Viroporins of Mpox Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequence Analysis
2.2. Experimental Channel Examination
2.2.1. Expression and Membrane Incorporation of Proteins
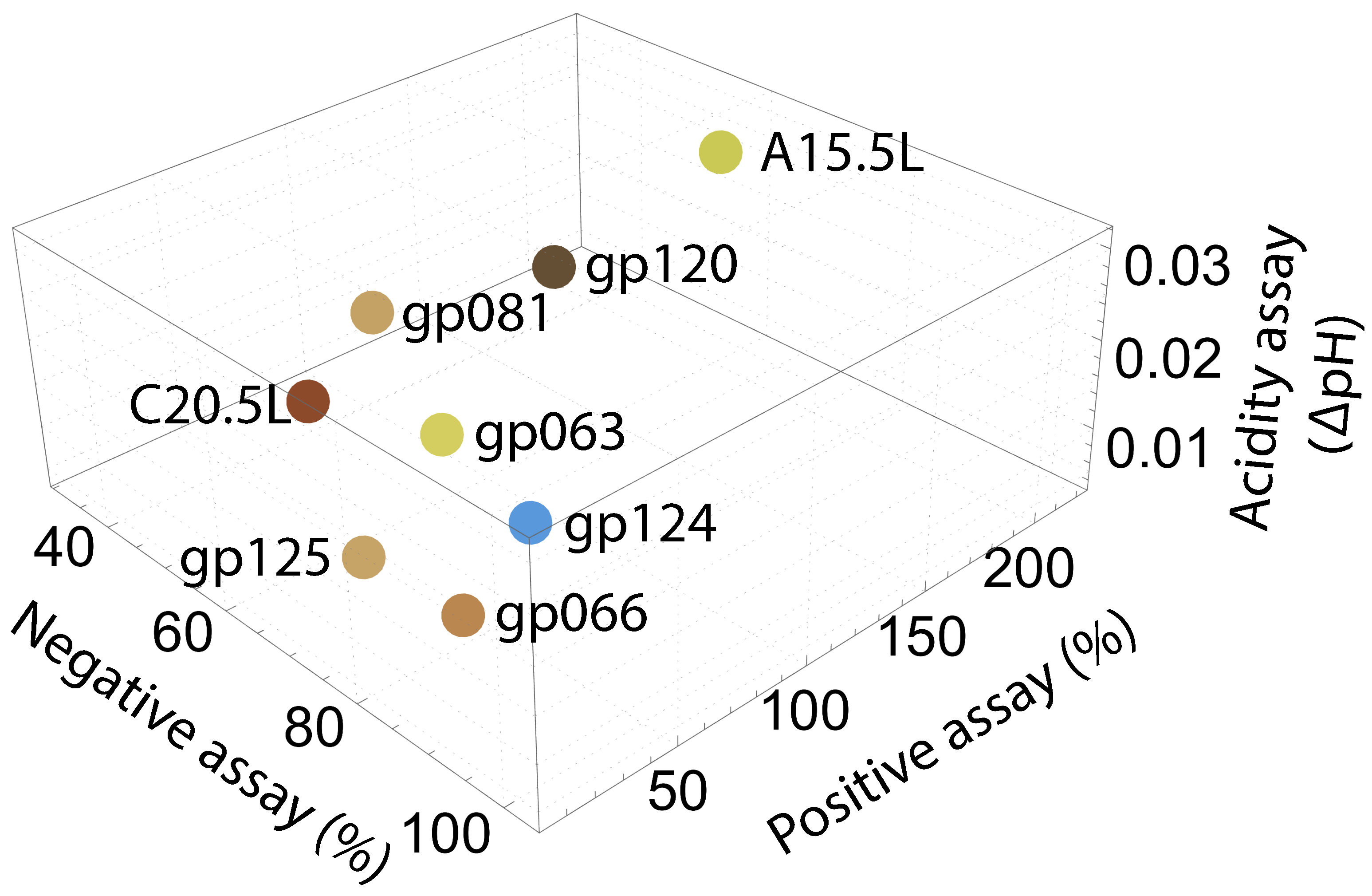
2.2.2. Negative Assay
2.2.3. Positive Assay
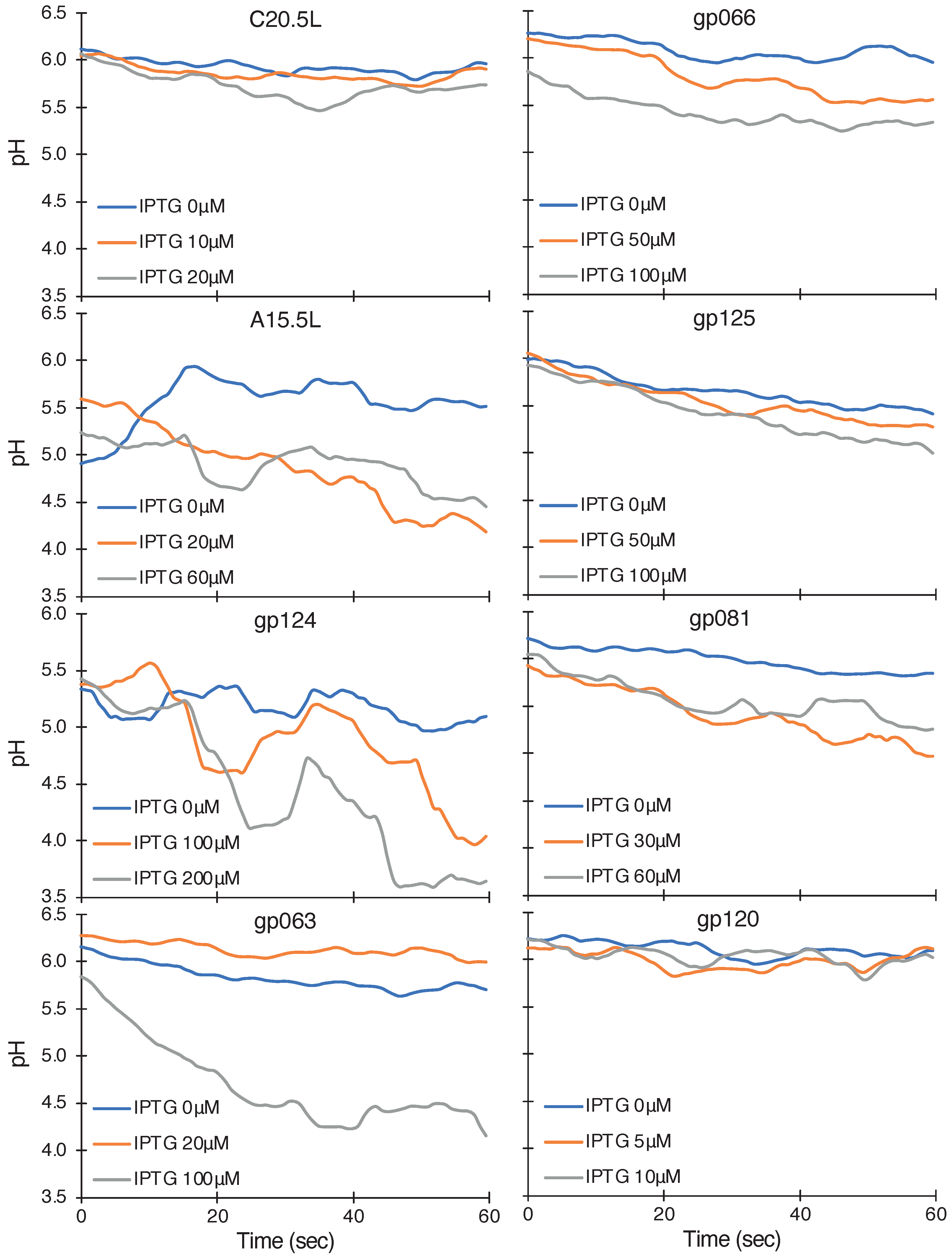
2.2.4. pH Assay
2.3. Computational Studies
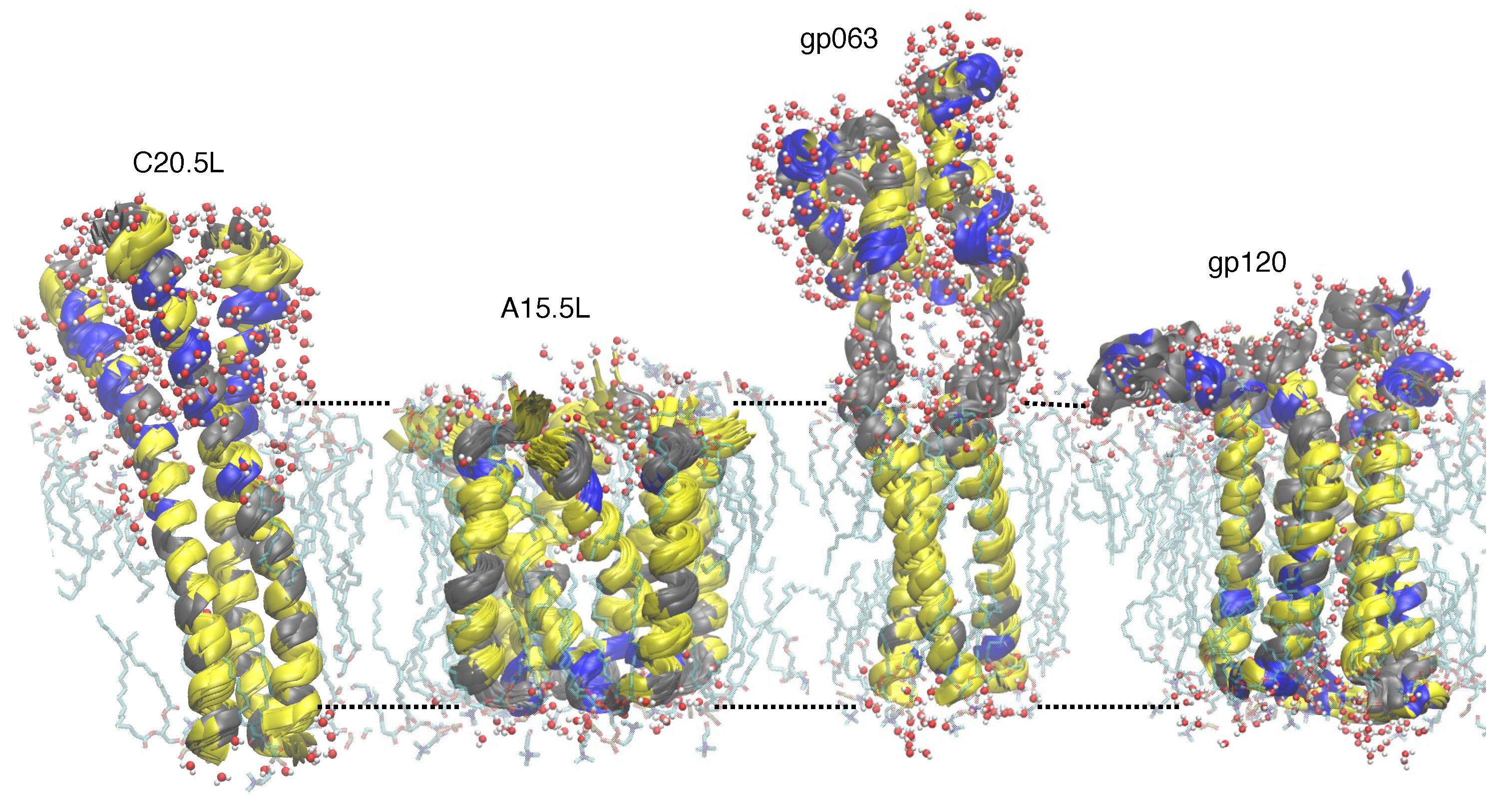
2.3.1. Structure Prediction
2.3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Searching Transmembrane Proteins
4.2. Bacterial Expression
4.3. Plasmids
4.4. Chemicals
4.5. Growth Media
4.6. Negative Ion Channel Assay
4.7. Positive Ion Channel Assay
4.8. Acidity Assay
4.9. Computational Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPXV | Mpox or monkeypox virus |
| IPTG | Isopropyl-β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside |
| DPPC | 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
References
- Lourie, B.; Bingham, P.G.; Evans, H.H.; Foster, S.O.; Nakano, J.H.; Herrmann, K.L. Human infection with monkeypox virus: Laboratory investigation of six cases in West Africa. Bull. World Health Organ. 1972, 46, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antinori, A.; Mazzotta, V.; Vita, S.; Carletti, F.; Tacconi, D.; Lapini, L.E.; D’Abramo, A.; Cicalini, S.; Lapa, D.; Pittalis, S.; et al. Epidemiological, clinical and virological characteristics of four cases of monkeypox support transmission through sexual contact, Italy, May 2022. Eurosurveillance 2022, 27, 2200421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez Duque, M.; Ribeiro, S.; Martins, J.V.; Casaca, P.; Leite, P.P.; Tavares, M.; Mansinho, K.; Duque, L.M.; Fernandes, C.; Cordeiro, R.; et al. Ongoing monkeypox virus outbreak, Portugal, 29 April to 23 May 2022. Eurosurveillance 2022, 27, 2200424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivancos, R.; Anderson, C.; Blomquist, P.; Balasegaram, S.; Bell, A.; Bishop, L.; Brown, C.S.; Chow, Y.; Edeghere, O.; Florence, I.; et al. Community transmission of monkeypox in the United Kingdom, April to May 2022. Eurosurveillance 2022, 27, 2200422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessain, A.; Nakoune, E.; Yazdanpanah, Y. Monkeypox. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchelkunov, S.N.; Totmenin, A.V.; Safronov, P.F.; Mikheev, M.V.; Gutorov, V.V.; Ryazankina, O.I.; Petrov, N.A.; Babkin, I.V.; Uvarova, E.A.; Sandakhchiev, L.S.; et al. Analysis of the monkeypox virus genome. Virology 2002, 297, 172–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, J.; Hussain, A.; Flores, G.; Kheiri, S.; Desrosiers, D. Monkeypox: A Comprehensive Review of Transmission, Pathogenesis, and Manifestation. Cureus 2022, 14, e26531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudisoit, A.; Tepage, F.; Colebunders, R. Oral Tecovirimat for the Treatment of Smallpox. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2084–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenois-Veyrat, G.; Gallardo, F.; Gorgé, O.; Marcheteau, E.; Ferraris, O.; Baidaliuk, A.; Favier, A.L.; Enfroy, C.; Holy, X.; Lourenco, J.; et al. Tecovirimat is effective against human monkeypox virus in vitro at nanomolar concentrations. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1951–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, H.; Gould, S.; Hine, P.; Snell, L.B.; Wong, W.; Houlihan, C.F.; Osborne, J.C.; Rampling, T.; Beadsworth, M.B.; Duncan, C.J.; et al. Clinical features and management of human monkeypox: A retrospective observational study in the UK. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Alshammari, M.K.; Arora, M.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Das, S.S.; Kamal, M.; Alqahtani, A.S.A.; Sahloly, M.A.Y.; Alshammari, A.H.; Alhomam, H.M.; et al. Oral Brincidofovir Therapy for Monkeypox Outbreak: A Focused Review on the Therapeutic Potential, Clinical Studies, Patent Literature, and Prospects. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, C.; Griffin, S. Viroporins: Structure, function and potential as antiviral targets. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2000–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royle, J.; Dobson, S.J.; Müller, M.; Macdonald, A. Emerging Roles of Viroporins Encoded by DNA Viruses: Novel Targets for Antivirals? Viruses 2015, 7, 5375–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, J.; Surya, W.; Torres, J. Targeting the Channel Activity of Viroporins. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2016, 104, 307–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, F.W.; Pearson, H.M.; Hover, S.; Lippiat, J.D.; Fontana, J.; Barr, J.N.; Mankouri, J. Ion channels as therapeutic targets for viral infections: Further discoveries and future perspectives. Viruses 2020, 12, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.H.; Holsinger, L.J.; Lamb, R.A. Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity. Cell 1992, 69, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, W.I.; Grunert, R.R.; Haff, R.F.; McGahen, J.W.; Neumayer, E.M.; Paulshock, M.; Watts, J.C.; Wood, T.R.; Hermann, E.C.; Hoffmann, C.E. Antiviral activity of 1-adamantanamine (amantadine). Science 1964, 144, 862–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Orba, Y.; Okada, Y.; Sunden, Y.; Kimura, T.; Tanaka, S.; Nagashima, K.; Hall, W.W.; Sawa, H. The human polyoma JC virus agnoprotein acts as a viroporin. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Orba, Y.; Makino, Y.; Okada, Y.; Sunden, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Hall, W.W.; Sawa, H. Viroporin activity of the JC polyomavirus is regulated by interactions with the adaptor protein complex 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18668–18673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coric, P.; Saribas, A.S.; Abou-Gharbia, M.; Childers, W.; White, M.K.; Bouaziz, S.; Safak, M. Nuclear magnetic resonance structure revealed that the human polyomavirus JC virus agnoprotein contains an α-helix encompassing the Leu/Ile/Phe-rich domain. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 6556–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, P.P.S.; Krugliak, M.; Arkin, I.T. Blockers of the SARS-CoV-2 3a Channel Identified by Targeted Drug Repurposing. Viruses 2021, 13, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, H.; Arkin, I.T. Searching for blockers of dengue and West Nile virus Viroporins. Viruses 2022, 14, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, P.P.S.; Arkin, I.T. SARS-CoV-2 E protein is a potential ion channel that can be inhibited by Gliclazide and Memantine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 530, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, P.P.S.; Oren, R.; Krugliak, M.; Arkin, I.T. Potential viroporin candidates from pathogenic viruses using bacteria-based bioassays. Viruses 2019, 11, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, B.W.; Damon, I.K.; Bennett, J.; Dolin, R.; Blaser, M. Orthopoxviruses: Vaccinia (smallpox vaccine), variola (smallpox), monkeypox, and cowpox. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Flamholz, A.; Phillips, R.; Milo, R. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) by the numbers. Elife 2020, 9, e57309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansiaux, E.; Jain, N.; Laivacuma, S.; Reinis, A. The virology of human monkeypox virus (hMPXV): A brief overview. Virus Res. 2022, 322, 198932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugelman, J.R.; Johnston, S.C.; Mulembakani, P.M.; Kisalu, N.; Lee, M.S.; Koroleva, G.; McCarthy, S.E.; Gestole, M.C.; Wolfe, N.D.; Fair, J.N.; et al. Genomic variability of monkeypox virus among humans, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käll, L.; Krogh, A.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction—The Phobius web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W429–W432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallgren, J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Pedersen, M.D.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Marcatili, P.; Nielsen, H.; Krogh, A.; Winther, O. DeepTMHMM predicts alpha and beta transmembrane proteins using deep neural networks. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, P.P.S.; Krugliak, M.; Arkin, I.T. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 E Channel Blockers from a Repurposed Drug Library. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrahan, P.; Flitman-Tene, R.; Bennett, E.R.; Krugliak, M.; Gilon, C.; Arkin, I.T. Quantitative analysis of influenza M2 channel blockers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1808, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Santner, P.; Martins, J.M.d.S.; Laursen, J.S.; Behrendt, L.; Riber, L.; Olsen, C.A.; Arkin, I.T.; Winther, J.R.; Willemoës, M.; Lindorff-Larsen, K. A Robust Proton Flux (pHlux) Assay for Studying the Function and Inhibition of the Influenza A M2 Proton Channel. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5949–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpe, S.; Bakker, E.P. Requirement of a Large K+-Uptake Capacity and of Extracytoplasmic Protease Activity for Protamine Resistance of Escherichia Coli. Arch. Microbiol. 1997, 167, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, R.; Alhadeff, R.; Assa, D.; Krugliak, M.; Arkin, I.T. Bacteria-based analysis of HIV-1 Vpu channel activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assa, D.; Alhadeff, R.; Krugliak, M.; Arkin, I.T. Mapping the Resistance Potential of Influenza’s H+ Channel against an Antiviral Blocker. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 4209–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miesenböck, G.; De Angelis, D.A.; Rothman, J.E. Visualizing secretion and synaptic transmission with pH-sensitive green fluorescent proteins. Nature 1998, 394, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schutze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, T.; Geisler, M.; Lukács, G.L.; Farkas, B. Ins and outs of AlphaFold2 transmembrane protein structure predictions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.E.; Carrasco, L. Viroporins. FEBS Lett. 2003, 552, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, A.; Islam, S.; Tankhilevich, E.; Sternberg, M.J. The AlphaFold database of protein structures: A biologist’s guide. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting Transmembrane Protein Topology With a Hidden Markov Model: Application to Complete Genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnhammer, E.L.; von Heijne, G.; Krogh, A. A Hidden Markov Model for Predicting Transmembrane Helices in Protein Sequences. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1998, 6, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- McIlvaine, T. A Buffer Solution for Colorimetric Comparison. J. Biol. Chem. 1921, 49, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, O.; Edholm, O.; Jähnig, F. Molecular dynamics simulations of a fluid bilayer of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine at full hydration, constant pressure, and constant temperature. Biophys. J. 1997, 72, 2002–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandt, C.; Ash, W.L.; Tieleman, D.P. Setting up and running molecular dynamics simulations of membrane proteins. Methods 2007, 41, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.; Dijkstra, E.; Achterop, S.; Vondrumen, R.; Vanderspoel, D.; Sijbers, A.; Keegstra, H.; Renardus, M. Gromacs—A parallel computer for molecular-dynamics simulations. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computational Physics (PC 92), Prague, Czech Republic, 24–28 August 1992; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 1993; pp. 252–256. [Google Scholar]
- Berendsen, H.J.; van der Spoel, D.; van Drunen, R. GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Van Der Spoel, D. GROMACS 3.0: A package for molecular simulation and trajectory analysis. Mol. Model. Annu. 2001, 7, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, S.; Páll, S.; Schulz, R.; Larsson, P.; Bjelkmar, P.; Apostolov, R.; Shirts, M.R.; Smith, J.C.; Kasson, P.M.; Van Der Spoel, D.; et al. GROMACS 4.5: A high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenbrink, C.; Villa, A.; Mark, A.E.; Van Gunsteren, W.F. A biomolecular force field based on the free enthalpy of hydration and solvation: The GROMOS force-field parameter sets 53A5 and 53A6. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1656–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.; Fraaije, J.G. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosé, S. A molecular dynamics method for simulations in the canonical ensemble. Mol. Phys. 1984, 52, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, W.G. Canonical dynamics: Equilibrium phase-space distributions. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 31, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosé, S.; Klein, M. Constant pressure molecular dynamics for molecular systems. Mol. Phys. 1983, 50, 1055–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N cdot log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.; Grigera, J.R.; Straatsma, T.P. The missing term in effective pair potentials. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 6269–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Protein | Accession No. | Size | Predicted Transmembrane Domain |
|---|---|---|---|
| C20.5L | WBK62766.1 | 49 | 6–29 (according to Phobius) |
| 5–23 (according to TMMHM) | |||
| A15.5L | WBK62635.1 | 53 | 7–24 and 30–50 (according to Phobius) |
| 7–25 and 30–50 (according to TMMHM) | |||
| gp124 | WBK62631.1 | 70 | 5–22 (according to Phobius) |
| 4–24 (according to TMMHM) | |||
| gp063 | WBK62763.1 | 73 | 45–69 (according to Phobius) |
| 46–69 (according to TMMHM) | |||
| gp066 | WBK62621.1 | 79 | 5–29 and 49–71 (according to Phobius) |
| 7–29 and 49–72 (according to TMMHM) | |||
| gp125 | WBK62620.1 | 90 | 10–33 and 46–67 (according to Phobius) |
| 9–30 and 46–69 (according to TMMHM) | |||
| gp081 | WBK62619.1 | 92 | 42–62 and 67–90 (according to Phobius) |
| 40–60 and 67–90 (according to TMMHM) | |||
| gp120 | WBK62749.1 | 100 | 45–68 (according to Phobius) |
| 45–69 (according to TMMHM) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basu, K.; Krugliak, M.; Arkin, I.T. Viroporins of Mpox Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813828
Basu K, Krugliak M, Arkin IT. Viroporins of Mpox Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(18):13828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813828
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasu, Kingshuk, Miriam Krugliak, and Isaiah T. Arkin. 2023. "Viroporins of Mpox Virus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 18: 13828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813828
APA StyleBasu, K., Krugliak, M., & Arkin, I. T. (2023). Viroporins of Mpox Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(18), 13828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241813828









