet 1990, 336, 763–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konikoff, M.R.; Denson, L.A. Role of fecal calprotectin as a biomarker of intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, B.E.; Clohessy, P.A.; Russell, G.; Fagerhol, M.K.; Blood, G.R.; Golden, B.E. Calprotectin as a marker of inflammation in cystic fibrosis. Arch. Dis. Child. 1996, 74, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madland, T.M.; Hordvik, M.; Haga, H.J.; Jonsson, R.; Brun, J.G. Leukocyte protein calprotectin and outcome in rheumatoid arthritis: A longitudinal study. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 31, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosch, M.; Metze, D.; Foell, D.; Vogl, T.; Sorg, C.; Sunderko, C.; Roth, J. Early activation of cutaneous vessels and epithelial cells is characteristic of acute systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Exp. Dermatol. 2005, 14, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, A.; Gustavsen, S.; Hasselbalch, I.C.; Langkilde, A.R.; Sellebjerg, F.; Oturai, A.B.; Søndergaard, H.B. Biomarkers of inflammation and epithelial barrier function in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 46, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerhol, M.K. Calprotectin, a faecal marker of organic gastrointestinal abnormality. Lancet 2000, 356, 1783–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, C.; Aziz, M.; Aubry, T.; Gourcerol, G.; Quillard, M.; Zalar, A.; Coëffier, M.; Dechelotte, P.; Leroi, A.M.; Ducrotté, P. Does calprotectin level identify a subgroup among patients suffering from irritable bowel syndrome? Results of a prospective study. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, R.J.; Eakin, M.N.; Czyzewski, D.I.; Jarrett, M.; Ou, C.N. Increased Gastrointestinal Permeability and Gut Inflammation in Children with Functional Abdominal Pain and Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Journal of Pediatrics. J. Pediatr. 2008, 153, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg-Hansen, P.; Vandvik, B.; Fagerhol, M.; Holmøy, T. Calprotectin levels in the cerebrospinal fluid reflect disease activity in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 216, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andréasson, K.; Scheja, A.; Saxne, T.; Ohlsson, B.; Hesselstrand, R. Faecal calprotectin: A biomarker of gastrointestinal disease in systemic sclerosis. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 270, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Røseth, A.G.; Kristinsson, J.; Fagerhol, M.K.; Schjønsby, H.; Aadland, E.; Nygaard, K.; Roald, B. Faecal calprotectin: A novel test for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer? Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1993, 28, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingberg, E.; Carlsten, H.; Hilme, E.; Hedberg, M.; Forsblad-D’Elia, H. Calprotectin in ankylosing spondylitis—Frequently elevated in feces, but normal in serum. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.A.; Gaya, D.R. Utility of faecal calprotectin analysis in adult inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 14, 6782–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogumil, T.; Rieckmann, P.; Kubuschok, B.; Felgenhauer, K.; Brück, W. Serum levels of macrophage-derived protein MRP-8/14 are elevated in active multiple sclerosis. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 247, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, S.; Van Der Goes, A.; Killestein, J.; Knol, D.L.; Barkhof, F.; Polman, C.H.; Dijkstra, C.D.; De Vries, H.E.; Meilof, J.F. Monocyte activation and disease activity in multiple sclerosis. A longitudinal analysis of serum MRP8/14 levels. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 148, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berstad, A.; Arslan, G.; Folvik, G. Relationship between Intestinal Permeability and Calprotectin Concentration in Gut Lavage Fluid. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 35, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Abuazab, M.; Schwiertz, A.; Walter, S.; Faßbender, K.C.; Fousse, M.; Unger, M.M. Short-chain fatty acids and intestinal inflammation in multiple sclerosis: Modulation of female susceptibility by microbial products? Auto Immun. Highlights 2021, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.M.L.; Nguyen, T.M.; Mcdonald, J.W.D.; Macdonald, J.K. Natalizumab for induction of remission in Crohn’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 8, CD006097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawisz, J.E.; Sharon, P.; Stenson, W.F. Quantitative Assay for Acute Intestinal Inflammation Based on Myeloperoxidase Activity Assessment of Inflammation in Rat and Hamster Models. Gastroenterology 1984, 87, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Droeser, R.A.; Hirt, C.; Eppenberger-Castori, S.; Zlobec, I.; Viehl, C.T.; Frey, D.M.; Nebiker, C.A.; Rosso, R.; Zuber, M.; Amicarella, F.; et al. High Myeloperoxidase Positive Cell Infiltration in Colorectal Cancer Is an Independent Favorable Prognostic Factor. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnhold, J.; Flemmig, J. Human myeloperoxidase in innate and acquired immunity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 500, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.Y. Intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in Crohn’s disease. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1997, 214, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez, J. Role of Th17 Cells in the Pathogenesis of Human IBD. ISRN Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 928461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljković, Đ.; Jevtić, B.; Stojanović, I.; Dimitrijević, M. ILC3, a Central Innate Immune Component of the Gut-Brain Axis in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 657622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Ito, N.; Mindur, J.E.; Kumar, H.; Youssef, M.; Suresh, S.; Kulkarni, R.; Rosario, Y.; Balashov, K.E.; Dhib-Jalbut, S.; et al. Fecal Lcn-2 level is a sensitive biological indicator for gut dysbiosis and intestinal inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 21, 1015372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverpil, E.; Glader, P.; Hansson, M.; Lindén, A. Impact of interleukin-17 on macrophage phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils and particles. Inflammation 2011, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ho, S.B. Intestinal goblet cells and mucins in health and disease: Recent insights and progress. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Khan, W.I. Goblet cells and mucins: Role in innate defense in enteric infections. Pathogens 2013, 2, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenewicz, L.A.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Murphy, A.J.; Stevens, S.; Flavell, R.A. Innate and Adaptive Interleukin-22 Protects Mice from Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Immunity 2008, 29, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz-Kuhnt, A.; Neurath, M.F.; Wirtz, S.; Atreya, I. Innate Lymphoid Cells as Regulators of Epithelial Integrity: Therapeutic Im-plications for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 656745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toward, T.J.; Broadley, K.J. Goblet cell hyperplasia, airway function, and leukocyte infiltration after chronic lipopolysaccharide exposure in conscious guinea pigs: Effects of rolipram and dexamethasone. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavasani, S.; Dzhambazov, B.; Nouri, M.; Fåk, F.; Buske, S.; Molin, G.; Thorlacius, H.; Alenfall, J.; Jeppsson, B.; Weström, B. A novel probiotic mixture exerts a therapeutic effect on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mediated by IL-10 producing regulatory T cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 2, e9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nouri, M.; Weström, B.; Lavasani, S. Elevated Fecal Calprotectin Accompanied by Intestinal Neutrophil Infiltration and Goblet Cell Hyperplasia in a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015367
Nouri M, Weström B, Lavasani S. Elevated Fecal Calprotectin Accompanied by Intestinal Neutrophil Infiltration and Goblet Cell Hyperplasia in a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(20):15367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015367
Chicago/Turabian StyleNouri, Mehrnaz, Björn Weström, and Shahram Lavasani. 2023. "Elevated Fecal Calprotectin Accompanied by Intestinal Neutrophil Infiltration and Goblet Cell Hyperplasia in a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 20: 15367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015367
APA StyleNouri, M., Weström, B., & Lavasani, S. (2023). Elevated Fecal Calprotectin Accompanied by Intestinal Neutrophil Infiltration and Goblet Cell Hyperplasia in a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(20), 15367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242015367




