Stimulatory Effect of Lactobacillus Metabolites on Colonic Contractions in Newborn Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
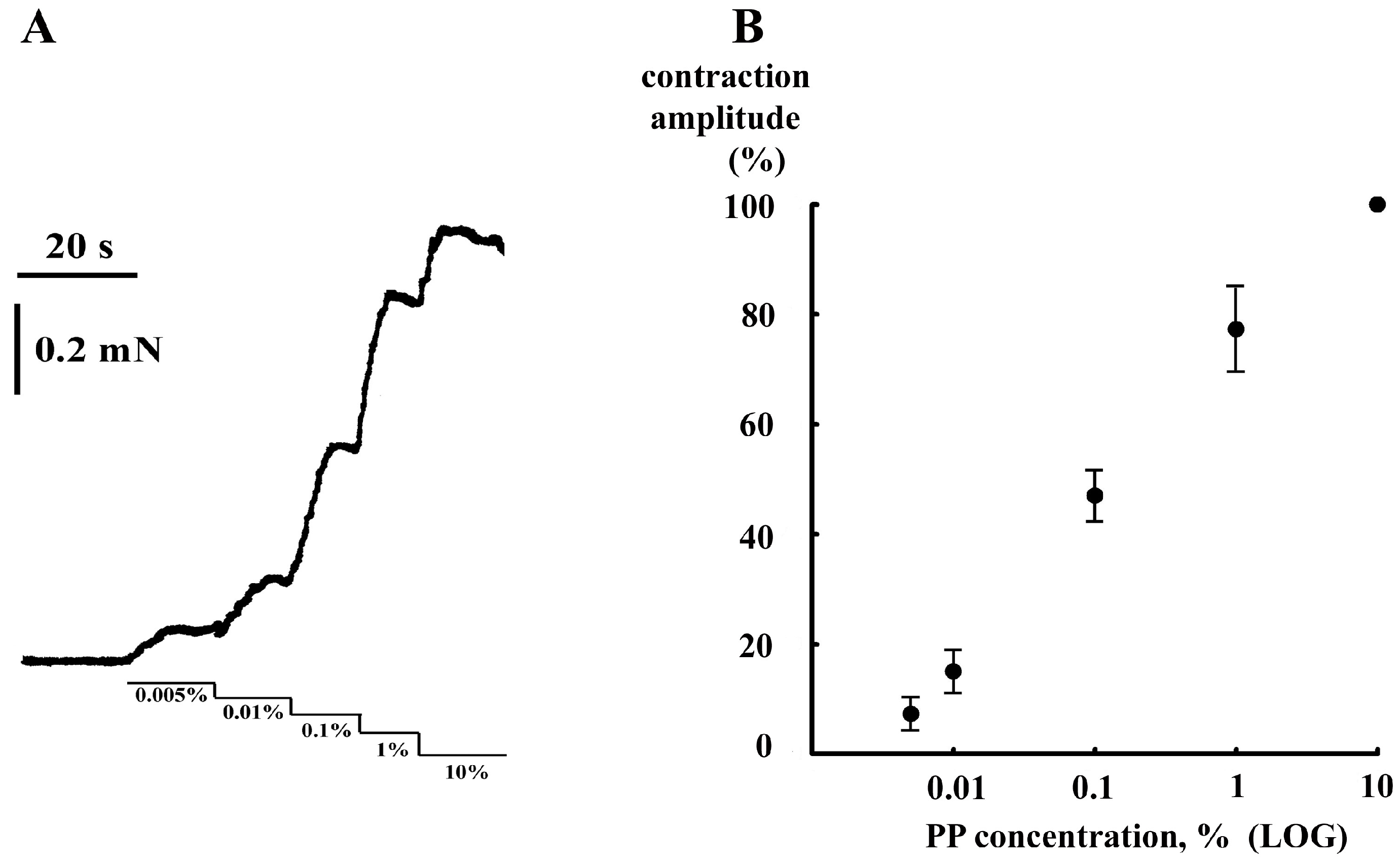
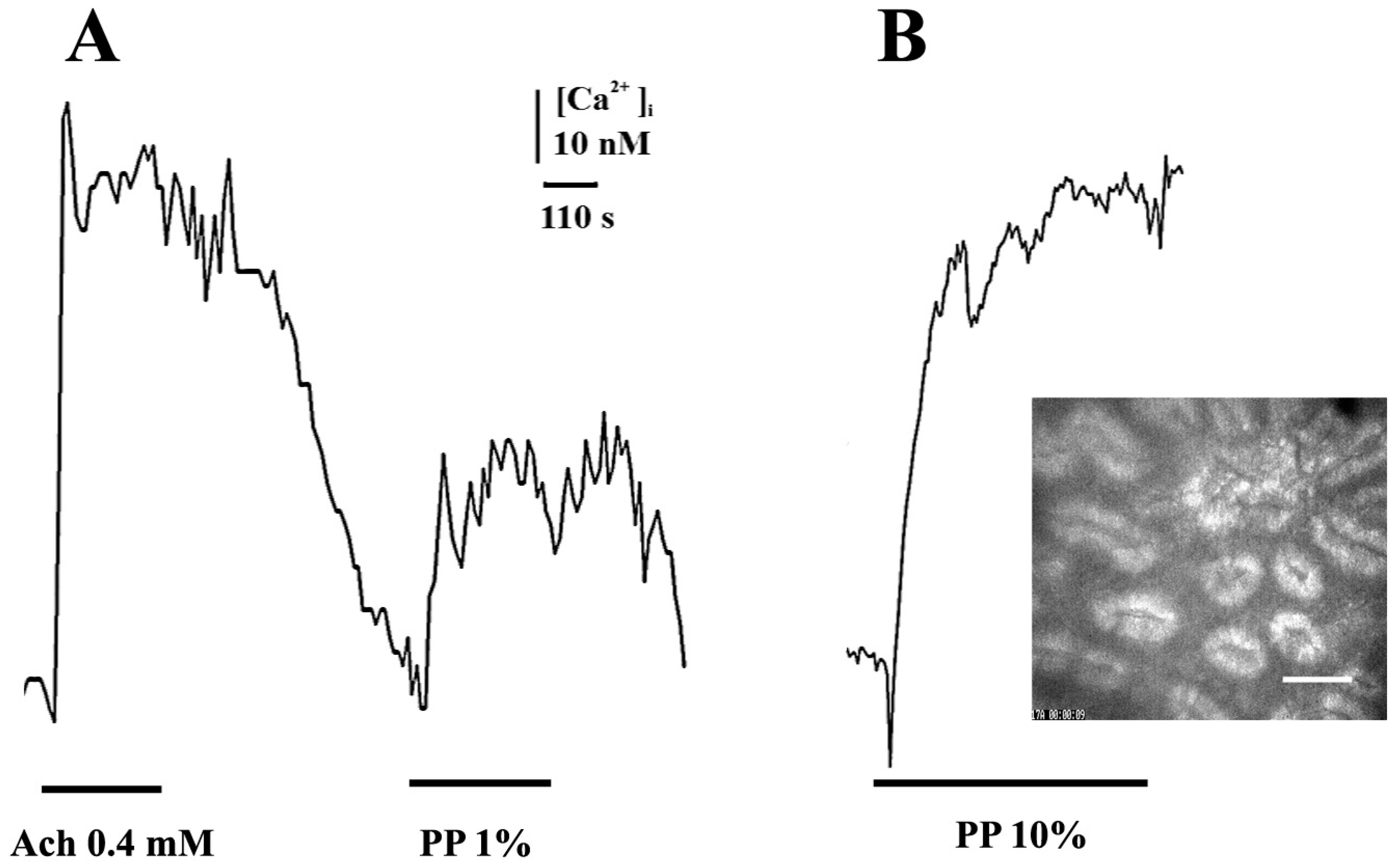
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Animals
3.2. Rat Colon Isolation and Recording of Contractile Activity
3.3. Registration of Intracellular Calcium
3.4. Drugs and Reagents
3.5. Statistical Analysis and Ethical Approval
4. Conclusions
5. U.S. Patent
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ach | acetylcholine |
| PP | probiotic/pharmabiotic product |
| U.S. | United States |
References
- Zheng, Z.; Tang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W. Role of gut microbiota-derived signals in the regulation of gastrointestinal motility. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 961703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasaly, N.; de Vos, P.; Hermoso, M.A. Impact of Bacterial Metabolites on Gut Barrier Function and Host Immunity: A Focus on Bacterial Metabolism and Its Relevance for Intestinal Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 658354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, H.; Xu, X.; Miwa, H. Role of Gut Microbiota-Gut Hormone Axis in the Pathophysiology of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waclawiková, B.; Codutti, A.; Alim, K.; El Aidy, S. Gut microbiota-motility interregulation: Insights from in vivo, ex vivo and in silico studies. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 1997296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matijašić, M.; Meštrović, T.; Paljetak, H.Č.; Perić, M.; Barešić, A.; Verbanac, D. Gut Microbiota beyond Bacteria-Mycobiome, Virome, Archaeome, and Eukaryotic Parasites in IBD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 1, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobol, C.V.; Korotkov, S.M.; Nesterov, V.P. Microbiota—Cardiovascular Axis: How we could improve cardiovascular system with microbiota metabolites. In Comprehensive Gut Microbiota; Glibetic, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshchina, V.V. Evolutionary considerations of neurotransmitters in microbial, plant, and animal cells. In Microbial Endocrinology: Interkingdom Signaling in Infectious Disease and Health; Lyte, M., Freestone, P.P.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 17–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lyte, M. Microbial endocrinology and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderov, B.A.; Sinitsa, A.V.; Zakharchenko, M.M.; Lang, C. Metabiotics, Present State, Challenges and Perspectives; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Šola, K.F.; Vladimir-Knežević, S.; Hrabač, P.; Mucalo, I.; Saso, L.; Verbanac, D. The effect of multistrain probiotics on functional constipation in the elderly: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 76, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W. Crosstalk between the Gut Microbiome and Colonic Motility in Chronic Constipation: Potential Mechanisms and Microbiota Modulation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, J.; Ren, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Bai, X.; Shan, S.; Dong, X. Gut Microbiota Composition Changes in Constipated Women of Reproductive Age. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 557515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metta, V.; Leta, V.; Mrudula, K.R.; Prashanth, L.K.; Goyal, V.; Borgohain, R.; Chung-Faye, G.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease: Molecular pathology and implications of gut microbiome, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Reynolds, R.; Tan, E.K.; Pettersson, S. The role of gut dysbiosis in Parkinson’s disease: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic options. Brain 2021, 144, 2571–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, D.; O’Leary, P.; Quigley, E.M. Aging and intestinal motility: A review of factors that affect intestinal motility in the aged. Drugs Aging 2002, 19, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lillo, A.R.; Rose, S. Functional bowel disorders in the geriatric patient: Constipation, fecal impaction, and fecal incontinence. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitar, K.N.; Patil, S.B. Aging and gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2004, 125, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitar, K.; Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B.; Saad, R.; Wiley, J.W. Aging and gastrointestinal neuromuscular function: Insights from within and outside the gut. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentili, C.; Picotto, G.; Morelli, S.; Boland, R.; de Boland, A.R. Effect of ageing in the early biochemical signals elicited by PTH in intestinal cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1593, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Smits, G.J.; Lefebvre, R.A. Influence of age on cholinergic and inhibitory nonadrenergic noncholinergic responses in the rat ileum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 303, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Kubota, H.; Gawad, A.; Gheyle, L.; Ramael, S.; Oishi, K. Effect of fermented milk containing Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota on constipation-related symptoms and haemorrhoids in women during puerperium. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Ren, F.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R. Effects of Fermented Milk Containing Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Strain Shirota on Constipation in Patients with Depression: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalziel, J.E.; Anderson, R.C.; Bassett, S.A.; Lloyd-West, C.M.; Haggarty, N.W.; Roy, N.C. Influence of Bovine Whey Protein Concentrate and Hydrolysate Preparation Methods on Motility in the Isolated Rat Distal Colon. Nutrients 2016, 8, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bär, F.; Von Koschitzky, H.; Roblick, U.; Bruch, H.P.; Schulze, L.; Sonnenborn, U.; Böttner, M.; Wedel, T. Cell-free supernatants of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 modulate human colonic motility: Evidence from an in vitro organ bath study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2009, 21, 559-e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, Y.; Inoue, R.; Tanaka, K.; Umesaki, Y.; Ushida, K. Strain gauge force transducer and its application in a pig model to evaluate the effect of probiotic on colonic motility. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2001, 47, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of the effects of probiotics on functional constipation in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2960–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, C.V. A new class of pharmabiotics with unique properties. In Soft Chemistry and Food Fermentation; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 79–112. [Google Scholar]
- Anitha, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Srinivasan, S. Gut microbial products regulate murine gastrointestinal motility via toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1006–1016.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, E.A.; King, K.Y.; Baldridge, M.T. Mouse Microbiota Models: Comparing Germ-Free Mice and Antibiotics Treatment as Tools for Modifying Gut Bacteria. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husebye, E.; Hellström, P.M.; Sundler, F.; Chen, J.; Midtvedt, T. Influence of microbial species on small intestinal myoelectric activity and transit in germ-free rats. Am. J. Physiol. 2001, 280, G368–G380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimidi, E.; Christodoulides, S.; Scott, S.M.; Whelan, K. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota on Gut Motility and Constipation. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Salam, M.H.; El-Shibiny, S. Preparation, properties, and uses of enzymatic milk protein hydrolysates. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuochi, V.; Coniglio, M.A.; Laghi, L.; Rescifina, A.; Caruso, M.; Stivala, A.; Furneri, P.M. Metabolic characterization of supernatants produced by Lactobacillus spp. with in vitro anti-Legionella activity. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrino, B.A. Calcium sensitization mechanisms in gastrointestinal smooth muscles. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraporda, C.; Romanin, D.E.; Bengoa, A.A.; Errea, A.J.; Cayet, D.; Foligné, B.; Sirard, J.C.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; Rumbo, M. Local Treatment with Lactate Prevents Intestinal Inflammation in the TNBS-Induced Colitis Model. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobol, C.V. Stimulatory Effect of Lactobacillus Metabolites on Colonic Contractions in Newborn Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010662
Sobol CV. Stimulatory Effect of Lactobacillus Metabolites on Colonic Contractions in Newborn Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(1):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010662
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobol, Constantin V. 2023. "Stimulatory Effect of Lactobacillus Metabolites on Colonic Contractions in Newborn Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 1: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010662
APA StyleSobol, C. V. (2023). Stimulatory Effect of Lactobacillus Metabolites on Colonic Contractions in Newborn Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(1), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010662





