Investigating the Regulatory Mechanism of the Sesquiterpenol Nerolidol from a Plant on Juvenile Hormone-Related Genes in the Insect Spodoptera exigua
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Toxicity of Nerolidol to S. exigua Larvae
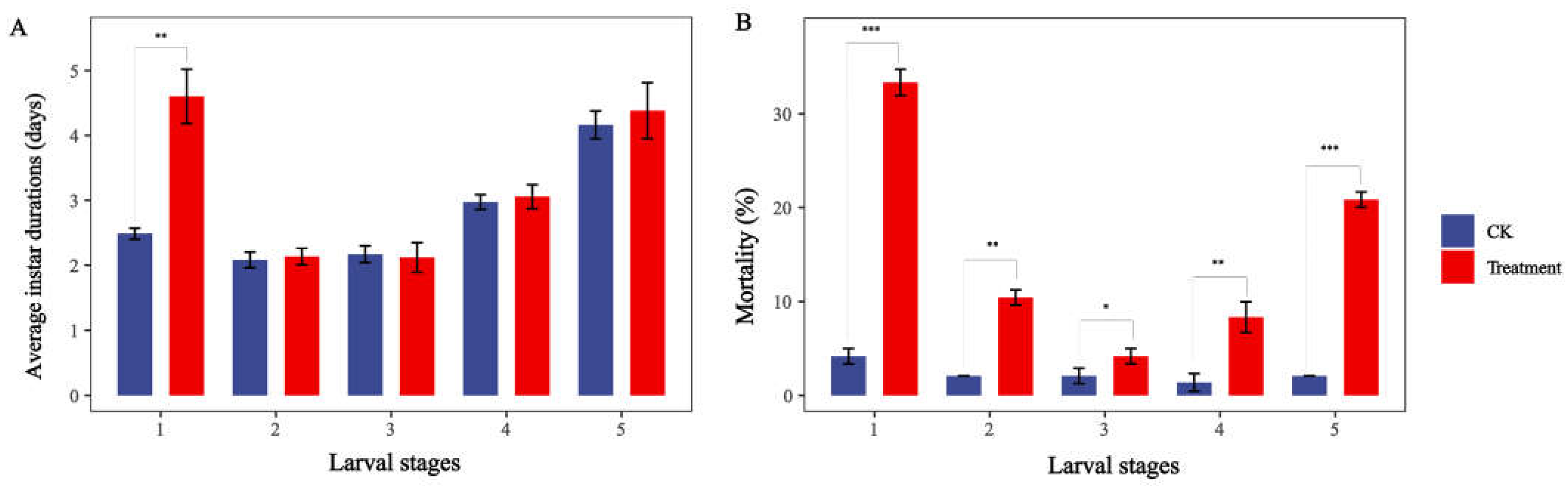
2.2. Effects of Different Sub-Lethal Doses of Nerolidol on Population Life Table Parameters of S. exigua
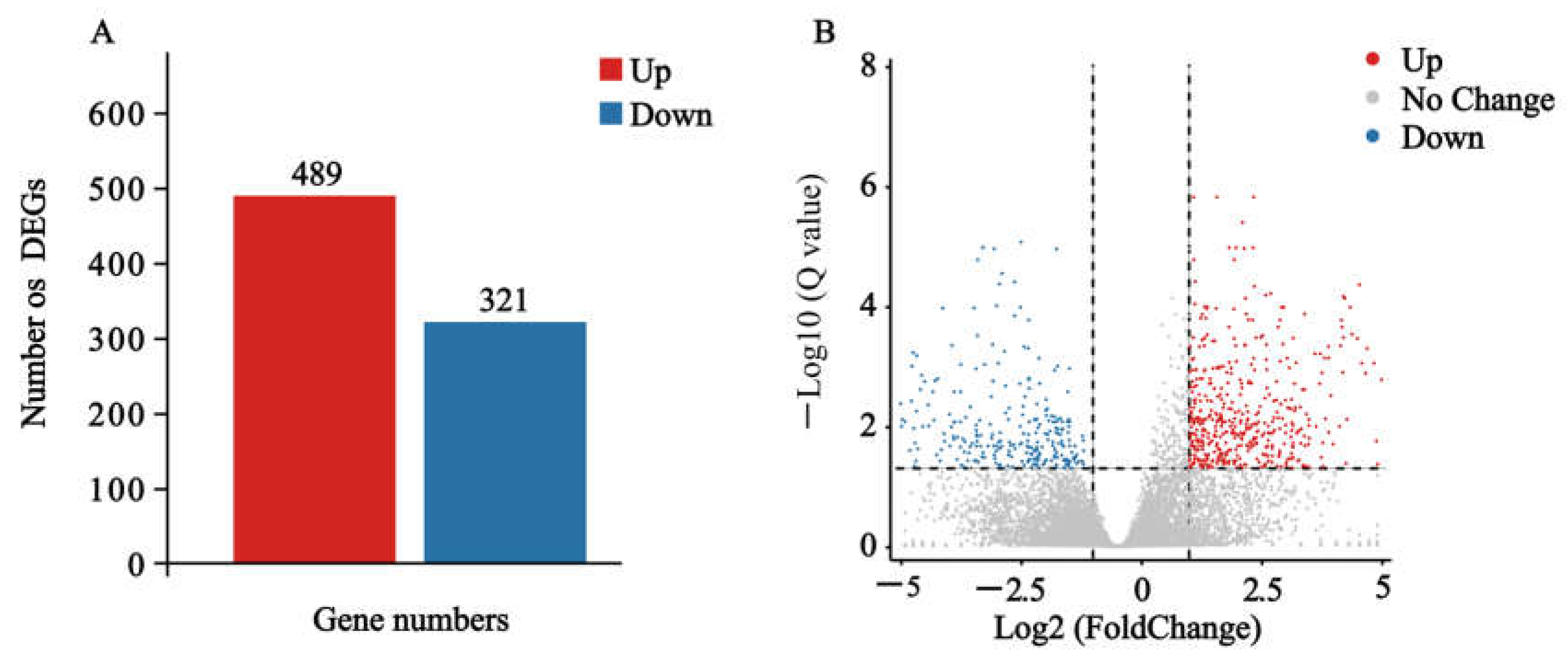
2.3. Effects of Nerolidol on Transcriptomes of S. exigua Larvae
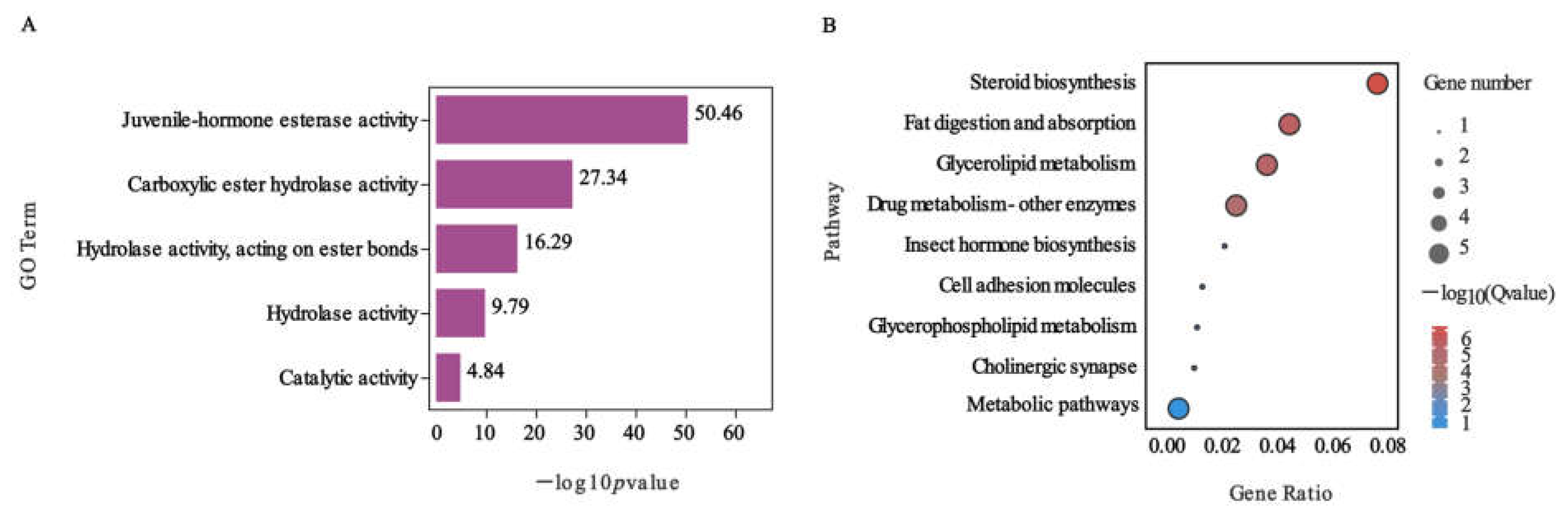
2.4. Function Analysis of DEGs Involved in Nerolidol Exposure of S. exigua
2.5. Structural and Sequence Analyses of JHE-Family Genes in S. exigua
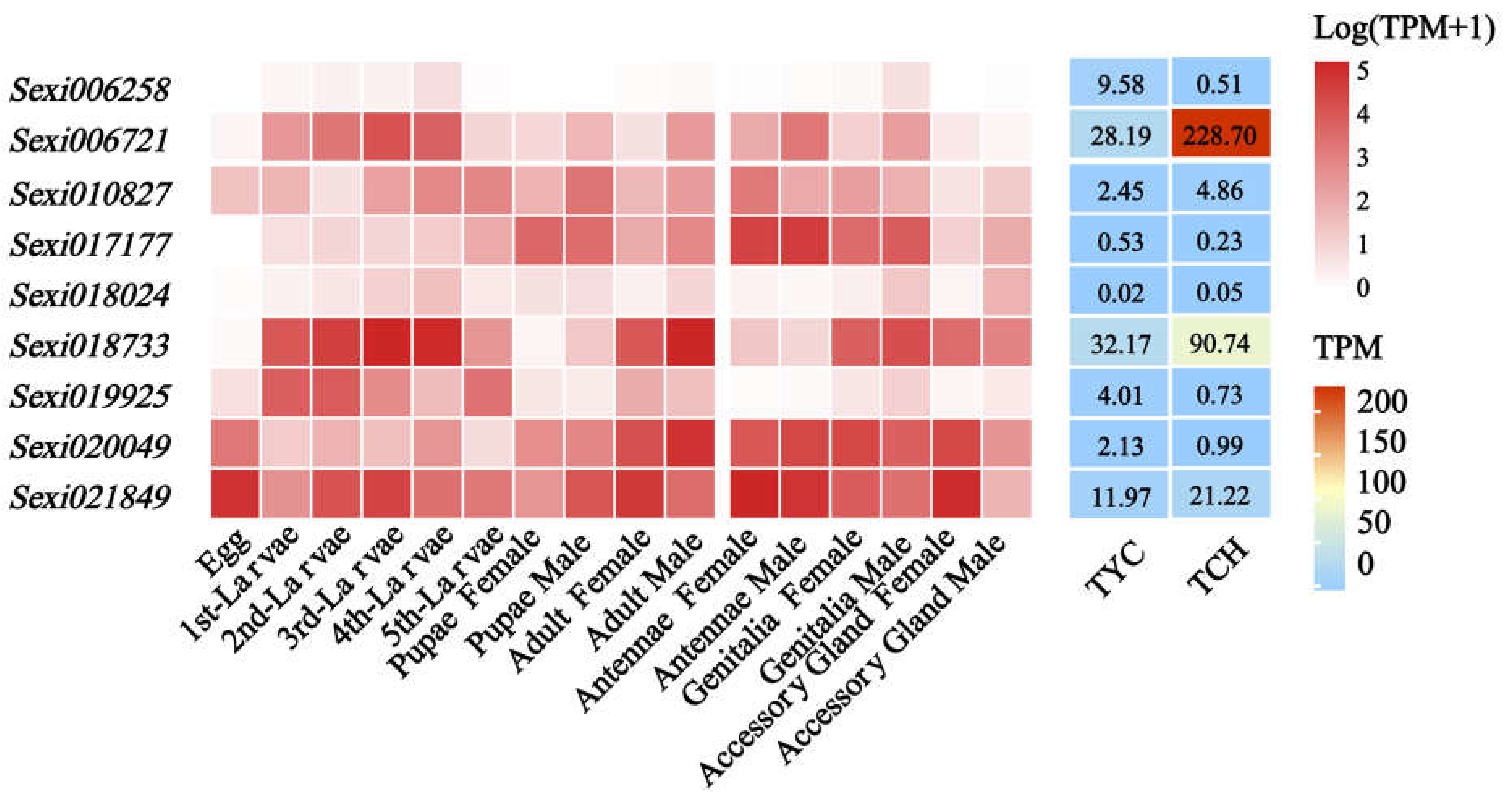
2.6. Expression Profiles of JHE-Family Genes in S. exigua Response to Nerolidol
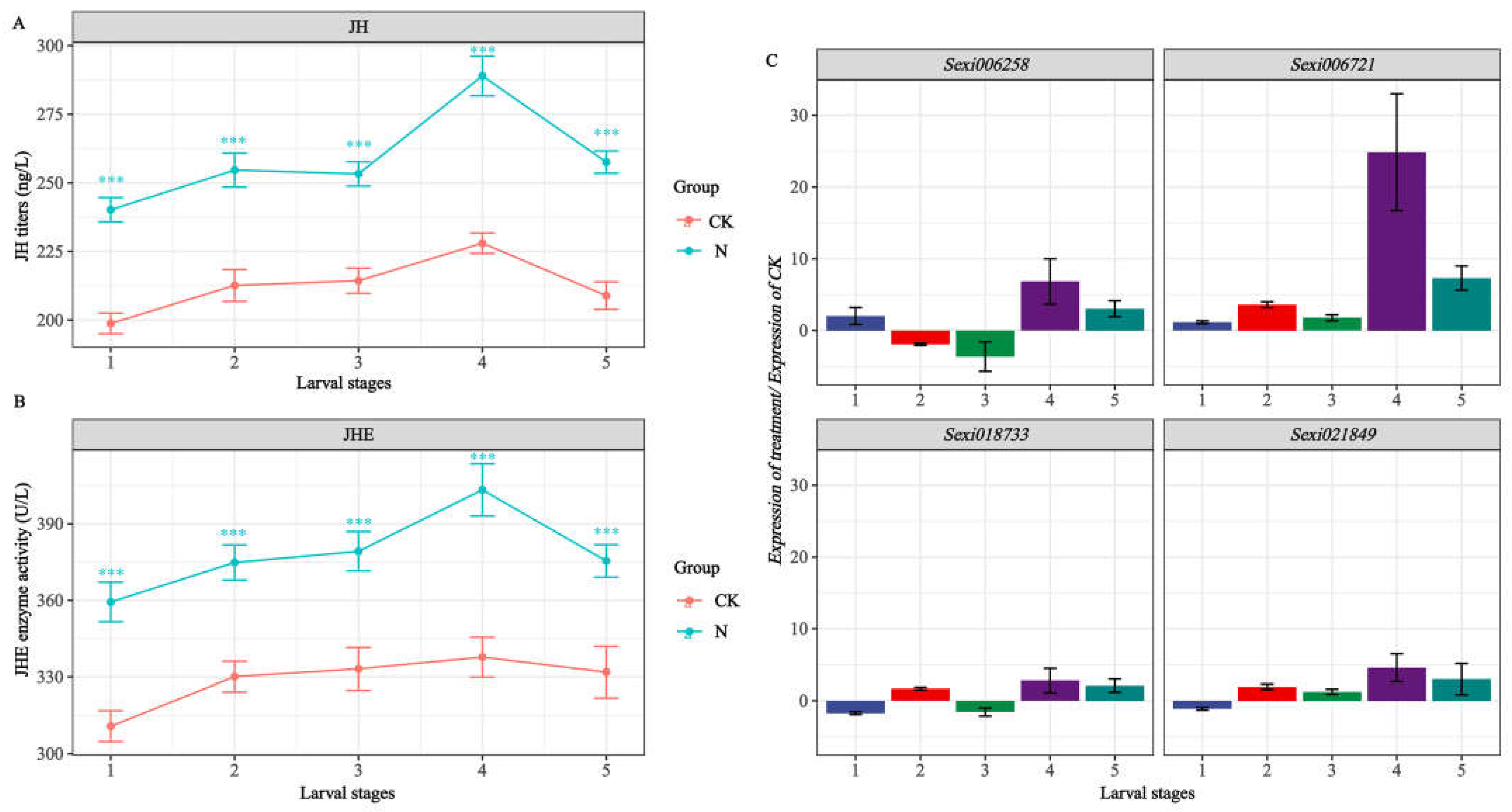
2.7. Detection of Target Gene Expression and Quantification of JH, JHE
2.8. Pearson Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Insect Strains
5.2. Chemicals and Bioassays
5.3. Construction of a Life Table for S. exigua under Sub-Lethal Nerolidol Treatment
5.4. Sample Collection, RNA Isolation, and Library Preparation for RNA-Seq
5.5. RNA-Seq Data Processing
5.6. GO, KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analyses, and Gene Functional Annotation
5.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase PCR Verification
5.8. Identification of Putative JHE and JHEL Genes in S. exigua
5.9. JH and JHE Assays
5.10. Data and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, C.; Wei, C.; Ma, Q.; Dong, H.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Foyer, C.H.; Yu, J. Ethylene response factors 15 and 16 trigger jasmonate biosynthesis in tomato during herbivore resistance. Plant Physiol. 2021, 185, 1182–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Gao, M.; Ye, M.; Lin, M.; Wu, D.; Guo, J.; Guan, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, K.; et al. Transcriptome and metabolome profiling reveal the resistance mechanisms of rice against brown planthopper. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tang, M.; Chen, H. Activation of the ROS/CncC signaling pathway regulates cytochrome P450 CYP4BQ1 responsible for (+)-α-pinene tolerance in Dendroctonus armandi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Tao, S.M.; Dai, H.Y.; Xu, X.T.; Sun, Y.X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.J. The main component of the aphid alarm pheromone (E)-β-farnesene affects the growth and development of Spodoptera exigua by mediating juvenile hormone-related genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 863626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; He, H.; Yan, M.; Zhao, C.; Lei, C.; Li, J.; Yan, F. Widely targeted analysis of metabolomic changes of Cucumis sativus induced by cucurbit chlorotic yellows virus. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, P.T.; Kou, D.R.; Han, Y.C.; Fang, J.C.; Ni, J.P.; Jiang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, W.; et al. Terpene synthases in rice pan-genome and their responses to Chilo suppressalis larvae infesting. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 905982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Yu, Q.; Huang, M.; Hung, W.; Grosser, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Gmitter, F.G.J. Proteomic and metabolomic analyses provide insight into the off-flavour of fruits from citrus trees infected with ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagegowda, D.A.; Gupta, P. Advances in biosynthesis, regulation, and metabolic engineering of plant specialized terpenoids. Plant Sci. 2020, 294, 110457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, L.; Cai, X.; Li, X.; Bian, L.; Luo, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xin, Z. (E)-Nerolidol is a volatile signal that induces defenses against insects and pathogens in tea plants. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Wu, S.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, L.; Qian, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Z. Involvement of histone deacetylase CsHDA2 in regulating (E)-nerolidol formation in tea (Camellia sinensis) exposed to tea green leafhopper infestation. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liu, X.; Gui, J.; Mei, X.; Fu, X.; Dong, F.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z. Formation of (E)-nerolidol in tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves exposed to multiple stresses during tea manufacturing. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, K.; Yu, Y.; Hu, B.; Song, H.; Liu, X. Transcriptional dynamics induced by diapause hormone in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biology 2022, 11, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddiford, L.M.; Truman, J.W.; Mirth, C.K.; Shen, Y.C. A role for juvenile hormone in the prepupal development of Drosophila melanogaster. Development 2010, 137, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Ye, X.Q.; Shi, M.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.N.; Gu, Q.J.; Wu, X.T.; Yin, C.L.; Guo, D.H.; et al. Parasitic insect-derived miRNAs modulate host development. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Qiu, D. Silencing the HaHR3 gene by transgenic plant-mediated RNAi to disrupt Helicoverpa armigera development. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, M.; Martinez, P.R.; Garcera, M.D.; Couillaud, F. Biological activities of natural sesquiterpene lactones and the effect of synthetic sesquiterpene derivatives on insect juvenile hormone biosynthesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2030–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, P.; Zhao, P. Structural characterization and functional analysis of juvenile hormone diol kinase from the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yao, X.; Liu, B.; Han, Y.; Ji, R.; Ju, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Fang, J.; Sun, Y. Caterpillar-induced rice volatile (E)-β-Farnesene impairs the development and survival of Chilo suppressalis larvae by disrupting insect hormone balance. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 904482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sheikh, E.A.; Mamtha, M.D.; Ragheb, D.A.; Ashour, M.B.A. Potential of juvenile hormone esterase as a bio-insecticide: An overview. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2011, 21, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Ramaseshadri, P.; Palli, S.R. Identification and characterization of juvenile hormone esterase gene from the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Kumar, S.; Kim, E.; Kim, Y. A whole genome screening and RNA interference identify a juvenile hormone esterase-like gene of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 80, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiannatos, D.; Michail, X.; Kourti, A. Molecular characterization of an ecdysteroid inducible carboxylesterase with GQSCG motif in the corn borer, Sesamia nonagrioides. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiannatos, D.; Swevers, L.; Maenaka, K.; Park, E.Y.; Iatrou, K.; Kourti, A. Functional characterization of a juvenile hormone esterase related gene in the moth Sesamia nonagrioides through RNA interference. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBoeuf, A.C.; Cohanim, A.B.; Stoffel, C.; Brent, C.S.; Waridel, P.; Privman, E.; Keller, L.; Benton, R. Molecular evolution of juvenile hormone esterase-like proteins in a socially exchanged fluid. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smagghe, G.; Pineda, S.; Carton, B.; Del Estal, P.; Budia, F.; Viñuela, E. Toxicity and kinetics of methoxyfenozide in greenhouse-selected Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest. Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.L.; Liu, S.W.; Baerson, S.R.; Qin, Z.; Ma, Z.H.; Su, Y.J.; Zhang, J.E. Identification and functional analysis of a novel cytochrome P450 gene CYP9A105 associated with pyrethroid detoxification in Spodoptera exigua Hübner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, M.; Liu, S.; Jan, S.; Shi, L.; Fernández-Grandon, G.M.; Gulzar, A.; Ali, B.; Rehman, M.; Wang, M. Knock-down of gossypol-inducing cytochrome P450 genes reduced deltamethrin sensitivity in Spodoptera exigua (Hübner). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.Y.; Ma, H.H.; Lu, W.J.; Wang, X.L.; Wu, S.W.; Nauen, R.; Wu, Y.D.; Yang, Y.H. Identification of the ryanodine receptor mutation I4743M and its contribution to diamide insecticide resistance in Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guan, F.; Zhang, J.; Feyereisen, R.; Fabrick, J.A.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y. Genome mapping coupled with CRISPR gene editing reveals a P450 gene confers avermectin resistance in the beet armyworm. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, X.; Pei, Y.; Aioub, A.A.A.; Hu, Z. Evidence for Multiple Origins of Knockdown Resistance (kdr) in Spodoptera exigua (Hübna) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) From China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, X.Z.; Ning, Y.S.; Jing, W.X.; Bruce, T.J.A.; Qi, F.j.; Xu, Q.X.; Wu, K.M.; Zhang, Y.J.; Guo, Y.Y. TPS46, a rice terpene synthase conferring natural resistance to bird cherry-oat aphid, Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 11183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Luo, J.; Zhang, S.; Lü, L.; Wang, C.; Cui, J. Effects of plant secondary metablites gossypol and rutin on the activities of protective enzymes and detoxification enzymes in green mirid bug Apolygus lucorum. J. Plant Prot. 2018, 45, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Li, X. Effects of plant secondary metabolite on detoxification enzyme activity of Spodoptera litura. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 37, 3495–3502. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, D.; Kerat, M.; Goldenberg, S.; Bartelt, R.J.; Williams, R.N. Responses to synthetic aggregation pheromones, host-related volatiles, and their combinations by carpophilus spp. (coleoptera: Nitidulidae) in laboratory and field tests. Environ. Entomol. 1993, 4, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyrat, N.; Robert, C.A.M.; Turlings, T.C.J.; Erb, M. Herbivore intoxication as a potential primary function of an inducible volatile plant signal. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, Â.A.B.; Ferreira, O.O.; Da Costa, L.S.; Almeida, L.Q.; Varela, E.L.P.; Cascaes, M.M.; De Jesus Pereira Franco, C.; Percário, S.; Nascimento, L.D.D.; De Oliveira, M.S.; et al. Phytochemical profile, preliminary toxicity and antioxidant capacity of the essential oils of Myrciaria floribunda (H. West ex Willd.) O. Berg. and Myrcia sylvatica (G. Mey) DC. (Myrtaceae). Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, M.; Jing, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Song, C. Scenarios of genes-to-terpenoids network led to the identification of a novel α/β-Farnesene/β-Ocimene synthase in Camellia sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Han, T.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y. Knockout of a P-glycoprotein gene increases susceptibility to abamectin and emamectin benzoate in Spodoptera exigua. Insect Mol. Biol. 2018, 27, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z. Metabolic changes in larvae of predator Chrysopa sinica fed on azadirachtin-treated Plutella xylostella larvae. Metabolites 2022, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denlinger, D.L.; Yocum, G.D.; Rinehart, J.P. Hormonal control of diapause. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 8, 353–412. [Google Scholar]
- Riddiford, L.M.; Hiruma, K.; Zhou, X.; Nelson, C.A. Insights into the molecular basis of the hormonal control of molting and metamorphosis from Manduca sexta and Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 33, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamita, S.G.; Hinton, A.C.; Wheelock, C.E.; Wogulis, M.D.; Wilson, D.K.; Wolf, N.M.; Stok, J.E.; Hock, B.; Hammock, B.D. Juvenile hormone (JH) esterase: Why are you so JH specific? Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 33, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, W.G.; Granger, N.A. The juvenile hormones. Compr. Mol. Insect Sci. 2005, 3, 319–408. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, T.C.; Hammock, B.D. Comparative inhibition of the juvenile hormone esterases from Trichoplusia ni, Tenebrio molitor, and Musca domestica. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 1980, 14, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.L.; Ladd, T.R.; Tomkins, B.L.; Sundaram, M.; Sohi, S.S.; Retnakaran, A.; Davey, K.G.; Palli, S.R. Spruce budworm (Choristoneura fumiferana) juvenile hormone esterase: Hormonal regulation, developmental expression and cDNA cloning. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 1999, 148, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munyiri, F.N.; Ishikawa, Y. Molecular cloning and developmental expression of the gene encoding juvenile hormone esterase in the yellow-spotted longicorn beetle, Psacothea hilaris. Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kort, C.A.D.; Granger, N.A. Regulation of JH titers: The relevance of degradative enzymes and binding proteins. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1996, 33, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, A. Effects of juvenile hormone on the secretion of prothoracicotropic hormone in the last- and penultimate-instar larvae of the silkworm Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 2001, 47, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddiford, L.M. Molecular aspects of juvenile hormone action in insect metamorphosis. In Metamorphosis; Gilbert, L.I., Tata, J.R., Atkinson, B.G., Eds.; Pergamon: London, UK, 1996; pp. 223–251. [Google Scholar]
- Atiyeh, M.; Parviz, M.; Andrea, M. Variation in terpene profiles of Thymus vulgaris in water deficit stress response. Molecules 2020, 25, 1091. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.Y.; Liu, J.T.; Xie, J.X.; Yi, C.Q.; Liu, X.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Sun, Y. Gene cloning and ligand binding characterization of the odorant-binding protein HvarOBP2 in Hippodamia variegata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2022, 65, 977–985. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated G4946E substitution in the ryanodine receptor of Spodoptera exigua confers high levels of resistance to diamide insecticides. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 89, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xiao, L.; Cao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Tan, Y.; Bai, L. Molecular characterisation of the vitellogenin gene (AlVg) and its expression after Apolygus lucorum had fed on different hosts. Pest Manag Sci. 2016, 72, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R Package Version 1.0. 12. 2019. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/pheatmap/ (accessed on 18 March 2023).
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant graphics for data analysis. J R STAT SOC A STAT. 2009, 174, 245–246. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamita, S.G.; Hammock, B.D. Juvenile hormone esterase: Biochemistry and structure. J. Pestic. Sci. 2010, 35, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Larval Stage (Instar) | LC5 (95% FL a) (mg/mL) | LC20 (95% FL) (mg/mL) | LC50 (95% FL) (mg/mL) | Slope ± SE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.23 (0.07–0.46) | 0.96 (0.48–1.52) | 4.30 (2.98–6.20) | 1.29 ± 0.18 |
| 2 | 3.46 (0.45–6.27) | 6.35 (1.97–10.41) | 12.01 (6.79–24.65) | 3.04 ± 0.31 |
| 3 | 6.72 (3.85–9.29) | 11.30 (7.87–14.45) | 19.48 (15.31–25.00) | 3.56 ± 0.36 |
| Key Life History Parameters | Different Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.25 mg/mL | 1.0 mg/mL | 4.0 mg/mL | |
| Larval stage (d) | 13.86 ± 0.63 a | 14.45 ± 0.79 ab | 15.26 ± 1.21 ab | 16.27 ± 1.46 b |
| Pupa stage (d) | 7.45 ± 0.44 a | 7.97 ± 0.44 ab | 9.02 ± 0.65 bc | 10.36 ± 0.97 c |
| Adult stage (d) | 10.15 ± 0.47 a | 9.79 ± 0.60 ab | 9.30 ± 0.19 b | 9.05 ± 0.48 b |
| Egg stage (d) | 2.03 ± 0.12 a | 2.11 ± 0.13 a | 2.23 ± 0.26 ab | 2.59 ± 0.13 b |
| The whole life-span of S. exigua (d) | 33.49 ± 0.74 a | 34.31 ± 1.02 a | 35.81 ± 1.94 ab | 38.27 ± 2.75 b |
| Larvae mortality (%) | 11.81 ± 5.20 a | 22.22 ± 8.56 a | 39.58 ± 7.80 b | 77.08 ± 9.47 c |
| Adult emergence rate (%) | 87.20 ± 0.53 a | 81.10 ± 6.67 ab | 78.17 ± 4.60 bc | 75.60 ± 3.45 bc |
| Per female fecundity | 468.33 ± 60.00 a | 472.67 ± 24.93 a | 435.00 ± 34.56 a | 215.00 ± 30.80 b |
| Hatching rate of eggs (%) | 74.40 ± 2.65 a | 72.63 ± 4.40 a | 68.70 ± 5.42 a | 65.07 ± 6.71 a |
| Intrinsic rate of increase (R) | 0.145 ± 0.007 a | 0.133 ± 0.010 a | 0.110 ± 0.011 b | 0.045 ± 0.008 c |
| Parameters | Other Parameters | Linear Equation | R2 | p | Linear Equation | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | Treated with Nerolidol | ||||||
| The expression of Sexi021849 | JH titer | y = 296.350x + 205.720 | 0.11 | <0.001 | y = 289.910x + 242.010 | 0.60 | <0.001 |
| JHE activity | y = 550.150x + 316.100 | 0.40 | <0.001 | y = 239.270x + 364.480 | 0.53 | <0.001 | |
| Larval stage | y = 42.166x + 1.806 | 0.35 | <0.001 | y = 4.202x + 3.014 | 0.03 | <0.001 | |
| Larvae mortality | y = −48.893x + 3.485 | 0.31 | 0.001 | y = −65.941x + 19.265 | 0.07 | 0.019 | |
| The expression of Sexi006258 | JH titer | y = −20.623x + 212.610 | <0.01 | <0.001 | y = −3062.300x + 265.610 | 0.09 | <0.001 |
| JHE activity | y = 293.600x + 327.710 | 0.02 | <0.001 | y = −2563.800x + 384.030 | 0.09 | <0.001 | |
| Larval stage | y = −138.510x + 3.263 | 0.51 | <0.001 | y = −328.730x + 3.976 | 0.25 | <0.001 | |
| Larvae mortality | y = −34.240x + 2.482 | 0.02 | 0.001 | y = −688.860x + 16.919 | 0.01 | 0.019 | |
| The expression of Sexi006721 | JH titer | y = 2.088x + 212.510 | <0.01 | <0.001 | y = 350.070x + 238.690 | 0.94 | <0.001 |
| JHE activity | y = 131.390x + 327.100 | 0.02 | <0.001 | y = 307.450x + 360.660 | 0.94 | <0.001 | |
| Larval stage | y = −60.755x + 3.534 | 0.50 | <0.001 | y = −9.661x + 3.818 | 0.17 | <0.001 | |
| Larvae mortality | y = −6.817x + 2.446 | <0.01 | 0.001 | y = −147.710x + 23.958 | 0.40 | 0.019 | |
| The expression of Sexi018733 | JH titer | y = 747.690x + 209.160 | 0.06 | <0.001 | y = 4682.900x + 230.850 | 0.61 | <0.001 |
| JHE activity | y = 1270.300x + 323.020 | 0.17 | <0.001 | y = 4458.600x + 351.710 | 0.72 | <0.001 | |
| Larval stage | y = −119.170x + 3.312 | 0.22 | <0.001 | y = −275.090x + 4.909 | 0.48 | <0.001 | |
| Larvae mortality | y = −106.110x + 2.839 | 0.12 | 0.001 | y = −3452.900x + 36.119 | 0.78 | 0.019 | |
| JH titer | JHE activity | y = 0.862x + 145.580 | 0.76 | <0.001 | y = 0.858x + 156.220 | 0.96 | <0.001 |
| Larval stage | y = 0.002x + 2.375 | <0.01 | <0.001 | y = −0.017x + 7.535 | 0.06 | <0.001 | |
| Larvae mortality | y = −0.089x + 21.174 | 0.79 | <0.001 | y = −0.361x + 108.820 | 0.31 | <0.001 | |
| JHE activity | Larval stage | y = 0.018x − 3.014 | 0.05 | <0.001 | y = −0.031x + 14.879 | 0.18 | <0.001 |
| Larvae mortality | y = −0.100x + 35.334 | 0.99 | <0.001 | y = −0.522x + 212.950 | 0.50 | <0.001 | |
| Larval stage | Larvae mortality | y = −0.255x + 3.070 | 0.04 | 0.513 | y = 8.817x − 13.321 | 0.80 | 0.050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, H.; Liu, B.; Yang, L.; Yao, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiao, W.; Li, S.; Ji, R.; Sun, Y. Investigating the Regulatory Mechanism of the Sesquiterpenol Nerolidol from a Plant on Juvenile Hormone-Related Genes in the Insect Spodoptera exigua. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713330
Dai H, Liu B, Yang L, Yao Y, Liu M, Xiao W, Li S, Ji R, Sun Y. Investigating the Regulatory Mechanism of the Sesquiterpenol Nerolidol from a Plant on Juvenile Hormone-Related Genes in the Insect Spodoptera exigua. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(17):13330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713330
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Hanyang, Baosheng Liu, Lei Yang, Yu Yao, Mengyun Liu, Wenqing Xiao, Shuai Li, Rui Ji, and Yang Sun. 2023. "Investigating the Regulatory Mechanism of the Sesquiterpenol Nerolidol from a Plant on Juvenile Hormone-Related Genes in the Insect Spodoptera exigua" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 17: 13330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713330
APA StyleDai, H., Liu, B., Yang, L., Yao, Y., Liu, M., Xiao, W., Li, S., Ji, R., & Sun, Y. (2023). Investigating the Regulatory Mechanism of the Sesquiterpenol Nerolidol from a Plant on Juvenile Hormone-Related Genes in the Insect Spodoptera exigua. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(17), 13330. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241713330





