Lamivudine (3TC), a Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor, Prevents the Neuropathological Alterations Present in Mutant Tau Transgenic Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
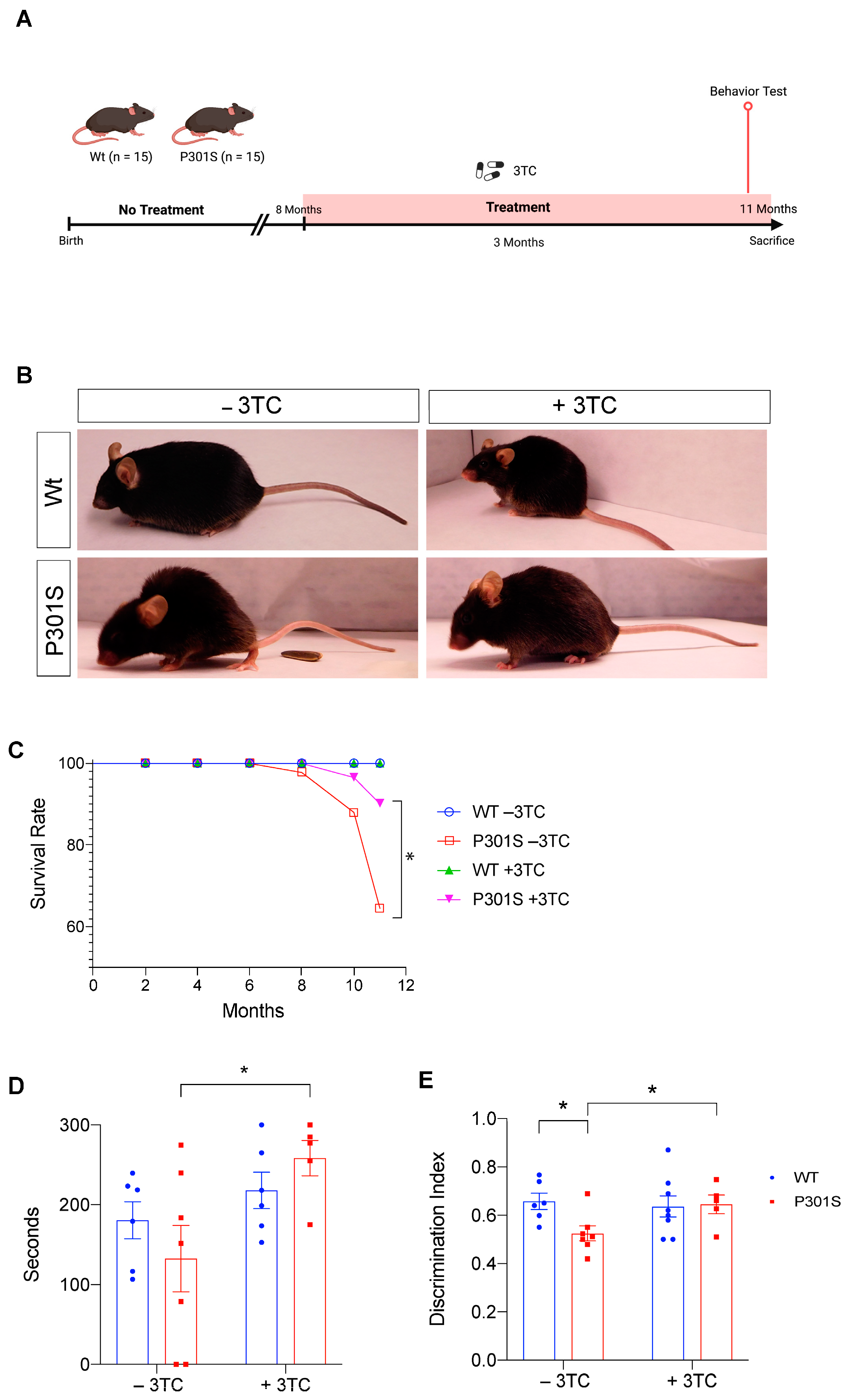
2.1. P301S Mice Show an Increase in Survival and an Improvement in Learning after 3TC Treatment
2.2. Pharmacological 3TC Treatment Modulates P301S-Dependent Tau Pathology In Vivo
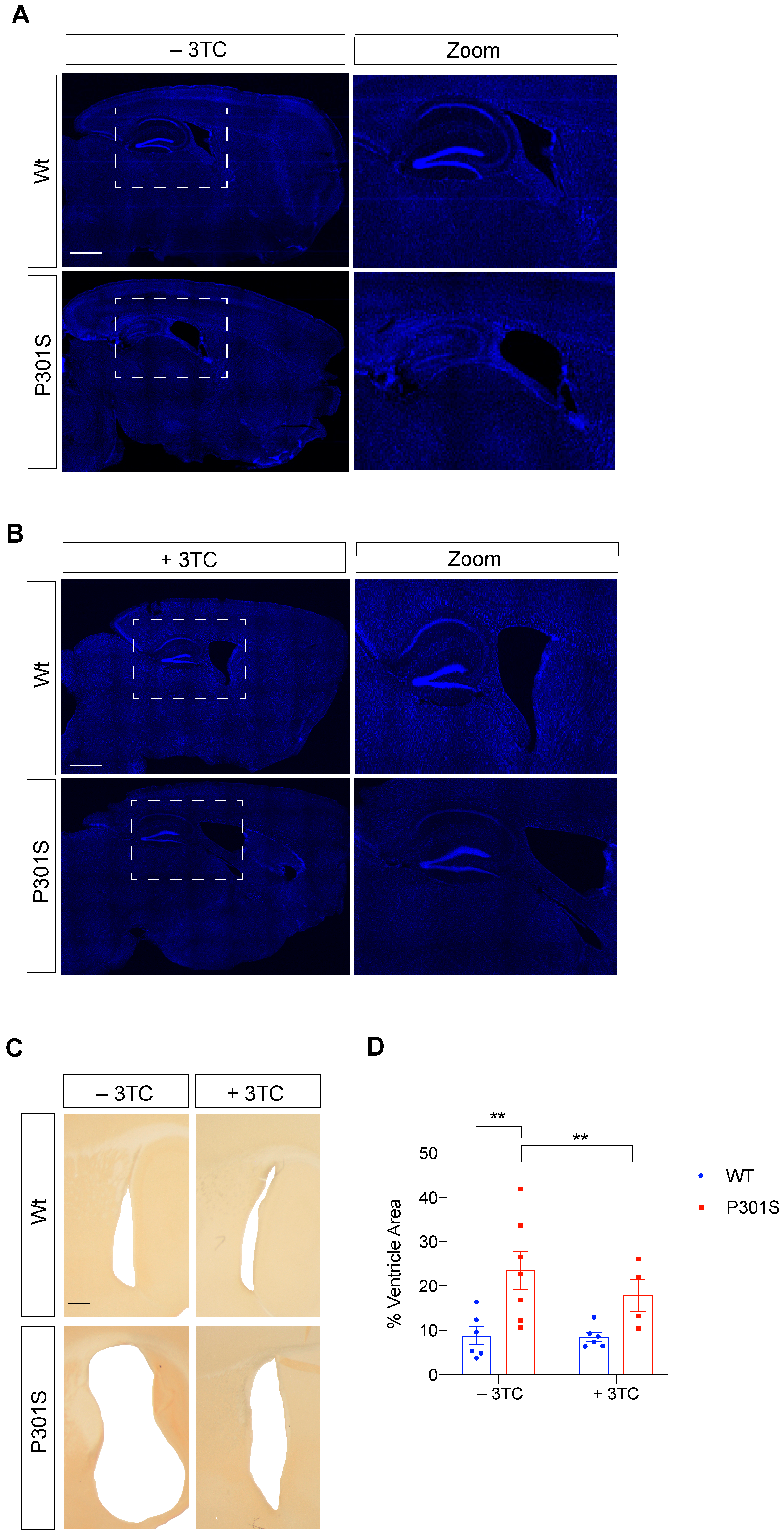
2.3. Partial Reversal of Atrophy, Neuronal Death, and Gliosis in 3TC-Treated P301S Mice
2.4. Histone-3 Trimethylation Levels and LINE-1 Insertion in Genomic DNA
2.5. Tau Promotes LINE-1 Insertion In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Driver, C.J.; McKechnie, S.W. Transposable elements as a factor in the aging of Drosophila melanogaster. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 673, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.G.; Helfand, S.L. Chromatin structure and transposable elements in organismal aging. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Prazak, L.; Chatterjee, N.; Gruninger, S.; Krug, L.; Theodorou, D.; Dubnau, J. Activation of transposable elements during aging and neuronal decline in Drosophila. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillie, J.K.; Barnett, M.W.; Upton, K.R.; Gerhardt, D.J.; Richmond, T.A.; De Sapio, F.; Brennan, P.M.; Rizzu, P.; Smith, S.; Fell, M.; et al. Somatic retrotransposition alters the genetic landscape of the human brain. Nature 2011, 479, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Moran, J.V.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr.; Boeke, J.D. Human L1 retrotransposon encodes a conserved endonuclease required for retrotransposition. Cell 1996, 87, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.L.; Cruceanu, M.; Branciforte, D.; Wai-Lun Li, P.; Kwok, S.C.; Hodges, R.S.; Williams, M.C. LINE-1 retrotransposition requires the nucleic acid chaperone activity of the ORF1 protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancks, D.C.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr. Active human retrotransposons: Variation and disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2012, 22, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cecco, M.; Criscione, S.W.; Peckham, E.J.; Hillenmeyer, S.; Hamm, E.A.; Manivannan, J.; Peterson, A.L.; Kreiling, J.A.; Neretti, N.; Sedivy, J.M. Genomes of replicatively senescent cells undergo global epigenetic changes leading to gene silencing and activation of transposable elements. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.G.; Jones, B.C.; Jiang, N.; Chang, C.; Hosier, S.; Wickremesinghe, P.; Garcia, M.; Hartnett, D.A.; Burhenn, L.; Neretti, N.; et al. Chromatin-modifying genetic interventions suppress age-associated transposable element activation and extend life span in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11277–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel-Godreuil, C.; Znaidi, R.; Bonnifet, T.; Joshi, R.L.; Fuchs, J. Transposable elements as new players in neurodegenerative diseases. FEBS Lett. 2021, 595, 2733–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, V. Are transposons a cause of ageing? Mutat. Res. 1990, 237, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Jeong, H.H.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Klein, H.U.; Bennett, D.A.; De Jager, P.L.; Liu, Z.; Shulman, J.M. Tau Activates Transposable Elements in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2874–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Samimi, H.; Gamez, M.; Zare, H.; Frost, B. Pathogenic tau-induced piRNA depletion promotes neuronal death through transposable element dysregulation in neurodegenerative tauopathies. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, P.; Zuniga, G.; Sun, W.; Beckmann, A.; Ochoa, E.; DeVos, S.L.; Hyman, B.; Chiu, G.; Roy, E.R.; Cao, W.; et al. Pathogenic tau accelerates aging-associated activation of transposable elements in the mouse central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 2022, 208, 102181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundman, J.; Spencer, B.; Sarsoza, F.; Rissman, R.A. Transcriptome analyses reveal tau isoform-driven changes in transposable element and gene expression. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, B.; Ricceri, L.; Sasiadek, M.M. Transposable Elements and Their Epigenetic Regulation in Mental Disorders: Current Evidence in the Field. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, D.M.; Devine, S.E. Aberrantly High Levels of Somatic LINE-1 Expression and Retrotransposition in Human Neurological Disorders. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siangphoe, U.; Archer, K.J.; Nguyen, C.; Lee, K.R. Associations of antiretroviral therapy and comorbidities with neurocognitive outcomes in HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS 2020, 34, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hache, C.; Villeneuve, J.P. Lamivudine treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B and cirrhosis. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2006, 7, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quercia, R.; Perno, C.F.; Koteff, J.; Moore, K.; McCoig, C.; St Clair, M.; Kuritzkes, D. Twenty-Five Years of Lamivudine: Current and Future Use for the Treatment of HIV-1 Infection. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2018, 78, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez de Lagran, M.; Elizalde-Torrent, A.; Paredes, R.; Clotet, B.; Dierssen, M. Lamivudine, a reverse transcriptase inhibitor, rescues cognitive deficits in a mouse model of down syndrome. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 4210–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Y.; Bai, X.; Lu, Z. Lamivudine improves cognitive decline in SAMP8 mice: Integrating in vivo pharmacological evaluation and network pharmacology. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 8490–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiyama, Y.; Higuchi, M.; Zhang, B.; Huang, S.M.; Iwata, N.; Saido, T.C.; Maeda, J.; Suhara, T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron 2007, 53, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchan-Rubira, J.; Sebastian-Serrano, A.; Diaz-Hernandez, M.; Avila, J.; Hernandez, F. Peripheral nervous system effects in the PS19 tau transgenic mouse model of tauopathy. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 698, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Vanmechelen, E. Monoclonal antibody AT8 recognises tau protein phosphorylated at both serine 202 and threonine 205. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 189, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, T.; Goni-Oliver, P.; Lucas, J.J.; Avila, J.; Hernandez, F. Chronic lithium administration to FTDP-17 tau and GSK-3beta overexpressing mice prevents tau hyperphosphorylation and neurofibrillary tangle formation, but pre-formed neurofibrillary tangles do not revert. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, J.; Hu, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, F.; Chen, C. Inhibition of 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Metabolism Alleviates Neuropathology and Improves Cognitive Function in a Tau Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4122–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, T.J.; Quarta, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Colville, A.; Paine, P.; Doan, L.; Tran, C.M.; Chu, C.R.; Horvath, S.; Qi, L.S.; et al. Transient non-integrative expression of nuclear reprogramming factors promotes multifaceted amelioration of aging in human cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, A.; Reddy, P.; Martinez-Redondo, P.; Platero-Luengo, A.; Hatanaka, F.; Hishida, T.; Li, M.; Lam, D.; Kurita, M.; Beyret, E.; et al. In Vivo Amelioration of Age-Associated Hallmarks by Partial Reprogramming. Cell 2016, 167, 1719–1733.E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Matellan, A.; Alcazar, N.; Hernandez, F.; Serrano, M.; Avila, J. In Vivo Reprogramming Ameliorates Aging Features in Dentate Gyrus Cells and Improves Memory in Mice. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 15, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagstaff, B.J.; Kroutter, E.N.; Derbes, R.S.; Belancio, V.P.; Roy-Engel, A.M. Molecular reconstruction of extinct LINE-1 elements and their interaction with nonautonomous elements. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montejo de Garcini, E.; de la Luna, S.; Dominguez, J.E.; Avila, J. Overexpression of tau protein in COS-1 cells results in the stabilization of centrosome-independent microtubules and extension of cytoplasmic processes. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1994, 130, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, B. Alzheimer’s disease: An acquired neurodegenerative laminopathy. Nucleus 2016, 7, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galas, M.C.; Bonnefoy, E.; Buee, L.; Lefebvre, B. Emerging Connections Between Tau and Nucleic Acids. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1184, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekanowski, C.; Wojda, U. Aneuploidy, chromosomal missegregation, and cell cycle reentry in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2009, 69, 232–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hancks, D.C.; Kazazian, H.H., Jr. Roles for retrotransposon insertions in human disease. Mob. DNA 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Suzuki, K.; Qu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Ren, R.; Xu, X.; Ocampo, A.; et al. Aging stem cells. A Werner syndrome stem cell model unveils heterochromatin alterations as a driver of human aging. Science 2015, 348, 1160–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhelli-Mokrani, H.; Mansuroglu, Z.; Chauderlier, A.; Albaud, B.; Gentien, D.; Sommer, S.; Schirmer, C.; Laqueuvre, L.; Josse, T.; Buee, L.; et al. Genome-wide identification of genic and intergenic neuronal DNA regions bound by Tau protein under physiological and stress conditions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 11405–11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, L.; Nino, S.A.; Guerrero, C.; Jimenez-Capdeville, M.E. Phospho-Tau and Chromatin Landscapes in Early and Late Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, G.; Misteli, T. The central role of chromatin maintenance in aging. Aging 2009, 1, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekharzadeh, B.; Daigle, J.G.; Kapinos, L.E.; Coyne, A.; Schiantarelli, J.; Carlomagno, Y.; Cook, C.; Miller, S.J.; Dujardin, S.; Amaral, A.S.; et al. Tau Protein Disrupts Nucleocytoplasmic Transport in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2018, 99, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, L.; Federico, C.; Pinedo, F.; Bruno, F.; Rebolledo, A.B.; Montoya, J.J.; Olazabal, I.M.; Ferrer, I.; Saccone, S. Aging dependent effect of nuclear tau. Brain Res. 2017, 1677, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Basurto-Islas, G.; Mena, R.; Cisneros, B.; Binder, L.I.; Avila, J.; Garcia-Sierra, F. Alterations in the nuclear architecture produced by the overexpression of tau protein in neuroblastoma cells. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 36, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Nogales, M.; Cabrera, J.R.; Santos-Galindo, M.; Hoozemans, J.J.; Ferrer, I.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Hernandez, F.; Avila, J.; Lucas, J.J. Huntington’s disease is a four-repeat tauopathy with tau nuclear rods. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Nogales, M.; Santos-Galindo, M.; Merchan-Rubira, J.; Hoozemans, J.J.M.; Rabano, A.; Ferrer, I.; Avila, J.; Hernandez, F.; Lucas, J.J. Tau-positive nuclear indentations in P301S tauopathy mice. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paonessa, F.; Evans, L.D.; Solanki, R.; Larrieu, D.; Wray, S.; Hardy, J.; Jackson, S.P.; Livesey, F.J. Microtubules Deform the Nuclear Membrane and Disrupt Nucleocytoplasmic Transport in Tau-Mediated Frontotemporal Dementia. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrasate, M.; Mitra, S.; Schweitzer, E.S.; Segal, M.R.; Finkbeiner, S. Inclusion body formation reduces levels of mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature 2004, 431, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacruz, K.; Lewis, J.; Spires, T.; Paulson, J.; Kotilinek, L.; Ingelsson, M.; Guimaraes, A.; DeTure, M.; Ramsden, M.; McGowan, E.; et al. Tau suppression in a neurodegenerative mouse model improves memory function. Science 2005, 309, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vallés-Saiz, L.; Ávila, J.; Hernández, F. Lamivudine (3TC), a Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor, Prevents the Neuropathological Alterations Present in Mutant Tau Transgenic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311144
Vallés-Saiz L, Ávila J, Hernández F. Lamivudine (3TC), a Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor, Prevents the Neuropathological Alterations Present in Mutant Tau Transgenic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):11144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311144
Chicago/Turabian StyleVallés-Saiz, Laura, Jesús Ávila, and Félix Hernández. 2023. "Lamivudine (3TC), a Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor, Prevents the Neuropathological Alterations Present in Mutant Tau Transgenic Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 11144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311144
APA StyleVallés-Saiz, L., Ávila, J., & Hernández, F. (2023). Lamivudine (3TC), a Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor, Prevents the Neuropathological Alterations Present in Mutant Tau Transgenic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 11144. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241311144






