Cell-Free Hemoglobin in Acute Kidney Injury after Lung Transplantation and Experimental Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics and Pre-, Peri-, and Postoperative Factors
2.2. CFH and Haptoglobin Levels in LuTx Patients
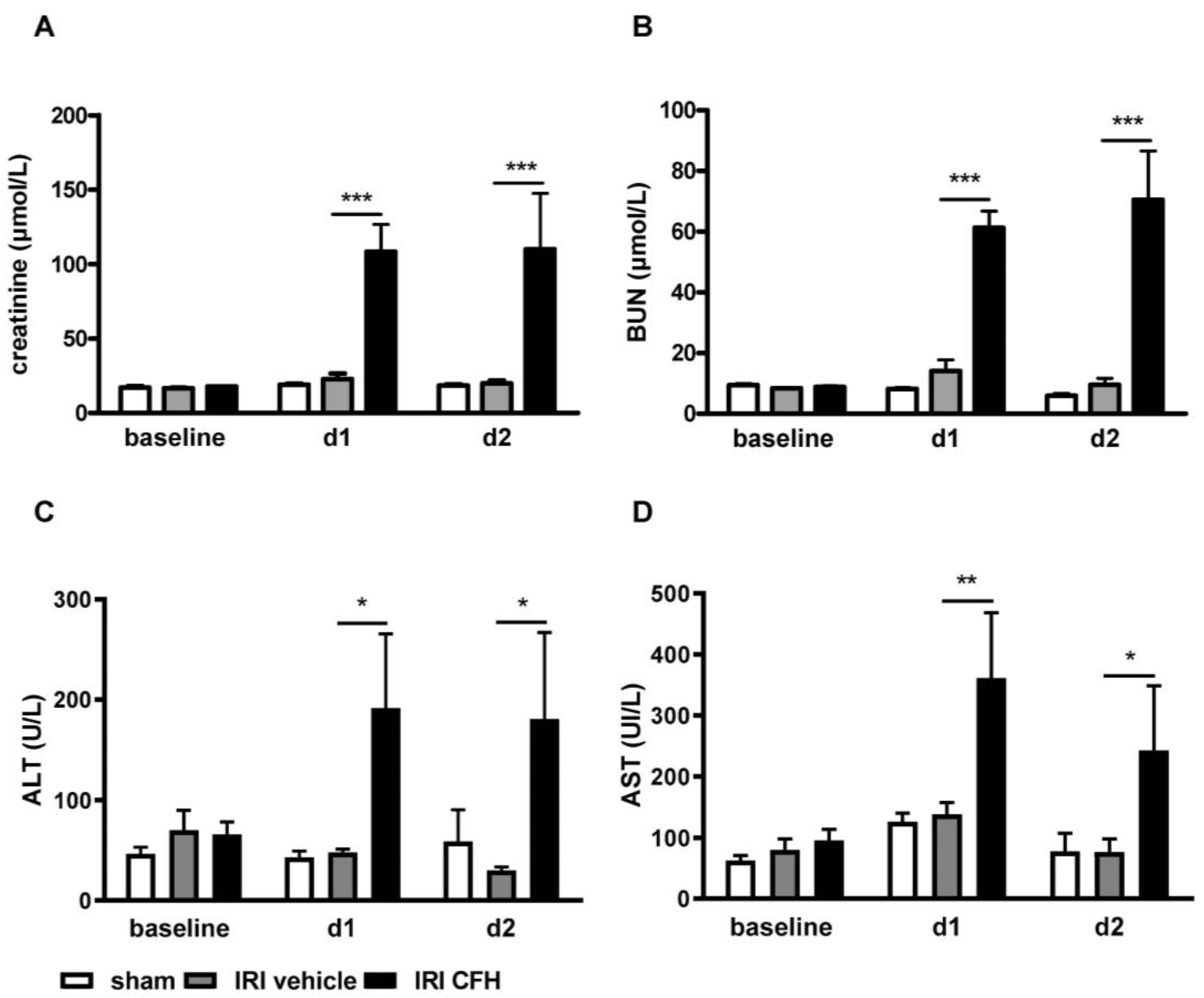
2.3. AKI and Distant Organ Injury in a Mouse Model of Mild Renal IRI and Exogenous CFH Administration
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Clinical Study
4.1.1. LuTx Patients
4.1.2. Sample Preparation and Measurement of CFH and Haptoglobin
4.1.3. AKI Definition
4.2. Experimental Study
4.2.1. Animals
4.2.2. Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury (IRI)
4.2.3. Organ Preservation
4.2.4. Measurement of Serum Creatinine, BUN and Liver Enzymes
4.2.5. Cytokine Expression
4.2.6. Renal Morphology and Immunofluorescence
4.2.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, D.; Fossi, A.; Marchetti, L.; Lanzarone, N.; Sisi, S.; Refini, R.M.; Sestini, P.; Luzzi, L.; Paladini, P.; Rottoli, P. Postoperative acute kidney injury in lung transplant recipients. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 28, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balci, M.K.; Vayvada, M.; Salturk, C.; Kutlu, C.A.; Ari, E. Incidence of Early Acute Kidney Injury in Lung Transplant Patients: A Single-Center Experience. Transpl. Proc. 2017, 49, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehbe, E.; Duncan, A.E.; Dar, G.; Budev, M.; Stephany, B. Recovery from AKI and short- and long-term outcomes after lung transplantation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karkouti, K.; Wijeysundera, D.N.; Yau, T.M.; Callum, J.L.; Cheng, D.C.; Crowther, M.; Dupuis, J.Y.; Fremes, S.E.; Kent, B.; Laflamme, C.; et al. Acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: Focus on modifiable risk factors. Circulation 2009, 119, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hobson, C.E.; Yavas, S.; Segal, M.S.; Schold, J.D.; Tribble, C.G.; Layon, A.J.; Bihorac, A. Acute kidney injury is associated with increased long-term mortality after cardiothoracic surgery. Circulation 2009, 119, 2444–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atchade, E.; Barour, S.; Tran-Dinh, A.; Jean-Baptiste, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tashk, P.; Snauwaert, A.; Lortat-Jacob, B.; Mourin, G.; Mordant, P.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury After Lung Transplantation: Perioperative Risk Factors and Outcome. Transpl. Proc. 2020, 52, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Chen, W.; Zhao, L.; Guo, L.; Liang, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Acute kidney injury following adult lung transplantation. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 135, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.E.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.E.; Lee, J.G.; Paik, H.C.; Park, M.S. Risk factors and mortality of acute kidney injury within 1 month after lung transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeder, B.J. The redox activity of hemoglobins: From physiologic functions to pathologic mechanisms. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1087–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, D.J.; Buehler, P.W.; Alayash, A.I.; Belcher, J.D.; Vercellotti, G.M. Hemolysis and free hemoglobin revisited: Exploring hemoglobin and hemin scavengers as a novel class of therapeutic proteins. Blood 2013, 121, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Avondt, K.; Nur, E.; Zeerleder, S. Mechanisms of haemolysis-induced kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 671–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.C.; Kim, A.Y.; Curley, S.P.; Chen, X.; Dworkin, L.D.; Cooper, C.J.; Gupta, R. Interleukin-10 attenuates renal injury after myocardial infarction in diabetes. J. Investig. Med. 2022, 70, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussavian, M.R.; Slotta, J.E.; Kollmar, O.; Menger, M.D.; Schilling, M.K.; Gronow, G. Hemoglobin induces cytotoxic damage of glycine-preserved renal tubules. Transpl. Int. 2007, 20, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; D’Agnillo, F.; Vallelian, F.; Pereira, C.P.; Williams, M.C.; Jia, Y.; Schaer, D.J.; Buehler, P.W. Hemoglobin-driven pathophysiology is an in vivo consequence of the red blood cell storage lesion that can be attenuated in guinea pigs by haptoglobin therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1444–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chintagari, N.R.; Nguyen, J.; Belcher, J.D.; Vercellotti, G.M.; Alayash, A.I. Haptoglobin attenuates hemoglobin-induced heme oxygenase-1 in renal proximal tubule cells and kidneys of a mouse model of sickle cell disease. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2015, 54, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaver, C.M.; Paul, M.G.; Putz, N.D.; Landstreet, S.R.; Kuck, J.L.; Scarfe, L.; Skrypnyk, N.; Yang, H.; Harrison, F.E.; de Caestecker, M.P.; et al. Cell-free hemoglobin augments acute kidney injury during experimental sepsis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2019, 317, F922–F929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamzik, M.; Hamburger, T.; Petrat, F.; Peters, J.; de Groot, H.; Hartmann, M. Free hemoglobin concentration in severe sepsis: Methods of measurement and prediction of outcome. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, H.R.; Mirsaeidi, M.; Socias, S.; Sprenker, C.; Caldeira, C.; Camporesi, E.M.; Mangar, D. Plasma Free Hemoglobin Is an Independent Predictor of Mortality among Patients on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graw, J.A.; Hildebrandt, P.; Krannich, A.; Balzer, F.; Spies, C.; Francis, R.C.; Kuebler, W.M.; Weber-Carstens, S.; Menk, M.; Hunsicker, O. The role of cell-free hemoglobin and haptoglobin in acute kidney injury in critically ill adults with ARDS and therapy with VV ECMO. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaver, C.M.; Wickersham, N.; McNeil, J.B.; Nagata, H.; Miller, A.; Landstreet, S.R.; Kuck, J.L.; Diamond, J.M.; Lederer, D.J.; Kawut, S.M.; et al. Cell-free hemoglobin promotes primary graft dysfunction through oxidative lung endothelial injury. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, P.N.; Rocha, A.T.; Palmer, S.M.; Davis, R.D.; Smith, S.R. Acute renal failure after lung transplantation: Incidence, predictors and impact on perioperative morbidity and mortality. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaoutakis, G.J.; George, T.J.; Robinson, C.W.; Gibbs, K.W.; Orens, J.B.; Merlo, C.A.; Shah, A.S. Severe acute kidney injury according to the RIFLE (risk, injury, failure, loss, end stage) criteria affects mortality in lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2011, 30, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacques, F.; El-Hamamsy, I.; Fortier, A.; Maltais, S.; Perrault, L.P.; Liberman, M.; Noiseux, N.; Ferraro, P. Acute renal failure following lung transplantation: Risk factors, mortality, and long-term consequences. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 41, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wehbe, E.; Brock, R.; Budev, M.; Xu, M.; Demirjian, S.; Schreiber, M.J., Jr.; Stephany, B. Short-term and long-term outcomes of acute kidney injury after lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2012, 31, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidalgo, P.; Ahmed, M.; Meyer, S.R.; Lien, D.; Weinkauf, J.; Cardoso, F.S.; Jackson, K.; Bagshaw, S.M. Incidence and outcomes of acute kidney injury following orthotopic lung transplantation: A population-based cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2014, 29, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lassnigg, A.; Schmidlin, D.; Mouhieddine, M.; Bachmann, L.M.; Druml, W.; Bauer, P.; Hiesmayr, M. Minimal changes of serum creatinine predict prognosis in patients after cardiothoracic surgery: A prospective cohort study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wajda-Pokrontka, M.; Nadziakiewicz, P.; Krauchuk, A.; Ochman, M.; Zawadzki, F.; Przybylowski, P. Incidence and Perioperative Risk Factors of Acute Kidney Injury among Lung Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2022, 54, 1120–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikma, M.A.; Hunault, C.C.; van de Graaf, E.A.; Verhaar, M.C.; Kesecioglu, J.; de Lange, D.W.; Meulenbelt, J. High tacrolimus blood concentrations early after lung transplantation and the risk of kidney injury. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doricic, J.; Greite, R.; Vijayan, V.; Immenschuh, S.; Leffler, A.; Ius, F.; Haverich, A.; Gottlieb, J.; Haller, H.; Scheffner, I.; et al. Kidney injury after lung transplantation: Long-term mortality predicted by post-operative day-7 serum creatinine and few clinical factors. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, M.; Jackson, K.; Singh, P.; Rosenheck, J.P.; Ganapathi, A.M.; Henn, M.C.; Howsare, M.M.; Mokadam, N.A.; Pesavento, T.; Whitson, B.A.; et al. Insights into early postoperative acute kidney injury following lung transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 36, e14568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.; Hill, A.; Melnyk, V.; Doney, L.; D’Cunha, J.; Kenkre, T.; Subramaniam, K.; Howard-Quijano, K. Intraoperative Hypoxia Independently Associated With the Development of Acute Kidney Injury Following Bilateral Orthotopic Lung Transplantation. Transplantation 2022, 106, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Vijayan, V.; Jang, M.S.; Thorenz, A.; Greite, R.; Rong, S.; Chen, R.; Shushakova, N.; Tudorache, I.; Derlin, K.; et al. Labile Heme Aggravates Renal Inflammation and Complement Activation After Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadee, C.; Raat, N.J.; Kanias, T.; Tejero, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kelley, E.E.; Zhao, X.; Liu, C.; Reynolds, H.; Azarov, I.; et al. Nitric oxide scavenging by red blood cell microparticles and cell-free hemoglobin as a mechanism for the red cell storage lesion. Circulation 2011, 124, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.J.; McQuilten, Z.K.; Nichol, A.; Ady, B.; Aubron, C.; Bailey, M.; Bellomo, R.; Gantner, D.; Irving, D.O.; Kaukonen, K.M.; et al. Age of Red Cells for Transfusion and Outcomes in Critically Ill Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1858–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Ma, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Dang, S.; Lv, Y.; Wu, R. Transfusion of Older Red Blood Cells Increases the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury After Orthotopic Liver Transplantation: A Propensity Score Analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 127, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rund, K.M.; Peng, S.; Greite, R.; Claassen, C.; Nolte, F.; Oger, C.; Galano, J.M.; Balas, L.; Durand, T.; Chen, R.; et al. Dietary omega-3 PUFA improved tubular function after ischemia induced acute kidney injury in mice but did not attenuate impairment of renal function. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020, 146, 106386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greite, R.; Thorenz, A.; Chen, R.; Jang, M.S.; Rong, S.; Brownstein, M.J.; Tewes, S.; Wang, L.; Baniassad, B.; Kirsch, T.; et al. Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury causes hypertension and renal perfusion impairment in the CD1 mice which promotes progressive renal fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2018, 314, F881–F892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greite, R.; Derlin, K.; Hensen, B.; Thorenz, A.; Rong, S.; Chen, R.; Hellms, S.; Jang, M.S.; Brasen, J.H.; Meier, M.; et al. Early antihypertensive treatment and ischemia-induced acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2020, 319, F563–F570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draeger, H.; Salman, J.; Aburahma, K.; Becker, L.S.; Siemeni, T.; Boethig, D.; Sommer, W.; Avsar, M.; Bobylev, D.; Schwerk, N.; et al. Impact of unilateral diaphragm elevation on postoperative outcomes in bilateral lung transplantation—A retrospective single-center study. Transpl. Int. 2021, 34, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ius, F.; Sommer, W.; Tudorache, I.; Avsar, M.; Siemeni, T.; Salman, J.; Molitoris, U.; Gras, C.; Juettner, B.; Puntigam, J.; et al. Five-year experience with intraoperative extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in lung transplantation: Indications and midterm results. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okusa, M.D.; Davenport, A. Reading between the (guide)lines—The KDIGO practice guideline on acute kidney injury in the individual patient. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| All pts. n = 20 | No AKI n = 10 | AKI n = 10 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | ||||
| Age (years) | 49.3 ± 11 | 48.7 ± 13 | 49.9 ± 8 | 0.813 |
| Sex n (%; male/female) | 10 (50)/10 (50) | 4 (40)/6 (60) | 6 (60)/4 (40) | 0.371 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.0 ± 3.9 | 21.1 ± 4.2 | 22.9 ± 3.5 | 0.773 |
| Indication for transplantation. n (%) | ||||
| COPD/emphysema | 10 (50) | 5 (50) | 5 (50) | - |
| Cystic fibrosis | 2 (10) | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | - |
| Fibrosis | 6 (30) | 2 (20) | 4 (40) | - |
| Other | 2 (10) | 2 (20) | 0 (0) | - |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Arterial hypertension. n (%) | 5 (25) | 3 (30) | 2 (20) | 0.606 |
| Diabetes mellitus. n (%) | 5 (25) | 2 (20) | 3 (30) | 0.606 |
| Preoperative factors | ||||
| FEV 1 (%) | 25.0 ± 17 | 26.1 ± 20 | 23.8 ± 15 | 0.773 |
| FVC (%) | 40.6 ± 18 | 42.8 ± 19 | 38.4 ± 18 | 0.599 |
| Baseline serum creatinine (µmol/L) | 61.0 ± 15 | 63.8 ± 14 | 58.1 ± 16 | 0.396 |
| Baseline eGFR (mL/min) | 106 ± 15 | 103 ± 20 | 109 ± 10 | 0.400 |
| Baseline serum C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 11.2 ± 13 | 16.4 ± 17 | 6.0 ± 6 | 0.090 |
| ECMO pre-operative. n (%) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 1 (10) | 0.305 |
| Perioperative factors | ||||
| Duration of surgery (min) | 302.5 ± 63 | 273.7 ± 44 | 331.2 ± 69 | 0.039 |
| Ischemia time first side (min) | 401.8 ± 98 | 356.0 ± 68 | 447.6 ± 105 | 0.033 |
| Ischemia time second side (min) | 518.8 ± 107 | 464.0 ± 76 | 573.5 ± 108 | 0.017 |
| ECMO intraoperative. n (%) | 5 (25) | 2 (20) | 3 (30) | 0.606 |
| Transfused packed red blood cells (pRBCs) during surgery | 1.4 ± 1.8 | 1.2 ± 1.5 | 1.6 ± 2.0 | 0.624 |
| Transfused fresh frozen plasma (FFP) during surgery | 1.5 ± 1.9 | 1.9 ± 1.9 | 1.1 ± 1.9 | 0.380 |
| Transfused platelets during surgery | 0.3 ± 0.7 | 0.4 ± 0.9 | 0.2 ± 0.6 | 0.493 |
| Serum creatinine 24 h (µmol/L) | 92.8 ± 45 | 69.2 ± 18 | 116.4 ± 52 | 0.019 |
| Serum creatinine 48 h (µmol/L) | 87.9 ± 48 | 61.8 ± 18 | 113.9 ± 55 | 0.016 |
| eGFR 24 h (mL/min) | 82 ± 30 | 97 ± 24 | 66 ± 29 | 0.019 |
| eGFR 48 h (mL/min) | 87 ± 36 | 104 ± 25 | 73 ± 34 | 0.026 |
| Reoperation. n (%) | 4 (20) | 1 (10) | 3 (30) | 0.264 |
| Transfused packed red blood cells (pRBC) postoperative | 2.5 ± 2.0 | 2.5 ± 2.4 | 2.5 ± 1.8 | 1.000 |
| ECMO postoperative. n (%) | 2 (10) | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | 1.000 |
| Hospital stay (days) | 28.2 ± 12 | 24.2 ± 6 | 32.1 ± 15 | 0.149 |
| Intensive care unit treatment (days) | 3.8 ± 4 | 2.8 ± 2 | 4.7 ± 4 | 0.257 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Greite, R.; Wang, L.; Gohlke, L.; Schott, S.; Kreimann, K.; Doricic, J.; Leffler, A.; Tudorache, I.; Salman, J.; Natanov, R.; et al. Cell-Free Hemoglobin in Acute Kidney Injury after Lung Transplantation and Experimental Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113272
Greite R, Wang L, Gohlke L, Schott S, Kreimann K, Doricic J, Leffler A, Tudorache I, Salman J, Natanov R, et al. Cell-Free Hemoglobin in Acute Kidney Injury after Lung Transplantation and Experimental Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(21):13272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113272
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreite, Robert, Li Wang, Lukas Gohlke, Sebastian Schott, Kirill Kreimann, Julian Doricic, Andreas Leffler, Igor Tudorache, Jawad Salman, Ruslan Natanov, and et al. 2022. "Cell-Free Hemoglobin in Acute Kidney Injury after Lung Transplantation and Experimental Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 21: 13272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113272
APA StyleGreite, R., Wang, L., Gohlke, L., Schott, S., Kreimann, K., Doricic, J., Leffler, A., Tudorache, I., Salman, J., Natanov, R., Ius, F., Fegbeutel, C., Haverich, A., Lichtinghagen, R., Chen, R., Rong, S., Haller, H., Vijayan, V., Gram, M., ... Immenschuh, S. (2022). Cell-Free Hemoglobin in Acute Kidney Injury after Lung Transplantation and Experimental Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(21), 13272. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232113272






