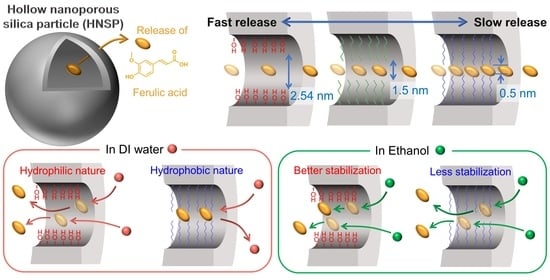
Time-Dependent Controlled Release of Ferulic Acid from Surface-Modified Hollow Nanoporous Silica Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
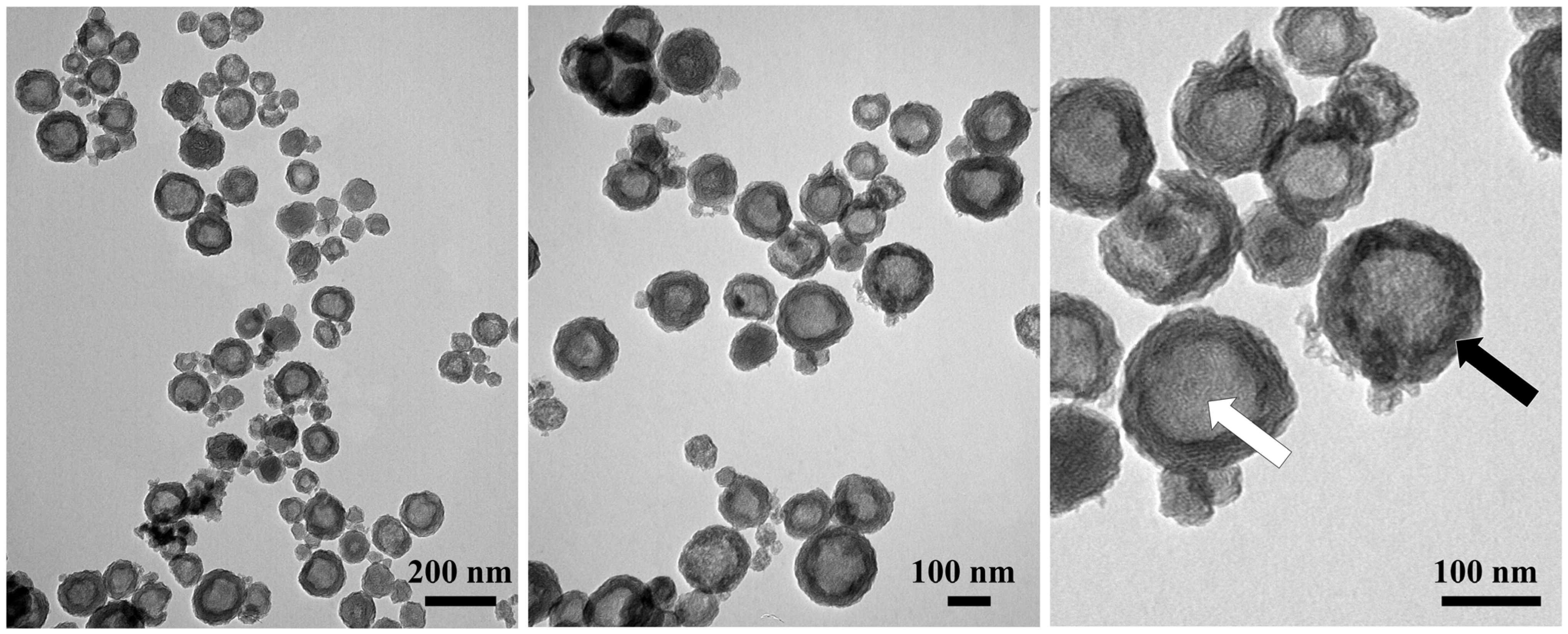
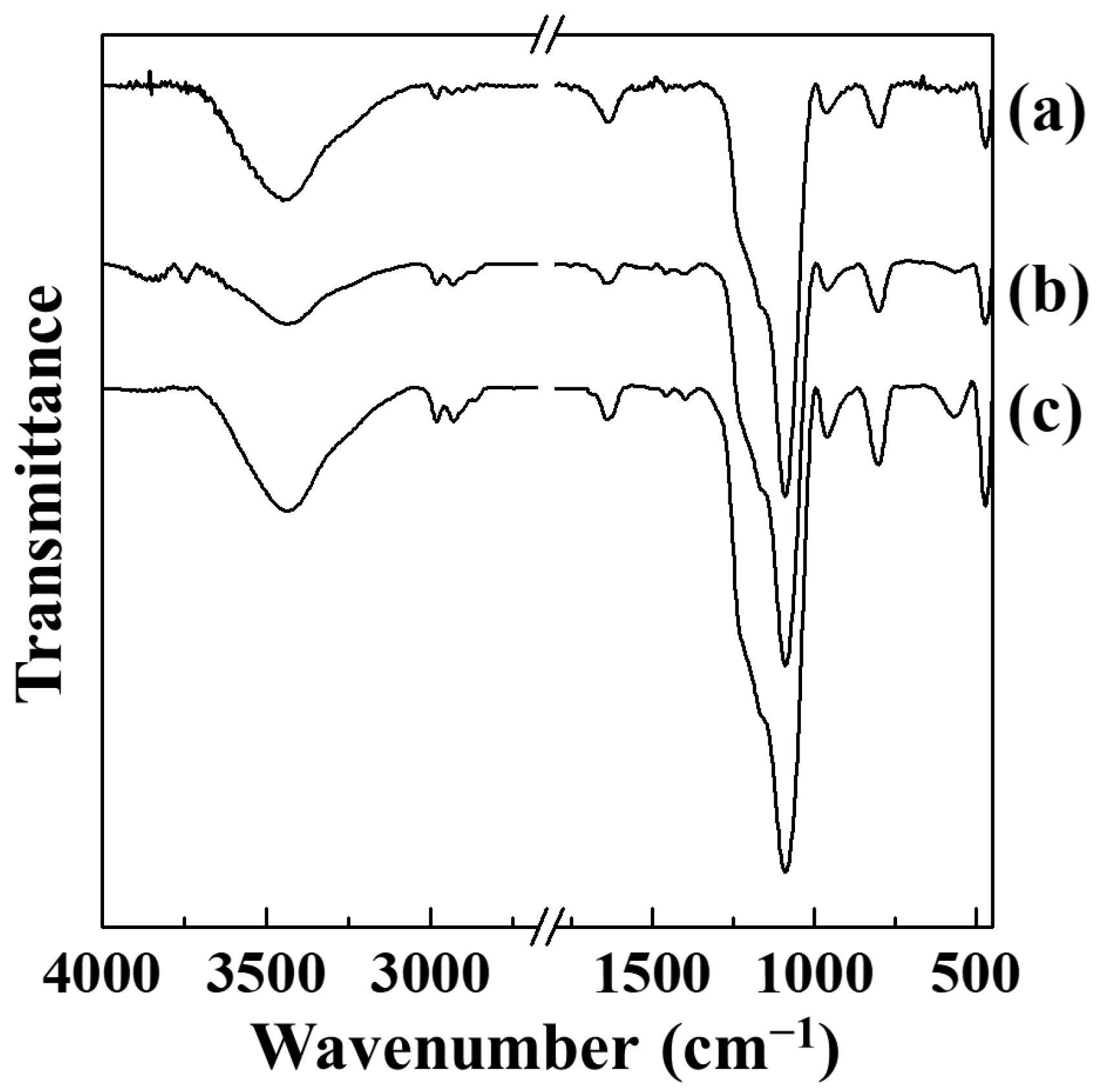
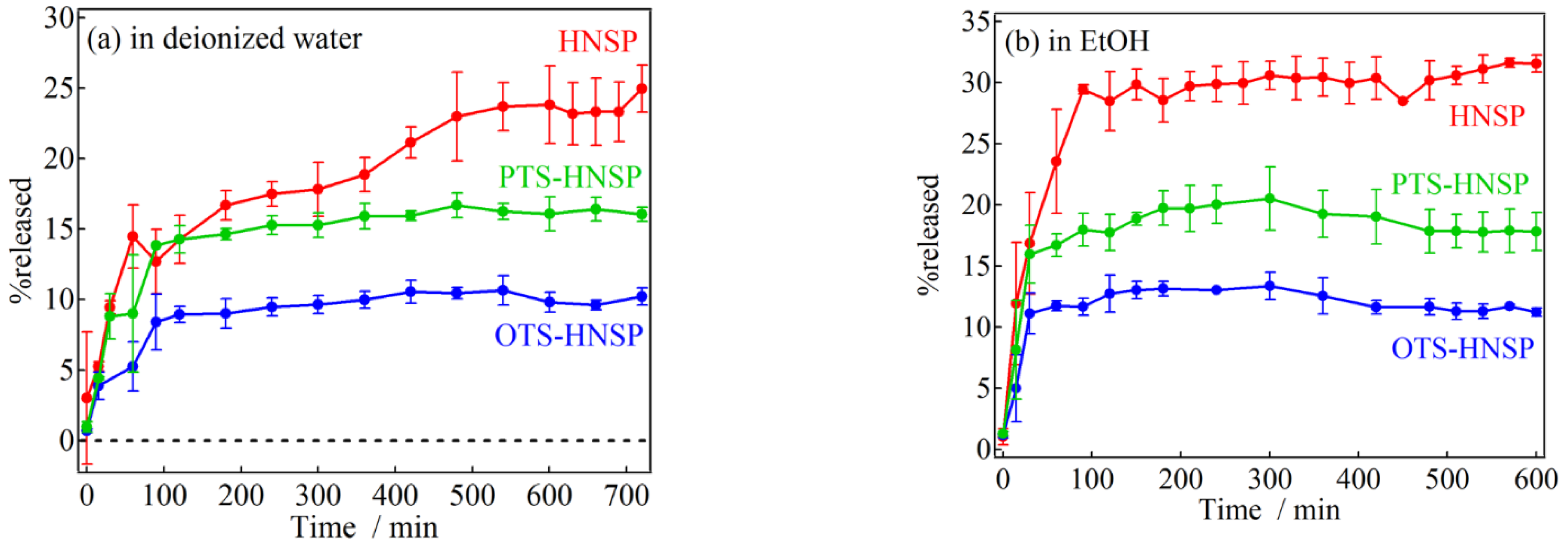
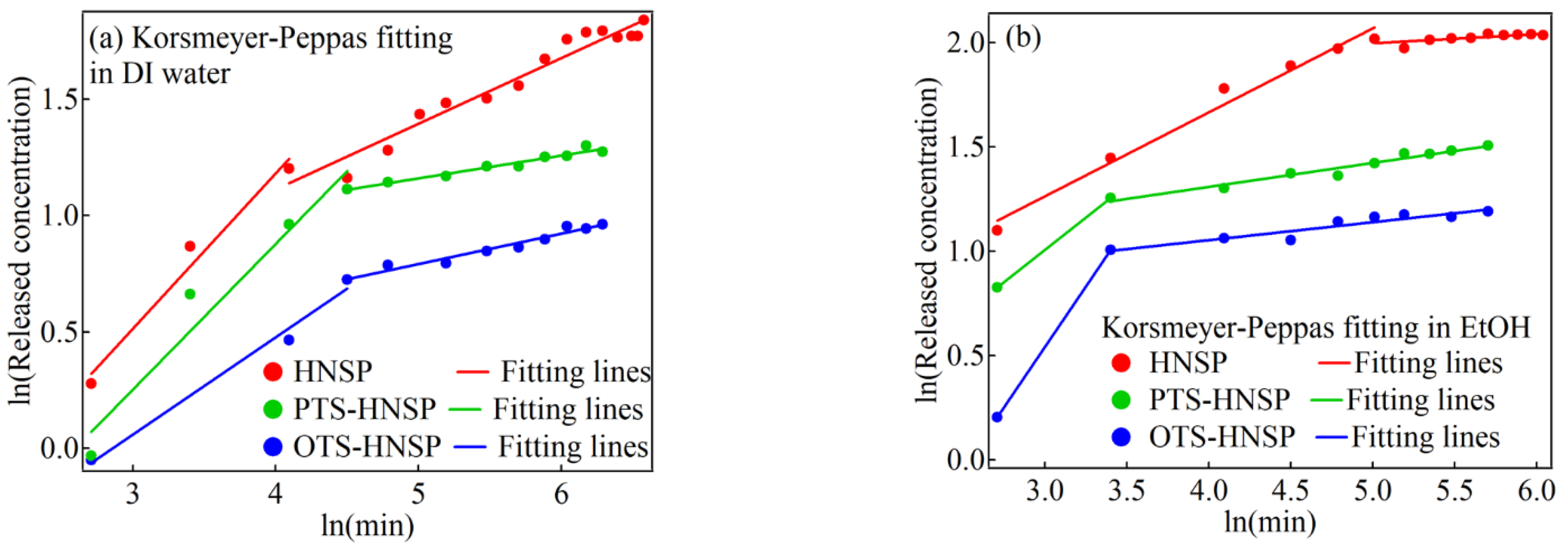
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Hollow Nanoporous Silica Particles (HNSPs)
3.3. Ferulic Acid Loading and Release
3.4. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, D.-H.; Hwang, S.-J.; Oh, J.-M.; Yang, J.-H.; Choy, J.-H. Polymer–inorganic supramolecular nanohybrids for red, white, green, and blue applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1442–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Ordered mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Gai, S.; Lin, J. Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3679–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-J.; Choy, J.-H. Layered double hydroxide nanoparticles as target-specific delivery carriers: Uptake mechanism and toxicity. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Kim, H.-M.; Jung, B.C.; Kim, Y.S.; Oh, J.-M. Size and surface charge effect of layered double hydroxide particles upon blood cells. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 225, 106549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Kim, H.-M.; Oh, J.-M. Photochemical Consideration in the Interactions between Blood Proteins and Layered Inorganic Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagimori, M.; Fuchigami, Y.; Kawakami, S. Peptide-based cancer-targeted DDS and molecular imaging. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etrych, T.; Janoušková, O.; Chytil, P. Fluorescence imaging as a tool in preclinical evaluation of polymer-based nano-DDS systems intended for cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cui, L.; Losic, D. Graphene and graphene oxide as new nanocarriers for drug delivery applications. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9243–9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Ryu, H.-J.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Alothman, Z.A.; Choy, J.-H. Drug–clay nanohybrids as sustained delivery systems. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 130, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, C.L.; Liu, H.Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y. Poly (ethylene glycol)-Graft-Hollow Silica Vesicles for Drug Delivery. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 3001–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J. mRNA-lipid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: Structure and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuberth-Wagner, C.; Ludwig, J.; Bruder, A.K.; Herzner, A.-M.; Zillinger, T.; Goldeck, M.; Schmidt, T.; Schmid-Burgk, J.L.; Kerber, R.; Wolter, S. A conserved histidine in the RNA sensor RIG-I controls immune tolerance to N1-2′ O-methylated self RNA. Immunity 2015, 43, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lee, J.; Kang, J.; Lee, K.; Suh, J.-S.; Yoon, H.-G.; Huh, Y.-M.; Haam, S. Hollow silica nanocontainers as drug delivery vehicles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3417–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-Z.; Wen, L.-X.; Shao, L.; Chen, J.-F. Fabrication of porous hollow silica nanoparticles and their applications in drug release control. J. Control. Release 2004, 98, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-F.; Ding, H.-M.; Wang, J.-X.; Shao, L. Preparation and characterization of porous hollow silica nanoparticles for drug delivery application. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, N.; Pan, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, L.; Tang, B. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with tunable structures for controlled drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Dwivedi, P.K.; Saxena, N. Hollow silica nanoparticles synthesized from core-shell nanoparticles as highly efficient adsorbent for methylene blue and its invitro release: Mechanism and kinetics study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 587, 124333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mao, Z.; Xiong, Y.; He, J.; Zhao, Q. Preparation of layered beta-cypermethrin-carrying microcapsules from Pickering emulsion of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103695. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Huang, B.; Lin, Y.; Pei, G.; Zhang, L. Effect of surface functionalization and pore structure type on the release performance of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 336, 111862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, B. Facile fabrication of hollow silica nanospheres and their hierarchical self-assemblies as drug delivery carriers through a new single-micelle-template approach. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-F.; Shi, J.-L.; Li, Y.-S.; Chen, H.-R.; Shen, W.-H.; Dong, X.-P. Storage and release of ibuprofen drug molecules in hollow mesoporous silica spheres with modified pore surface. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 85, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, M.; Chen, F.; Guo, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J. Double mesoporous silica shelled spherical/ellipsoidal nanostructures: Synthesis and hydrophilic/hydrophobic anticancer drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5290–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Borchardt, L.; Kaskel, S. PEGylated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as potential drug delivery vehicles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 141, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevão, B.M.; Comparetti, E.J.; Rissi, N.C.; Zucolotto, V. Anti-GPC1-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers for combination therapy and targeting of PANC-1 cells. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 5224–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ang, C.Y.; Li, M.; Tan, S.Y.; Qu, Q.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, Y. Polymer-coated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for triple-responsive drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18179–18187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, C.; Mishra, A.; Nayak, D.; Chakraborty, A. Drug delivery system composed of mesoporous silica and hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres for chemotherapeutic drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, F.R.; Saputra, O.A.; Lestari, W.W.; Koketsu, M.; Mukti, R.R.; Martien, R. pH-triggered drug release controlled by poly (styrene sulfonate) growth hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 4261–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajebi, S.; Abdollahi, A.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Hybrid and hollow Poly (N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) nanogels as stimuli-responsive carriers for controlled release of doxorubicin. Polymer 2019, 180, 121716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, G.; Zhou, H.; Ma, S.; Guo, L.; Liu, X. Temperature and H2O2-operated nano-valves on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug release and kinetics. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 187, 110643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarani, G.M.; Malmir, M.; Lashgari, N.; Badiei, A. The role of hollow magnetic nanoparticles in drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25094–25106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Ayral, A.; Choy, J.-H.; Oh, J.-M. Diffusivity control in nanoporous membrane through organic–inorganic hybridization. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2010, 71, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Ayral, A.; Park, C.-B.; Choy, J.-H.; Oh, J.-M. Diffusion control of porous membrane by modifying the nanopore properties. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, V.; Gelde, L.; González, A.; Prida, V.; Hernando, B.; Benavente, J. Diffusive transport through surface functionalized nanoporous alumina membranes by atomic layer deposition of metal oxides. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 52, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.S.; Vega, V.; Cuevas, A.L.; Yuso, M.d.V.M.d.; Prida, V.M.; Benavente, J. Surface modification of nanoporous anodic alumina during self-catalytic atomic layer deposition of silicon dioxide from (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane. Materials 2021, 14, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Qian, X.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y. Atomic layer deposition for membrane modification, functionalization and preparation: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 658, 120740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färm, E.; Kemell, M.; Ritala, M.; Leskelä, M. Selective-area atomic layer deposition with microcontact printed self-assembled octadecyltrichlorosilane monolayers as mask layers. Thin Solid Films 2008, 517, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, B.C.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Yin, K.-M.; Gandomi, Y.A.; Huang, K.-T. On atomic layer deposition: Current progress and future challenges. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, N55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinu, A.; Hossain, K.Z.; Ariga, K. Recent advances in functionalization of mesoporous silica. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 347–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science; Elsevier: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, A.; Melde, B.J.; Schroden, R.C. Hybrid inorganic–organic mesoporous silicates—Nanoscopic reactors coming of age. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1403–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, N.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, C.; Shezad, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Tao, J. Dacarbazine-loaded hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles grafted with folic acid for enhancing antimetastatic melanoma response. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21673–21687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ang, C.Y.; Li, M.; Tan, S.Y.; Qu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Polymeric prodrug grafted hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles encapsulating near-infrared absorbing dye for potent combined photothermal-chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6869–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Yang, Y.-J.; Liu, S.; Zheng, Y.-Z.; Fu, J.; Chen, J.-F. Poly (amidoamine) dendrimer-grafted porous hollow silica nanoparticles for enhanced intracellular photodynamic therapy. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6431–6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutto, A.A.; Kalay, Ş.; Sherazi, S.; Culha, M. Quantitative structure–activity relationship between antioxidant capacity of phenolic compounds and the plasmonic properties of silver nanoparticles. Talanta 2018, 189, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersanetti, P.A.; Escobar, V.H.; Nogueira, R.F.; dos Santos Ortega, F.; Schor, P.; de Araújo Morandim-Giannetti, A. Enzymatically obtaining hydrogels of PVA crosslinked with ferulic acid in the presence of laccase for biomedical applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G.; Consoli, G.M.; Nigro, R.L.; Geraci, C. Hydroxycinnamic acids loaded in lipid-core nanocapsules. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, P.; Bondi, M.L.; Picone, P.; Bondi, M.L.; Montana, G.; Bruno, A.; Pitarresi, G.; Giammona, G.; Di Carlo, M. Ferulic acid inhibits oxidative stress and cell death induced by Ab oligomers: Improved delivery by solid lipid nanoparticles. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniraj, M.G.; Leena, M.M.; Moses, J.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Cross-linked chitosan microparticles preparation by modified three fluid nozzle spray drying approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 1268–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, W.; Luo, H. Anthocyanin encapsulated by ferulic acid-grafted-maltodextrin (FA-g-MD) microcapsules potentially improved its free radical scavenging capabilities against H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwansh, R.K.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Bahadur, S.; Biswas, R. Enhanced permeability of ferulic acid loaded nanoemulsion based gel through skin against UVA mediated oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2015, 141, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Fahr, A. Skin delivery of ferulic acid from different vesicular systems. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Bedi, R. FTO/SnSe heterojunction for photovoltaic conversion. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 29, L792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.; Jaswal, V.S.; Choudhary, S.; Sharma, A.; Beniwal, V.; Tuli, H.S.; Sharma, S. Ferulic acid: A promising therapeutic phytochemical and recent patents advances. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2019, 13, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, D.; Nandi, N.K.; Singh, B.; Singh, A.; Kumar, B.; Narang, R.K.; Singh, C. Ferulic acid-loaded drug delivery systems for biomedical applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Development of ferulic acid/cyclodextrin inclusion complex nanofibers for fast-dissolving drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Fang, K.; He, W.; Li, K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J. Evaluation of chitosan-ferulic acid microcapsules for sustained drug delivery: Synthesis, characterizations, and release kinetics in vitro. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1227, 129353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Kim, H.-J.; Yang, J.-H.; Kim, T.-H.; Choi, G.; Paek, S.-M.; Choi, A.-J.; Choy, J.-H.; Oh, J.-M. Intracrystalline structure and release pattern of ferulic acid intercalated into layered double hydroxide through various synthesis routes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 112, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, N.; Sharif, S.N.M.; Muda, Z.; Md Isa, I.; Ali, N.M.; Bakar, S.A.; Sidik, S.M.; Hussein, M.Z. Preparation of zinc layered hydroxide-ferulate and coated zinc layered hydroxide-ferulate nanocomposites for controlled release of ferulic acid. Mater. Res. Innov. 2019, 23, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethaji, M.; Pattabhi, V.; Desiraju, G. Structure of 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-propenoic acid (ferulic acid). Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Commun. 1988, 44, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.; Schmitt, K.; Chu, C.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.; McCullen, S. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, M.; Unger, K.K.; Matsumoto, A.; Tsutsumi, K. Novel pathways for the preparation of mesoporous MCM-41 materials: Control of porosity and morphology. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Terasaki, O.; Ryoo, R.; Ko, C.H. Determination of pore size and pore wall structure of MCM-41 by using nitrogen adsorption, transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray diffraction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkett, S.L.; Sims, S.D.; Mann, S. Synthesis of hybrid inorganic–organic mesoporous silica by co-condensation of siloxane and organosiloxane precursors. Chem. Commun. 1996, 11, 1367–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, A.; Tatsumi, T. Organically modified titanium-rich Ti-MCM-41, efficient catalysts for epoxidation reactions. J. Catal. 2000, 189, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Ogawa, M. Hydrophilic internal pore and hydrophobic particle surface of organically modified mesoporous silica particle to host photochromic molecules. Chem. Lett. 2019, 48, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inumaru, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kakii, S.; Nakano, T.; Yamanaka, S. Organic–inorganic cooperative molecular recognition in nanostructure of alkyl-grafted MCM-41. Chem. lett. 2003, 32, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manayil, J.C.; dos Santos, V.C.; Jentoft, F.C.; Granollers Mesa, M.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. Octyl Co-grafted PrSO3H/SBA-15: Tunable hydrophobic solid acid catalysts for acetic acid esterification. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhong, N.; Cheong, L.-Z.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Lin, S. Immobilization of Candida antarctica Lipase B onto organically-modified SBA-15 for efficient production of soybean-based mono and diacylglycerols. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.C.; Chuang, S.S.; Gray, M.; Soong, Y. In-situ infrared study of CO2 adsorption on SBA-15 grafted with γ-(aminopropyl) triethoxysilane. Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, F.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Haq, N.; Siddiqui, N.A. Solubility and thermodynamics of ferulic acid in different neat solvents: Measurement, correlation and molecular interactions. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixson, A.; Crowell, J. Dependence of reaction velocity upon surface and agitation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1931, 23, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Higuchi equation: Derivation, applications, use and misuse. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 418, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Rosenholm, J.; Areva, S.; Lindén, M. Influences of material characteristics on ibuprofen drug loading and release profiles from ordered micro-and mesoporous silica matrices. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4160–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhu, G.; Huang, S.; Li, S.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, S. Controlled release of Captopril by regulating the pore size and morphology of ordered mesoporous silica. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 92, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spange, S.; Zimmermann, Y.; Graeser, A. Hydrogen-bond-donating acidity and dipolarity/polarizability of surfaces within silica gels and mesoporous MCM-41 materials. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 3245–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkland, C.; Kipper, M.J.; Narasimhan, B.; Kim, K.K.; Pack, D.W. Microsphere size, precipitation kinetics and drug distribution control drug release from biodegradable polyanhydride microspheres. J. Control. Release 2004, 94, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, P.; Ramila, A.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Influence of pore size of MCM-41 matrices on drug delivery rate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 68, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Leelaphattharaphan, N.N.; Shin, H.; Ogawa, M. Acceleration of photochromism and negative photochromism by the interactions with mesoporous silicas. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
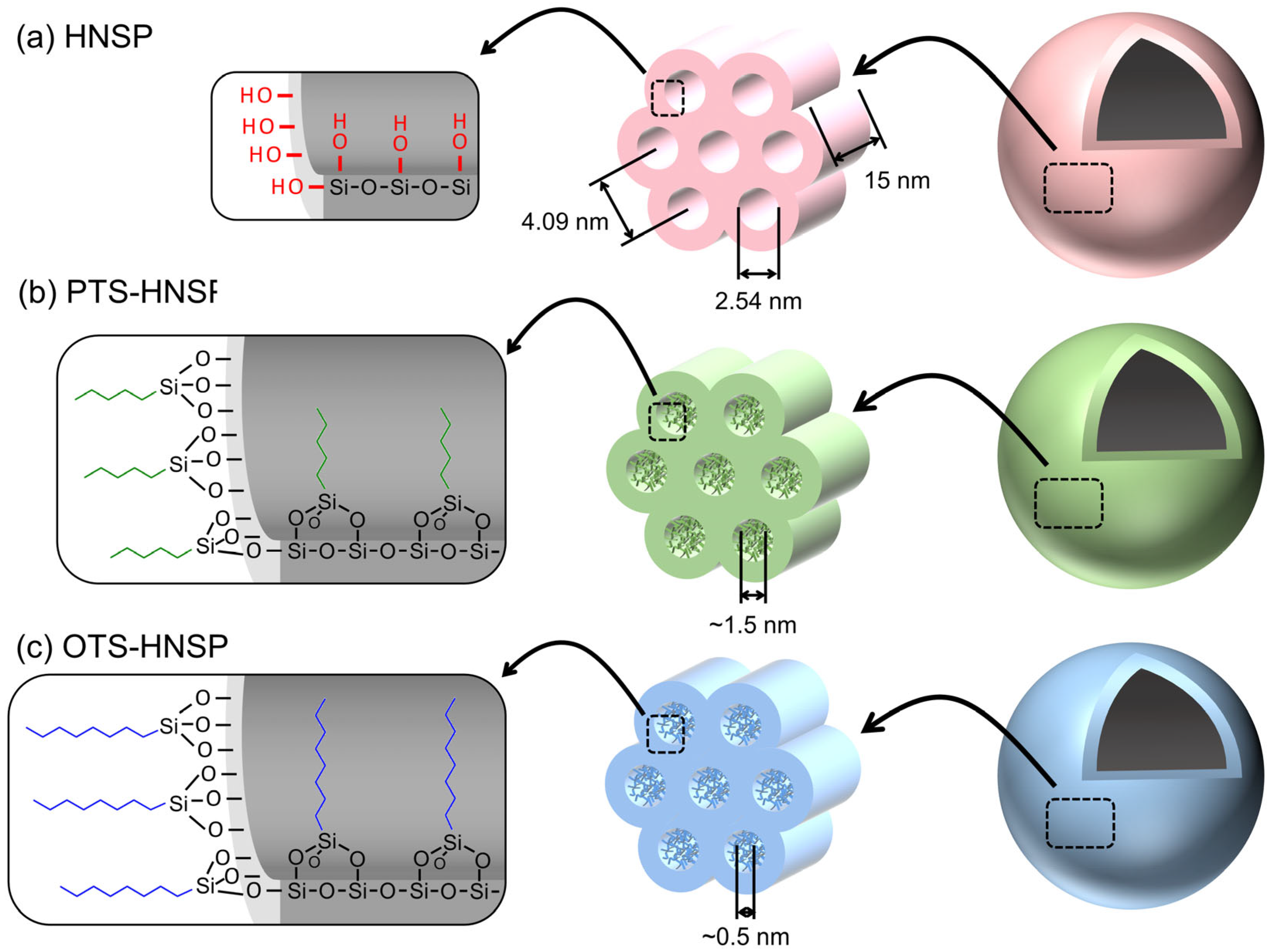
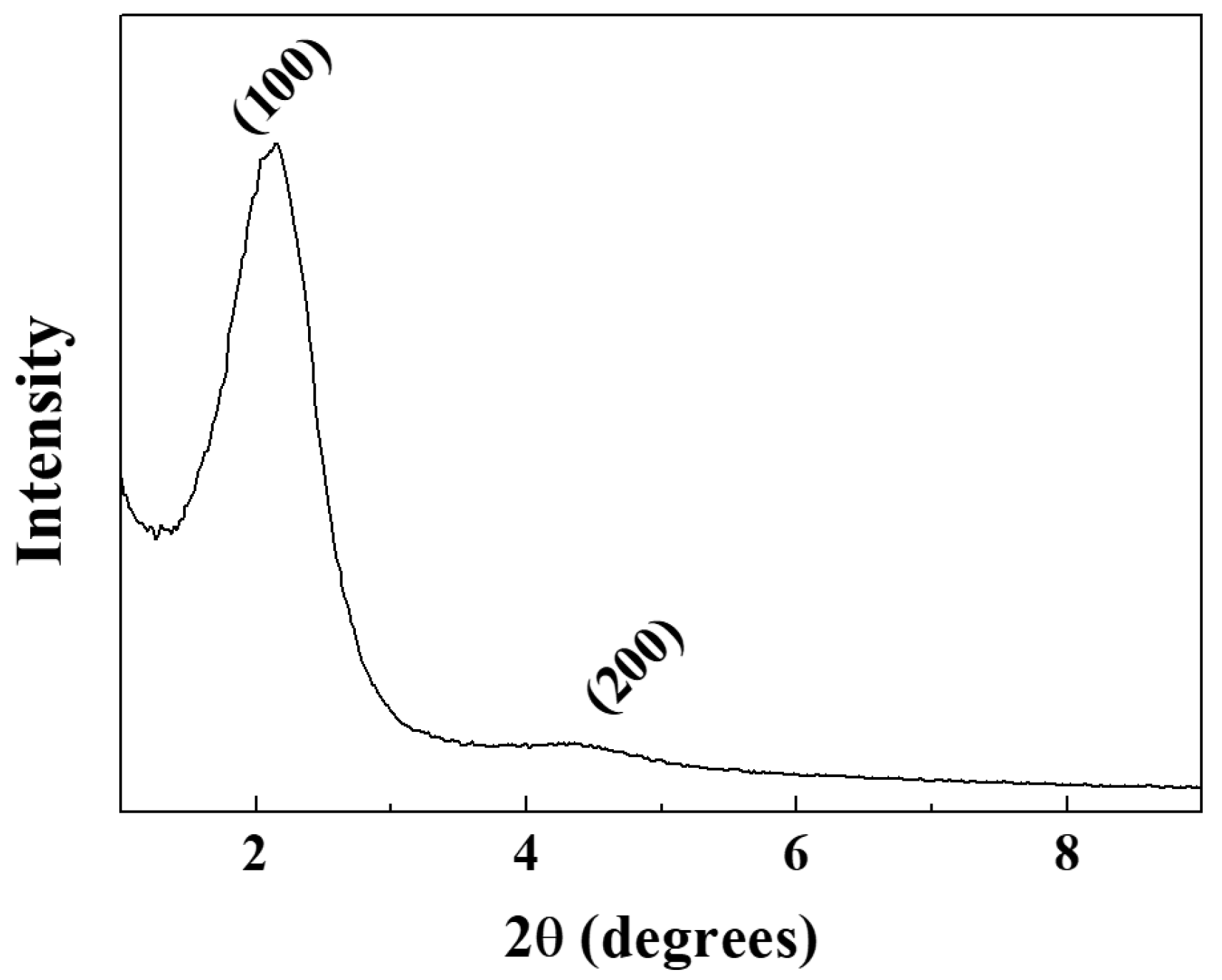
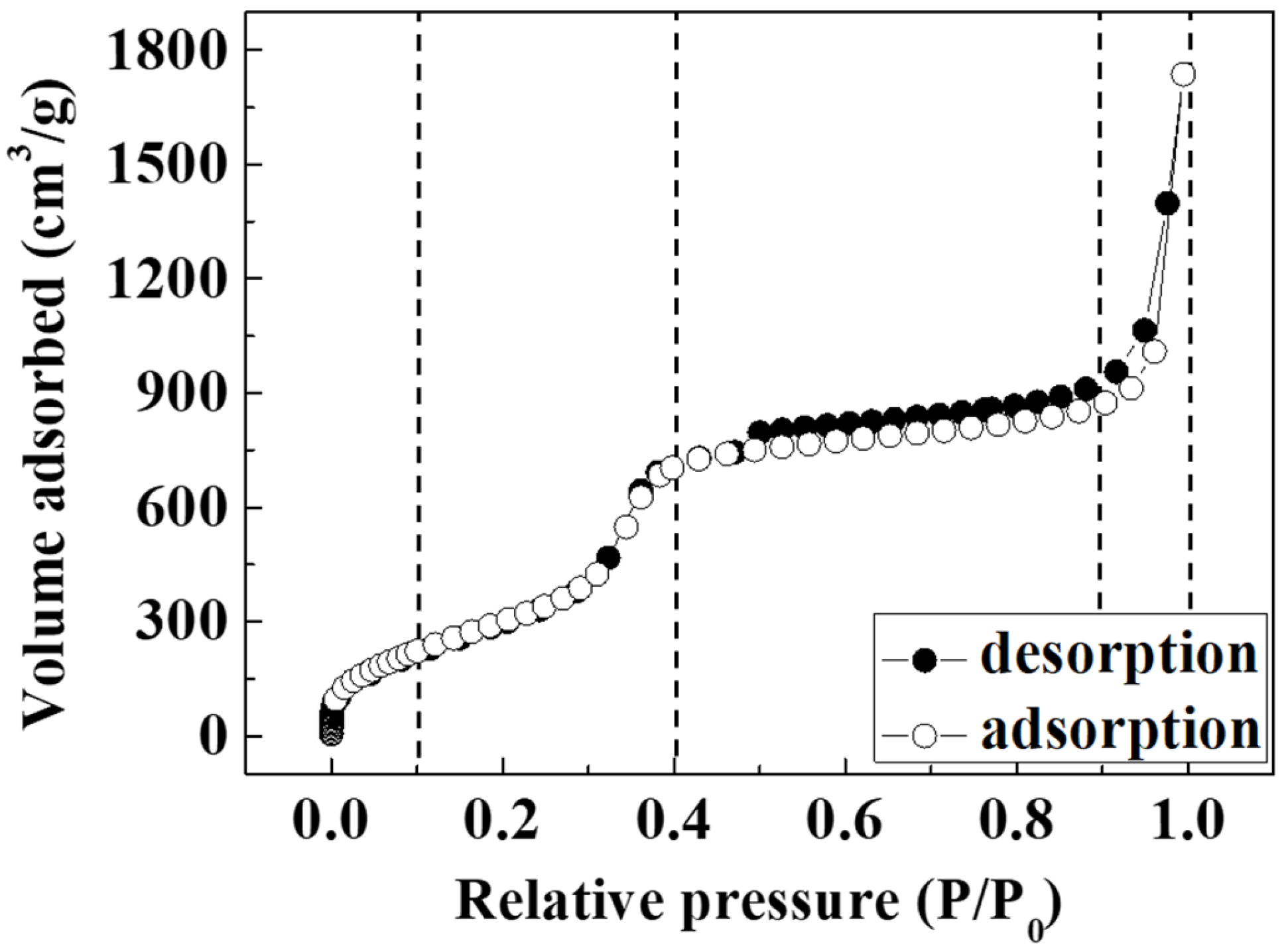
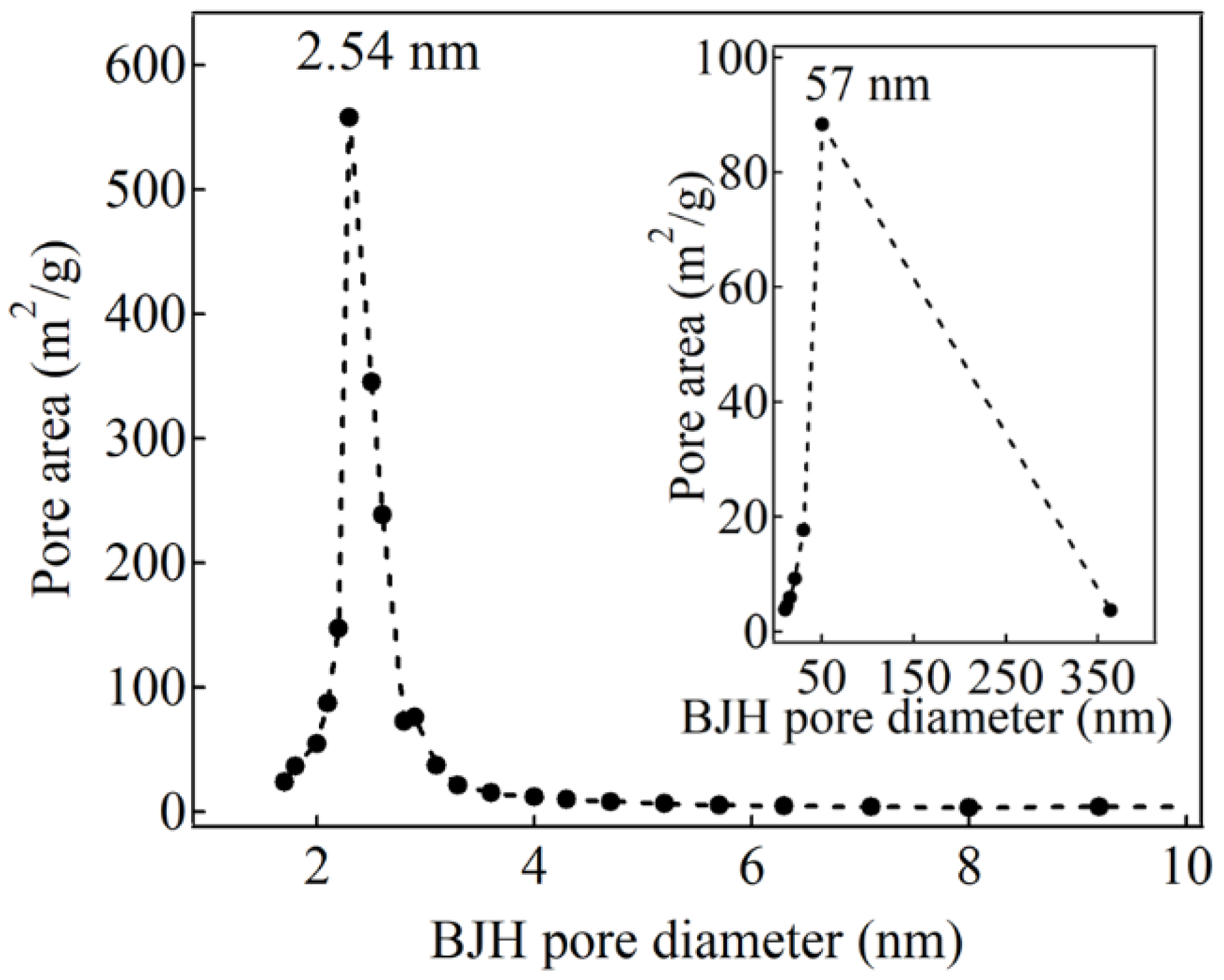
| d100 (nm) | bd (nm) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | BJH Pore Size, Wd (nm) | Vp (cm3/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HNSP | 4.09 | 0.46 | 1328 | 2.54 | 1.983 |
| Solvent | Carrier | kKP (min−n) | n | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DI water | HNSP | 0.227 | 0.666 | 0.0110 |
| 0.984 | 0.282 | 0.0360 | ||
| PTS-HNSP | 0.197 | 0.626 | 0.0425 | |
| 1.95 | 0.098 | 1.25 × 10−3 | ||
| OTS-HNSP | 0.0303 | 0.418 | 0.00426 | |
| 1.15 | 0.130 | 2.15 × 10−3 | ||
| EtOH | HNSP | 0.943 | 0.402 | 0.0119 |
| 5.93 | 0.0435 | 1.70 × 10−3 | ||
| PTS-HNSP | 0.426 | 0.620 | 1.97 × 10−30 | |
| 2.33 | 0.166 | 2.56 × 10−3 | ||
| OTS-HNSP | 0.0536 | 1.16 | 1.97 × 10−30 | |
| 2.03 | 0.0858 | 3.57 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamaguchi, T.; Kim, T.; Park, J.-K.; Oh, J.-M. Time-Dependent Controlled Release of Ferulic Acid from Surface-Modified Hollow Nanoporous Silica Particles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310560
Yamaguchi T, Kim T, Park J-K, Oh J-M. Time-Dependent Controlled Release of Ferulic Acid from Surface-Modified Hollow Nanoporous Silica Particles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(13):10560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310560
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamaguchi, Tetsuo, Taeho Kim, Jin-Kuen Park, and Jae-Min Oh. 2023. "Time-Dependent Controlled Release of Ferulic Acid from Surface-Modified Hollow Nanoporous Silica Particles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 13: 10560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310560
APA StyleYamaguchi, T., Kim, T., Park, J.-K., & Oh, J.-M. (2023). Time-Dependent Controlled Release of Ferulic Acid from Surface-Modified Hollow Nanoporous Silica Particles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(13), 10560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310560