A Review on Cyclodextrins/Estrogens Inclusion Complexes
Abstract
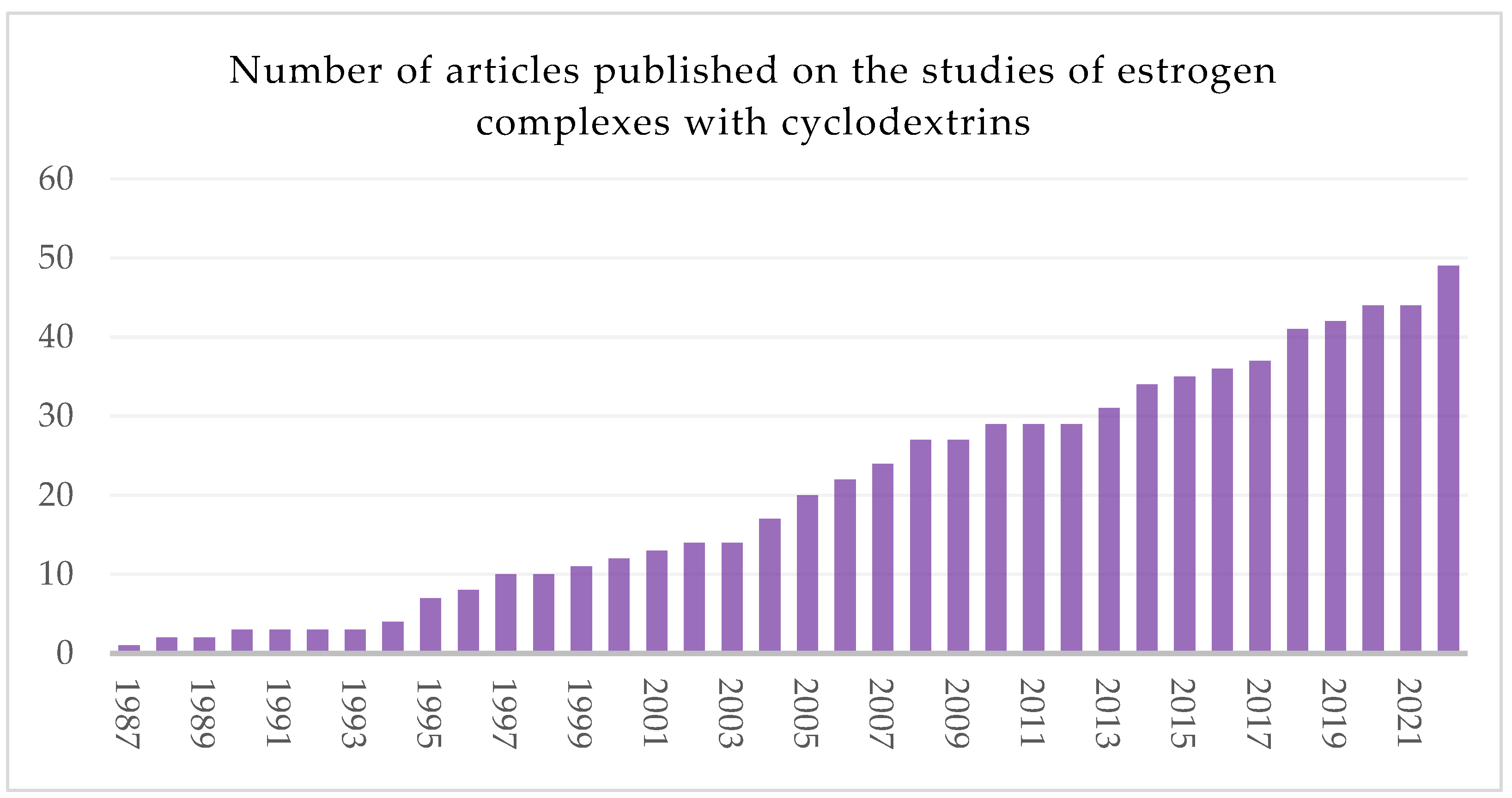
1. Introduction
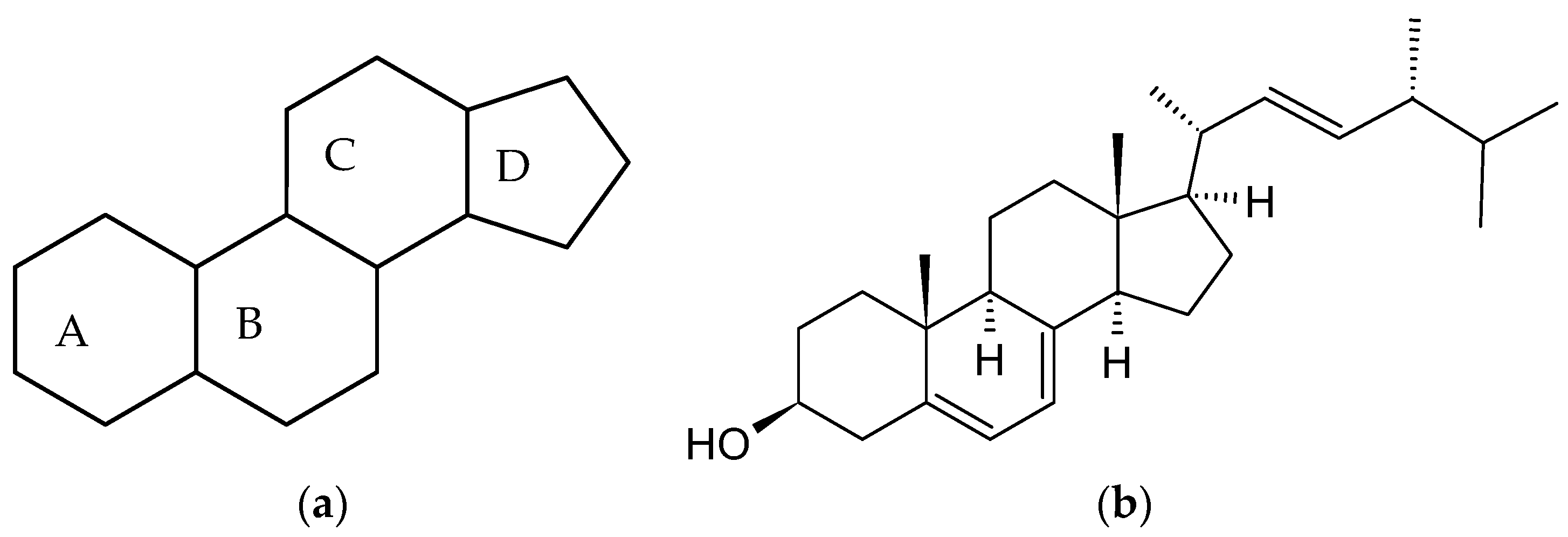
2. Estrogens
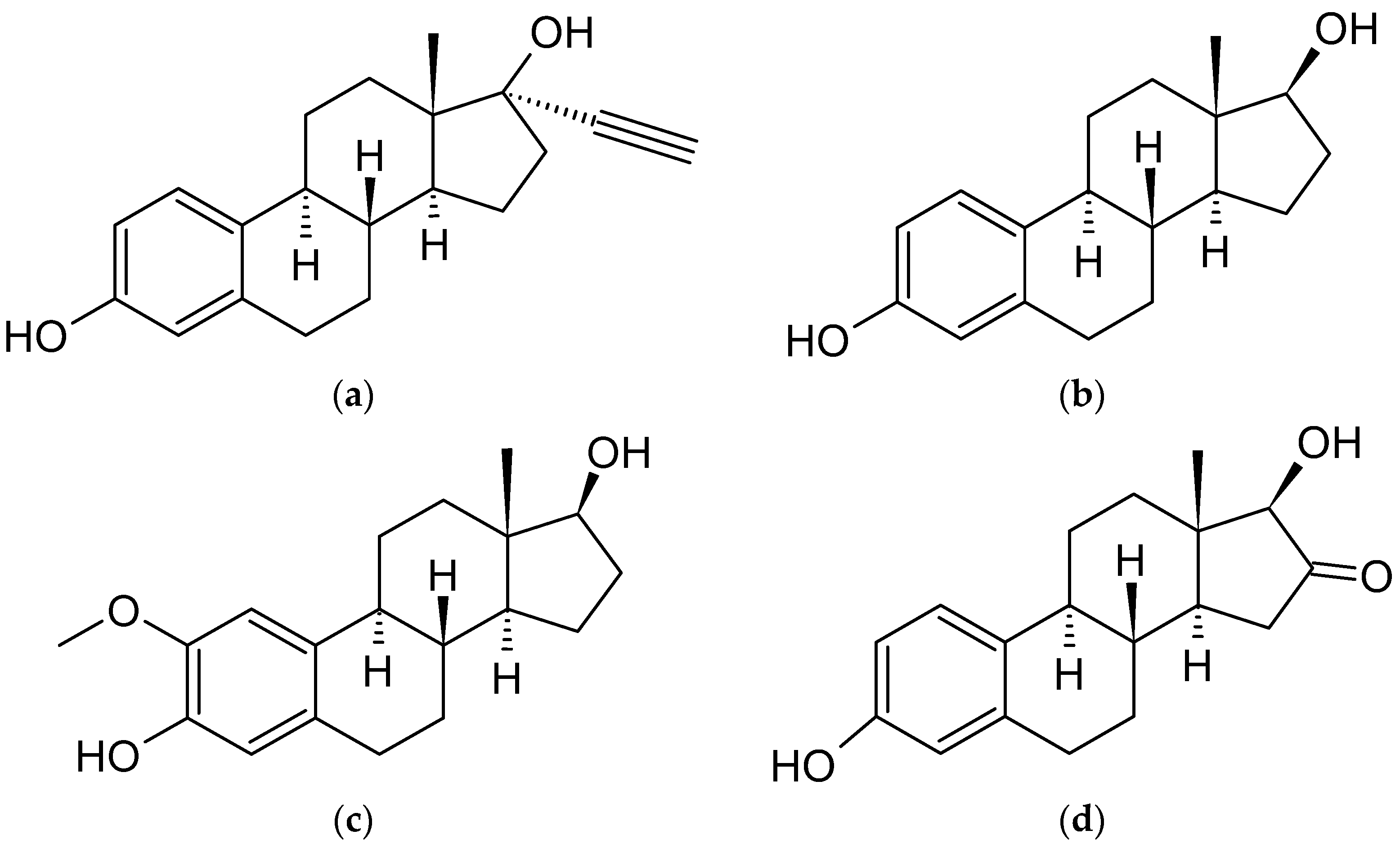
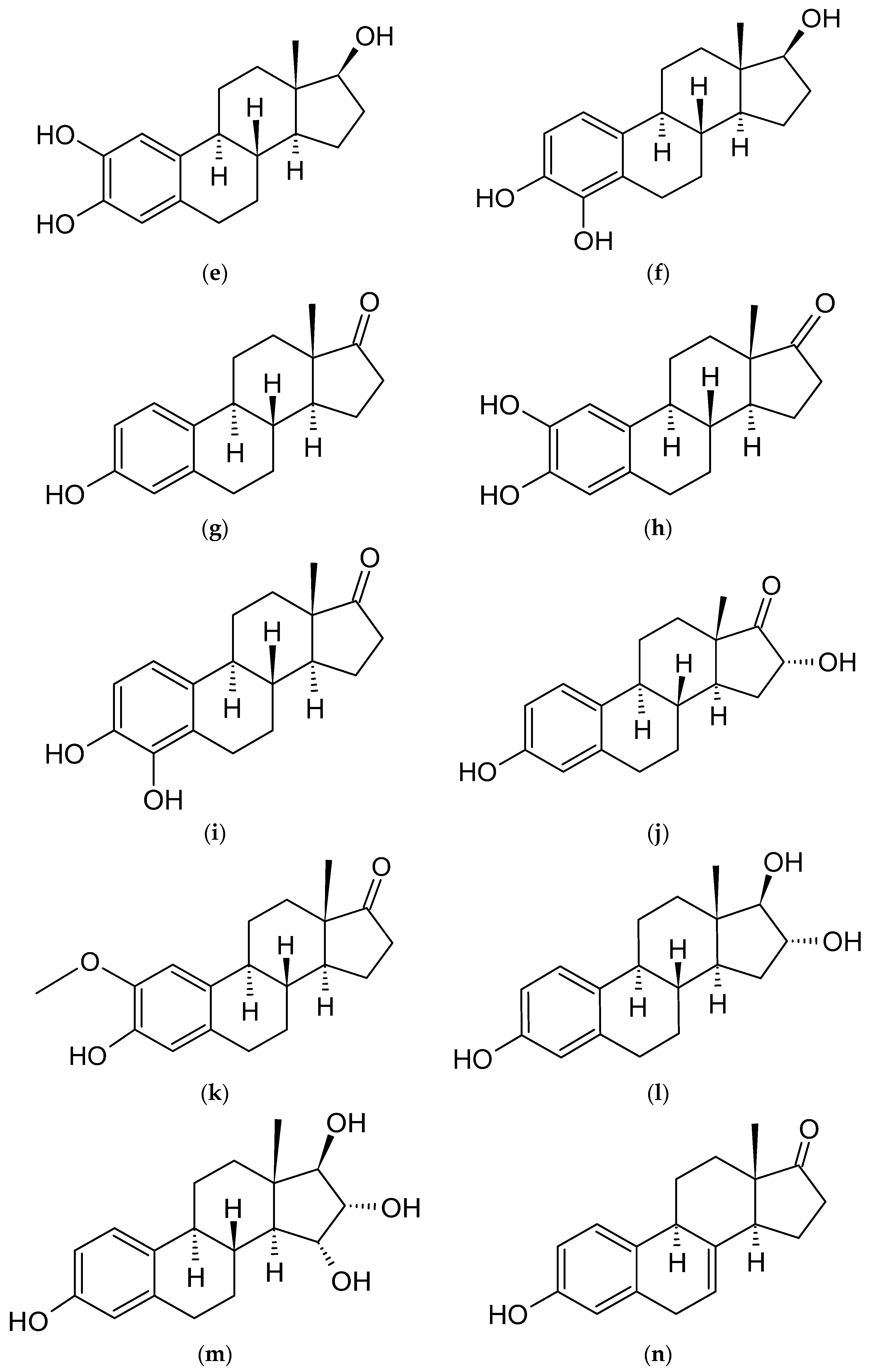
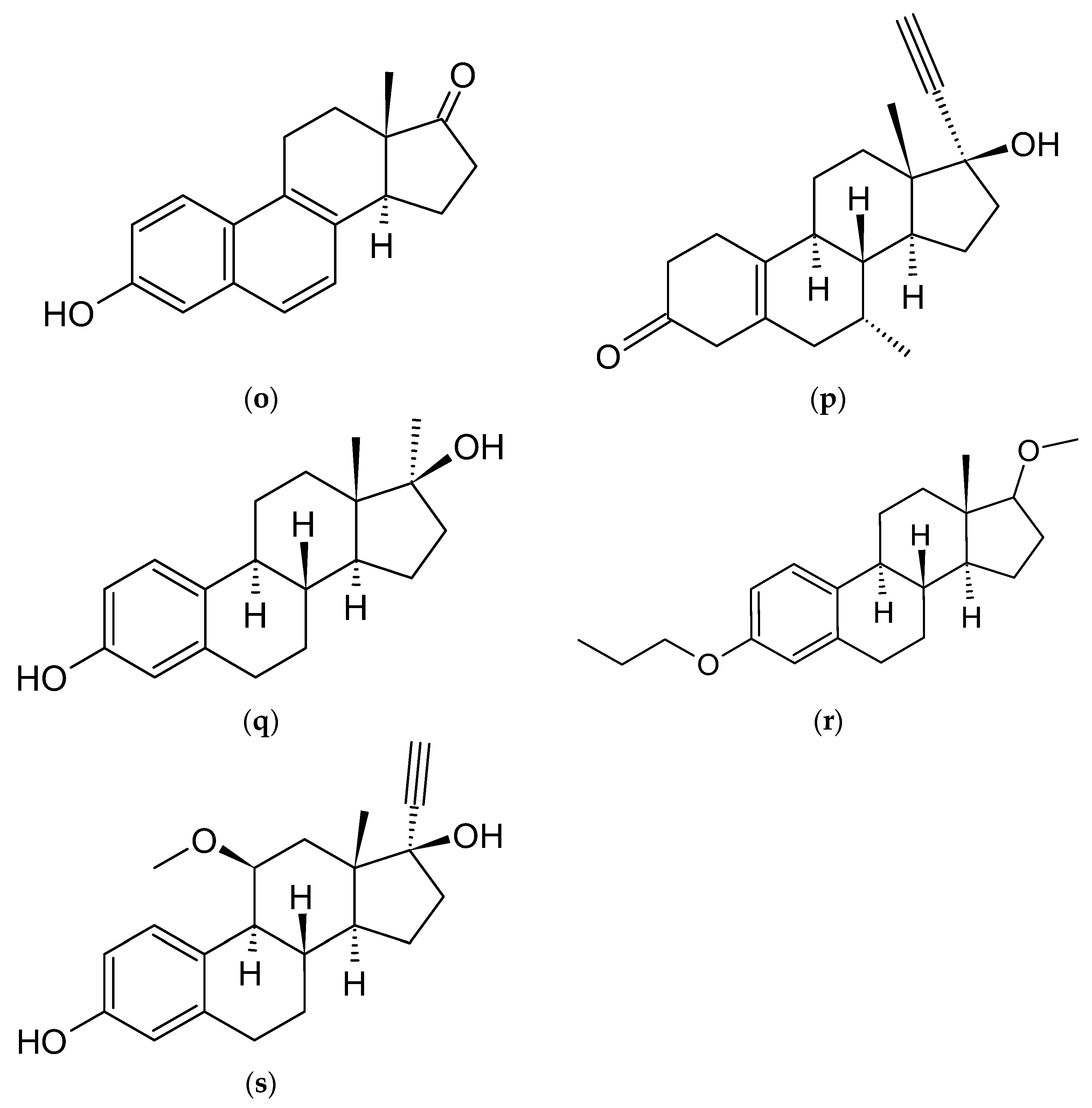
2.1. Chemical Structures of Different Estrogens
2.2. Biological Functions and Applications of Estrogens as Therapeutic Agents
2.3. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs)
3. Cyclodextrins and Their Inclusion Complexes with Steroids
4. Estrogens That form Host-Guest Complexes with Cyclodextrins
4.1. Ethinylestradiol (EE2)
4.1.1. Complex Preparation Methods
4.1.2. Complex Structure Analysis
4.1.3. Application of the Complexes
4.2. Estradiol (E2)
4.2.1. Complex Preparation Methods
4.2.2. Complex Structure Analysis
4.2.3. Increased Solubility Resulting from Complexation
4.2.4. In Vitro and In Vivo Analysis
4.2.5. Application of the Complexes
4.3. Estradiol Derivatives
4.4. Estrone (E1)
4.4.1. Structure of the Complexes and Complex Formation Mechanism
4.4.2. Methods of Complex Preparation
4.4.3. Application of the Complexes
4.5. Estrone Derivatives
4.6. Estriol (E3)
4.6.1. Complex Preparation and Structural Studies
4.6.2. Increased Solubility Resulting from Complexation
4.6.3. Application of the Complexes
4.7. Estetrol (E4)
4.8. Equilin and Equilenin
4.9. Tibolone (T)
5. Estrogens That Most Likely Do Not form Host-Guest Complexes with Cyclodextrins
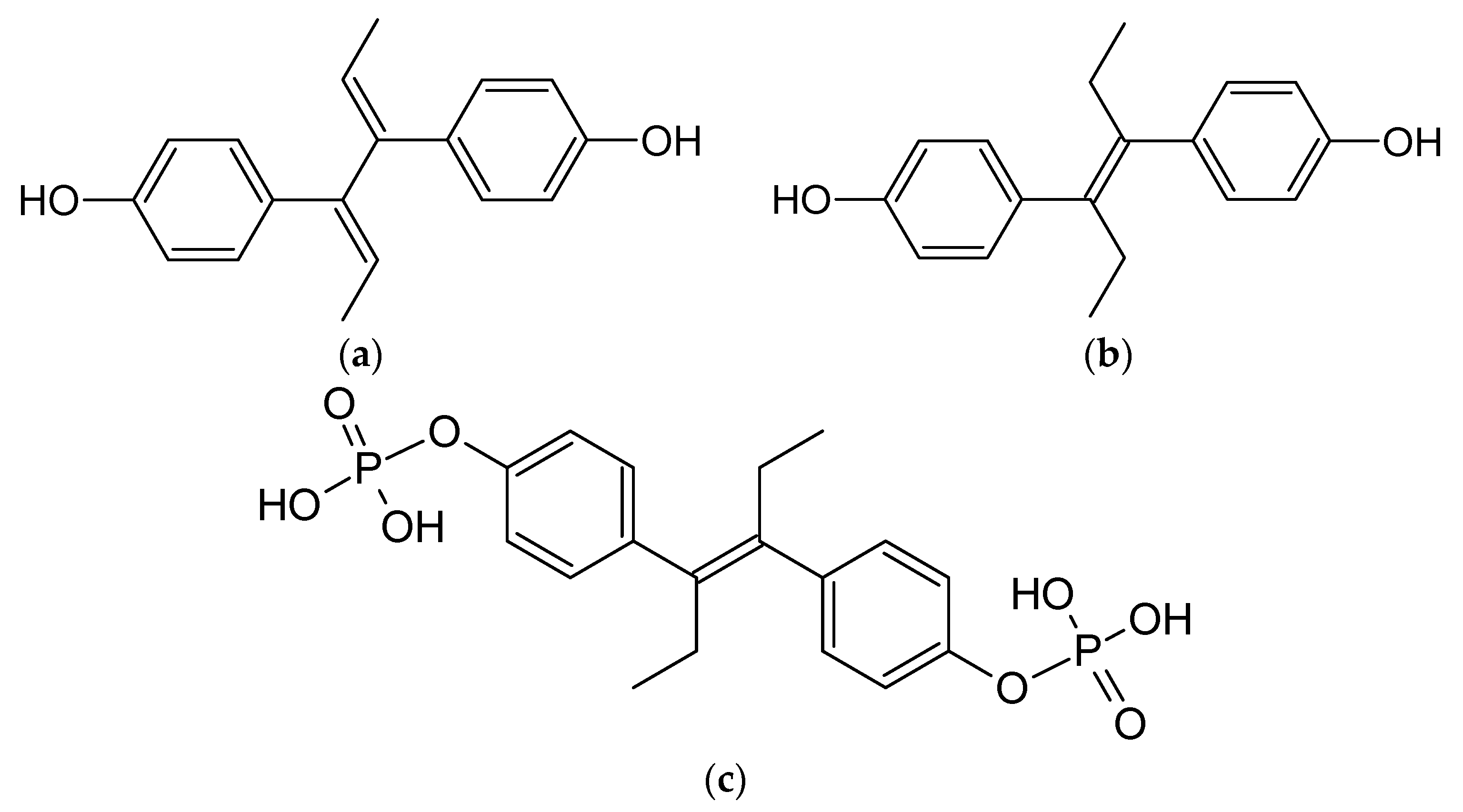
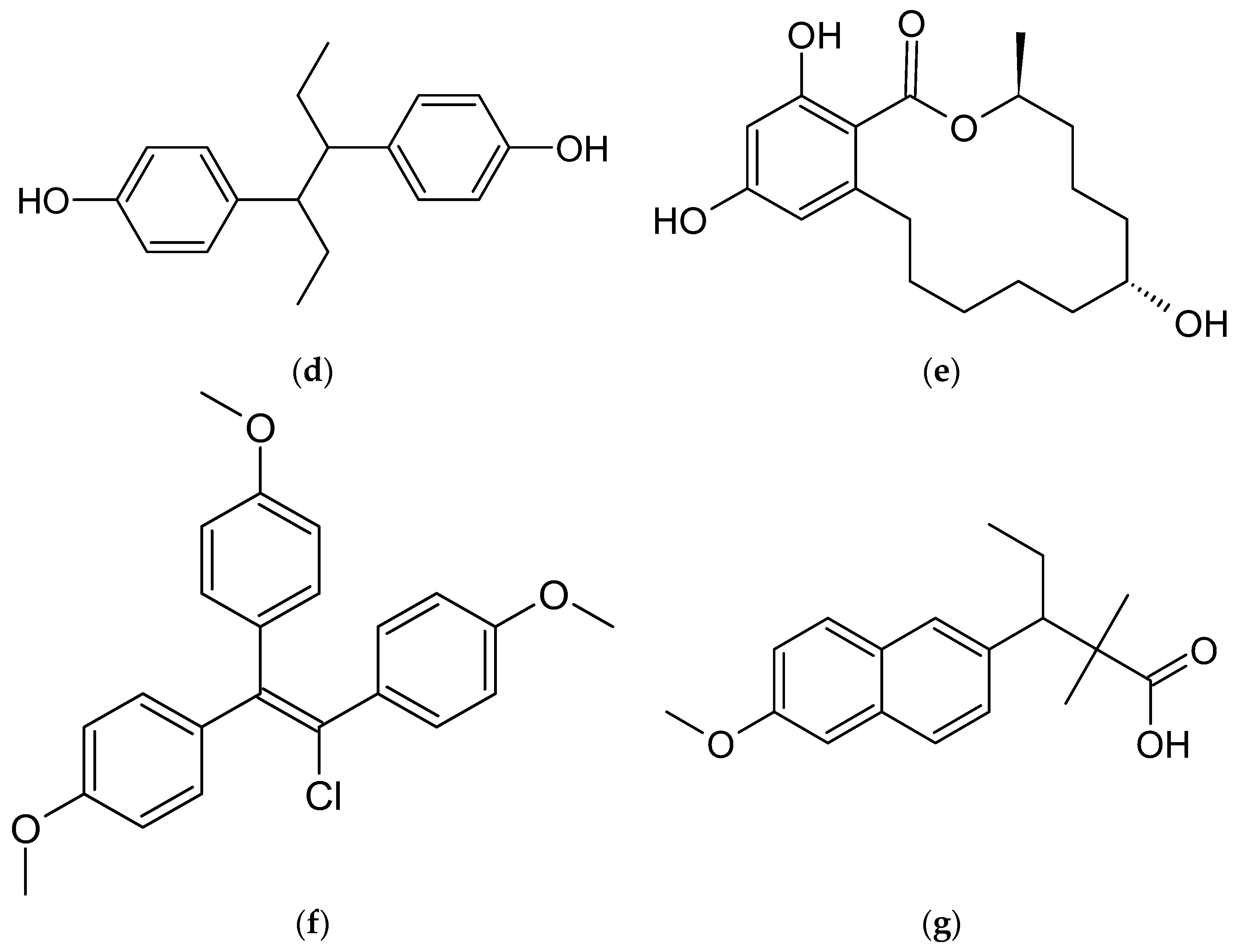
5.1. Diensterol
5.2. Diethylstilbestrol
6. Estrogens with No Evidence of Forming Host-Guest Complexes with Cyclodextrins
| Estrogen (Guest) | Cyclodextrin (Host) | Method of Analysis | Host:Guest Ratio of the Complex | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ethinyloestradiol | α-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] |
| β-CD | E | 1:1 | [82] | |
| IS | 1:1; 1:1 | [85,92] | ||
| F | 1:1; 1:1; 1:1; 1:1 | [81,85,90,91] | ||
| NMR | 1:1; 1:1; 1:1 | [85,87,119] | ||
| HPLC | ND; 1:1 | [84,88] | ||
| FTIR | 1:1 | [85] | ||
| UV | 1:1 | [85] | ||
| EDA-β-CD | UV | 1:1 | [83] | |
| HPLC | 1:1 | [83] | ||
| DM-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HP-β-CD | HPLC | 1:1; 1:1 | [83,85] | |
| F | 1:1; 1:1 | [85,90] | ||
| SEM | 1:1 | [83] | ||
| UV | 1:1; 1:1 | [83,85] | ||
| IS | 1:1 | [85] | ||
| FTIR | 1:1 | [85] | ||
| 2HP-β-CD | E | 1:1 | [82] | |
| DETA-β-CD | UV | 1:1 | [83] | |
| HPLC | 1:1 | [83] | ||
| NMR | 1:1 | [83] | ||
| TETA-β-CD | UV | 1:1 | [83] | |
| HPLC | 1:1 | [83] | ||
| TEPA-β-CD | UV | 1:1 | [83] | |
| HPLC | 1:1 | [83] | ||
| γ-CD | E | 1:1 | [82] | |
| IS | 1:1 | [92] | ||
| F | 1:1; 1:1 | [90,91] | ||
| HPLC | 1:1 | [88] | ||
| NMR | 1:2 | [87] | ||
| 2HP-γ-CD | E | 1:1 | [82] | |
| S-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HE-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| M-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| estradiol | HP-β-CD in liposomes | TEM | 1:1 | [97] |
| HP-β-CD | UV | 1:1; 1:1 | [101,108] | |
| F | 1:1; 1:1 | [90,101] | ||
| IV | ND | [111] | ||
| HPLC | ND | [103] | ||
| IS | 1:1 | [101] | ||
| NMR | 1:3 | [109] | ||
| DSC | 1:3 | [109] | ||
| SBE-β-CD | E | ND | [107] | |
| IS | ND | [107] | ||
| β-CD | UV | 1:1 | [108] | |
| IS | 1:1 | [92] | ||
| IV | 1:1; 1:1; 1:2; | [97,98,112,113] | ||
| FTIR | ND | [99] | ||
| F | 1:1; 1:1; 1:1 | [90,91,101] | ||
| FM | ND | [99] | ||
| XRD | ND; 2:1 | [99,100] | ||
| HPLC | ND; ND; ND | [103,104,105] | ||
| MEKC | [106] | |||
| UV | 1:1; 1:1 | [101,108] | ||
| DSC | ND; 2:1; 1:2; 1:1 | [99,100,112,113] | ||
| NMR | 1:1; 2:1; ND | [87,100,102] | ||
| HSM | 2:1 | [100] | ||
| TGA | 2:1 | [100] | ||
| RM-β-CD | IS | 1:1 | [101] | |
| NMR | 1:1, 1:2,4 | [109] | ||
| DSC | 1:1, 1:2,4 | [109] | ||
| HSES-β-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [108] | |
| HTG-β-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [108] | |
| HTMT-β-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [108] | |
| A-β-CD (many options) | CM | ND | [110] | |
| γ-CD | HPLC | ND | [110] | |
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| NMR | 1:2; 1:1; ND | [87,100,102] | ||
| F | 1:1; 1:1 | [90,91] | ||
| IS | 1:1 | [92] | ||
| α-CD | HPLC | ND | [103] | |
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| F | 1:1; ND | [90,102] | ||
| NMR | ND | [102] | ||
| HP-γ-CD | HPLC | ND | [103] | |
| HP-α-CD | F | ND | [102] | |
| HPLC | ND | [103] | ||
| S-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HE-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| M-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| DM-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| estriol | α-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] |
| HPLC | ND; 1:1; 1:1 | [103,122,123] | ||
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| HP-α-CD | HPLC | ND | [103] | |
| β-CD | NMR | 1:1 | [119] | |
| HPLC | ND; 1:1; ND; ND; ND; 1:1; 1:1 | [84,88,103,104,105,122,123] | ||
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| F | [90,91] | |||
| IS | 1:1; 1:1 | [92] | ||
| γ-CD | F | 1:1 | [91] | |
| IS | 1:1 | [92] | ||
| HPLC | 1:1; ND; 1:1 | [88,103,122] | ||
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| S-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HE-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| M-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HP-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HPLC | 1:1 | [103] | ||
| DM-β-CD | F | ND | [90] | |
| HP-γ-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [103] | |
| SBE-β-CD | E | ND | [107] | |
| IS | ND | [107] | ||
| Glc-β-CD | IV | ND | [120] | |
| HPLC | ND; 1:1; 1:1 | [121,122,123] | ||
| DSC | 1:1 | [123] | ||
| Man-β-CD | IV | [120] | ||
| HPLC | ND | [121] | ||
| Gal-β-CD | IV | 1:1 | [120] | |
| HPLC | ND | [121] | ||
| Maltosyl-β-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [122] | |
| Maltotriosyl-β-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [122] | |
| Glc-α-CD | HPLC | 1:1; 1:1 | [122,123] | |
| Glc-γ-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [122] | |
| Maltosyl-α-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [122] | |
| Maltosyl-γ-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [122] | |
| Maltotriosyl-α-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [122] | |
| Maltotriosyl-γ-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [122] | |
| 2Glc-β-CD | HPLC | 1:1 | [123] | |
| chlorotrianisene | ND | ND | ND | |
| estrone | α-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] |
| HPLC | ND | [103] | ||
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| β-CD | HPLC | ND; 1:1; ND; ND; ND; ND | [84,88,103,104,105,117] | |
| IS | 1:1 | [92] | ||
| F | 1:1 | [90] | ||
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| γ-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| IS | 1:1 | [92] | ||
| HPLC | 1:1; ND | [88,103] | ||
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| S-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HE-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HPLC | ND | [117] | ||
| DM-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HPLC | ND | [117] | ||
| M-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HP-β-CD | F | 1:1 | [90] | |
| HPLC | ND | [103] | ||
| HP-α-CD | HPLC | ND | [103] | |
| HP-γ-CD | HPLC | ND | [103] | |
| SBE-β-CD | E | ND | [107] | |
| IS | ND | [107] | ||
| E1-β-CD | IV | 1:1; 1:2 | [118] | |
| NMR | 1:1; 1:2 | [118] | ||
| TEM | 1:1; 1:2 | [118] | ||
| SEM | 1:1; 1:2 | [118] | ||
| promestriene | ND | ND | ND | |
| dienestreol | ND | ND | ND | |
| diethylstilbestrol | ND | ND | ND | |
| methallenestril | ND | ND | ND | |
| moxestrol | ND | ND | ND | |
| tibolone | β-CD | FTIR | ND | [126] |
| UV | ND | [126] | ||
| 2-hydroxyestrone | SBE-β-CD | IS | ND | [107] |
| E | ND | [107] | ||
| β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] | |
| DM-β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] | |
| HE-β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] | |
| 4-hydroxyestrone | β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] |
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| DM-β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] | |
| HE-β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] | |
| α-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| γ-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| 16α-hydroxyestrone | β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] |
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| DM-β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] | |
| HE-β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] | |
| α-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| γ-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| 2-metoxyestrone | α-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] |
| β-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| γ-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| 2-methoxyestradiol | SBE-β-CD | IS | ND | [107] |
| E | ND | [107] | ||
| DM-β-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| HSM | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| TGM | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| DSC | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| FTIR | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| XRD | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| IS | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| TM-β-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| HSM | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| TGM | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| DSC | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| FTIR | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| XRD | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| IS | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | ||
| α-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| β-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| γ-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| MEKC | ND | [106] | ||
| RM-β-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| TM-α-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| HP-β-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| TA-β-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| TA- γ-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| TE- γ-CD | UV | 1:1; 2:1 | [116] | |
| 16-Keto-17β-estradiol | α-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] |
| β-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| γ-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| 2-hydroxyestradiol | α-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] |
| β-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| IV | ND; 1:1 | [112,113] | ||
| γ-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| 4-hydroxyestradiol | α-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] |
| β-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| IV | ND; 1:1 | [112,113] | ||
| γ-CD | MEKC | ND | [106] | |
| equilin | β-CD | HPLC | ND; ND | [104,105] |
| DM-β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] | |
| HE-β-CD | HPLC | ND | [117] | |
| equilenin | β-CD | HPLC | ND | [104] |
| estetrol | β-CD | HPLC | ND | [105] |
| HP-β-CD | IV | 1:1 | [124] | |
| methylestradiol | ND | ND | ND | |
| fosfestrol | ND | ND | ND | |
| hexestrol | ND | ND | ND | |
| zeranol | ND | ND | ND |
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Percec, V.; Xiao, Q. From organic chemistry to chemical biology via macromolecules with Hermann Staudinger. Giant 2020, 4, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shampo, M.A.; Kyle, R.A.; Steensma, D.P. Vladimir Prelog—Nobel Prize for Work in Stereochemistry. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkovska, K.; Klingler, J.; Oberwinkler, J.; Keller, S.; Hub, J.S. Rationalizing Steroid Interactions with Lipid Membranes: Conformations, Partitioning, and Kinetics. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 9, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyńska, A.; Herman, A.P.; Antushevich, H.; Bochenek, J.; Dziendzikowska, K.; Gajewska, A.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J. Modifications of Western-type diet regarding protein, fat and sucrose levels as modulators of steroid metabolism and activity in liver. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 165, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, C. Zinc-Enriched Yeast May Improve Spermatogenesis by Regulating Steroid Production and Antioxidant Levels in Mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 3712–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Yassin, M.; Cayetano, A.; Tharakan, T.; Jayasena, C.N.; Minhas, S. Understanding and managing the suppression of spermatogenesis caused by testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) and anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS). Ther. Adv. Urol. 2022, 14, 17562872221105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochud, M.; Ponte, B.; Pruijm, M.; Ackermann, D.; Guessous, I.; Ehret, G.; Escher, G.; Groessl, M.; Estoppey Younes, S.; d’Uscio, C.H.; et al. Urinary Sex Steroid and Glucocorticoid Hormones Are Associated with Muscle Mass and Strength in Healthy Adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 2195–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Salerno, M.; Calvano, G.; Agliozzo, R.; Ficarra, V.; Sessa, F.; Favilla, V.; Cimino, S.; Pomara, C. Impact of anabolic androgenic steroids on male sexual and reproductive function: A systematic review. Panminerva Med. 2023, 65, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sech, L.A.; Mishell, D.R., Jr. Oral steroid contraception. Womens Health 2015, 11, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, E.; Gallardo, E.; Morgado-Nunes, S.; Fonseca-Moutinho, J. Steroid hormone levels and bone mineral density in women over 65 years of age. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuniyil, A.; Pal, S.; Sachdev, N.; Yadav, T.P. Effect of 2–6 weeks of systemic steroids on bone mineral density in children. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2022, 65, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, T.; Nagy, P.; Panyi, G.; Szente, L.; Varga, Z.; Zakany, F. Cyclodextrins: Only Pharmaceutical Excipients or Full-Fledged Drug Candidates? Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Ferreira, L.; Peixoto, D.; Silva, F.; Soares, M.J.; Zeinali, M.; Zafar, H.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Raza, F.; Mazzola, P.G.; et al. Cyclodextrins as an encapsulation molecular strategy for volatile organic compounds- Pharmaceutical applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 218, 112758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boczar, D.; Michalska, K. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes with Antibiotics and Antibacterial Agents as Drug-Delivery Systems—A Pharmaceutical Perspective. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, N.; El Hoffy, N.M.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Elkasabgy, N.A. Cyclodextrin Stabilized Freeze-Dried Silica/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Improved Terconazole Ocular Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Ye, Z.; Su, Y.; Ouyang, D. Predicting complexation performance between cyclodextrins and guest molecules by integrated machine learning and molecular modeling techniques. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.; Madi, F.; Nouar, L.; Bouhadiba, A.; Haiahem, S.; Khatmi, D.E.; Belhocine, Y. Driving forces and electronic structure in β-cyclodextrin/3,3′-diaminodiphenylsulphone complex. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 199, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Q.X. The Driving Forces in the Inclusion Complexation of Cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcas, A.; Resmerita, A.-M.; Balan-Porcarasu, M.; Cojocaru, C.; Peptu, C.; Sava, I. Inclusion Complexes of 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene with Per-Modified β- and γ-Cyclodextrins. Molecules 2023, 28, 3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Available online: https://www.who.int/tools/atc-ddd-toolkit/atc-classification (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Sun, J.; Hong, H.; Zhu, N.; Han, L.; Suo, Q. Effect of preparation methods on tosufloxa-cin tosylate/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 58, e18650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid-Samamed, A.; Rakmai, J.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Astray, G. Cyclodextrins inclusion complex: Preparation methods, analytical techniques and food industry ap-plications. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckmann Nicoletti, C.; de Sá Haddad Queiroz, M.; de Souza Lima, C.G.; de Carvalho da Silva, F.; Futuro, D.O.; Ferreira, V.F. An improved method for the preparation of β-lapachone:2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, A.H.; Szeleszczuk, Ł. A Review of Applications of Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (ssNMR) for the Analysis of Cyclodextrin-Including Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurek, A.H.; Szeleszczuk, Ł. Current Status of Quantum Chemical Studies of Cyclodextrin Host–Guest Complexes. Molecules 2022, 27, 3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmeja, S.; Gubica, T.; Ostrowski, A.; Zalewska, A.; Szeleszczuk, Ł.; Zawada, K.; Zielińska-Pisklak, M.; Skowronek, K.; Wiweger, M. Caffeine-Cyclodextrin Complexes as Solids: Synthesis, Biological and Physicochemical Characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, J.; Song, X.; Lai, S.; Zhong, S.; Jia, Y. The effect of exogenous estrogen on depressive mood in women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2023, 162, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva-Gallegos, R.; Carazo, A.; Mladěnka, P. Toxicity overview of endocrine disrupting chemicals interacting in vitro with the oestrogen receptor. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 99, 104089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Xiao, T. Environmental estrogens shape disease susceptibility. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 249, 114125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvetcov, A.; Ruitenberg, M.J.; Delerue, F.; Gold, W.A.; Brown, D.A.; Finney, C.A. The neuroprotective effects of estrogen and estrogenic compounds in spinal cord injury. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 146, 105074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, K.M.; Patra, S.; Swain, S.K. Host-guest drug delivery by β-cyclodextrin assisted polysaccharide vehicles: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghitman, J.; Voicu, S.I. Controlled drug delivery mediated by cyclodextrin-based supramolecular self-assembled carriers: From design to clinical performances. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 5, 100266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, J. Cyclodextrin-metal-organic frameworks in molecular delivery, detection, separation, and capture: An updated critical review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 306, 120598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Sigurdsson, H.H.; Jansook, P. Anomalous Properties of Cyclodextrins and Their Complexes in Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2023, 16, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miedl, H.; Oswald, D.; Haslinger, I.; Gstoettner, M.; Wenzl, R.; Proestling, K.; Schneeberger, C.; Yotova, I.; Schreiber, M. Association of the Estrogen Receptor 1 Polymorphisms rs2046210 and rs9383590 with the Risk, Age at Onset and Prognosis of Breast Cancer. Cells 2023, 12, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, S.; Pacifici, R. Estrogen deficiency and the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. In Marcus and Feldman’s Osteoporosis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 773–797. [Google Scholar]
- Brann, D.W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Sareddy, G.R.; Pratap, U.P.; Zhang, Q.; Tekmal, R.R.; Vadlamudi, R.K. Brain-Derived Estrogen and Neurological Disorders. Biology 2022, 11, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytz, C.L.; Turino Miranda, K.; Ronksley, P.E.; Dumanski, S.M.; Saad, N.; Raj, S.R.; Somayaji, R.; Ganshorn, H.; Newbert, A.M.; Peace, L.; et al. Serum oestradiol levels and risk of adverse cardiovascular events associated with gender-affirming oestrogen therapy: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e064961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paoli, M.; Zakharia, A.; Werstuck, G.H. The Role of Estrogen in Insulin Resistance: A Review of Clinical and Preclinical Data. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Peng, L.; Ma, J.; He, L.; Long, K.; Ouyang, X.; Wu, C.; Xie, M.; Dai, L.; Cai, X. Low expression of estrogen receptor β in renal tubular epithelial cells may cause hyperuricemia in premenopausal patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2021, 30, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães Ferreira, L.R.; Cavalcanti, T.; Zomer, M.; Kondo, W.; Araujo Júnior, E.; Kulak Junior, J. Estrogen and progesterone receptors in endometriosis. Minerva Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 74, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryłowicz, A. Estrogens in Adipose Tissue Physiology and Obesity-Related Dysfunction. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.P.; Potter, B.V. The structural biology of oestrogen metabolism. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 137, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.J.; Petrossian, K.; Chen, S. Structural and functional characterization of aromatase, estrogen receptor, and their genes in endocrine-responsive and -resistant breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 161, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, N.; Silveyra, P. Estrogen receptor signaling mechanisms. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2019, 116, 135–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Galluzzo, P.; Ascenzi, P. Estrogen signaling multiple pathways to impact gene transcription. Curr. Genom. 2006, 7, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pofi, R.; Feliciano, C.; Sbardella, E.; Argese, N.; Woods, C.P.; Grossman, A.B.; Jafar-Mohammadi, B.; Gleeson, H.; Lenzi, A.; Isidori, A.M.; et al. The Short Synacthen (Corticotropin) Test Can Be Used to Predict Recovery of Hypothalamo-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Function. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3050–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Itonaga, T.; Ikegawa, K.; Nishigaki, S.; Kawai, M.; Koga, E.; Sakakibara, H.; Ross, J.L. Ultra-low-dose estrogen therapy for female hypogonadism. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2020, 29, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilakivi-Clarke, L.; Wärri, A.; Bouker, K.B.; Zhang, X.; Cook, K.L.; Jin, L.; Zwart, A.; Nguyen, N.; Hu, R.; Cruz, M.I.; et al. Effects of In Utero Exposure to Ethinyl Estradiol on Tamoxifen Resistance and Breast Cancer Recurrence in a Preclinical Model. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 109, djw188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, D.; Wilson, J.Y. Waterborne pharmaceutical uptake and toxicity is modified by pH and dissolved organic carbon in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 210, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Niño, E.D.; Moreno-Rodríguez, A.; Juárez-Chávez, L.; Santillan, R.; Ochoa, M.A.; Argueta-Figueroa, L.; Torres-Rosas, R.; Domínguez-Diaz, L.R.; Soto-Castro, D. Synthesis of acetylenic 17α-ethynylestradiol derivatives as potential trypanocidal oral drugs: In vitro and in silico evaluation. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1274, 134431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisesi, J.H., Jr.; Robinson, S.E.; Lavelle, C.M.; Ngo, T.; Castillo, B.; Crosby, H.; Liu, K.; Das, D.; Plazas-Tuttle, J.; Saleh, N.B.; et al. Influence of the Gastrointestinal Environment on the Bioavailability of Ethinyl Estradiol Sorbed to Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Ning, L.; Li, S. Ethinyl estradiol cocrystals assembled by chain structures: Improvement in stability and solubility. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 16889–16897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafik, A. Contraceptive efficacy of polyester-induced azoospermia in normal men. Contraception 1992, 45, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hajeb, P.; Fauser, P.; Vorkamp, K. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in indoor dust: A review of temporal and spatial trends, and human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modica, R.; Benevento, E.; Colao, A. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and cancer: New perspectives on an old relationship. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2023, 46, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.; Jeung, E.-B. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Disease Endpoints. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbes, G.; Blázquez, M.; Fernandino, J.I.; Grigorova, P.; Hales, B.F.; Metcalfe, C.; Navarro-Martín, L.; Parent, L.; Robaire, B.; Rwigemera, A.; et al. Effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on gonad development: Mechanistic insights from fish and mammals. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross-Sorokin, M.Y.; Brighty, G.; Roast, S. Assessment of Feminization of Male Fish in English Rivers by the Environment Agency of England and Wales. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 114, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhind, S.; Kyle, C.; Mackie, C.; McDonald, L. Accumulation of endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in sheep fetal and maternal liver tissue following exposure to pastures treated with sewage sludge. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Cheng, W.; Feng, Y.; Wei, H.; Liang, F.; Wang, Y. Interactions between three typical endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in binary mixtures exposure on myocardial differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkhawasi, M.; Kerdpol, K.; Ismail, A.; Nutho, B.; Hanpiboon, C.; Wolschann, P.; Krusong, K.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Hannongbua, S. In Vitro and In Silico Study on the Molecular Encapsulation of α-Tocopherol in a Large-Ring Cyclodextrin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusong, K.; Ismail, A.; Wangpaiboon, K.; Pongsawasdi, P. Production of Large-Ring Cyclodextrins by Amylomaltases. Molecules 2022, 27, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Yue, M.; Qiu, C.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, L.; Long, J.; Jiao, A.; Wang, J.; et al. Interactions between plant-derived antioxidants and cyclodextrins and their application for improving separation, detection, and food quality issues. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Rashwan, A.K.; Osman, A.I.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Omar, M.; Li, Y.; Mehanni, A.E.; Chen, W.; et al. Synthesis and potential applications of cyclodextrin-based metal-organic frameworks: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 447–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeilpour, D.; Broscheit, J.A.; Shityakov, S. Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials Bound to Corona Protein for Theranostic Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnes, M.; Pancani, E.; Malanga, M.; Fenyvesi, É.; Manet, I. Implementation of Water-Soluble Cyclodextrin-Based Polymers in Biomedical Applications: How Far Are We? Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2200090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Jiang, L.; Jia, Q. Advances in cyclodextrin polymers adsorbents for separation and enrichment: Classification, mechanism and applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 33, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matencio, A.; Rubin Pedrazzo, A.; Difalco, A.; Navarro-Orcajada, S.; Khazeai Monfared, Y.; Conesa, I.; Rezayat, A.; López-Nicolás, J.M.; Trotta, F. Advances and Classification of Cyclodextrin-Based Polymers for Food-Related Issues. Polymers 2021, 13, 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiassa, V.; Garnero, C.; Longhi, M.R.; Zoppi, A. Cyclodextrin Multicomponent Complexes: Pharmaceutical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayoubi, A.; Daihom, B.; Adhikari, H.; Mishra, S.; Helms, R.; Almoazen, H. Development of a taste-masked oral suspension of clindamycin HCl using ion exchange resin Amberlite IRP 69 for use in pediatrics. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ONO Pharmaceutical. Available online: https://www.ono-pharma.com/en/company/history/300th.html (accessed on 21 April 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en (accessed on 21 April 2023).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA). Available online: https://www.fda.gov (accessed on 22 April 2023).
- Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency. Available online: https://www.pmda.go.jp/english/index.html (accessed on 23 April 2023).
- Yousefi, N.A.; Zimmermann, M.L.; Bols, M. A study of the DIBAL-promoted selective debenzylation of α-cyclodextrin protected with two different benzyl groups. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpupa, A.; Nqombolo, A.; Mizaikoff, B.; Nomngongo, P.N. Beta-Cyclodextrin-Decorated Magnetic Activated Carbon as a Sorbent for Extraction and Enrichment of Steroid Hormones (Estrone, β-Estradiol, Hydrocortisone and Progesterone) for Liquid Chromatographic Analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleniecka, A.; Zarzycki, P.K. Analysis of Selected Endocrine Disrupters Fraction Including Bisphenols Extracted from Daily Products, Food Packaging and Treated Wastewater Using Optimized Solid-Phase Extraction and Temperature-Dependent Inclusion Chromatography. Molecules 2019, 24, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chankvetadze, B.; Scriba, G.K.E. Cyclodextrins as chiral selectors in capillary electrophoresis: Recent trends in mechanistic studies. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 160, 116987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, P.; Landy, D.; Nakhle, L.; Dallocchio, R.; Dessì, A.; Krait, S.; Salgado, A.; Chankvetadze, B.; Scriba, G.K.E. Isothermal titration calorimetry and molecular modeling study of the complex formation of daclatasvir by γ-cyclodextrin and trimethyl-β-cyclodextrin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 313, 120870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Duan, A.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Zeng, A.; Wang, X. The joint effects of room temperature ionic liquids and ordered media on fluorescence characteristics of estrogens in water and methanol. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 128, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakalisava, Y.; Regan, F. Determination of association constants of inclusion complexes of steroid hormones and cyclodextrins from their electrophoretic mobility. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 3048–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Lv, R.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, T. Synthesis and Characterization of Water Soluble Diethylenetriamine-β-Cyclodextrin/Ethinylestradiol Inclusion Complex. Chem. Eur. 2022, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlej-Sosnowska, N. Molecular complexation: β-cyclodextrin and steroid hormones inclusion complexes studied by high performance liquid chromatography. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Kou, S.B.; Wang, B.L.; Shi, J.H. Characterization of the inclusion interaction of ethinyloestradiol with β-cyclodextrin and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin: Multi-spectroscopic and molecular modeling methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 311, 113290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenyvesi, É.; Puskás, I.; Szente, L. Chapter 2 Cyclodextrin-Steroid Interactions and Applications to Pharmaceuticals, Food, Biotechnology and Environment. In Cyclodextrin Applications in Medicine, Food, Environment and Liquid Crystals; Fourmentin, S., Crini, G., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 19–57. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P.; Sun, Q.; Suo, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yang, H.; Xiong, X.; Pu, H.; Gan, N.; Li, H. Rapid and efficient removal of estrogenic pollutants from water by using beta- and gamma-cyclodextrin polymers. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 344, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlej-Sosnowska, N. Inclusion complexes of steroid hormones with cyclodextrins studied by the Hummel-Dreyer method using reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1995, 13, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadlej-Sosnowska, N. Thermodynamic parameters of the formation of a complex between cyclodextrins and steroid hormones. J. Chromatogr. 1996, 728, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.L.; Escandar, G.M. Spectrofluorimetric study of estrogen–cyclodextrin inclusion complexes in aqueous systems. Analyst 2013, 138, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadlej-Sosnowska, N. Fluorometric Determination of Association Constants of Three Estrogens with Cyclodextrins. J. Flouresc. 1997, 7, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensheng, C.; Xuexia, Y.; Xueguang, S.; Zhongxiao, P. Bimodal Complexations of Steroids with Cyclodextrins by a Flexible Docking Algorithm. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2005, 51, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: Basic science and product development. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blode, H.; Schürmann, R.; Benda, N. Novel ethinyl estradiol-beta-cyclodextrin clathrate formulation does not influence the relative bioa-vailability of ethinyl estradiol or coadministered drospirenone. Contraception 2008, 77, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenyvesia, É.; Barkácsb, K.; Gruizc, K.; Vargaa, E.; Kenyeresd, I.; Zárayb, G.; Szentea, L. Removal of hazardous mi-cropollutants from treated wastewater using cyclodextrin bead polymer—A pilot demonstration case. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.; Molnár, M.; Fekete-Kertész, I.; Molnár-Perl, I.; Fenyvesi, É.; Gruiz, K. Removal of emerging micropollutants from water using cyclodextrin. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallez, A.; Palazzo, C.; Blacher, S.; Tskitishvili, E.; Noël, A.; Foidart, J.-M.; Evrard, B.; Pequeux, C.; Piel, G. Liposomes and drug-in-cyclodextrin-in-liposomes formulations encapsulating 17β-estradiol: An innovative drug delivery system that prevents the activation of the membrane-initiated steroid signaling (MISS) of estrogen receptor α. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 573, 118861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.C.G.D.; Silva, J.F.D.; Santos, T.P.; Silva, N.P.C.D.; Santos, A.R.D.; Andrade, A.L.C.; Souza, E.H.L.D.S.; Sales Cadena, M.R.; Sá, F.B.; Silva Junior, V.A.D.; et al. The complexation of steroid hormones into cyclodextrin alters the toxic effects on the biological parameters of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2019, 214, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimhoffer, Á.; Vas, A.; Árvai, G.; Fenyvesi, É.; Jicsinszky, L.; Budai, I.; Bényei, A.; Regdon, G., Jr.; Rusznyák, Á.; Vasvári, G.; et al. Investigation of the Drug Carrier Properties of Insoluble Cyclodextrin Polymer Microspheres. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicatos, A.I.; Hoossen, Z.; Caira, M.R. Inclusion complexes of the steroid hormones 17β-estradiol and progesterone with β- and γ-cyclodextrin hosts: Syntheses, X-ray structures, thermal analyses and API solubility enhancements. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1749–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Wang, X.X.; Kou, S.B.; Shi, J.H. Exploring the inclusion interaction of estradiol with β-CD and HP-β-CD with the help of molecular dynamics simulation as well as multi-spectroscopic approaches. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 269, 120764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, K.; Toyao, K.; Kawano, Y. Suppression of estrogenic activity of 17 β-estradiol by β-cyclodextrin. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1788–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzycki, P.K.; Ohta, H.; Saito, Y.; Jinno, K. Interaction of native α-cyclodextrin, β-cyclodextrin and γ-cyclodextrin and their hydroxypropyl derivatives with selected organic low molecular mass compounds at elevated and subambient temperature under RP-HPLC conditions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzycki, P.K.; Wierzbowska, M.; Lamparczyk, H. The influence of temperature on the multiple separation of estrogenic steroids using mobile phases modified with beta-cyclodextrin in high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1997, 15, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzycki, P.K.; Smith, R. Separation of steroids using temperature-dependent inclusion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 912, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.; Muschik, G.M.; Issaq, H.J.; Siiteri, P.K. Separation of estrogens by micellar electrokinetic chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 690, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Huang, M. Capillary Electrophoretic Separation and Theoretical Study of Inclusion Complexes of Sulfobutyl Ether β-Cyclodextrin with Estrogens. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2004, 100, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, D.H.; Engelke, A.; Wenz, G. Solubilizing steroidal drugs by β-cyclodextrin derivatives. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paula, D.; Oliveira, D.; Tedesco, A.; Bentley, M. Enhancing effect of modified beta-cyclodextrins on in vitro skin permeation of estradiol. Rev. Cienc. Farm. 2007, 43, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Sohn, J.; Wijewickrama, G.T.; Edirisinghe, P.; Gherezghiher, T.; Hemachandra, M.; Lu, P.Y.; Chandrasena, R.E.; Molloy, M.E.; Tonetti, D.A.; et al. Click synthesis of estradiol-cyclodextrin conjugates as cell compartment selective estrogens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagenc, L.; Lane, M.; Gardner, D.K. Oestradiol, cyclodextrin-encapsulated 17β-oestradiol and the oestradiol solubilizer 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin all impair preimplantation mouse embryo development. Reprod. BioMed. Online 2004, 9, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerdenbag, H.J.; Pras, N.; Frijlink, H.W.; Lerk, C.F.; Malingré, T.M. Cyclodextrin-facilitated bioconversion of 17 beta-estradiol by a phenoloxidase from Mucuna pruriens cell cultures. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 1551–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Uden, W.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Pras, N. Cyclodextrins as a useful tool for bioconversions in plant cell biotechnology. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1994, 38, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Tenreiro, C.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.; Concheiro, A.; Torres-Labandeira, J.J. Estradiol sustained release from high affinity cyclodextrin hydrogels. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 66, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, U.; Damgé, C.; Maincent, P.; Bodmeier, R. Properties of in situ gelling nasal inserts containing estradiol/methyl β-cyclodextrin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2004, 14, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caira, M.R.; Bourne, S.A.; Samsodien, H.; Smith, V.J. Inclusion complexes of 2-methoxyestradiol with dimethylated and permethylated β-cyclodextrins: Models for cyclodextrin-steroid interaction. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2616–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.J.; William, C. Purdy, High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Separation of Equilin, Estrone, and Estrone Derivatives with Cyclodextrins as Mobile Phase Additives. J. Liq. Chromat. 2006, 450, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.J.; Shumyak, S.P.; Burgess, C.; Zhou, Z.W.; He, Z.X.; Zhang, X.J.; Pan, S.T.; Yang, T.X.; Duan, W.; Qiu, J.X.; et al. Controllable drug uptake and nongenomic response through estrogen-anchored cyclodextrin drug complex. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4717–4730. [Google Scholar]
- Bednarek, E.; Bocian, W.; Poznański, J.; Sitkowski, J.; Sadlej-Sosnowska, N.; Kozerski, L. Complexation of steroid hor-mones: Prednisolone, ethinyloestradiol and estriol with B-cyclodextrin. An aqueous 1 H NMR study. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2002, 2, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, Y.; Sanbe, H.; Koizumi, K. Absorption, Distribution and Excretion of Gakaktyosyl-β-cyclodextrin and Mannosyl-β-cyclodextrin in rats. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuyo, O.; Kazuha, M.; Koji, H.; Kenichi, H.; Hitoshi, H.; Kyoko, K. Properties and the inclusion behavior of 6-O-α-D-galactosyl- and 6-O- α-D-mannosyl-cyclodextrins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, Y.; Kubota, Y.; Koizumi, K.; Hizukuri, S.; Ohfuji, T.; Ogata, K. Some properties and the inclusion behavior of branched cyclodextrins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, K.; Okada, Y.; Kubota, Y.; Utamura, T. Inclusion complexes of poorly water-soluble drugs with glucosyl-cyclodextrins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 3413–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, C.; Laloy, J.; Delvigne, A.S.; Nys, G.; Fillet, M.; Dogne, J.M.; Pequeux, C.; Foidart, J.M.; Evrard, B.; Piel, G. Development of injectable liposomes and drug-in-cyclodextrin-in-liposome formulations encapsulating estetrol to prevent cerebral ischemia of premature babies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 127, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavnani, B.R.; Stanczyk, F.Z. Pharmacology of conjugated equine estrogens: Efficacy, safety and mechanism of action. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 142, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engelgem, T.; Marechal, J. Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising Cyclodextrin Complex of Tibolone; Pharmaceutical Services Inc.: Exton, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Huang, Y.; He, M.; Hu, B. Hollow fiber liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatog-raphy-ultraviolet detection for the determination of various environmental estrogens in environmental and biological samples. J. Chromat. A 2013, 1305, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veurink, M.; de Jong-van den Berg, L.T.W. The history of DES, lessons to be learned. Pharm. World Sci. 2005, 27, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araj, S.K.; Szeleszczuk, Ł. A Review on Cyclodextrins/Estrogens Inclusion Complexes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108780
Araj SK, Szeleszczuk Ł. A Review on Cyclodextrins/Estrogens Inclusion Complexes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(10):8780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108780
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraj, Szymon Kamil, and Łukasz Szeleszczuk. 2023. "A Review on Cyclodextrins/Estrogens Inclusion Complexes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 10: 8780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108780
APA StyleAraj, S. K., & Szeleszczuk, Ł. (2023). A Review on Cyclodextrins/Estrogens Inclusion Complexes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(10), 8780. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24108780








