Modified Polymer Surfaces: Thin Films of Silicate Composites via Polycaprolactone Melt Fusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
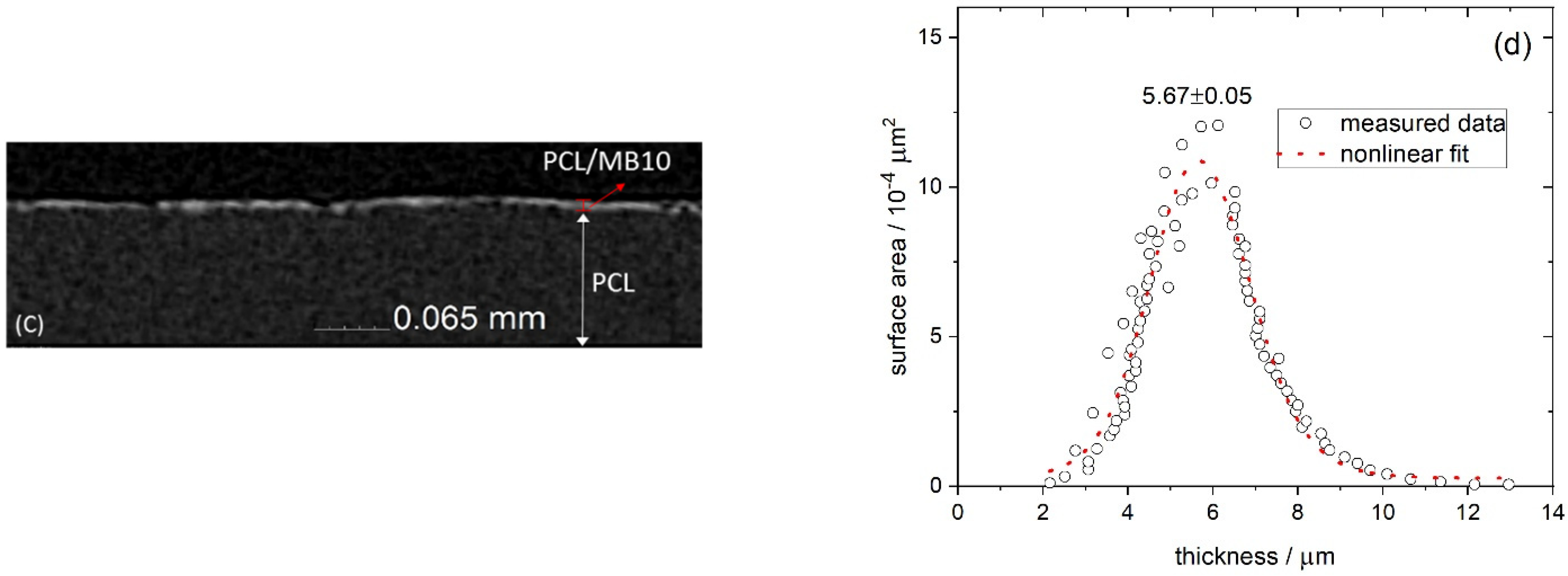
2.1. Thickness of the Films
2.2. Hydrophobicity of the Surface of Prepared Materials
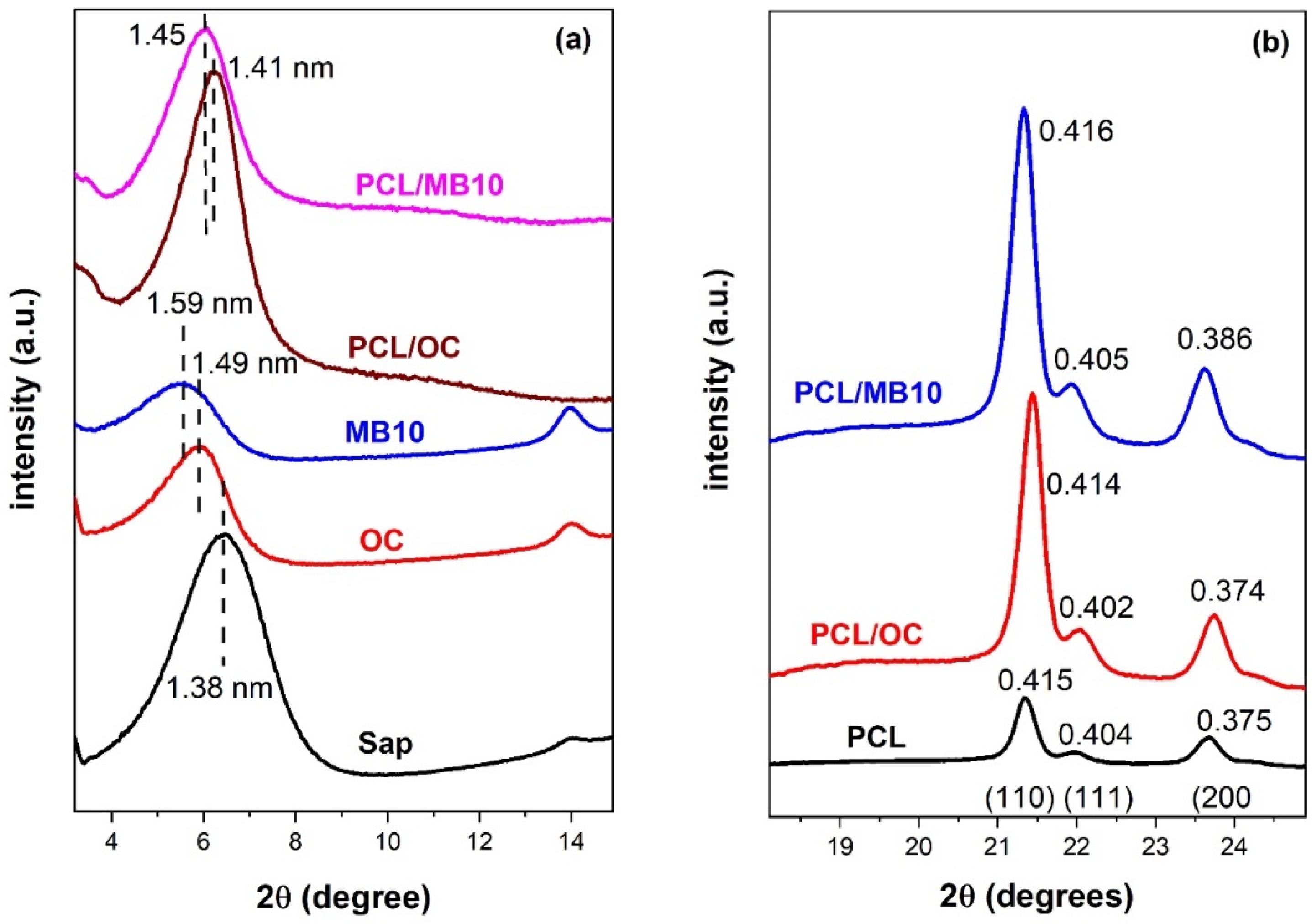
2.3. Crystallinity by X-ray Diffraction
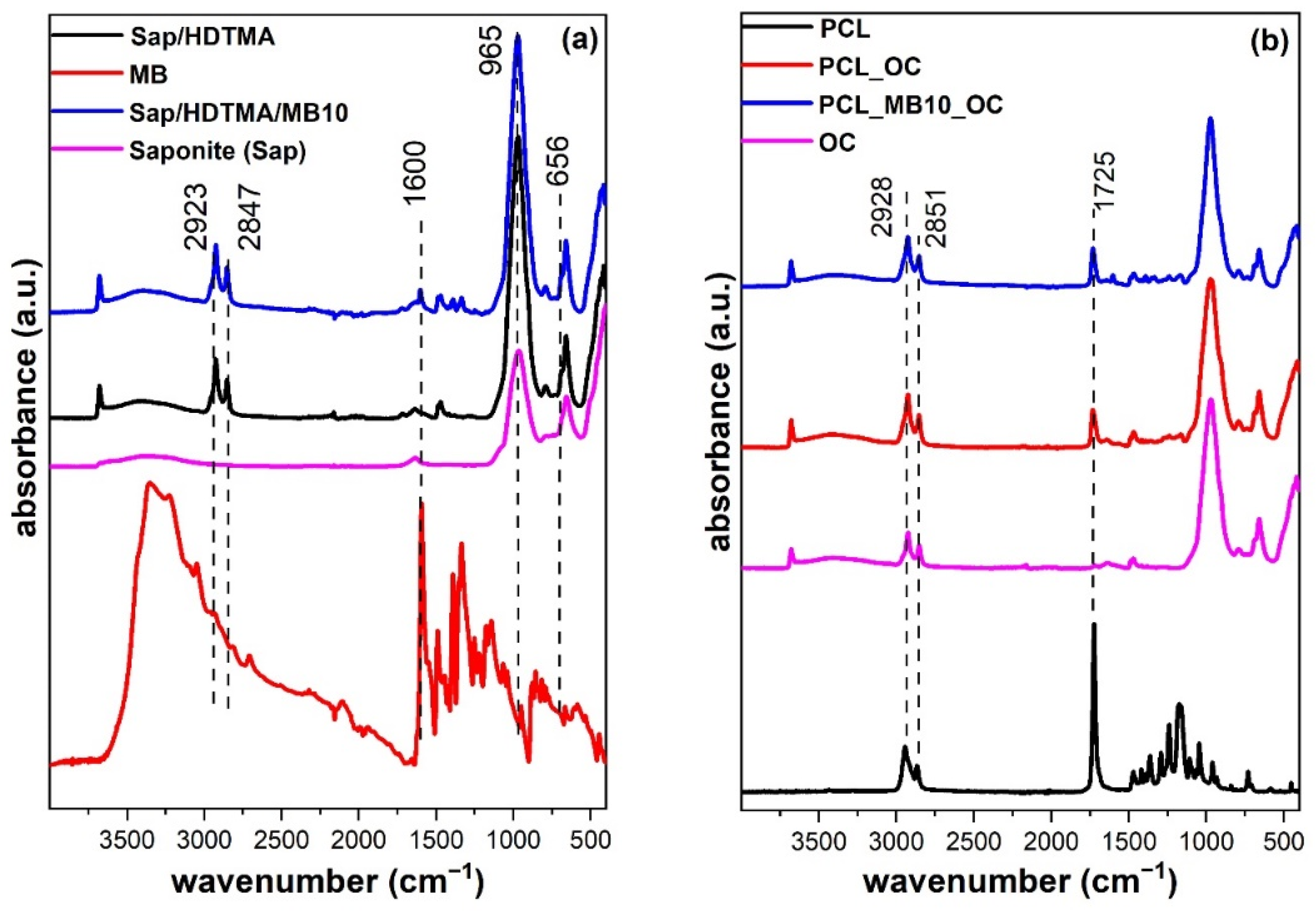
2.4. Chemical Functionality by Infrared Spectroscopy
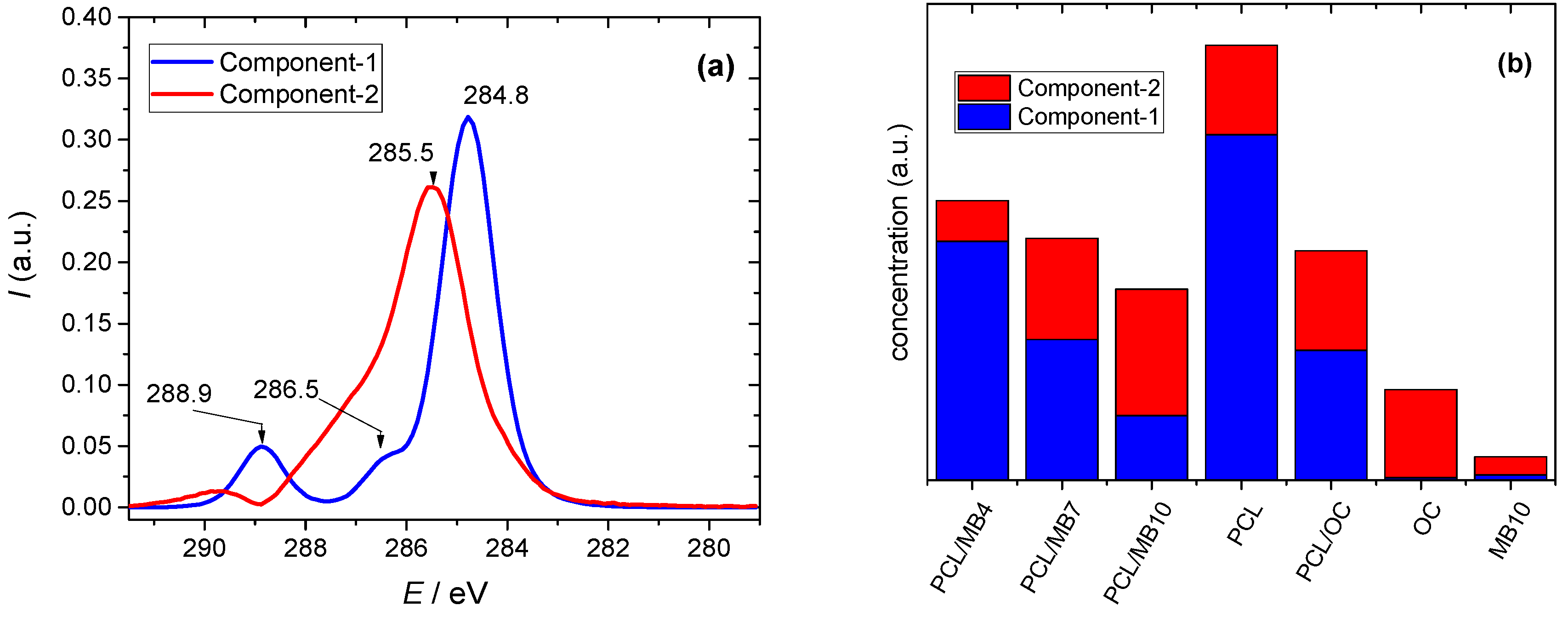
2.5. Surface Elemental Composition by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
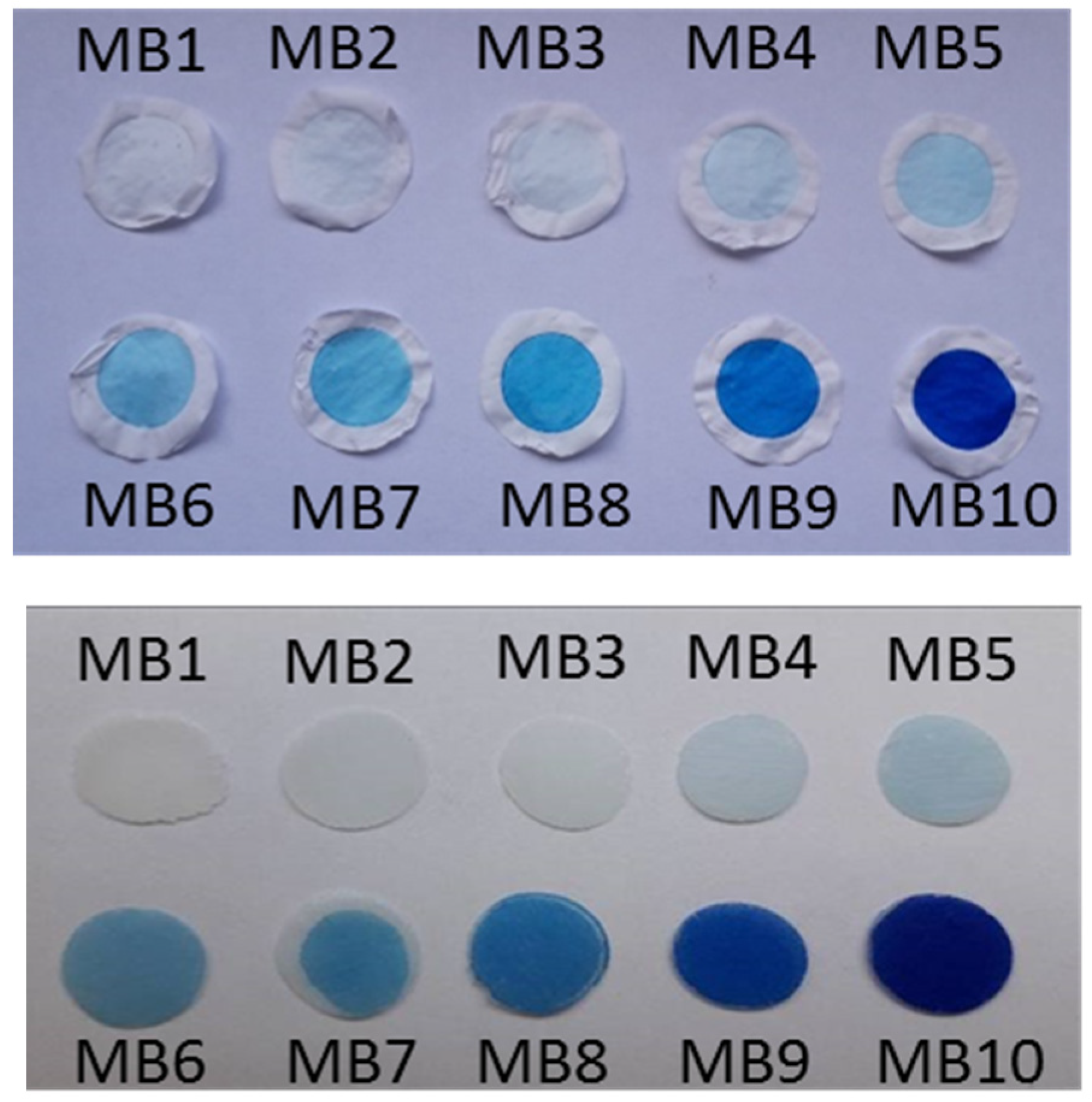
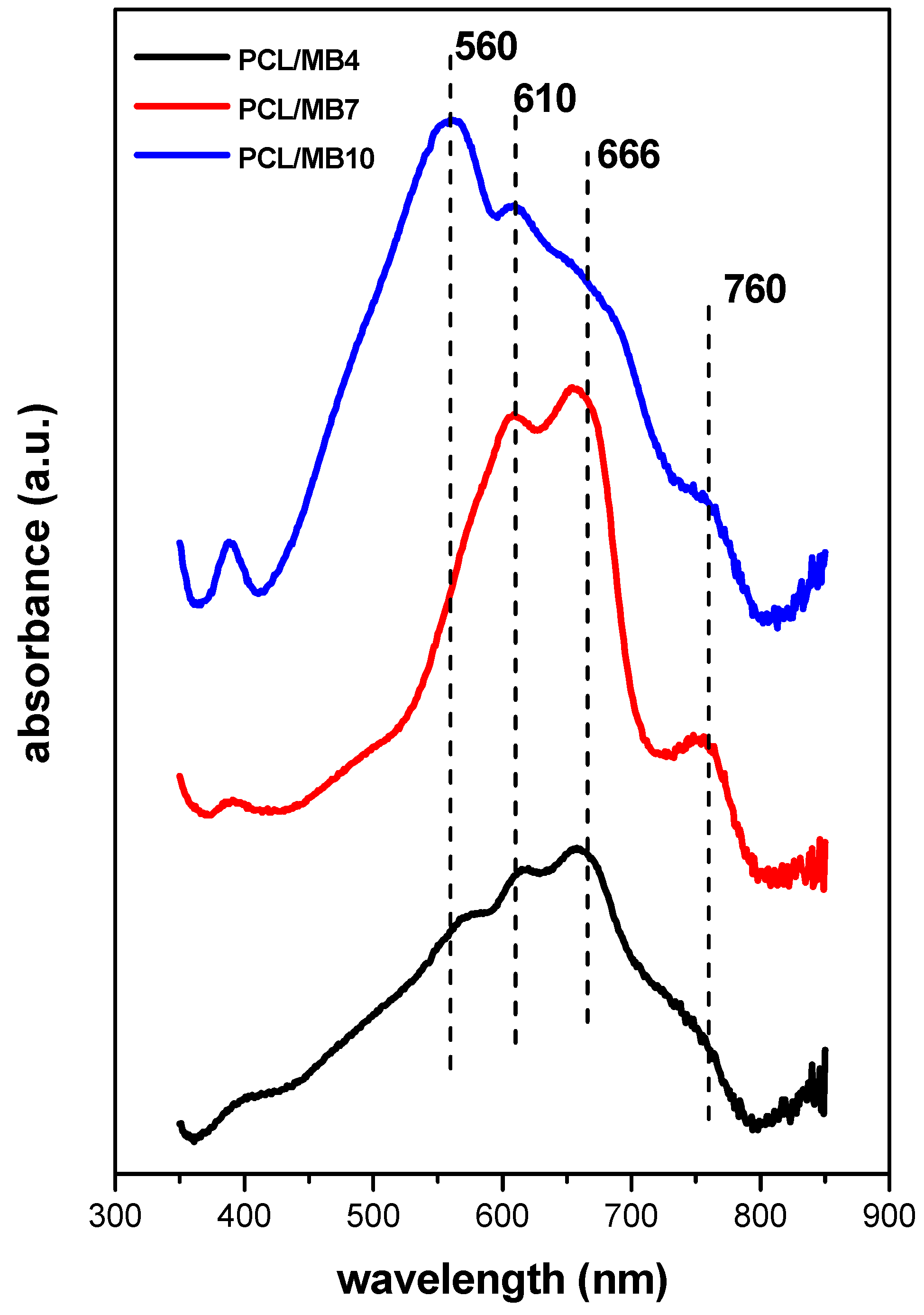
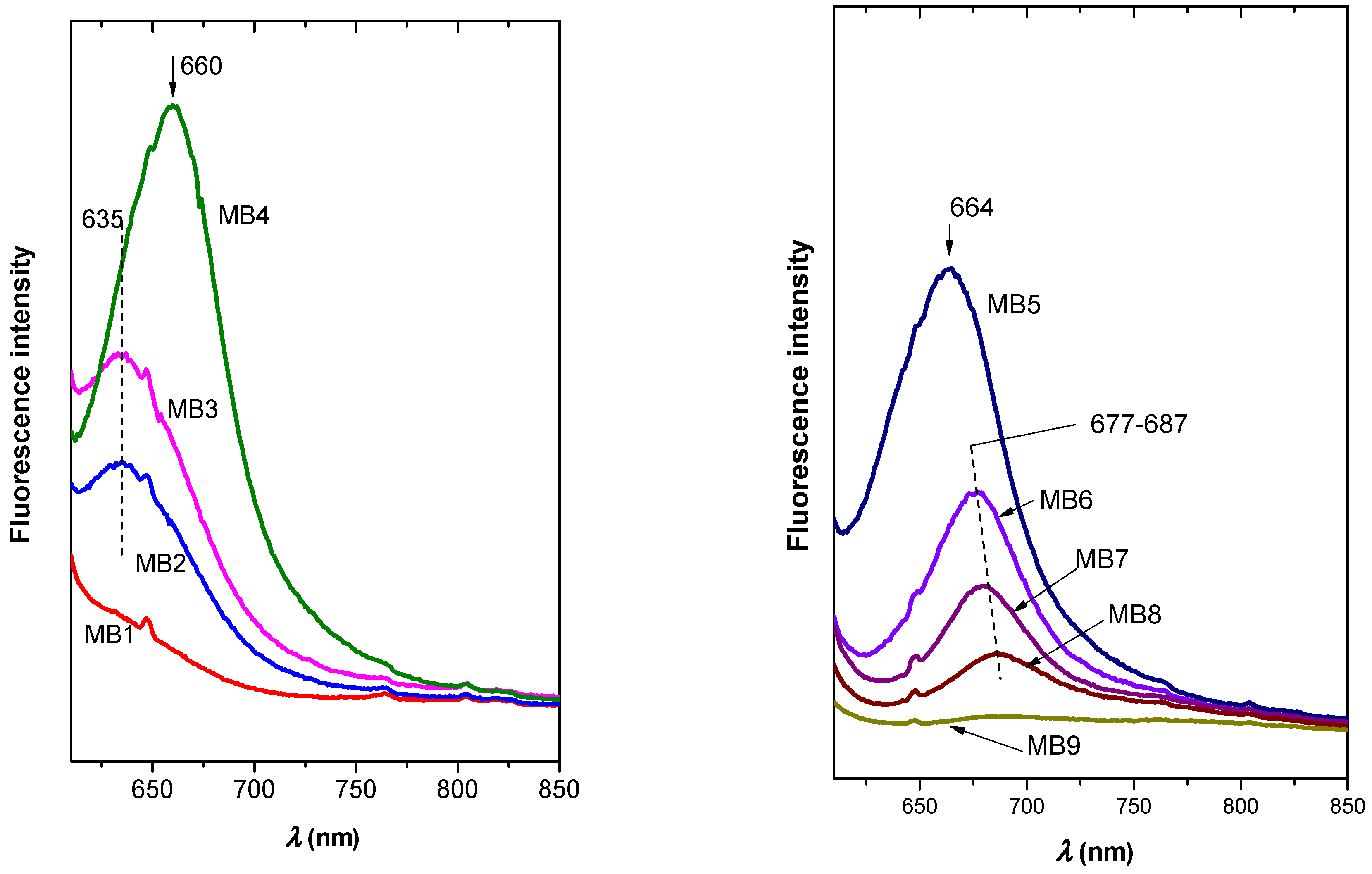
2.6. Optical Properties of Colloidal Precursors, Organoclay Films, and Polymer Composites
2.6.1. Colloidal Precursors
2.6.2. Films of Functionalized Organoclays and Nanocomposite Membranes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Organoclay Films on Teflon Filtration Membranes
3.3. Preparation of PCL Membranes
3.4. Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexandre, M.; Dubois, P. Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: Preparation, properties and uses of a new class of materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2000, 28, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Okamoto, M. Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: A review from preparation to processing. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1539–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alateyah, A.I.; Dhakal, H.; Zhang, Z. Processing, Properties, and Applications of Polymer Nanocomposites Based on Layer Silicates: A Review. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2013, 32, 21368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Hojjati, M.; Okamoto, M.; Gorga, R.E. Review article: Polymer-matrix nanocomposites, processing, manufacturing, and application: An overview. J. Compos. Mater. 2006, 40, 1511–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, N.C.T.; Bujdák, J.; Medvecká, V.; Pálková, H.; Barlog, M.; Bujdáková, H. Surface characterization and anti-biofilm effectiveness of hybrid films of polyurethane functionalized with saponite and Phloxine B. Materials 2021, 14, 7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludueña, L.N.; Vázquez, A.; Alvarez, V.A. Effect of the type of clay organo-modifier on the morphology, thermal/mechanical/impact/barrier properties and biodegradation in soil of polycaprolactone/clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 128, 2648–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, H.; Mosadegh, M.; Hayasi, M. New Developments in Polycaprolactone-Layered Silicate Nano-Biocomposites: Fabrication and Properties. In Handbook of Polymernanocomposites. Processing, Performance and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 21–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, Y.-T.; Lai, J.-G.; Tang, W.-L.; Yang, C.-H.; Wang, T.-L. Supercritical CO2 intercalation of polycaprolactone in layered silicates. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2009, 49, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeros-Guerrero, N.; de Cartagena, U.; Marsiglia-Fuentes, R.; Ortega-Toro, R. Improvement of the physicochemical properties of composite materials based on cassava starch and polycaprolactone reinforced with sodium montmorillonite. Rev. Mex. De Ing. Química 2021, 20, Alim2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyrek, M.E.; Okur, M.; Saraçoğlu, N. Improvement of mechanical, thermal and antimicrobial properties of organically modified montmorillonite loaded polycaprolactone for food packaging. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2021, 27, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.M.A.; Aquino, R.R.; Tolentino, M.S.; Eleazar, E.G.; Basilia, B.A. Synthesis and characterization of polycaprolactone(Pcl)/organo-montmorillonite(o-mmt) blendvia solvent casting. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2020, 998, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhacine, F.; Abdellaoui, N.; Arous, O.; Hadj-Hamou, A.S. Behaviours of poly(ε-caprolactone)/silver-montmorillonite nanocomposite in membrane ultrafiltration for wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouakaz, B.S.; Habi, A.; Grohens, Y.; Pillin, I. Effect of combinations of nanofillers on rheology-structure relations in biodegradable poly(ε-caprolactone) nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghianmaryan, A.; Yazdanpanah, Z.; Soltani, Y.A.; Sardroud, H.A.; Nasirtabrizi, M.H.; Chen, X. Curcumin-loaded electrospun polycaprolactone/montmorillonite nanocomposite: Wound dressing application with anti-bacterial and low cell toxicity properties. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, T.; Larraza, I.; Catalina, F.; Portolés, T.; Ramírez-Santillán, C.; Matesanz, M.; Abrusci, C. In vitro biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of poly(ε-caprolactone)/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 4247–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakre, L.G.; Sarvaiya, J.I.; Agrawal, Y.K. Synthesis, Characterization, and Study of Drug Release Properties of Curcumin from Polycaprolactone/Organomodified Montmorillonite Nanocomposite. J. Pharm. Innov. 2016, 11, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Snyder, C.R.; Al-Enizi, A.; Eltazahry, A.; Simmons, D.S.; Karim, A. Structure, nanomechanics, and dynamics of dispersed surfactant-free clay nanocomposite films. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaly, G.; Weiss, A. The layer charge of smectitic layer silicates. In Proceedings of the International Clay Conference, Mexico City, Mexico, 16–23 July 1975; Applied Publishing: Wilmette, IL, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Labet, M.; Thielemans, W. Synthesis of polycaprolactone: A review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3484–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilgör, E.; Isik, M.; Söz, C.K.; Yilgör, I. Synthesis and structure-property behavior of polycaprolactone-polydimethylsiloxane-polycaprolactone triblock copolymers. Polymer 2016, 83, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaia, R.A.; Jandt, K.D.; Kramer, E.J.; Giannelis, E.P. Kinetics of Polymer Melt Intercalation. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 8080–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoustier, N.; Lepoittevin, B.; Alexandre, M.; Dubois, P.; Kubies, D.; Calberg, C.; Jérôme, R. Biodegradable polyester layered silicate nanocomposites based on poly(ε-caprolactone). Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassa, A.; Benhamida, A.; Kaci, M.; Bruzaud, S. Effects of montmorillonite, sepiolite, and halloysite clays on the morphology and properties of polycaprolactone bionanocomposites. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2019, 28, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovič, L.; Végsö, K.; Siffalovic, P.; Šauša, O.; Čaplovič, L.; Čaplovičová, M.; Medlín, R.; Uhlík, P.; Nógellová, Z. XRD, SAXS, and PALS investigations of three different polymers reinforced with tetraoctylammonium exchanged montmorillonite. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2016, 21, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepoittevin, B.; Devalckenaere, M.; Pantoustier, N.; Alexandre, M.; Kubies, D.; Calberg, C.; Jérôme, R.; Dubois, P. Poly (ε-caprolactone)/clay nanocomposites prepared by melt intercalation: Mechanical, thermal and rheological properties. Polymer 2002, 43, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janigová, I.; Lednický, F.; Mošková, D.J.; Chodák, I. Nanocomposites with Biodegradable Polycaprolactone Matrix. Macromol. Symp. 2011, 301, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkin-Tas, E.; Goswami, S.K.; Nayak, B.R.; Mathias, L.J. Highly exfoliated poly(ε-caprolactone)/organomontmorillonite nanocomposites prepared by in situ polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, C.P.; Kloprogge, J.T. Urea-Assisted synthesis and characterization of saponite with different octahedral (Mg, Zn, Ni, Co) and tetrahedral metals (Al, Ga, B), a review. Life 2020, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chang, P.-H.; Jiang, W.-T.; Jean, J.-S.; Hong, H. Mechanism of methylene blue removal from water by swelling clays. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, O.V.; Evtukhova, A.V.; Kondratenko, T.S.; Smirnov, M.S.; Khokhlov, V.Y.; Erina, O.V. Manifestation of intermolecular interactions in FTIR spectra of methylene blue molecules. Vib. Spectrosc. 2016, 86, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.S.; Lee, J.-S.; Han, J. Development of a biodegradable polycaprolactone film incorporated with an antimicrobial agent via an extrusion process. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelichmann, J. Surface and depth-profile analysis using FTIR spectroscopy. Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 1989, 333, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Xu, H.; Kopelman, R.; Philbert, M.A. Photodynamic characterization and in vitro application of methylene blue-containing nanoparticle platforms. Photochem. Photobiol. 2005, 81, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šuteková, M.; Bujdák, J. The “blue bottle” experiment in the colloidal dispersions of smectites. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 186, 109010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujdák, J. Effect of the layer charge of clay minerals on optical properties of organic dyes. A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 34, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwalinski, T.; Polom, W.; Marano, L.; Roviello, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Cwalina, N.; Matuszewski, M.; Roviello, F.; Jaskiewicz, J.; Polom, K. Methylene Blue-Current Knowledge, Fluorescent Properties, and Its Future Use. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belušáková, S.; Sola-Llano, R.; Arbeloa, I.L.; Martínez-Martínez, V.; Bujdák, J. Resonance energy transfer between dye molecules in hybrid films of a layered silicate, including the effect of dye concentration thereon. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 155, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlog, M.; Pálková, H.; Bujdák, J. Luminescence of a laser dye in organically-modified layered silicate pigments. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 191, 109380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Mills, A. Luminescence of Leuco-Thiazine Dyes. J. Fluoresc. 2003, 13, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyaiová, T.; Bujdák, J. Reaction kinetics of molecular aggregation of rhodamine 123 in colloids with synthetic saponite nanoparticles. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 134, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A.; Sepehr, M.; Boccaleri, E. Synthetic, layered nanoparticles for polymeric nanocomposites (PNCs). Polym. Adv. Technol. 2007, 18, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pálková, H.; Barlog, M.; Madejová, J.; Hronský, V.; Petra, L.; Šimon, E.; Billik, P.; Zimowska, M. Structural changes in smectites subjected to mechanochemical activation: The effect of the occupancy of the octahedral sites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 213, 106214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitre, S.; McTiernan, C.D.; Scaiano, J.C. Library of Cationic Organic Dyes for Visible-Light-Driven Photoredox Transformations. ACS Omega 2016, 1, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinanian, M.M.; Cook, D.W.; Rutan, S.C.; Wijesinghe, D.S. Multivariate Curve Resolution-Alternating Least Squares Analysis of High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Data. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11092–11099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandas, P.J.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Morphology and Thermal Properties of Renewable Resource-Based Polymer Blend Nanocomposites Influenced by a Reactive Compatibilizer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danko, M.; Basko, M.; Ďurkáčová, S.; Duda, A.; Mosnáček, J. Functional polyesters with pendant double bonds prepared by coordination–insertion and cationic ring-opening copolymerizations of ε-caprolactone with renewable Tulipalin A. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3582–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Organoclay | Water Contact Angle/° | Composite | Water Contact Angle/° |
|---|---|---|---|
| OC | 66 ± 10 | PCL | 62 ± 5 |
| MB4 | 63 ± 9 | PCL/MB4 | 65 ± 6 |
| MB10 | 47 ± 5 | PCL/MB10 | 65 ± 9 |
| PCLMCR | OCMCR | MBMCR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OC | 0 | 98 | 0 |
| MB10 | 0 | 94 | 5.2 |
| MB | 2.7 | 1.1 | 100 |
| PCL | 100 | 0 | 0.8 |
| PCL/OC | 19 | 100 | 1.4 |
| PCL/MB10 | 18 | 83 | 2.2 |
| Sample | MB1 | MB2 | MB3 | MB4 | MB5 | MB6 | MB7 | MB8 | MB9 | MB10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cMB /10−5 mol L−1 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| nMB/mSap/ 10−6 mol g−1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.25 | 2.5 | 5 | 10 | 12.5 | 25 | 50 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skoura, E.; Boháč, P.; Barlog, M.; Palková, H.; Danko, M.; Šurka, J.; Mautner, A.; Bujdák, J. Modified Polymer Surfaces: Thin Films of Silicate Composites via Polycaprolactone Melt Fusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169166
Skoura E, Boháč P, Barlog M, Palková H, Danko M, Šurka J, Mautner A, Bujdák J. Modified Polymer Surfaces: Thin Films of Silicate Composites via Polycaprolactone Melt Fusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(16):9166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169166
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkoura, Eva, Peter Boháč, Martin Barlog, Helena Palková, Martin Danko, Juraj Šurka, Andreas Mautner, and Juraj Bujdák. 2022. "Modified Polymer Surfaces: Thin Films of Silicate Composites via Polycaprolactone Melt Fusion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 16: 9166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169166
APA StyleSkoura, E., Boháč, P., Barlog, M., Palková, H., Danko, M., Šurka, J., Mautner, A., & Bujdák, J. (2022). Modified Polymer Surfaces: Thin Films of Silicate Composites via Polycaprolactone Melt Fusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 9166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23169166






