Interferon-β Activity Is Affected by S100B Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
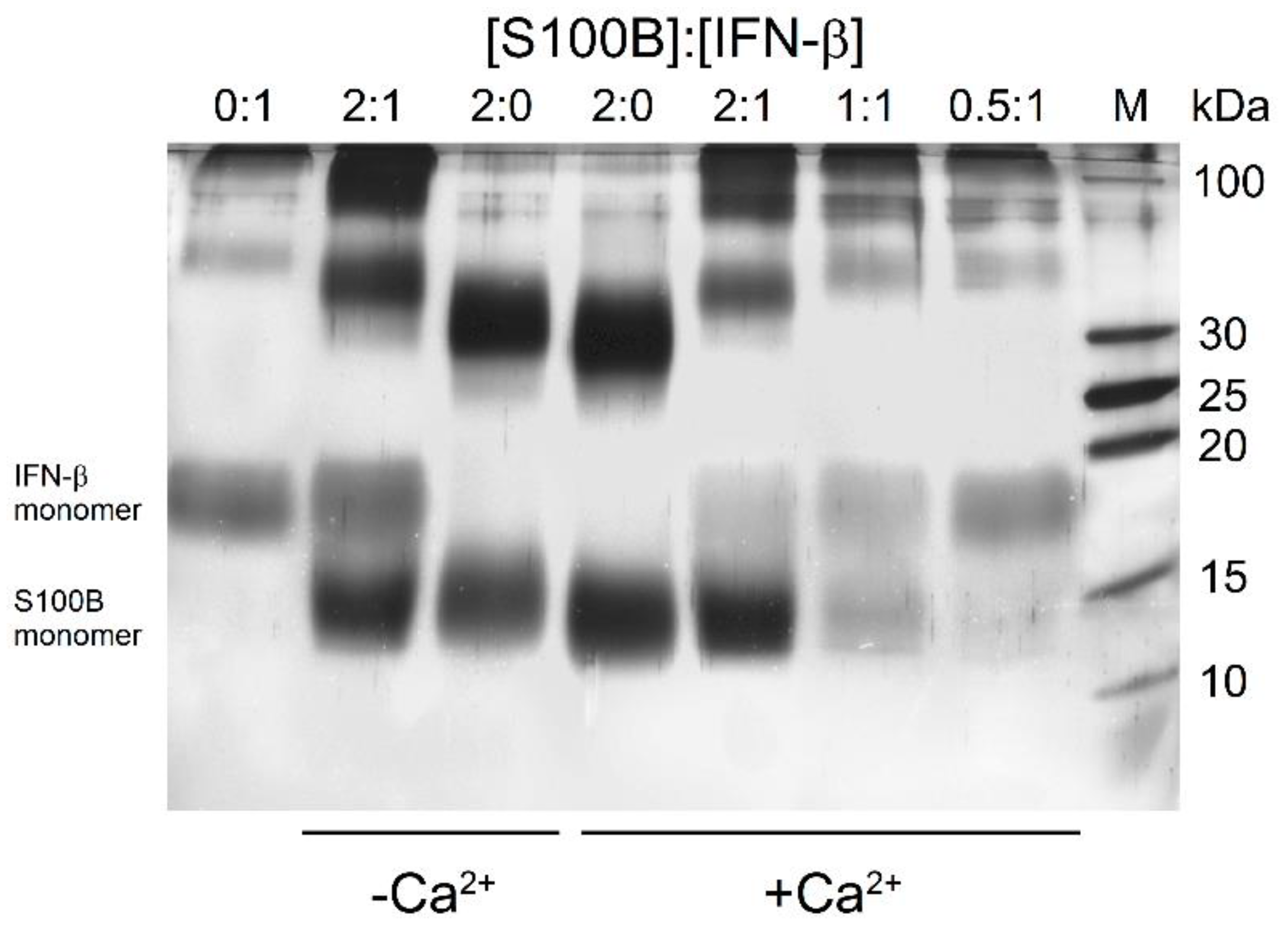
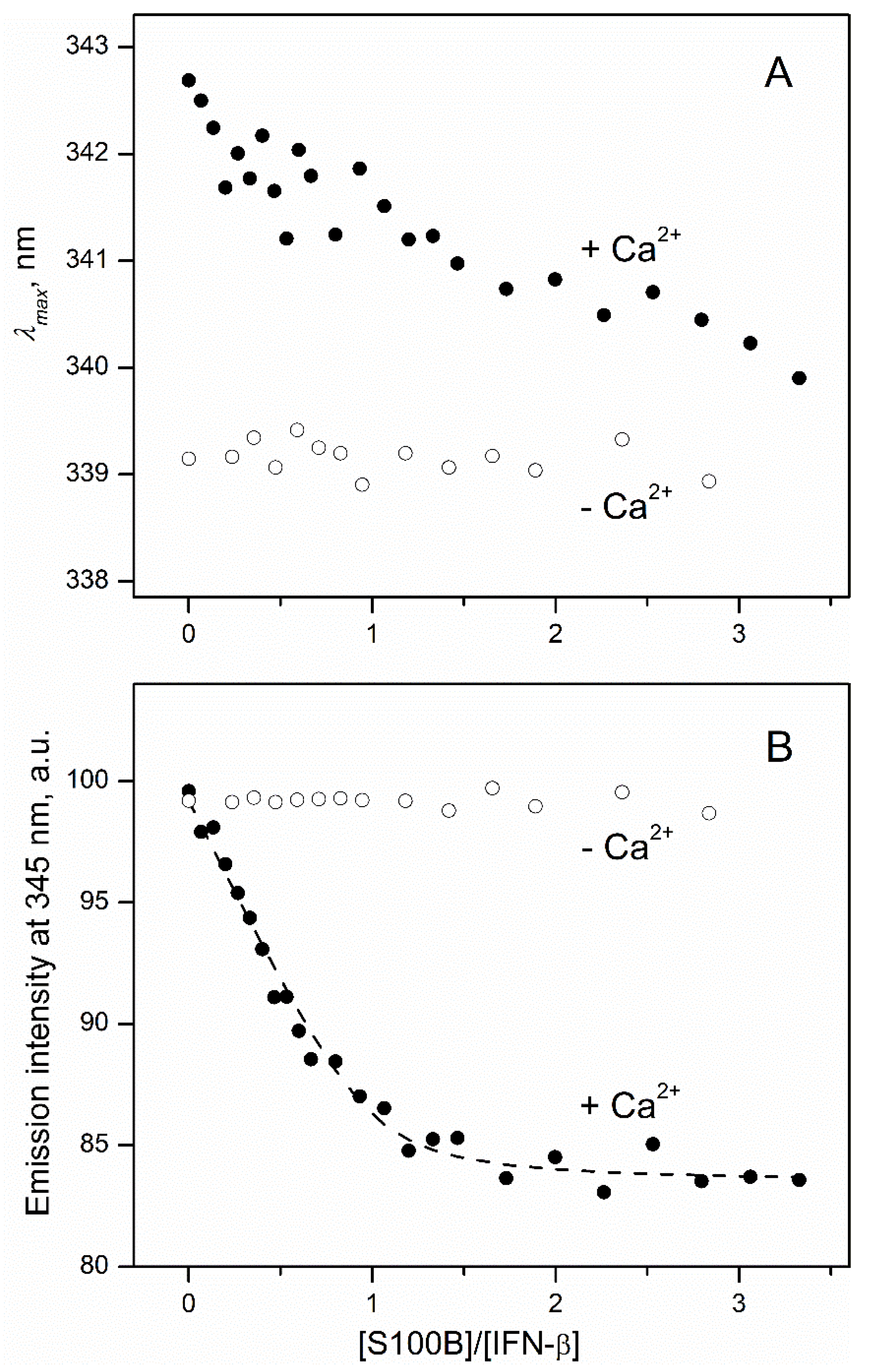
2.1. High-Affinity Interaction between IFN-β and S100B
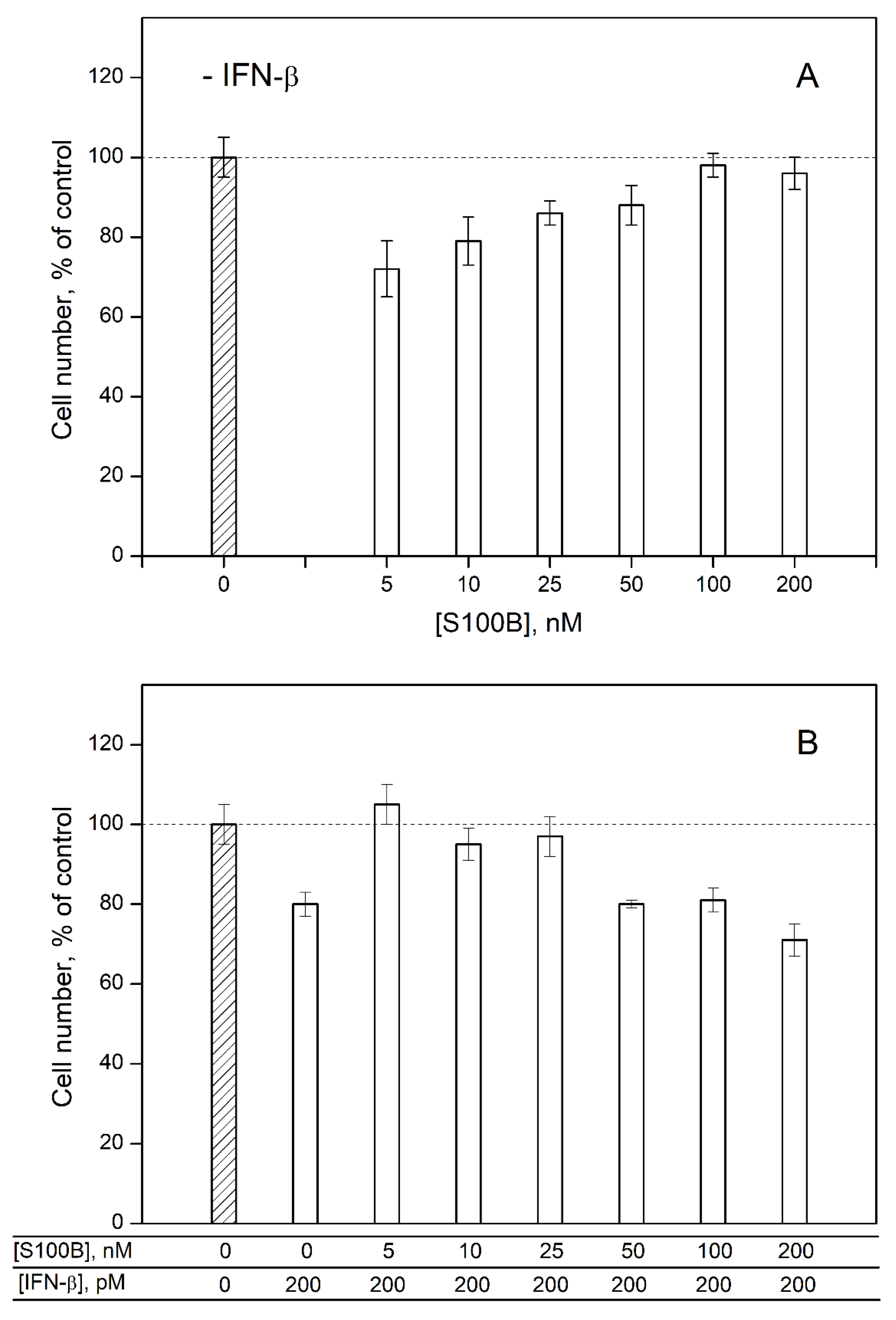
2.2. Modulation of IFN-β Cytotoxicity towards MCF-7 Cells by S100B
2.3. Human Diseases Associated with Dysregulation of IFN-β and S100B
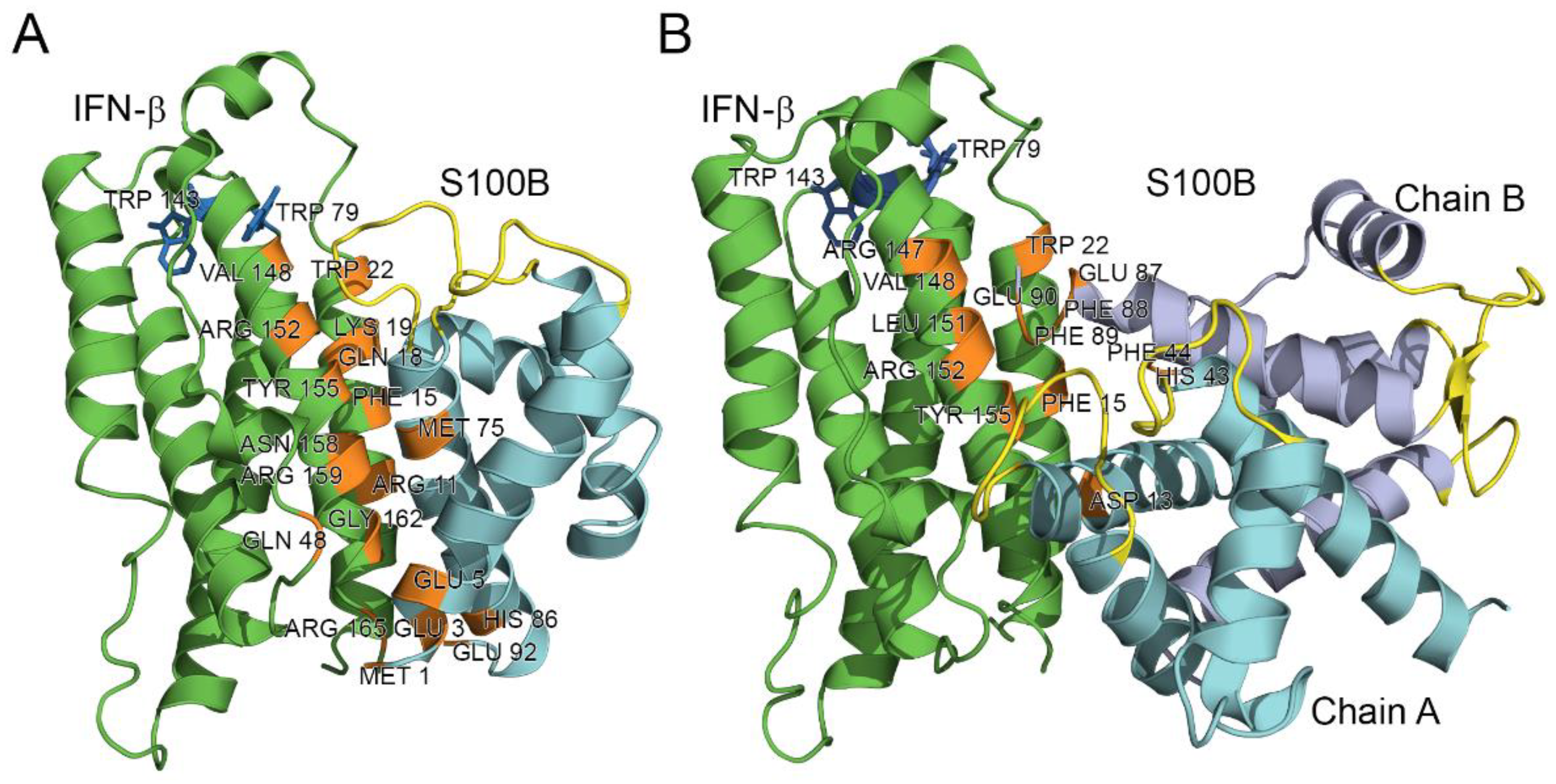
2.4. Modeling of S100B–IFN-β Complexes
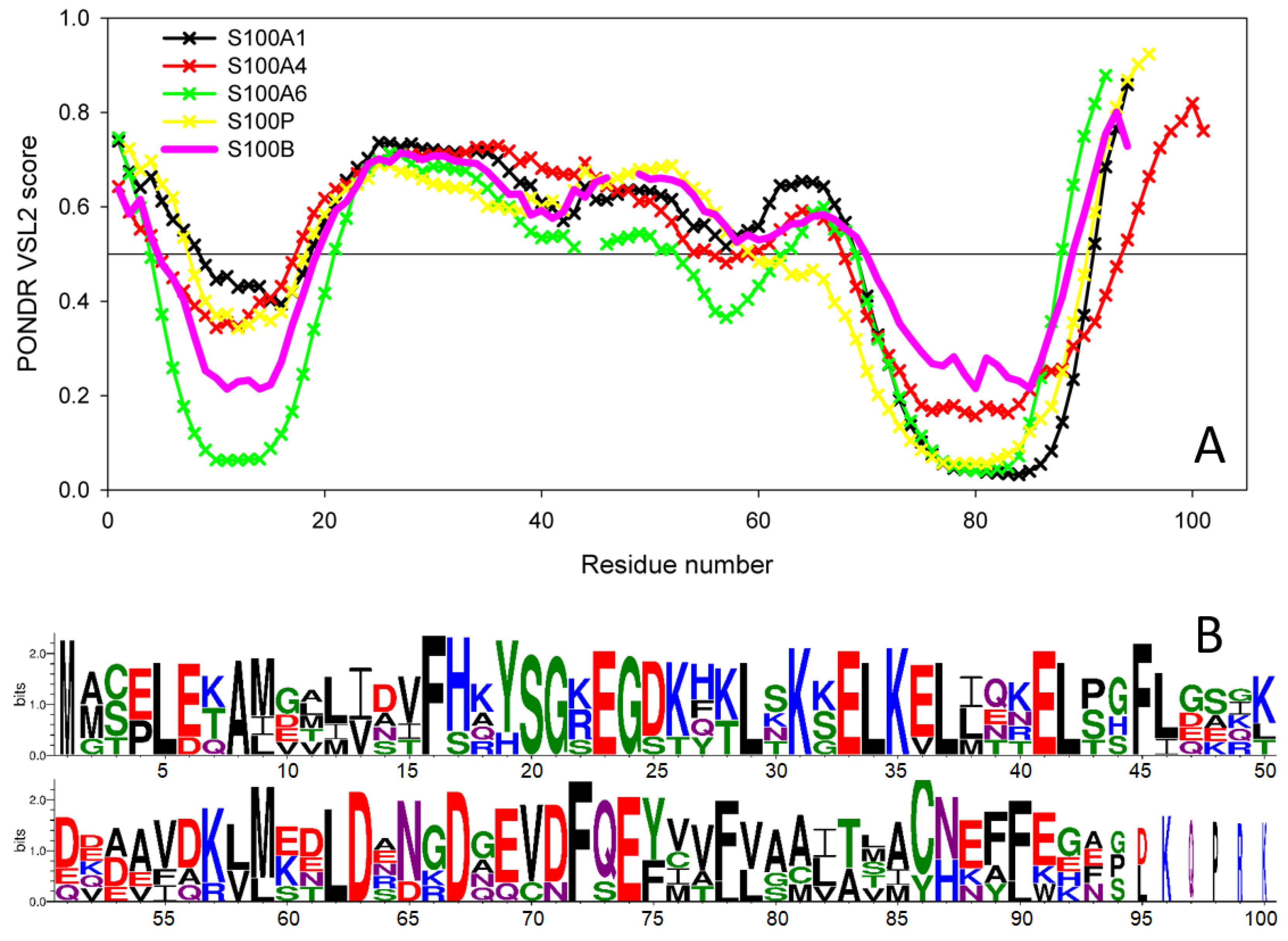
2.5. Intrinsic Disorder Propensity of S100B
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Chemical Crosslinking
3.3. Fluorescence Measurements
3.4. Surface Plasmon Resonance Studies
L1 + A ↔ L1A; L2 + A ↔ L2A
kd1 kd2
3.5. Cell Viability Studies
3.6. Search of Diseases Associated with IFN-β and S100B
3.7. Modeling of S100B–IFN-β Complexes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADSVSL2 | average disorder score evaluated by PONDR® VSL2 algorithm |
| CHO-K1 | cell line from Chinese hamster ovary cells |
| DisGeNET | database of human gene–disease associations and variant–disease associations [67] |
| DTT | DL-dithiothreitol |
| EDAC | N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid |
| IFNAR1/2 | subunits of interferon receptor |
| IFNB1 | gene of human interferon-β |
| IFN-β | Interferon-β |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| MCF-7 | human breast cancer cell line |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| OTP | Open Targets Platform [67] |
| PAGE | polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| PONDR® | Predictor of Natural Disordered Regions (http://www.pondr.com/ accessed on 26 November 2021) |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| RAGE | receptor for advanced glycation end products |
| RU | resonance unit |
| SARS-CoV-2 | severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SPR | surface plasmon resonance |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| sulfo-NHS | N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide |
| S100A1, S100A4, S100A6, S100B, S100P | members of S100 protein family |
| TWEEN 20 | polyethylene glycol sorbitan monolaurate |
References
- Abdolvahab, M.H.; Mofrad, M.; Schellekens, H. Interferon Beta: From Molecular Level to Therapeutic Effects. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 326, 343–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, U. Induction and Function of IFNβ During Viral and Bacterial Infection. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 31, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiscott, J.; Nguyen, H.; Lin, R. Molecular mechanisms of interferon beta gene induction. Semin. Virol. 1995, 6, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-F.; Gong, M.-J.; Zhao, F.-R.; Shao, J.-J.; Xie, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-G.; Chang, H.-Y. Type I Interferons: Distinct Biological Activities and Current Applications for Viral Infection. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 2377–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, R.F.V.; Hunger, A.; Mendonça, S.A.; Barbuto, J.A.M.; Strauss, B.E. Immunomodulatory and antitumor effects of type I interferons and their application in cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 71249–71284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxx, G.M.; Cheng, G. The Roles of Type I Interferon in Bacterial Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar, S.; Anfossi, R.; Humeres, C.; Vivar, R.; Boza, P.; Munoz, C.; Pardo-Jimenez, V.; Olivares-Silva, F.; Diaz-Araya, G. IFN-beta Plays Both Pro- and Anti-inflammatory Roles in the Rat Cardiac Fibroblast Through Differential STAT Protein Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohan, S.L.; Hendin, B.A.; Reder, A.T.; Smoot, K.; Avila, R.; Mendoza, J.P.; Weinstock-Guttman, B. Interferons and Multiple Sclerosis: Lessons from 25 Years of Clinical and Real-World Experience with Intramuscular Interferon Beta-1a (Avonex). CNS Drugs 2021, 35, 743–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolvahab, M.H.; Darvishi, B.; Zarei, M.; Majidzadeh-A, K.; Farahmand, L. Interferons: Role in cancer therapy. Immunotherapy 2020, 12, 833–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, P.D.; Marsden, R.J.; Tear, V.J.; Brookes, J.; Batten, T.N.; Mankowski, M.; Gabbay, F.J.; Davies, D.E.; Holgate, S.T.; Ho, L.P.; et al. Safety and efficacy of inhaled nebulised interferon beta-1a (SNG001) for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, H.E.; Antos, D.; Melton, N.R.; Alcorn, J.F.; Manni, M.L. Insights Into Type I and III Interferons in Asthma and Exacerbations. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 574027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borden, E.C. Interferons alpha and beta in cancer: Therapeutic opportunities from new insights. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, C.; Bertagna, M.; Cohen, M. Cutaneous Side-effects of Immunomodulators in MS. Int. MS J. 2011, 17, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Durelli, L.; Ferrero, B.; Oggero, A.; Verdun, E.; Ghezzi, A.; Montanari, E.; Zaffaroni, M. Liver and thyroid function and autoimmunity during interferon-beta 1b treatment for MS. Neurology 2001, 57, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reder, A.T.; Oger, J.F.; Kappos, L.; O’Connor, P.; Rametta, M. Short-term and long-term safety and tolerability of interferon beta-1b in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2014, 3, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba Pale, L.; Leon Caballero, J.; Samso Buxareu, B.; Salgado Serrano, P.; Perez Sola, V. Systematic review of depression in patients with multiple sclerosis and its relationship to interferonbeta treatment. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2017, 17, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.; Lee, M.W.; Wolf, A.J.; Limon, J.J.; Becker, C.A.; Ding, M.; Murali, R.; Lee, E.Y.; Liu, G.Y.; Wong, G.C.L.; et al. Direct Antimicrobial Activity of IFN-beta. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4036–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabir, N.; Hussain, T.; Shah, S.Z.A.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, X. IFN-beta: A Contentious Player in Host-Pathogen Interaction in Tuberculosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.J.; Rajaiah, R.; Tennant, S.M.; Ramachandran, G.; Higginson, E.E.; Dyson, T.N.; Vogel, S.N. SalmonellaTyphimurium Co-Opts the Host Type I IFN System To Restrict Macrophage Innate Immune Transcriptional Responses Selectively. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 2461–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.R.; Wang, B.; Wan, Y.-W.; Chiu, G.; Cole, A.; Yin, Z.; Propson, N.E.; Xu, Y.; Jankowsky, J.L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Type I interferon response drives neuroinflammation and synapse loss in Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1912–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-J. Type1 Interferons Potential Initiating Factors Linking Skin Wounds With Psoriasis Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rackov, G.; Shokri, R.; De Mon, M.Á.; Balomenos, D. The Role of IFN-β during the Course of Sepsis Progression and Its Therapeutic Potential. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.P.; Henry, R.; Shirey, K.A.; Doran, S.J.; Makarevich, O.D.; Ritzel, R.; Meadows, V.A.; Vogel, S.N.; Faden, A.I.; Stoica, B.A.; et al. Interferon-β Plays a Detrimental Role in Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury by Enhancing Neuroinflammation That Drives Chronic Neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 2357–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khsheibun, R.; Paperna, T.; Volkowich, A.; Lejbkowicz, I.; Avidan, N.; Miller, A. Gene Expression Profiling of the Response to Interferon Beta in Epstein-Barr-Transformed and Primary B Cells of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoggins, J.W. Interferon-Stimulated Genes: What Do They All Do? Annu. Rev. Virol. 2019, 6, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Weerd, N.A.; Vivian, J.P.; Nguyen, T.K.; Mangan, N.E.; Gould, J.A.; Braniff, S.J.; Zaker-Tabrizi, L.; Fung, K.Y.; Forster, S.C.; Beddoe, T.; et al. Structural basis of a unique interferon-beta signaling axis mediated via the receptor IFNAR1. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daman, A.W.; Josefowicz, S.Z. Epigenetic and transcriptional control of interferon-β. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, 20210039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R.; Cannon, B.R.; Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Hsu, K.; Weber, D.J.; Geczy, C.L. Functions of S100 Proteins. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 24–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreejit, G.; Flynn, M.C.; Patil, M.; Krishnamurthy, P.; Murphy, A.J.; Nagareddy, P.R. S100 family proteins in inflammation and beyond. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2020, 98, 173–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakov, A.S.; Mayorov, S.A.; Deryusheva, E.; Avkhacheva, N.V.; Denessiouk, K.A.; Denesyuk, A.I.; Rastrygina, V.A.; Permyakov, E.A.; Permyakov, S.E. Highly specific interaction of monomeric S100P protein with interferon beta. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakov, A.; Sofin, A.; Avkhacheva, N.; Denesyuk, A.; Deryusheva, E.; Rastrygina, V.; Sokolov, A.; Permyakova, M.; Litus, E.; Uversky, V.; et al. Interferon Beta Activity Is Modulated via Binding of Specific S100 Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamken, P.; Lata, S.; Gavutis, M.; Piehler, J. Ligand-induced Assembling of the Type I Interferon Receptor on Supported Lipid Bilayers. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 341, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudier, J.; Deloulme, J.C.; Shaw, G.S. The Zn2+ and Ca2+-binding S100B and S100A1 proteins: Beyond the myths. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 738–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, D.B.; Weber, D.J. The Calcium-Dependent Interaction of S100B with Its Protein Targets. Cardiovasc. Psychiatry Neurol. 2010, 2010, 728052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R.; Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Arcuri, C.; Bianchi, R.; Brozzi, F.; Tubaro, C.; Giambanco, I. S100B’s double life: Intracellular regulator and extracellular signal. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 1008–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria-Kisiel, L.; Rintala-Dempsey, A.C.; Shaw, G.S. Calcium-dependent and -independent interactions of the S100 protein family. Biochem. J. 2006, 396, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, M.; Michel, P.-A.; Gateau, A.; Nikitin, F.; Schaeffer, M.; Audot, E.; Gaudet, P.; Duek, P.D.; Teixeira, D.; de Laval, V.R.; et al. The neXtProt knowledgebase in 2020: Data, tools and usability improvements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D328–D334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michetti, F.; Di Sante, G.; Clementi, M.E.; Sampaolese, B.; Casalbore, P.; Volonté, C.; Spica, V.R.; Parnigotto, P.P.; Di Liddo, R.; Amadio, S.; et al. Growing role of S100B protein as a putative therapeutic target for neurological- and nonneurological-disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 127, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, F.; Misiak, B.; Crocamo, C.; Carrà, G. Glial and neuronal markers in bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis testing S100B and NSE peripheral blood levels. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 101, 109922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.A.M.; El-Khateeb, E.A.; Harvy, M.; Emam, H.M.E.-S.; Abdelaal, W.; El Nemr, R.; El-Hagry, O.O. Study of serum levels and skin expression of S100B protein in psoriasis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2017, 92, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksovska, K.; Leoncini, E.; Bonassi, S.; Cesario, A.; Boccia, S.; Frustaci, A. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Circulating S100B Blood Levels in Schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güleş, E.; Iosifescu, D.V.; Tural, Ü. Plasma Neuronal and Glial Markers and Anterior Cingulate Metabolite Levels in Major Depressive Disorder: A Pilot Study. Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceti, A.; Margarucci, L.M.; Scaramucci, E.; Orsini, M.; Salerno, G.; Di Sante, G.; Gianfranceschi, G.; Di Liddo, R.; Valeriani, F.; Ria, F.; et al. Serum S100B protein as a marker of severity in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heizmann, C.W. S100 proteins: Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in laboratory medicine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2019, 1866, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-J.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.-M.D.; Leung, C.-H.; Ma, D.-L. Interfering with S100B–effector protein interactions for cancer therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Kuhn, M.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Minguez, P.; Doerks, T.; Stark, M.; Muller, J.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D561–D568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permyakov, E.A. Luminescent Spectroscopy of Proteins; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Ann Arbor, MI, USA; London, UK; Tokyo, Japan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Drohat, A.C.; Weber, D.J.; Nenortas, E.; Beckett, D. Oligomerization state of S100B at nanomolar concentration determined by large-zone analytical gel filtration chromatography. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 1577–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, E.; Fritz, G.; Vetter, S.W.; Heizmann, C.W. Binding of S100 proteins to RAGE: An update. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Sagar, R.; Mehta, M.; Pallavi, P.; Sharma, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. Serum S100B levels in patients with depression. Indian J. Psychiatry 2019, 61, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, O.A.; Dhib-Jalbut, S.S. Serum interferon beta-1a (Avonex) levels following intramuscular injection in relapsing-remitting MS patients. Neurology 1998, 51, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raabe, A.; Grolms, C.; Sorge, O.; Zimmermann, M.; Seifert, V. Serum S-100B Protein in Severe Head Injury. Neurosurgery 1999, 45, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Dong, X.-Q.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Yu, W.-H.; Zhang, Z.-Y. High S100B levels in cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood of patients with acute basal ganglial hemorrhage are associated with poor outcome. World J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.Y.; Seol, J.H.; Yi, C.H.; Lee, W.H. Cerebrospinal fluid type I interferon and cytokine profiles in enteroviral meningitis according to the presence or absence of pleocytosis. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2021, 62, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, D.J.; Kolla, V.; Kalvakolanu, D.V.; Borden, E.C. Tamoxifen enhances interferon-regulated gene expression in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1997, 167, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, D.J.; Hofmann, E.R.; Karra, S.; Kalvakolanu, D.V. The interferon-β and tamoxifen combination induces apoptosis using thioredoxin reductase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1496, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ambjørn, M.; Ejlerskov, P.; Liu, Y.; Lees, M.; Jäättelä, M.; Issazadeh-Navikas, S. IFNB1/interferon-β-induced autophagy in MCF-7 breast cancer cells counteracts its proapoptotic function. Autophagy 2013, 9, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, H.M.; Fritz, G.; Gomes, C.M. Analysis of S100 Oligomers and Amyloids. Program. Necrosis 2012, 849, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, I.T.; Porter, K.A.; Xia, B.; Kozakov, D.; Vajda, S. Performance and Its Limits in Rigid Body Protein-Protein Docking. Structure 2020, 28, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permyakov, S.E.; Ismailov, R.G.; Xue, B.; Denesyuk, A.I.; Uversky, V.N.; Permyakov, E.A. Intrinsic disorder in S100 proteins. Mol. BioSyst. 2011, 7, 2164–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.-M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A Sequence Logo Generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Stephens, R.M. Sequence logos: A new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6097–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Bravo, À.; Queralt-Rosinach, N.; Gutiérrez-Sacristán, A.; Deu-Pons, J.; Centeno, E.; García-García, J.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. DisGeNET: A comprehensive platform integrating information on human disease-associated genes and variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D833–D839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Silva, D.; Pierleoni, A.; Pignatelli, M.; Ong, C.K.; Fumis, L.; Karamanis, N.; Carmona, M.; Faulconbridge, A.; Hercules, A.; McAuley, E.; et al. Open Targets Platform: New developments and updates two years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1056–D1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.A.; Ecsédi, P.; Kovács, G.M.; Póti, Á.L.; Reményi, A.; Kardos, J.; Gógl, G.; Nyitray, L. High-throughput competitive fluorescence polarization assay reveals functional redundancy in the S100 protein family. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 2834–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresnick, A.R.; Weber, D.J.; Zimmer, D.B. S100 proteins in cancer. Nat. Cancer 2015, 15, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazakov, A.S.; Sofin, A.D.; Avkhacheva, N.V.; Deryusheva, E.I.; Rastrygina, V.A.; Permyakova, M.E.; Uversky, V.N.; Permyakov, E.A.; Permyakov, S.E. Interferon-β Activity Is Affected by S100B Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23041997
Kazakov AS, Sofin AD, Avkhacheva NV, Deryusheva EI, Rastrygina VA, Permyakova ME, Uversky VN, Permyakov EA, Permyakov SE. Interferon-β Activity Is Affected by S100B Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(4):1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23041997
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazakov, Alexey S., Alexander D. Sofin, Nadezhda V. Avkhacheva, Evgenia I. Deryusheva, Victoria A. Rastrygina, Maria E. Permyakova, Vladimir N. Uversky, Eugene A. Permyakov, and Sergei E. Permyakov. 2022. "Interferon-β Activity Is Affected by S100B Protein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 4: 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23041997
APA StyleKazakov, A. S., Sofin, A. D., Avkhacheva, N. V., Deryusheva, E. I., Rastrygina, V. A., Permyakova, M. E., Uversky, V. N., Permyakov, E. A., & Permyakov, S. E. (2022). Interferon-β Activity Is Affected by S100B Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(4), 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23041997









