Familial Linkage and Association of the NR3C1 Gene with Type 2 Diabetes and Depression Comorbidity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bădescu, S.; Tătaru, C.; Kobylinska, L.; Georgescu, E.; Zahiu, D.; Zăgrean, A.; Zăgrean, L. The association between Diabetes mellitus and Depression. J. Med. Life 2016, 9, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, J.P.; McKlveen, J.M.; Ghosal, S.; Kopp, B.; Wulsin, A.; Makinson, R.; Myers, B. Regulation of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenocortical Stress Response. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nandam, L.S.; Brazel, M.; Zhou, M.; Jhaveri, D.J. Cortisol and Major Depressive Disorder—Translating Findings from Humans to Animal Models and Back. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.-D.; Rizak, J.; Feng, X.-L.; Yang, S.-C.; Lü, L.-B.; Pan, L.; Yin, Y.; Hu, X.-T. Prolonged secretion of cortisol as a possible mechanism underlying stress and depressive behaviour. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, R.I.; de Groot, M.; Golden, S.H. Diabetes and depression. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.J.; Golden, S.H. Cortisol dysregulation: The bidirectional link between stress, depression, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1391, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, M.; Pivonello, C.; Simeoli, C.; Di Gennaro, G.; Venneri, M.A.; Sciarra, F.; Ferrigno, R.; de Angelis, C.; Sbardella, E.; De Martino, M.C.; et al. Cortisol Circadian Rhythm and Insulin Resistance in Muscle: Effect of Dosing and Timing of Hydrocortisone Exposure on Insulin Sensitivity in Synchronized Muscle Cells. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 111, 1005–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2012, 61, 778–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragnoli, C. Hypothesis of the neuroendocrine cortisol pathway gene role in the comorbidity of depression, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2014, 7, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerstad, J.K.; Lightman, S.L.; Spiga, F. Role of glucocorticoid negative feedback in the regulation of HPA axis pulsatility. Stress 2018, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, G.; Damjanovic, S.; Xekouki, P.; Lefebvre, H.; Stratakis, C.A. The Glucocorticoid Receptor and its Expression in the Anterior Pituitary and the Adrenal Cortex: A Source of Variation in Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Function; Implications for Pituitary and Adrenal Tumors. Endocr. Pr. 2011, 17, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstathopoulos, P.; Andersson, F.; Melas, P.A.; Yang, L.L.; Villaescusa, J.C.; Rȕegg, J.; Ekström, T.J.; Forsell, Y.; Galanti, M.R.; Lavebratt, C. NR3C1 hypermethylation in depressed and bullied adolescents. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, J.D.A.; Freitas, F.V.; Borçoi, A.R.; Mendes, S.O.; Conti, C.L.; Arpini, J.K.; Vieira, T.D.S.; de Souza, R.A.; dos Santos, D.P.; Barbosa, W.M.; et al. Alcohol consumption, depression, overweight and cortisol levels as determining factors for NR3C1 gene methylation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borçoi, A.R.; Mendes, S.O.; dos Santos, J.G.; DE Oliveira, M.M.; Moreno, I.A.A.; Freitas, F.V.; Pinheiro, J.A.; Arpini, J.K.; Cunha, E.R.; Archanjo, A.; et al. Risk factors for depression in adults: NR3C1 DNA methylation and lifestyle association. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 121, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Yan, H.; Wen, Y.; Lai, C.; Shi, L. Association between NR3C1 rs41423247 polymorphism and depression: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uher, R.; Huezo-Diaz, P.; Perroud, N.; Smith, R.; Rietschel, M.; Mors, O.; Hauser, J.; Maier, W.; Kozel, D.; Henigsberg, N.; et al. Genetic predictors of response to antidepressants in the GENDEP project. Pharmacogenom. J. 2009, 9, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.A.; Halpin, C.G.; Irving, J.A.E.; Unwin, N.; White, M.; Bhopal, R.S.; Redfern, C.P.F.; Weaver, J.U. A common intron 2 polymorphism of the glucocorticoid receptor gene is associated with insulin resistance in men. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 68, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trementino, L.; Appolloni, G.; Concettoni, C.; Cardinaletti, M.; Boscaro, M.; Arnaldi, G. Association of glucocorticoid receptor polymorphism A3669G with decreased risk of developing diabetes in patients with Cushing’s syndrome. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Liu, X.; Huo, W.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Mao, Z. Serum cortisone and glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1) polymorphism in human dysglycemia. Hormones 2020, 19, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautanen, A.; Eriksson, J.G.; Kere, J.; Andersson, S.; Osmond, C.; Tienari, P.; Sairanen, H.; Barker, D.J.P.; Phillips, D.I.W.; Forsén, T.; et al. Associations of Body Size at Birth with Late-Life Cortisol Concentrations and Glucose Tolerance Are Modified by Haplotypes of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4544–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, E.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, J.; Xiang, L.; Qian, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, L.; Xiong, X.; et al. Obesity-induced excess of 17-hydroxyprogesterone promotes hyperglycemia through activation of glucocorticoid receptor. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3791–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skupio, U.; Tertil, M.; Sikora, M.; Golda, S.; Wawrzczak-Bargiela, A.; Przewlocki, R. Behavioral and molecular alterations in mice resulting from chronic treatment with dexamethasone: Relevance to depression. Neuroscience 2015, 286, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van West, D.; Eede, F.V.D.; Del Favero, J.; Souery, D.; Norrback, K.-F.; Van Duijn, C.; Sluijs, S.; Adolfsson, R.; Mendlewicz, J.; Deboutte, D.; et al. Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene-Based SNP Analysis in Patients with Recurrent Major Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 31, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mezuk, B.; Eaton, W.W.; Albrecht, S.; Golden, S.H. Depression and type 2 diabetes over the lifespan: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demakakos, P.; Pierce, M.B.; Hardy, R. Depressive symptoms and risk of type 2 diabetes in a national sample of middle-aged and older adults: The English longitudinal study of aging. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Lucas, M.; Sun, Q.; van Dam, R.; Franco, O.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Ascherio, A.; Hu, F.B. Bidirectional Association Between Depression and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1884–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustad, J.K.; Musselman, D.L.; Nemeroff, C.B. The relationship of depression and diabetes: Pathophysiological and treatment implications. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Ott, J.; Gordon, D.; Wu, R.; Postolache, T.T.; Vergare, M.; Gragnoli, C. Comorbidity of Novel CRHR2 Gene Variants in Type 2 Diabetes and Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Ott, J.; Wu, R.; Postolache, T.T.; Gragnoli, C. Implication of Melanocortin Receptor Genes in the Familial Comorbidity of Type 2 Diabetes and Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udina, M.; Navinés, R.; Egmond, E.; Oriolo, G.; Langohr, K.; Giménez, D.; Valdés, M.; Gómez-Gil, E.; Grande, I.; Gratacòs, M.; et al. Glucocorticoid Receptors, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Serotonin and Dopamine Neurotransmission are Associated with Interferon-Induced Depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 19, pyv135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, J.; Räikkönen, K.; Bruce, S.; Heinonen, K.; Pesonen, A.-K.; Rautanen, A.; Wahlbeck, K.; Kere, J.; Kajantie, E.; Eriksson, J. Glucocorticoid receptor gene haplotype predicts increased risk of hospital admission for depressive disorders in the Helsinki birth cohort study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Galfalvy, H.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Rosoklija, G.B.; Dwork, A.J.; Burke, A.; Arango, V.; Oquendo, M.A.; Mann, J.J. Glucocorticoid receptor-related genes: Genotype and brain gene expression relationships to suicide and major depressive disorder. Depress. Anxiety 2016, 33, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supriyanto, I.; Sasada, T.; Fukutake, M.; Asano, M.; Ueno, Y.; Nagasaki, Y.; Shirakawa, O.; Hishimoto, A. Association of FKBP5 gene haplotypes with completed suicide in the Japanese population. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.S.; Elias, D.; Colli, L.M.; Couri, C.E.; Souza, M.C.; Moreira, A.C.; de Castro, M. HPA axis dysregulation, NR3C1 polymorphisms and glucocorticoid receptor isoforms imbalance in metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2017, 33, e2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaganathan, K.; Panagiotopoulou, S.K.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.D.; Oscanoa, J.; Wang, J.; Nagano, A.; Lemoine, N.R.; Chelala, C. SNPnexus: Assessing the functional relevance of genetic variation to facilitate the promise of precision medicine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W109–W113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Taylor, J.A. SNPinfo: Integrating GWAS and candidate gene information into functional SNP selection for genetic association studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37 (Suppl. 2), W600–W605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, A.P.; Hong, E.L.; Hariharan, M.; Cheng, Y.; Schaub, M.A.; Kasowski, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Park, J.; Hitz, B.C.; Weng, S.; et al. Annotation of functional variation in personal genomes using RegulomeDB. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Li, T.; Lu, M.; Wang, L.; Yue, W.; Zhang, D. MirSNP, a database of polymorphisms altering miRNA target sites, identifies miRNA-related SNPs in GWAS SNPs and eQTLs. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firouzabadi, N.; Nouraei, H.; Mandegary, A. Genetic Variant of Glucocorticoid Receptor Gene at rs41423247 and Its Association with Major Depressive Disorder: A Case-Control Study. Galen Med. J. 2018, 7, e1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawiejska, A.; Bogacz, A.; Iciek, R.; Lewicka-Rabska, A.; Brązert, M.; Mikołajczak, P.; Brązert, J. A 646C > G (rs41423247) polymorphism of the glucocorticoid receptor as a risk factor for hyperglycaemia diagnosed in pregnancy—data from an observational study. Geol. Rundsch. 2021, 59, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.-X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; He, Y. Polymorphisms in NR3C1 gene associated with risk of metabolic syndrome in a Chinese population. Endocrine 2014, 47, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiekkalinna, T.; Schäffer, A.A.; Lambert, B.; Norrgrann, P.; Göring, H.H.; Terwilliger, J.D. PSEUDOMARKER: A Powerful Program for Joint Linkage and/or Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis on Mixtures of Singletons and Related Individuals. Hum. Hered. 2011, 71, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LDmatrix Function-RDocumentation. Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/LDlinkR/versions/1.1.2/topics/LDmatrix (accessed on 28 September 2021).
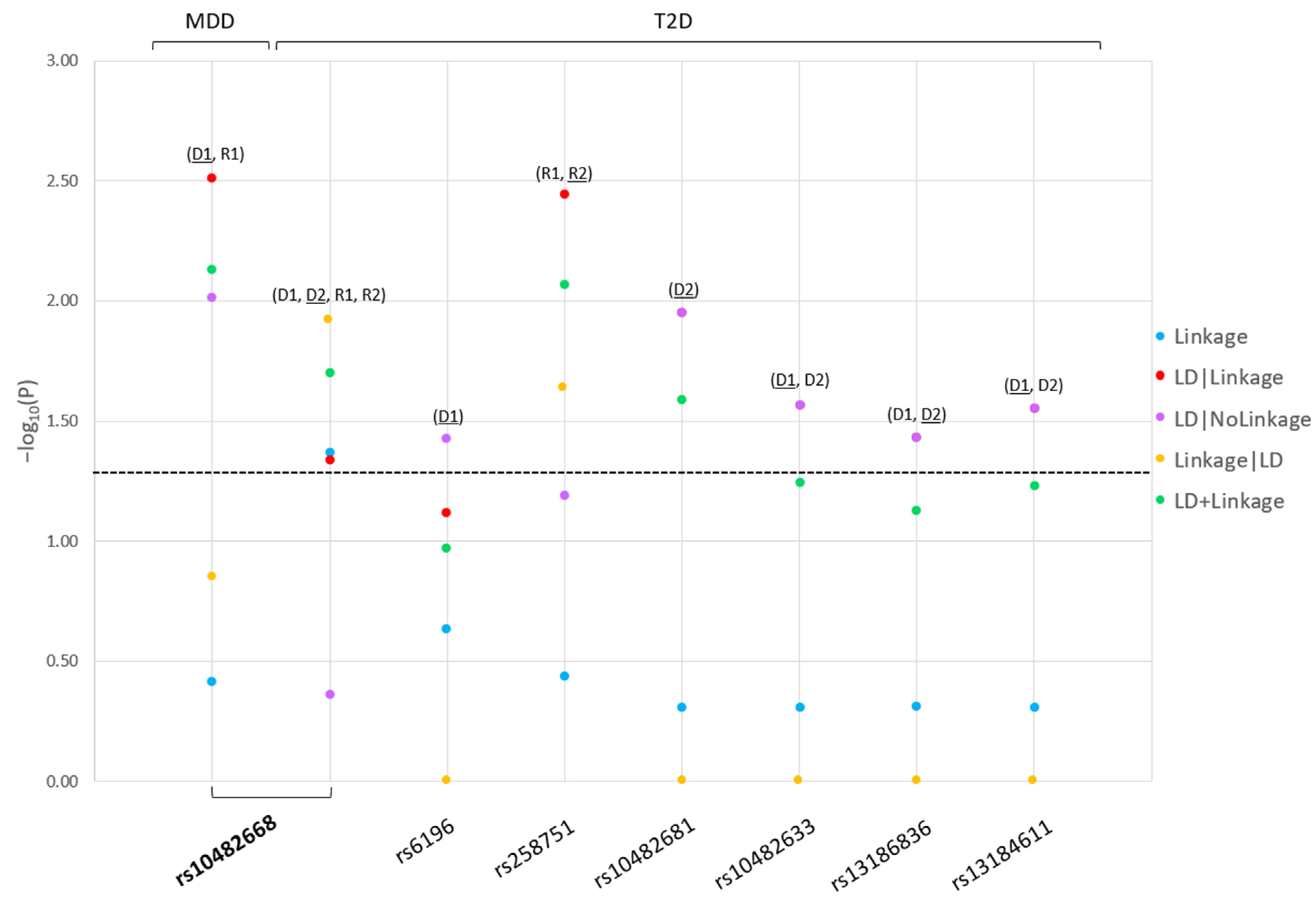
| Disease | Model 1 | SNP | Position | Ref | Alt | Risk Allele | Consequence | LD Block | Reported in MDD or T2D? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDD | D1, R1 | rs10482668 | 143313762 | T | A | T | Intronic | Independent | Novel |
| T2D | D1 | rs6196 | 143281925 | A | G | A | Synonymous | Independent | Yes (MDD) [23] |
| R1, R2 | rs258751 | 143282715 | G | A | G | Synonymous | Independent | Novel | |
| D2 | rs10482681 | 143299858 | A | C | C | Intronic | Independent | Novel | |
| D1, D2, R1, R2 | rs10482668 | 143313762 | T | A | T | Intronic | Independent | Novel | |
| D1, D2 | rs10482633 | 143370968 | T | G | G | Intronic | Independent | Novel | |
| D1, D2 | rs13186836 | 143418420 | T | C | C | Intronic | NA | Novel | |
| D1, D2 | rs13184611 | 143422369 | C | T | T | Intronic | NA | Novel |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, M.; Syed, S.; Wu, R.; Postolache, T.T.; Gragnoli, C. Familial Linkage and Association of the NR3C1 Gene with Type 2 Diabetes and Depression Comorbidity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911951
Amin M, Syed S, Wu R, Postolache TT, Gragnoli C. Familial Linkage and Association of the NR3C1 Gene with Type 2 Diabetes and Depression Comorbidity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911951
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Mutaz, Shumail Syed, Rongling Wu, Teodor Tudorel Postolache, and Claudia Gragnoli. 2022. "Familial Linkage and Association of the NR3C1 Gene with Type 2 Diabetes and Depression Comorbidity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911951
APA StyleAmin, M., Syed, S., Wu, R., Postolache, T. T., & Gragnoli, C. (2022). Familial Linkage and Association of the NR3C1 Gene with Type 2 Diabetes and Depression Comorbidity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911951







