Integrative Genome-Based Survey of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB.1.16 Variant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
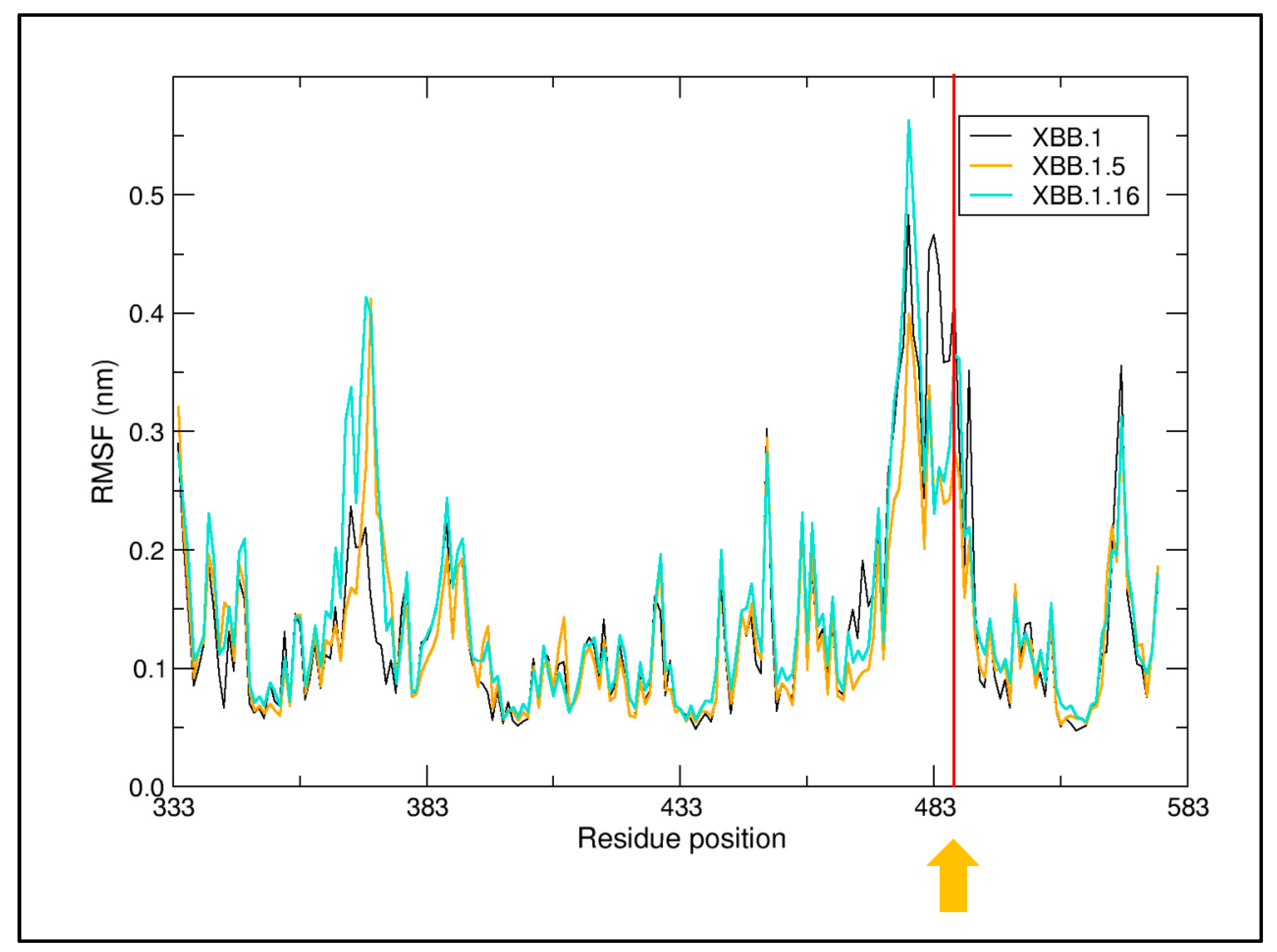
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Phylodynamic Analyses
4.2. Structural Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wu, T.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z. The SARS-CoV-2 outbreak: What we know. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- World Health Organization. Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19—27 July 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---27-july-2023 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Borsetti, A.; Scarpa, F.; Maruotti, A.; Divino, F.; Ceccarelli, G.; Giovanetti, M.; Ciccozzi, M. The unresolved question on COVID-19 virus origin: The three cards game? J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillen, H.S.; Kokic, G.; Farnung, L.; Dienemann, C.; Tegunov, D.; Cramer, P. Structure of replicating SARS-CoV-2 polymerase. Nature 2020, 584, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. XBB.1.16 Initial Risk Assessment, 17 April 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/21042023xbb.1.16ra-v2.pdf?sfvrsn=84577350_1 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- World Health Organization. WHO Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- GISAID. Genomic Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 with Subsampling Focused Globally over the Past 6 Months. Available online: https://gisaid.org/phylodynamics/global/nextstrain/ (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Scarpa, F.; Sanna, D.; Azzena, I.; Casu, M.; Cossu, P.; Fiori, P.L.; Benvenuto, D.; Imperia, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Ceccarelli, G.; et al. Genome-based comparison between the recombinant SARS-CoV-2 XBB and its parental lineages. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, F.; Azzena, I.; Locci, C.; Casu, M.; Fiori, P.L.; Ciccozzi, A.; Angeletti, S.; Imperia, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Maruotti, A.; et al. Molecular In-Depth on the Epidemiological Expansion of SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1.5. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. XBB.1.16 Updated Risk Assessment, 5 June 2023. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/05062023xbb.1.16.pdf?sfvrsn=f1845468_3 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Wang, Q.; Iketani, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bowen, A.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; et al. Alarming antibody evasion properties of rising SARS-CoV-2 BQ and XBB subvariants. Cell 2023, 186, 279–286.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Ito, M.; Kiso, M.; Yamayoshi, S.; Uraki, R.; Fukushi, S.; Watanabe, S.; Suzuki, T.; Maeda, K.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; et al. Efficacy of Antiviral Agents against Omicron Subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 388, 89–91. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMc2214302 (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- GISAID Lineage Comparison. Available online: https://gisaid.org/lineage-comparison/ (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Magazine, N.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; McGee, M.C.; Veggiani, G.; Huang, W. Mutations and Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Viruses 2022, 14, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, F.; Locci, C.; Azzena, I.; Casu, M.; Fiori, P.L.; Ciccozzi, A.; Giovanetti, M.; Quaranta, M.; Ceccarelli, G.; Pascarella, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Recombinants: Genomic Comparison between XBF and Its Parental Lineages. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, F.; Sanna, D.; Azzena, I.; Giovanetti, M.; Benvenuto, D.; Angeletti, S.; Ceccarelli, G.; Pascarella, S.; Casu, M.; Fiori, P.L.; et al. On the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.75 variant: A genetic and structural point of view. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, F.; Sanna, D.; Benvenuto, D.; Borsetti, A.; Azzena, I.; Casu, M.; Fiori, P.L.; Giovanetti, M.; Maruotti, A.; Ceccarelli, G.; et al. Genetic and Structural Data on the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BQ.1 Variant Reveal Its Low Potential for Epidemiological Expansion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, F.; Giovanetti, M.; Azzena, I.; Locci, C.; Casu, M.; Fiori, P.L.; Ciccozzi, A.; Imperia, E.; Bazzani, L.; Borsetti, A.; et al. Genome-based survey of the SARS-CoV-2 BF.7 variant from Asia. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzani, L.; Imperia, E.; Scarpa, F.; Sanna, D.; Casu, M.; Borsetti, A.; Pascarella, S.; Petrosillo, N.; Cella, E.; Giovanetti, M.; et al. SARS-CoV CH.1.1 Variant: Genomic and Structural Insight. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2023, 15, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuto, D.; Giovanetti, M.; Salemi, M.; Prosperi, M.; De Flora, C.; Alcantara, L.C.J.; Angeletti, S.; Ciccozzi, M. The global spread of 2019-nCoV: A molecular evolutionary analysis. Pathog. Glob. Health 2020, 114, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauster, D.; Osterrieder, K.; Haag, R.; Ballauff, M.; Herrmann, A. Respiratory viruses interacting with cells: The importance of electrostatics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1169547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Golosova, O.; Fursov, M. UGENE Team. Unipro UGENE: A unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, R.E.; Raftery, A.E. Bayes factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarisation in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Protein structure modeling with MODELLER. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1654, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrodinger, LLC. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8; Schrodinger, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Delgado, J.; Radusky, L.G.; Cianferoni, D.; Serrano, L. FoldX 5.0: Working with RNA, small molecules and a new graphical interface. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4168–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, M.H.M.; Søndergaard, C.R.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. PROPKA3: Consistent treatment of internal and surface residues in empirical p K a predictions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurrus, E.; Engel, D.; Star, K.; Monson, K.; Brandi, J.; Felberg, L.E.; Brookes, D.H.; Wilson, L.; Chen, J.; Liles, K.; et al. Improvements to the APBS biomolecular solvation software suite. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweke, H.; Mucchielli, M.H.; Chevrollier, N.; Gosset, S.; Lopes, A. SURFMAP: A Software for Mapping in Two Dimensions Protein Surface Features. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2022, 62, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, G.; Wang, E.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, F.; Li, D.; Hou, T. HawkDock: A web server to predict and analyze the protein–protein complex based on computational docking and MM/GBSA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W322–W330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Kastritis, P.L.; Bonvin, A.M.; Vangone, A. PRODIGY: A web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein–protein complexes. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, btw514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páll, S.; Zhmurov, A.; Bauer, P.; Abraham, M.; Lundborg, M.; Gray, A.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. Heterogeneous parallelization and acceleration of molecular dynamics simulations in GROMACS. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 134110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, P. XMGRACE, Version 5.1.19; Center for Coastal and Land-Margin Research, Oregon Graduate Institute of Science and Technology: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2005.
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual Comparisons by Ranking Methods. Biom. Bull. 1945, 1, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
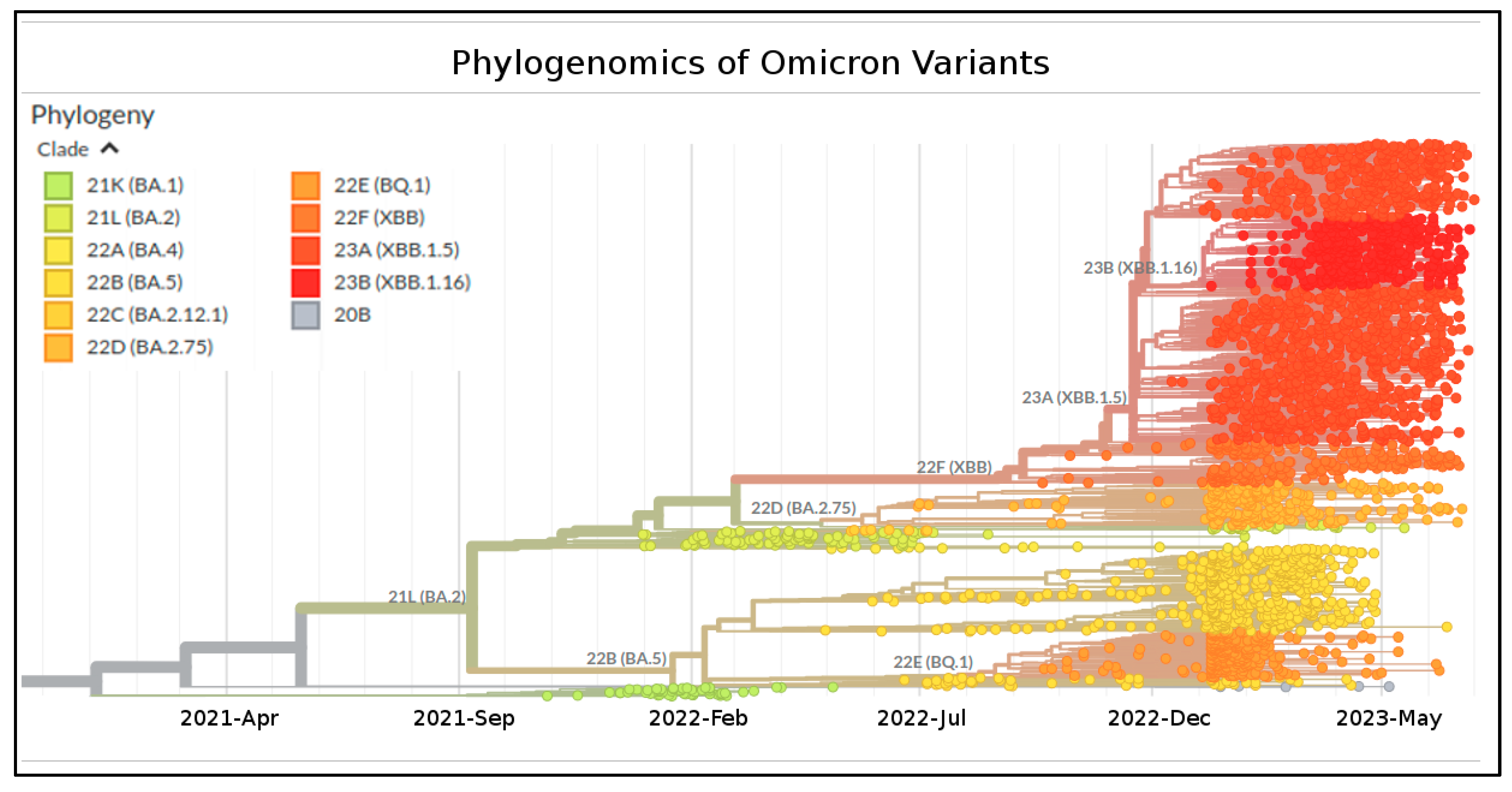
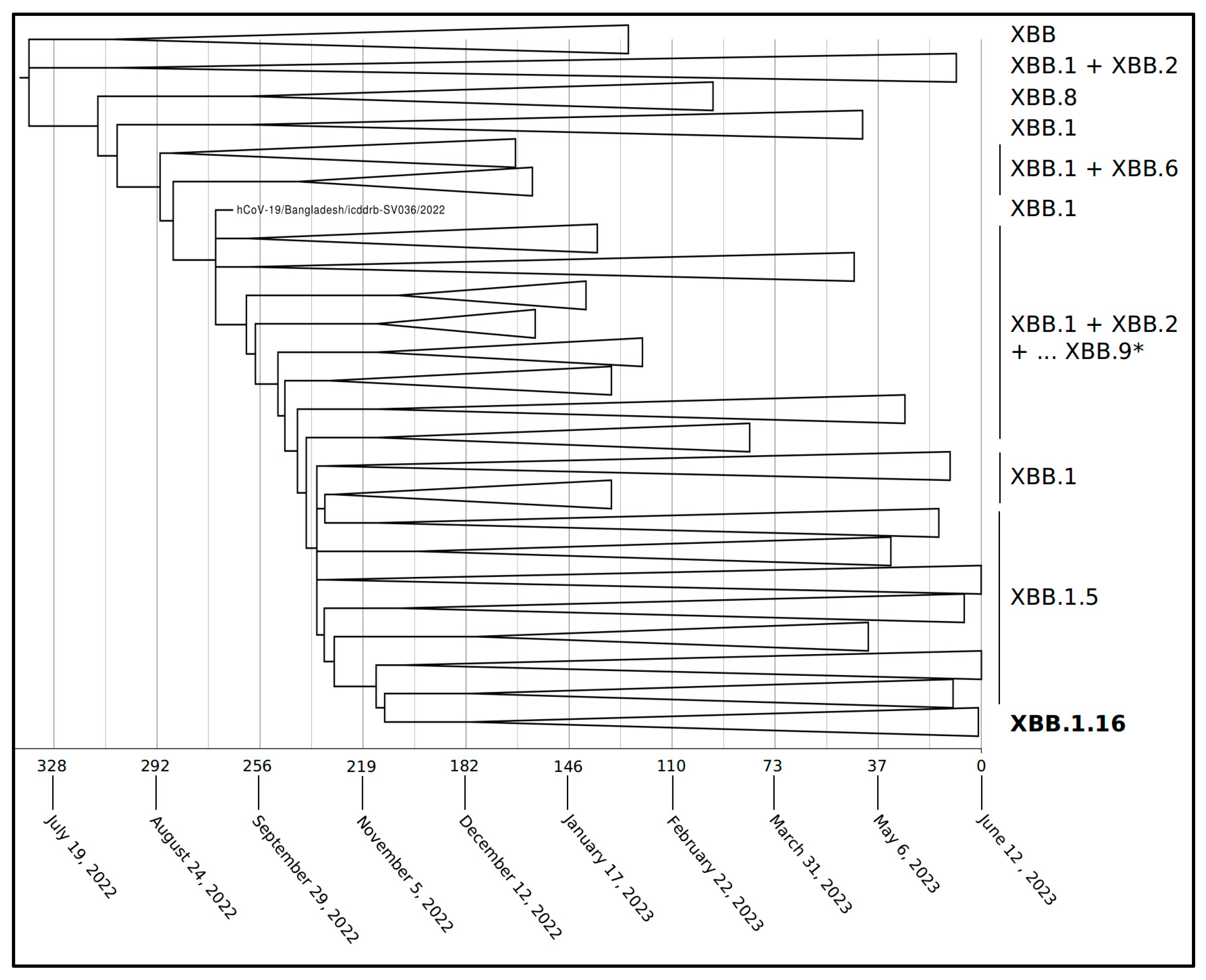
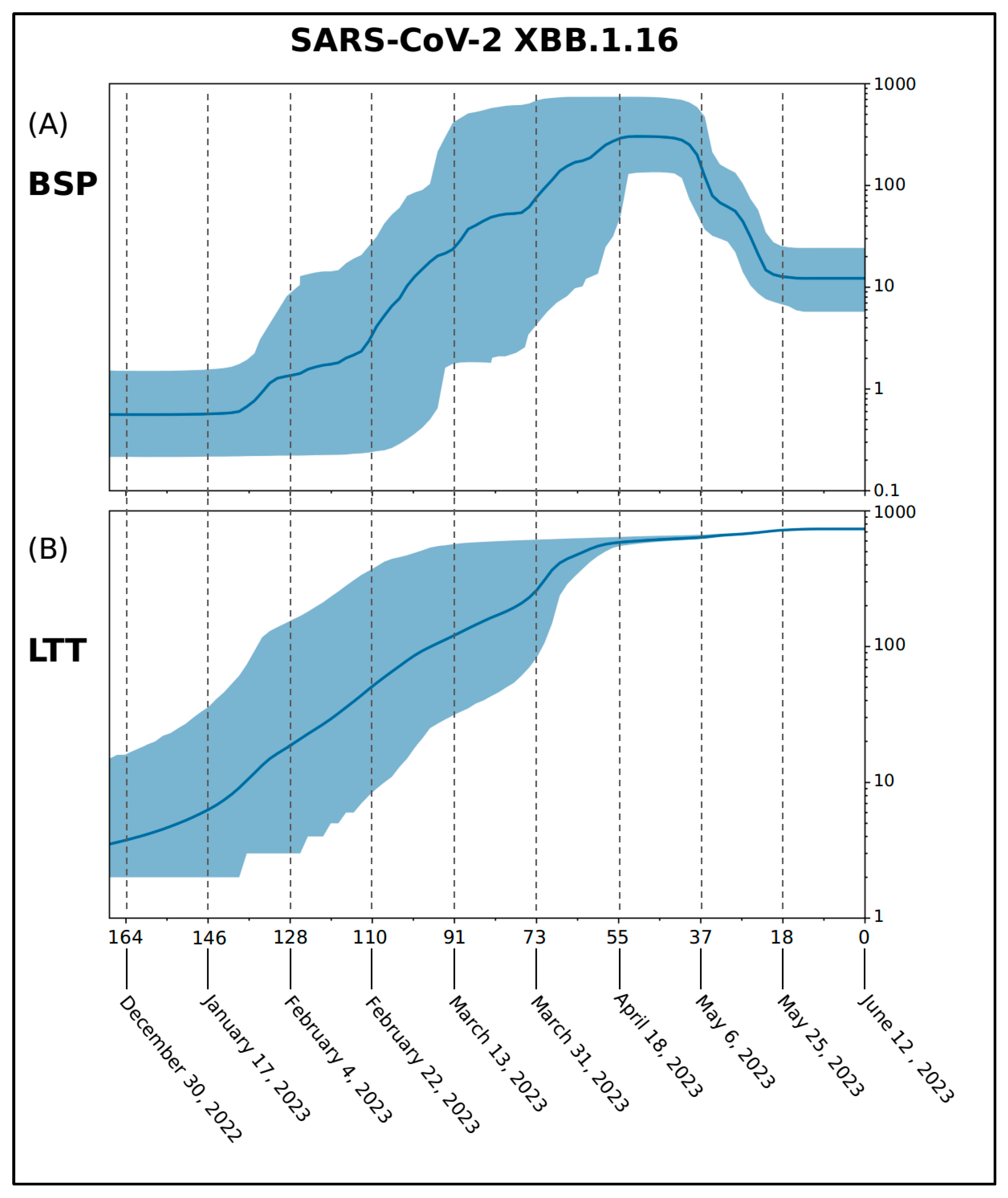
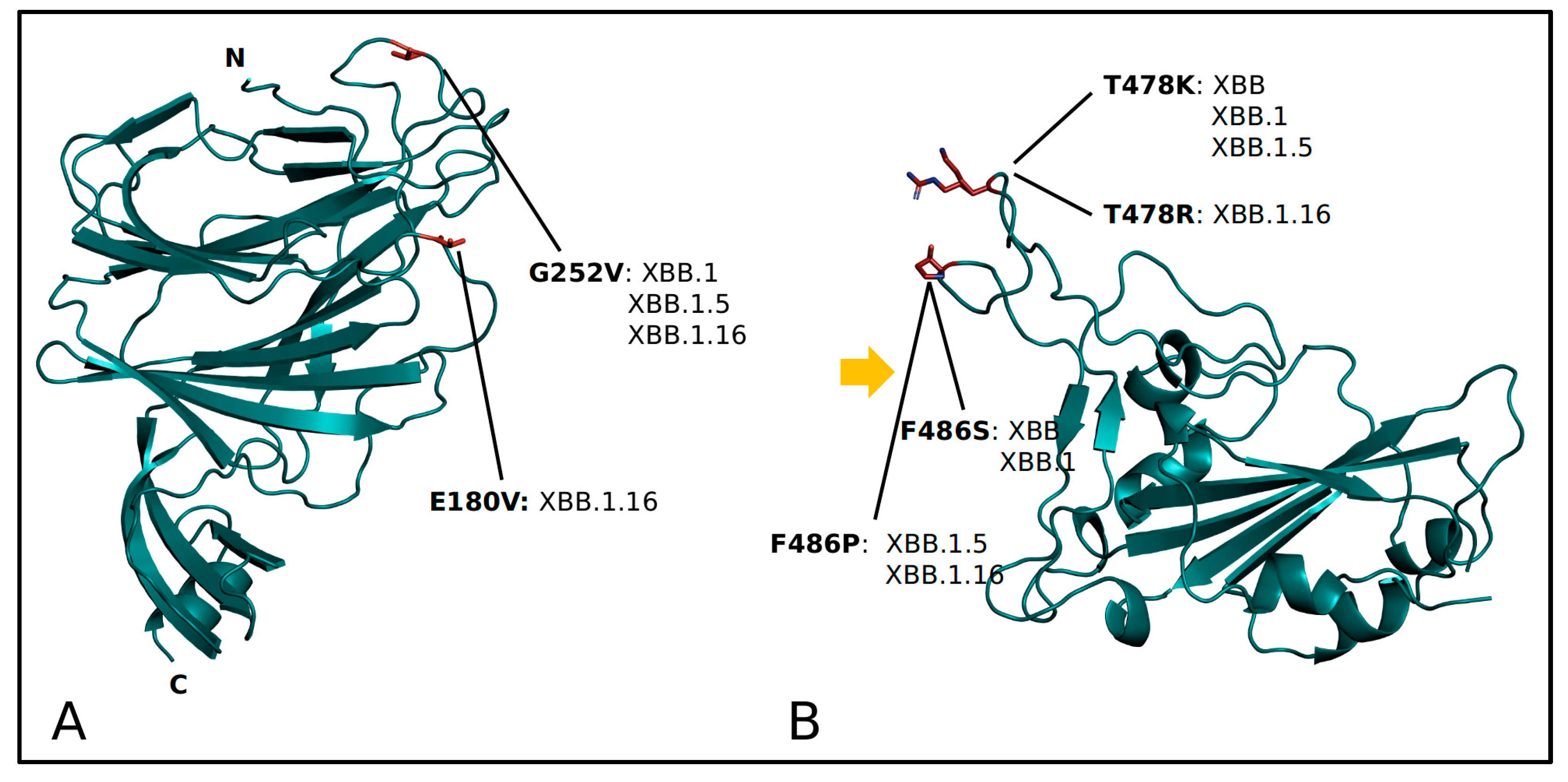
| Nextstrain Clade | Pango Lineage | WHO Label |
|---|---|---|
| 21K (Omicron) | BA.1 | o (Omicron) |
| 21L (Omicron) | BA.2 | o (Omicron) |
| 22C (Omicron) | BA.2.12.1 | o (Omicron) |
| 22D (Omicron) | BA.2.75 | o (Omicron) |
| 22A (Omicron) | BA.4 | o (Omicron) |
| 22B (Omicron) | BA.5 | o (Omicron) |
| 22E (Omicron) | BQ.1 | o (Omicron) |
| 22F (Omicron) | XBB | o (Omicron) |
| 23A (Omicron) | XBB.1.5 | o (Omicron) |
| 23B (Omicron) | XBB.1.16 | o (Omicron) |
| XBB | XBB.1 | XBB.1.5 | XBB.1.16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTD | −1.24 ± 0.00 | −1.18 ± 0.01 | −1.18 ± 0.01 | −0.06 ± 0.03 |
| RBD | 5.45 ± 0.02 | 5.45 ± 0.02 | 5.42 ± 0.01 | 5.57 ± 0.02 |
| XBB | XBB.1 | XBB.1.5 | XBB.1.16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FoldX_5.0 | −3.54 ± 0.30 | −3.54 ± 0.30 | −4.57 ± 0.27 | −4.12 ± 0.33 |
| PRODIGY | −11.48 ± 0.05 | −11.48 ± 0.05 | −10.84 ± 0.05 | −10.94 ± 0.04 |
| MM/GBSA | −60.82 ± 0.99 | −60.82 ± 0.99 | −62.44 ± 2.28 | −62.49 ± 0.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scarpa, F.; Azzena, I.; Ciccozzi, A.; Giovanetti, M.; Locci, C.; Casu, M.; Fiori, P.L.; Borsetti, A.; Cella, E.; Quaranta, M.; et al. Integrative Genome-Based Survey of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB.1.16 Variant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713573
Scarpa F, Azzena I, Ciccozzi A, Giovanetti M, Locci C, Casu M, Fiori PL, Borsetti A, Cella E, Quaranta M, et al. Integrative Genome-Based Survey of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB.1.16 Variant. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713573
Chicago/Turabian StyleScarpa, Fabio, Ilenia Azzena, Alessandra Ciccozzi, Marta Giovanetti, Chiara Locci, Marco Casu, Pier Luigi Fiori, Alessandra Borsetti, Eleonora Cella, Miriana Quaranta, and et al. 2023. "Integrative Genome-Based Survey of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB.1.16 Variant" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713573
APA StyleScarpa, F., Azzena, I., Ciccozzi, A., Giovanetti, M., Locci, C., Casu, M., Fiori, P. L., Borsetti, A., Cella, E., Quaranta, M., Pascarella, S., Sanna, D., & Ciccozzi, M. (2023). Integrative Genome-Based Survey of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB.1.16 Variant. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713573















