Ionic Levothyroxine Formulations: Synthesis, Bioavailability, and Cytotoxicity Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
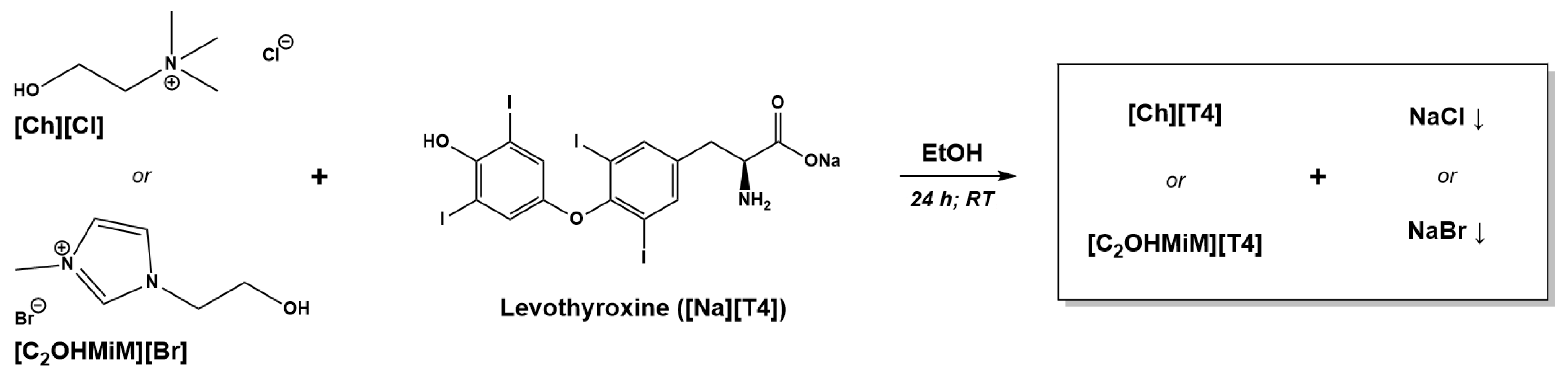
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of API-ILs Based Levothyroxine
2.1.1. Synthesis of T4-ILs
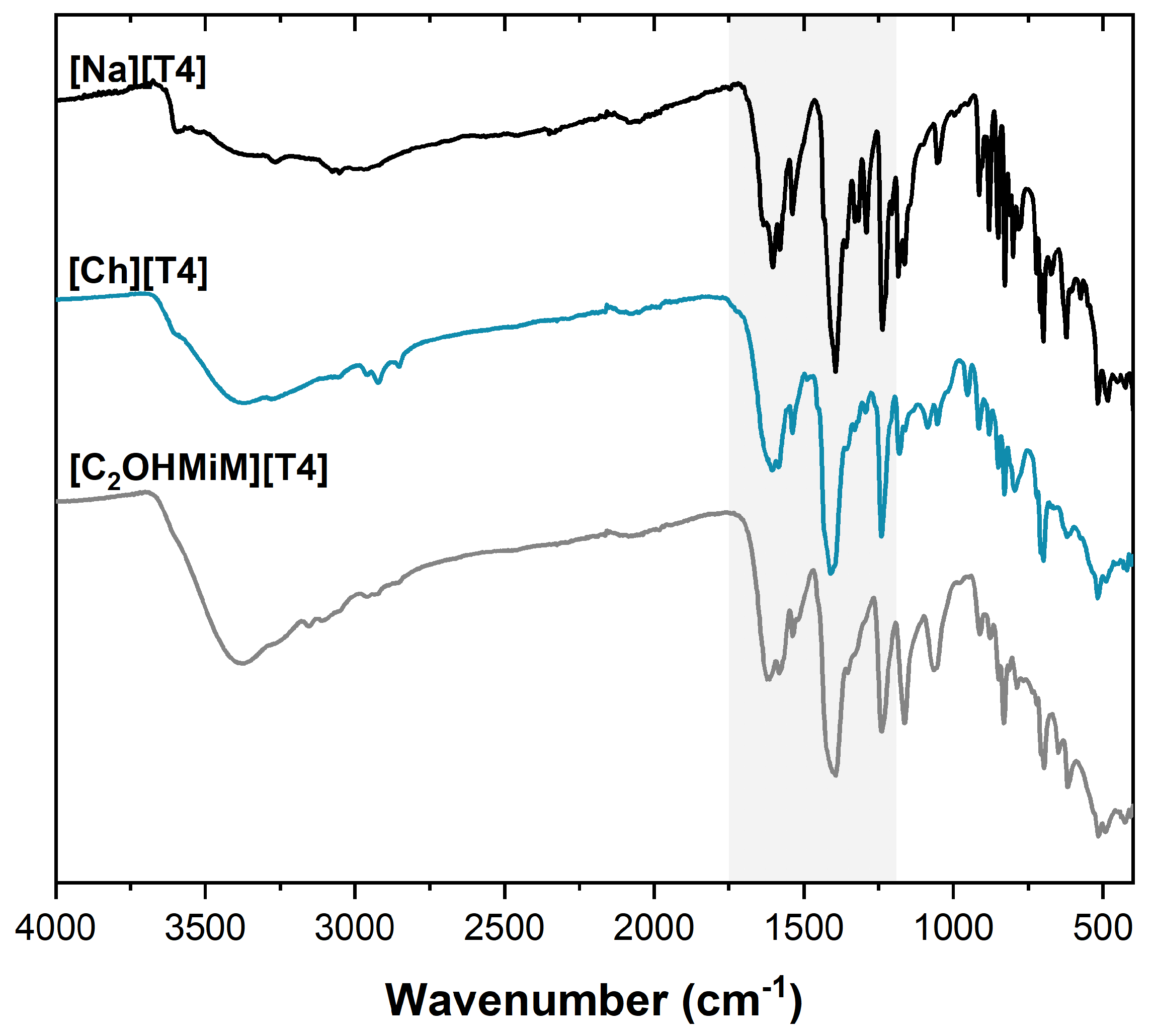
2.1.2. Characterization of T4-ILs
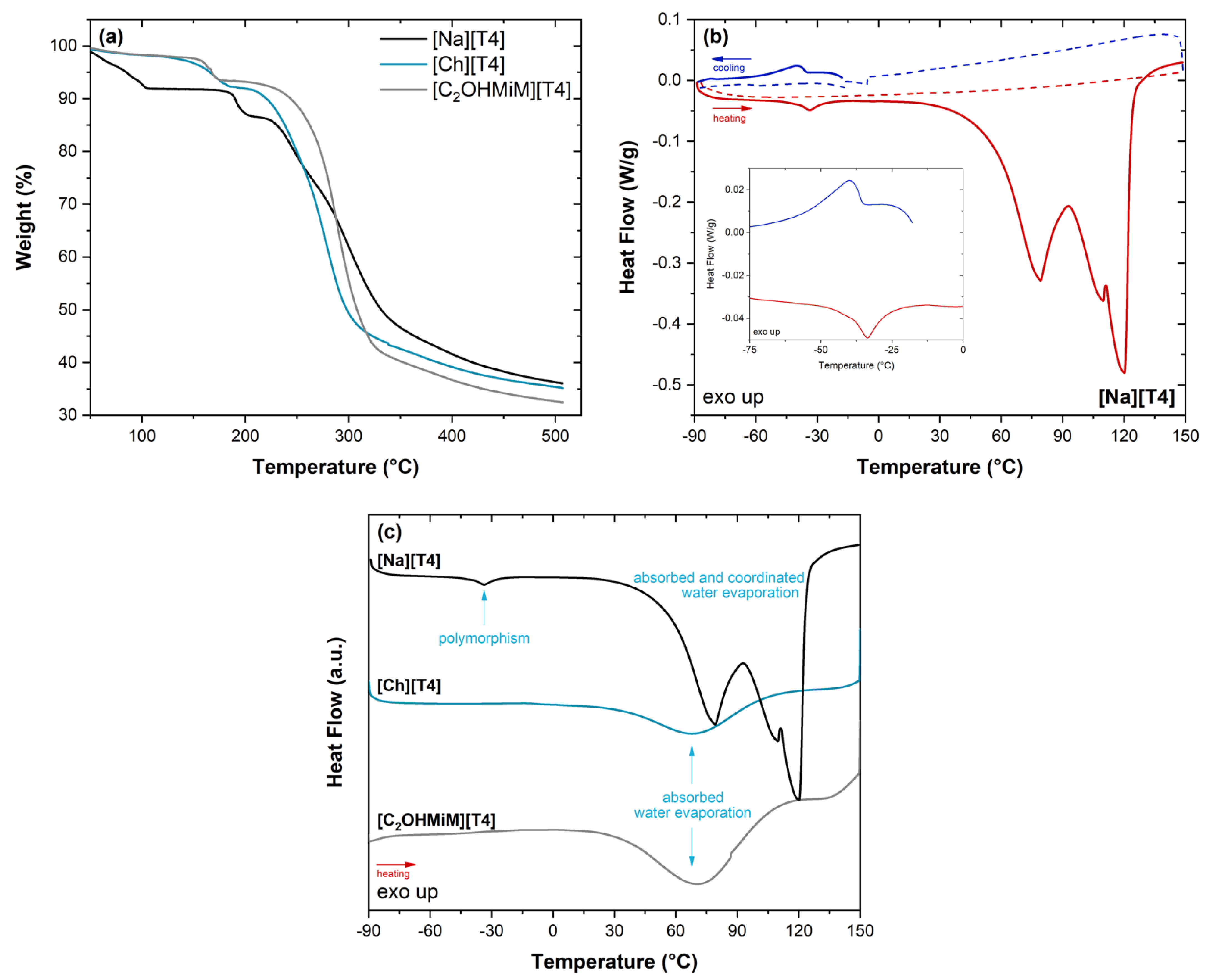
Thermal Characterization
2.2. Bioavailability Studies
2.2.1. Solubility Assays
2.2.2. Permeability Assays
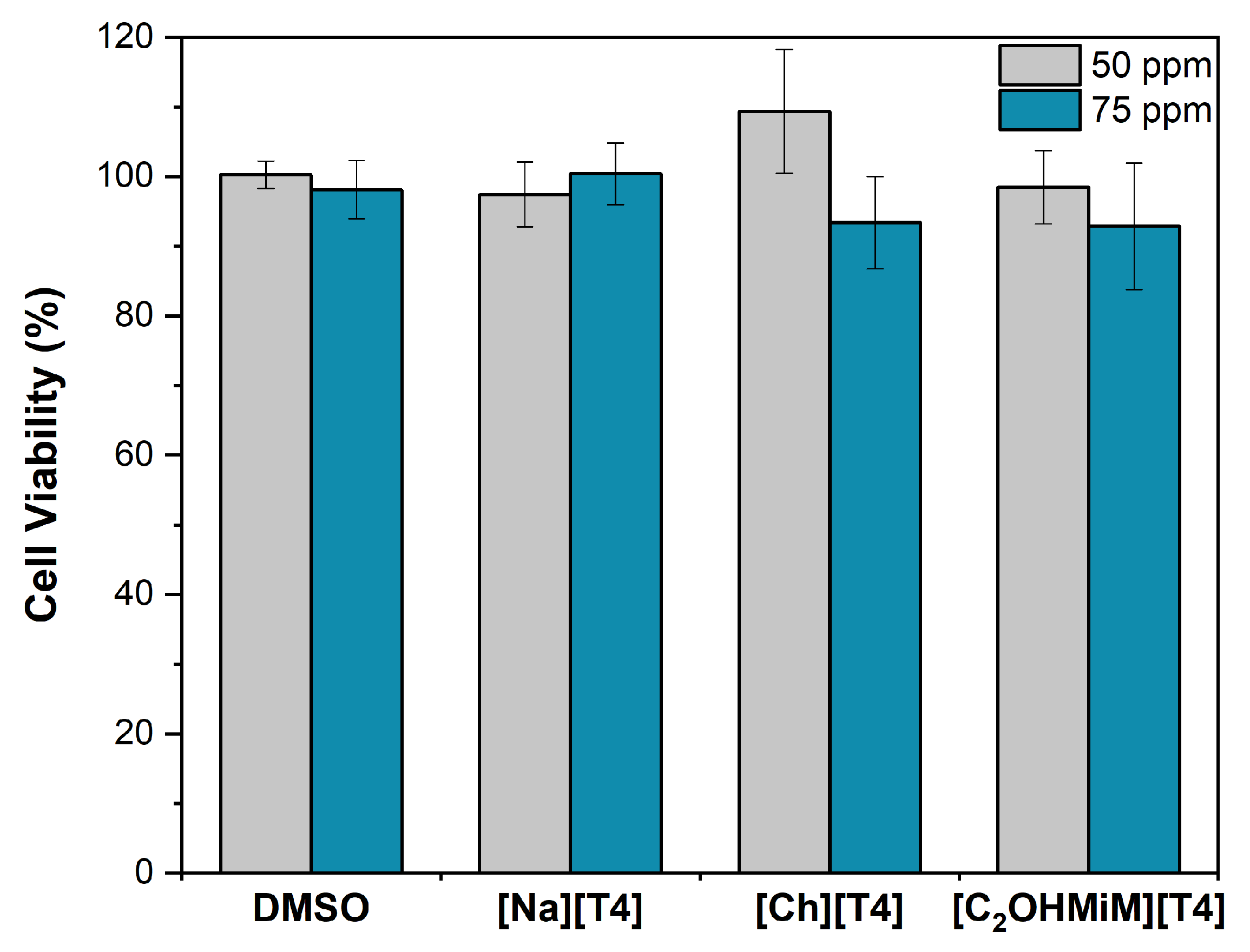
2.2.3. Cytotoxicity Assays
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Synthesis of API-Ionic Liquids Based on Levothyroxine
3.2.1. Synthesis of Choline Levothyroxine, [Ch][T4]
3.2.2. Synthesis of 1-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-3-Methylimidazolium Levothyroxine, [C2OHMiM][T4]
3.3. Characterization of API-ILs Based on Levothyroxine
3.3.1. Chemical Characterization (NMR, ATR-FTIR, and Elemental Analysis)
3.3.2. Thermal Characterization (TGA and DSC)
3.4. Solubility Assays
3.5. Permeability Assays
3.6. Cytotoxicity Assays
3.6.1. Stock solution preparation
3.6.2. Cell Viability Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiovato, L.; Magri, F.; Carlé, A. Hypothyroidism in Context: Where We’ve Been and Where We’re Going. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, O.; Razvi, S. Hypothyroidism in the older population. Thyroid Res. 2019, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaitonde, D.Y.; Rowley, K.D.; Sweeney, L.B. Hypothyroidism: An update. Am. Fam. Physician 2012, 86, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaker, L.; Razvi, S.; Bensenor, I.M.; Azizi, F.; Pearce, E.N.; Peeters, R.P. Hypothyroidism. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2022, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.I.; Ali, M.Z.; Islam, M.S.; Solayman, M.; Hoque, S. Hypothyroidism—A New View On An Old Disease. KYAMC J. 2017, 7, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueston, W.J. Treatment of hypothyroidism. Am. Fam. Physician 2001, 64, 1717–1724, Erratum in: Am. Fam. Physician 2002, 65, 2438. [Google Scholar]
- Obeidat, K.A.; Saadeh, N.A.; As’Ad, A.; Bakkar, S. Successful management of hypothyroidism in gastric outlet obstruction using levothyroxine rectal enemas: A case report. Am. J. Case Rep. 2018, 19, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguay, M.; Girard, J.; Scarsi, C.; Mautone, G.; Larouche, R. Pharmacokinetics and Comparative Bioavailability of a Levothyroxine Sodium Oral Solution and Soft Capsule. Clin. Pharm. Drug Dev. 2019, 8, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Young, V.G.; Su, Y.; Suryanarayanan, R. Partial Dehydration of Levothyroxine Sodium Pentahydrate in a Drug Product Environment: Structural Insights into Stability. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 3915–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalani, D.V.; Nutan, B.; Kumar, A.; Chandel, A.K.S. Bioavailability Enhancement Techniques for Poorly Aqueous Soluble Drugs and Therapeutics. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, S.N.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, M.G. The role of ionic liquids in the pharmaceutical field: An overview of relevant applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, M.; Almalki, W.H.; Shukla, R.; Afzal, O.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Beg, S.; Rahman, M. Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) in ionic liquids: An effective approach for API physiochemical parameter optimization. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakulina, O.D.; Ivanov, M.Y.; Alimov, D.V.; Prikhod’ko, S.A.; Adonin, N.Y.; Fedin, M.V. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient-Ionic Liquids (API-ILs): Nanostructure of the Glassy State Studied by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Molecules 2022, 27, 5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Neves, M.C.; Shimizu, K.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. The magic of aqueous solutions of ionic liquids: Ionic liquids as a powerful class of catanionic hydrotropes. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3948–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarque, F.S.; Gautério, G.V.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Lemes, A.C.; Ribeiro, B.D. Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Based on Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for the Recovery of Non-Protein Bioactive Compounds—A Review. Processes 2023, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balk, A.; Wiest, J.; Widmer, T.; Galli, B.; Holzgrabe, U.; Meinel, L. Transformation of acidic poorly water soluble drugs into ionic liquids. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.M.; Raposo, L.R.; Carrera, G.V.S.M.; Costa, A.; Dionísio, M.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R.; Branco, L.C. Ionic Liquids and Salts from Ibuprofen as Promising Innovative Formulations of an Old Drug. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintra, T.E.; Abranches, D.O.; Benfica, J.; Soares, B.P.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Cholinium-based ionic liquids as bioinspired hydrotropes to tackle solubility challenges in drug formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 164, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, F. Physical chemistry of ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafforgue, G.; Arellano, C.; Vachoux, C.; Woodley, J.; Philibert, C.; Dupouy, V.; Bousquet-Mélou, A.; Gandia, P.; Houin, G. Oral absorption of ampicillin: Role of paracellular route vs. PepT1 transporter. Fundam. Clin. Pharm. 2008, 22, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; da Ponte, M.N.; Prudêncio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Ž. Development of novel ionic liquids based on ampicillin. MedChemComm 2012, 3, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; de Araújo, J.M.M.; Alves, F.; Matos, C.; Ferraz, R.; Prudêncio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Ž.; Branco, L.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; et al. Evaluation of solubility and partition properties of ampicillin-based ionic liquids. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiani-Skiba, M.; Barbot, C.; Bounoure, F.; Joudieh, S.; Skiba, M. Solubility and dissolution rate of progesterone-cyclodextrin-polymer systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2006, 32, 1043–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demurtas, M.; Onnis, V.; Zucca, P.; Rescigno, A.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Engelbrecht, L.d.V.; Nieddu, M.; Ennas, G.; Scano, A.; Mocci, F.; et al. Cholinium-Based Ionic Liquids from Hydroxycinnamic Acids as New Promising Bioactive Agents: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Investigation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 2975–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claus, J.; Sommer, F.O.; Kragl, U. Ionic liquids in biotechnology and beyond. Solid State Ion. 2018, 314, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeţi, I.; Ledeţi, A.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Matusz, P.; Bercean, V.; Şuta, L.-M.; Piciu, D. Thermal stability of synthetic thyroid hormone l-thyroxine and l-thyroxine sodium salt hydrate both pure and in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 125, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeți, I.; Romanescu, M.; Cîrcioban, D.; Ledeți, A.; Vlase, G.; Vlase, T.; Suciu, O.; Murariu, M.; Olariu, S.; Matusz, P.; et al. Stability and compatibility studies of levothyroxine sodium in solid binary systems—Instrumental screening. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, J.W.; Shah, R.B.; Gupta, A.; Sayeed, V.; Habib, M.J.; Khan, M.A. Influence of formulation and processing factors on stability of levothyroxine sodium pentahydrate. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.; Mugesh, G. Structure Elucidation and Characterization of Different Thyroxine Polymorphs. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 10983–10987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, M.; Oztas, E.; Yanar, F.; Aksakal, N.; Ozcinar, B.; Ozhan, G. Association between genetic polymorphism and levothyroxine bioavailability in hypothyroid patients. Endocr. J. 2018, 65, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, D.; Casali, L.; Grepioni, F. The Relevance of Crystal Forms in the Pharmaceutical Field: Sword of Damocles or Innovation Tools? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savjani, K.T.; Gajjar, A.K.; Savjani, J.K. Drug Solubility: Importance and Enhancement Techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 195727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, N. Thyroid Preparations. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evert, H.E. The solubility of l-thyroxine (Na) in the presence of phosphate buffer and of neutral salts. J. Phys. Chem. 1960, 64, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoccia, D.; Ravaioli, S.; Santi, S.; Mariani, V.; Santarcangelo, C.; De Filippis, A.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R.; Daglia, M. Exploring the anticancer effects of standardized extracts of poplar-type propolis: In vitro cytotoxicity toward cancer and normal cell lines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannella, V.; Altomare, R.; Chiaramonte, G.; Di Bella, S.; Mira, F.; Russotto, L.; Pisano, P.; Guercio, A. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Endodontic Pins on L929 Cell Line. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, L.C.; Rosa, J.N.; Ramos, J.J.M.; Afonso, C.A.M. Preparation and characterization of new room temperature ionic liquids. Chem. A Eur. J. 2002, 8, 3671–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Solubility in Water 25 °C (mg mL−1) | Solubility in Water 37 °C (mg mL−1) | Solubility in PBS 37 °C (mg mL−1) | Solubility in Serum 37 °C (mg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Na][T4] | 0.149 ± 0.015 (1) | 0.155 ± 0.002 | 0.163 ± 0.004 (1) | 0.485 ± 0.005 |
| [Ch][T4] | 0.247 ± 0.035 | 0.386 ± 0.015 | 0.284 ± 0.017 | 0.334 ± 0.005 |
| [C2OHMiM][T4] | 0.277 ± 0.034 | 0.379 ± 0.022 | 0.324 ± 0.004 | 0.321 ± 0.007 |
| Compound | Permeability (×10−5) cm s−1 | Diffusion (×10−6) cm2 s−1 | Kd |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Na][T4] | 2.04 | 0.49 | 0.63 |
| [Ch][T4] | 0.61 | 0.10 | 0.94 |
| [C2OHMiM][T4] | 1.02 | 0.34 | 0.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barreira, A.; Santos, A.F.M.; Dionísio, M.; Jesus, A.R.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Petrovski, Ž.; Paninho, A.B.; Ventura, M.G.; Branco, L.C. Ionic Levothyroxine Formulations: Synthesis, Bioavailability, and Cytotoxicity Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108822
Barreira A, Santos AFM, Dionísio M, Jesus AR, Duarte ARC, Petrovski Ž, Paninho AB, Ventura MG, Branco LC. Ionic Levothyroxine Formulations: Synthesis, Bioavailability, and Cytotoxicity Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108822
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarreira, António, Andreia F. M. Santos, Madalena Dionísio, Ana R. Jesus, Ana Rita C. Duarte, Željko Petrovski, Ana B. Paninho, Márcia G. Ventura, and Luis C. Branco. 2023. "Ionic Levothyroxine Formulations: Synthesis, Bioavailability, and Cytotoxicity Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108822
APA StyleBarreira, A., Santos, A. F. M., Dionísio, M., Jesus, A. R., Duarte, A. R. C., Petrovski, Ž., Paninho, A. B., Ventura, M. G., & Branco, L. C. (2023). Ionic Levothyroxine Formulations: Synthesis, Bioavailability, and Cytotoxicity Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108822













