Molecular Toxicology and Pathophysiology of Comorbid Alcohol Use Disorder and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Associated with Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. The Main Characteristics of AUD/PTSD
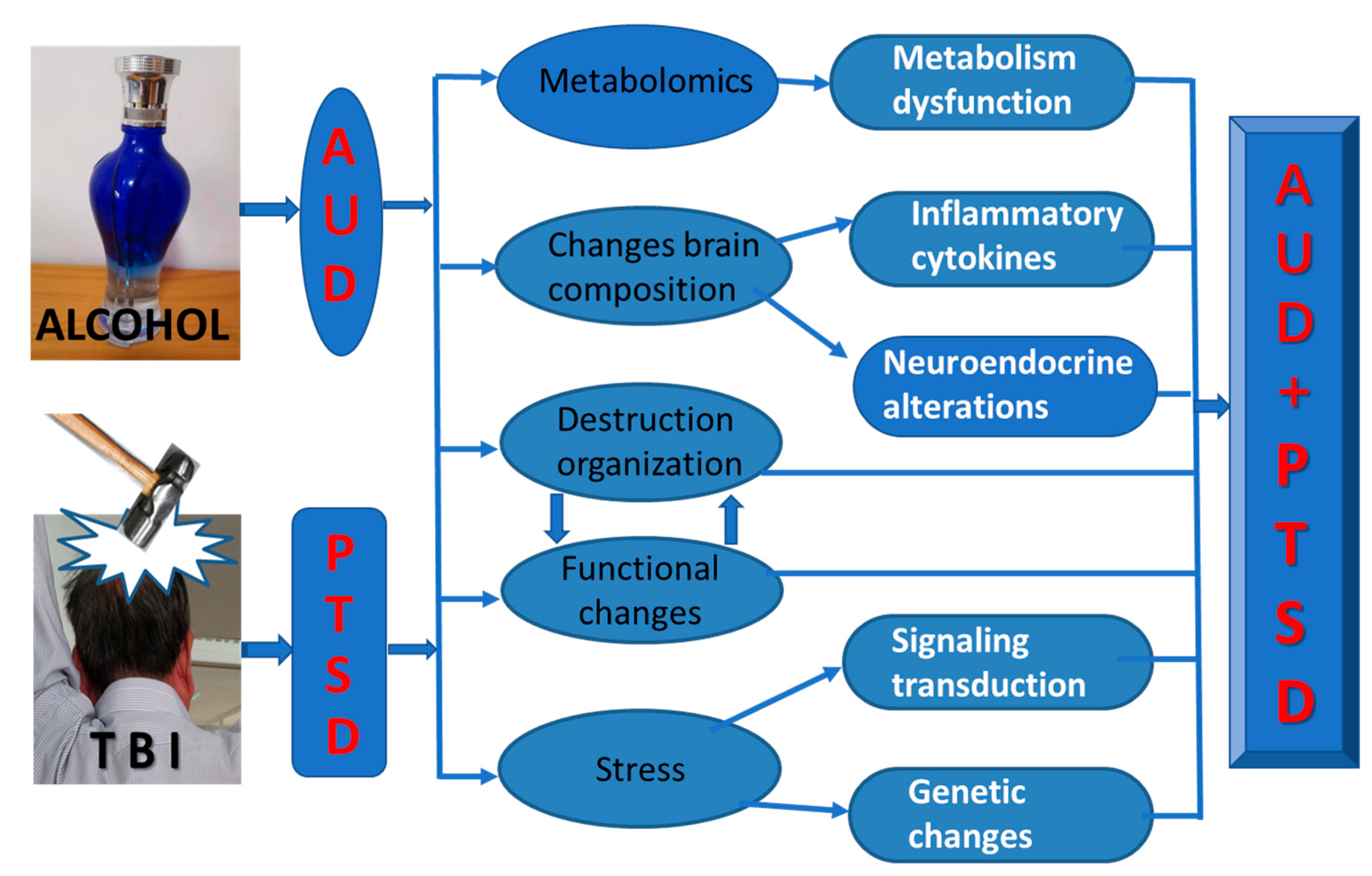
4. Molecular Toxicology and Pathophysiological Mechanisms of AUD/PTSD
4.1. Metabolomics in AUD/PTSD
4.2. Changes in Inflammatory Cytokines
4.3. Neuroendocrine Alterations
4.4. Altered Signaling Transduction Pathways in the Brain
4.5. Genetic and Epigenetic Changes in the Brain
5. A Variety of Possible Hypotheses Leading to AUD/PTSD
5.1. Metabolic Dysfunction Hypothesis
5.2. Inflammation Hypothesis
5.3. Neuroendocrine Alterations Hypothesis
5.4. Genetic Changes Hypotheses
5.5. Integrated Hypotheses
6. Implications and Further Research Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norman, S.B.; Haller, M.; Hamblen, J.L.; Southwick, S.M.; Pietrzak, R.H. The burden of co-occurring alcohol use disorder and PTSD in U.S. Military veterans: Comorbidities, functioning, and suicidality. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2018, 32, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possemato, K.; Maisto, S.A.; Wade, M.; Barrie, K.; Johnson, E.M.; Ouimette, P.C. Natural Course of Co-Occurring PTSD and Alcohol Use Disorder among Recent Combat Veterans. J. Trauma Stress 2017, 30, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlinchey, E.; Ross, J.; Murphy, D.; Shorter, G.W.; Armour, C. Disentangling the Symptom-Level Nuances in Comorbid Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Problematic Alcohol Use in Northern Irish Military Veterans: A Network Analysis. J. Trauma Stress 2022, 35, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, B.I.; Gorman, P.; Catts, S.V. Military Combat, Posttraumatic Stress Disorder, and the Course of Alcohol Use Disorders in a Cohort of Australian Vietnam War Veterans. J. Trauma Stress 2020, 33, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Berardis, D.; Marini, S.; Serroni, N.; Iasevoli, F.; Tomasetti, C.; de Bartolomeis, A.; Mazza, M.; Tempesta, D.; Valchera, A.; Fornaro, M.; et al. Targeting the Noradrenergic System in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prazosin Trials. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1094–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Berardis, D.; Vellante, F.; Fornaro, M.; Anastasia, A.; Olivieri, L.; Rapini, G.; Serroni, N.; Orsolini, L.; Valchera, A.; Carano, A.; et al. Alexithymia, suicide ideation, affective temperaments and homocysteine levels in drug naive patients with post-traumatic stress disorder: An exploratory study in the everyday ‘real world’ clinical practice. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2020, 24, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, E.; Norman, S.B.; Haller, M.; Southwick, S.M.; Hamblen, J.L.; Pietrzak, R.H. Differences in protective factors among U.S. Veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder, alcohol use disorder, and their comorbidity: Results from the National Health and Resilience in Veterans Study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 194, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawn, S.E.; Cusack, S.E.; Amstadter, A.B. A Systematic Review of the Self-Medication Hypothesis in the Context of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Comorbid Problematic Alcohol Use. J. Trauma Stress 2020, 33, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Liverant, G.I.; Lowmaster, S.E.; Gradus, J.L.; Sloan, D.M. PTSD and reasons for living: Associations with depressive symptoms and alcohol use. Psychiatry Res. 2014, 219, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evren, C.; Sar, V.; Dalbudak, E.; Cetin, R.; Durkaya, M.; Evren, B.; Celik, S. Lifetime PTSD and quality of life among alcohol-dependent men: Impact of childhood emotional abuse and dissociation. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 186, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najavits, L.M.; Walsh, M. Dissociation, PTSD, and substance abuse: An empirical study. J. Trauma Dissociation 2012, 13, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, B.F.; Goldstein, R.B.; Saha, T.D.; Chou, S.P.; Jung, J.; Zhang, H.; Pickering, R.P.; Ruan, W.J.; Smith, S.M.; Huang, B.; et al. Epidemiology of DSM-5 Alcohol Use Disorder: Results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.L.; Lopez, M.F.; Archer, K.J.; Wolen, A.R.; Becker, H.C.; Miles, M.F. Time-Course Analysis of Brain Regional Expression Network Responses to Chronic Intermittent Ethanol and Withdrawal: Implications for Mechanisms Underlying Excessive Ethanol Consumption. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.; Egli, M.; Cho, Y.E.; Song, B.J.; Noronha, A. Medications for alcohol use disorders: An overview. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 185, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakupcak, M.; Tull, M.T.; McDermott, M.J.; Kaysen, D.; Hunt, S.; Simpson, T. PTSD symptom clusters in relationship to alcohol misuse among Iraq and Afghanistan war veterans seeking post-deployment VA health care. Addict. Behav. 2010, 35, 840–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, S.V.; Batki, S.L.; Pennington, D.L. Working memory and alcohol demand relationships differ according to PTSD symptom severity among veterans with AUD. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 29, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, A.; Kalk, N.; Sewell, G.; Ritchie, C.W.; Lingford-Hughes, A. Alcohol and Alzheimer’s Disease-Does Alcohol Dependence Contribute to Beta-Amyloid Deposition, Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s Disease? Alcohol Alcohol. 2017, 52, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Rehm, J.; Anderson, P.; Manthey, J.; Shield, K.D.; Struzzo, P.; Wojnar, M.; Gual, A. Alcohol Use Disorders in Primary Health Care: What Do We Know and Where Do We Go? Alcohol Alcohol. 2016, 51, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungratanawanich, W.; Qu, Y.; Wang, X.; Essa, M.M.; Song, B.J. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and other adducts in aging-related diseases and alcohol-mediated tissue injury. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Adelson, P.D.; Andelic, N.; Bell, M.J.; Belli, A.; Bragge, P.; Brazinova, A.; Buki, A.; Chesnut, R.M.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 987–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, H.S.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.R. Diagnosis, prognosis, and clinical management of mild traumatic brain injury. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Naalt, J.; Timmerman, M.E.; de Koning, M.E.; van der Horn, H.J.; Scheenen, M.E.; Jacobs, B.; Hageman, G.; Yilmaz, T.; Roks, G.; Spikman, J.M. Early predictors of outcome after mild traumatic brain injury (UPFRONT): An observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weil, Z.M.; Corrigan, J.D.; Karelina, K. Alcohol Use Disorder and Traumatic Brain Injury. Alcohol Res. 2018, 39, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan, J.D. Substance abuse as a mediating factor in outcome from traumatic brain injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1995, 76, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachadourian, L.K.; Pilver, C.E.; Potenza, M.N. Trauma, PTSD, and binge and hazardous drinking among women and men: Findings from a national study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 55, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Huynh, J.; Hylin, M.J.; O’Malley, J.J.; Perez, A.; Moore, A.N.; Dash, P.K. Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Reduces Spine Density of Projection Neurons in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Impairs Extinction of Contextual Fear Memory. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskalakis, N.P.; Rijal, C.M.; King, C.; Huckins, L.M.; Ressler, K.J. Recent Genetics and Epigenetics Approaches to PTSD. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilpin, N.W.; Weiner, J.L. Neurobiology of comorbid post-traumatic stress disorder and alcohol-use disorder. Genes Brain Behav. 2017, 16, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, D.G.; Resnick, H.S.; Milanak, M.E.; Miller, M.W.; Keyes, K.M.; Friedman, M.J. National estimates of exposure to traumatic events and PTSD prevalence using DSM-IV and DSM-5 criteria. J. Trauma Stress 2013, 26, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.L.; Teesson, M.; Ross, J.; Peters, L. Trauma, PTSD, and substance use disorders: Findings from the Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Well-Being. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betthauser, L.M.; Brenner, L.A.; Cole, W.; Scher, A.I.; Schwab, K.; Ivins, B.J. A Clinical Evidence-Based Approach to Examine the Effects of mTBI and PTSD Symptoms on ANAM Performance in Recently Deployed Active Duty Soldiers: Results from the Warrior Strong Study. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2018, 33, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardier, C.H.; Rimmele, C.T.; Zintel, H. The magnitude and correlates of alcohol and drug use before traumatic brain injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltell, K.C.; Smith, R.L.; Kansky, J.; Cox, C.M.; Amstadter, A.B.; Dick, D.; Salvatore, J.E.; Berenz, E.C.; The Spit for Science Working Group. Posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms, relationship quality, and risky alcohol use among trauma-exposed students. Addict. Behav. 2020, 102, 106216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkiewitz, K.; Kranzler, H.R.; Hallgren, K.A.; O’Malley, S.S.; Falk, D.E.; Litten, R.Z.; Hasin, D.S.; Mann, K.F.; Anton, R.F. Drinking Risk Level Reductions Associated with Improvements in Physical Health and Quality of Life among Individuals with Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 2453–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmar, C.R.; Brown, A.D.; Qian, M.; Laska, E.; Siegel, C.; Li, M.; Abu-Amara, D.; Tsiartas, A.; Richey, C.; Smith, J.; et al. Speech-based markers for posttraumatic stress disorder in US veterans. Depress. Anxiety 2019, 36, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuens, M.; Van Hoofstadt, K.; Hoogmartens, O.; Van den Eede, N.; Sabbe, M. Pooled Urine Analysis at a Belgian Music Festival: Trends in Alcohol Consumption and Recreational Drug Use. Prehosp. Disaster Med. 2022, 37, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhinaraset, M.; Wigglesworth, C.; Takeuchi, D.T. Social and Cultural Contexts of Alcohol Use: Influences in a Social-Ecological Framework. Alcohol Res. 2016, 38, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, T.D.; Chou, S.P.; Grant, B.F. The performance of DSM-5 alcohol use disorder and quantity-frequency of alcohol consumption criteria: An item response theory analysis. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020, 216, 108299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanvisens, A.; Zuluaga, P.; Rubio, G.; Short, A.; Gual, A.; Alvarez, F.J.; Torrens, M.; Rodriguez de Fonseca, F.; Muga, R.; Estudio Coh, R.T.A. DSM-5 in patients seeking their first treatment for alcohol use disorder. Sex differences in the multicenter CohRTA study. Adicciones 2020, 32, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, T.; Mewton, L.; O’Dean, S.; Tibbetts, J.; Clay, P.; Isik, A.; Johnson, P.; McCraw, S.; Upton, E.; Kypri, K.; et al. DSM-5 and ICD-11 alcohol use disorder criteria in young adult regular drinkers: Lifetime prevalence and age of onset. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 229, 109184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DSM-5. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, R.; Panza, K.E.; Helm, J.; Angkaw, A.C.; Straus, E.; Norman, S.B. Psychosocial functioning in integrated treatment of co-occurring posttraumatic stress disorder and alcohol use disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 142, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ayoubi, H.; Brunault, P.; Barrault, S.; Mauge, D.; Baudin, G.; Ballon, N.; El-Hage, W. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Is Highly Comorbid with Adult ADHD in Alcohol Use Disorder Inpatients. J. Atten. Disord. 2021, 25, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, C.T.; Livingston, N.A.; Wong, M.M.; Rosen, R.C.; Marx, B.P.; Keane, T.M. Parallel process modeling of posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms and alcohol use severity in returning veterans. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2020, 34, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, S.K.; Davis, J.P.; Prindle, J.J.; Castro, C.A.; Pedersen, E.R. Associations between symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, pain, and alcohol use disorder among OEF/OIF/OND veterans. Addict. Behav. 2021, 122, 107031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.A. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2018, 392, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Roerecke, M.; Rehm, J. Cause-specific mortality risk in alcohol use disorder treatment patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, E.R.; Wanklyn, S.; Stasiewicz, P.R.; Coffey, S.F. PTSD symptom presentation among people with alcohol and drug use disorders: Comparisons by substance of abuse. Addict. Behav. 2018, 76, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.; Spencer-Harper, L.; Carson, C.; Palmer, E.; Hill, K.; Sorfleet, N.; Wessely, S.; Busuttil, W. Long-term responses to treatment in UK veterans with military-related PTSD: An observational study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignogna, K.M.; Bacanu, S.A.; Riley, B.P.; Wolen, A.R.; Miles, M.F. Cross-species alcohol dependence-associated gene networks: Co-analysis of mouse brain gene expression and human genome-wide association data. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0202063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenewald, P.J.; Mair, C. Heterogeneous Dose-Response Analyses of Alcohol Abuse and Dependence. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piniewska-Rog, D.; Heidegger, A.; Pospiech, E.; Xavier, C.; Pisarek, A.; Jarosz, A.; Wozniak, A.; Wojtas, M.; Phillips, C.; Kayser, M.; et al. Impact of excessive alcohol abuse on age prediction using the VISAGE enhanced tool for epigenetic age estimation in blood. Int. J. Legal Med. 2021, 135, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccini, T.; Ottonello, M.; Spigno, P.; Malovini, A.; Fiabane, E.; Roda, E.; Signorini, C.; Pistarini, C. Biomarkers for alcohol abuse/withdrawal and their association with clinical scales and temptation to drink. A prospective pilot study during 4-week residential rehabilitation. Alcohol 2021, 94, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Zion, Z.; Zeevi, Y.; Keynan, N.J.; Admon, R.; Kozlovski, T.; Sharon, H.; Halpern, P.; Liberzon, I.; Shalev, A.Y.; Benjamini, Y.; et al. Multi-domain potential biomarkers for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) severity in recent trauma survivors. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijdam, M.J.; Vermetten, E.; McFarlane, A.C. Toward staging differentiation for posttraumatic stress disorder treatment. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2023, 147, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, J.R.; Taffe, K.M.; Kochanek, P.M.; DeKosky, S.T. The antioxidant enzymes glutathione peroxidase and catalase increase following traumatic brain injury in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 146, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.J.; Abdelmegeed, M.A.; Cho, Y.E.; Akbar, M.; Rhim, J.S.; Song, M.K.; Hardwick, J.P. Contributing Roles of CYP2E1 and Other Cytochrome P450 Isoforms in Alcohol-Related Tissue Injury and Carcinogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1164, 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.Y.; Zhang, H.; Gatta, E.; Glover, E.J.; Pandey, S.C.; Lasek, A.W. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid (SAHA) Alleviates Depression-Like Behavior and Normalizes Epigenetic Changes in the Hippocampus During Ethanol Withdrawal. Alcohol 2019, 78, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsebaaly, J.; Dugast, E.; Favot, L.; Rabbaa Khabbaz, L.; Solinas, M.; Thiriet, N. Persistent Neuroadaptations in the Expression of Genes Involved in Cholesterol Homeostasis Induced by Chronic, Voluntary Alcohol Intake in Rats. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.M.; Hill-Kapturczak, N.; Lopez-Cruzan, M.; Alvarado, L.A.; Dwivedi, A.K.; Javors, M.A. Phosphatidylethanol in Postmortem Brain and Serum Ethanol at Time of Death. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 40, 2557–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Chen, D.; Ma, X.; Sudweeks, S.; Yorgason, J.T.; Gao, M.; Turner, D.; Eaton, J.B.; McIntosh, J.M.; Lukas, R.J.; et al. Alpha6-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is a highly sensitive target of alcohol. Neuropharmacology 2019, 149, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.W.; Maniates, H.; Wolf, E.J.; Logue, M.W.; Schichman, S.A.; Stone, A.; Milberg, W.; McGlinchey, R. CRP polymorphisms and DNA methylation of the AIM2 gene influence associations between trauma exposure, PTSD, and C-reactive protein. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 67, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; Xu, M.; Frank, J.A.; Luo, J. Role of MCP-1 and CCR2 in ethanol-induced neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the developing brain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, N.; Akbarpour, A.; Mors, K.; Voth, M.; Stormann, P.; Auner, B.; Lehnert, M.; Marzi, I.; Relja, B. Alcohol Intoxication Reduces Systemic Interleukin-6 Levels and Leukocyte Counts After Severe TBI Compared With Not Intoxicated TBI Patients. Shock 2016, 46, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoch, M.A.; Gorodetsky, E.; Hodgkinson, C.; Roy, A.; Goldman, D. Functional genetic variants that increase synaptic serotonin and 5-HT3 receptor sensitivity predict alcohol and drug dependence. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, J.S.; Simons, R.M.; O’Brien, C.; Stoltenberg, S.F.; Keith, J.A.; Hudson, J.A. PTSD, alcohol dependence, and conduct problems: Distinct pathways via lability and disinhibition. Addict. Behav. 2017, 64, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zai, C.C.; Manchia, M.; Zai, G.C.; Woo, J.; Tiwari, A.K.; de Luca, V.; Kennedy, J.L. Association study of BDNF and DRD3 genes with alcohol use disorder in Schizophrenia. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 671, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dretsch, M.N.; Williams, K.; Emmerich, T.; Crynen, G.; Ait-Ghezala, G.; Chaytow, H.; Mathura, V.; Crawford, F.C.; Iverson, G.L. Brain-derived neurotropic factor polymorphisms, traumatic stress, mild traumatic brain injury, and combat exposure contribute to postdeployment traumatic stress. Brain Behav. 2016, 6, e00392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Marchena, N.; Silva-Pena, D.; Martin-Velasco, A.I.; Villanua, M.A.; Araos, P.; Pedraz, M.; Maza-Quiroga, R.; Romero-Sanchiz, P.; Rubio, G.; Castilla-Ortega, E.; et al. Decreased plasma concentrations of BDNF and IGF-1 in abstinent patients with alcohol use disorders. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadnie, C.A.; Park, J.H.; Abdel Gawad, N.; Ho, A.M.; Hinton, D.J.; Choi, D.S. Gut-brain peptides in corticostriatal-limbic circuitry and alcohol use disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; He, L.; Vatsalya, V.; Ma, X.; Kim, S.; Mueller, E.G.; Feng, W.; McClain, C.J.; Zhang, X. Metabolomics analysis of urine from patients with alcohol-associated liver disease reveals dysregulated caffeine metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2023, 324, G142–G154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, R.; Suk, K.T. Microbiome and metabolomics in alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Huang, J.; Huang, S.; Wen, Y.; Lan, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, C.; Wang, Z.; Fan, N.; Shang, D. Combining Metabolomics and Interpretable Machine Learning to Reveal Plasma Metabolic Profiling and Biological Correlates of Alcohol-Dependent Inpatients: What About Tryptophan Metabolism Regulation? Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 760669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashem, M.A.; Sery, O.; Pow, D.V.; Rowlands, B.D.; Rae, C.D.; Balcar, V.J. Actions of Alcohol in Brain: Genetics, Metabolomics, GABA Receptors, Proteomics and Glutamate Transporter GLAST/EAAT1. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo-Berto, R.; Favretto, D.; Cecchetto, G.; Vincenti, M.; Kronstrand, R.; Ferrara, S.D.; Viel, G. Sensitivity and specificity of EtG in hair as a marker of chronic excessive drinking: Pooled analysis of raw data and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ther. Drug. Monit. 2014, 36, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo-Berto, R.; Viel, G.; Montisci, M.; Terranova, C.; Favretto, D.; Ferrara, S.D. Ethyl glucuronide concentration in hair for detecting heavy drinking and/or abstinence: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Legal Med. 2013, 127, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetto, L.; Perilli, M.; Cinquetti, A.; Giraudo, C.; Gardi, M.; Cecchetto, G.; Viel, G. Phosphatidylethanol in Maternal or Neonatal Blood to Detect Alcohol Exposure during Pregnancy: A Systematic Review. Life 2022, 12, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waszkiewicz, N.; Kratz, E.M.; Chojnowska, S.; Zalewska, A.; Zwierz, K.; Szulc, A.; Szajda, S.D.; Nestsiarovich, A.; Kapitau, A.; Kepka, A.; et al. Long-term changes of salivary exoglycosidases and their applicability as chronic alcohol-drinking and dependence markers. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 20, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmings, S.M.J.; Malan-Muller, S.; van den Heuvel, L.L.; Demmitt, B.A.; Stanislawski, M.A.; Smith, D.G.; Bohr, A.D.; Stamper, C.E.; Hyde, E.R.; Morton, J.T.; et al. The Microbiome in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Trauma-Exposed Controls: An Exploratory Study. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somvanshi, P.R.; Mellon, S.H.; Flory, J.D.; Abu-Amara, D.; Consortium, P.S.B.; Wolkowitz, O.M.; Yehuda, R.; Jett, M.; Hood, L.; Marmar, C.; et al. Mechanistic inferences on metabolic dysfunction in PTSD from an integrated model and multi-omic analysis: Role of glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 317, E879–E898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, M.; Essa, M.M.; Daradkeh, G.; Abdelmegeed, M.A.; Choi, Y.; Mahmood, L.; Song, B.J. Mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death in neurodegenerative diseases through nitroxidative stress. Brain Res. 2016, 1637, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla, M.E.; Rivera-Meza, M.; Berrios-Carcamo, P.; Cassels, B.K.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Israel, Y. (R)-Salsolinol, a product of ethanol metabolism, stereospecifically induces behavioral sensitization and leads to excessive alcohol intake. Addict. Biol. 2016, 21, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimatkin, S.M.; Pronko, S.P.; Vasiliou, V.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Deitrich, R.A. Enzymatic mechanisms of ethanol oxidation in the brain. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rungratanawanich, W.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Kawamoto, T.; Chidambaram, S.B.; Song, B.J. ALDH2 deficiency increases susceptibility to binge alcohol-induced gut leakiness, endotoxemia, and acute liver injury in mice through the gut-liver axis. Redox Biol. 2023, 59, 102577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromek, E.; Haduch, A.; Golembiowska, K.; Daniel, W.A. Cytochrome P450 mediates dopamine formation in the brain in vivo. J. Neurochem. 2011, 118, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissbrandt, H.; Bergquist, F.; Jonason, J.; Engberg, G. Inhibition of cytochrome P450 2E1 induces an increase in extracellular dopamine in rat substantia nigra: A new metabolic pathway? Synapse 2001, 40, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, V.E.; Walsh, M.J. Alcohol addiction and tetrahydropapaveroline. Science 1970, 169, 1105–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, C.L.; Myers, R.D. Preference for alcohol evoked by tetrahydropapaveroline (THP) chronically infused in the cerebral ventricle of the rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1977, 7, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, V.E.; Walsh, M.J. Alcohol, amines, and alkaloids: A possible biochemical basis for alcohol addiction. Science 1970, 167, 1005–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, W.J.; Li, T.K.; Deitrich, R.A.; Zimatkin, S.; Smith, B.R.; Rodd-Henricks, Z.A. Involvement of acetaldehyde in alcohol addiction. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodd-Henricks, Z.A.; Melendez, R.I.; Zaffaroni, A.; Goldstein, A.; McBride, W.J.; Li, T.K. The reinforcing effects of acetaldehyde in the posterior ventral tegmental area of alcohol-preferring rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 72, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliou, V.; Ziegler, T.L.; Bludeau, P.; Petersen, D.R.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Deitrich, R.A. CYP2E1 and catalase influence ethanol sensitivity in the central nervous system. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2006, 16, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, Y.; Karahanian, E.; Ezquer, F.; Morales, P.; Ezquer, M.; Rivera-Meza, M.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Quintanilla, M.E. Acquisition, Maintenance and Relapse-Like Alcohol Drinking: Lessons from the UChB Rat Line. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quertemont, E. Genetic polymorphism in ethanol metabolism: Acetaldehyde contribution to alcohol abuse and alcoholism. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, K.H.; Shatnawi, A.; Al-Qudah, M.A.; Alfaqih, M.A. Edaravone prevents memory impairment in an animal model of post-traumatic distress. Behav. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Alzoubi, K.H.; Khabour, O.F.; Ahmed, M. Pentoxifylline prevents post-traumatic stress disorder induced memory impairment. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 139, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsett, C.R.; McGuire, J.L.; DePasquale, E.A.; Gardner, A.E.; Floyd, C.L.; McCullumsmith, R.E. Glutamate Neurotransmission in Rodent Models of Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrak, C.S.; Wilkinson, C.S.; Blount, H.L.; Schwendt, M.; Knackstedt, L.A. The role of mGlu receptors in susceptibility to stress-induced anhedonia, fear, and anxiety-like behavior. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2023, 168, 221–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ureña-Peralta, J.R.; Alfonso-Loeches, S.; Cuesta-Diaz, C.M.; García-García, F.; Guerri, C. Deep sequencing and miRNA profiles in alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and the TLR4 response in mice cerebral cortex. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordillo, P.P.; Sordillo, L.A.; Helson, L. Bifunctional role of pro-inflammatory cytokines after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2016, 30, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, M.R.; Liu, J.; Zou, Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Zuo, Y.X.; Wang, T.H. Propofol administration improves neurological function associated with inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines in adult rats after traumatic brain injury. Neuropeptides 2016, 58, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraly, S.A.; Nievergelt, C.M.; Maihofer, A.X.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Biswas, N.; Agorastos, A.; O’Connor, D.T.; Baker, D.G.; Marine Resiliency Study Team. Assessment of plasma C-reactive protein as a biomarker of posttraumatic stress disorder risk. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Cao, C.; Liu, P.; Luo, S.; Duan, Q.; Ellenbroek, B.; Zhang, X. Characteristics of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines alteration in PTSD patients exposed to a deadly earthquake. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 248, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlop, B.W.; Wong, A. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in PTSD: Pathophysiology and treatment interventions. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 89, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhart, M.; Wand, G.S. Stress, alcohol and drug interaction: An update of human research. Addict. Biol. 2009, 14, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, E.P.; Logrip, M.L.; Koob, G.F. Corticotropin releasing factor: A key role in the neurobiology of addiction. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 35, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirven, B.C.J.; Homberg, J.R.; Kozicz, T.; Henckens, M. Epigenetic programming of the neuroendocrine stress response by adult life stress. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 59, R11–R31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosen, E.; Littlefield, A.K.; Schumacher, J.A.; Stasiewicz, P.R.; Coffey, S.F. Treatment of co-occurring PTSD-AUD: Effects of exposure-based and non-trauma focused psychotherapy on alcohol and trauma cue-reactivity. Behav. Res. Ther. 2014, 61, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Wang, L.P.; Tsien, J.Z. Dopamine Rebound-Excitation Theory: Putting Brakes on PTSD. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Yang, Q.; Tong, G.; Fu, E.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Akbar, M.; Song, B.J.; Wang, X. Therapeutic strategies of small molecules in the microbiota-gut-brain axis for alcohol use disorder. Drug. Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinoff, B. Neurobiologic processes in drug reward and addiction. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2004, 12, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemm, S.E.; Sinha, R. Drug-induced stress responses and addiction risk and relapse. Neurobiol. Stress. 2019, 10, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S.C.; Schick, M.R.; Weyandt, L.L.; Sullivan, T.P.; Saint-Eloi Cadely, H.; Weiss, N.H. Posttraumatic stress as a moderator of the association between HPA-axis functioning and alcohol use disorder among a community sample of women currently experiencing intimate partner violence. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2023, 31, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, M.I.; Moser, D.A.; Manini, A.; Suardi, F.; Sancho-Rossignol, A.; Torrisi, R.; Rossier, M.F.; Ansermet, F.; Dayer, A.G.; Rusconi-Serpa, S.; et al. Effects of interpersonal violence-related post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) on mother and child diurnal cortisol rhythm and cortisol reactivity to a laboratory stressor involving separation. Horm. Behav. 2017, 90, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyan, V.; Chakravarthi, S.; Jegasothy, R.; Seng, W.Y.; Fuloria, N.K.; Fuloria, S.; Hazarika, I.; Das, A. Alcohol-associated liver disease: A review on its pathophysiology, diagnosis and drug therapy. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, T.; Kirschbaum, C. Analysis of cortisol in hair—State of the art and future directions. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Heuvel, L.L.; Stalder, T.; du Plessis, S.; Suliman, S.; Kirschbaum, C.; Seedat, S. Hair cortisol levels in posttraumatic stress disorder and metabolic syndrome. Stress 2020, 23, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, T.; Steudte-Schmiedgen, S.; Alexander, N.; Klucken, T.; Vater, A.; Wichmann, S.; Kirschbaum, C.; Miller, R. Stress-related and basic determinants of hair cortisol in humans: A meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 77, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, T.; Kirschbaum, C.; Heinze, K.; Steudte, S.; Foley, P.; Tietze, A.; Dettenborn, L. Use of hair cortisol analysis to detect hypercortisolism during active drinking phases in alcohol-dependent individuals. Biol. Psychol. 2010, 85, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.L.; Nixon, S.J. Retrospective Hair Cortisol Concentrations from Pretreatment to Early Recovery in Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol Alcohol. 2021, 56, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerlhag, E. Alcohol-mediated behaviours and the gut-brain axis; with focus on glucagon-like peptide-1. Brain Res. 2020, 1727, 146562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallof, D.; Kalafateli, A.L.; Jerlhag, E. Brain region-specific neuromedin U signalling regulates alcohol-related behaviours and food intake in rodents. Addict. Biol. 2019, 25, e12764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerlhag, E. Gut-brain axis and addictive disorders: A review with focus on alcohol and drugs of abuse. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 196, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farokhnia, M.; Faulkner, M.L.; Piacentino, D.; Lee, M.R.; Leggio, L. Ghrelin: From a gut hormone to a potential therapeutic target for alcohol use disorder. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 204, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, K.S.; Peterson, V.L.; Halfon, O.; Ahern, G.; Fouhy, F.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Boutrel, B. Gut microbiome correlates with altered striatal dopamine receptor expression in a model of compulsive alcohol seeking. Neuropharmacology 2018, 141, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Chakraborty, N.; Muhie, S.; Hoke, A.; Hammamieh, R.; Jett, M. Altered fecal microbiota composition in all male aggressor-exposed rodent model simulating features of post-traumatic stress disorder. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Sikaroodi, M.; Fagan, A.; Heuman, D.; Gilles, H.; Gavis, E.A.; Fuchs, M.; Gonzalez-Maeso, J.; Nizam, S.; Gillevet, P.M.; et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder is associated with altered gut microbiota that modulates cognitive performance in veterans with cirrhosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G661–G669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassouneh, R.; Bajaj, J.S. Gut Microbiota Modulation and Fecal Transplantation: An Overview on Innovative Strategies for Hepatic Encephalopathy Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Reddy, K.R.; Tandon, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Kamath, P.S.; O’Leary, J.G.; Wong, F.; Lai, J.; Vargas, H.; Thuluvath, P.J.; et al. Association of serum metabolites and gut microbiota at hospital admission with nosocomial infection development in patients with cirrhosis. Liver Transpl. 2022, 28, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Alikunju, S.; Abdul-Muneer, P.M. NADPH oxidase-induced activation of transforming growth factor-beta-1 causes neuropathy by suppressing antioxidant signaling pathways in alcohol use disorder. Neuropharmacology 2022, 213, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, D.E.; Luk, H.Y.; Vingren, J.L. Alcohol, Resistance Exercise, and mTOR Pathway Signaling: An Evidence-Based Narrative Review. Biomolecules 2022, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetreno, R.P.; Qin, L.; Coleman, L.G., Jr.; Crews, F.T. Increased Toll-like Receptor-MyD88-NFkappaB-Proinflammatory neuroimmune signaling in the orbitofrontal cortex of humans with alcohol use disorder. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 45, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Poulsen, K.L.; Sanz-Garcia, C.; Huang, E.; McMullen, M.R.; Roychowdhury, S.; Dasarathy, S.; Nagy, L.E. MLKL-dependent signaling regulates autophagic flux in a murine model of non-alcohol-associated fatty liver and steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.P.; Reagan, A.; Logue, M.W.; Hayes, S.M.; Sadeh, N.; Miller, D.R.; Verfaellie, M.; Wolf, E.J.; McGlinchey, R.E.; Milberg, W.P.; et al. BDNF genotype is associated with hippocampal volume in mild traumatic brain injury. Genes Brain Behav. 2018, 17, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chu, H.; Kong, L.; Yin, L.; Ma, H. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Increases Synaptic Protein Levels via the MAPK/Erk Signaling Pathway and Nrf2/Trx Axis Following the Transplantation of Neural Stem Cells in a Rat Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3073–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.R.; Corsi-Travali, S.; Neumeister, A. The Role of BDNF-TrkB Signaling in the Pathogenesis of PTSD. J. Depress. Anxiety 2013, S4, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Takei, S.; Morinobu, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Fuchikami, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Yamawaki, S. Enhanced hippocampal BDNF/TrkB signaling in response to fear conditioning in an animal model of posttraumatic stress disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hutchison, K.E.; Calhoun, V.D.; Claus, E.D.; Turner, J.A.; Sui, J.; Liu, J. CREB-BDNF pathway influences alcohol cue-elicited activation in drinkers. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 3007–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.P.; Yu, X.J.; Qian, H.; Wei, L.; Lv, J.Y.; Xu, X.H. Chronic alcoholism-mediated impairment in the medulla oblongata: A mechanism of alcohol-related mortality in traumatic brain injury? Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 67, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, D.; Berger, A. Targeting the intracellular signaling “STOP” and “GO” pathways for the treatment of alcohol use disorders. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 1727–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reker, A.N.; Oliveros, A.; Sullivan, J.M., 3rd; Nahar, L.; Hinton, D.J.; Kim, T.; Bruner, R.C.; Choi, D.S.; Goeders, N.E.; Nam, H.W. Neurogranin in the nucleus accumbens regulates NMDA receptor tolerance and motivation for ethanol seeking. Neuropharmacology 2018, 131, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulisiak, C.T.; Harris, R.A.; Ponomarev, I. DNA modifications in models of alcohol use disorders. Alcohol 2017, 60, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gelernter, J. Review: DNA methylation and alcohol use disorders: Progress and challenges. Am. J. Addict. 2017, 26, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnie, M.; Morrison, R.; Camara, R.; Strauss, K.I. Temporal changes of cytochrome P450 (Cyp) and eicosanoid-related gene expression in the rat brain after traumatic brain injury. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seah, C.; Breen, M.S.; Rusielewicz, T.; Bader, H.N.; Xu, C.; Hunter, C.J.; McCarthy, B.; Deans, P.J.M.; Chattopadhyay, M.; Goldberg, J.; et al. Modeling gene x environment interactions in PTSD using human neurons reveals diagnosis-specific glucocorticoid-induced gene expression. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnsack, J.P.; Teppen, T.; Kyzar, E.J.; Dzitoyeva, S.; Pandey, S.C. The lncRNA BDNF-AS is an epigenetic regulator in the human amygdala in early onset alcohol use disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gelernter, J.; Zhang, H. Differential Expression of miR-130a in Postmortem Prefrontal Cortex of Subjects with Alcohol Use Disorders. J. Addict. Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 18179. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, P.Y.; Tong, L.; Li, M.D.; Fu, C.H.; Peng, J.B.; Ji, L.L. miR-142 downregulation alleviates rat PTSD-like behaviors, reduces the level of inflammatory cytokine expression and apoptosis in hippocampus, and upregulates the expression of fragile X mental retardation protein. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutte, D.; Calhoun, V.D.; Chen, J.; Sabbineni, A.; Hutchison, K.; Liu, J. Association of genetic copy number variations at 11 q14.2 with brain regional volume differences in an alcohol use disorder population. Alcohol 2012, 46, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilker, S.; Schneider, A.; Conrad, D.; Pfeiffer, A.; Boeck, C.; Lingenfelder, B.; Freytag, V.; Vukojevic, V.; Vogler, C.; Milnik, A.; et al. Genetic variation is associated with PTSD risk and aversive memory: Evidence from two trauma-Exposed African samples and one healthy European sample. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, A.; Aksan, B.; Heuvel, F.O.; Forstner, P.; Sinske, D.; Rehman, R.; Palmer, A.; Ludolph, A.; Huber-Lang, M.; Bockers, T.; et al. Neuroprotective effect of acute ethanol intoxication in TBI is associated to the hierarchical modulation of early transcriptional responses. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 302, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lori, A.; Schultebraucks, K.; Galatzer-Levy, I.; Daskalakis, N.P.; Katrinli, S.; Smith, A.K.; Myers, A.J.; Richholt, R.; Huentelman, M.; Guffanti, G.; et al. Transcriptome-wide association study of post-trauma symptom trajectories identified GRIN3B as a potential biomarker for PTSD development. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, C.; Tolstrup, J.S.; Sorensen, H.J.; Pisinger, V.S.C.; Becker, U. Parental alcohol use disorder with and without other mental disorders and offspring alcohol use disorder. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2019, 139, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrinli, S.; King, A.P.; Duval, E.R.; Smith, A.K.; Rajaram, N.; Liberzon, I.; Rauch, S.A.M. DNA methylation GrimAge acceleration in US military veterans with PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023, 48, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Dong, G.; Luo, H.; Cao, J.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Feng, Y.Q.; Yue, J. Induction of brain CYP2E1 by chronic ethanol treatment and related oxidative stress in hippocampus, cerebellum, and brainstem. Toxicology 2012, 302, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heit, C.; Dong, H.; Chen, Y.; Thompson, D.C.; Deitrich, R.A.; Vasiliou, V.K. The role of CYP2E1 in alcohol metabolism and sensitivity in the central nervous system. Subcell. Biochem. 2013, 67, 235–247. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmegeed, M.A.; Banerjee, A.; Jang, S.; Yoo, S.H.; Yun, J.W.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Keshavarzian, A.; Song, B.J. CYP2E1 potentiates binge alcohol-induced gut leakiness, steatohepatitis, and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, B.J.; Shoaf, S.E.; Jeong, K.S.; Song, B.J. Induction of CYP2E1 in liver, kidney, brain and intestine during chronic ethanol administration and withdrawal: Evidence that CYP2E1 possesses a rapid phase half-life of 6 hours or less. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 205, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.J.; Akbar, M.; Abdelmegeed, M.A.; Byun, K.; Lee, B.; Yoon, S.K.; Hardwick, J.P. Mitochondrial dysfunction and tissue injury by alcohol, high fat, nonalcoholic substances and pathological conditions through post-translational protein modifications. Redox Biol. 2014, 3, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguet, E.; Ozdarska, K.; Moroy, G.; Jeanblanc, J.; Naassila, M. Class I HDAC Inhibitors: Potential New Epigenetic Therapeutics for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 1745–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzler, H.R.; Zhou, H.; Kember, R.L.; Vickers Smith, R.; Justice, A.C.; Damrauer, S.; Tsao, P.S.; Klarin, D.; Baras, A.; Reid, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol consumption and use disorder in 274,424 individuals from multiple populations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolentino, N.J.; Wierenga, C.E.; Hall, S.; Tapert, S.F.; Paulus, M.P.; Liu, T.T.; Smith, T.L.; Schuckit, M.A. Alcohol effects on cerebral blood flow in subjects with low and high responses to alcohol. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheerin, C.M.; Lind, M.J.; Bountress, K.; Nugent, N.R.; Amstadter, A.B. The Genetics and Epigenetics of PTSD: Overview, Recent Advances, and Future Directions. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2017, 14, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacker, C.J.; Frye, M.A.; Morava, E.; Kozicz, T.; Veldic, M. A Review of Epigenetics of PTSD in Comorbid Psychiatric Conditions. Genes 2019, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, A.; Jung, J.; Longley, M.; Rosoff, D.B.; Charlet, K.; Muench, C.; Lee, J.; Hodgkinson, C.A.; Goldman, D.; Horvath, S.; et al. Epigenetic aging is accelerated in alcohol use disorder and regulated by genetic variation in APOL2. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deak, J.D.; Miller, A.P.; Gizer, I.R. Genetics of alcohol use disorder: A review. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2019, 27, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khantzian, E.J. Addiction as a self-regulation disorder and the role of self-medication. Addiction 2013, 108, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khantzian, E.J. Commentary: It Is Not About Supply, It Is About Demand: Why the Self-Medication Hypotheses Is Still So Important. Am. J. Addict. 2021, 30, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Berardis, D.; Vellante, F.; Pettorruso, M.; Lucidi, L.; Tambelli, A.; Di Muzio, I.; Gianfelice, G.; Ventriglio, A.; Fornaro, M.; Serafini, G.; et al. Suicide and Genetic Biomarkers: Toward Personalized Tailored-treatment with Lithium and Clozapine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 3293–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoratto, F.; Sbriccoli, M.; Martinelli, A.; Glennon, J.C.; Macri, S.; Laviola, G. Intranasal oxytocin administration promotes emotional contagion and reduces aggression in a mouse model of callousness. Neuropharmacology 2018, 143, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigos, C.; Chrousos, G.P. Physiology of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in health and dysregulation in psychiatric and autoimmune disorders. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 1994, 23, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Fagan, A.; McGeorge, S.; Sterling, R.K.; Rogal, S.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Area Deprivation Index and Gut-Brain Axis in Cirrhosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, e00495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Baron, D.; Jalali, R.; Modestino, E.J.; Steinberg, B.; Elman, I.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Gold, M.S. Polygenic and multi locus heritability of alcoholism: Novel therapeutic targets to overcome psychological deficits. J. Syst. Integr. Neurosci. 2020, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballway, J.W.; Song, B.J. Translational Approaches with Antioxidant Phytochemicals against Alcohol-Mediated Oxidative Stress, Gut Dysbiosis, Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, and Fatty Liver Disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Sim, Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Kwun, I.S.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.I.; Baek, M.C.; Akbar, M.; Seo, W.; et al. Ellagic Acid Prevents Binge Alcohol-Induced Leaky Gut and Liver Injury through Inhibiting Gut Dysbiosis and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zack Ishikawa, R.; Steere, R.; Conteh, N.; Cramer, M.A.; Rao, V.; Sprich, S.; Cohen, J.N. Treating PTSD and Alcohol Use Disorder: Concurrent Cognitive Processing Therapy and Psychopharmacology. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2022, 84, 22ct14636. [Google Scholar]
- Lucidi, L.; Pettorruso, M.; Vellante, F.; Di Carlo, F.; Ceci, F.; Santovito, M.C.; Di Muzio, I.; Fornaro, M.; Ventriglio, A.; Tomasetti, C.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Bipolar Disorder: An Overview on a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Diagnostic Criteria or Characteristics |
|---|---|
| The diagnostic criteria of AUD (DSM-5) | The DSM-5 defines AUD as a problematic pattern of alcohol use leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, as manifested by at least 2 of the following 11 symptoms occurring within 12-months [38,39,40].
|
| The diagnostic criteria of PTSD (DSM-5) | Under DSM-5, for those older than six years of age, PTSD includes four clusters of symptoms [41]:
|
| The characteristics of AUD/PTSD | The main characteristics of comorbidity between PTSD and AUD following TBI:
|
| Change Composition | Effect | State | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolism/Pharmacokinetics | |||
| Catalase | Ethanol oxidation in cortical brain tissue↑ | PTSD | [56] |
| CYP2E1 | Oxidative alcohol and acetaldehyde metabolism↑ | AUD, AUD/PTSD | [57] |
| Glutamate | Forebrain reward circuit; Forebrain glutamate↑ | AUD, AUD/PTSD | [58] |
| Cholesterol | Synaptogenesis, and synaptic communication↓ | AUD | [59] |
| Phosphatidylethanol | Brain lipid membranes | AUD | [60] |
| alpha 6-nicotinic acetylcholine | Target sensitivity↓ | AUD | [61] |
| Inflammatory factors | |||
| CRP | CRP levels in the clinically elevated range↑ | PTSD, AUD/PTSD | [62] |
| TLR4 | Microglia activation/neuroinflammation↑ | AUD | [63] |
| IL-6 | Immunosuppressive effects↑ | PTSD | [64] |
| Neuroendocrine components | |||
| 5-HT | Receptor responsiveness↑ Dopamine transmission↑ | AUD | [65] |
| Serotonin transporter | Moderate associations between TBI and PTSD | PTSD | [66] |
| BDNF Val66Met | Alcohol dependence | AUD | [67] |
| BDNF Met/Met genotype | Post-deployment PTSD score changes | PTSD | [68] |
| IGF-1 | Plasma concentrations↓ | AUD/PTSD | [69] |
| Gut-brain peptides | Regulate addictive behaviors | AUD/PTSD | [70] |
| Genes | Cause | State | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNA | |||
| MCP-1 | Methylation changes | Chronic AUD | [143] |
| CYP2E1 | Gene expression changes | Chronic AUD hippocampus ↑ | [144] |
| SNP changes | Epigenetic changes | PTSD | [62] |
| Polygenic | Induced gene changes | PTSD | [145] |
| Methylation | Gene changes | Higher risk PTSD | [143] |
| RNA | |||
| lncRNAs | Synaptic plasticity | Adolescence | [146] |
| microRNAs | Neuroadaptations | Chronic AUD | [147] |
| miR-130a | miRNA expression alters | Prefrontal cortex AUD | [147] |
| miR-142 | Neuroinflammation ↓ | Alleviate PTSD | [148] |
| Chromosome | |||
| 11q14.2 | Brain structural variation | AUD behavior | [149] |
| rs3852144 | Emotional memory formation | PTSD development | [150] |
| Transcriptomics and genetics | |||
| Atf3, c-Fos, Egr1, Npas4 | Reduced downregulation | AUD after TBI | [151] |
| GRIN3B | mRNA level | Biomarker of PTSD | [152] |
| Gadd45b, Gadd45c | Upregulation | TBI | [151] |
| Parental AUD | More likely offspring AUD | AUD | [153] |
| Subcategories | Characteristics of Participants or Animals | Assessments and Tests | Main DATA Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epidemiological data | A representative US non-institutionalized civilian adult (≥18 years) sample (N = 36,309) as the 2012-2013 NESARC-III. | DSM-5 for AUD | AUD prevalence of 12-months and lifetime were 13.9% and 29.1%, respectively. | [12] |
| A national sample of US adults (N = 2953) recruited from an online panel. | DSM-5 for PTSD | PTSD prevalence of lifetime, past 12-months, and past 6-months was 8.3%, 4.7%, and 3.8%, respectively. | [29] | |
| A stratified sample of 10,641 participants as part of the Australian national survey of mental health and wellbeing. | The composite international diagnostic interview | AUD is responsible for 24.1% of substance-use problems in PTSD. (DSM-substance-use disorders and ICD-10 personality disorders). | [30] | |
| Metabolism data | Rat cortical contusion model. | The activity of catalase | Three-fold increase in catalase activities in a time course. | [56] |
| The enzymes of ethanol oxidation in the homogenates from the perfused brains of rats and mice. | Gas chromatography | About 60% of the ethanol oxidation process in rodent brains may be attributed to catalase. | [83] | |
| Severe TBI in rats. | Microdialysis determination | Extracellular glutamate levels increased 9-fold compared with uninjured control rats. | [97] | |
| Inflammatory factor data | A total of 2600 warzone-deployed marines. | Plasma CRP concentration | Each 10-fold increment in CRP concentration was associated with an odds ratio of a nonzero outcome (presence vs. absence of any PTSD symptoms) of 1.51- and 1-fold increase in outcome with a nonzero value (extent of symptoms when present) of 1.06. | [102] |
| C57BL/6 mice and mice deficient in MCP-1 exposed to ethanol. | MCP-1 levels | Ethanol-induced microglial activation, neuroinflammation, and a drastic increase in the mRNA and protein levels of MCP-1. | [63] | |
| Patients with an injury severity score and abbreviated injury scale of the head of at least 3 were included upon arrival in the emergency room and grouped according to positive BAC (>0.5%, BAC) vs. less than 0.5% alcohol (no BAC). | Systemic IL-6 levels | Systemic IL-6 levels and leukocyte counts (IL-6: 65.0 ± 8.0 vs. 151.8 ± 22.3; leukocytes: 10.2 ± 0.9 vs. 13.2 ± 0.8, both p < 0.05) were significantly lower in BAC-positive patients. | [64] | |
| Neuroendocrine component data | A total of 635 African-American substance-dependent men were recruited. | 5-HT levels,5-HT transporter gene | The HTR3B Ser129 allele and low 5-HTTLPR activity had an additive effect on alcohol + drug dependence (OR = 6.0 (2.1–16.6)) that accounted for 13% of the variance. | [65] |
| Both pre- and post-deployment data on 231 of 458 soldiers were analyzed. | BDNF Met/Met genotype | The BDNF Met/Met genotype accounted for 22% of the variance of post-deployment PTSD scores (R (2) = 0.22, p < 0.001). | [68] | |
| Abstinent AUD patients (N = 91) and healthy control subjects (N = 55). | Plasma concentrations of BDNF, IGF-1, and IGFBP-3 | AUD patients displayed a high prevalence of dual diagnosis (39.3%) and comorbid substance-use disorders (40.7%). Plasma BDNF and IGF-1 concentrations were significantly lower in the alcohol group than in the control group (p < 0.001). | [69] | |
| Genetic data | Genome-wide miRNA and mRNA expression were examined in postmortem PFCs of 23 European and Australian AUD cases and 23 matched controls using the Illumina HumanHT-12 v4 Expression BeadChip array. | Target gene prediction, gene set enrichment analysis, and DAVID functional annotation clustering analysis | Two miRNAs and 787 coding genes were differentially expressed in the PFC of AUD cases. Downregulation of miR-130a may lead to altered expression of a number of genes in the PFC of AUD. | [147] |
| A total of 924 Northern Ugandan rebel war survivors; identified seven suggestively significant SNPs; p ≤ 1 × 10−5 for lifetime PTSD risk. | Genome-wide association studies | Emotional memory formation seems to decline with the increasing number of rs3852144 G-alleles, rendering individuals more resilient to PTSD development. | [150] | |
| Danish nationwide registers; 15,477 offspring with parental AUD and 154,392 reference individuals from the general population. | Parental AUD was defined as registration for AUD treatment. AUD in offspring was identified from medical, pharmacy, treatment, and cause of death registers. | Paternal AUD plus other mental disorders (hazard ratio (HR) = 2.27, 95% confidence interval (CI): 2.10–2.46) and paternal AUD alone (HR = 2.21, 95% CI: 2.07–2.36) were associated with higher offspring AUD risk. | [153] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Luo, C.; Zhou, E.W.; Sandhu, A.F.; Yuan, X.; Williams, G.E.; Cheng, J.; Sinha, B.; Akbar, M.; Bhattacharya, P.; et al. Molecular Toxicology and Pathophysiology of Comorbid Alcohol Use Disorder and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Associated with Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108805
Wang Z, Luo C, Zhou EW, Sandhu AF, Yuan X, Williams GE, Cheng J, Sinha B, Akbar M, Bhattacharya P, et al. Molecular Toxicology and Pathophysiology of Comorbid Alcohol Use Disorder and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Associated with Traumatic Brain Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108805
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zufeng, Chengliang Luo, Edward W. Zhou, Aaron F. Sandhu, Xiaojing Yuan, George E. Williams, Jialu Cheng, Bharati Sinha, Mohammed Akbar, Pallab Bhattacharya, and et al. 2023. "Molecular Toxicology and Pathophysiology of Comorbid Alcohol Use Disorder and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Associated with Traumatic Brain Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108805
APA StyleWang, Z., Luo, C., Zhou, E. W., Sandhu, A. F., Yuan, X., Williams, G. E., Cheng, J., Sinha, B., Akbar, M., Bhattacharya, P., Zhou, S., Song, B.-J., & Wang, X. (2023). Molecular Toxicology and Pathophysiology of Comorbid Alcohol Use Disorder and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Associated with Traumatic Brain Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108805









