Genome-Wide Identification and Evolution Analysis of R2R3-MYB Gene Family Reveals S6 Subfamily R2R3-MYB Transcription Factors Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Carrot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
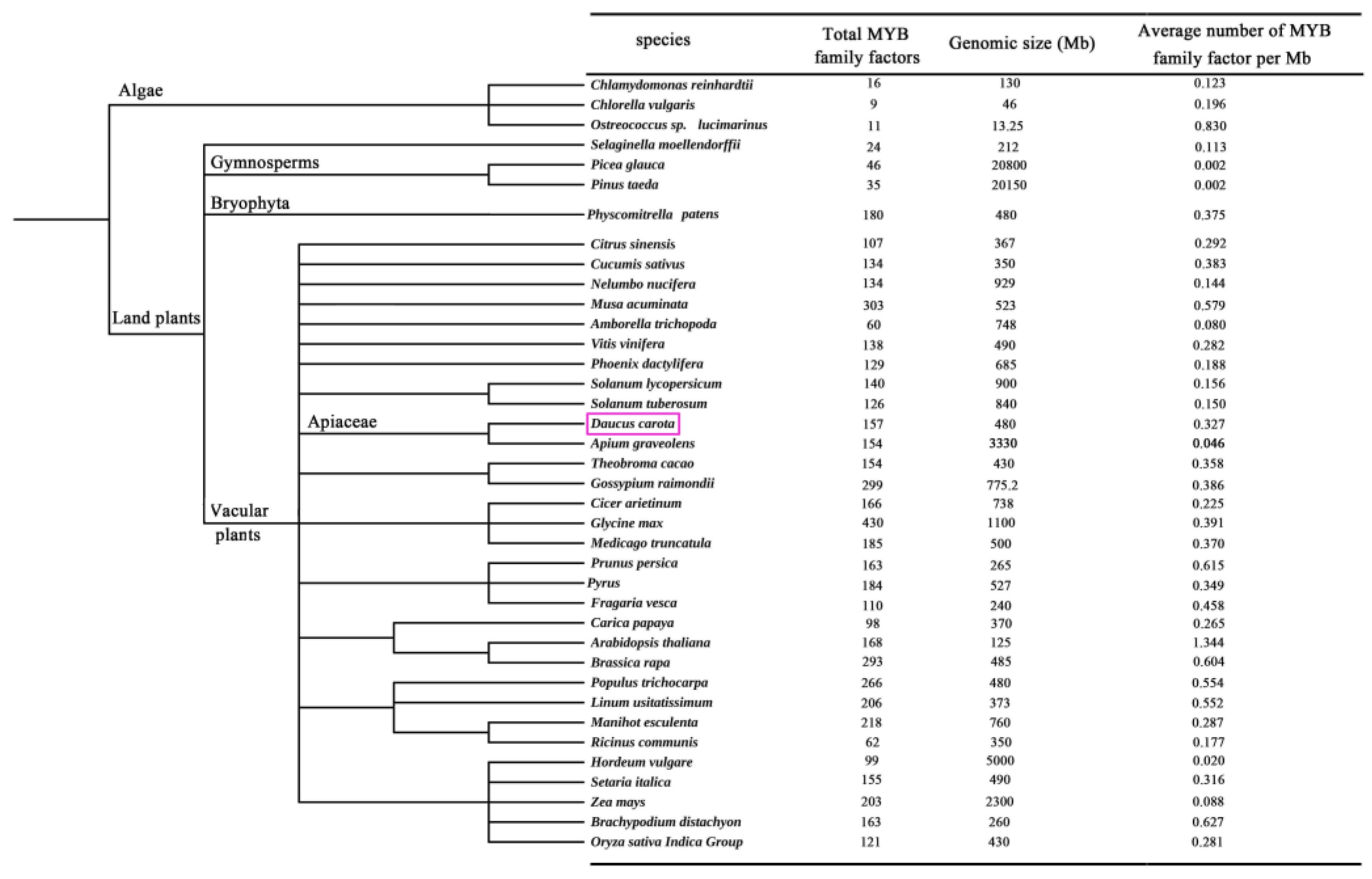
2.1. Evolution of MYB TFs of Carrot in Different Species
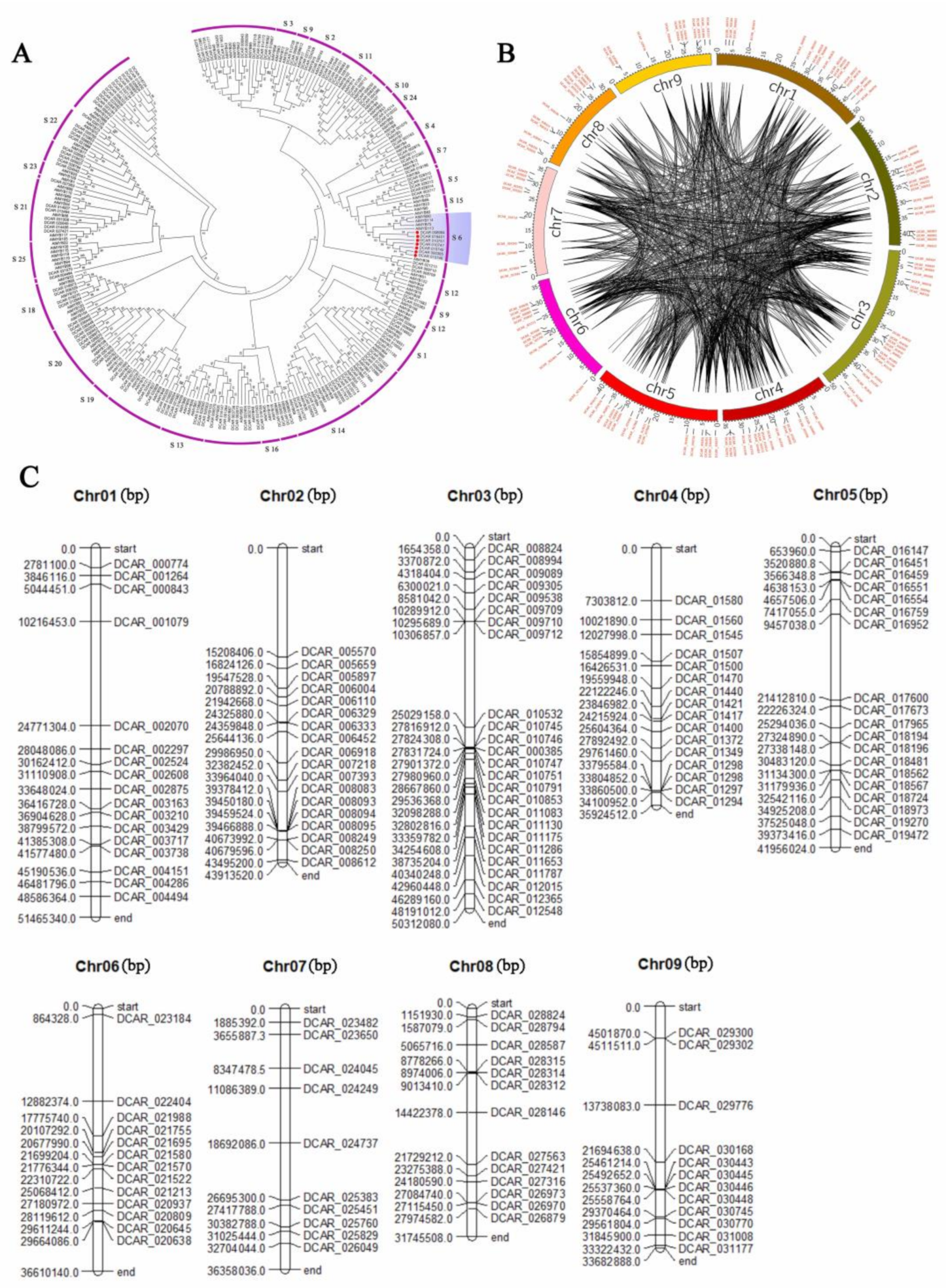
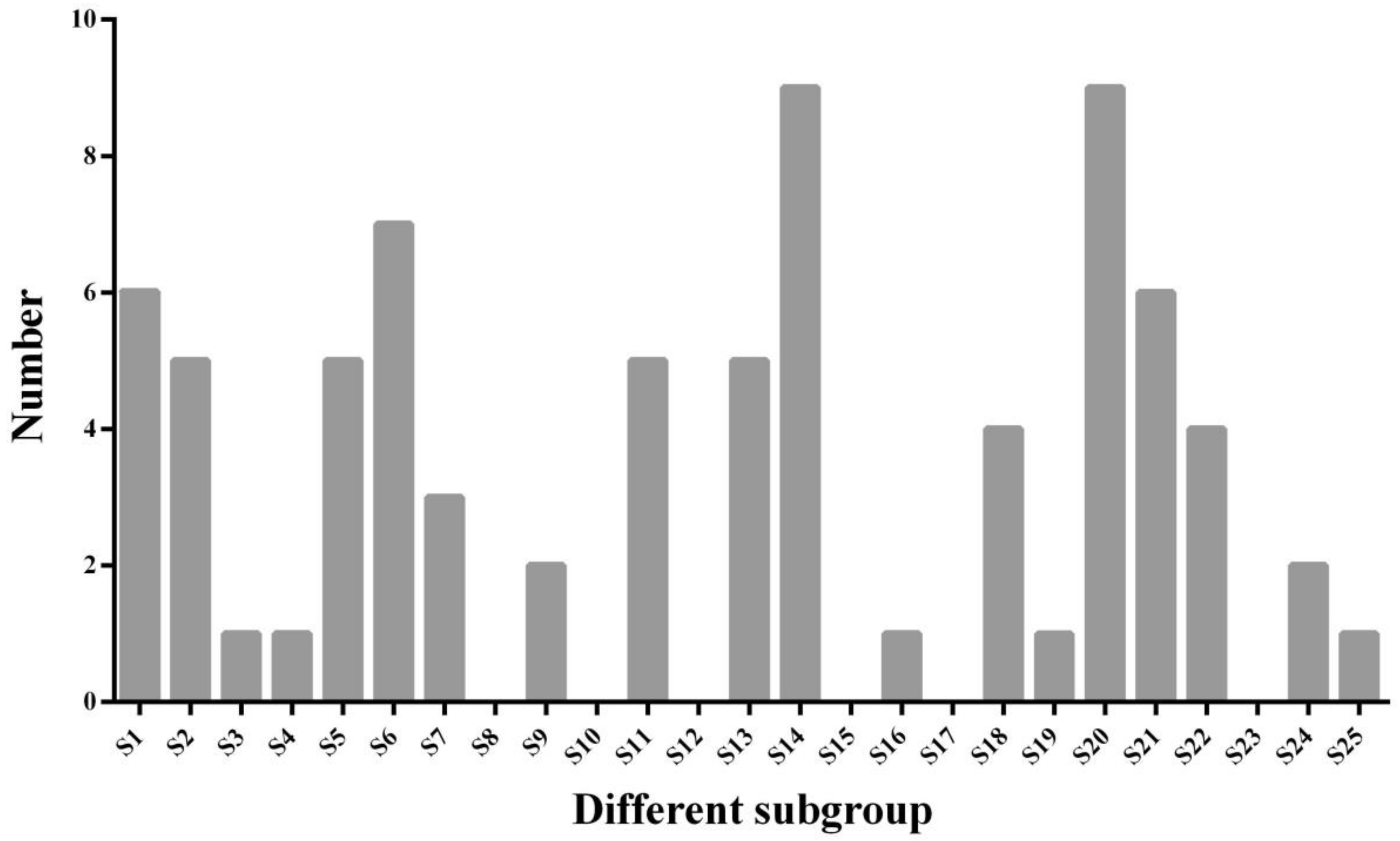
2.2. Classification and Phylogenetic Analysis of R2R3-MYB TFs in D. carota and A. thaliana and Analyses of Chromosomal Locations
2.3. Conserved Motifs of R2R3-MYB Proteins Based on the Analysis of MEME
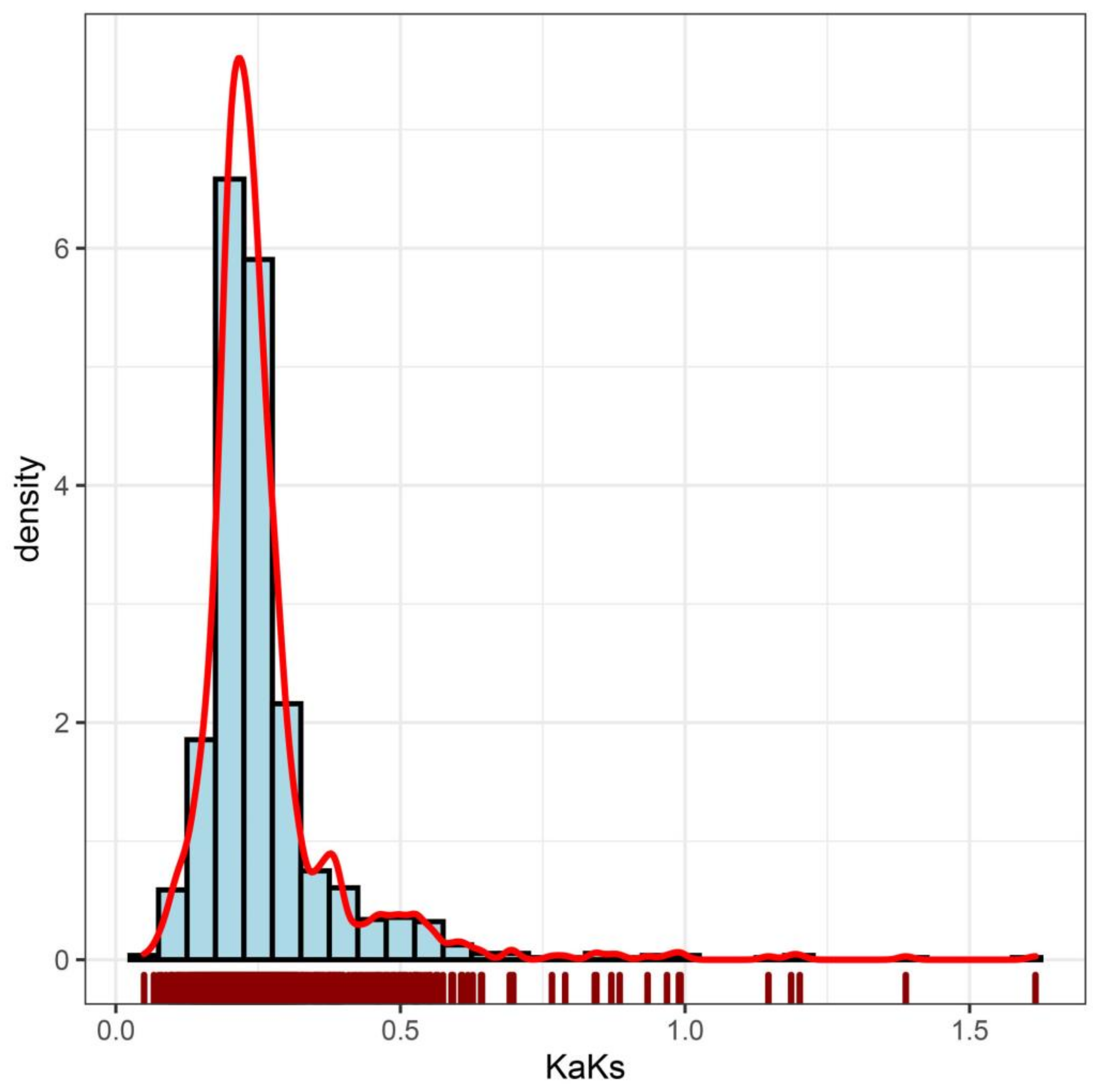
2.4. Selection Pressure in Carrot
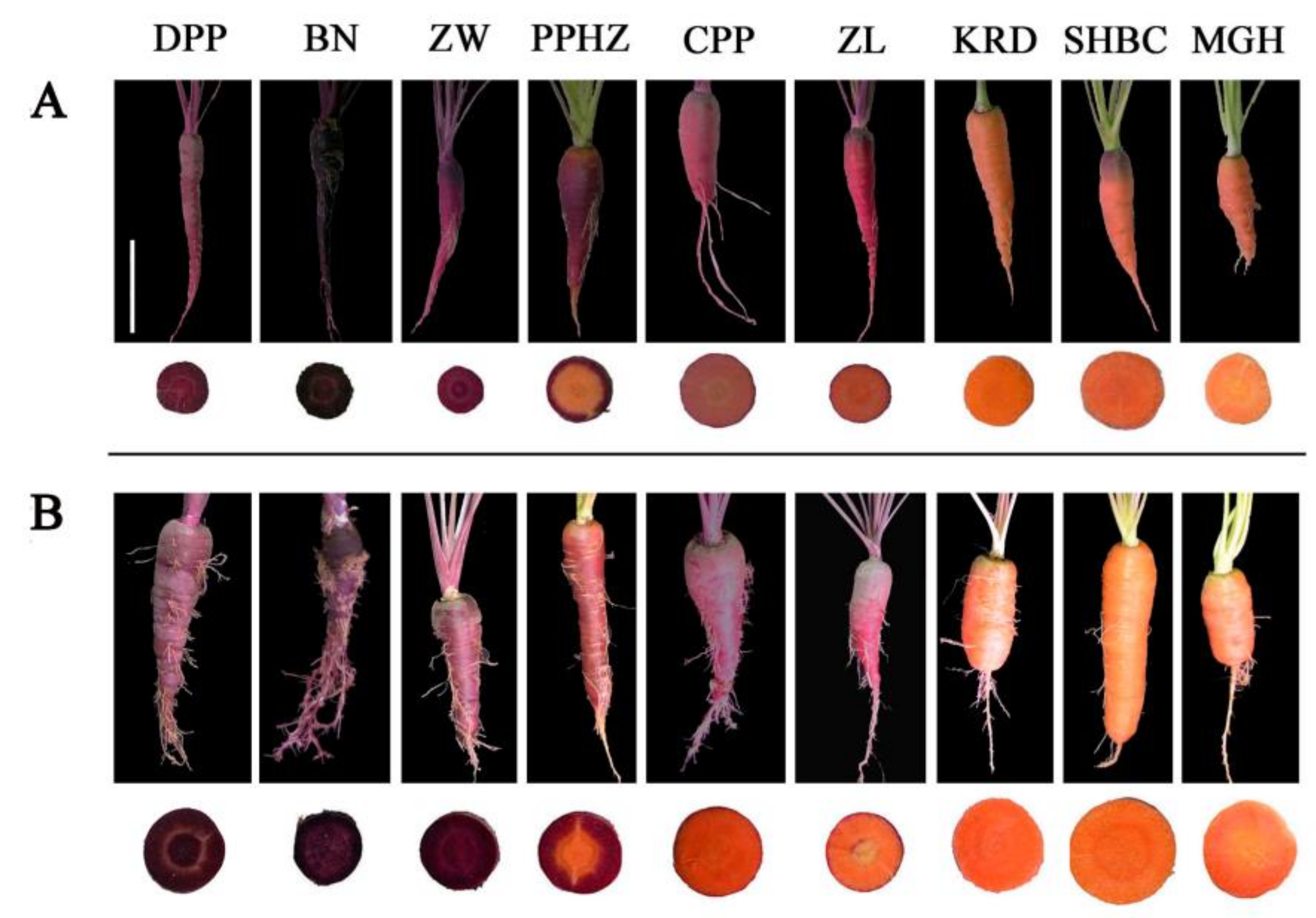
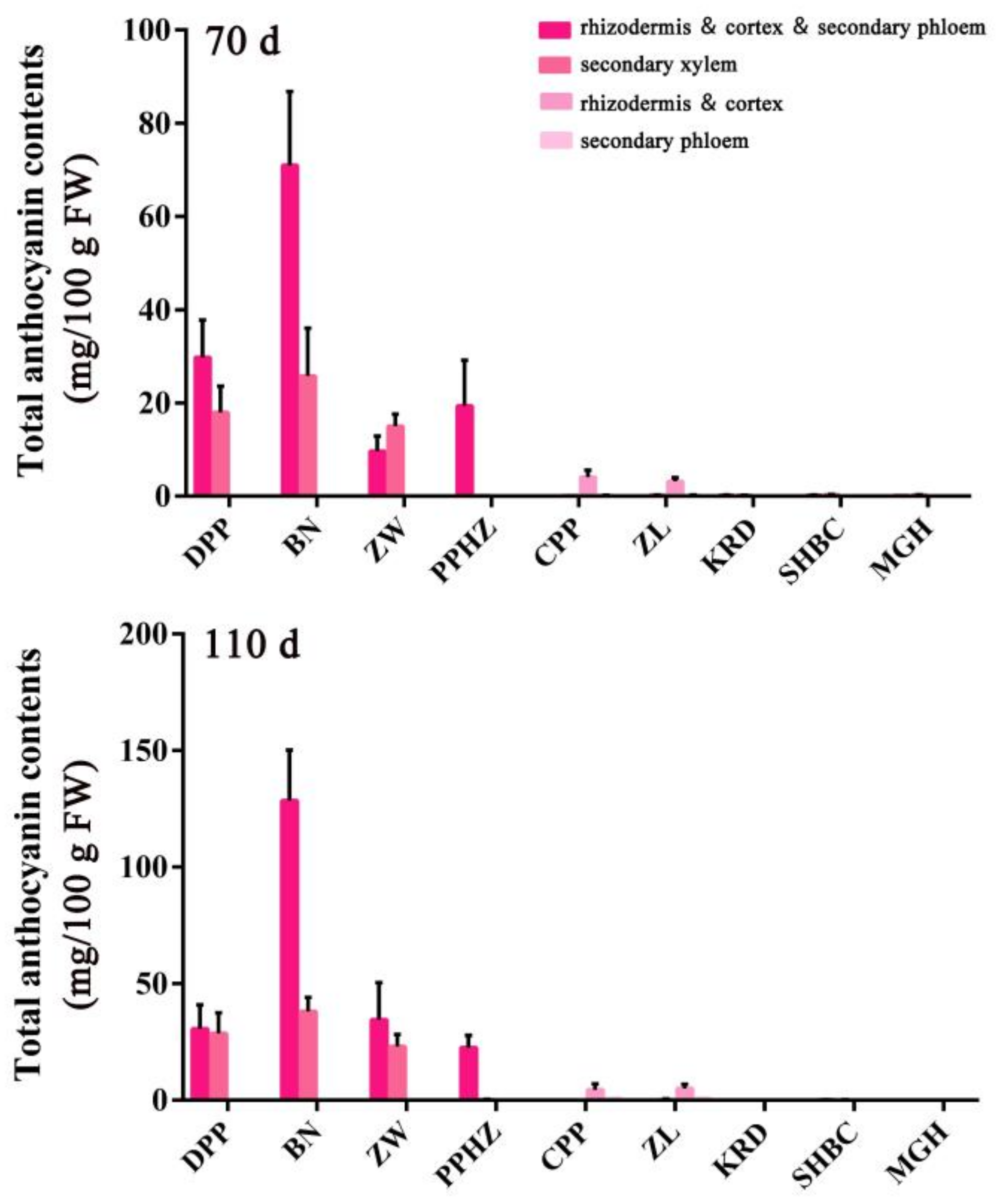
2.5. Anthocyanin Content in Different Root Tissues of Nine Carrot Cultivars at Different Development Stages
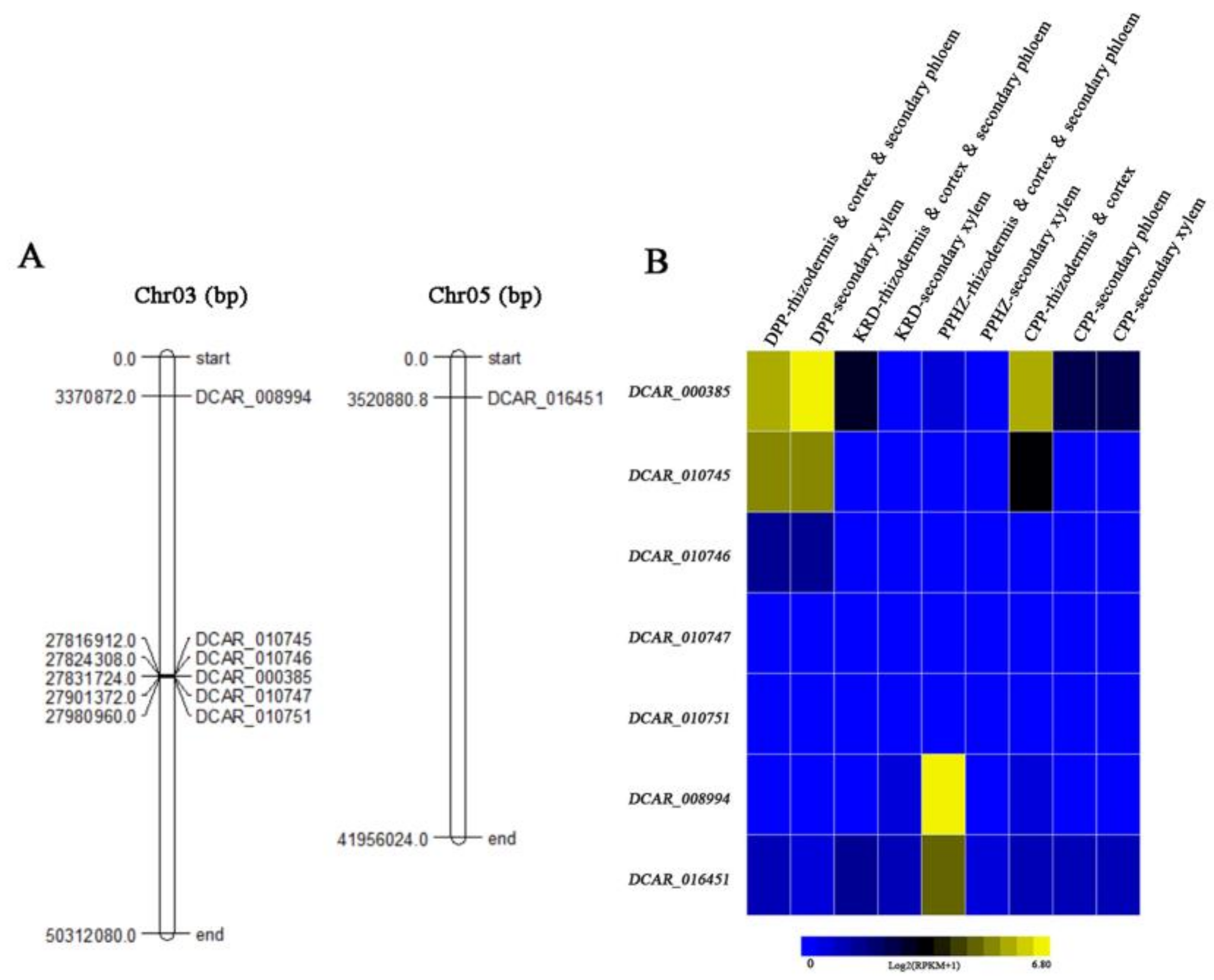
2.6. Expression Profiles of DcMYB TFs in S6 Subfamily of Different Carrot Cultivars and Position of DcMYB Genes in S6 Subfamily on Chromosome
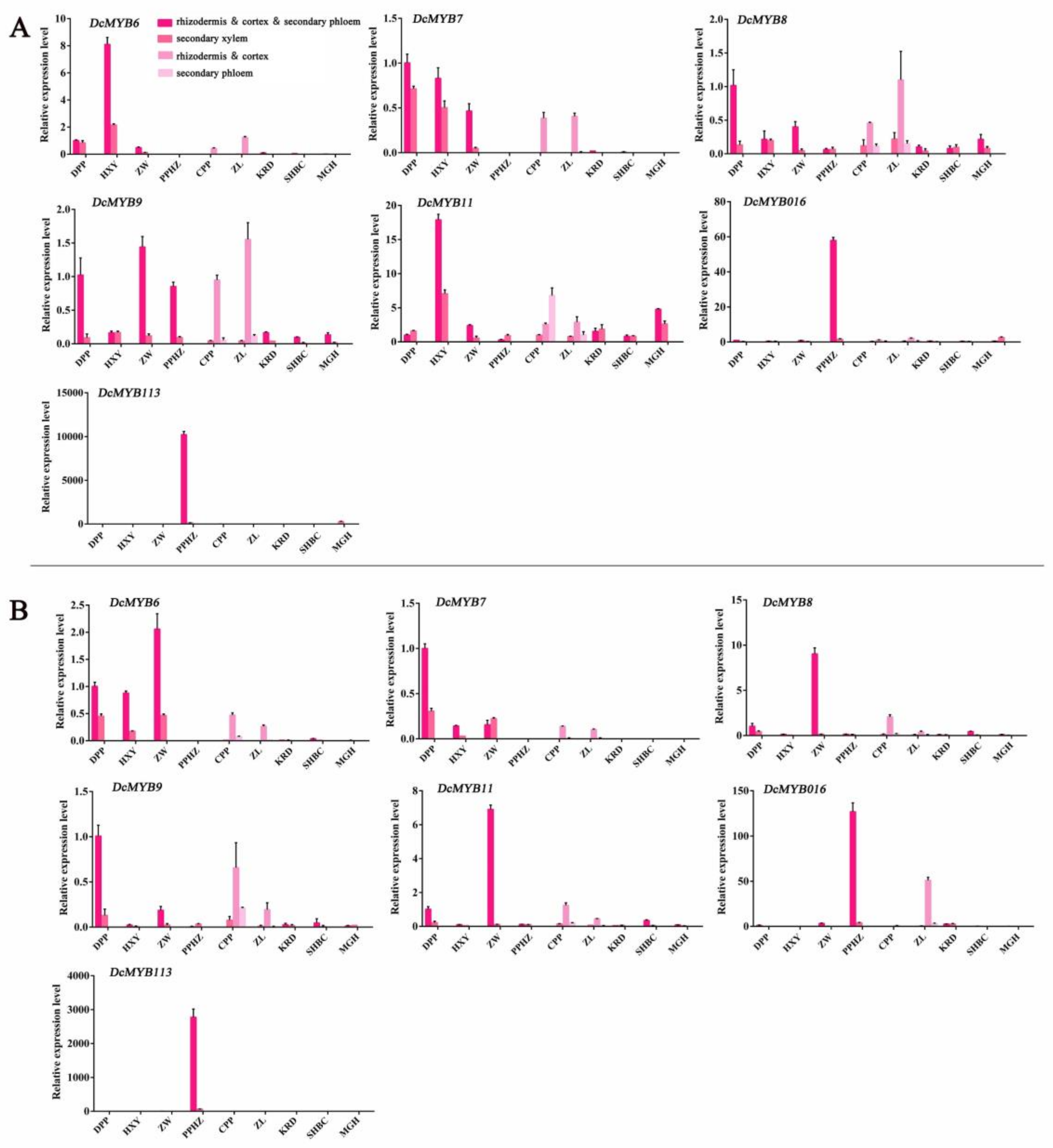
2.7. Relative Transcript Levels of S6 Subfamily DcMYBs in Different Root Tissues of Nine Carrot Cultivars
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Identification of R2R3-MYB TFs in Carrot
4.3. Constructions of Phylogenetic Tree, Evolutionary Analysis and Sequence Features Analysis
4.4. Collinearity and Non-Synonymous Substitution Rate (Ka)/Synonymous Substitution Rate (Ks) Analyses
4.5. Anthocyanin Measurement
4.6. RT-qPCR Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arscott, S.A.; Tanumihardjo, S.A. Carrots of many colors provide basic nutrition and bioavailable phytochemicals acting as a functional food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, D.; Carle, R.; Schieber, A. Detection of peonidin and pelargonidin glycosides in black carrots (Daucus carota ssp. sativus var. atrorubens Alef.) by high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 17, 2407–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.S.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Song, X.; Wang, G.L.; Xiong, A.S. Transcript profiling of structural genes involved in cyanidin-based anthocyanin biosynthesis between purple and non-purple carrot (Daucus carota L.) cultivars reveals distinct patterns. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, F.; Hou, X.L.; Wang, G.L.; Xu, Z.S.; Xiong, A.S. Advances in research on the carrot, an important root vegetable in the Apiaceae family. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Deng, Y.J.; Liu, J.X.; Duan, A.Q.; Liu, H.; Xiong, A.S. DcCCD4 catalyzes the degradation of α-carotene and β-carotene to affect carotenoid accumulation and taproot color in carrot. Plant J. 2021, 108, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannoud, F.; Ellison, S.; Paolinelli, M.; Horejsi, T.; Senalik, D.; Fanzone, M.; Iorizzo, M.; Simon, P.W.; Cavagnaro, P.F. Dissecting the genetic control of root and leaf tissue-specific anthocyanin pigmentation in carrot (Daucus carota L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2485–2507. [Google Scholar]
- Bannoud, F.; Carvajal, S.; Ellison, S.; Senalik, D.; Talquenca, S.G.; Iorizzo, M.; Simon, P.W.; Cavagnaro, P.F. Genetic and transcription profile analysis of tissue-specific anthocyanin pigmentation in carrot root ploem. Genes 2021, 12, 1464–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, N. Purple is the new orange: Anthocyanin regulation coming together in carrot. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.S.; Yang, Q.Q.; Feng, K.; Xiong, A.S. Changing carrot color: Insertions in DcMYB7 alter the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis and modification. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Dahuja, A.; Sachdev, A.; Kaur, C.; Varghese, E.; Saha, S.; Sairam, K.V.S.S. Valorisation of black carrot pomace: Microwave assisted extraction of bioactive phytoceuticals and antioxidant activity using Box-Behnken design. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 995–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Iorizzo, M.; Curaba, J.; Pottorff, M.; Simon, P.W.; Cavagnaro, P.F. Carrot anthocyanin genetics: Status and perspectives to optimize applications for the food colorant industry. Genes 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, K.; Hojo, H.; Aimoto, S.; Nakai, T.; Nakamura, H.; Sarai, A.; Ishii, S.; Nishimura, Y. Solution structure of a DNA-binding unit of Myb: A helix-turn-helix-related motif with conserved tryptophans forming a hydrophobic core. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 6428–6432. [Google Scholar]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Martin, C. Multifunctionality and diversity within the plant MYB-gene family. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 41, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.K.; Abeysinghe, J.K.; Kamali, M. Regulating the regulators: The control of transcription factors in plant defense signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 1999, 19, 3737. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, A.; Zhao, M.; Leavitt, J.M.; Lloyd, A.M. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J. 2010, 53, 814–827. [Google Scholar]
- Kodama, M.; Brinch-Pedersen, H.; Sharma, S.; Holme, I.B.; Joernsgaard, B.; Dzhanfezova, T.; Amby, D.B.; Vieira, F.G.; Liu, S.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Identification of transcription factor genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in carrot (Daucus carota L.) using RNA-Seq. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 811. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Cooney, J.M.; Wang, T.C.; Espley, R.V.; Allan, A.C. Differential regulation of the anthocyanin profile in purple kiwifruit (Actinidia species). Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.P.; Tian, F.; Yang, D.C.; Meng, Y.Q.; Kong, L.; Luo, J.C.; Cao, G. PlantTFDB 4.0: Toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracke, R.; Werber, M.; Weisshaar, B. The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001, 4, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Jones, D.C.; Li, W.; Xie, F.; Ma, J.; Sun, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, B. Genome-wide identification of R2R3-MYB Genes and expression analyses during abiotic stress in Gossypium raimondii. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yang, S.S.; Liang, Z.; Feng, B.R.; Lei, L.; Huang, Y.B.; Tang, Y.X. Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, A.; Smita, S.; Lenka, S.; Rajwanshi, R.; Chinnusamy, V.; Bansal, K. Genome-wide classification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.H.; Zhang, S.Z.; Wang, R.K.; Zhang, R.F.; Hao, Y.J. Genome wide analysis of the apple MYB transcription factor family allows the identification of MdoMYB121 gene confering abiotic stress tolerance in plants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.P.; Han, Y.H.; Li, D.H.; Lin, Y.; Cai, Y.P. MYB Transcription Factors in Chinese Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.): Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression profiling during fruit development. Front Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 577. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Wang, P.J.; Gu, M.Y.; Lin, X.Y.; Hou, B.H.; Zheng, Y.C.; Sun, Y.; Jin, S.; Ye, N.X. R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in tea plant (Camellia sinensis): Genome-wide characterization, phylogeny, chromosome location, structure and expression patterns. Genomics 2021, 113, 1565–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kähkönen, M.; Heinonen, M. Antioxidant activity of anthocyanins and their aglycons. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 628–633. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.Y.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.L.; Chen, Y.N.; Tan, T.T.; Jia, Y.H.; Xie, Q.L.; Chen, G.P. Anthocyanin accumulation and transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple pepper. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 845–880. [Google Scholar]
- Netzel, M.; Netzel, G.; Kammerer, D.R.; Schieber, A.; Carle, R.; Simons, L.; Bitsch, I.; Bitsch, R.; Konczak, I. Cancer cell antiproliferation activity and metabolism of black carrot anthocyanins. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2007, 8, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Giusti, M.M. Anthocyanins: Natural colorants with health-promoting properties. Nnu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Cawood, M.; Iqbal, Q.; Ario, A.; Akhtar, S. Phytochemicals in Daucus carota and their health benefits-review article. Foods 2019, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.U.; Park, J.I.; Jung, H.J.; Hur, Y.K.; Nou, I.S. Anthocyanin biosynthesis for cold and freezing stress tolerance and desirable color in Brassica rapa. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2015, 15, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, K.; Liu, J.X.; Duan, A.Q.; Li, T.; Yang, Q.Q.; Xu, Z.S.; Xiong, A.S. AgMYB2 transcription factor is involved in the regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple celery (Apium graveolens L.). Planta 2018, 248, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Feng, K.; Hou, X.L.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Z.S.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, J.X.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.S. The genome sequence of celery (Apium graveolens L.), an important leaf vegetable crop rich in apigenin in the Apiaceae family. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroni, K.; Tonelli, C. Recent advances on the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in reproductive organs. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.M.; Sun, P.C.; Yuan, J.Q.; Gong, K.; Li, N.; Meng, F.B.; Zhang, Z.K.; Li, X.Y.; Hu, J.J.; Wang, J.P.; et al. The celery genome sequence reveals sequential paleo-polyploidizations, karyotype evolution and resistance gene reduction in apiales. Plant Bio. Technol. J. 2021, 19, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorizzo, M.; Ellison, S.; Senalik, D.; Zeng, P.; Satapoomin, P.; Huang, J.; Bowman, M.; Iovene, M.; Sanseverino, W.; Cavagnaro, P. A high-quality carrot genome assembly provides new insights into carotenoid accumulation and asterid genome evolution. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, N.W.; Lewis, D.H.; Zhang, H.B.; Schwinn, K.E.; Jameson, P.E.; Davies, K.M. Members of an R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in Petunia are developmentally and environmentally regulated to control complex floral and vegetative pigmentation patterning. Plant J. 2011, 65, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subban, P.; Prakash, S.; Mann, A.B.; Kutsher, Y.; Evenor, D.; Levin, I.; Reuveni, M. Functional analysis of MYB alleles from Solanum chilense and Solanum lycopersicum in controlling anthocyanin levels in heterologous tobacco plants. Physiol. Plant 2021, 172, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, P.J.; Xiang, F.; Qiao, M.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, Y.N.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, W.J.; Park, C.M. The MYB96 transcription factor mediates abscisic acid signaling during drought stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Zhong, M.; Qu, L.; Yang, J.X.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, X.M.; Zhao, X.Y. AtMYB32 regulates the ABA response by targeting ABI3, ABI4 and ABI5 and the drought response by targeting CBF4 in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2021, 310, 110983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepiniec, L.; Debeaujon, I.; Routaboul, J.M.; Baudry, A.; Pourcel, L.; Nesi, N.; Caboche, M. Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, C.; Katayama, H.; Makino, I.; Inagaki, A.; Arakawa, O.; Martin, C. Peace, a MYB-like transcription factor, regulates petal pigmentation in flowering peach ‘Genpei’ bearing variegated and fully pigmented flowers. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshiba, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Tobimatsu, Y.; Yamamura, M.; Suzuki, S.; Hattori, T.; Mukai, M.; Noda, S.; Shibata, D.; Sakamoto, M.; et al. MYB-mediated upregulation of lignin biosynthesis in Oryza sativa towards biomass refinery. Plant Biotechnol. 2017, 34, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Misra, P.; Trivedi, P.K. Constitutive expression of Arabidopsis MYB transcription factor, AtMYB11, in tobacco modulates flavonoid biosynthesis in favor of flavonol accumulation. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lam, P.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Jeon, H.S.; Tobimatsu, Y.; Park, O.K. The Arabidopsis R2R3 MYB transcription factor MYB15 is a key regulator of lignin biosynthesis in effector-triggered immunity. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 583153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Cao, G.Y.; Qu, L.J.; Gu, H.Y. Involvement of an R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene AtMYB118 in embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Hou, X.L.; Wang, F.; Tan, G.F.; Xu, Z.S.; Xiong, A.S. Advances in the research of celery, an important Apiaceae vegetable crop. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Luo, Q.; Li, T.; Meng, P.H.; Pu, Y.T.; Liu, J.X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Tan, G.F.; Xiong, A.S. Origin, evolution, breeding and omics of Apiaceae: A family of vegetables and medicinal plants. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhac076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorizzo, M.; Cavagnaro, P.F.; Bostan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yildiz, M.; Simon, P.W. A cluster of MYB transcription factors regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in carrot (Daucus carota L.) root and leaf. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Tian, C.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Z.S.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.S. Comparison of nine reference genes for real-time quantitative PCR in roots and leaves during five developmental stages in carrot (Daucus carota L.). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, J.; Ghosal, D.; Wienand, U.; Peterson, P.A.; Saedler, H. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to myb proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3553–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matus, J.T.; Aquea, F.; Arce-Johnson, P. Analysis of the grape MYB R2R3 subfamily reveals expanded wine quality-related clades and conserved gene structure organization across Vitis and Arabidopsis genomes. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavagnaro, P.F.; Chung, S.M.; Manin, S.; Yildiz, M.; Simon, P.W. Microsatellite isolation and marker development in carrot-genomic distribution, linkage mapping, genetic diversity analysis and marker transferability across Apiaceae. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorizzo, M.; Senalik, D.A.; Ellison, S.L.; Grzebelus, D.; Cavagnaro, P.F.; Allender, C.; Brunet, J.; Spooner, D.M.; Deynze, V.A.; Simon, P.W. Genetic structure and domestication of carrot (Daucus carota subsp. sativus) (Apiaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2013, 100, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stracke, R.; Ishihara, H.; Huep, G.; Barsch, A.; Weisshaar, B. Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J. 2010, 50, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, A.; Machemer, K.; Braun, E.L.; Grotewold, E. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. 2011, 66, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borevitz, J.O.; Xia, Y.; Blount, J.; Dixon, R.A.; Lamb, C. Activation tagging identifies a conserved MYB regulator of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.S.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wang, X.L.; Han, X.; Wei, B.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, B.X.; Yu, H.; Huang, Q.P.; Gu, H.Y. The WRKY transcription factor WRKY71/EXB1 controls shoot branching by transcriptionally regulating RAX Genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, F. Genome-wide characterization and expression analyses of the MYB superfamily genes during developmental stages in Chinese jujube. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6353. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.S.; Feng, K.; Que, F.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.S. A MYB transcription factor, DcMYB6, is involved in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple carrot taproots. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavagnaro, P.F.; Iorizzo, M.; Yildiz, M.; Senalik, D.; Parsons, J.; Ellison, S.; Simon, P.W. A gene-derived SNP-based high resolution linkage map of carrot including the location of QTL conditioning root and leaf anthocyanin pigmentation. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curaba, J.; Bostan, H.; Cavagnaro, P.F.; Senalik, D.; Mengist, M.F.; Zhao, Y.; Simon, P.W.; Iorizzo, M. Identification of an SCPL gene controlling anthocyanin acylation in carrot (Daucus carota L.) root. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.S.; Tan, H.W.; Wang, F.; Hou, X.L.; Xiong, A.S. CarrotDB: A genomic and transcriptomic database for carrot. Database 2014, 2014, bau096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yon, R.S.; William, B.; Berardini, T.Z.; Chen, G.; David, D.; Aisling, D.; Margarita, G.H.; Eva, H.; Gabriel, L.; Mary, M. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): A model organism database providing a centralized, curated gateway to Arabidopsis biology, research materials and community. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 224–228. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhir, K.; Glen, S.; Koichiro, T. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.K.; Wang, Y.B.; Liu, Z.X.; Cheng, H.; Xue, Y. HemI: A toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, J.F.; Wu, J.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, G.M.; Wang, X.M.; Lin, D. ParaAT: A parallel tool for constructing multiple protein-coding DNA alignments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 419, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Gojobori, T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1986, 3, 418–426. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.P.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: A toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2010, 8, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene ID | Forward Primer (5’→3’) | Reverse Primer (5’→3’) |
|---|---|---|
| DCAR_000385 | AGTGGCATCCTCAAGTGGTTCA | CCCAAATGTCACTCCAGCAACT |
| DCAR_010745 | AGCGGCAACGACATTAACAACA | TTCATCTGGTAAGGCGGTGGTT |
| DCAR_010746 | GCAGCAGCAACATCAACAACGA | TTCATCTGGTAAGGCGGTGGTT |
| DCAR_010747 | TGCCACTACTTGTACCGCTACC | TCCTCCACCACTCGTTTCCATC |
| DCAR_010751 | AAGCCTGTTCCGCAGACCTTAA | GGACGCCACTTGAGGACACAT |
| DCAR_008994 | AGTGGCACCTTGTTCCTCAGAG | GCTGGCAATGATGGCTTCTTGT |
| DCAR_016451 | GTGGCACCTTGTTCCTCAGAGA | TCGTCATTCAGTGGCAGTGTTG |
| DcActin1 | CGGTATTGTGTTGGACTCTGGTGAT | CAGCAAGGTCAAGACGGAGTATGG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, A.-Q.; Tan, S.-S.; Deng, Y.-J.; Xu, Z.-S.; Xiong, A.-S. Genome-Wide Identification and Evolution Analysis of R2R3-MYB Gene Family Reveals S6 Subfamily R2R3-MYB Transcription Factors Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Carrot. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911859
Duan A-Q, Tan S-S, Deng Y-J, Xu Z-S, Xiong A-S. Genome-Wide Identification and Evolution Analysis of R2R3-MYB Gene Family Reveals S6 Subfamily R2R3-MYB Transcription Factors Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Carrot. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911859
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Ao-Qi, Shan-Shan Tan, Yuan-Jie Deng, Zhi-Sheng Xu, and Ai-Sheng Xiong. 2022. "Genome-Wide Identification and Evolution Analysis of R2R3-MYB Gene Family Reveals S6 Subfamily R2R3-MYB Transcription Factors Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Carrot" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 19: 11859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911859
APA StyleDuan, A.-Q., Tan, S.-S., Deng, Y.-J., Xu, Z.-S., & Xiong, A.-S. (2022). Genome-Wide Identification and Evolution Analysis of R2R3-MYB Gene Family Reveals S6 Subfamily R2R3-MYB Transcription Factors Involved in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Carrot. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(19), 11859. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911859







