Deletion of TNF in Winnie-APCMin/+ Mice Reveals Its Dual Role in the Onset and Progression of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
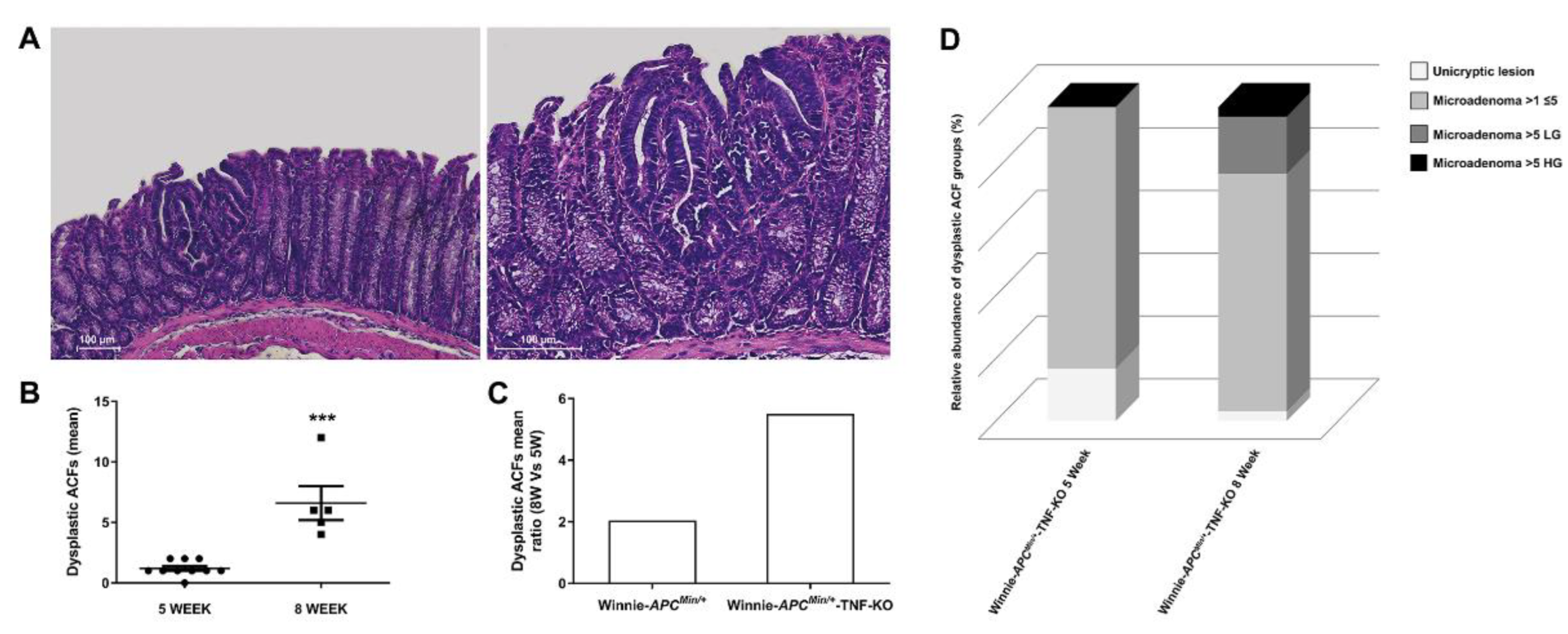
2.1. The Absence of TNF Does Not Protect 5-Wk-Old Winnie-ApcMin/+-TNF-KO Mice from the Development of Dysplastic Lesions
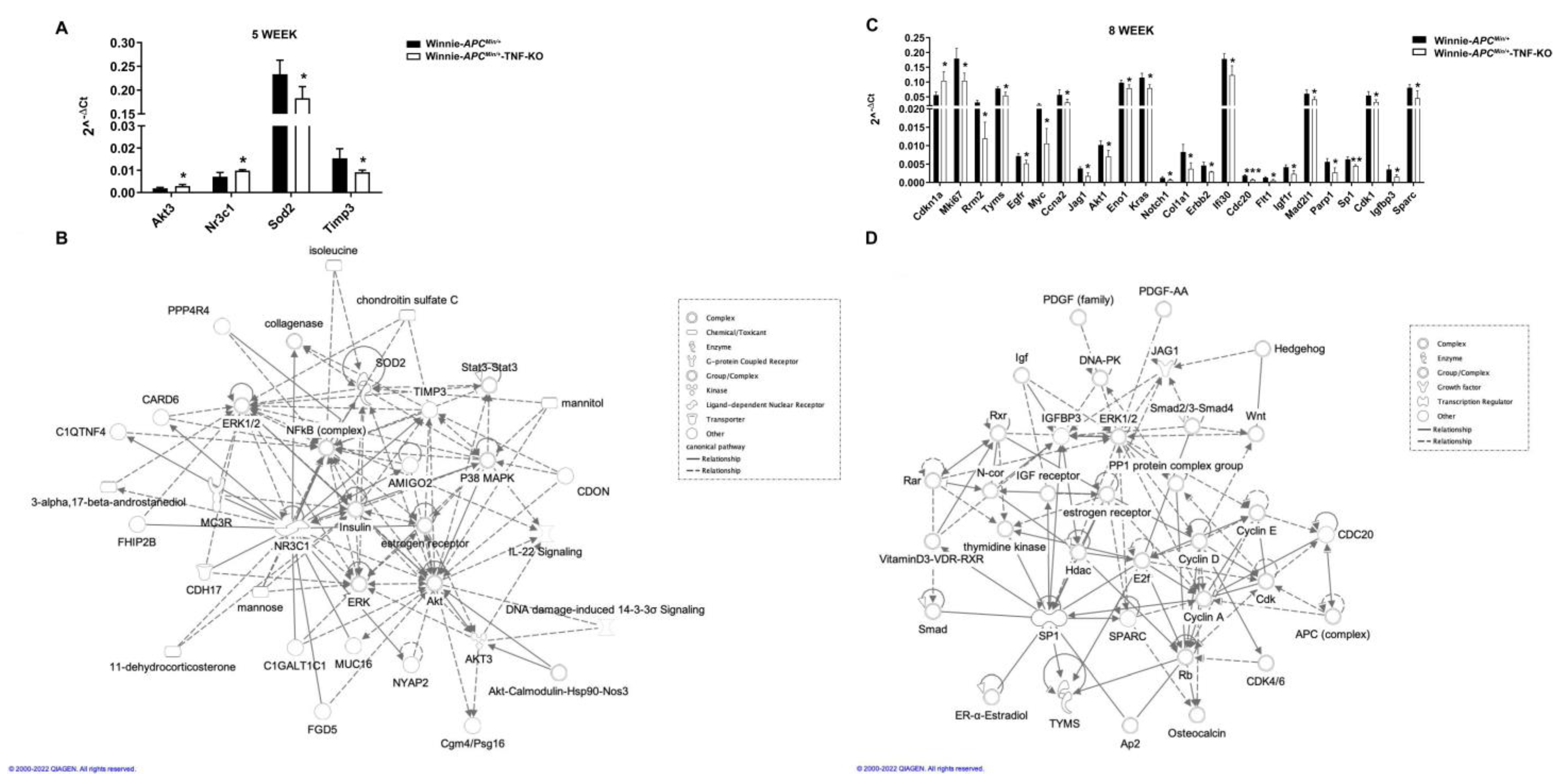
2.2. Deletion of TNF Increases Multiplicity and Tumor Grading of Dysplastic ACFs in 8-wk-Old Winnie-ApcMin/+-TNF-KO Mice
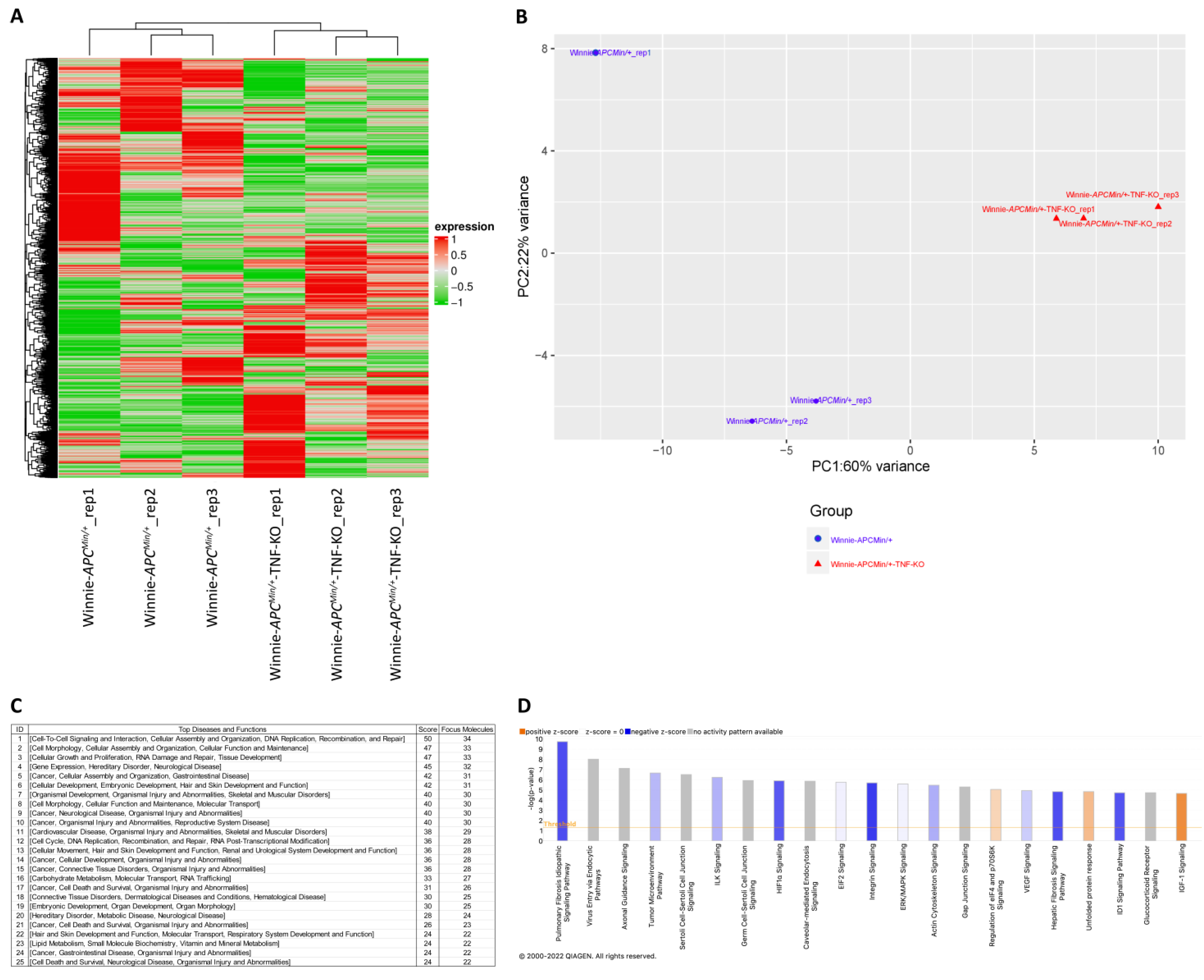
2.3. Molecular Profiling of Whole Tissue and Macrodissected Tumoral Lesions Reveals the Activation of Cancer-Related Pathways with a More Aggressive Phenotype in 8-Wk-Old Winnie-ApcMin/+-TNF-KO Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Studies
4.2. Histology
4.3. RNA Extraction from Colon Tissue and qPCR Analysis
4.4. RNA Extraction from Macrodissected Tumors
4.5. RNA Exome Sequencing
4.6. Statistical and Bioinformatics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molodecky, N.A.; Kaplan, G.G. Environmental risk factors for inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 6, 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzick, J.; Otto, F.; Baron, J.A.; Brown, P.H.; Burn, J.; Greenwald, P.; Jankowski, J.; La Vecchia, C.; Meyskens, F.; Senn, H.J.; et al. Aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for cancer prevention: An international consensus statement. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colotta, F.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: Links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, C.; Cho, J.H. Inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jess, T.; Simonsen, J.; Jorgensen, K.T.; Pedersen, B.V.; Nielsen, N.M.; Frisch, M. Decreasing risk of colorectal cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease over 30 years. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 375–381.e1; quiz e313–e374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jess, T.; Rungoe, C.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: A meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peneau, A.; Savoye, G.; Turck, D.; Dauchet, L.; Fumery, M.; Salleron, J.; Lerebours, E.; Ligier, K.; Vasseur, F.; Dupas, J.L.; et al. Mortality and cancer in pediatric-onset inflammatory bowel disease: A population-based study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, G.C.; Yan, F.; Polk, D.B. Mesalamine blocks tumor necrosis factor growth inhibition and nuclear factor kappaB activation in mouse colonocytes. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaik, F.D.; van Oijen, M.G.; Smeets, H.M.; van der Heijden, G.J.; Siersema, P.D.; Oldenburg, B. Thiopurines prevent advanced colorectal neoplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2012, 61, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayos, F.S.; Terdiman, J.P.; Walsh, J.M. Effect of 5-aminosalicylate use on colorectal cancer and dysplasia risk: A systematic review and metaanalysis of observational studies. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jess, T.; Lopez, A.; Andersson, M.; Beaugerie, L.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Thiopurines and risk of colorectal neoplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1793–1800.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Vuitton, L.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Biologic agents for IBD: Practical insights. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, O.H.; Ainsworth, M.A. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liso, M.; Verna, G.; Cavalcanti, E.; De Santis, S.; Armentano, R.; Tafaro, A.; Lippolis, A.; Campiglia, P.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mastronardi, M.; et al. Interleukin 1β Blockade Reduces Intestinal Inflammation in a Murine Model of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Independent Ulcerative Colitis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedano, R.; Ma, C.; Jairath, V.; Feagan, B.G. Janus Kinase Inhibitors for the Management of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 18, 14–27. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, C.; Kwok, H.; Harrow, P.; Vega, R.; Seward, E.; Mehta, S.; Rahman, F.; McCartney, S.; Parisi, I.; Lim, S.H.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of a second-line biologic in patients with ulcerative colitis: Vedolizumab followed by an anti-TNF versus anti-TNF followed by vedolizumab. Front. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, R.; Neurath, M.F. IL-23 Blockade in Anti-TNF Refractory IBD: From Mechanisms to Clinical Reality. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, ii54–ii63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onali, S.; Pugliese, D.; Caprioli, F.A.; Orlando, A.; Biancone, L.; Nardone, O.M.; Imperatore, N.; Fiorino, G.; Cappello, M.; Viola, A.; et al. An Objective Comparison of Vedolizumab and Ustekinumab Effectiveness in Crohn’s Disease Patients’ Failure to TNF-Alpha Inhibitors. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyboe Andersen, N.; Pasternak, B.; Basit, S.; Andersson, M.; Svanstrom, H.; Caspersen, S.; Munkholm, P.; Hviid, A.; Jess, T. Association between tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists and risk of cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. JAMA 2014, 311, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Loftus, E.V. Balancing the risks and benefits of infliximab in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2004, 53, 780–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertazza, L.; Mocellin, S. The dual role of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in cancer biology. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 3337–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deventer, S.J. Transmembrane TNF-alpha, induction of apoptosis, and the efficacy of TNF-targeting therapies in Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlosarek, P.; Charles, K.A.; Balkwill, F.R. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha as a tumour promoter. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnini, C.; Cominelli, F. Tumor Necrosis Factor’s Pathway in Crohn’s Disease: Potential for Intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruder, B.; Atreya, R.; Becker, C. Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha in Intestinal Homeostasis and Gut Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, S.; Verna, G.; Serino, G.; Armentano, R.; Cavalcanti, E.; Liso, M.; Dicarlo, M.; Coletta, S.; Mastronardi, M.; Lippolis, A.; et al. Winnie-APC(Min/+) Mice: A Spontaneous Model of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer Combining Genetics and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, S.; Liso, M.; Vacca, M.; Verna, G.; Cavalcanti, E.; Coletta, S.; Calabrese, F.M.; Eri, R.; Lippolis, A.; Armentano, R.; et al. Dysbiosis Triggers ACF Development in Genetically Predisposed Subjects. Cancers 2021, 13, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasparakis, M.; Alexopoulou, L.; Episkopou, V.; Kollias, G. Immune and inflammatory responses in TNF alpha-deficient mice: A critical requirement for TNF alpha in the formation of primary B cell follicles, follicular dendritic cell networks and germinal centers, and in the maturation of the humoral immune response. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 1397–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, S.; Kunde, D.; Galleggiante, V.; Liso, M.; Scandiffio, L.; Serino, G.; Pinto, A.; Campiglia, P.; Sorrentino, R.; Cavalcanti, E.; et al. TNFalpha deficiency results in increased IL-1beta in an early onset of spontaneous murine colitis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, R.J.; Arends, M.J.; Churchhouse, A.M.D.; Din, S. Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Associated Colorectal Cancer: Translational Risks from Mechanisms to Medicines. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2021, 15, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.C.; Itzkowitz, S.H. Colorectal Cancer in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Mechanisms and Management. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 715–730.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafimehr, H.; Aghdaei, H.A.; Pourhoseingholi, M.A.; Shalmani, H.M.; Vahedian-Azimi, A.; Kroh, M.; Zali, M.R.; Sahebkar, A. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Association between Inflammatory Bowel Disease Family History and Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 4874459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri, S.; Kuenzig, M.E.; Benchimol, E.I. Long-term outcomes of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 26, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Zong, X.; Li, Z.; Li, N.; Hur, J.; Fritz, C.D.; Chapman, W., Jr.; Nickel, K.B.; Tipping, A.; et al. Metabolic syndrome, metabolic comorbid conditions and risk of early-onset colorectal cancer. Gut 2021, 70, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofseth, L.J.; Hebert, J.R.; Chanda, A.; Chen, H.; Love, B.L.; Pena, M.M.; Murphy, E.A.; Sajish, M.; Sheth, A.; Buckhaults, P.J.; et al. Early-onset colorectal cancer: Initial clues and current views. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreis, N.-N.; Louwen, F.; Yuan, J. The Multifaceted p21 (Cip1/Waf1/CDKN1A) in Cell Differentiation, Migration and Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Bian, F.; Ma, P.; De Paiva, C.S.; Stern, M.; Pflugfelder, S.C.; Li, D.Q. Induction of Th17 differentiation by corneal epithelial-derived cytokines. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 222, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.P.; Schön, M.P.; Wallbrecht, K.; Michaelis, K.; Rinner, B.; Mayer, G.; Schmidbauer, U.; Strohmaier, H.; Wang, X.-J.; Wolf, P. 8-methoxypsoralen plus ultraviolet A therapy acts via inhibition of the IL-23/Th17 axis and induction of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells involving CTLA4 signaling in a psoriasis-like skin disorder. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 7257–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiki, Y.; Michelsen, K.S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Doherty, T.M.; Arditi, M. Transforming growth factor-beta differentially inhibits MyD88-dependent, but not TRAM- and TRIF-dependent, lipopolysaccharide-induced TLR4 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 5491–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principe, D.R.; DeCant, B.; Staudacher, J.; Vitello, D.; Mangan, R.J.; Wayne, E.A.; Mascariñas, E.; Diaz, A.M.; Bauer, J.; McKinney, R.D.; et al. Loss of TGFβ signaling promotes colon cancer progression and tumor-associated inflammation. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 3826–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itatani, Y.; Kawada, K.; Sakai, Y. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer and Its Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massagué, J.; Seoane, J.; Wotton, D. Smad transcription factors. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2783–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, S.; Hirata, Y.; Koike, K. TGF-β in inflammatory bowel disease: A key regulator of immune cells, epithelium, and the intestinal microbiota. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, R.; Andrés, E.; Gonzalez, L.; Llonch, E.; Igea, A.; Gutierrez-Prat, N.; Berenguer-Llergo, A.; Nebreda, A.R. Regulation of tumor angiogenesis and mesenchymal–endothelial transition by p38α through TGF-β and JNK signaling. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. The Subread aligner: Fast, accurate and scalable read mapping by seed-and-vote. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 5 Week | Non Dysplastic ACFs | Dysplastic ACFs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Groups | Unicryptic Lesion | Microadenoma >1 ≤ 5−LG | ||||||
| Genotype (nr. Mice) | Incidence (%) | Multiplicity (Mean ± SEM) | Incidence (%) | Multiplicity (Mean ± SEM) | Incidence (%) | Multiplicity (Mean ± SEM) | Incidence (%) | Multiplicity (Mean ± SEM) |
| PROXIMAL COLON | ||||||||
| TNF-KO (8) | 12.5 | 0.125 ± 0.125 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Winnie-TNF-KO (8) | 12.5 | 0.2 ± 0.25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| APCMin/+-TNF-KO (10) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Winnie-APCMin/+-TNF-KO (10) | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| MEDIAL COLON | ||||||||
| TNF-KO (8) | 12.5 | 0.125 ± 0.125 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Winnie-TNF-KO (8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| APCMin/+-TNF-KO (10) | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 100 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| Winnie-APCMin/+-TNF-KO (10) | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0.2 ± 0.13 | 50 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 50 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| DISTAL COLON | ||||||||
| TNF-KO (8) | 12.5 | 0.125 ± 0.125 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Winnie-TNF-KO (8) | 0 | 0 | 12.5 | 0.11 ± 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0.11 ± 0.13 |
| APCMin/+-TNF-KO (10) | 0 | 0 | 30 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 50 | 0.3 ± 0.21 | 50 | 0.3 ± 0.21 |
| Winnie-APCMin/+-TNF-KO (10) | 0 | 0 | 90 | 1.2 ± 0.26 | 16.7 | 0.2 ± 0.13 | 83.3 | 1 ± 0.25 |
| Top Upstream Regulators | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name | p-Value | Predicted Activation |
| MYC | 1.07 × 10−17 | |
| Beta-estradiol | 6.23 × 10−16 | Inhibited |
| KRAS | 8.47 × 10−16 | |
| APP | 2.81 × 10−14 | Inhibited |
| TGFβ | 9.12 × 10−14 | Inhibited |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verna, G.; Liso, M.; Cavalcanti, E.; Armentano, R.; Miraglia, A.; Monsurrò, V.; Chieppa, M.; De Santis, S. Deletion of TNF in Winnie-APCMin/+ Mice Reveals Its Dual Role in the Onset and Progression of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315145
Verna G, Liso M, Cavalcanti E, Armentano R, Miraglia A, Monsurrò V, Chieppa M, De Santis S. Deletion of TNF in Winnie-APCMin/+ Mice Reveals Its Dual Role in the Onset and Progression of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):15145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315145
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerna, Giulio, Marina Liso, Elisabetta Cavalcanti, Raffaele Armentano, Alessandro Miraglia, Vladia Monsurrò, Marcello Chieppa, and Stefania De Santis. 2022. "Deletion of TNF in Winnie-APCMin/+ Mice Reveals Its Dual Role in the Onset and Progression of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 15145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315145
APA StyleVerna, G., Liso, M., Cavalcanti, E., Armentano, R., Miraglia, A., Monsurrò, V., Chieppa, M., & De Santis, S. (2022). Deletion of TNF in Winnie-APCMin/+ Mice Reveals Its Dual Role in the Onset and Progression of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 15145. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315145










