RvD1n-3 DPA Downregulates the Transcription of Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Oral Epithelial Cells and Reverses Nuclear Translocation of Transcription Factor p65 after TNF-α Stimulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
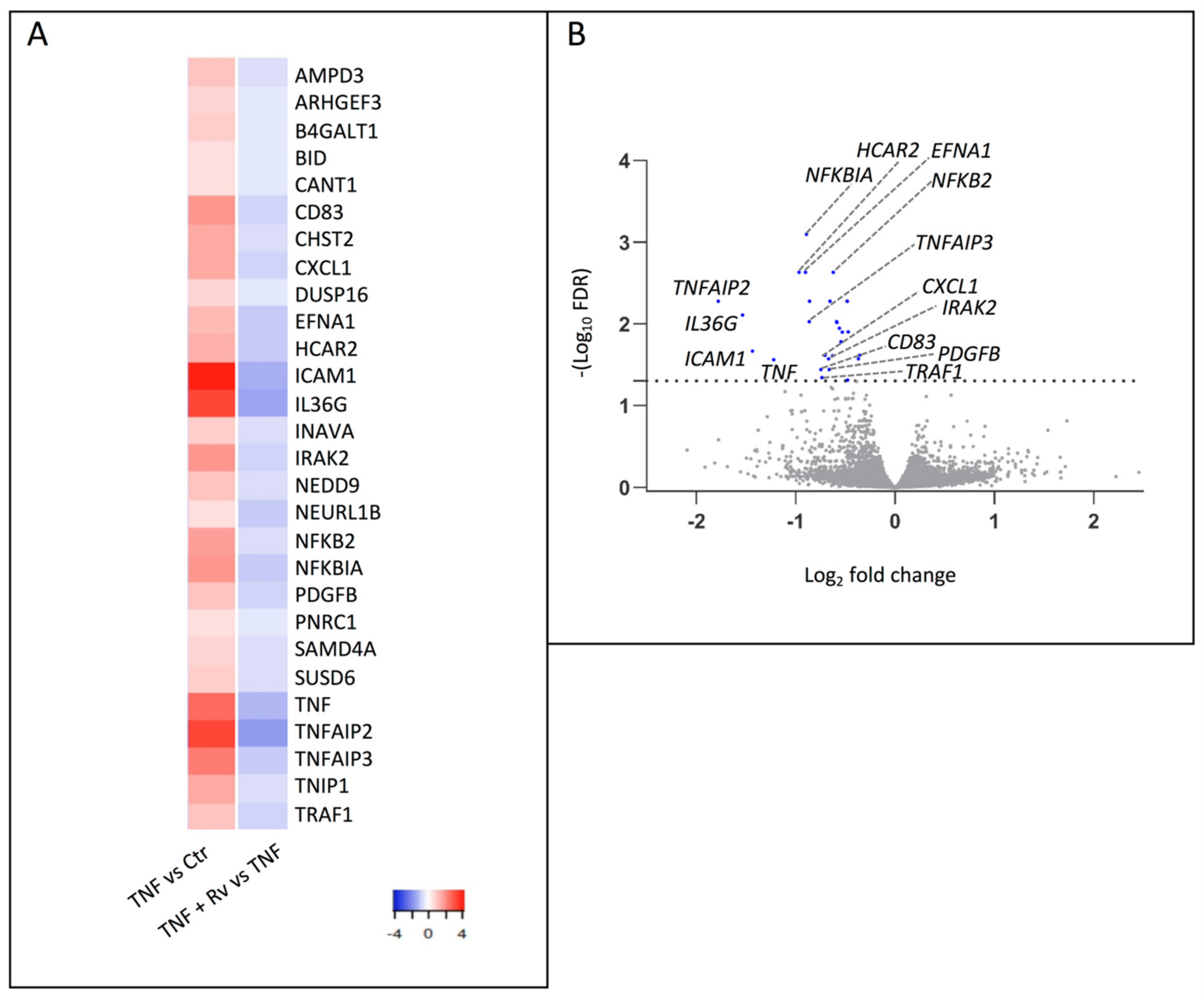
2.1. mRNA-seq Analysis
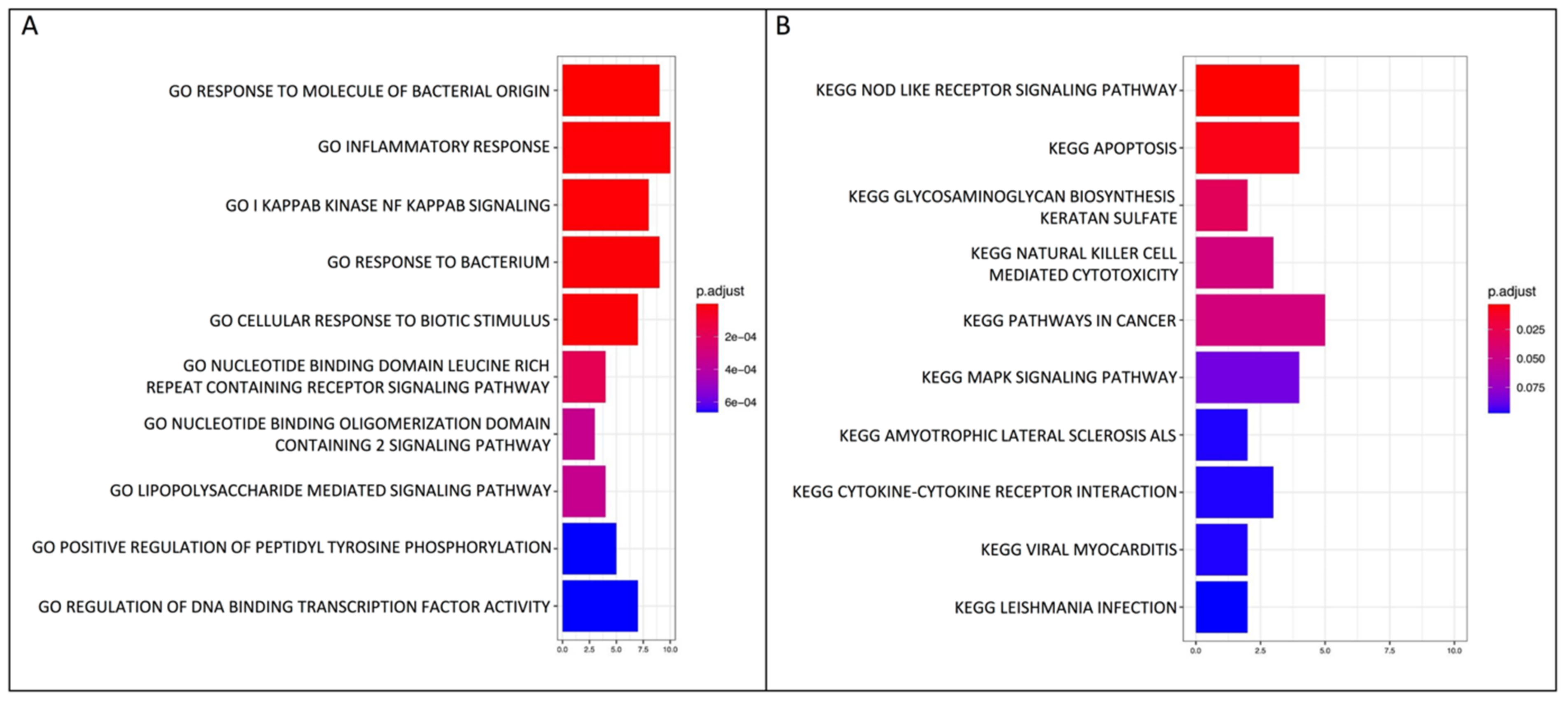
2.2. GO Biological Process and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analyses
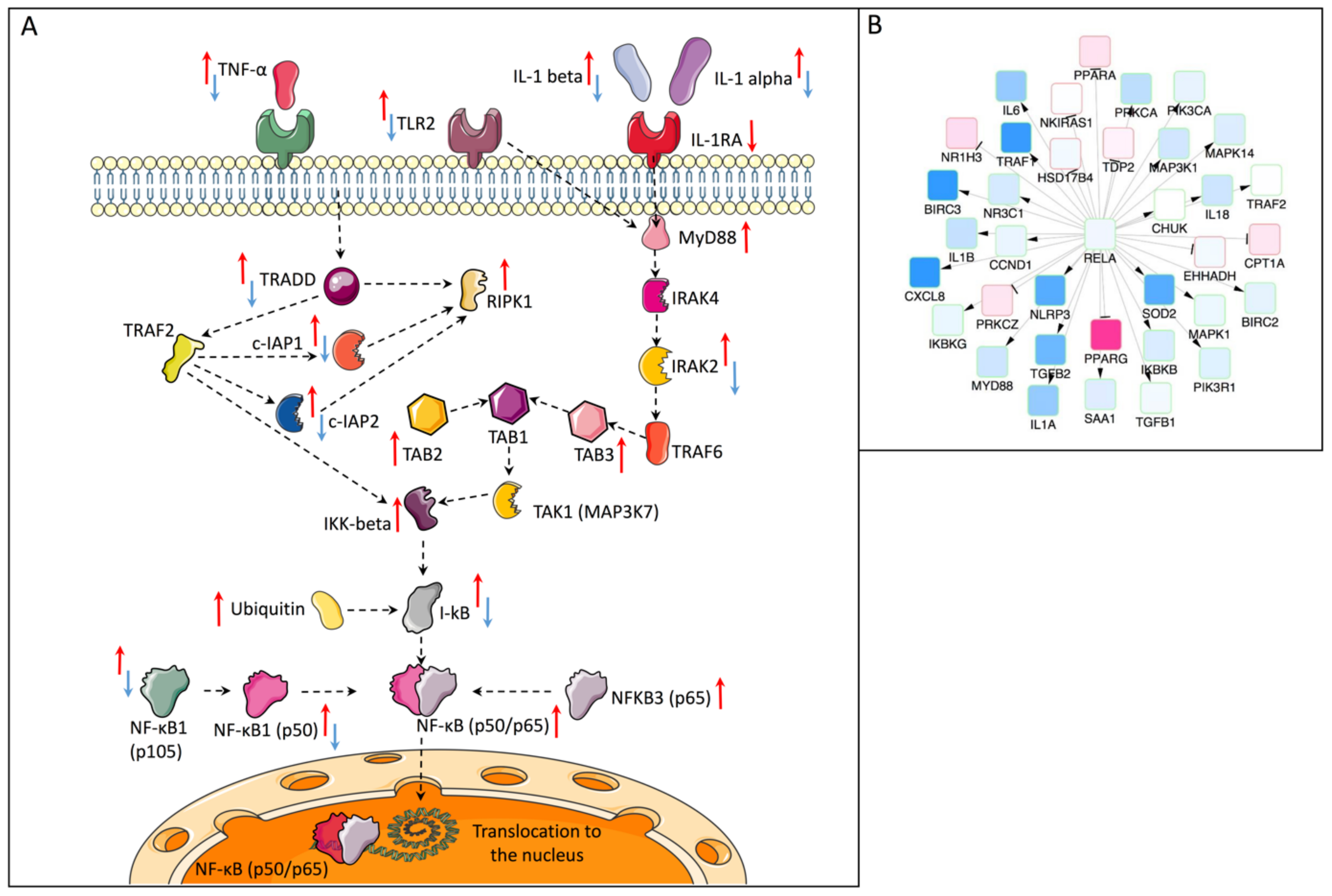
2.3. Causal Network Analysis (Causal Reasoning)
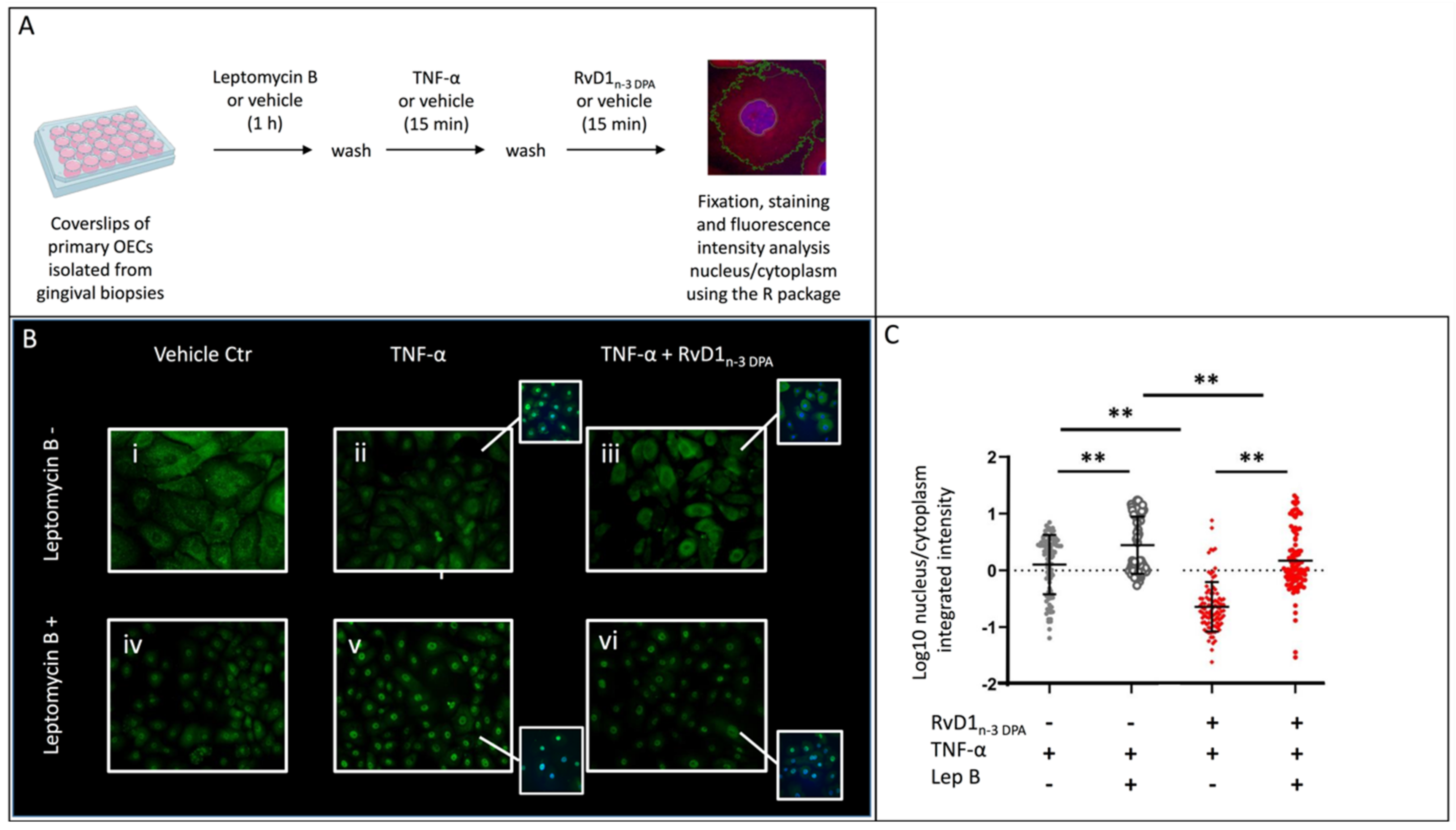
2.4. Nuclear Localization of p65
3. Discussion
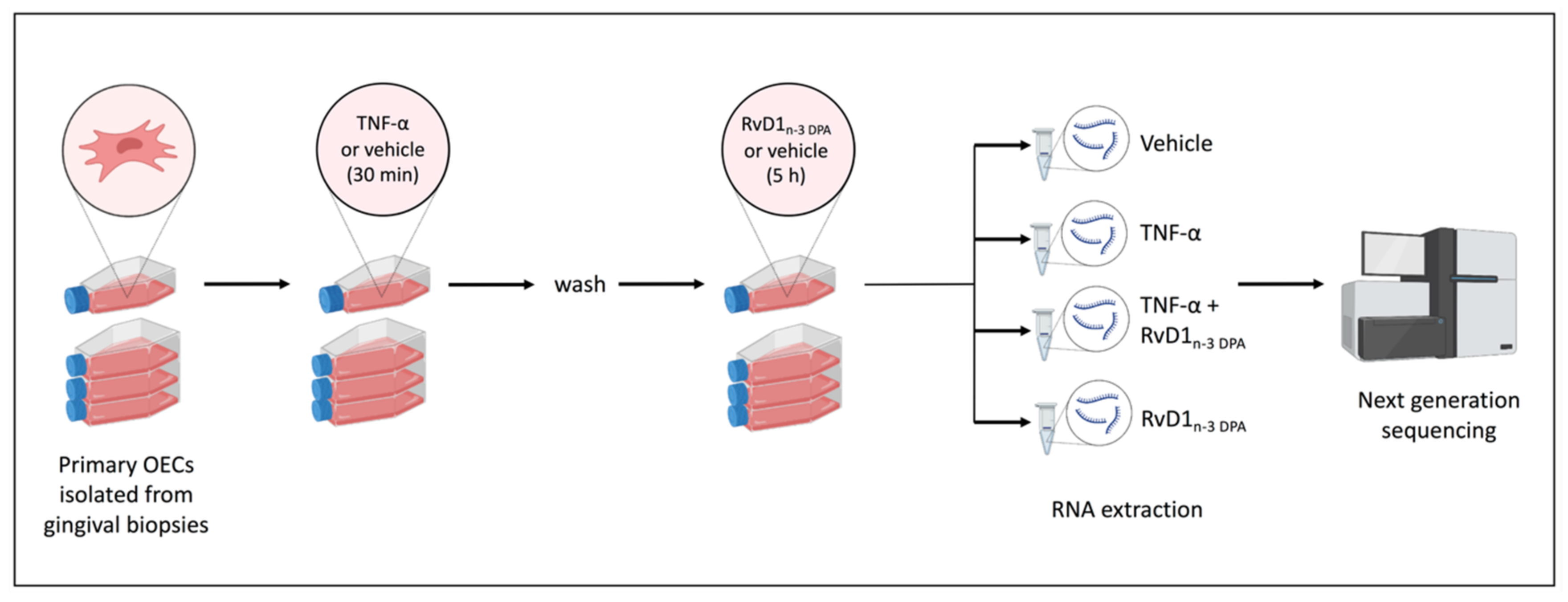
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Biopsy Material
4.2. Isolation of Primary Oral Epithelial Cells
4.3. Resolvin
4.4. RNA High-Throughput Sequencing and Data Processing
4.5. Immunocytofluorescence and Fluorescence Intensity Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diamond, G.; Beckloff, N.; Ryan, L.K. Host defense peptides in the oral cavity and the lung: Similarities and differences. J. Dent. Res. 2008, 87, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnig, C.; Bezema, T.; Calder, P.C.; Charloux, A.; Frossard, N.; Garssen, J.; Haworth, O.; Dilevskaya, K.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Lonsdorfer, E.; et al. Activation of Resolution Pathways to Prevent and Fight Chronic Inflammation: Lessons From Asthma and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cn, S. Novel lipid mediators and resolution mechanisms in acute inflammation: To resolve or not? Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1576–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Balta, M.G.; Loos, B.G.; Nicu, E.A. Emerging Concepts in the Resolution of Periodontal Inflammation: A Role for Resolvin E1. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croasdell, A.; Sime, P.J.; Phipps, R.P. Resolvin D2 decreases TLR4 expression to mediate resolution in human monocytes. Faseb J. 2016, 30, 3181–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Kholy, K.; Freire, M.; Chen, T.; Van Dyke, T.E. Resolvin E1 Promotes Bone Preservation under Inflammatory Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, M.J.; Hellmann, J.; Kosuri, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Spite, M. Proresolution therapy for the treatment of delayed healing of diabetic wounds. Diabetes 2013, 62, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohr, S.; Patel, S.J.; Sarin, D.; Irimia, D.; Yarmush, M.L.; Berthiaume, F. Resolvin D2 prevents secondary thrombosis and necrosis in a mouse burn wound model. Wound Repair Regen. 2013, 21, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papathanasiou, E.; Trotman, C.A.; Scott, A.R.; Van Dyke, T.E. Current and Emerging Treatments for Postsurgical Cleft Lip Scarring: Effectiveness and Mechanisms. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 1370–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balta, M.G.; Papathanasiou, E.; Blix, I.J.; Van Dyke, T.E. Host Modulation and Treatment of Periodontal Disease. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, J.; Sansbury, B.E.; Wong, B.; Li, X.; Singh, M.; Nuutila, K.; Chiang, N.; Eriksson, E.; Serhan, C.N.; Spite, M. Biosynthesis of D-Series Resolvins in Skin Provides Insights into their Role in Tissue Repair. J. Investig. Derm. 2018, 138, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, P.; Melo, C.P.B.; Martinez, R.M.; Fattori, V.; Cezar, T.L.C.; Pinto, I.C.; Bussmann, A.J.C.; Vignoli, J.A.; Georgetti, S.R.; Baracat, M.M.; et al. The Lipid Mediator Resolvin D1 Reduces the Skin Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced by UV Irradiation in Hairless Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balta, M.G.; Schreurs, O.; Hansen, T.V.; Tungen, J.E.; Vik, A.; Glaab, E.; Küntziger, T.M.; Schenck, K.; Baekkevold, E.S.; Blix, I.J.S. Expression and function of resolvin RvD1(n-3 DPA) receptors in oral epithelial cells. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 130, e12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; Yoshida, M.; Arita, M.; Nishitani, Y.; Nishiumi, S.; Masuda, A.; Mizuno, S.; Takagawa, T.; Morita, Y.; Kutsumi, H.; et al. Resolvin E1, an endogenous lipid mediator derived from eicosapentaenoic acid, prevents dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colby, J.K.; Abdulnour, R.-E.E.; Sham, H.P.; Dalli, J.; Colas, R.A.; Winkler, J.W.; Hellmann, J.; Wong, B.; Cui, Y.; El-Chemaly, S.; et al. Resolvin D3 and Aspirin-Triggered Resolvin D3 Are Protective for Injured Epithelia. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Ye, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ye, D.; Zhao, M.; Wan, J. The Anti-inflammatory Mediator Resolvin E1 Protects Mice Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Heart Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chindelevitch, L.; Ziemek, D.; Enayetallah, A.; Randhawa, R.; Sidders, B.; Brockel, C.; Huang, E.S. Causal reasoning on biological networks: Interpreting transcriptional changes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalli, J.; Colas, R.A.; Serhan, C.N. Novel n-3 Immunoresolvents: Structures and Actions. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tungen, J.E.; Gerstmann, L.; Vik, A.; De Matteis, R.; Colas, R.A.; Dalli, J.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N.; Kalesse, M.; Hansen, T.V. Resolving Inflammation: Synthesis, Configurational Assignment, and Biological Evaluations of RvD1(n-3 DPA). Chemistry 2019, 25, 1476–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vik, A.; Dalli, J.; Hansen, T.V. Recent advances in the chemistry and biology of anti-inflammatory and specialized pro-resolving mediators biosynthesized from n-3 docosapentaenoic acid. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Tu, Y.H.; Wu, X.; Ji, S.; Shen, J.L.; Wu, H.M.; Fei, G.H. ResolvinD1 Protects the Airway Barrier Against Injury Induced by Influenza A Virus Through the Nrf2 Pathway. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 616475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odusanwo, O.; Chinthamani, S.; McCall, A.; Duffey, M.E.; Baker, O.J. Resolvin D1 prevents TNF-α-mediated disruption of salivary epithelial formation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 302, C1331–C1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizraji, G.; Heyman, O.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Wilensky, A. Resolvin D2 Restrains Th1 Immunity and Prevents Alveolar Bone Loss in Murine Periodontitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Shen, D.; Zhu, J.; Liu, K. Role of Resolvins in the Inflammatory Resolution of Neurological Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopategi, A.; Flores-Costa, R.; Rius, B.; López-Vicario, C.; Alcaraz-Quiles, J.; Titos, E.; Clària, J. Frontline Science: Specialized proresolving lipid mediators inhibit the priming and activation of the macrophage NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giridharan, S.; Srinivasan, M. Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azmi, A.S.; Uddin, M.H.; Mohammad, R.M. The nuclear export protein XPO1—From biology to targeted therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreurs, O.; Karatsaidis, A.; Balta, M.G.; Grung, B.; Hals, E.K.B.; Schenck, K. Expression of keratins 8, 18, and 19 in epithelia of atrophic oral lichen planus. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 128, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Sena Brandine, G.; Smith, A.D. Falco: High-speed FastQC emulation for quality control of sequencing data. F1000Res 2019, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. The R package Rsubread is easier, faster, cheaper and better for alignment and quantification of RNA sequencing reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Computer Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, A. A description of the Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) Web site. Methods Mol Biol 2014, 1150, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balta, M.G.; Schreurs, O.; Halder, R.; Küntziger, T.M.; Saetre, F.; Blix, I.J.S.; Baekkevold, E.S.; Glaab, E.; Schenck, K. RvD1n-3 DPA Downregulates the Transcription of Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Oral Epithelial Cells and Reverses Nuclear Translocation of Transcription Factor p65 after TNF-α Stimulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314878
Balta MG, Schreurs O, Halder R, Küntziger TM, Saetre F, Blix IJS, Baekkevold ES, Glaab E, Schenck K. RvD1n-3 DPA Downregulates the Transcription of Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Oral Epithelial Cells and Reverses Nuclear Translocation of Transcription Factor p65 after TNF-α Stimulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314878
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalta, Maria G., Olav Schreurs, Rashi Halder, Thomas M. Küntziger, Frank Saetre, Inger Johanne S. Blix, Espen S. Baekkevold, Enrico Glaab, and Karl Schenck. 2022. "RvD1n-3 DPA Downregulates the Transcription of Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Oral Epithelial Cells and Reverses Nuclear Translocation of Transcription Factor p65 after TNF-α Stimulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 23: 14878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314878
APA StyleBalta, M. G., Schreurs, O., Halder, R., Küntziger, T. M., Saetre, F., Blix, I. J. S., Baekkevold, E. S., Glaab, E., & Schenck, K. (2022). RvD1n-3 DPA Downregulates the Transcription of Pro-Inflammatory Genes in Oral Epithelial Cells and Reverses Nuclear Translocation of Transcription Factor p65 after TNF-α Stimulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(23), 14878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314878





