Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Epithelial Associated Malignancies: Exploring Pathologies and Current Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. EBV Latency
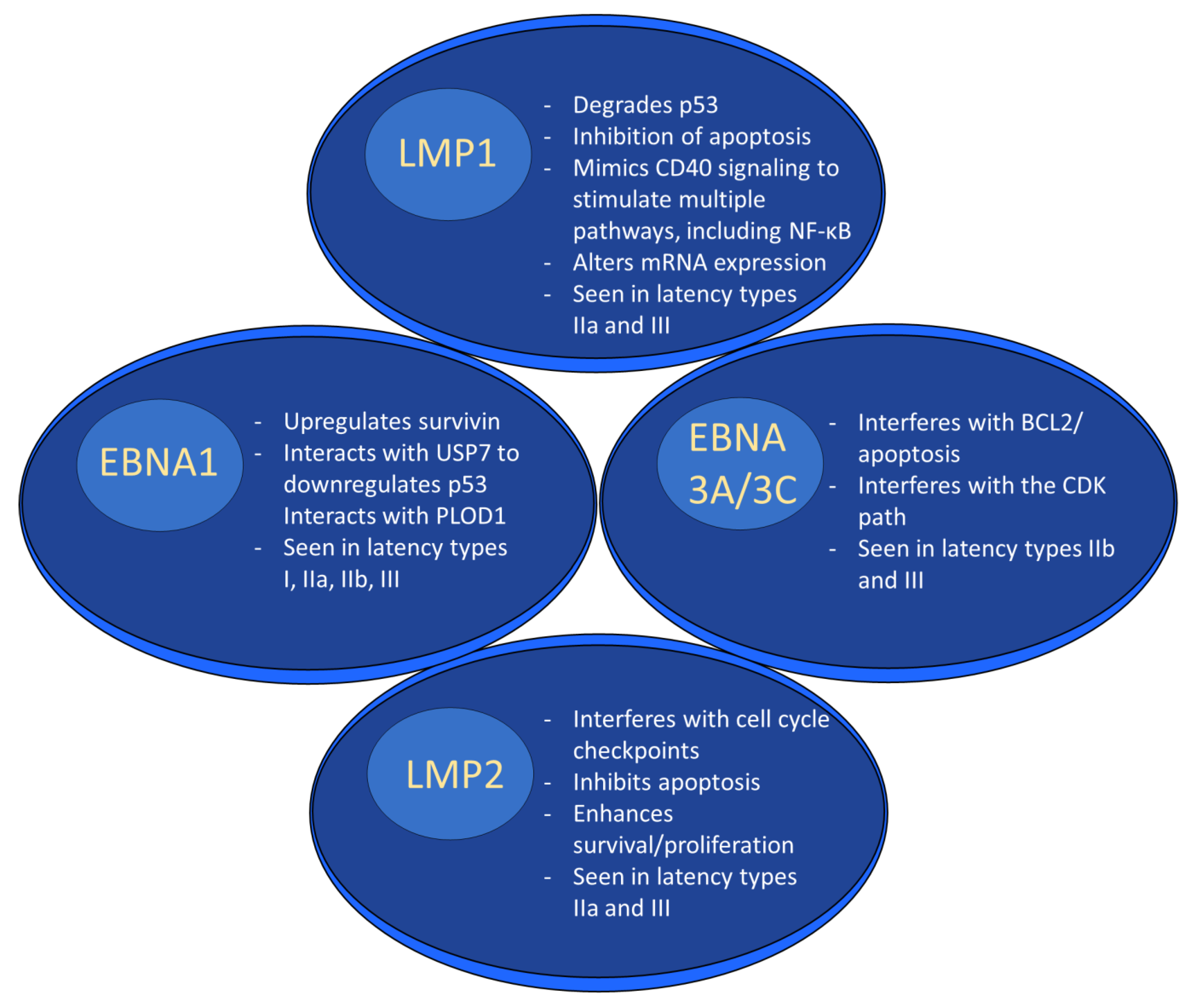
EBV Latent Proteins and Oncogenesis
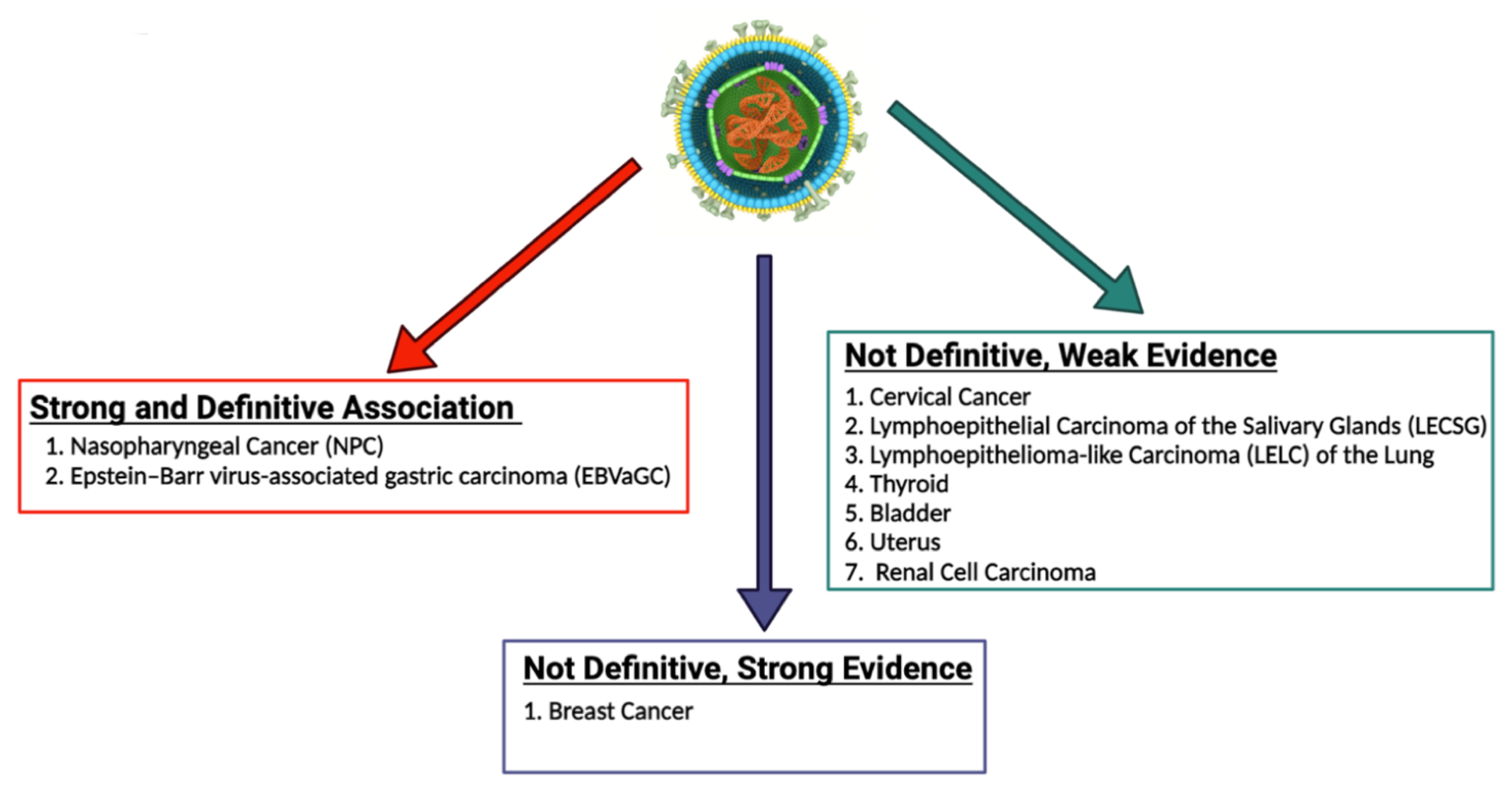
3. EBV and Epithelial Malignancies
4. EBV and Gastric Carcinoma
Gastric Cancer Therapies
5. EBV and Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Nasopharyngeal Cancer Therapies
6. EBV and Other Malignancies
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zanella, L.; Riquelme, I.; Buchegger, K.; Abanto, M.; Ili, C.; Brebi, P. A reliable Epstein-Barr Virus classification based on phylogenomic and population analyses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, P.M. Virology. Epstein-Barr virus turns 50. Science 2014, 343, 1323–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.H. EBV and human cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, P.J. Epstein-Barr Virus and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2019, 14, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, K.; Satoh, Y.; Hoshikawa, Y.; Sairenji, T. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus in salivas and throat washings in healthy adults and children. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunmire, S.K.; Verghese, P.S.; Balfour, H.H., Jr. Primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 102, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gares, V.; Panico, L.; Castagne, R.; Delpierre, C.; Kelly-Irving, M. The role of the early social environment on Epstein Barr virus infection: A prospective observational design using the Millennium Cohort Study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 3405–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivailler, P.; Cho, Y.G.; Wang, F. Complete genomic sequence of an Epstein-Barr virus-related herpesvirus naturally infecting a new world primate: A defining point in the evolution of oncogenic lymphocryptoviruses. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12055–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Masters, J.C.; Huebner, S.M.; Ohashi, M.; Bristol, J.A.; Benner, B.E.; Barlow, E.A.; Turk, G.L.; Nelson, S.E.; Baiu, D.C.; Van Sciver, N.; et al. B cells infected with Type 2 Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) have increased NFATc1/NFATc2 activity and enhanced lytic gene expression in comparison to Type 1 EBV infection. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimber, U.; Adldinger, H.K.; Lenoir, G.M.; Vuillaume, M.; Knebel-Doeberitz, M.V.; Laux, G.; Bornkamm, G.W. Geographical prevalence of two types of Epstein-Barr virus. Virology 1986, 154, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, T.A.F.; Costa, I.B.; Costa, I.B.; Correa, T.; Coelho, B.M.R.; Silva, A.E.S.; Ramos, F.L.P.; Filho, A.J.M.; Monteiro, J.L.F.; Siqueira, J.A.M.; et al. Genotypes of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV1/EBV2) in individuals with infectious mononucleosis in the metropolitan area of Belem, Brazil, between 2005 and 2016. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 24, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingeroth, J.D.; Weis, J.J.; Tedder, T.F.; Strominger, J.L.; Biro, P.A.; Fearon, D.T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 4510–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.A.; Herbert, A.P.; Barlow, P.N.; Holers, V.M.; Hannan, J.P. Molecular basis of the interaction between complement receptor type 2 (CR2/CD21) and Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gp350. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11217–11227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, C.M.; Deng, W.; Yip, Y.L.; Zeng, M.S.; Lo, K.W.; Tsao, S.W. Epstein-Barr virus infection and persistence in nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, N.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Epstein-Barr virus enters B cells and epithelial cells by different routes. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 3409–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemerow, G.R.; Mold, C.; Schwend, V.K.; Tollefson, V.; Cooper, N.R. Identification of gp350 as the viral glycoprotein mediating attachment of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) to the EBV/C3d receptor of B cells: Sequence homology of gp350 and C3 complement fragment C3d. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loesing, J.B.; Di Fiore, S.; Ritter, K.; Fischer, R.; Kleines, M. Epstein-Barr virus BDLF2-BMRF2 complex affects cellular morphology. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnokova, L.S.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Fusion of Epstein-Barr virus with epithelial cells can be triggered by alphavbeta5 in addition to alphavbeta6 and alphavbeta8, and integrin binding triggers a conformational change in glycoproteins gHgL. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 13214–13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnokova, L.S.; Nishimura, S.L.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Fusion of epithelial cells by Epstein-Barr virus proteins is triggered by binding of viral glycoproteins gHgL to integrins alphavbeta6 or alphavbeta8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20464–20469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moquin, S.A.; Thomas, S.; Whalen, S.; Warburton, A.; Fernandez, S.G.; McBride, A.A.; Pollard, K.S.; Miranda, J.L. The Epstein-Barr Virus Episome Maneuvers between Nuclear Chromatin Compartments during Reactivation. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01413-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Laing, J.; Yan, B.; Zhou, H.; Ke, L.; Wang, C.; Narita, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Olson, M.R.; Afzali, B.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus Episome Physically Interacts with Active Regions of the Host Genome in Lymphoblastoid Cells. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01390-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempkes, B.; Robertson, E.S. Epstein-Barr virus latency: Current and future perspectives. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 14, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sausen, D.G.; Bhutta, M.S.; Gallo, E.S.; Dahari, H.; Borenstein, R. Stress-Induced Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houen, G.; Trier, N.H. Epstein-Barr Virus and Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 587380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathee, M.; Jain, P. Hairy Leukoplakia. In StatPearls; Statpearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Zuo, Y.; Jiang, L.; Peng, Y.; Huang, X.; Zuo, L. Epstein-Barr Virus and Neurological Diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 816098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornevik, K.; Cortese, M.; Healy, B.C.; Kuhle, J.; Mina, M.J.; Leng, Y.; Elledge, S.J.; Niebuhr, D.W.; Scher, A.I.; Munger, K.L.; et al. Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis. Science 2022, 375, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lipton, H.L.; Perelson, A.S.; Dahari, H. Modeling the acute and chronic phases of Theiler murine encephalomyelitis virus infection. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4052–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.A.; Achong, B.G.; Barr, Y.M. Virus Particles in Cultured Lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s Lymphoma. Lancet 1964, 1, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, C.Y.; Li, L.; Young, K.H. EBV-driven B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders: From biology, classification and differential diagnosis to clinical management. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A.B.; Bell, A.I. Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphomas. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, R.W.; Tong, J.H.; To, K.F. Emerging roles of small Epstein-Barr virus derived non-coding RNAs in epithelial malignancy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17378–17409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahmand, M.; Monavari, S.H.; Shoja, Z.; Ghaffari, H.; Tavakoli, M.; Tavakoli, A. Epstein-Barr virus and risk of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.D.R.; Whaley, R.D. Lymphoepithelial Carcinoma of Salivary Glands. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2021, 14, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.C.; Kao, H.L.; Lee, K.L.; Wu, M.H.; Ho, H.L.; Chou, T.Y. Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Pulmonary Carcinoma: Proposing an Alternative Term and Expanding the Histologic Spectrum of Lymphoepithelioma-like Carcinoma of the Lung. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becnel, D.; Abdelghani, R.; Nanbo, A.; Avilala, J.; Kahn, J.; Li, L.; Lin, Z. Pathogenic Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in Lung Cancers. Viruses 2021, 13, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadi, A.; Namdari, S.; Chong, P.P.; Geramizadeh, B.; Behzad-Behbahani, A.; Sekawi, Z.; Sharifzadeh, S. Epstein-Barr virus infection is associated with the nuclear factor-kappa B p65 signaling pathway in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Urol. 2022, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimakage, M.; Kawahara, K.; Harada, S.; Sasagawa, T.; Shinka, T.; Oka, T. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus in renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 18, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Han, E.M.; Lee, E.S.; Park, H.S.; Kim, I.; Kim, Y.S. Epstein-Barr virus infection in sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma tissues. BJU Int. 2005, 96, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghoofei, M.; Mostafaei, S.; Nesaei, A.; Etemadi, A.; Sadri Nahand, J.; Mirzaei, H.; Rashidi, B.; Babaei, F.; Khodabandehlou, N. Epstein-Barr virus and thyroid cancer: The role of viral expressed proteins. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 3790–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayouni, M.; Mohammad Arabzadeh, S.A.; Nili, F.; Razi, F.; Amoli, M.M. Evaluation of the presence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in Iranian patients with thyroid papillary carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 854–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, M.A.P.; Neto, P.J.N.; Lima, L.P.M.; Goncalves Junior, J.; Teixeira Junior, A.G.; Teodoro, I.P.P.; Facundo, H.T.; da Silva, C.G.L.; Lima, M.V.A. Association between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and cervical carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 148, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranic, S.; Cyprian, F.S.; Akhtar, S.; Al Moustafa, A.E. The Role of Epstein-Barr Virus in Cervical Cancer: A Brief Update. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzaniga, P.; Vercillo, R.; Gradilone, A.; Silvestri, I.; Gandini, O.; Napolitano, M.; Giuliani, L.; Fioravanti, A.; Gallucci, M.; Agliano, A.M. Prevalence of papillomavirus, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus type 2 in urinary bladder cancer. J. Med. Virol. 1998, 55, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Shinohara, N.; Tada, M.; Harabayashi, T.; Sazawa, A.; Maruyama, S.; Moriuchi, T.; Takada, K.; Nonomura, K. Infiltration of Epstein-Barr virus-harboring lymphocytes occurs in a large subset of bladder cancers. Int. J. Urol. 2008, 15, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, K.L.; Leach, C.T.; Jenson, H.B.; Joshi, V.V.; Pollock, B.H.; Parmley, R.T.; DiCarlo, F.J.; Chadwick, E.G.; Murphy, S.B. Association of Epstein-Barr virus with leiomyosarcomas in young people with AIDS. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G. Epstein-Barr virus: More than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller Coan, B.G.; Cesarman, E.; Acencio, M.L.; Elgui de Oliveira, D. Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) from Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Strains M81 and B95.8 Modulate miRNA Expression When Expressed in Immortalized Human Nasopharyngeal Cells. Genes 2022, 13, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, K.; Comoglio, F.; Shaffer, A.L., 3rd; Ji, Y.; Pan, K.T.; Scheich, S.; Oellerich, A.; Doebele, C.; Ikeda, M.; Schaller, S.J.; et al. Rewiring of B cell receptor signaling by Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26318–26327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Piubelli, M.L.; Salas, Y.I.; Pachas, C.; Becker-Hecker, R.; Vega, F.; Miranda, R.N. Epstein-Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders and lymphomas: A review. Pathology 2020, 52, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki-Ushiku, A.; Kunita, A.; Fukayama, M. Update on Epstein-Barr virus and gastric cancer (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Jung, S.W.; Huh, S.; Cho, H.; Kang, H. Phylogenetic comparison of Epstein-Barr virus genomes. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massini, G.; Siemer, D.; Hohaus, S. EBV in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Mediterr J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 1, e2009013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard-Hartmann, E.; Johrens, K.; Schinagl, L.M.; Zamo, A.; Rosenwald, A.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Rosenfeldt, M. Epstein-Barr virus infection patterns in nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. Histopathology 2022, 80, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzetti, M.A.; De Matteo, E.; Gass, H.; Martinez Vazquez, P.; Lara, J.; Gonzalez, P.; Preciado, M.V.; Chabay, P.A. Characterization of Epstein Barr virus latency pattern in Argentine breast carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granai, M.; Mundo, L.; Akarca, A.U.; Siciliano, M.C.; Rizvi, H.; Mancini, V.; Onyango, N.; Nyagol, J.; Abinya, N.O.; Maha, I.; et al. Immune landscape in Burkitt lymphoma reveals M2-macrophage polarization and correlation between PD-L1 expression and non-canonical EBV latency program. Infect. Agent Cancer 2020, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T. EBV-Encoded Latent Genes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1045, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, T.; Sugimoto, A.; Inagaki, T.; Yanagi, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Sato, Y.; Kimura, H. Molecular Basis of Epstein-Barr Virus Latency Establishment and Lytic Reactivation. Viruses 2021, 13, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrebaeck, C.A. Strategy for the production of human monoclonal antibodies using in vitro activated B cells. J. Immunol. Methods 1989, 123, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahir McFarland, E.D.; Izumi, K.M.; Mosialos, G. Epstein-barr virus transformation: Involvement of latent membrane protein 1-mediated activation of NF-kappaB. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6959–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Nagy, N.; Masucci, M.G. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 upregulates the cellular antioxidant defense to enable B-cell growth transformation and immortalization. Oncogene 2020, 39, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymula, A.; Palermo, R.D.; Bayoumy, A.; Groves, I.J.; Ba Abdullah, M.; Holder, B.; White, R.E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA-LP is essential for transforming naive B cells, and facilitates recruitment of transcription factors to the viral genome. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernando, H.; Islam, A.B.; Rodriguez-Ubreva, J.; Forne, I.; Ciudad, L.; Imhof, A.; Shannon-Lowe, C.; Ballestar, E. Epstein-Barr virus-mediated transformation of B cells induces global chromatin changes independent to the acquisition of proliferation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Jha, H.C.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Robertson, E.S. Epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes during in vitro Epstein-Barr virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5199–E5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, S.; Liang, J.; Narita, Y.; Hou, I.; Zhong, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Xiao, H.; et al. RNA Sequencing Analyses of Gene Expression during Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of Primary B Lymphocytes. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00226-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.W.; Jiang, S.; Gewurz, B.E. Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1-Mediated Oncogenicity. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01718-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laherty, C.D.; Hu, H.M.; Opipari, A.W.; Wang, F.; Dixit, V.M. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene product induces A20 zinc finger protein expression by activating nuclear factor kappa B. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 24157–24160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Chen, Y.; Jia, X.; Liu, Y. The Anti-Apoptotic Role of EBV-LMP1 in Lymphoma Cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 8801–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, K.; Das, P.; Chattopadhyay, N.R.; Mal, S.; Choudhuri, T.C. The interplay between Epstein-Bar virus (EBV) with the p53 and its homologs during EBV associated malignancies. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, H.; Ma, C.; Wei, L. LMP-1 induces survivin expression to inhibit cell apoptosis through the NF-kappaB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatton, O.; Lambert, S.L.; Krams, S.M.; Martinez, O.M. Src kinase and Syk activation initiate PI3K signaling by a chimeric latent membrane protein 1 in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)+ B cell lymphomas. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Murakami, M.; Verma, S.C.; Cai, Q.; Haldar, S.; Kaul, R.; Wasik, M.A.; Middeldorp, J.; Robertson, E.S. Epstein-Barr Virus nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) confers resistance to apoptosis in EBV-positive B-lymphoma cells through up-regulation of survivin. Virology 2011, 410, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, M.D.; Li, L.L.; Zhao, X.R.; Wu, Y.; Gong, J.P.; Cao, Y. Regulation of survivin and CDK4 by Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein 1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Valentine, R.; Dawson, C.W.; Hu, C.; Shah, K.M.; Owen, T.J.; Date, K.L.; Maia, S.P.; Shao, J.; Arrand, J.R.; Young, L.S.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 inhibits the canonical NF-kappaB pathway in carcinoma cells by inhibiting IKK phosphorylation. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saridakis, V.; Sheng, Y.; Sarkari, F.; Holowaty, M.N.; Shire, K.; Nguyen, T.; Zhang, R.G.; Liao, J.; Lee, W.; Edwards, A.M.; et al. Structure of the p53 binding domain of HAUSP/USP7 bound to Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 implications for EBV-mediated immortalization. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shire, K.; Marcon, E.; Greenblatt, J.; Frappier, L. Characterization of a cancer-associated Epstein-Barr virus EBNA1 variant reveals a novel interaction with PLOD1 and PLOD3. Virology 2021, 562, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F. High Expression of PLOD1 Drives Tumorigenesis and Affects Clinical Outcome in Gastrointestinal Carcinoma. Genet. Test Mol. Biomark. 2018, 22, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Lian, Y.F.; Huang, Y.L.; Huang, Y.H.; Xiao, J. Overexpressing PLOD family genes predict poor prognosis in gastric cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Robertson, E.S. Mechanisms of B-Cell Oncogenesis Induced by Epstein-Barr Virus. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00238-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allday, M.J.; Bazot, Q.; White, R.E. The EBNA3 Family: Two Oncoproteins and a Tumour Suppressor that Are Central to the Biology of EBV in B Cells. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 391, 61–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.E.; Ramer, P.C.; Naresh, K.N.; Meixlsperger, S.; Pinaud, L.; Rooney, C.; Savoldo, B.; Coutinho, R.; Bodor, C.; Gribben, J.; et al. EBNA3B-deficient EBV promotes B cell lymphomagenesis in humanized mice and is found in human tumors. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 1487–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Epstein-Barr virus replicating in epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16242–16243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Uchio, Y.; Pangnguriseng, U.A.; Kartika, A.V.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Loh, K.S. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of Pseudostratified Nasopharyngeal Epithelium Disrupts Epithelial Integrity. Cancers 2020, 12, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Lin, Y.X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H.J.; Chen, K.M.; He, G.P.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Feng, Q.S.; Chen, M.Y.; et al. Vasculogenic mimicry formation in EBV-associated epithelial malignancies. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. EBV Infection in Epithelial Malignancies Induces Resistance to Antitumor Natural Killer Cells via F3-Mediated Platelet Aggregation. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Jia, K.; Lv, H.; Wang, S.Q.; Wu, Y.; Lei, H.; Chen, X. EBV-Positive Gastric Cancer: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 583463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Liao, W.; Tan, G.; Liao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Feng, D.; Tang, F.; et al. Therapeutic evaluation of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1 targeted DNAzyme for treating of nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hau, P.M.; Lung, H.L.; Wu, M.; Tsang, C.M.; Wong, K.L.; Mak, N.K.; Lo, K.W. Targeting Epstein-Barr Virus in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, A.; Monavari, S.H.; Solaymani Mohammadi, F.; Kiani, S.J.; Armat, S.; Farahmand, M. Association between Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.C.; Hsieh, S.S.; Hsu, W.L.; Chen, Y.F.; Ho, H.H.; Sheu, L.F. Expression of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 in gastric carcinoma cells is associated with enhanced tumorigenicity and reduced cisplatin sensitivity. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 36, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van der Weyden, L.; Adams, D.J. The Ras-association domain family (RASSF) members and their role in human tumourigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1776, 58–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.J.; Chang, M.S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.; Koo, B.K.; Yun, S.C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Woo, J.H. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART5-5p upregulates PD-L1 through PIAS3/pSTAT3 modulation, worsening clinical outcomes of PD-L1-positive gastric carcinomas. Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kase, K.; Saito, M.; Nakajima, S.; Takayanagi, D.; Saito, K.; Yamada, L.; Ashizawa, M.; Nakano, H.; Hanayama, H.; Onozawa, H.; et al. ARID1A deficiency in EBV-positive gastric cancer is partially regulated by EBV-encoded miRNAs, but not by DNA promotor hypermethylation. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhao, M.; Luo, B. Eukaryotic initiating factor eIF4E is targeted by EBV-encoded miR-BART11-3p and regulates cell cycle and apoptosis in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma. Virus Genes 2021, 57, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb Pal, A.; Banerjee, S. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A mediated activation of Sonic Hedgehog pathway induces HLA class Ia downregulation in gastric cancer cells. Virology 2015, 484, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Sakai, K.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Yanagihara, M.; Shuto, T.; Shimokuri, K.; Kanda, T.; Suehiro, Y.; et al. EBV-associated gastric cancer evades T-cell immunity by PD-1/PD-L1 interactions. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Kono, K. Landscape of EBV-positive gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2021, 24, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, M.; Lequesne, J.; Leconte, A.; Corbinais, S.; Parzy, A.; Guilloit, J.M.; Varatharajah, S.; Brachet, P.E.; Dorbeau, M.; Vaur, D.; et al. Perioperative treatment in resectable gastric cancer with spartalizumab in combination with fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin and docetaxel (FLOT): A phase II study (GASPAR). BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, H.; Saito, M.; Nakajima, S.; Saito, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Kase, K.; Yamada, L.; Kanke, Y.; Hanayama, H.; Onozawa, H.; et al. PD-L1 overexpression in EBV-positive gastric cancer is caused by unique genomic or epigenomic mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shitara, K.; Van Cutsem, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Fuchs, C.; Wyrwicz, L.; Lee, K.W.; Kudaba, I.; Garrido, M.; Chung, H.C.; Lee, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab or Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy vs Chemotherapy Alone for Patients With First-line, Advanced Gastric Cancer: The KEYNOTE-062 Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.; Oliveira, C.; Malta, M.; Sousa, H. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression and latency pattern in gastric carcinomas: A systematic review. Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Shitara, K.; Moehler, M.; Garrido, M.; Salman, P.; Shen, L.; Wyrwicz, L.; Yamaguchi, K.; Skoczylas, T.; Campos Bragagnoli, A.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, A.; Kawazoe, A.; Eto, T.; Okunaka, M.; Mishima, S.; Sawada, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Kotani, D.; Kuboki, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; et al. Improved efficacy of taxanes and ramucirumab combination chemotherapy after exposure to anti-PD-1 therapy in advanced gastric cancer. ESMO Open 2020, 4, e000775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, I.; Yuan, Z.M. The Basally Expressed p53-M.Mediated Homeostatic Function. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 775312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holowaty, M.N.; Zeghouf, M.; Wu, H.; Tellam, J.; Athanasopoulos, V.; Greenblatt, J.; Frappier, L. Protein profiling with Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen-1 reveals an interaction with the herpesvirus-associated ubiquitin-specific protease HAUSP/USP7. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 29987–29994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivachandran, N.; Dawson, C.W.; Young, L.S.; Liu, F.F.; Middeldorp, J.; Frappier, L. Contributions of the Epstein-Barr virus EBNA1 protein to gastric carcinoma. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, A.M.; Walesch, S.K.; Wurl, P.; Taubert, H.; Dammann, R.H. The tumor suppressor RASSF10 is upregulated upon contact inhibition and frequently epigenetically silenced in cancer. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.W.; Huang, X.D.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhou, G.Q.; Tang, L.L.; Mao, Y.P.; Li, W.F.; Lin, A.H.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y. A National Study of Survival Trends and Conditional Survival in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Analysis of the National Population-Based Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Registry. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e180–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.T.; Ye, W.; Zeng, Y.X.; Adami, H.O. The Evolving Epidemiology of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.T.; Adami, H.O. The enigmatic epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 1765–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, F.; Mariame, B.; Gence, R.; Tilkin-Mariame, A.F. Macrocyclic lactones inhibit nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells proliferation through PAK1 inhibition and reduce in vivo tumor growth. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 2805–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyene, E.T.; Ketema, S.G.; Alebachew, A.N.; Saleh, M.Y.; Gebremariam, T.A. Descriptive epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma at Tikur Anbessa Hospital, Ethiopia. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottenberg, Y.; Levine, H.; Keinan-Boker, L.; Derazne, E.; Leiba, A.; Kark, J.D. Risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma penetrates across immigrant generations: A migrant cohort study of 2.3 million Jewish Israeli adolescents. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Guo, Q.; Lin, K.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, C.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; et al. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs BART7-3p and BART13-3p as novel biomarkers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarza, R.; Bover, M.; Agullo-Ortuno, M.T.; Iglesias-Docampo, L.C. Current approach and novel perspectives in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: The role of targeting proteasome dysregulation as a molecular landmark in nasopharyngeal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunven, P.; Klein, G.; Henle, G.; Henle, W.; Clifford, P. Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt’s lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Antibodies to EBV associated membrane and viral capsid antigens in Burkitt lymphoma patients. Nature 1970, 228, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.K.J.; Chan, K.C.A.; Lo, Y.M.D. Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA as an archetypal circulating tumour DNA marker. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Dawson, C.W. Epstein-Barr virus and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Roles of the PI3K/Akt pathway in Epstein-Barr virus-induced cancers and therapeutic implications. World J. Virol. 2012, 1, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Huo, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xie, S.; Huang, Z. In vivo and in vitro study of co-expression of LMP1 and Cripto-1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 86, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, A.K.; Dawson, C.W.; Lung, H.L.; Wong, K.L.; Young, L.S. The Role of EBV-Encoded LMP1 in the NPC Tumor Microenvironment: From Function to Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 640207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikawa, T.; Yoshizaki, T.; Sheen, T.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Furukawa, M. Association of latent membrane protein 1 and matrix metalloproteinase 9 with metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 89, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, X.; Tao, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, K.; Peng, J.; Li, D.; Shen, L.; Yang, L. EBV-LMP1 promotes radioresistance by inducing protective autophagy through BNIP3 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, L.; Yao, Q.Y.; Rickinson, A.B.; Young, L.S. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene transcription in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: Coexpression of EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2 transcripts. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.D.; Young, L.S.; Dawson, C.W. The Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP2A and LMP2B proteins promote epithelial cell spreading and motility. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1789–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tsang, C.M.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bruce, J.P.; Pugh, T.J.; Lo, K.W. Translational genomics of nasopharyngeal cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.; Kamara, S.; Gu, M.; Tang, W.; Chen, S.; Dong, H.; Xue, X.; Zheng, Z.M.; et al. Novel EBV LMP-2-affibody and affitoxin in molecular imaging and targeted therapy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longnecker, R. Epstein-Barr virus latency: LMP2, a regulator or means for Epstein-Barr virus persistence? Adv. Cancer Res. 2000, 79, 175–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, A.K.; Dawson, C.W.; Lung, H.L.; Wong, K.L.; Young, L.S. The Therapeutic Potential of Targeting BARF1 in EBV-Associated Malignancies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, A.L.; Cambareri, A.C.; Zannettino, A.C.; Miller, B.L.; Doherty, K.V.; Hughes, T.P.; Lyons, A.B. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor c-fms is a novel target of imatinib. Blood 2005, 105, 3127–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, E.; Ooka, T.; Middeldorp, J.; Takada, K. Reconstitution of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-type EBV infection induces tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, A.H.; Chang, R.A.; Chen, X.; Longnecker, R.; He, X. Multipronged attenuation of macrophage-colony stimulating factor signaling by Epstein-Barr virus BARF1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12962–12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Tariq, S.; Khan, G. Tracking EBV-encoded RNAs (EBERs) from the nucleus to the excreted exosomes of B-lymphocytes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, K. Role of EBER and BARF1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) tumorigenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Moss, W.N.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. EBV noncoding RNA binds nascent RNA to drive host PAX5 to viral DNA. Cell 2015, 160, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Duan, Y.; Cheng, S.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, J.; Liao, Q.; Yang, L.; Sun, L.Q. EBV-encoded RNA via TLR3 induces inflammation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24291–24303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, R.J.A.; Tong, S.; Mok, B.W.; Liu, J.; He, S.; Zong, J.; Chen, Y.; Tsao, S.W.; Lung, M.L.; Chen, H. Epstein-Barr Virus BART Long Non-coding RNAs Function as Epigenetic Modulators in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Shu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. BART miRNAs: An unimaginable force in the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 26, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, R.W.; Hau, P.M.; Yu, K.H.; Yip, K.Y.; Tong, J.H.; Chak, W.P.; Chan, A.W.; Lam, K.H.; Lo, A.K.; Tin, E.K.; et al. EBV-encoded miRNAs target ATM-mediated response in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.; Hung, E.C.; Woo, J.K.; Chan, P.K.; Leung, S.F.; Lai, F.P.; Cheng, A.S.; Yeung, S.W.; Chan, Y.W.; Tsui, T.K.; et al. Early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA analysis in a surveillance program. Cancer 2013, 119, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.T.C.; Hui, E.P.; Ngan, R.K.C.; Tung, S.Y.; Cheng, A.C.K.; Ng, W.T.; Lee, V.H.F.; Ma, B.B.Y.; Cheng, H.C.; Wong, F.C.S.; et al. Analysis of Plasma Epstein-Barr Virus DNA in Nasopharyngeal Cancer After Chemoradiation to Identify High-Risk Patients for Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3091–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, R.H.; Ngan, R.; Wei, W.I.; Gullane, P.J.; Phillips, J. Trans-oral brush biopsies and quantitative PCR for EBV DNA detection and screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2014, 150, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D.; Woo, J.K.S.; Ai, Q.Y.; Chan, J.S.M.; Lam, W.K.J.; Tse, I.O.L.; Bhatia, K.S.; Zee, B.C.Y.; Hui, E.P.; Ma, B.B.Y.; et al. Complementary roles of MRI and endoscopic examination in the early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Hu, G.Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, X.D.; Yang, K.Y.; Jin, F.; Shi, M.; Chen, Y.P.; Hu, W.H.; et al. Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Induction Chemotherapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Peng, P.; Peng, J.; Jia, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Q.; et al. Gemcitabine Plus Cisplatin Versus Fluorouracil Plus Cisplatin as First-Line Therapy for Recurrent or Metastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Final Overall Survival Analysis of GEM20110714 Phase III Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3273–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.-H.; Mai, H.-Q.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Chen, D.; Hu, C.; Yang, K.; Wen, J.; Li, J.-G.; Shi, Y.; Jin, F.; et al. JUPITER-02: Randomized, double-blind, phase III study of toripalimab or placebo plus gemcitabine and cisplatin as first-line treatment for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.Q.; Chen, Q.Y.; Chen, D.; Hu, C.; Yang, K.; Wen, J.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.R.; Jin, F.; Xu, R.; et al. Toripalimab or placebo plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A multicenter randomized phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Shen, G.; Yang, F.; Duan, J.; Wu, Z.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, S. Loss of AKR1C1 is a good prognostic factor in advanced NPC cases and increases chemosensitivity to cisplatin in NPC cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6438–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Li, J.Z.; Chen, S.Q.; Chu, C.Y.; Chan, J.Y.; Wong, T.S. BEX3 contributes to cisplatin chemoresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, M.; Lopez Pousa, A.; Del Barco, E.; Perez Segura, P.; Astorga, B.G.; Castelo, B.; Bonfill, T.; Martinez Trufero, J.; Grau, J.J.; Mesia, R. SEOM clinical guideline in nasopharynx cancer (2017). Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Venigalla, P.; Leeman, J.E.; LaPlant, Q.; Setton, J.; Sherman, E.; Tsai, J.; McBride, S.; Riaz, N.; Lee, N. Patterns of nodal failure after intensity modulated radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitapanarux, I.; Lorvidhaya, V.; Kamnerdsupaphon, P.; Sumitsawan, Y.; Tharavichitkul, E.; Sukthomya, V.; Ford, J. Chemoradiation comparing cisplatin versus carboplatin in locally advanced nasopharyngeal cancer: Randomised, non-inferiority, open trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.S.; Huang, G.J.; Liu, H.B. Oncologic outcomes of IMRT versus CRT for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e15951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Kitpanit, S.; Chilov, M.; Langendijk, J.A.; Lu, J.; Lee, N.Y. A Systematic Review of Proton Therapy for the Management of Nasopharyngeal Cancer. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2021, 8, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamboo, A.; Patel, V.S.; Hwang, P.H. 5-year outcomes of salvage endoscopic nasopharyngectomy for recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2021, 50, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.P.; Wen, Y.H.; Tang, J.; Wei, Y.; You, R.; Zhu, X.L.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Ling, L.; Zhang, N.; et al. Endoscopic surgery compared with intensity-modulated radiotherapy in resectable locally recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, R.; Gao, K.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. Comparing the Effectiveness of Endoscopic Surgeries With Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy for Recurrent rT3 and rT4 Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 703954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Miller, K.D.; Kramer, J.L.; Newman, L.A.; Minihan, A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 524–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrecque, L.G.; Barnes, D.M.; Fentiman, I.S.; Griffin, B.E. Epstein-Barr virus in epithelial cell tumors: A breast cancer study. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Su, J.; Yan, D.; Wu, S. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and Increased Sporadic Breast Carcinoma Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Med. Princ. Pract. 2020, 29, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.T.; Zhu, G.L.; Xu, W.Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.Z.; Wang, Y.B.; Li, Y.X. Association of PD-1/PD-L1 expression and Epstein--Barr virus infection in patients with invasive breast cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2022, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Luo, M.L.; Desmedt, C.; Nabavi, S.; Yadegarynia, S.; Hong, A.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Gabrielson, E.; Hines-Boykin, R.; Pihan, G.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of Mammary Epithelial Cells Promotes Malignant Transformation. EBioMedicine 2016, 9, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Chu, J.S.; Chen, J.Y.; Takada, K.; Shew, J.Y. Dysregulation of HER2/HER3 signaling axis in Epstein-Barr virus-infected breast carcinoma cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5705–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowran, R.; Joharinia, N.; Safaei, A.; Bakhtiyarizadeh, S.; Alidadi Soleimani, A.; Alizadeh, R.; Mir-Shiri, S.; Sarvari, J. No detection of EBV, BKV and JCV in breast cancer tissue samples in Iran. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, M.M.; Higgo, A.A.; Khalifa, A.S.; Eed, E.M. Incidence of Epstein-Barr Virus Among Women With Breast Cancer Using Monoclonal Antibodies for Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1). Vivo 2022, 36, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whaley, R.D.; Carlos, R.; Bishop, J.A.; Rooper, L.; Thompson, L.D.R. Lymphoepithelial Carcinoma of Salivary Gland EBV-association in Endemic versus Non-Endemic Patients: A Report of 16 Cases. Head Neck Pathol. 2020, 14, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.F.M.; Peres, K.C.; Teixeira, E.S.; Teodoro, L.; Bo, I.F.D.; Ward, L.S. Epstein-Barr Virus and Thyroid Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2019, 24, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magg, T.; Schober, T.; Walz, C.; Ley-Zaporozhan, J.; Facchetti, F.; Klein, C.; Hauck, F. Epstein-Barr Virus(+) Smooth Muscle Tumors as Manifestation of Primary Immunodeficiency Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.X.; Peng, X.T.; Tan, L.; Zhai, G.Q.; Chen, G.; Gan, T.Q.; Li, J.J. EBV as a potential risk factor for hepatobiliary system cancer: A meta-analysis with 918 cases. Pathol. Res. Pract 2019, 215, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.J.; Oh, J.H.; Chun, S.M.; Kim, D.; Ryu, Y.M.; Hwang, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; An, J.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, H.; et al. Immunogenomic landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma with immune cell stroma and EBV-positive tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisusi, F.A.; Akala, E.O. Drug Combinations in Breast Cancer Therapy. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2019, 7, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Le Du, F.; Xiao, L.; Kogawa, T.; Barcenas, C.H.; Alvarez, R.H.; Valero, V.; Shen, Y.; Ueno, N.T. Effectiveness of an Adjuvant Chemotherapy Regimen for Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrahennadi, S.; Sami, A.; Manna, M.; Pauls, M.; Ahmed, S. Current Landscape of Targeted Therapy in Hormone Receptor-Positive and HER2-Negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1803–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Xie, D.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Su, Y. Is Surgery an Inevitable Treatment for Advanced Salivary Lymphoepithelial Carcinoma? Three Case Reports. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, NP402–NP406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Ji, Q. A clinical analysis of 37 cases with lymphoepithelial carcinoma of the major salivary gland treated by surgical resection and postoperative radiotherapy: A single institution study. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, M.R.; Mastrogiulio, M.G.; Barone, A.; Rocca, B.J.; Gallo, C.; Lazzi, S.; Leoncini, L.; Bellan, C. Lymphoepithelial-like carcinoma of the parotid gland: A case report and a brief review of the western literature. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrason, M.; Martin, A.; Soussan, M.; Chouahnia, K.; Pailler, M.C.; Boudabous, H.; Brillet, P.Y.; Bousquet, G.; Zelek, L.; Duchemann, B. Immunotherapy for LELC: Case Report and a Focused Review. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e393–e401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, P.P.; Chen, Y.Y.; Ding, Z.Y. Pulmonary Lymphoepithelioma-Like Carcinoma Treated with Immunotherapy or Chemotherapy: A Single Institute Experience. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xian, X.; Wang, K.; Cheng, D.; Li, W.; Chen, B. Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy May Be a Feasible Option for Primary Pulmonary Lymphoepithelioma-like Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 626566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.W.; Klaassen, Z.; Agarwal, N.; Haaland, B.; Esther, J.; Ye, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Pal, S.K.; Wallis, C.J.D. First-line Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 2, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, P.C.; Rini, B.I. Treatment of renal cell carcinoma: Current status and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laha, D.; Nilubol, N.; Boufraqech, M. New Therapies for Advanced Thyroid Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xia, L.; Chen, X.; Fu, Y.; Wu, X. Simple conization and pelvic lymphadenectomy in early-stage cervical cancer: A retrospective analysis and review of the literature. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 158, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenis, A.T.; Lec, P.M.; Chamie, K.; Mshs, M.D. Bladder Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetti, L.; Bargellini, I.; Cioni, R. Loco-regional treatment of HCC: Current status. Clin. Radiol. 2017, 72, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Ming, X.; Jiang, G.L.; Wang, W. Indications of IMRT, PRT and CIRT for HCC from comparisons of dosimetry and normal tissue complication possibility. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2022, 198, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvry, C.; Palard, X.; Edeline, J.; Ardisson, V.; Loyer, P.; Garin, E.; Lepareur, N. Transarterial Radioembolization (TARE) Agents beyond (90)Y-Microspheres. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1435302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Liu, J.; Jin, Z.; Qiu, G.; Xie, Q.; Mi, S.; Huang, J. Use of chemotherapy to treat hepatocellular carcinoma. Biosci. Trends 2022, 16, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, F.; Gairing, S.J.; Ilyas, S.I.; Galle, P.R. Emerging immunotherapy for HCC: A guide for hepatologists. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1604–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, G.; Hashim, M.J. Global burden of deaths from Epstein-Barr virus attributable malignancies 1990–2010. Infect. Agent Cancer 2014, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhl, J.; Leung, C.S.; Munz, C. Vaccination against the Epstein-Barr virus. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 4315–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Snapper, C.M. Epstein Barr Virus: Development of Vaccines and Immune Cell Therapy for EBV-Associated Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teow, S.Y.; Yap, H.Y.; Peh, S.C. Epstein-Barr Virus as a Promising Immunotherapeutic Target for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treatment. J. Pathog. 2017, 2017, 7349268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Latency 0 | Latency I | Latency IIa | Latency IIb | Latency III | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBNA1 | − | + | + | + | + |
| EBNA2 | − | − | − | + | + |
| EBNA3 | − | − | − | + | + |
| EBNA-LP | − | − | − | + | + |
| LMP1 | − | − | + | − | + |
| LMP2 | − | − | + | − | + |
| BARTs | − | + | + | + | + |
| EBERs | + | + | + | + | + |
| Latency Type | Associated Malignancies |
|---|---|
| Latency I | EBVaGC, Burkitt lymphoma |
| Latency II | EBVaGC, NPC, DLCBL, classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma, NLPHL |
| Latency III | DLBCL |
| Cancer Type | Treatment Options | References |
|---|---|---|
| EBV-associated gastric cancer | Chemotherapy, radiation, and surgical resection, fluorouracil, leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel or fluoropyrimidine and oxaliplatin, pembrolizumab, enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) inhibitors | [97,100,107] |
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Surgery, platinum-based concurrent chemoradiotherapy, gemcitabine and cisplatin induction chemotherapy + toripalimab, intensity-modulated (IMRT), particle therapy | [145,148, 152,154] |
| Breast cancer | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, doxorubin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel (AC-T), docetaxel, paclitaxel, selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), (tamoxifen, raloxifene, toremifene), aromatase inhibitors (non-steroidal anastrozole and letrozole and steroidal exemestane), (SERD), selective estrogen receptor degrader (fulvestrant), cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitors (palbociclib, ribociclib and abemaciclib), PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors, mTOR inhibitor (everolimus), PI3K inhibitor (alpelisib), lumpectomy, whole breast irradiation, mastectomy | [173,174,175] |
| Lymphoepithelial carcinoma of the salivary glands | Surgery (parotidectomy or submandibular gland excision) and induction chemotherapy, concurrent therapy, postoperative radiotherapy | [176,177,178] |
| Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the lung | Surgery, cisplatin-based chemotherapy, pembrolizumab nivolumab, arezolizumab, nivolumab and gemcitabine, other combination therapies | [179,180,181] |
| Renal cell | Pembrolizumab and axitinib, cabozantinib, pazopanib, bevacizumab, temsirolimus, surgery, cytoreductive nephrectomy | [182,183] |
| Thyroid | Surgical resection, TSH suppression, radioiodine therapy, pembrolizumab, vemurafenib, dabrafenib, selumetinib, everolimus, sorafenib, lenvatinib, pazopanib and treametinib | [184] |
| Cervical | Conization, hysterectomy, radiotherapy | [185] |
| Bladder | Trans-urethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT), chemotherapy, induction intravesical therapy, induction BCG | [186] |
| Leiomyomas/leiomyosarcomas | EBV-CTL therapy, antiretroviral therapy, reduction of immunosuppressive treatment, surgery | [170] |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | Surgical resection, radiation therapy, chemo/immunotherapy (doxorubicin, FOLFOX [folinic acid, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin], sorafenib, regorafenib, atezolizumab + bevacizumab, others), image-guided tumor ablation, transcatheter arterial chemo/radioembolisation, combination therapies (ie systemic + intra-arterial treatment), | [187,188,189,190,191] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shechter, O.; Sausen, D.G.; Gallo, E.S.; Dahari, H.; Borenstein, R. Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Epithelial Associated Malignancies: Exploring Pathologies and Current Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214389
Shechter O, Sausen DG, Gallo ES, Dahari H, Borenstein R. Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Epithelial Associated Malignancies: Exploring Pathologies and Current Treatments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(22):14389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214389
Chicago/Turabian StyleShechter, Oren, Daniel G. Sausen, Elisa S. Gallo, Harel Dahari, and Ronen Borenstein. 2022. "Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Epithelial Associated Malignancies: Exploring Pathologies and Current Treatments" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 22: 14389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214389
APA StyleShechter, O., Sausen, D. G., Gallo, E. S., Dahari, H., & Borenstein, R. (2022). Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Epithelial Associated Malignancies: Exploring Pathologies and Current Treatments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(22), 14389. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214389






