Therapeutic Anti-KIR Antibody of 1–7F9 Attenuates the Antitumor Effects of Expanded and Activated Human Primary Natural Killer Cells on In Vitro Glioblastoma-like Cells and Orthotopic Tumors Derived Therefrom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
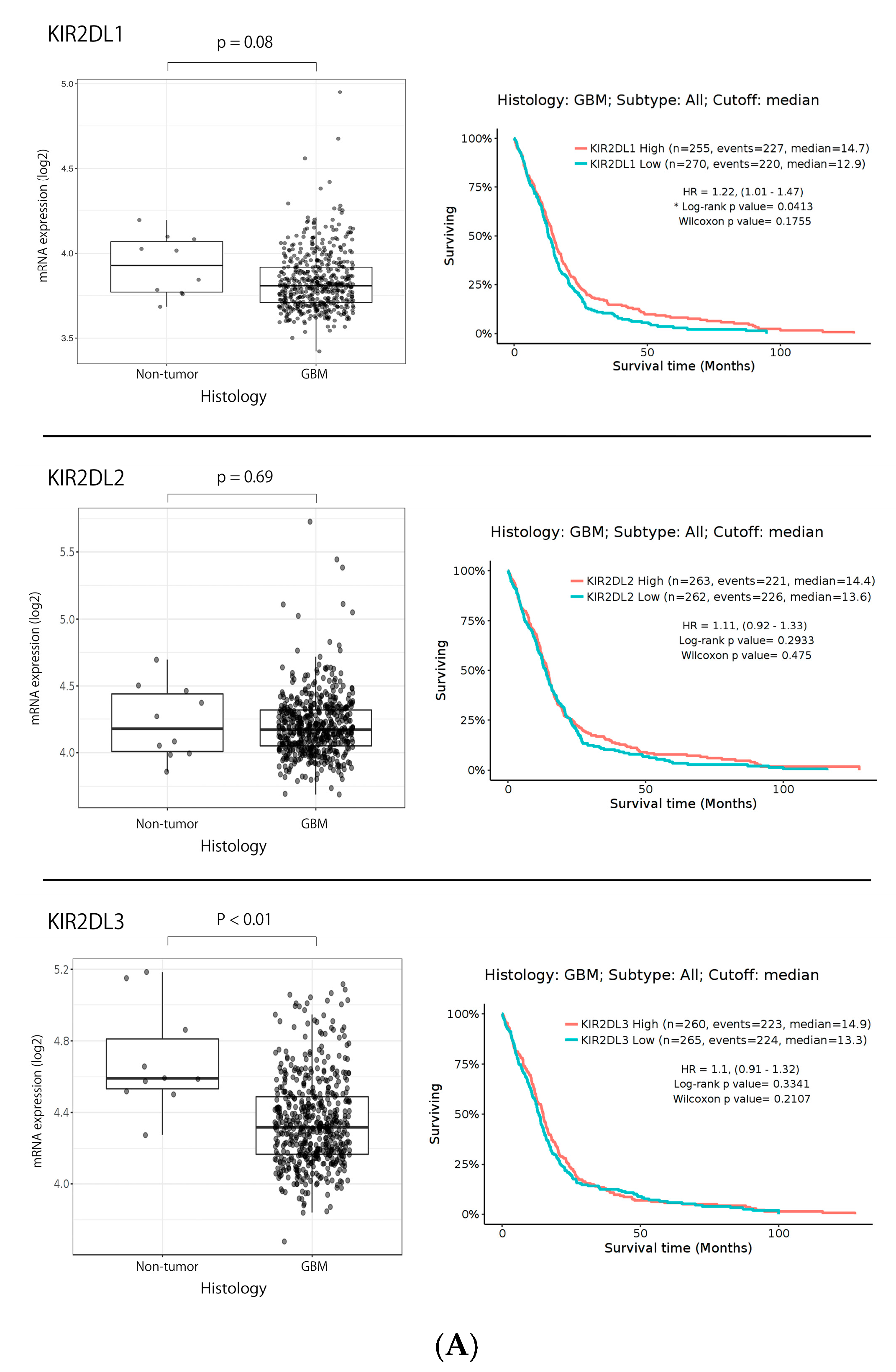
2.1. KIR2DL1 and KIR2DL2/3 Expression in Gliomas Based on TCGA Data Set
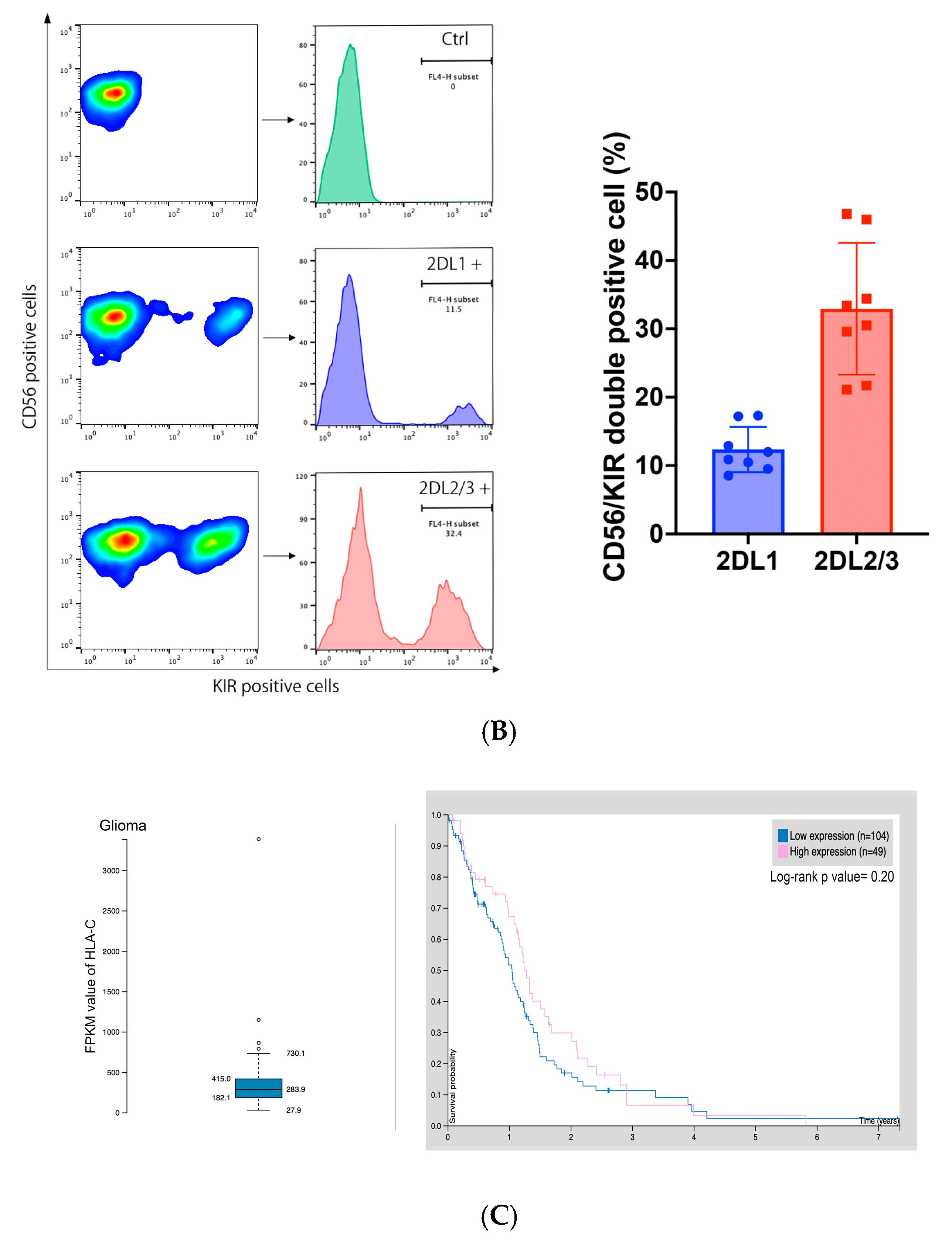
2.2. KIR2DL1 and KIR2DL2/3 Expression on GiNKs
2.3. HLA-C Expression in Gliomas in the Human Protein Atlas Data Set and GBM Cell Lines
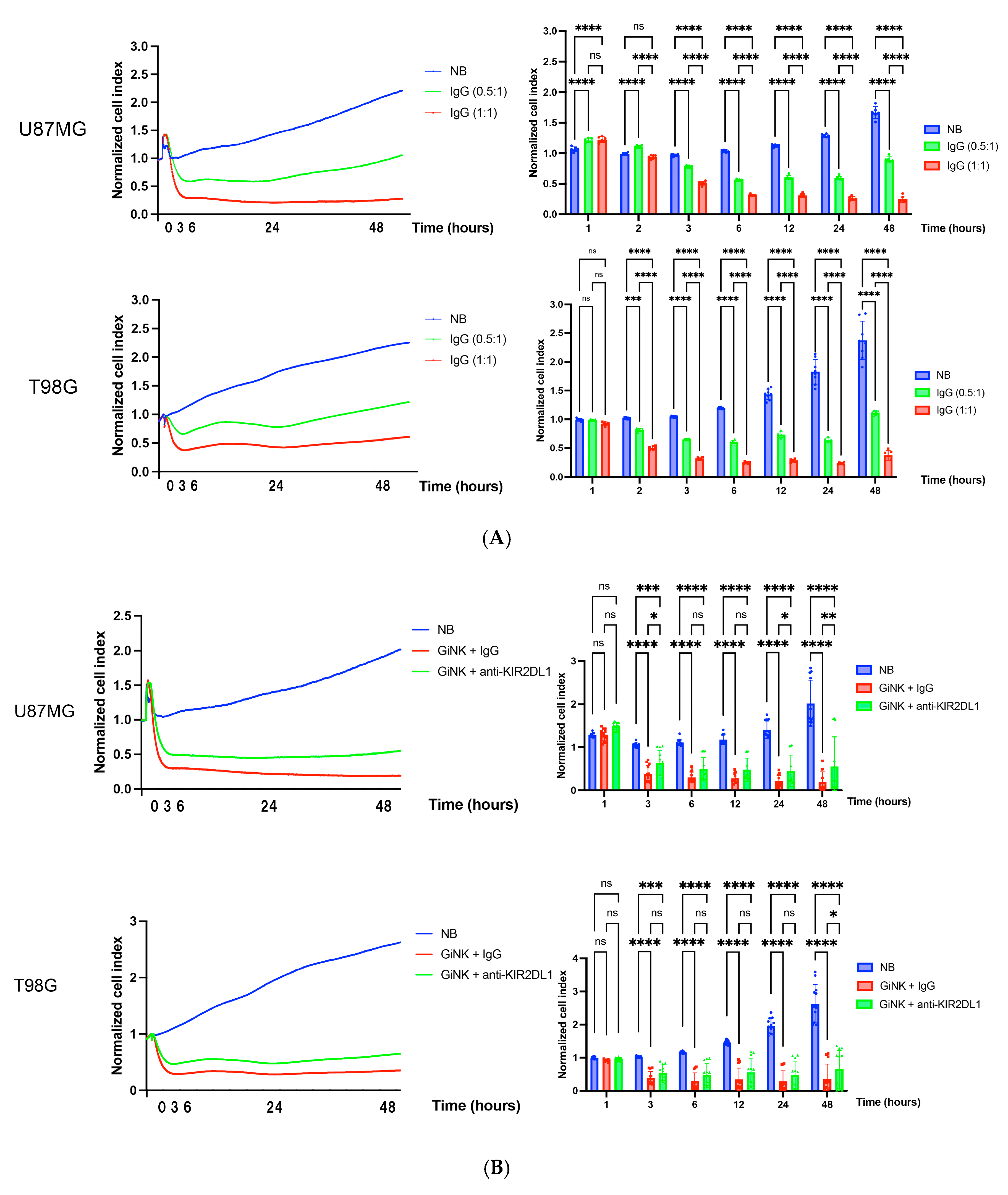
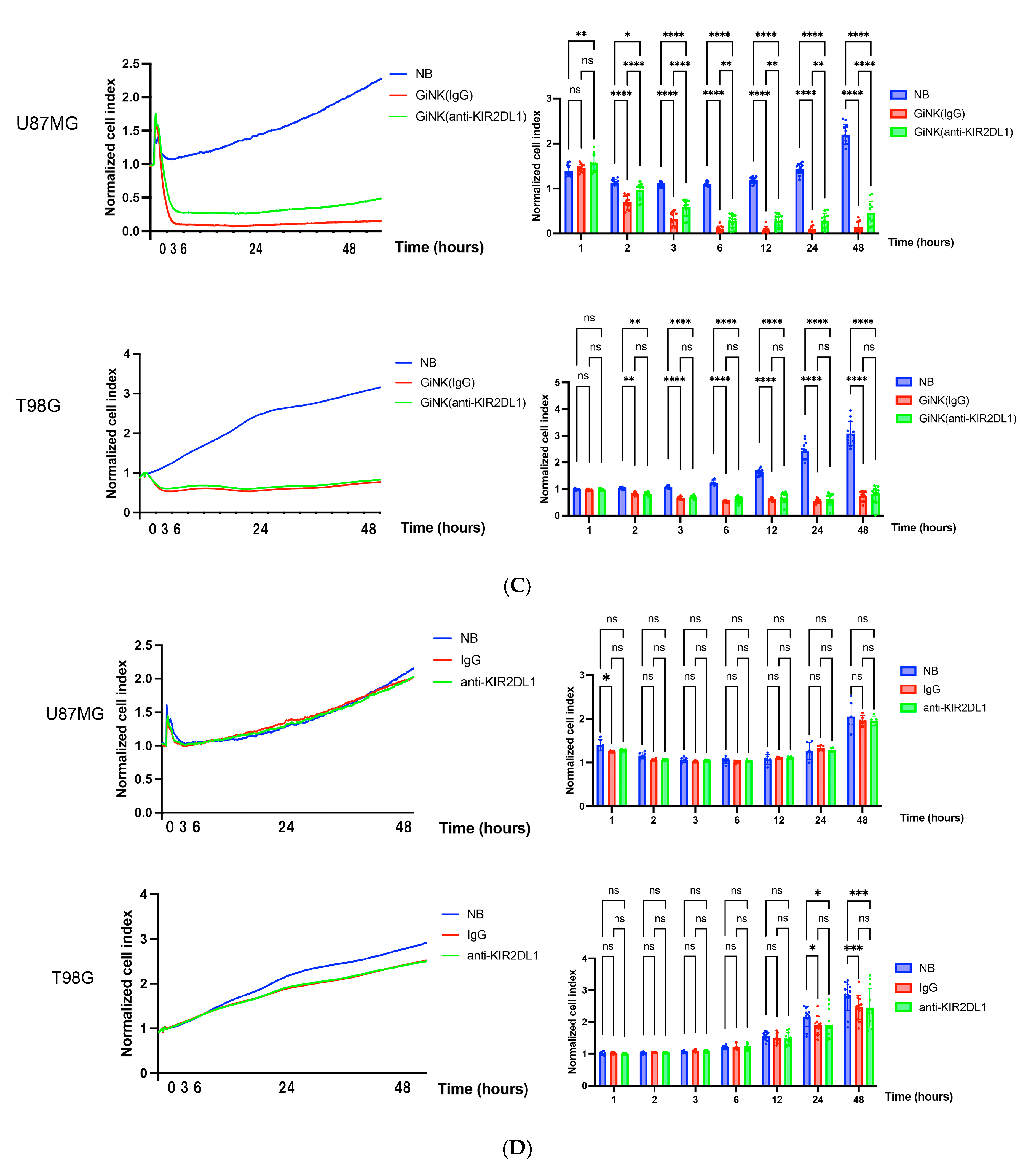
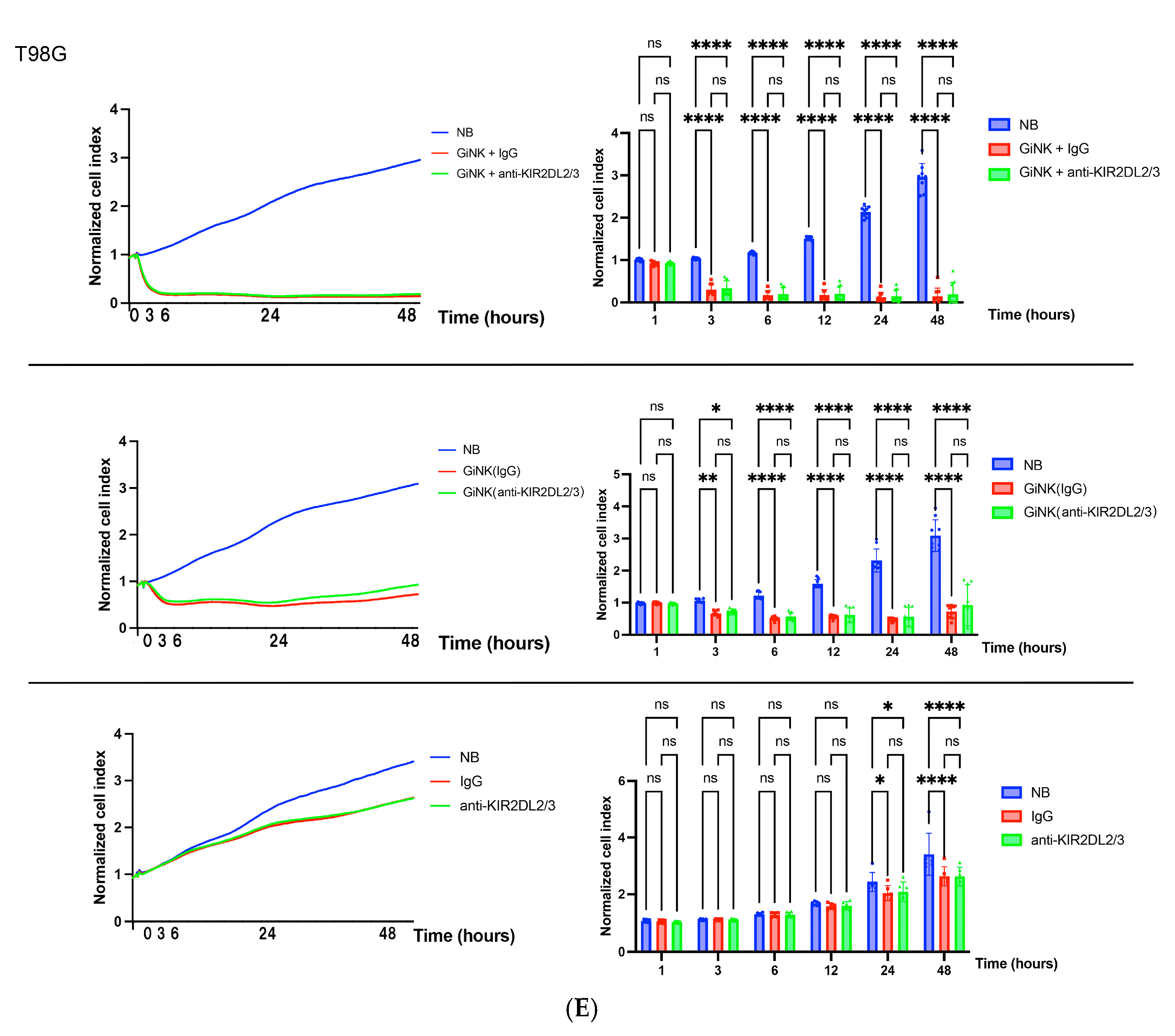
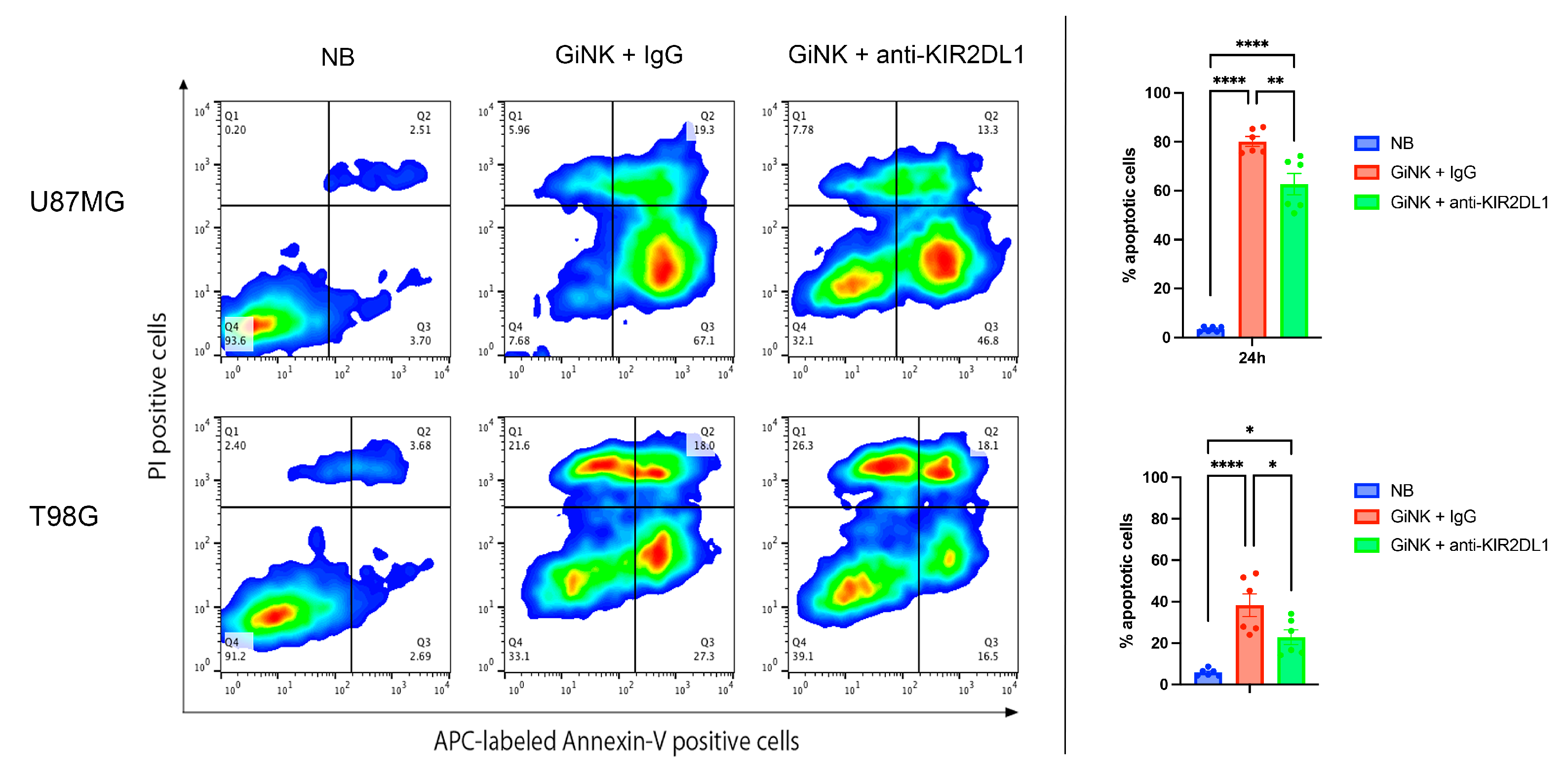
2.4. Effects of GiNKs Both Alone and in Combination with Antibodies (IgG and Anti-KIR2DLs) Treatment In Vitro
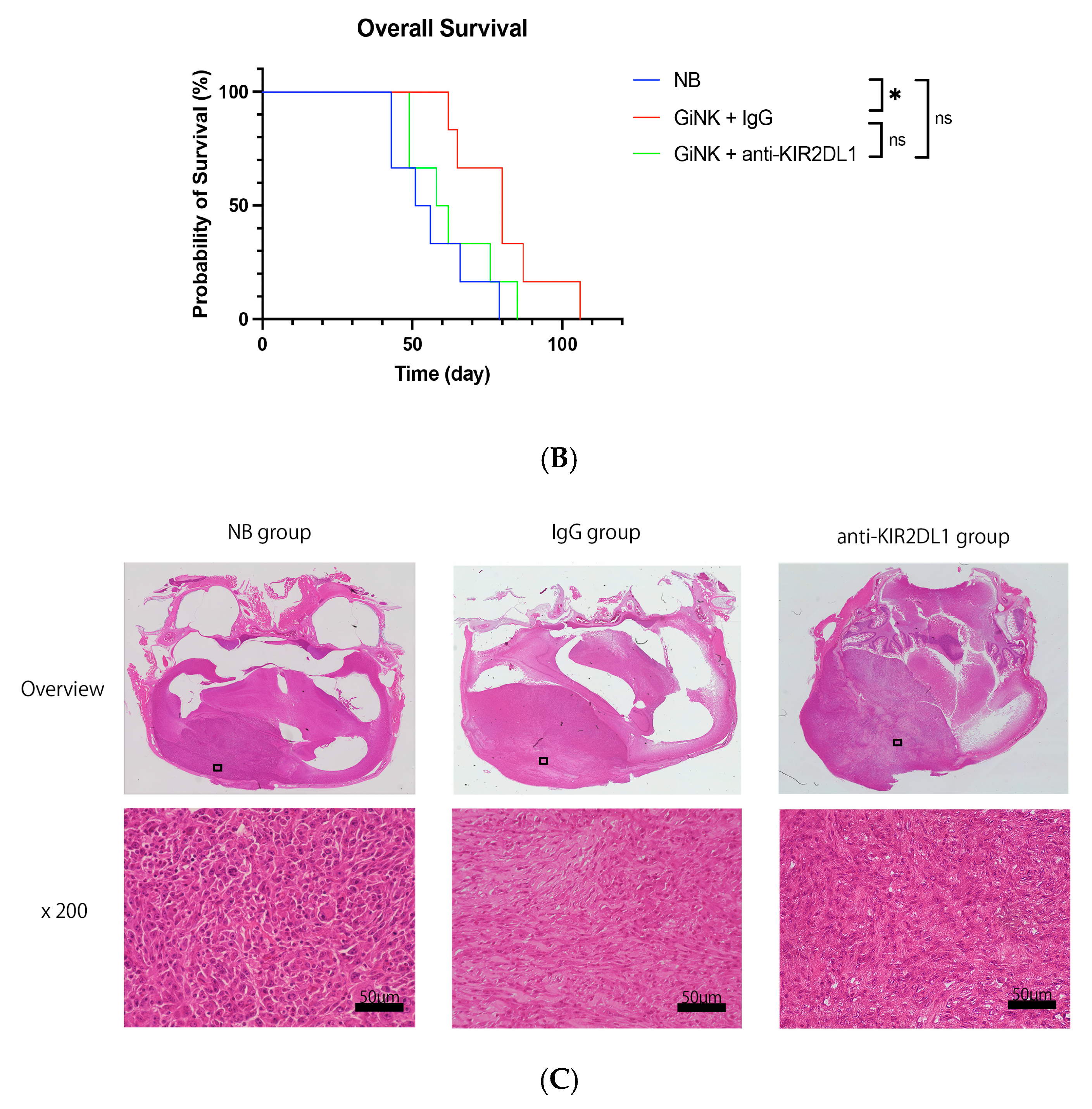
2.5. Effects of GiNK Treatment on an Orthotopic GBM-like Cell-Derived Xenograft Model
2.6. Histological Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. GBM Cell Lines
4.3. Animals
4.4. Expansion of GiNKs
4.5. Determination of Surface Antigen Expression
4.6. Growth Inhibition Assays
4.7. Apoptosis Detection Assays
4.8. In Vivo Orthotopic Xenograft Assays
4.9. Histochemical Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Taillibert, S.; Kanner, A.; Read, W.; Steinberg, D.; Lhermitte, B.; Toms, S.; Idbaih, A.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Fink, K.; et al. Effect of Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Maintenance Temozolomide vs Maintenance Temozolomide Alone on Survival in Patients with Glioblastoma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinot, O.L.; Wick, W.; Mason, W.; Henriksson, R.; Saran, F.; Nishikawa, R.; Carpentier, A.F.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Kavan, P.; Cernea, D.; et al. Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Long, G.V.; Brady, B.; Dutriaux, C.; Maio, M.; Mortier, L.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; McNeil, C.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E.; et al. Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonds, E.F.; Lu, E.D.; Badillo, O.; Karimi, S.; Liu, E.V.; Tamaki, W.; Rancan, C.; Downey, K.M.; Stultz, J.; Sinha, M.; et al. Deep immune profiling reveals targetable mechanisms of immune evasion in immune checkpoint inhibitor-refractory glioblastoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Brandes, A.A.; Omuro, A.; Mulholland, P.; Lim, M.; Wick, A.; Baehring, J.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Roth, P.; Bahr, O.; et al. Effect of Nivolumab vs Bevacizumab in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma: The CheckMate 143 Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mende, A.L.; Schulte, J.D.; Okada, H.; Clarke, J.L. Current Advances in Immunotherapy for Glioblastoma. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, N.D.; Cursons, J.; Rautela, J. The cancer-natural killer cell immunity cycle. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Pietra, G.; Mingari, M.C.; Moretta, L. Effect of tumor cells and tumor microenvironment on NK-cell function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Tomasello, E.; Baratin, M.; Walzer, T.; Ugolini, S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, R. Tumor immunotherapy: New aspects of natural killer cells. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 30, 173–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Nakazawa, T.; Nakamura, M.; Nishimura, F.; Matsuda, R.; Omoto, K.; Shida, Y.; Murakami, T.; Nakagawa, I.; Motoyama, Y.; et al. Ex vivo-expanded highly purified natural killer cells in combination with temozolomide induce antitumor effects in human glioblastoma cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, T.; Morimoto, T.; Maeoka, R.; Matsuda, R.; Nakamura, M.; Nishimura, F.; Yamada, S.; Nakagawa, I.; Park, Y.S.; Nakase, H.; et al. Establishment of an efficient ex vivo expansion strategy for human natural killer cells stimulated by defined cytokine cocktail and antibodies against natural killer cell activating receptors. Regen. Ther. 2022, 21, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shida, Y.; Nakazawa, T.; Matsuda, R.; Morimoto, T.; Nishimura, F.; Nakamura, M.; Maeoka, R.; Yamada, S.; Nakagawa, I.; Park, Y.S.; et al. Ex Vivo Expanded and Activated Natural Killer Cells Prolong the Overall Survival of Mice with Glioblastoma-like Cell-Derived Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, K.B.; Matosevic, S. CD155 immunoregulation as a target for natural killer cell immunotherapy in glioblastoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.-Y.; Choi, Y.-D.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, S.-K.; Jung, S.; Cho, D. Immunological Characterization of Glioblastoma Cells for Immunotherapy. Anticancer. Res. 2013, 33, 2525–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Braud, V.M.; Allan, D.S.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Söderström, K.; D’Andrea, A.; Ogg, G.S.; Young, N.T.; Bell, J.I.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L.; et al. HLA-E binds to natural killer cell receptors CD94:NKG2A, B and C. Nature 1998, 391, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nduom, E.K.; Wei, J.; Yaghi, N.K.; Huang, N.; Kong, L.Y.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; Ling, X.; Zhou, S.; Ivan, C.; Chen, J.Q.; et al. PD-L1 expression and prognostic impact in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.C.; Gumperz, J.E.; Parham, P.; Eric, O.L.; Wagtmann, N. Direct Binding and Functional Transfer of NK Cell Inhibitory Receptors Reveal Novel Patterns of HLA-C Allotype Recognition. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, D.H.; Bronte, V. Immune suppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Tian, Z. NK Cell Dysfunction and Checkpoint Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Tian, Z. NK Cell Exhaustion. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Kim, H.S. Targeting Checkpoint Receptors and Molecules for Therapeutic Modulation of Natural Killer Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viel, S.; Marçais, A.; Guimaraes, F.S.-F.; Loftus, R.; Rabilloud, J.; Grau, M.; Degouve, S.; Djebali, S.; Sanlaville, A.; Charrier, E.; et al. TGF-β inhibits the activation and functions of NK cells by repressing the mTOR pathway. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C.; Joller, N.; Kuchroo, V.K. Lag-3, Tim-3, and TIGIT: Co-inhibitory Receptors with Specialized Functions in Immune Regulation. Immunity 2016, 44, 989–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanietsky, N.; Rovis, T.L.; Glasner, A.; Seidel, E.; Tsukerman, P.; Yamin, R.; Enk, J.; Jonjic, S.; Mandelboim, O. Mouse TIGIT inhibits NK-cell cytotoxicity upon interaction with PVR. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2138–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, S.; Coleman, A.; Kuri-Cervantes, L.; Bower, M.; Nelson, M.; Goodier, M.R. PD-1 expression on natural killer cells and CD8(+) T cells during chronic HIV-1 infection. Viral Immunol. 2012, 25, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Hu, D.; Li, C.; Ge, B.; Jin, B.; Fan, Z. Recruitment of Grb2 and SHIP1 by the ITT-like motif of TIGIT suppresses granule polarization and cytotoxicity of NK cells. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, I.B.; Pasquinelli, V.; Jurado, J.O.; Abbate, E.; Musella, R.M.; de la Barrera, S.S.; Garcia, V.E. Role played by the programmed death-1-programmed death ligand pathway during innate immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, S.J.; Stannard, K.; Liu, J.; Allen, S.; Yong, M.C.; Mittal, D.; Aguilera, A.R.; Miles, J.J.; Lutzky, V.P.; de Andrade, L.F.; et al. Suppression of Metastases Using a New Lymphocyte Checkpoint Target for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagne, F.; Andre, P.; Spee, P.; Zahn, S.; Anfossi, N.; Gauthier, L.; Capanni, M.; Ruggeri, L.; Benson, D.M., Jr.; Blaser, B.W.; et al. Preclinical characterization of 1–7F9, a novel human anti-KIR receptor therapeutic antibody that augments natural killer-mediated killing of tumor cells. Blood 2009, 114, 2667–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.G.; Eguchi, J.; Kruse, C.A.; Gomez, G.G.; Fakhrai, H.; Schroter, S.; Ma, W.; Hoa, N.; Minev, B.; Delgado, C.; et al. Antigenic profiling of glioma cells to generate allogeneic vaccines or dendritic cell-based therapeutics. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moesta, A.K.; Parham, P. Diverse functionality among human NK cell receptors for the C1 epitope of HLA-C: KIR2DS2, KIR2DL2, and KIR2DL3. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.L.; Wang, Q.; Carro, A.; Verhaak, R.G.; Squatrito, M. GlioVis data portal for visualization and analysis of brain tumor expression datasets. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlen, M.; Bjorling, E.; Agaton, C.; Szigyarto, C.A.; Amini, B.; Andersen, E.; Andersson, A.C.; Angelidou, P.; Asplund, A.; Asplund, C.; et al. A human protein atlas for normal and cancer tissues based on antibody proteomics. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2005, 4, 1920–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todo, T.; Ito, H.; Ino, Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Ota, Y.; Shibahara, J.; Tanaka, M. Intratumoral oncolytic herpes virus G47 for residual or recurrent glioblastoma: A phase 2 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todo, T.; Ino, Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Shibahara, J.; Tanaka, M. A phase I/II study of triple-mutated oncolytic herpes virus G47 in patients with progressive glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liau, L.M.; Ashkan, K.; Brem, S.; Campian, J.L.; Trusheim, J.E.; Iwamoto, F.M.; Tran, D.D.; Ansstas, G.; Cobbs, C.S.; Heth, J.A.; et al. Association of Autologous Tumor Lysate-Loaded Dendritic Cell Vaccination with Extension of Survival Among Patients with Newly Diagnosed and Recurrent Glioblastoma: A Phase 3 Prospective Externally Controlled Cohort Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, T.; Natsume, A.; Nishimura, F.; Morimoto, T.; Matsuda, R.; Nakamura, M.; Yamada, S.; Nakagawa, I.; Motoyama, Y.; Park, Y.S.; et al. Effect of CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated PD-1-Disrupted Primary Human Third-Generation CAR-T Cells Targeting EGFRvIII on In Vitro Human Glioblastoma Cell Growth. Cells 2020, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, T.; Nakamura, M.; Matsuda, R.; Nishimura, F.; Park, Y.S.; Motoyama, Y.; Hironaka, Y.; Nakagawa, I.; Yokota, H.; Yamada, S.; et al. Antitumor effects of minodronate, a third-generation nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate, in synergy with γδT cells in human glioblastoma in vitro and in vivo. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 129, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberman, R.B.; Nunn, M.E.; Lavrin, D.H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumors. I. Distribution of reactivity and specificity. Int. J. Cancer 1975, 16, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppendahl, L.D.; Dahl, C.M.; Miller, J.S.; Felices, M.; Geller, M.A. Natural Killer Cell-Based Immunotherapy in Gynecologic Malignancy: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiuri, M.A. Human natural killer cells. Blood 2008, 112, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, M.J.; Thia, K.Y.; Street, S.E.; Cretney, E.; Trapani, J.A.; Taniguchi, M.; Kawano, T.; Pelikan, S.B.; Crowe, N.Y.; Godfrey, D.I. Differential tumor surveillance by natural killer (NK) and NKT cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmadge, J.E.; Meyers, K.M.; Prieur, D.J.; Starkey, J.R. Role of NK cells in tumour growth and metastasis in beige mice. Nature 1980, 284, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimasaki, N.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Kamiya, T.; Campana, D. Expanded and armed natural killer cells for cancer treatment. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.S. Therapeutic applications- natural killer cells in the clinic. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2013, 2013, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Raulet, D.H.; Moretta, A.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Zitvogel, L.; Lanier, L.L.; Yokoyama, W.M.; Ugolini, S. Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells. Science 2011, 331, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyer, J.L.; Gitto, S.B.; Altomare, D.A.; Copik, A.J. PD-L1 blockade enhances anti-tumor efficacy of NK cells. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1509819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonmez, C.; Wolfer, J.; Holling, M.; Brokinkel, B.; Stummer, W.; Wiendl, H.; Thomas, C.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Grauer, O.M. Blockade of inhibitory killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors and IL-2 triggering reverses the functional hypoactivity of tumor-derived NK-cells in glioblastomas. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pende, D.; Falco, M.; Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, C.; Munari, E.; Bertaina, A.; Moretta, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Pietra, G.; et al. Killer Ig-Like Receptors (KIRs): Their Role in NK Cell Modulation and Developments Leading to Their Clinical Exploitation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milito, N.D.; Zingoni, A.; Stabile, H.; Soriani, A.; Capuano, C.; Cippitelli, M.; Gismondi, A.; Santoni, A.; Paolini, R.; Molfetta, R. NKG2D engagement on human NK cells leads to DNAM-1 hypo-responsiveness through different converging mechanisms. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 53, 2250198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourmentraux-Neves, E.; Jalil, A.; Da Rocha, S.; Pichon, C.; Chouaib, S.; Bismuth, G.; Caignard, A. Two opposite signaling outputs are driven by the KIR2DL1 receptor in human CD4 + T cells. Blood 2008, 112, 2381–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.A.; Kim, Y.H.; Duong, T.H.; Thangaraj, J.; Chu, T.H.; Jung, S.; Kim, I.Y.; Moon, K.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, T.K.; et al. Natural killer cell therapy potentially enhances the antitumor effects of bevacizumab plus irinotecan in a glioblastoma mouse model. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1009484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitis, C.D.; Ferraro, G.B.; Jain, R.K. The blood-brain barrier and blood-tumour barrier in brain tumours and metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunnaike, E.A.; Valdivia, A.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Leon, E.; Nandi, S.; Hudson, H.; Du, H.; Khagi, S.; Gu, Z.; Savoldo, B.; et al. Fibrin gel enhances the antitumor effects of chimeric antigen receptor T cells in glioblastoma. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazvinian, Z.; Abdolahi, S.; Tokhanbigli, S.; Tarzemani, S.; Piccin, A.; Reza Zali, M.; Verdi, J.; Baghaei, K. Contribution of natural killer cells in innate immunity against colorectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1077053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adotevi, O.; Godet, Y.; Galaine, J.; Lakkis, Z.; Idirene, I.; Certoux, J.M.; Jary, M.; Loyon, R.; Laheurte, C.; Kim, S.; et al. In situ delivery of allogeneic natural killer cell (NK) combined with Cetuximab in liver metastases of gastrointestinal carcinoma: A phase I clinical trial. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1424673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, L.; Mu, Q.; Wu, X.; Yang, S.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Lai, Y.; Wu, H.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. Cytotoxicity of Donor Natural Killer Cells to Allo-Reactive T Cells Are Related with Acute Graft-vs.-Host-Disease Following Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, N.; Ishikawa, T.; Kokura, S.; Okayama, T.; Oka, K.; Ideno, M.; Sakai, F.; Kato, A.; Tanabe, M.; Enoki, T.; et al. Phase I clinical trial of autologous NK cell therapy using novel expansion method in patients with advanced digestive cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maeoka, R.; Nakazawa, T.; Matsuda, R.; Morimoto, T.; Shida, Y.; Yamada, S.; Nishimura, F.; Nakamura, M.; Nakagawa, I.; Park, Y.-S.; et al. Therapeutic Anti-KIR Antibody of 1–7F9 Attenuates the Antitumor Effects of Expanded and Activated Human Primary Natural Killer Cells on In Vitro Glioblastoma-like Cells and Orthotopic Tumors Derived Therefrom. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814183
Maeoka R, Nakazawa T, Matsuda R, Morimoto T, Shida Y, Yamada S, Nishimura F, Nakamura M, Nakagawa I, Park Y-S, et al. Therapeutic Anti-KIR Antibody of 1–7F9 Attenuates the Antitumor Effects of Expanded and Activated Human Primary Natural Killer Cells on In Vitro Glioblastoma-like Cells and Orthotopic Tumors Derived Therefrom. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(18):14183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814183
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaeoka, Ryosuke, Tsutomu Nakazawa, Ryosuke Matsuda, Takayuki Morimoto, Yoichi Shida, Shuichi Yamada, Fumihiko Nishimura, Mitsutoshi Nakamura, Ichiro Nakagawa, Young-Soo Park, and et al. 2023. "Therapeutic Anti-KIR Antibody of 1–7F9 Attenuates the Antitumor Effects of Expanded and Activated Human Primary Natural Killer Cells on In Vitro Glioblastoma-like Cells and Orthotopic Tumors Derived Therefrom" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 18: 14183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814183
APA StyleMaeoka, R., Nakazawa, T., Matsuda, R., Morimoto, T., Shida, Y., Yamada, S., Nishimura, F., Nakamura, M., Nakagawa, I., Park, Y.-S., Tsujimura, T., & Nakase, H. (2023). Therapeutic Anti-KIR Antibody of 1–7F9 Attenuates the Antitumor Effects of Expanded and Activated Human Primary Natural Killer Cells on In Vitro Glioblastoma-like Cells and Orthotopic Tumors Derived Therefrom. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(18), 14183. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241814183





