Isolinderalactone Induces Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Cycle Arrest and MAPK Activation through ROS–Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
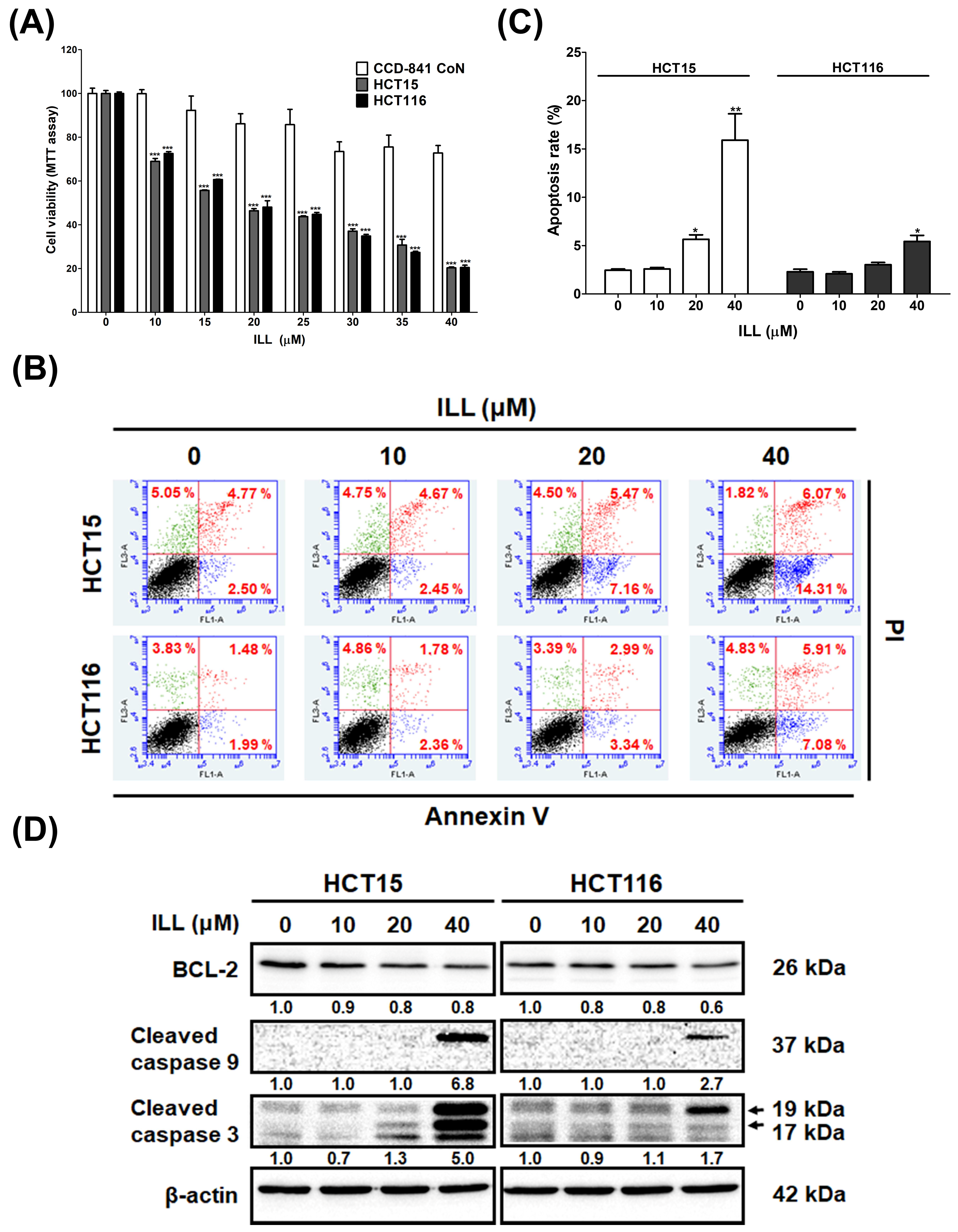
2.1. ILL Inhibited the Proliferation of Human CRC Cells
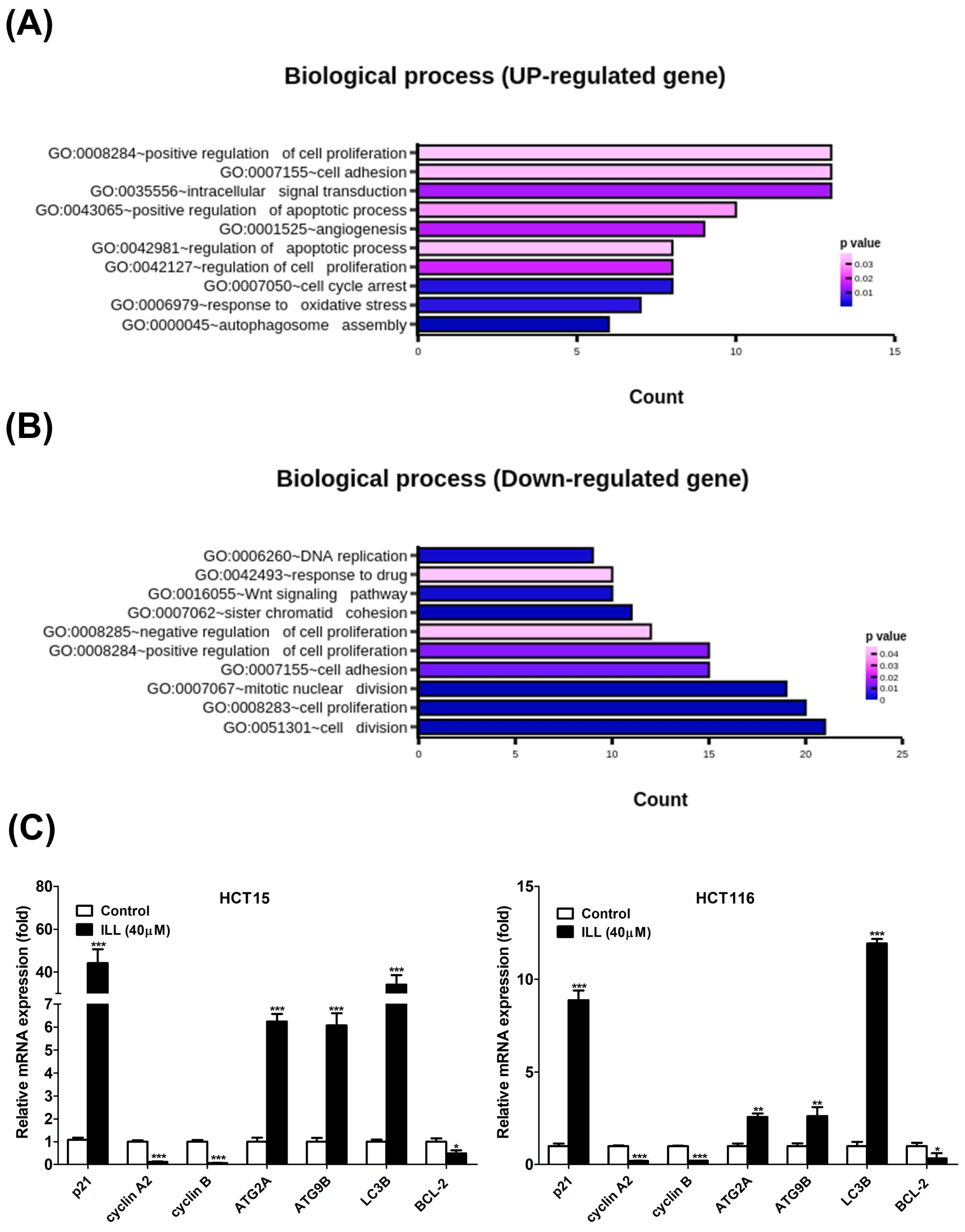
2.2. Transcriptome Analysis of ILL–Treated Human CRC Cells
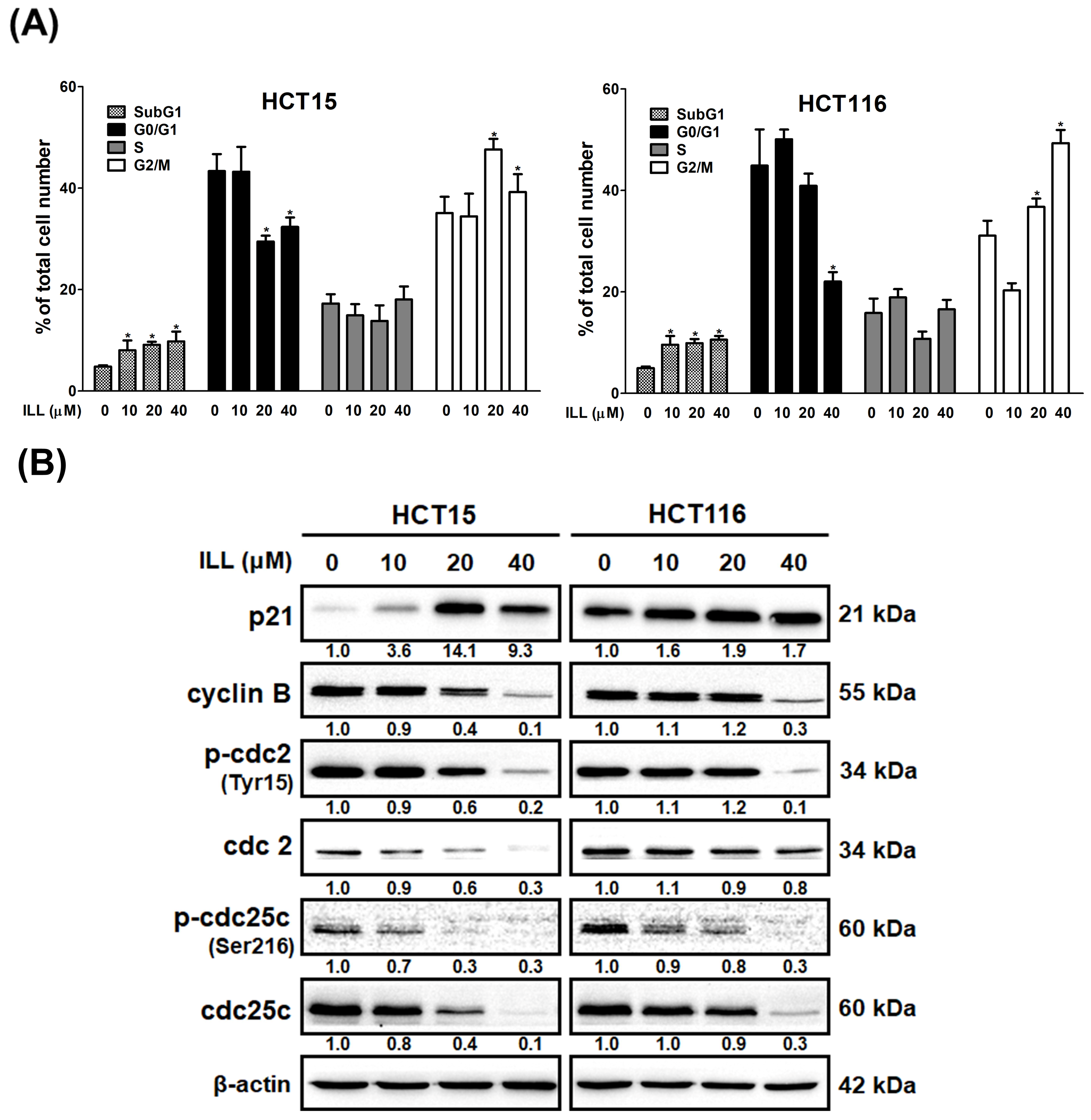
2.3. ILL Induced Cell Cycle G2/M Arrest in Human CRC Cells
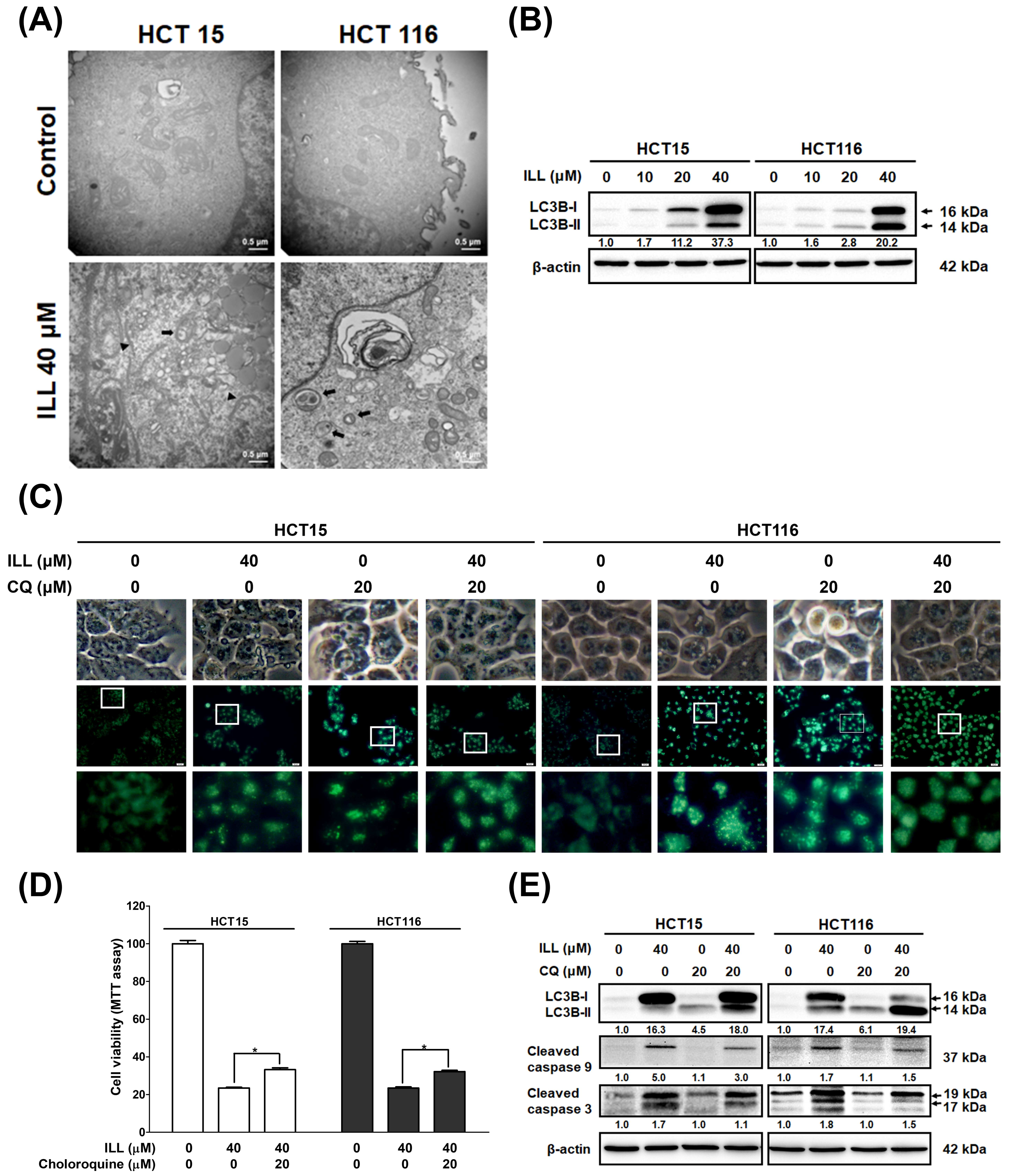
2.4. ILL Stimulated Autophagy in Human CRC Cells
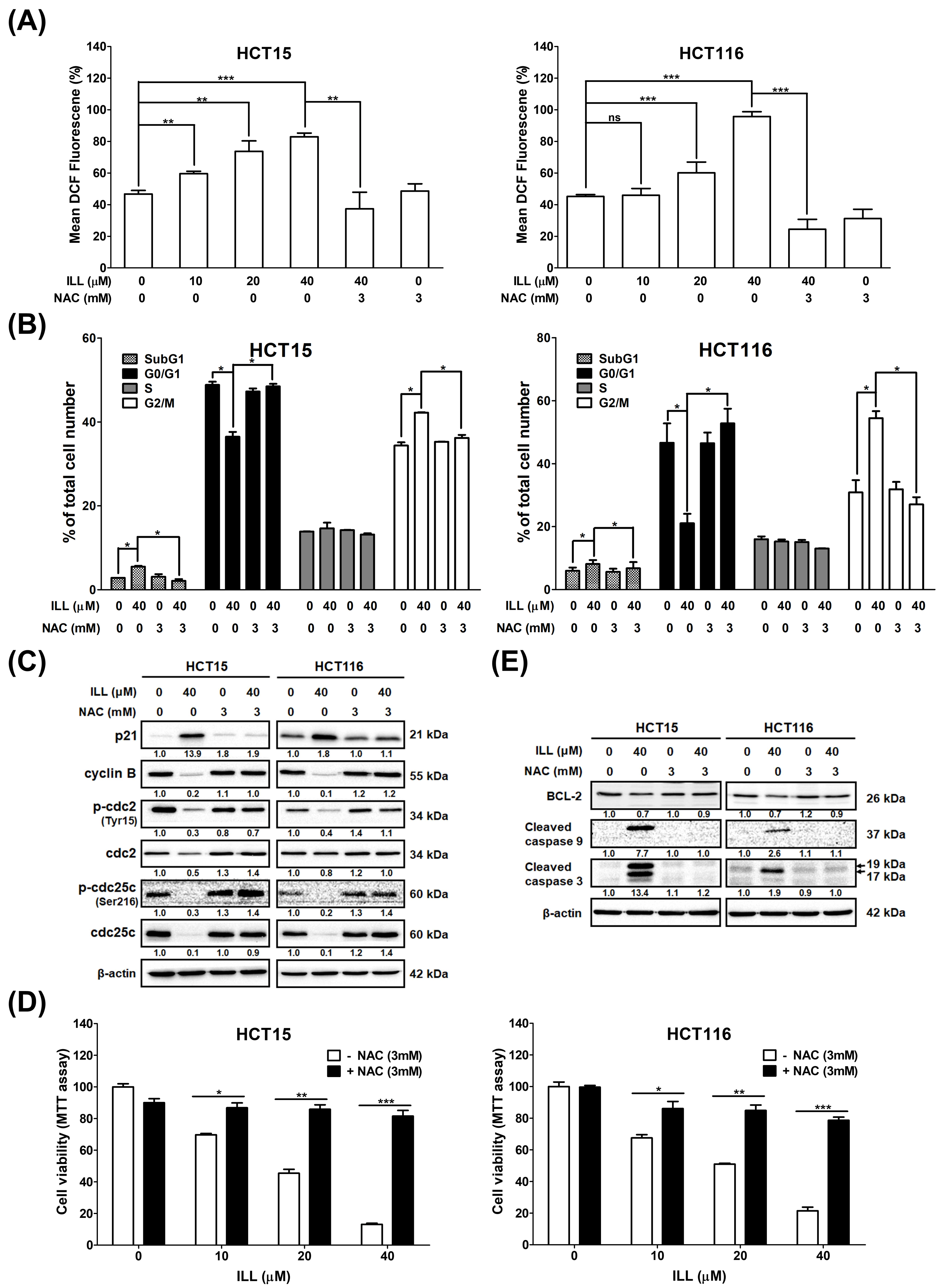
2.5. Generation of ROS in Human CRC Cells after ILL Treatment
2.6. ILL–Mediated ROS Generation Contributed to Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Cell Cycle Arrest
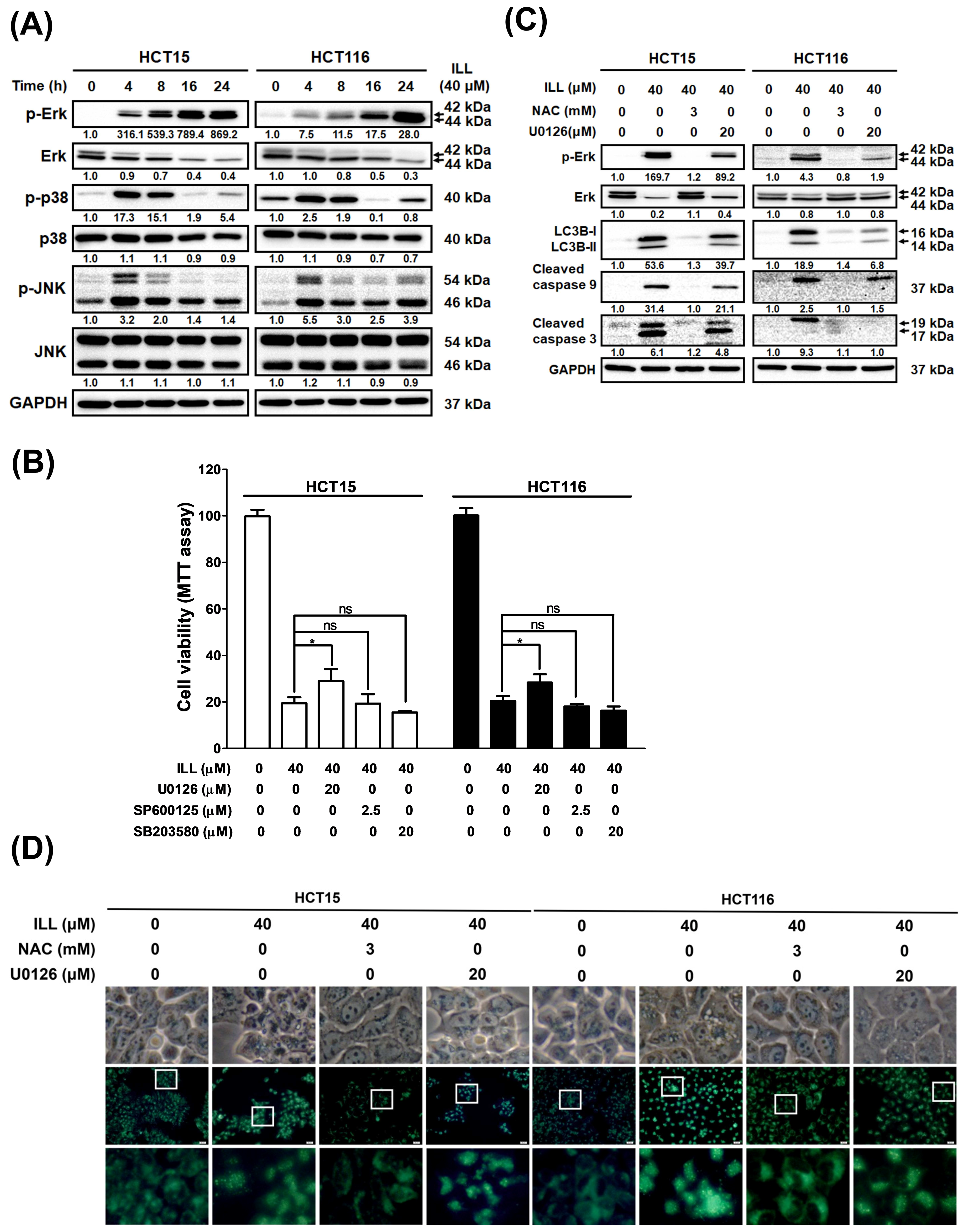
2.7. ILL Activated MAPK Signaling and Affected Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Cell Cycle Arrest
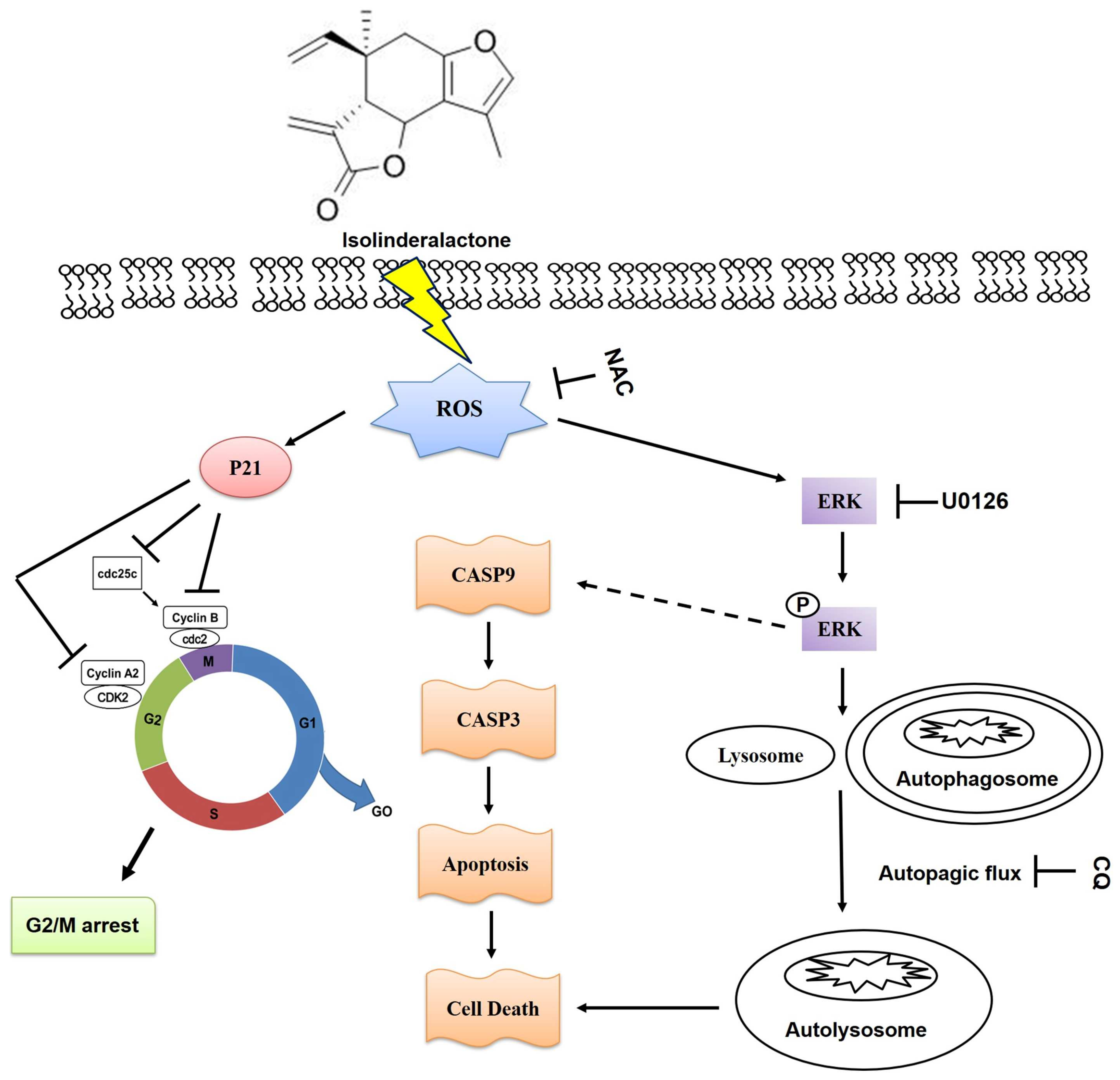
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. RNA Isolation and Bioinformatics
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. DCFDA Assay
4.7. Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) Staining
4.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.9. Annexin V–FITC Staining
4.10. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.Q.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.H.; Piao, X.J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.R.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.T.; et al. Quinalizarin Induces Apoptosis through Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)–Mediated Mitogen–Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3710–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Zalckvar, E.; Kimchi, A.; Kroemer, G. Self–eating and self–killing: Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Xu, W.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Gong, Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L. Photodynamic therapy induces autophagy–mediated cell death in human colorectal cancer cells via activation of the ROS/JNK signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhu, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Lin, K.; Wu, W.; et al. Isoalantolactone Induces Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis and Autophagy in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 903599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.M.M.; Towers, C.G.; Thorburn, A. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Deng, L.; Wang, H. Combination of an Autophagy Inducer and an Autophagy Inhibitor: A Smarter Strategy Emerging in Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.S.; Zheng, Y.L.; Mo, J.X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.H.; Zhou, C.X. Sesquiterpene lactones from the root tubers of Lindera aggregata. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.A.; Lin, E.S.; Tsai, M.J.; Huang, M.S.; Kuo, P.L. Isolinderalactone inhibits proliferation of A549 human nonsmall cell lung cancer cells by arresting the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase and inducing a Fas receptor and soluble Fas ligand–mediated apoptotic pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, W.J.; Ha, K.T.; Choi, B.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Shin, H.K. Isolinderalactone regulates the BCL–2/caspase–3/PARP pathway and suppresses tumor growth in a human glioblastoma multiforme xenograft mouse model. Cancer Lett. 2019, 443, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, M.C.; Shih, Y.C.; Hsu, Y.L.; Lin, E.S.; Lin, Y.S.; Tsai, E.M.; Ho, Y.W.; Hou, M.F.; Kuo, P.L. Isolinderalactone enhances the inhibition of SOCS3 on STAT3 activity by decreasing miR–30c in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajina, S.; Kim, W.J.; Shim, J.H.; Chun, K.S.; Joo, S.H.; Shin, H.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, J.S. Isolinderalactone Induces Cell Death via Mitochondrial Superoxide– and STAT3–Mediated Pathways in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, J.; Baehrecke, E.H. Life, death and autophagy. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biller, L.H.; Schrag, D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, V.; Singh, M.P.; Amaravadi, R.K. Recent advances in targeting autophagy in cancer. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.K.; Bialik, S.; Levin–Zaidman, S.; Levin–Salomon, V.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Futerman, A.H.; Kimchi, A. Signalome–wide RNAi screen identifies GBA1 as a positive mediator of autophagic cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1288–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Tu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Mwangi, J.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Lai, R. Targeting surface nucleolin induces autophagy–dependent cell death in pancreatic cancer via AMPK activation. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1832–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, R.; Collin, A.; Guizzardi, S.; Tolosa de Talamoni, N.; Picotto, G. Reactive oxygen species in cancer: A paradox between pro– and anti–tumour activities. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perillo, B.; Di Donato, M.; Pezone, A.; Di Zazzo, E.; Giovannelli, P.; Galasso, G.; Castoria, G.; Migliaccio, A. ROS in cancer therapy: The bright side of the moon. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi–Marjaneh, R.; Hassanian, S.M.; Mehramiz, M.; Rezayi, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Khazaei, M.; Avan, A. Reactive oxygen species in colorectal cancer: The therapeutic impact and its potential roles in tumor progression via perturbation of cellular and physiological dysregulated pathways. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 10072–10079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, A.W.; Park, J.W.; Lee, S.O.; Lee, J.Y.; Seo, J.H.; Yoon, G.; Lee, M.H.; Choi, J.S.; Shim, J.H. Isolinderalactone sensitizes oxaliplatin–resistance colorectal cancer cells through JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; McMillan–Ward, E.; Kong, J.; Israels, S.J.; Gibson, S.B. Mitochondrial electron–transport–chain inhibitors of complexes I and II induce autophagic cell death mediated by reactive oxygen species. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120 Pt 23, 4155–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; McMillan–Ward, E.; Kong, J.; Israels, S.J.; Gibson, S.B. Oxidative stress induces autophagic cell death independent of apoptosis in transformed and cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttis, K.; Machado, A.R.T.; Santos, P.; Antunes, L.M.G. Sulforaphane Combined with Vitamin D Induces Cytotoxicity Mediated by Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage, Autophagy, and JNK/MAPK Pathway Modulation in Human Prostate Tumor Cells. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, Y.H.; Chen, C.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Fuh, L.J.; Lan, W.C.; Wang, T.H.; Chiu, K.C.; Nguyen, T.V.; Hsia, S.M.; Shieh, T.M. Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester and Caffeamide Derivatives Suppress Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Jia, L.; Huang, C.; Qi, Q.; Jahangir, A.; Xia, Y.; Liu, W.; Shi, R.; Tang, L.; Chen, Z. Polyphyllin I Promotes Autophagic Cell Death and Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells via the ROS–Inhibited AKT/mTOR Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Liao, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Feng, J.; Yu, L.; Zhu, W.G. Cytosolic FoxO1 is essential for the induction of autophagy and tumour suppressor activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.Y.; Zhang, L.; Geng, Y.D.; Wang, B.; Feng, X.J.; Chen, Z.L.; Wei, W.; Jiang, L. beta–Elemene induces apoptosis and autophagy in colorectal cancer cells through regulating the ROS/AMPK/mTOR pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2022, 20, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova–Kostova, A.T.; Tew, K.D. Oxidative Stress in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ruan, H.J.; Gu, P.Q.; Ding, W.Y.; Luo, X.H.; Huang, R.; Zhao, W.; Gao, L.J. The Roles of p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 in Coplanar Polychlorinated Biphenyls–Induced Apoptosis of Human Extravillous Cytotrophoblast–Derived Transformed Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 2418–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persons, D.L.; Yazlovitskaya, E.M.; Pelling, J.C. Effect of extracellular signal–regulated kinase on p53 accumulation in response to cisplatin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 35778–35785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, N.K.; Peng, B.Y.; Lin, C.M.; Wang, P.D.; Wang, J.R.; Chan, C.H.; Wei, H.J.; Deng, W.P. NSC 95397 Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells through MKP–1 and the ERK1/2 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventura, J.J.; Hubner, A.; Zhang, C.; Flavell, R.A.; Shokat, K.M.; Davis, R.J. Chemical genetic analysis of the time course of signal transduction by JNK. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Todokoro, K. Requirement of activation of JNK and p38 for environmental stress–induced erythroid differentiation and apoptosis and of inhibition of ERK for apoptosis. Blood 1999, 94, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulston, A.; Reinhard, C.; Amiri, P.; Williams, L.T. Early activation of c–Jun N–terminal kinase and p38 kinase regulate cell survival in response to tumor necrosis factor alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 10232–10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnol, S.; Chambard, J.C. ERK and cell death: Mechanisms of ERK–induced cell death—Apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powley, I.R.; Patel, M.; Miles, G.; Pringle, H.; Howells, L.; Thomas, A.; Kettleborough, C.; Bryans, J.; Hammonds, T.; MacFarlane, M.; et al. Patient–derived explants (PDEs) as a powerful preclinical platform for anti–cancer drug and biomarker discovery. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.Y.; Chen, W.F.; Lee, Y.C.; Su, J.H.; Juan, Y.S.; Lin, I.P.; Zhang, Y.H.; Chang, M.K.; Lin, M.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. Rhopaloic acid A induces apoptosis, autophagy and MAPK activation through ROS–mediated signaling in bladder cancer. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.C.; Chiu, T.L.; Huang, S.Y.; Chang, S.F.; Chen, S.P.; Pang, C.Y.; Hsieh, T.F. Potential therapeutic effects of N–butylidenephthalide from Radix Angelica Sinensis (Danggui) in human bladder cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.Y.; Chang, S.F.; Liao, K.F.; Chiu, S.C. Tanshinone IIA Inhibits Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Bladder Cancer Cells via Modulation of STAT3–CCL2 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.F.; Chiu, T.L.; Huang, S.Y.; Hsieh, T.F.; Chang, S.F.; Ruan, J.W.; Chen, S.P.; Pang, C.Y.; Chiu, S.C. Anti–Cancer Effects of Radix Angelica Sinensis (Danggui) and N–Butylidenephthalide on Gastric Cancer: Implications for REDD1 Activation and mTOR Inhibition. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 2231–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-S.; Chiu, S.-C.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chang, S.-F.; Liao, K.-F. Isolinderalactone Induces Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Cycle Arrest and MAPK Activation through ROS–Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814246
Chen J-S, Chiu S-C, Huang S-Y, Chang S-F, Liao K-F. Isolinderalactone Induces Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Cycle Arrest and MAPK Activation through ROS–Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(18):14246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814246
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jith-Shyan, Sheng-Chun Chiu, Sung-Ying Huang, Shu-Fang Chang, and Kuan-Fu Liao. 2023. "Isolinderalactone Induces Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Cycle Arrest and MAPK Activation through ROS–Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 18: 14246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814246
APA StyleChen, J.-S., Chiu, S.-C., Huang, S.-Y., Chang, S.-F., & Liao, K.-F. (2023). Isolinderalactone Induces Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Cycle Arrest and MAPK Activation through ROS–Mediated Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(18), 14246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814246




