Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles Conjugated with Dexamethasone Prevent Cisplatin Ototoxicity In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
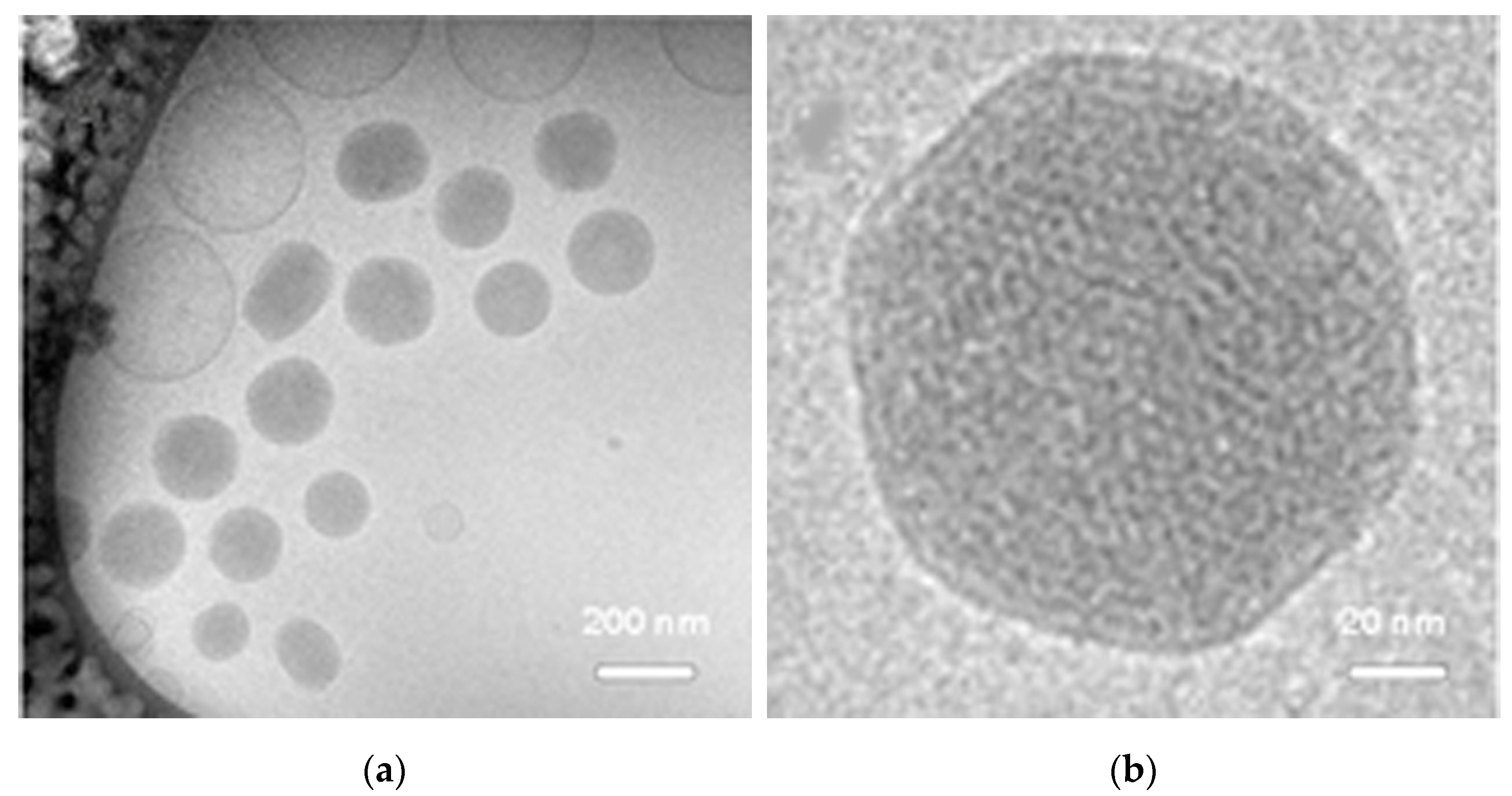
2.1. NPD Physical Chemical Characterization
2.2. NPD Cytotoxic and Protective Effects
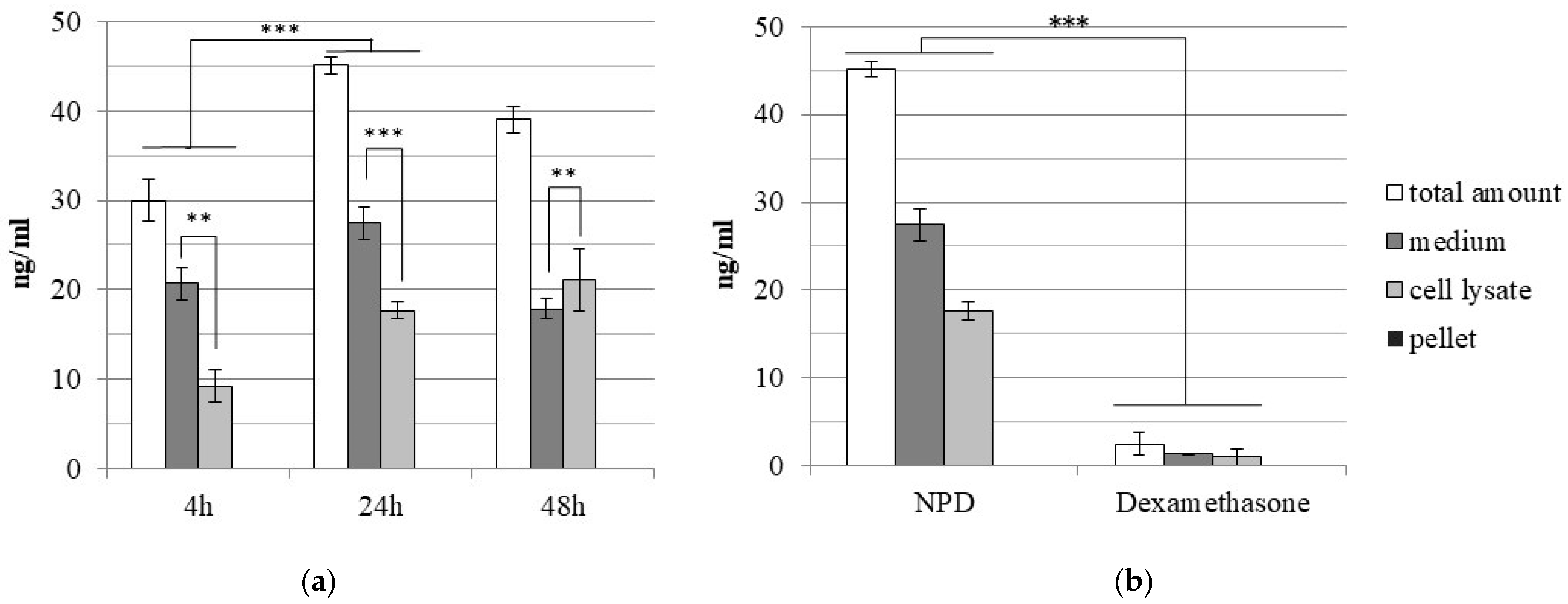
2.3. Dexamethasone Loading Efficiency
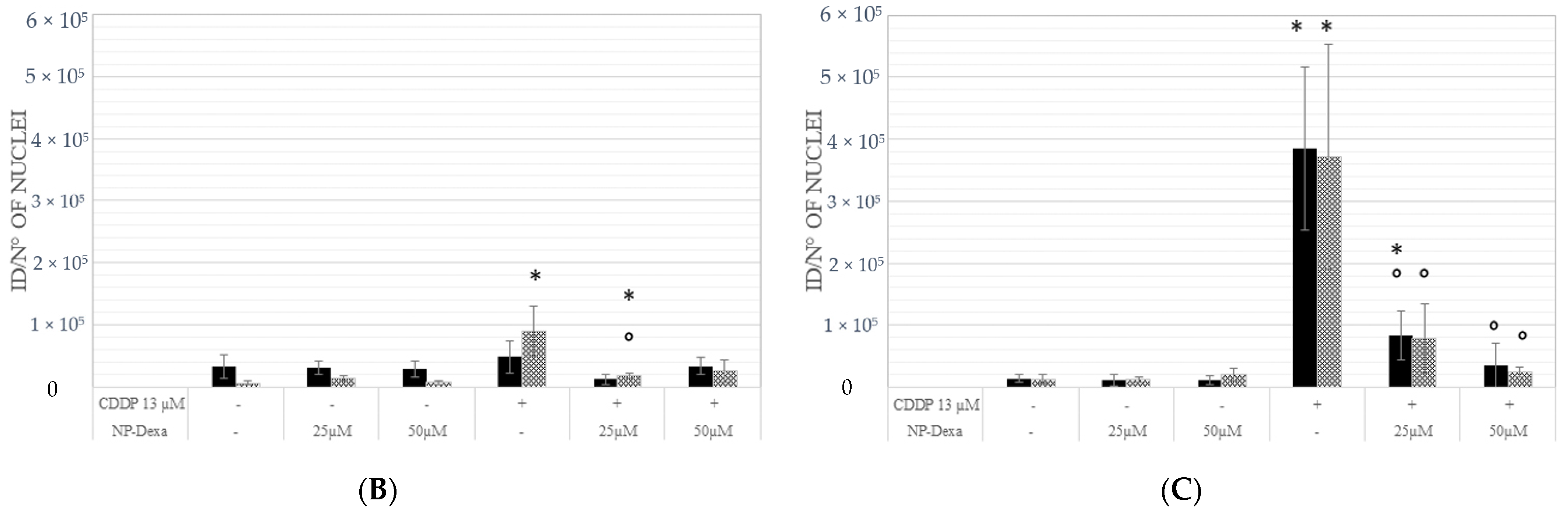
2.4. Effects of Treatment on the Cell Cycle
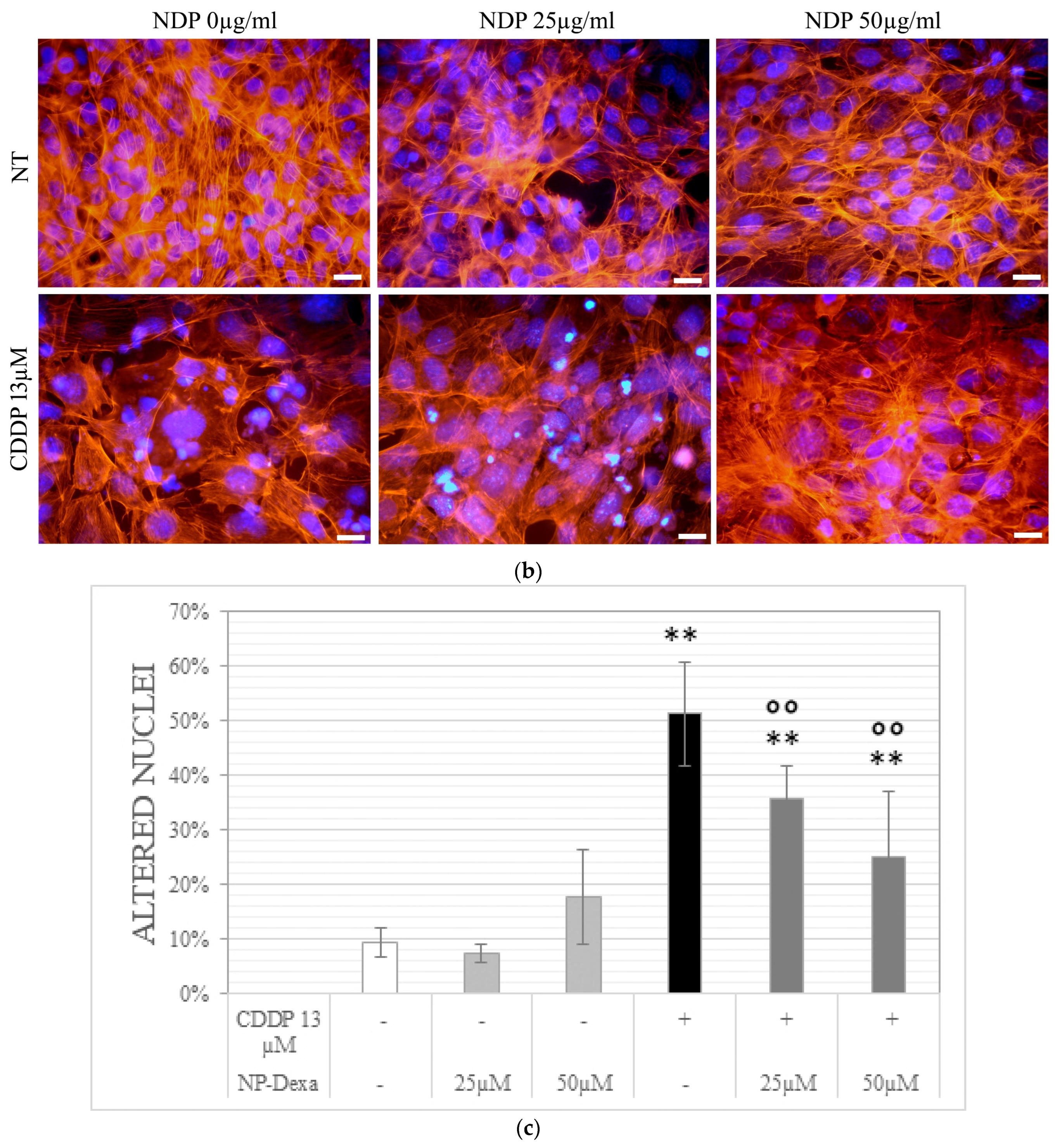
2.5. Cell Morphology Analysis
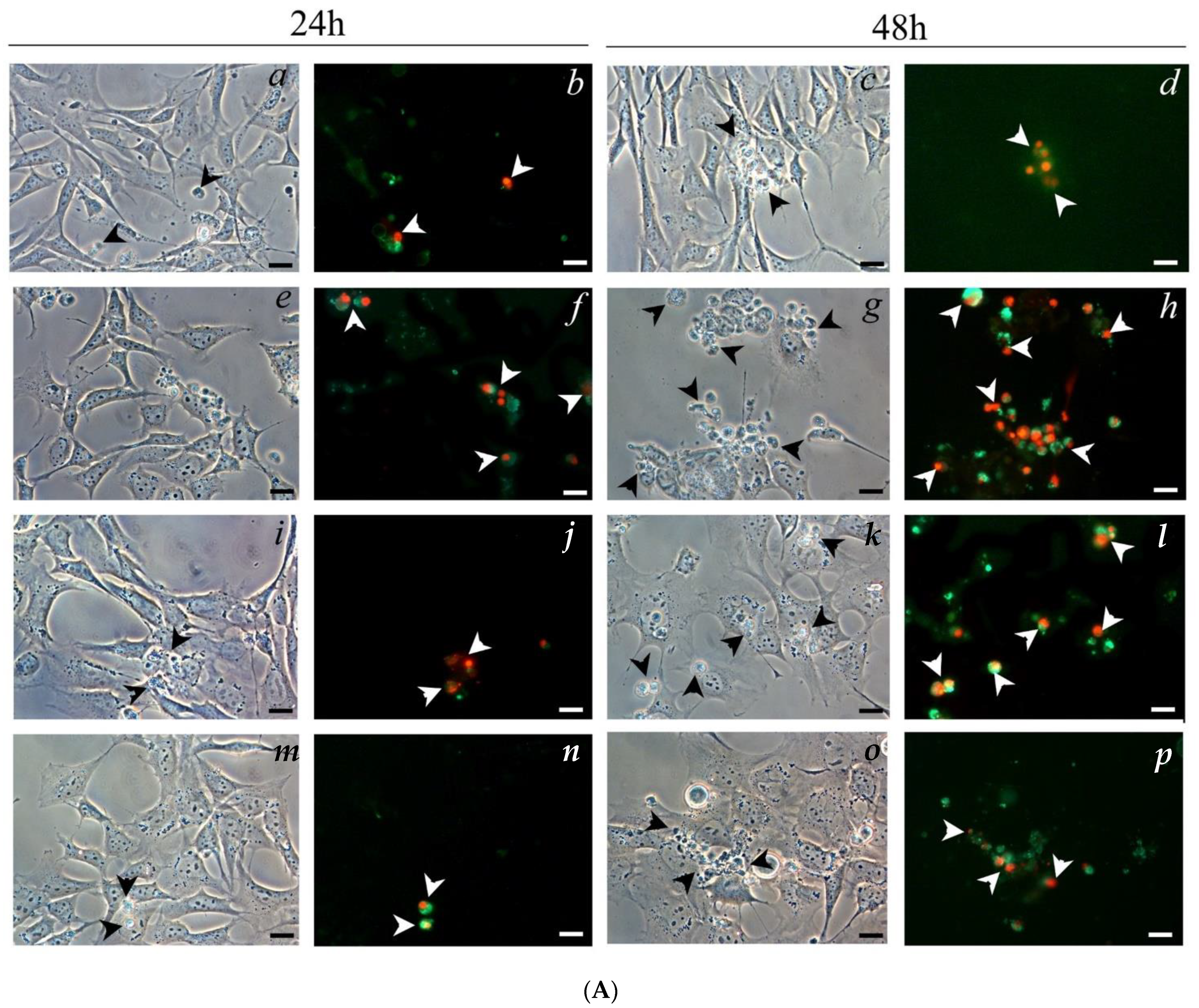
2.6. Glucocorticoid Receptor Staining
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Nanoparticles Production and Characterization
4.2. In Vitro Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC)
4.5. Cell Cycle Analyses
4.6. Cell Morphology Analysis
4.7. Glucocorticoid Receptor Staining
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fetoni, A.R.; Astolfi, L. Cisplatin ototoxicity and role of antioxidant on its prevention. Hear. Balanc. Commun. 2020, 18, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deafness and Hearing Loss. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Ciorba, A.; Astolfi, L.; Martini, A. Otoprotection and inner ear regeneration. Audiol. Med. 2008, 6, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, L.; Ghiselli, S.; Guaran, V.; Chicca, M.; Simoni, E.; Olivetto, E.; Lelli, G.; Martini, A. Correlation of adverse effects of cisplatin administration in patients affected by solid tumours: A retrospective evaluation. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The first metal based anticancer drug. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilin, E.; Simoni, E.; Candito, M.; Cazzador, D.; Astolfi, L. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: Updates on molecular targets. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Mi, Y.; Liu, L.; Dong, M.; Chen, Y.; Zou, Z. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: Updates on molecular mechanisms and otoprotective strategies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 163, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovec, T. Cisplatin and beyond: Molecular mechanisms of action and drug resistance development in cancer chemotherapy. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.C.M.; Le Prell, C.G. Drug-induced ototoxicity: Diagnosis and monitoring. Drug Saf. 2018, 41, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, S.E.; Taylor, J.; Patel, P.; Baguley, D.M. Cancer survivors treated with platinum-based chemotherapy affected by ototoxicity and the impact on quality of life: A narrative synthesis systematic review. Int. J. Audiol. 2019, 58, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiço-Costa, D.; Gil-da-Costa, M.J.; Barbosa, J.P.; Bom-Sucesso, M.; Spratley, J. Platinum-drugs ototoxicity in pediatric patients with brain tumors: A 10-Year Review. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 42, e25–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ruijven, M.W.; de Groot, J.C.; Klis, S.F.; Smoorenburg, G.F. The cochlear targets of cisplatin: An electrophysiological and morphological time-sequence study. Hear. Res. 2005, 205, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Previati, M.; Lanzoni, I.; Astolfi, L.; Fagioli, F.; Vecchiati, G.; Pagnoni, A.; Martini, A.; Capitani, S. Cisplatin cytotoxicity in organ of Corti-derived immortalized cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 101, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giari, L.; Dezfuli, B.S.; Astolfi, L.; Martini, A. Ultrastructural effects of cisplatin on the inner ear and lateral line system of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Eramo, S.L.; Paciello, F.; Rolesi, R.; Podda, M.V.; Troiani, D.; Paludetti, G. Curcuma longa (curcumin) decreases in vivo cisplatin-induced ototoxicity through heme oxygenase-1 induction. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, e169–e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldán-Fidalgo, A.; Martín Saldaña, S.; Trinidad, A.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B.; Rodríguez-Valiente, A.; García-Berrocal, J.R.; Ramírez-Camacho, R. In vitro and in vivo effects of lutein against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 68, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, L.; Simoni, E.; Ciorba, A.; Martini, A. In vitro protective effects of Ginkgo biloba against cisplatin toxicity in mouse cell line OCk3. Audiol. Med. 2008, 6, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, B.; Arana, L.; Murillo-Cuesta, S.; Bruno, M.; Alkorta, I.; Varela-Nieto, I. Solid lipid nanoparticles loaded with glucocorticoids protect auditory cells from cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnes, L.S.; Sun, A.H.; Freeman, D.J. Corticosteroid pharmacokinetics in the inner ear fluids: An animal study followed by clinical application. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, F.; Astolfi, L.; Simoni, E.; Danti, S.; Franceschini, V.; Chicca, M.; Martini, A. Nanoparticle drug delivery systems for inner ear therapy: An overview. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 39, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plontke, S.K.; Liebau, A.; Lehner, E.; Bethmann, D.; Mäder, K.; Rahne, T. Safety and audiological outcome in a case series of tertiary therapy of sudden hearing loss with a biodegradable drug delivery implant for controlled release of dexamethasone to the inner ear. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 892777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.H.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, H.J.; Na, G.; Kim, S.H. Effect of dexamethasone combination with gentamicin in chemical labyrinthectomy on hearing preservation and vertigo control in patients with unilateral Meniere’s disease: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himeno, C.; Komeda, M.; Izumikawa, M.; Takemura, K.; Yagi, M.; Weiping, Y.; Doi, T.; Kuriyama, H.; Miller, J.M.; Yamashita, T. Intra-cochlear administration of dexamethasone attenuates aminoglycoside ototoxicity in the guinea pig. Hear. Res. 2002, 167, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemura, K.; Komeda, M.; Yagi, M.; Himeno, C.; Izumikawa, M.; Doi, T.; Kuriyama, H.; Miller, J.M.; Yamashita, T. Direct inner ear infusion of dexamethasone attenuates noise-induced trauma in guinea pig. Hear. Res. 2004, 196, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daldal, A.; Odabasi, O.; Serbetcioglu, B. The protective effect of intratympanic dexamethasone on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 137, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, C.T.; Chen, S.; Bas, E.; Dinh, J.; Goncalves, S.; Telischi, F.; Angeli, S.; Eshraghi, A.A.; Van De Water, T. Dexamethasone protects against apoptotic cell death of cisplatin-exposed auditory hair cells in vitro. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhn, S.K.; Rybak, L.P. Labyrinthine barriers and cochlear homeostasis. Acta Otolaryngol. 1981, 91, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamura, N.; Salt, A.N. Permeability changes of the blood-labyrinth barrier measured in vivo during experimental treatments. Hear. Res. 1992, 61, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.S.; Yang, R. Inner ear drug delivery for sensorineural hearing loss: Current challenges and opportunities. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 867453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, E.; Valente, F.; Boge, L.; Eriksson, M.; Gentilin, E.; Candito, M.; Cazzador, D.; Astolfi, L. Biocompatibility of glycerol monooleate nanoparticles as tested on inner ear cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zook, J.M.; Maccuspie, R.I.; Locascio, L.E.; Halter, M.D.; Elliott, J.T. Stable nanoparticle aggregates/agglomerates of different sizes and the effect of their size on hemolytic cytotoxicity. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, T.M.; Grusche, F.; Acharya, D.; Shukla, R.; Bansal, V.; Waddington, L.J.; Monaghan, P.; Muir, B.W. Bicontinuous cubic phase nanoparticle lipid chemistry affects toxicity in cultured cells. Toxicol. Res. 2014, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, F.; Bysell, H.; Simoni, E.; Boge, L.; Eriksson, M.; Martini, A.; Astolfi, L. Evaluation of toxicity of glycerol monooleate nanoparticles on PC12 cell line. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 539, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Che, X.; Bao, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, J. The effect of surface charge of glycerol monooleate-based nanoparticles on the round window membrane permeability and cochlear distribution. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spicer, P.T.; Small, W.B.; Small, W.B.; Lynch, M.L.; Burns, J.L. Dry powder precursors of cubic liquid crystalline nanoparticles (cubosomes). J. Nanopart. Res. 2002, 4, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boge, L.; Bysell, H.; Ringstad, L.; Wennman, D.; Umerska, A.; Cassisa, V.; Eriksson, J.; Joly-Guillou, M.L.; Edwards, K.; Andersson, M. Lipid-based liquid crystals as carriers for antimicrobial peptides: Phase behavior and antimicrobial effect. Langmuir 2016, 32, 4217–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Han, S.; Shen, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Gan, Y. Self-assembled liquid crystalline nanoparticles as a novel ophthalmic delivery system for dexamethasone: Improving preocular retention and ocular bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 396, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.M.; Bodmeier, R. Swelling of and drug release from monoglyceride-based drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, P.; Gui, S. Cubic and hexagonal liquid crystals as drug delivery systems. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 815981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milak, S.; Zimmer, A. Glycerol monooleate liquid crystalline phases used in drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özel, H.E.; Özdoğan, F.; Gürgen, S.G.; Esen, E.; Genç, S.; Selçuk, A. Comparison of the protective effects of intratympanic dexamethasone and methylprednisolone against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2016, 130, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.P.; Chen, H.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, H.K.; Wang, H.; Kuo, C.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wang, C.H. Middle-ear dexamethasone delivery via ultrasound microbubbles attenuates noise-induced hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hou, S.X.; Hu, P.; Hu, Q.H.; Guo, D.D.; Xiao, Y. In vitro dexamethasone release from nanoparticles and its pharmacokinetics in the inner ear after administration of the drug-loaded nanoparticles via the round window. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2008, 28, 1022–1024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rhen, T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids—New mechanisms for old drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, J.; Tong, L.; Shi, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, D.; Wu, H. Dexamethasone-loaded injectable silk-polyethylene glycol hydrogel alleviates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4211–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.; Schittenhelm, M.; Honecker, F.; Malenke, E.; Lauber, K.; Wesselborg, S.; Hartmann, J.T.; Bokemeyer, C.; Mayer, F. Cell-cycle progression and response of germ cell tumors to cisplatin in vitro. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 29, 471–479. [Google Scholar]
- Granada, A.E.; Jiménez, A.; Stewart-Ornstein, J.; Blüthgen, N.; Reber, S.; Jambhekar, A.; Lahav, G. The effects of proliferation status and cell cycle phase on the responses of single cells to chemotherapy. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2020, 31, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazlitt, R.A.; Min, J.; Zuo, J. Progress in the development of preventative drugs for cisplatin-induced hearing loss. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5512–5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Tao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yu, D.; Wu, H. A666-conjugated nanoparticles target prestin of outer hair cells preventing cisplatin-induced hearing loss. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7517–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Kang, J.; Hwang, J.S.; Li, J.; Boese, A.C.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Boggon, T.J.; Chen, G.Z.; Saba, N.F.; et al. Cisplatin-mediated activation of glucocorticoid receptor induces platinum resistance via MAST1. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Sun, L.; Peng, J.; Wu, A.; Chen, X.; Wen, L.; Bai, C.; Chen, G. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of dexamethasone-salvianolic acid b conjugates and nanodrug delivery against cisplatin-induced hearing loss. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 3115–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.S.; Yeh, P.Y.; Chuang, S.E.; Gao, M.; Kuo, M.L.; Cheng, A.L. Glucocorticoids enhance cytotoxicity of cisplatin via suppression of NF-κB activation in the glucocorticoid receptor-rich human cervical carcinoma cell line SiHa. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 188, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, Q.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Wu, T.; Jiang, W.; Tang, W. Application of nanomedicine in inner ear diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 809443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Schwieger, J.; Matin-Mann, F.; Behrens, P.; Lenarz, T.; Scheper, V. Dexamethasone for inner ear therapy: Biocompatibility and bio-efficacy of different dexamethasone formulations in vitro. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, I.; Ucur, E.; Herzer, K.; Okouoyo, S.; Ridder, R.; Krammer, P.H.; von Knebel Doeberitz, M.; Debatin, K.M. Glucocorticoid cotreatment induces apoptosis resistance toward cancer therapy in carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 3112–3120. [Google Scholar]
- Astolfi, L.; Simoni, E.; Giarbini, N.; Giordano, P.; Pannella, M.; Hatzopoulos, S.; Martini, A. Cochlear implant and inflammation reaction: Safety study of a new steroid-eluting electrode. Hear. Res. 2016, 336, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheper, V.; Hessler, R.; Hütten, M.; Wilk, M.; Jolly, C.; Lenarz, T.; Paasche, G. Local inner ear application of dexamethasone in cochlear implant models is safe for auditory neurons and increases the neuroprotective effect of chronic electrical stimulation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, E.; Gentilin, E.; Candito, M.; Borile, G.; Romanato, F.; Chicca, M.; Nordio, S.; Aspidistria, M.; Martini, A.; Cazzador, D.; et al. Immune response after cochlear implantation. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, G.W.; Morest, D.K.; Parham, K. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: Effect of intratympanic dexamethasone injections. Otol. Neurotol. 2008, 29, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Saldaña, S.; Palao-Suay, R.; Aguilar, M.R.; Ramírez-Camacho, R.; San Román, J. Polymeric nanoparticles loaded with dexamethasone or α-tocopheryl succinate to prevent cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Shi, F.; Yu, D.; Wu, H. A single dose of dexamethasone encapsulated in polyethylene glycol-coated polylactic acid nanoparticles attenuates cisplatin-induced hearing loss following round window membrane administration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3567–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Lin, X.; Yu, D.; Wu, H. Dexamethasone loaded nanoparticles exert protective effects against Cisplatin-induced hearing loss by systemic administration. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 619, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astolfi, L.; Simoni, E.; Valente, F.; Ghiselli, S.; Hatzopoulos, S.; Chicca, M.; Martini, A. Coenzyme Q10 plus Multivitamin Treatment Prevents Cisplatin Ototoxicity in Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinec, F.; Kalinec, G.; Boukhvalova, M.; Kachar, B. Establishment and characterization of conditionally immortalized organ of Corti cell lines. Cell Biol. Int. 1999, 23, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Time 1 | Day 0 | Day 30 | Day 60 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size 2 | 218 ± 1.9 | 227 ± 1.2 | 226 ± 1.4 |
| PDI 3 | 0.036 | 0.042 | 0.026 |
| Z p 4 | −20.4 | −17.3 | −20.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valente, F.; Simoni, E.; Gentilin, E.; Martini, A.; Zanoletti, E.; Marioni, G.; Nicolai, P.; Astolfi, L. Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles Conjugated with Dexamethasone Prevent Cisplatin Ototoxicity In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314881
Valente F, Simoni E, Gentilin E, Martini A, Zanoletti E, Marioni G, Nicolai P, Astolfi L. Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles Conjugated with Dexamethasone Prevent Cisplatin Ototoxicity In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314881
Chicago/Turabian StyleValente, Filippo, Edi Simoni, Erica Gentilin, Alessandro Martini, Elisabetta Zanoletti, Gino Marioni, Piero Nicolai, and Laura Astolfi. 2022. "Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles Conjugated with Dexamethasone Prevent Cisplatin Ototoxicity In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314881
APA StyleValente, F., Simoni, E., Gentilin, E., Martini, A., Zanoletti, E., Marioni, G., Nicolai, P., & Astolfi, L. (2022). Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles Conjugated with Dexamethasone Prevent Cisplatin Ototoxicity In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314881









