Exploring Extracellular Vesicles of Probiotic Yeast as Carriers of Biologically Active Molecules Transferred to Human Intestinal Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
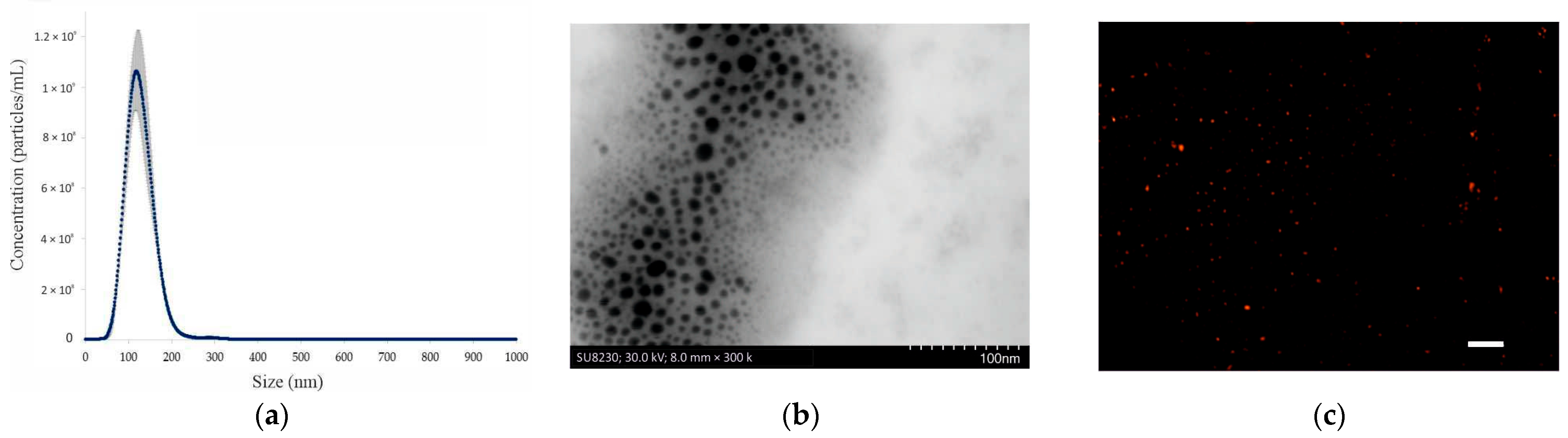
2.1. Characterization of EVs Produced by S. boulardii CNCM I-745
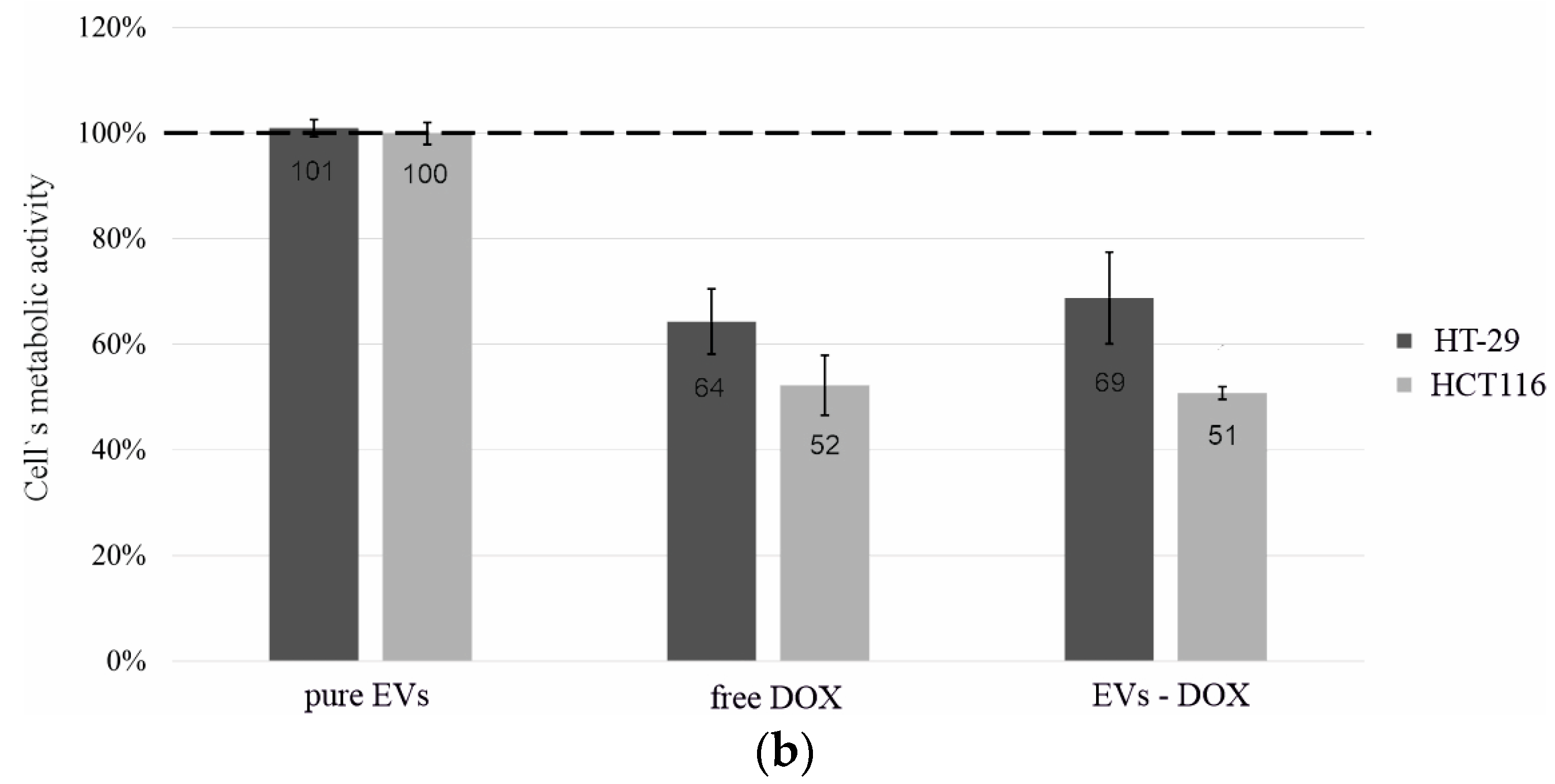
2.2. Metabolic Activity Tests on Human Intestinal Cell Lines Treated with the EVs of Probiotic Yeast
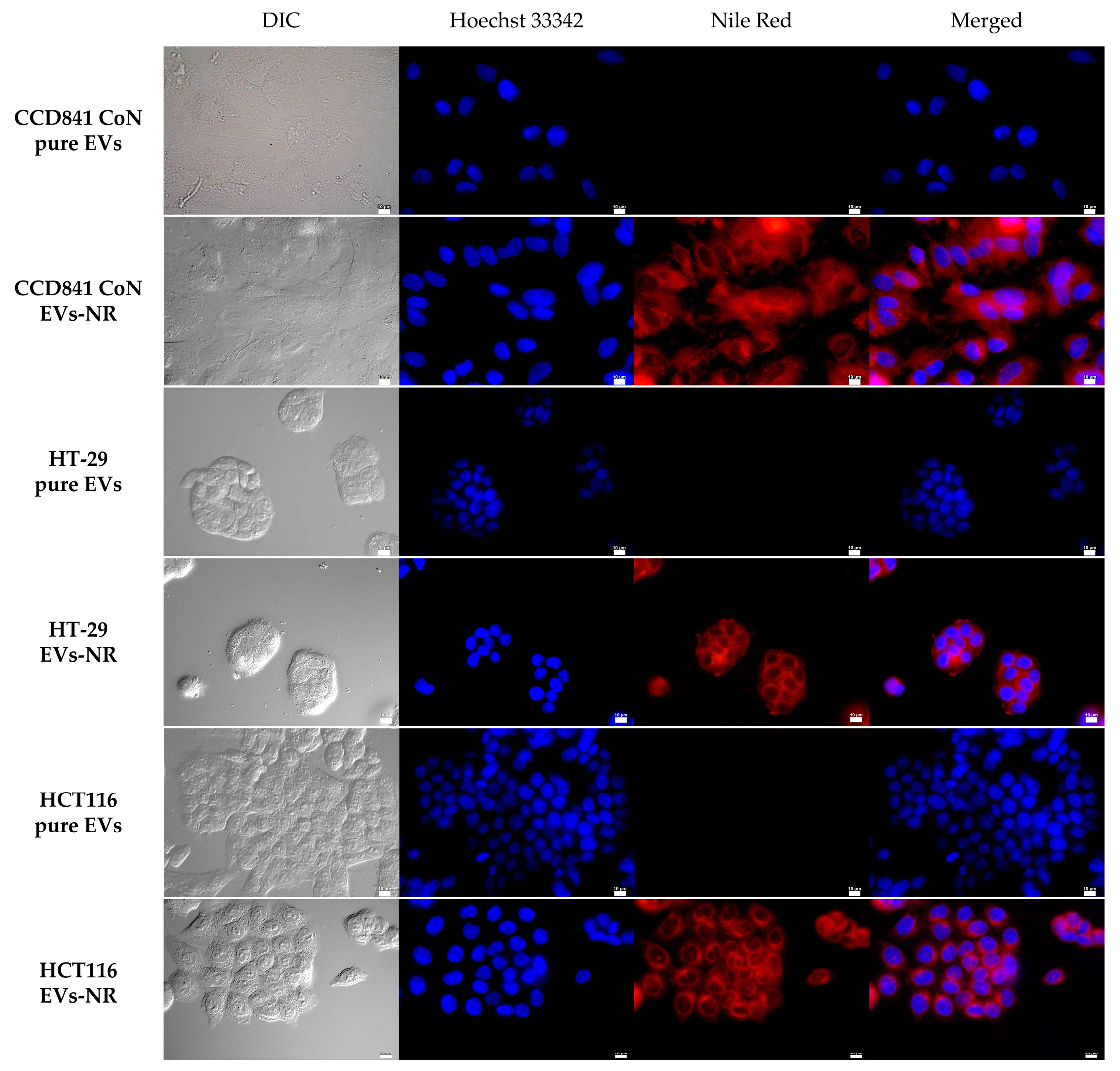
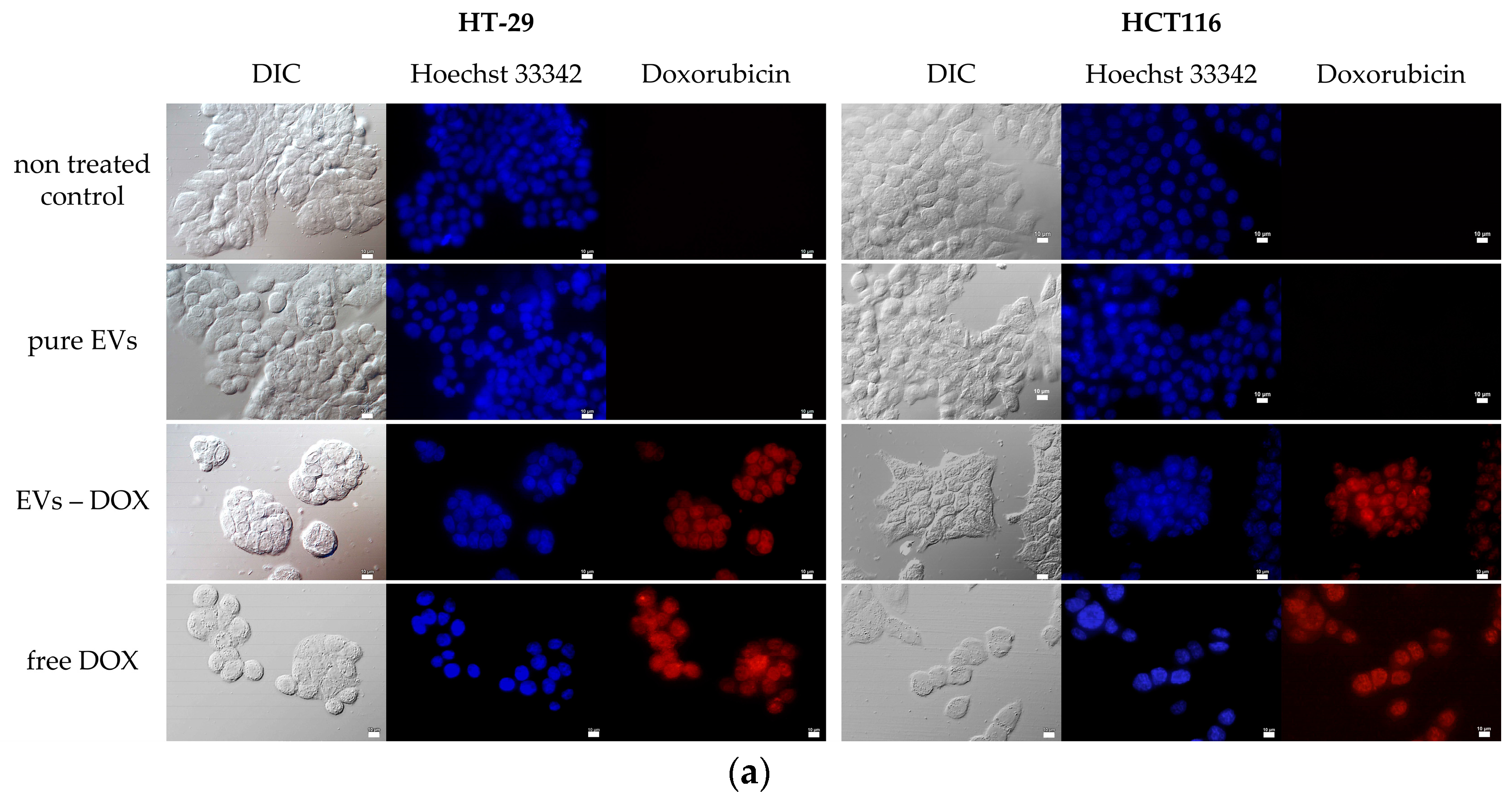
2.3. Determination of Whether Extracellular Vesicles of Probiotic Yeast Can Transfer Biologically Active Substances into Human Cells
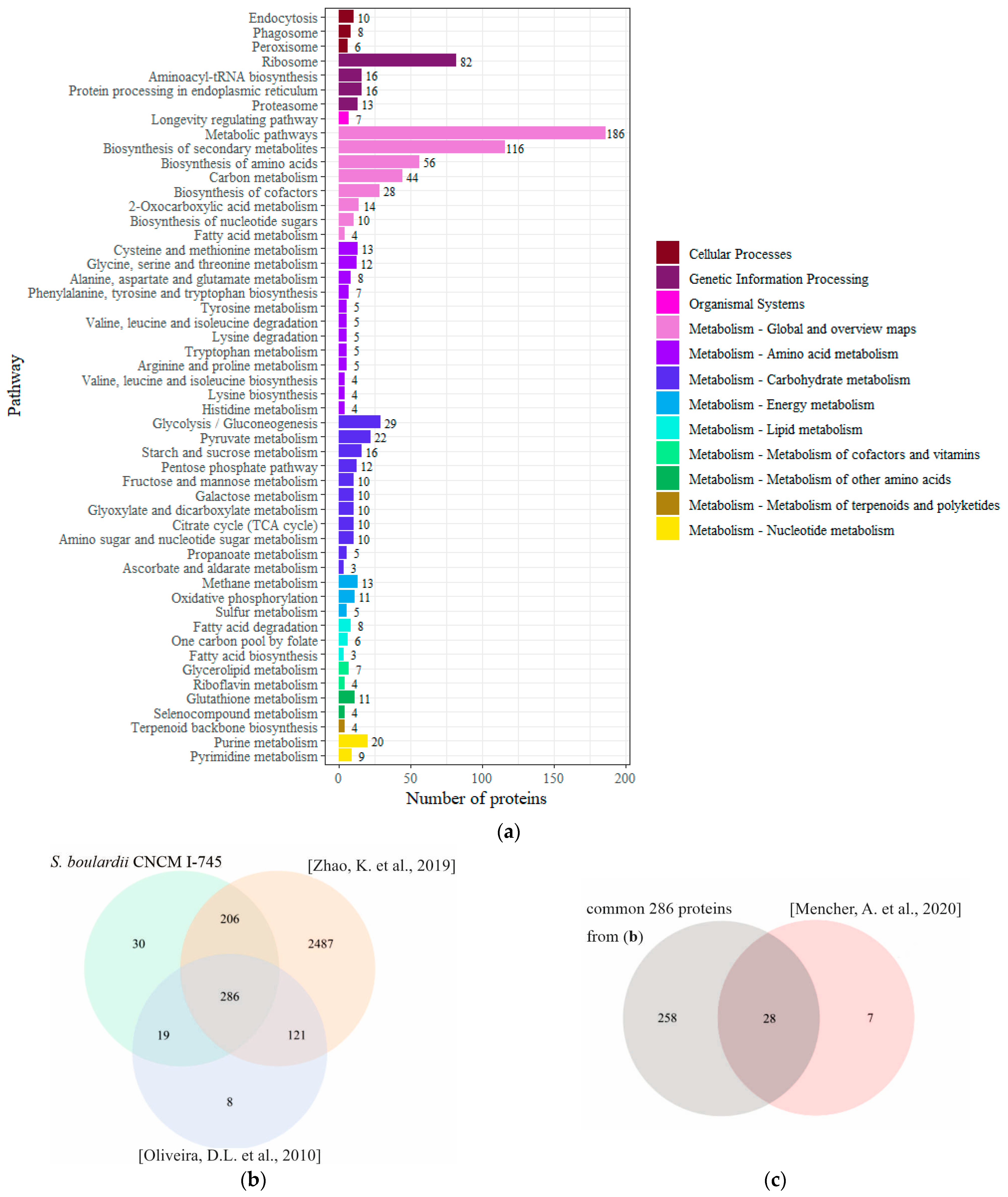
2.4. Proteins Identified in the EVs of S. boulardii
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Yeast Culture for EVs Production
3.2. Isolation of EVs from Liquid Yeast Cultures
3.3. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
3.4. Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM)
3.5. Nile Red Staining of EVs
3.6. Human Intestinal Cell Lines
3.7. Metabolic Activity Tests—MTT, Crystal Violet, and ROS Assays
3.8. Loading of EVs with Doxorubicin
3.9. Incubation of Human Cells with EVs-NR and EVs-DOX
3.10. Isolation of Proteins from EVs
3.11. Mass Spectrometry (MS) Analysis and Profiling of EV Proteins
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freitas, M.S.; Bonato, V.L.D.; Pessoni, A.M.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Casadevall, A.; Almeida, F. Fungal Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Targets for Immune Interventions. mSphere 2019, 4, e00747-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.H.; Park, Y.-D.; Dragotakes, Q.; Ramirez, L.S.; Smith, D.Q.; Reis, F.C.G.; Dziedzic, A.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Baker, R.P.; Williamson, P.R.; et al. Cryptococcus neoformans releases proteins during intracellular residence that affect the outcome of the fungal–macrophage interaction. Microlife 2022, 3, uqac015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, R.; Hernáez, M.L.; Redondo, E.; Calvo, G.; Radau, S.; Pardo, M.; Gil, C.; Monteoliva, L. Candida albicans Hyphal Extracellular Vesicles Are Different from Yeast Ones, Carrying an Active Proteasome Complex and Showing a Different Role in Host Immune Response. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0069822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, J.; Rodrigues, M.L.; Janbon, G. Extracellular Vesicles in Fungi: Past, Present, and Future Perspectives. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebana-Jordan, M.; Brotons, B.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Gonzalez, E. Extracellular Vesicles in the Fungi Kingdom. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielska, E.; May, R.C. Extracellular vesicles of human pathogenic fungi. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 52, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencher, A.; Morales, P.; Valero, E.; Tronchoni, J.; Patil, K.R.; Gonzalez, R. Proteomic characterization of extracellular vesicles produced by several wine yeast species. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarbati, A.; Canonico, L.; Marini, E.; Zannini, E.; Ciani, M.; Comitini, F. Potential Probiotic Yeasts Sourced from Natural Environmental and Spontaneous Processed Foods. Foods 2020, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Mansell, T.J. Yeasts as probiotics: Mechanisms, outcomes, and future potential. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2020, 137, 103333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-López, V.; Hernández-Belmonte, A.; Pérez Soto, M.I.; Ayo-González, M.; Losa-Rodríguez, G.; Ros-Sánchez, E.; Martínez-Gabarrón, M.; Sánchez-Pellicer, P.; Aguera-Santos, J.; Núñez-Delegido, E.; et al. Oral intake of Kluyveromyces marxianus B0399 plus Lactobacillus rhamnosus CECT 30579 to mitigate symptoms in COVID-19 patients: A randomized open label clinical trial. Med. Microecol. 2022, 14, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moré, M.I.; Swidsinski, A. Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 supports regeneration of the intestinal microbiota after diarrheic dysbiosis—A review. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2015, 8, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo-Villena, M.; Briones-Perez, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Bevilacqua, A. Biotechnological application of yeasts in food science: Starter cultures, probiotics and enzyme production. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothoulakis, C. Review article: Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of action of Saccharomyces boulardii. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez Rubio, A.P.; D’antoni, C.L.; Piuri, M.; Pérez, O.E. Probiotics, Their Extracellular Vesicles and Infectious Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 864720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, A.; Morishita, M.; Nagata, R.; Maruoka, K.; Katsumi, H.; Yamamoto, A. Functional Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles from Baker’s Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae as a Novel Vaccine Material for Immune Cell Maturation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards-Ingram, L.; Gitsham, P.; Burton, N.; Warhurst, G.; Clarke, I.; Hoyle, D.; Oliver, S.G.; Stateva, L. Genotypic and physiological characterization of Saccharomyces boulardii, the probiotic strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2458–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Černoša, A.; Gostinčar, C.; Lavrin, T.; Kostanjšek, R.; Lenassi, M.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles from biotechnologically important fungus Aureobasidium pullulans. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulig, K.; Karnas, E.; Woznicka, O.; Kuleta, P.; Zuba-Surma, E.; Pyza, E.; Osyczka, A.; Kozik, A.; Rapala-Kozik, M.; Karkowska-Kuleta, J. Insight Into the Properties and Immunoregulatory Effect of Extracellular Vesicles Produced by Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis Biofilms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, C.A.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobiepanek, A.; Paone, A.; Cutruzzolà, F.; Kobiela, T. Biophysical characterization of melanoma cell phenotype markers during metastatic progression. Eur. Biophys. J. 2021, 50, 523–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, T.M.; Gandhi, S.C.; Wilding, J.L.; Muschel, R.; Bodmer, W.F. Cancer stem cells from colorectal cancer-derived cell lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3722–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.-U.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2000, 5, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Bleackley, M.; Chisanga, D.; Gangoda, L.; Fonseka, P.; Liem, M.; Kalra, H.; Al Saffar, H.; Keerthikumar, S.; Ang, C.-S.; et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by Saccharomyces cerevisiae are involved in cell wall remodelling. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.L.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Joffe, L.S.; Guimarães, A.J.; Sobreira, T.J.P.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Cordero, R.J.B.; Frases, S.; Casadevall, A.; Almeida, I.C.; et al. Characterization of Yeast Extracellular Vesicles: Evidence for the Participation of Different Pathways of Cellular Traffic in Vesicle Biogenesis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Bona, A.; Llama-Palacios, A.; Parra, C.M.; Vivanco, F.; Nombela, C.; Monteoliva, L.; Gil, C. Proteomics unravels extracellular vesicles as carriers of classical cytoplasmic proteins in Candida albicans. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzycka-Ayoush, M.; Nowicka, A.M.; Kowalczyk, A.; Gluchowska, A.; Targonska, A.; Mosieniak, G.; Sobczak, K.; Donten, M.; Grudzinski, I.P. Exosomes derived from lung cancer cells: Isolation, characterization, and stability studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 181, 106369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobiepanek, A.; Milner-Krawczyk, M.; Musolf, P.; Starecki, T.; Kobiela, T. Anandamide-Modulated Changes in Metabolism, Glycosylation Profile and Migration of Metastatic Melanoma Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennaárd, A.J.; Mamand, D.R.; Wiklander, R.J.; EL Andaloussi, S.; Wiklander, O.P.B. Optimised Electroporation for Loading of Extracellular Vesicles with Doxorubicin. Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamińska, K.; Godakumara, K.; Świderska, B.; Malinowska, A.; Midekessa, G.; Sofińska, K.; Barbasz, J.; Fazeli, A.; Grzesiak, M. Characteristics of size-exclusion chromatography enriched porcine follicular fluid extracellular vesicles. Theriogenology 2023, 205, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulkowska, A.; Auber, A.; Sikorski, P.J.; Silhavy, D.N.; Auth, M.; Sitkiewicz, E.; Jean, V.; Merret, R.M.; Bousquet-Antonelli, C.C.; Kufel, J. RNA Helicases from the DEA(D/H)-Box Family Contribute to Plant NMD Efficiency. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Bai, J.; Bandla, C.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kamatchinathan, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Prakash, A.; Frericks-Zipper, A.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database resources in 2022: A hub for mass spectrometry-based proteomics evidences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D543–D552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D587–D592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mierzejewska, J.; Kowalska, P.; Marlicka, K.; Dworakowska, S.; Sitkiewicz, E.; Trzaskowski, M.; Głuchowska, A.; Mosieniak, G.; Milner-Krawczyk, M. Exploring Extracellular Vesicles of Probiotic Yeast as Carriers of Biologically Active Molecules Transferred to Human Intestinal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411340
Mierzejewska J, Kowalska P, Marlicka K, Dworakowska S, Sitkiewicz E, Trzaskowski M, Głuchowska A, Mosieniak G, Milner-Krawczyk M. Exploring Extracellular Vesicles of Probiotic Yeast as Carriers of Biologically Active Molecules Transferred to Human Intestinal Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(14):11340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411340
Chicago/Turabian StyleMierzejewska, Jolanta, Patrycja Kowalska, Klaudia Marlicka, Sara Dworakowska, Ewa Sitkiewicz, Maciej Trzaskowski, Agata Głuchowska, Grażyna Mosieniak, and Małgorzata Milner-Krawczyk. 2023. "Exploring Extracellular Vesicles of Probiotic Yeast as Carriers of Biologically Active Molecules Transferred to Human Intestinal Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 14: 11340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411340
APA StyleMierzejewska, J., Kowalska, P., Marlicka, K., Dworakowska, S., Sitkiewicz, E., Trzaskowski, M., Głuchowska, A., Mosieniak, G., & Milner-Krawczyk, M. (2023). Exploring Extracellular Vesicles of Probiotic Yeast as Carriers of Biologically Active Molecules Transferred to Human Intestinal Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(14), 11340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411340





