Biochemical Correction of GM2 Ganglioside Accumulation in AB-Variant GM2 Gangliosidosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
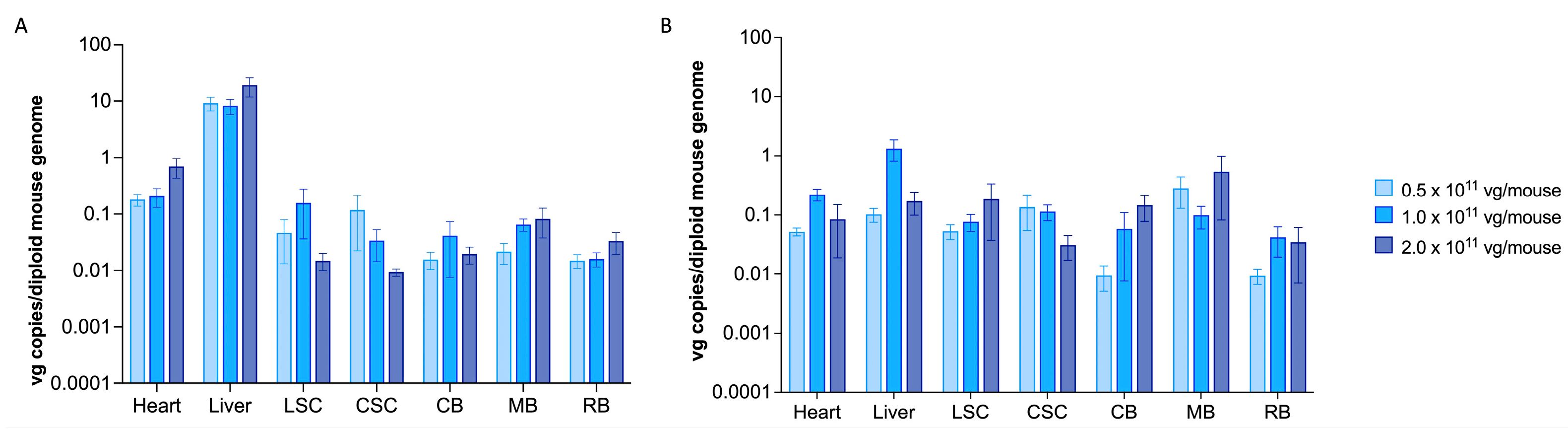
2.1. scAAV9.hGM2A Efficiently Distributes to the CNS of Gm2a−/− Mice Fourteen Weeks after Treatment and Remains Detectable for Their Lifespan
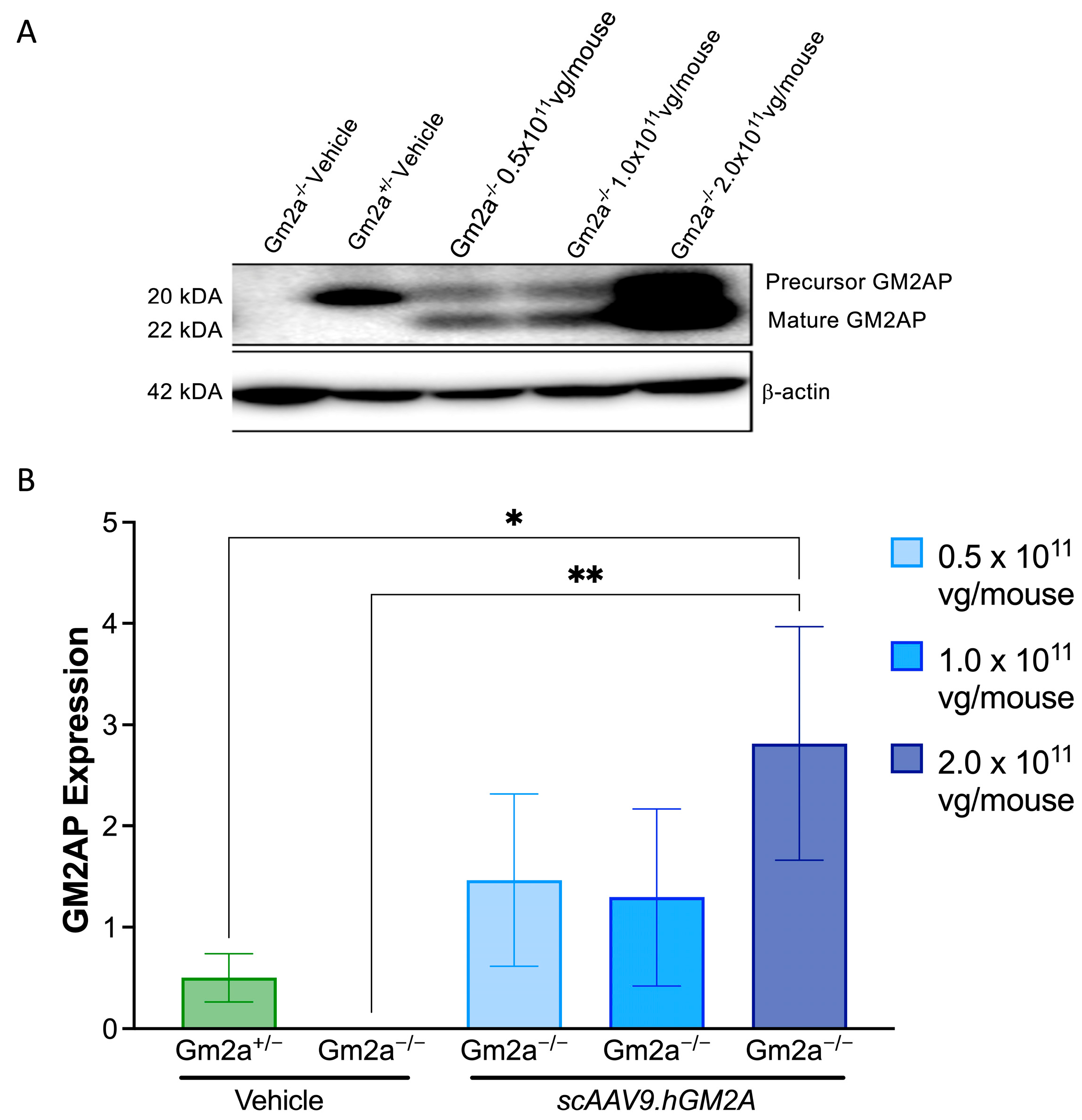
2.2. scAAV9.hGM2A Mediates Expression of Human GM2AP in Gm2a−/− Mice
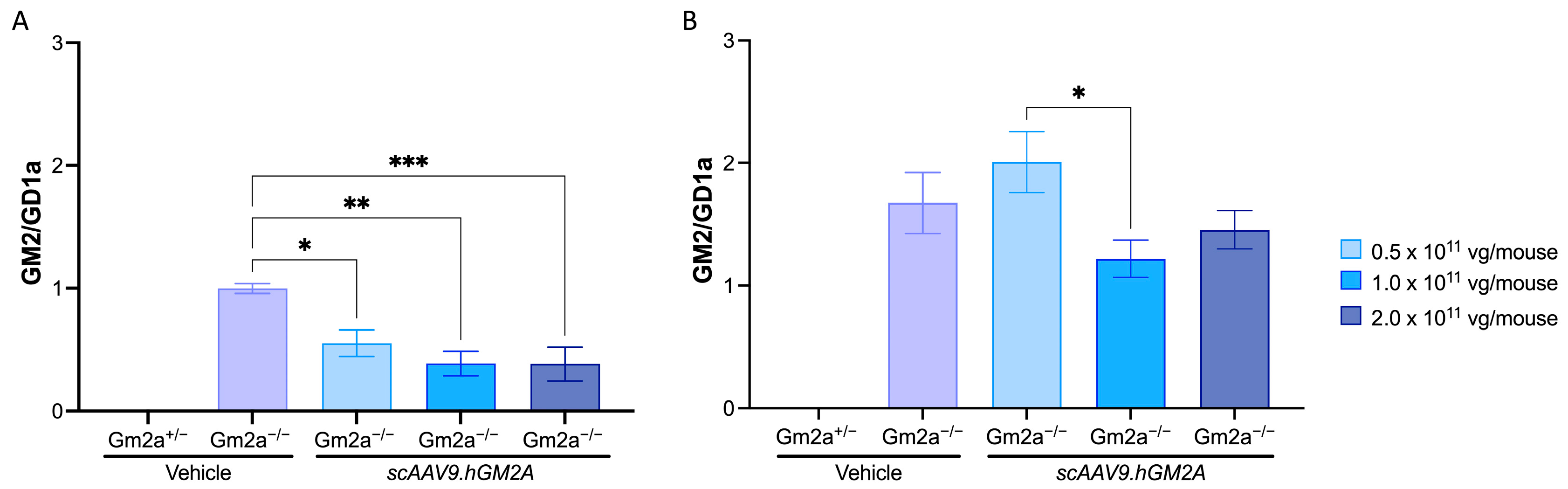
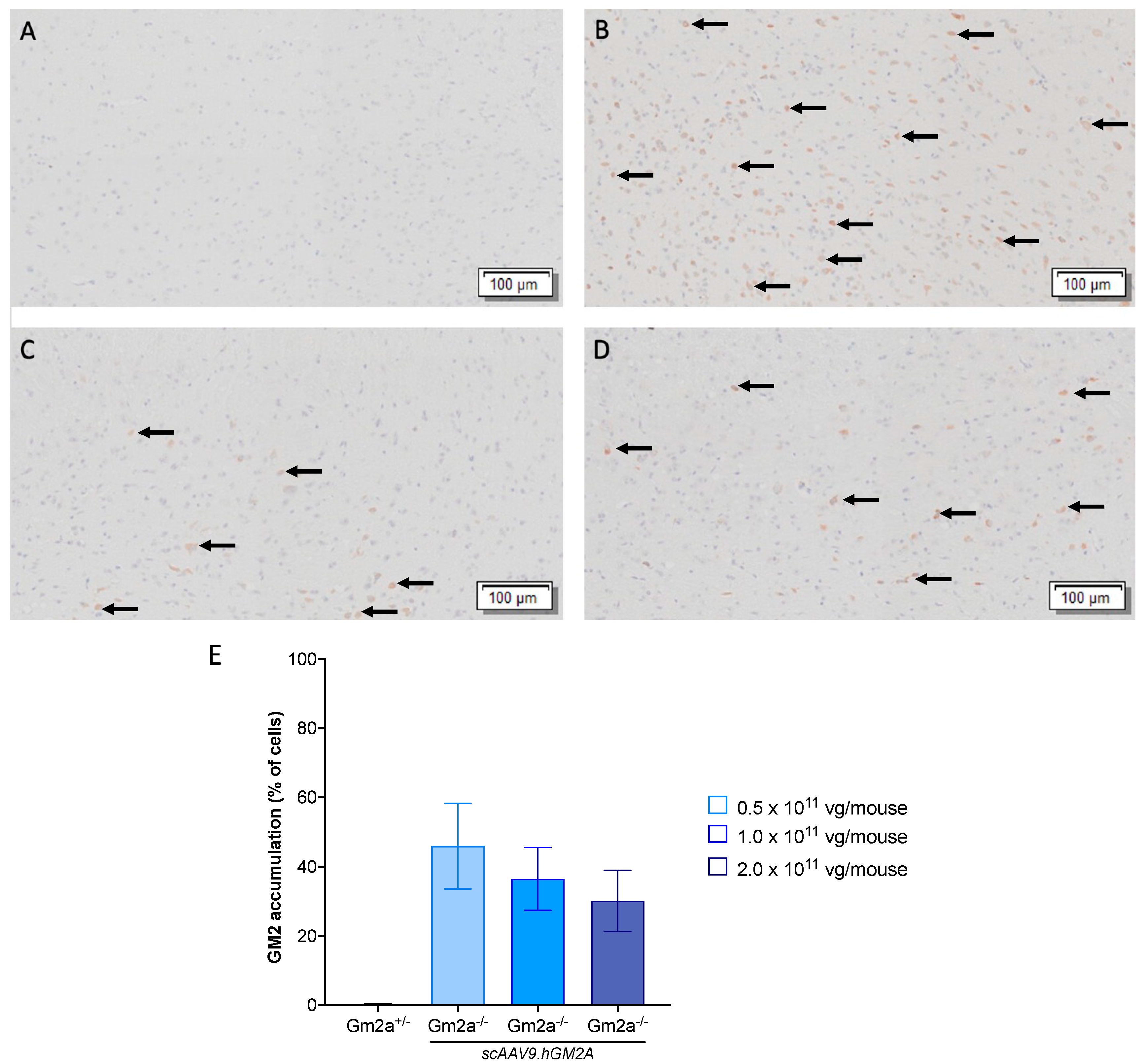
2.3. scAAV9.hGM2A Dose-Dependently Diminishes GM2 Accumulation in Gm2a−/− Mice
2.4. scAAV9.hGM2A Is Tolerable over the Lifespan of Treated Animals
2.5. Similar Comorbidity Profiles of scAAV9.hGM2A-Treated and Untreated Cohorts Support Its Safety as a Gene Therapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmid Construct
4.2. Mice
- Gm2a Mutation Forward 5′-CTTGGGTGGAGAGGCTATTC-3′
- Gm2a Mutation Reverse 5′-AGGTGAGATGACAGGAGATC-3′
- Gm2a WT Forward 5′-TACCTACTCACTACCCACGAGC-3′
- Gm2a WT Reverse 5′-ACACAGAAGAAGAGGCCTGC-3′
4.3. Drug Administration
4.4. Immunosuppressant Administration
4.5. Behavioural Testing
4.6. Euthanization
4.7. Vector Biodistribution
- GM2A WT forward 5′-TATGGGCTTCCTTGCCACTG-3′
- GM2A WT reverse 5′-CTCAGGACGCTCTCTATGCG-3′
- Mouse LaminB2 primers used for quantification of mouse genomic DNA are as follows:
- LaminB2 WT forward 5′-GGACCCAAGGACTACCTCAAGGG-3′
- LaminB2 WT reverse 5′-AGGGCACCTCCATCTCGGAAAC-3′.
- Data is shown as the number of viral genomes (vector DNA copies) per mouse genome (vg/mouse).
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Ganglioside Quantification Assay
4.10. Histology
4.11. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahuran, D.; Lowden, J.A. The subunit and polypeptide structure of hexosaminidases from human placenta. Can. J. Biochem. 1980, 58, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, E.M.; Schwarzmann, G.; Fürst, W.; Sandhoff, K. The human GM2 activator protein. A substrate specific cofactor of beta-hexosaminidase A. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, T.; Strater, N.; Schuette, C.; Klingenstein, R.; Sandhoff, K.; Saenger, W. The X-ray Crystal Structure of Human β-Hexosaminidase B Provides New Insights into Sandhoff Disease. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 328, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, B.L.; Mahuran, D.J.; Cherney, M.M.; Zhao, D.; Knapp, S.; James, M.N. Crystal Structure of Human β-Hexosaminidase B: Understanding the Molecular Basis of Sandhoff and Tay–Sachs Disease. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 327, 1093–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, M.J.; Mark, B.L.; Cherney, M.M.; Withers, S.G.; Mahuran, D.J.; James, M.N. Crystallographic Structure of Human β-Hexosaminidase A: Interpretation of Tay-Sachs Mutations and Loss of GM2 Ganglioside Hydrolysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 359, 913–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Deng, H.; Leung, A.; Mahuran, D. Identification of the 6-Sulfate Binding Site Unique to α-Subunit-Containing Isozymes of Human β-Hexosaminidase. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 5440–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Bukovac, S.; Callahan, J.; Mahuran, D. A single site in human β-hexosaminidase A binds both 6-sulfate-groups on hexosamines and the sialic acid moiety of GM2 ganglioside. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2003, 1637, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarghooni, M.; Bukovac, S.; Tropak, M.; Callahan, J.; Mahuran, D. An α-subunit loop structure is required for GM2 activator protein binding by β-hexosaminidase A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlynn, R.; Dobrenis, K.; Walkley, S.U. Differential subcellular localization of cholesterol, gangliosides, and glycosaminoglycans in murine models of mucopolysaccharide storage disorders. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 480, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantopoulos, G.; Iqbal, K.; Dekaban, A.S. Mucopolysaccharidosis Types IH, IS, II and IIIA: Glycosaminoglycans and Lipids of Isolated Brain Cells and Other Fractions from Autopsied Tissues. J. Neurochem. 1980, 34, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantopoulos, G.; Dekaban, A.S. Neurochemistry of the Mucopolysaccharidoses: Brain Lipids and Lysosomal Enzymes in Patients with Four Types of Mucopolysaccharidosis and in Normal Controls. J. Neurochem. 1978, 30, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.A.; Walkley, S.U. Growth of Ectopic Dendrites on Cortical Pyramidal Neurons in Neuronal Storage Diseases Correlates with Abnormal Accumulation of GM2 Ganglioside. J. Neurochem. 1994, 62, 1852–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Davidson, C.; McGlynn, R.; Stephney, G.; Dobrenis, K.; Vanier, M.T.; Walkley, S.U. Endosomal/Lysosomal Processing of Gangliosides Affects Neuronal Cholesterol Sequestration in Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myerowitz, R.; Hogikyan, N.D. Different Mutations in Ashkenazi Jewish and Non-Jewish French Canadians with Tay-Sachs Disease. Science 1986, 232, 1646–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, B.F.; Klavins, M.H.; Willard, H.F.; Gravel, R.; Lowden, J.A.; Mahuran, D.J. Molecular heterogeneity in the infantile and juvenile forms of Sandhoff disease (O-variant GM2 gangliosidosis). J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 12680–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhoff, K.; Harzer, K.; Wässle, W.; Jatzkewitz, H. Enzyme alterations and lipid storage in three variants of tay-sachs disease. J. Neurochem. 1971, 18, 2469–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganne, B.; Dauriat, B.; Richard, L.; Lamari, F.; Ghorab, K.; Magy, L.; Benkirane, M.; Perani, A.; Marquet, V.; Calvas, P.; et al. GM2 gangliosidosis AB variant: First case of late onset and review of the literature. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 6517–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Brunel-Guitton, C.; Lortie, A.; Gauvin, F.; Morales, C.R.; Mitchell, G.A.; Pshezhetsky, A.V. Atypical juvenile presentation of GM2 gangliosidosis AB in a patient compound-heterozygote for c.259G > T and c.164C > T mutations in the GM2A gene. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2017, 11, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, D.; Brodsky, M. GM2-Gangliosidosis, AB Variant: Clinical, Ophthalmological, MRI, and Molecular Findings. JIMD Rep. 2015, 25, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, J.; Datar, C.; Mistri, M.; Bhavsar, R.; Sheth, F.; Shah, K. GM2 gangliosidosis AB variant: Novel mutation from India—A case report with a review. BMC Pediatr. 2016, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bley, A.E.; Giannikopoulos, O.A.; Hayden, D.; Kubilus, K.; Tifft, C.J.; Eichler, F.S. Natural History of Infantile GM2 Gangliosidosis. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e1233–e1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maegawa, G.H.B.; Stockley, T.; Tropak, M.; Banwell, B.; Blaser, S.; Kok, F.; Giugliani, R.; Mahuran, D.; Clarke, J.T. The Natural History of Juvenile or Subacute GM2 Gangliosidosis: 21 New Cases and Literature Review of 134 Previously Reported. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e1550–e1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neudorfer, O.; Pastores, G.M.; Zeng, B.J.; Gianutsos, J.; Zaroff, C.M.; Kolodny, E.H. Late-onset Tay-Sachs disease: Phenotypic characterization and genotypic correlations in 21 affected patients. Genet. Med. 2005, 7, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, C.; Zainab, M.; Tifft, C.J. The GM2 gangliosidoses: Unlocking the mysteries of pathogenesis and treatment. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 764, 136195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.R.; Hudry, E.; Maguire, C.A.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Grandi, P. Viral vectors for therapy of neurologic diseases. Neuropharmacology 2017, 120, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, P.; Shera, D.; McPhee, S.W.; Francis, J.S.; Kolodny, E.H.; Bilaniuk, L.T.; Wang, D.-J.; Assadi, M.; Goldfarb, O.; Goldman, H.W.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up After Gene Therapy for Canavan Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 165ra163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandendriessche, T.; Thorrez, L.; Acosta-Sanchez, A.; Petrus, I.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; De Waele, L.; Iwasaki, Y.; Gillijns, V.; Wilson, J.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of adeno-associated viral vectors based on serotype 8 and 9 vs. lentiviral vectors for hemophilia B gene therapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, B.L.; Stein, C.S.; Heth, J.A.; Martins, I.; Kotin, R.M.; Derksen, T.A.; Zabner, J.; Ghodsi, A.; Chiorini, J.A. Recombinant adeno-associated virus type 2, 4, and 5 vectors: Transduction of variant cell types and regions in the mammalian central nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3428–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, D.M.; Young, S.M.; Samulski, R.J. Integration of Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) and Recombinant AAV Vectors. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2004, 38, 819–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bey, K.; Ciron, C.; Dubreil, L.; Deniaud, J.; Ledevin, M.; Cristini, J.; Blouin, V.; Aubourg, P.; Colle, M.-A. Efficient CNS targeting in adult mice by intrathecal infusion of single-stranded AAV9-GFP for gene therapy of neurological disorders. Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salegio, E.A.; Samaranch, L.; Kells, A.P.; Mittermeyer, G.; Sebastian, W.S.; Zhou, S.; Beyer, J.; Forsayeth, J.; Bankiewicz, K.S. Axonal transport of adeno-associated viral vectors is serotype-dependent. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castle, M.J.; Perlson, E.; Holzbaur, E.L.; Wolfe, J.H. Long-distance Axonal Transport of AAV9 Is Driven by Dynein and Kinesin-2 and Is Trafficked in a Highly Motile Rab7-positive Compartment. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, F.; Samaranch, L.; Zhang, H.S.; Manning-Bog, A.; Meyer, K.; Forsayeth, J.; Bankiewicz, K.S. Axonal transport of AAV9 in nonhuman primate brain. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hoffmann, A.; Grinberg, A.; Westphal, H.; McDonald, M.P.; Miller, K.M.; Crawley, J.N.; Sandhoff, K.; Suzuki, K.; Proia, R.L. Mouse model of G M2 activator deficiency manifests cerebellar pathology and motor impairment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8138–8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.J.; Kalburgi, S.N.; McCown, T.J.; Samulski, R.J. Global CNS gene delivery and evasion of anti-AAV-neutralizing antibodies by intrathecal AAV administration in non-human primates. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, S.; Karumuthil-Melethil, S.; Woodley, E.; Zaric, V.; Thompson, P.; Chen, Z.; Lykken, E.; Keimel, J.G.; Kaemmerer, W.F.; Gray, S.J.; et al. Investigating Immune Responses to the scAAV9-HEXM Gene Therapy Treatment in Tay–Sachs Disease and Sandhoff Disease Mouse Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.J.; Foti, S.B.; Schwartz, J.W.; Bachaboina, L.; Taylor-Blake, B.; Coleman, J.; Ehlers, M.D.; Zylka, M.J.; McCown, T.J.; Samulski, R.J. Optimizing Promoters for Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Gene Expression in the Peripheral and Central Nervous System Using Self-Complementary Vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011, 22, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réu, P.; Khosravi, A.; Bernard, S.; Mold, J.E.; Salehpour, M.; Alkass, K.; Perl, S.; Tisdale, J.; Possnert, G.; Druid, H.; et al. The Lifespan and Turnover of Microglia in the Human Brain. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sender, R.; Milo, R. The distribution of cellular turnover in the human body. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, S.A.; Timur, Z.K.; Ateş, N.; Martínez, L.A.; Seyrantepe, V. GM2 ganglioside accumulation causes neuroinflammation and behavioral alterations in a mouse model of early onset Tay-Sachs disease. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.J.; Blake, B.L.; Criswell, H.E.; Nicolson, S.C.; Samulski, R.J.; McCown, T.J. Directed Evolution of a Novel Adeno-associated Virus (AAV) Vector That Crosses the Seizure-compromised Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB). Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.J.; Matagne, V.; Bachaboina, L.; Yadav, S.; Ojeda, S.R.; Samulski, R.J. Preclinical Differences of Intravascular AAV9 Delivery to Neurons and Glia: A Comparative Study of Adult Mice and Nonhuman Primates. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodley, E.; Osmon, K.J.; Thompson, P.; Richmond, C.; Chen, Z.; Gray, S.J.; Walia, J.S. Efficacy of a Bicistronic Vector for Correction of Sandhoff Disease in a Mouse Model. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2019, 12, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zincarelli, C.; Soltys, S.; Rengo, G.; Rabinowitz, J.E. Analysis of AAV Serotypes 1–9 Mediated Gene Expression and Tropism in Mice After Systemic Injection. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbury, A.M.; Bagel, J.H.; Nguyen, D.; Lykken, E.A.; Salvador, J.P.; Jiang, X.; Swain, G.P.; Assenmacher, C.A.; Hendricks, I.J.; Miyadera, K.; et al. Krabbe disease successfully treated via monotherapy of intrathecal gene therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4906–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.M.; Armao, D.; Kalburgi, S.N.; Gray, S.J. Development of Intrathecal AAV9 Gene Therapy for Giant Axonal Neuropathy. Mol. Ther.-Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 9, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, T.; Hu, Y.; Shaffo, F.C.; Belur, N.R.; Mazzulli, J.R.; Gray, S.J. AAV9/MFSD8 gene therapy is effective in preclinical models of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 7 disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hordeaux, J.; Dubreil, L.; Robveille, C.; Deniaud, J.; Pascal, Q.; Dequéant, B.; Pailloux, J.; Lagalice, L.; Ledevin, M.; Babarit, C.; et al. Long-term neurologic and cardiac correction by intrathecal gene therapy in Pompe disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, J.S.; Osmon, K.J.; Thompson, P.; Woodley, E.; Karumuthil-Melethil, S.; Heindel, C.; Keimel, J.G.; Kaemmerer, W.F.; Gray, S.J. Treatment of GM2 Gangliosidosis in Adult Sandhoff Mice using an Intravenous Self-Complementary Hexosaminidase Vector. Curr. Gene Ther. 2022, 22, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phaneuf, D.; Wakamatsu, N.; Huang, J.-Q.; Borowski, A.; Peterson, A.C.; Fortunato, S.R.; Ritter, G.; Igdoura, S.A.; Morales, C.R.; Benoit, G.; et al. Dramatically Different Phenotypes in Mouse Models of Human Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff Diseases. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolter, T.; Sandhoff, K. Glycosphingolipid degradation and animal models of GM2-gangliosidoses. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 1998, 21, 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyrantepe, V.; Demir, S.A.; Timur, Z.K.; Von Gerichten, J.; Marsching, C.; Erdemli, E.; Oztas, E.; Takahashi, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ates, N.; et al. Murine Sialidase Neu3 facilitates GM2 degradation and bypass in mouse model of Tay-Sachs disease. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 299, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccariotto, E.; Cox, T.M. Genetics and Therapies for GM2 Gangliosidosis. Curr. Gene Ther. 2018, 18, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulcha, J.T.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Viral vector platforms within the gene therapy landscape. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathwani, A.C.; Tuddenham, E.G.D.; Rangarajan, S.; Rosales, C.; McIntosh, J.; Linch, D.C.; Chowdary, P.; Riddell, A.; Pie, A.J.; Harrington, C.; et al. Adenovirus-Associated Virus Vector–Mediated Gene Transfer in Hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathwani, A.C.; Reiss, U.M.; Tuddenham, E.G.; Rosales, C.; Chowdary, P.; McIntosh, J.; Della Peruta, M.; Lheriteau, E.; Patel, N.; Raj, D.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Factor IX Gene Therapy in Hemophilia B. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1994–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, V.M.; Gao, G.-P.; Grant, R.L.; Schnell, M.A.; Zoltick, P.W.; Rozamus, L.W.; Clackson, T.; Wilson, J.M. Long-term pharmacologically regulated expression of erythropoietin in primates following AAV-mediated gene transfer. Blood 2005, 105, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golebiowski, D.; Van Der Bom, I.M.J.; Kwon, C.-S.; Miller, A.D.; Petrosky, K.; Bradbury, A.M.; Maitland, S.A.; Kühn, A.L.; Bishop, N.; Curran, E.; et al. Direct Intracranial Injection of AAVrh8 Encoding Monkey β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase Causes Neurotoxicity in the Primate Brain. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.F.; Benincore-Flórez, E.; Solano-Galarza, D.; Jaramillo, R.G.G.; Echeverri-Peña, O.Y.; Suarez, D.A.; Alméciga-Díaz, C.J.; Espejo-Mojica, A.J. GM2 Gangliosidoses: Clinical Features, Pathophysiological Aspects, and Current Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, H.; Yu, J.; Yeom, J.; Song, S.H.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, K. Differential Urinary Proteome Analysis for Predicting Prognosis in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Renal Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hao, Y.; Shao, C.; Wu, Q.; Prager, B.C.; Gimple, R.C.; Sulli, G.; Kim, L.J.; Zhang, G.; Qiu, Z.; et al. ADAR1-mediated RNA editing links ganglioside catabolism to glioblastoma stem cell maintenance. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e143397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, Y.S.; Yu, G.H.; Lee, S.-T.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, C. Identification of ganglioside GM2 activator playing a role in cancer cell migration through proteomic analysis of breast cancer secretomes. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaspyridonos, M.; Smith, A.; Burnand, K.G.; Taylor, P.; Padayachee, S.; Suckling, K.E.; James, C.H.; Greaves, D.R.; Patel, L. Novel Candidate Genes in Unstable Areas of Human Atherosclerotic Plaques. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flurkey, K.; Mcurrer, J.M.; Harrison, D.E. Chapter 20—Mouse Models in Aging Research. In The Mouse in Biomedical Research, 2nd ed.; Fox, J.G., Davisson, M.T., Quimby, F.W., Barthold, S.W., Newcomer, C.E., Smith, A.L., Eds.; American College of Laboratory Animal Medicine; Academic Press: Burlington, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 637–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, T.G.; Kim, J.-H.; Grange, R.W.; McLoon, L.K.; Thompson, L.V. C57BL/6 life span study: Age-related declines in muscle power production and contractile velocity. Age 2015, 37, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettan-Brewer, C.; Treuting, P.M.M. Practical pathology of aging mice. Pathobiol. Aging Age-Relat. Dis. 2011, 1, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.P.; Boyd, K.L.; Wallace, J.M. Evaluation of Mice Undergoing Serial Oral Gavage While Awake or Anesthetized. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2016, 55, 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, D.M. Self-complementary AAV Vectors; Advances and Applications. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccarty, D.M.; Monahan, P.E.; Samulski, R.J. Self-complementary recombinant adeno-associated virus (scAAV) vectors promote efficient transduction independently of DNA synthesis. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, M.L.; Shao, G.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Chicoine, L.G.; Martin, P.T. Induction of T-Cell Infiltration and Programmed Death Ligand 2 Expression by Adeno-Associated Virus in Rhesus Macaque Skeletal Muscle and Modulation by Prednisone. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flotte, T.R.; Cataltepe, O.; Puri, A.; Batista, A.R.; Moser, R.; McKenna-Yasek, D.; Douthwright, C.; Gernoux, G.; Blackwood, M.; Mueller, C.; et al. AAV gene therapy for Tay-Sachs disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliani, A.; Boisgerault, F.; Hardet, R.; Marmier, S.; Collaud, F.; Ronzitti, G.; Leborgne, C.; Verdera, H.C.; Sola, M.S.; Charles, S.; et al. Antigen-selective modulation of AAV immunogenicity with tolerogenic rapamycin nanoparticles enables successful vector re-administration. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmon, K.J.; Vyas, M.; Woodley, E.; Thompson, P.; Walia, J.S. Battery of Behavioral Tests Assessing General Locomotion, Muscular Strength, and Coordination in Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 131, e55491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmon, K.J.; Woodley, E.; Thompson, P.; Ong, K.; Karumuthil-Melethil, S.; Keimel, J.G.; Mark, B.L.; Mahuran, D.; Gray, S.J.; Walia, J.S. Systemic Gene Transfer of a Hexosaminidase Variant Using an scAAV9.47 Vector Corrects GM2Gangliosidosis in Sandhoff Mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 2016, 27, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tropak, M.B.; Bukovac, S.W.; Rigat, B.A.; Yonekawa, S.; Wakarchuk, W.; Mahuran, D.J. A sensitive fluorescence-based assay for monitoring GM2 ganglioside hydrolysis in live patient cells and their lysates. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernández, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deschenes, N.M.; Cheng, C.; Ryckman, A.E.; Quinville, B.M.; Khanal, P.; Mitchell, M.; Chen, Z.; Sangrar, W.; Gray, S.J.; Walia, J.S. Biochemical Correction of GM2 Ganglioside Accumulation in AB-Variant GM2 Gangliosidosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119217
Deschenes NM, Cheng C, Ryckman AE, Quinville BM, Khanal P, Mitchell M, Chen Z, Sangrar W, Gray SJ, Walia JS. Biochemical Correction of GM2 Ganglioside Accumulation in AB-Variant GM2 Gangliosidosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119217
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeschenes, Natalie M., Camilyn Cheng, Alex E. Ryckman, Brianna M. Quinville, Prem Khanal, Melissa Mitchell, Zhilin Chen, Waheed Sangrar, Steven J. Gray, and Jagdeep S. Walia. 2023. "Biochemical Correction of GM2 Ganglioside Accumulation in AB-Variant GM2 Gangliosidosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119217
APA StyleDeschenes, N. M., Cheng, C., Ryckman, A. E., Quinville, B. M., Khanal, P., Mitchell, M., Chen, Z., Sangrar, W., Gray, S. J., & Walia, J. S. (2023). Biochemical Correction of GM2 Ganglioside Accumulation in AB-Variant GM2 Gangliosidosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119217





