Abstract
The exact neurobiological mechanisms of bipolar disorder (BD) remain unknown. However, some neurometabolites could be implicated, including Glutamate (Glu), Glutamine (Gln), Glx, and N-acetylaspartate (NAA). Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H-MRS) allows one to quantify these metabolites in the human brain. Thus, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature to compare their levels between BD patients and healthy controls (HC). The main inclusion criteria for inclusion were 1H-MRS studies comparing levels of Glu, Gln, Glx, and NAA in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), and hippocampi between patients with BD in clinical remission or a major depressive episode and HC. Thirty-three studies were included. NAA levels were significantly lower in the left white matter PFC (wmPFC) of depressive and remitted BD patients compared to controls and were also significantly higher in the left dorsolateral PFC (dlPFC) of depressive BD patients compared to HC. Gln levels were significantly higher in the ACC of remitted BD patients compared to in HC. The decreased levels of NAA of BD patients may be related to the alterations in neuroplasticity and synaptic plasticity found in BD patients and may explain the deep white matter hyperintensities frequently observed via magnetic resonance imagery.
1. Introduction
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a mental illness with a lifetime prevalence of approximately 2.4% in the general population [1]. BD is characterized by successive mood episodes (depressive, manic/hypomanic, or mixed episodes) with inter-episodic periods, during which the patients are in clinical remission. This classical view, however, has been challenged as a large number of euthymic BD patients suffer numerous, persistent symptoms and/or cognitive problems during these periods of apparent clinical stability.
It is relatively common for BD to begin with depressive episodes since, on average, a patient with BD will have 2.5 major depressive episodes compared to 1 manic or hypomanic episode [2]. Consequently, the early diagnosis of BD may be very difficult and, thus, delayed from the onset of illness, which may result in inappropriate therapeutic management. In order to improve the management of BD patients, a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying BD remains of interest.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data have been used to identify several areas with altered structure or function in BD patients. The prefrontal regions tend to be hypo-activated, which alters the regulation of the hyperactive limbic regions and, therefore, leads to an increased emotional response [3,4]. This cortico-limbic dysregulation could be related to connectivity problems between the prefrontal and limbic regions [5]. This hypothesis seems to be supported by several arguments, notably that a decrease in total white matter volume was observed in BD patients [6] and that T2 or FLAIR hyperintensities were found in the deep prefrontal and periventricular white matter in various studies [7,8]. The emergence of diffusion MRI has supported the dysconnectivity model in BD. In a recent mega-analysis, BD patients showed significant damage to the corpus callosum and the cingulate, as well as to many other regions, including those allowing the association between the prefrontal and limbic regions [9]. Hyperactivity of the limbic regions in these patients, however, does not seem to be explained solely by poor frontal regulation, as volumetric anomalies were identified in anatomical MRI. For instance, Ellison-Wright et al. found a decrease in the volume of the rostral part of the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) in BD patients when compared to healthy subjects [10]; a similar decrease was also observed in the meta-analysis of Bora et al., which similarly identified a decrease in the volume of the fronto-insular region in BD patients [11].
Several abnormalities have also been observed at the cellular level in BD. The hypothesis of dysfunction in the cerebral mitochondria has been the subject of numerous publications, with Morris et al. even proposing a model in which the various periods of mood episodes relate to mitochondrial energy production. Under this framework, manic episodes would be caused by an increase in energy production, whereas depressive episodes would be caused by a decrease in production [12]. Genetic studies have also highlighted involvement of the mitochondria in the pathophysiology of BD in such a way that mutations in mitochondrial DNA could be the origin of impairments in intracellular calcium signaling systems [13]. N-acetylaspartate (NAA) is the second most abundant molecule in the brain (after water), and its concentration is quantifiable by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS). NAA levels can be considered a marker of the integrity of mitochondrial energy metabolism, as they closely correlate with the concentration of ATP produced in the mitochondria [14,15,16]. The involvement of NAA in the pathophysiology of BD has been explored by many authors, including further evaluation in a meta-analysis of 1H-MRS studies, which found significantly lower levels of NAA in the basal ganglia and hippocampi of BD patients [17]. However, due to a lack of data, Kraguljac et al. could not analyze the levels of NAA according to the mood states of the patients. The euthymic and depressive phases seem to be the most interesting states because no alterations in NAA levels were identified in major depressive disorder (MDD) patients. Therefore, modifications during the depressive or euthymic phases of BD may help in the differential diagnostic process [18]. Furthermore, it is difficult to perform 1H-MRS studies during manic or hypomanic episodes without administering sedative treatments, and the impacts of these treatments on 1H-MRS data have not yet been fully studied.
The glutamatergic system plays important roles in various functions, including brain plasticity, neurotransmission, and energy metabolism [19]. The glutamatergic system is directly linked to NAA through the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), with the synthesis of NAA requiring transamination of glutamate (Glu) to aspartate [15]. Additionally, Clark et al. proposed that NAA could, under certain circumstances, serve as a reservoir for Glu [20]. A growing body of evidence continues to underline the involvement of NAA in BD pathophysiology [21,22,23,24].
Therefore, in this study, we conducted a meta-analysis to determine whether BD patients have alterations in NAA levels in various regions of the prefrontal cortex (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC), ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (vlPFC), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), white matter prefrontal cortex (wmPFC)), ACC, or hippocampi compared to healthy controls. In addition to NAA, we compared levels of Glu, glutamine (Gln), and Glx (essentially corresponding to the sum of Glu and Gln levels) between BD patients and healthy subjects within the various regions of the brain mentioned above.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol Registration
This study was carried out following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement.
The full protocol was uploaded to the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42020182638).
2.2. Study Search
The search was performed using Medline, Embase, and PsycInfo. All studies published before 18 November 2021 were included.
The following search equation was used in the All Fields mode: Bipolar AND (MRS OR « Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy » OR « Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopies »). The search was supplemented by bibliographic and textbook cross-referencing, as well as reviewing previous meta-analyses and systematic reviews, in order to avoid missing any potential studies for inclusion.
2.3. Study Selection
2.3.1. Publication Type
The selected studies were required to be written in English and provide complete articles in the form of cross-sectional studies or randomized controlled trials. Additionally, the selected studies were required to include both a group of BD patients and a group of healthy controls (HCs).
2.3.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Studies were included if
- (1)
- Patients met the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) 3rd, 4th, or 5th edition criteria for BD or the International Classification of Disease diagnostic (ICD) criteria for BD.
- (2)
- HCs did not have any mental illnesses according to these same references.
- (3)
- BD patients met the criteria for a major depressive episode or clinical remission.
- (4)
- BD patients and HCs were between the ages of 18 and 65 years.
- (5)
- The regions of interest (ROI) targeted were the mPFC, dlPFC, vlPFC or wmPFC, ACC, and/or hippocampi.
Studies were excluded if
- (1)
- BD patients and HCs had any other history of psychiatric or neurological conditions, head injuries, or addictive co-morbidities (except for smoking).
- (2)
- The 1H-MRS technique was not used.
- (3)
- The following metabolites were not quantified: NAA, Glu, Glx, and Gln.
- (4)
- None of the ROIs were targeted.
2.4. Data Extraction
Two authors (JC and EA) jointly determined the keywords and screened the abstracts and titles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The authors then evaluated the full texts independently in order to determine eligible studies. Any study exclusions were justified in accordance with the PRISMA criteria. Disagreements between authors on whether or not to include a study were resolved through discussion. Data were extracted by JC and EA independently, stored in an Excel spreadsheet, and compared. Again, disagreements were resolved through discussion. If different publications reported data from the same population, we included data from the publication with the larger sample size. If data or necessary information were missing from a published article, the authors of the studies were contacted for retrieval.
2.5. Quality Assessment
The quality of the original studies was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale after arrangement for a cross-sectional study design, similar to the meta-analysis conducted by Moriguchi et al. [25].
2.6. Statistical Analyses
Statistical analyses were performed with the Stata software (version 15, StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA). The meta-analysis considered between- and within-study variability. To address the non-independence of data due to study effects, random-effects models [26] were preferred over the usual statistical tests to assess standardized mean differences (SMDs) and their 95% confidence intervals. Means and standard deviations were compiled when available or estimated using Hozo et al. when median and interquartile ranges were reported [27]. SMDs were interpreted according to Cohen, where <0.2 was considered trivial, 0.2–0.3 was considered small, 0.5–0.8 was considered moderate, and >0.8 was considered large [28,29].
At the lateral ROIs (wmPFC, dlPFC, vlPFC, or hippocampi), the calculation of SMDs was performed for both the right and left hemispheres. At the level of medial ROIs (ACC or mPFC) many, although not all, studies used a single voxel spanning both hemispheres, thereby precluding separate results for each hemisphere. Thus, similar to Moriguchi et al., data for the left lobe were used at the level of medial ROIs when data from bilateral lobes were reported separately, as the left lobe was examined in most studies [25].
The same statistical approach was adapted for stratified analyses. Heterogeneity in the study results was assessed using forest plots and the I2 statistic, which is typically considered low at 25%, modest at 25% to 50%, and high when above 50% [30]. Publication bias was assessed by funnel plots and confidence intervals for each assessment method, one at a time, due to their great effects on heterogeneity.
Subgroup analyses were then performed. First, we divided the ACC studies into perigenual ACC (composed of pre- and subgenual regions) and dorsal ACC (sometimes also called the MCC). Second, we performed comparisons for each region according to the method used to quantify the metabolites (absolute vs. relative), since creatine relative quantification is a less accurate technique.
To check the robustness of the results, sensitivity analyses were performed, excluding studies that would not be evenly distributed around the base of the funnel. More precisely, for our significant results that contained more than two studies, we performed a leave-one-out meta-analysis. As studies commonly produce exaggerated effect sizes, which may distort the overall results, leave-one-out meta-analysis is a useful statistical approach to (i) investigate the influence of each study on the overall effect-size estimate and (ii) identify influential studies.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
The search identified 33 studies [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] (Figure 1), which included a total of 800 HCs and 873 BD patients. Among these 33 studies, 11 studies included patients in a major depressive episode (238 patients), 21 studies included BD patients in clinical remission (603 patients), and one study combined BD patients in a major depressive episode and in clinical remission (22 patients in each group). The characteristics of these studies are described in Table 1 and Table 2.
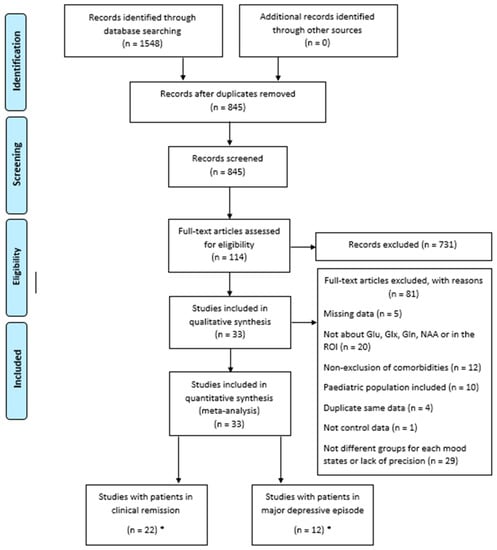
Figure 1.
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) diagram for study search. * One study featured two groups (clinical remission and depressive episode) and thus was counted twice, once in each category.

Table 1.
Characteristics of studies including BD patients in clinical remission.

Table 2.
Characteristics of studies including BD patients in a major depressive episode.
In depressed patients, ten studies examined NAA (83%), including four examining the wmPFC, two examining the dlPFC, one examining the mPFC, eight examining the ACC, and three examining the hippocampi. Four studies examined Glu (33%), including three examining Glu in the ACC and one examining Glu in the hippocampi. Five studies examined Glx levels (42%), with two examining the dlPFC, one examining the mPFC, and four examining the ACC.
In remitted patients, nineteen studies examined NAA (86%), including four examining the wmPFC, five examining the dlPFC, one examining the mPFC, one examining unspecified the PFC, seven examining the ACC, and eight examining the hippocampi. Seven studies examined Glu (32%), including four examining Glu in the wmPFC, two examining Glu in the dlPFC, one examining Glu in the mPFC, one examining Glu in unspecified PFC, seven examining Glu in ACC, and two examining Glu in the hippocampi. Two studies examined Glx (9%), with four examining Glx in the wmPFC, two examining Glx in the dlPFC, one examining Glx in the mPFC, one examining Glx in unspecified PFC, seven examining Glx in ACC, and three examining Glx in hippocampi. Additionally, three studies examined Gln (14%), all in the ACC.
Four studies used a magnetic field of 1.5 Tesla on depressed patients (33% of studies with depressed patients) and nine studies used a magnetic field of 1.5 Tesla on remitted patients (41% of studies with remitted patients). A magnetic field of 3 Tesla was used in seven studies on depressed patients (58%) and nine studies on remitted patients (41%). Only one study used a 4 Tesla magnetic field on depressed patients (8%), and two used a 4 Tesla magnetic field on remitted patients (9%). Two studies involving patients in remission did not give the intensity of the magnetic fields used (see Table 1).
Only cross-sectional studies were found, and there was no RCT.
The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale score ranged from 3 to 6, with the average being 4.48, suggesting that the quality of the included studies was good on average (see Supplementary Tables S1 and S2).
3.2. Meta-Analysis
3.2.1. BD Patients in Major Depressive Episode
NAA levels in the wmPFC were measured in four studies, including 124 BD patients and 118 HCs. In the left hemisphere, there were significantly lower levels of NAA in BD patients compared to the controls (SMD = −0.92; 95% CI: −1.30 to −0.53; I2 = 48.1%; p = 0.123) (Figure 2 and Figure 3). In the right hemisphere, there were no significant differences observed (SMD = −0.52; 95% CI: −1.16 to 0.11; I2 = 82.1%; p = 0.001) (Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S12).
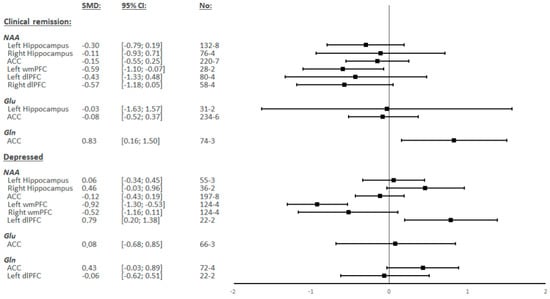
Figure 2.
Summary of Standardized Mean Differences (SMDs) and their confidence intervals (95% CI) for each metabolite in each of the different regions by the mood status of bipolar patients.
Figure 3.
Studies Standardized Mean Differences (SMDs) of N-acetylaspartate differences between bipolar patients and controls in the left white matter prefrontal cortex [44,46,47,61,62].
NAA levels in the dlPFC were measured in two studies, including 22 BD patients and 27 HCs in the left hemisphere, but no study measured these levels in the right hemisphere. In the left hemisphere, there were significantly higher levels of NAA observed in BD patients compared to the controls (SMD = 0.79; 95% CI: 0.20 to 1.38; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.336) (Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S13).
NAA levels in the other regions, as well as Glu, Glx, and Gln levels in all analyzed regions, showed no significant differences between BD patients and HCs (Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S3, Figure S4, Figure S7, Figure S9A, Figure S10A and Figure S16).
3.2.2. BD Patients in Clinical Remission
NAA levels in the wmPFC were measured in two studies including 31 BD patients and 33 HCs in the left hemisphere and in one study in the right hemisphere. In the left hemisphere, there were significantly lower levels of NAA observed in BD patients compared to the controls (SMD = −0.59; 95% CI: −1.10 to −0.07; I2 = 0.0%; p = 0.933) (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The study by Liu et al. [46] was the only research to measure NAA in the right wmPFC but did not find any significant difference.
Gln levels in ACC were measured in three studies including 85 BD patients and 103 HCs. There were significantly higher levels of Gln observed in BD patients compared to the controls (SMD = 0.83; 95% CI: 0.16 to 1.50; I2 = 66.6%; p = 0.050) (Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S6A).
NAA levels in the other regions, as well as Glu and Glx levels in all regions, showed no significant differences between BD patients and HCs (Figure 2 and Supplementary Figure S1, Figure S2A, Figure S5A, Figure S8A, Figure S11A, Figure S14 and Figure S15A).
3.3. Sensitivity-Analysis and Subgroup Analyses
We performed a leave-one-out sensitivity analysis on our significant results and found that our results were robust.
Our results obtained in the ACC were further analyzed by dividing our studies into two groups according to mood state: those whose ROI was the perigenual part of the ACC, and those whose ROI was the dorsal part of the ACC. Only the study by Croarkin et al. [36] could not be classified, as it did not provide the exact positioning of the ROI, and no clarification was obtained from the authors. No significant difference was found in either subgroup for any metabolite between BD patients (remitted or depressed) and HCs (Supplementary Figures S8C, S10C,D and S11C,D).
When possible, other subgroup analyses were also conducted for each metabolite in each region based on varying reference methods (absolute quantification vs. relative quantification). No significant differences were found in these analyses (Supplementary Figures S2B, S5B, S6B, S8B, S9B, S10B, S11B and S15B).
4. Discussion
Our meta-analysis aimed to determine whether the quantification of NAA, Glu, Gln, and/or Glx levels in the brains of BD patients without comorbidities could be used to better understand the neurobiological mechanisms of BD. Our results show that NAA levels in BD patients were significantly decreased in the left wmPFC during depressive and euthymic periods, as well as significantly increased in the left dlPFC during depressive periods. Meanwhile, Gln levels were significantly increased in the ACC in BD patients during euthymic periods when compared to HCs. The levels of NAA, Gln, Glu, and Glx were not statistically different between BD patients and HCs in any other regions analyzed.
The decrease in NAA levels in the wmPFC observed in BD patients was one of the most interesting findings of our study, even though the quantification was relative with creatine and not absolute. NAA is produced in the neural mitochondria from L-aspartate and acetyl coenzyme A. Studies have shown that NAA production is closely correlated with that of ATP and mitochondrial oxygen consumption [64,65,66], suggesting that NAA levels may reflect the integrity of mitochondrial energy metabolism [15,16]. Through energy production, as well as many other mechanisms, mitochondria are involved in neuroplasticity processes, development, and axonal regeneration [67,68]. The decrease in NAA localized within the white matter of the prefrontal cortex is, therefore, consistent with the alterations in neuroplasticity and synaptic plasticity found in BD patients [69]. NAA plays a unique role in the lipid synthesis of myelin sheaths since NAA allows the transfer of acetate groups from the neurons to the oligodendrocytes [15,16]. Thus, in addition to the abnormalities of energy production, neuroplasticity and synaptic plasticity may be indirectly impaired within the wmPFC via decreased NAA levels in BD patients. This decrease could also generate direct impairments of synaptic transmission and explain the T2 and FLAIR hypersignals found by MRI [8], especially since the voxels of the studies included in our meta-analysis appeared to be located in the same region as the hypersignals (deep white matter of the PFC). Unfortunately, due to the location of the voxels where numerous nerve fibers with different destinations pass, it is difficult to link our outcomes with functional abnormalities known in BD. A decrease in NAA was observed during both depressive periods and clinical remission, but our results in the left hemisphere for patients in clinical remission were clearly influenced by one of the two studies. Therefore, it will be interesting for future studies to confirm this tendency and evaluate whether NAA levels vary according to the duration of clinical remission. Furthermore, it remains necessary to test whether decreased NAA levels are also present during manic episodes.
NAA levels were also significantly increased in the left dlPFC of depressed BD patients compared to HCs. Although this increase was also found by Kraguljac et al. in their previous meta-analysis [17], the functional and anatomical MRI data did not specifically find abnormalities in this region during depressive episodes [70,71]. One explanatory hypothesis could be related to the effects of lithium or valproate medication on the included BD patients [49]. Indeed, these treatments lead to an increase in Bcl-2 protein in the frontal cortex, which is a protein located in the mitochondrial membrane and involved in mitochondrial oxidation–reduction processes, as well as in neuroprotection [72,73]. However, 1H-MRS could also reveal anomalies not found using other MRI techniques. If these results are not explained by the effects of medications, it will be relevant to more precisely investigate this region based on the hypothesis that it may over-function in bipolar depression.
Regarding Glu and Gln metabolites, very few studies met our inclusion criteria in the PFC, resulting in a meta-analysis that could include only Glx in the dlPFC and did not find any significant differences between depressed BD patients and HCs. It would be interesting to be able to include more studies feature additional regions of the PFC.
In the two hippocampi, there were no significant differences found between BD patients and HCs for any of the investigated metabolites. The hippocampal formation is a very plastic and vulnerable brain region in which anomalies in the sizes of neurons and a reduction in the number of glial cells was identified in BD patients [74,75]. Therefore, we expected to discover decreased NAA levels in BD patients, as post-mortem studies have found mitochondrial dysfunction in the hippocampi of these patients, including decreased expression of nuclear mRNA encoding mitochondrial proteins [76]. Alterations of proteins involved in glycogenogenesis, glycogenolysis, and mitochondrial energy functions have also been identified [77]. Our findings differ from those of Kraguljac et al., who found a significant decrease in NAA/Cr in the hippocampi [17], even though, as explained previously, this meta-analysis mixed patients of various mood states. Conversely, an increase in Glu levels was also expected, since stress and glucocorticoids, which are very present in BD patients, can increase the concentrations of extracellular Glu in the hippocampi [78] alongside high levels of expression of the GCP II enzyme in the hippocampi of BD patients, which hydrolyzes NAAG into Glu in the glial cells [24]. However, 1H-MRS techniques do not measure glutamatergic transmission, which is a small part of cerebral Glu stocks, but instead measure total brain Glu, which is used in many brain functions other than neurotransmission [19]. This factor could explain the absence of significant increases in glutamatergic metabolites in the hippocampi of BD patients. Another explanation could be the difficulty of obtaining quality spectra in this region due to its proximity to air–tissue interfaces.
In the ACC, no significant differences were found between BD patients and HCs, regardless of the metabolites studied. Scotti-Muzzi et al. conducted a meta-analysis comparing several neurometabolites between BD patients and HCs, specifically targeting the ACC region. Although our meta-analysis included several studies that were not included in the analyses of Scotti-Muzzi et al. due to their more recent publication dates, our results for NAA, Glu, and Gln levels remain consistent with the results of this previous study [79]. Regarding Glx levels, the results from our study were only available for BD patients in depressive episodes, and these results differ from those of Scotti-Muzzi et al. [79]. However, it is important to specify that the outcomes of Scotti-Muzzi et al. could not be evaluated according to the mood state, as the number of studies available was lower than three. This increase in Glx levels could, therefore, be due to the non-depressive periods of the disease and may be caused, in particular, by the significant increase in Gln levels found in BD patients in the euthymic period. In another meta-analysis, Taylor et al. compared Glx levels in the ACC of BD patients in major depressive episodes to HCs [80]. Although the authors included studies that did not fully meet our inclusion criteria (including a study with adolescent BD patients, another with some patients in a mixed episode, and one study in which the ROI encompassed part of the mPFC), they also did not find any significant differences. The ACC is a complex region encompassing various sub-regions with specific connectivity and functions, the limits of which are mainly derived from the Brodmann classification [81,82]. Brain imaging studies usually divide the ACC into two main parts: the peri-genual ACC and the dorsal ACC (also commonly called the midcingulate cortex (MCC)). In our study, we performed a subgroup analysis to see if there were variations in the results according to the parts of the ACC being examined. However, we did not find any significant differences.
This meta-analysis has some limitations. First, although the meta-analysis analyzed data region by region, as well as by sub-region in the ACC, voxel sizes and ROIs were not similar between the included studies. These differences may have skewed the results of the ROI analyses. Second, the magnetic field strength, 1H-MRS editing techniques, and echo-time also differed between included studies. Third the Cramer–Rao lower bound (CRLB), which is a marker of spectrum quality, was rarely precise in the different studies. Fourth, because many studies did not detail the patients’ treatments, we could not perform meta-regression by treatment to assess the influences of different approaches. Some studies showed that treatments can partially modify the concentrations of certain metabolites in certain regions [24]. However, notably, for our primary outcome of decreased NAA in the left wmPFC in depressed patients, BD patients were not medicated in three of the four included studies, yet the heterogeneity was described as modest. Fifth, because of the lack of data and inconsistency in the scales used, we could not verify whether metabolite concentrations were dependent on the intensity of depression. Likewise, we could not verify whether metabolite concentrations were dependent on the age of onset or number of mood episodes. These factors potentially influenced our results.
In summary, in the present study, we observed decreased NAA levels in the wmPFC of both euthymic and depressed BD patients. These results emphasize the role of mitochondrial energy metabolism in neuroplasticity and synaptic plasticity in BD.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms23168974/s1. References [35,42,73,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162] are cited in the supplementary materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C., E.A., C.C., I.D.C., P.F., J.-Y.R., P.-M.L. and L.S.; methodology, J.C., E.A. and B.P.; software, B.P.; validation, J.C., E.A. and B.P.; formal analysis, J.C., E.A. and B.P.; investigation, J.C. and E.A.; resources, B.P.; data curation, B.P.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.; writing—review and editing, J.C., E.A., B.P., C.C., I.D.C., P.F., J.-Y.R., P.-M.L. and L.S.; visualization, J.C. and L.S.; supervision, L.S.; project administration, J.C. and L.S.; funding acquisition, E.A., P.-M.L. and L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from CHU of Clermont-Ferrand.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Merikangas, K.R.; Jin, R.; He, J.P.; Kessler, R.C.; Lee, S.; Sampson, N.A.; Viana, M.C.; Andrade, L.H.; Hu, C.; Karam, E.G.; et al. Prevalence and correlates of bipolar spectrum disorder in the world mental health survey initiative. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlis, R.H.; Ostacher, M.; Patel, J.K.; Marangell, L.B.; Zhang, H.; Wisniewski, S.; Ketter, T.A.; Miklowitz, D.J.; Otto, M.; Gyulai, L.; et al. Predictors of recurrence in bipolar disorder: Primary outcomes from the Systematic Treatment Enhancement Program for Bipolar Disorder (STEP-BD). Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.L.; Swartz, H.A. A Critical Appraisal of Neuroimaging Studies of Bipolar Disorder: Toward a New Conceptualization of Underlying Neural Circuitry and a Road Map for Future Research. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.; Phillips, M.; Leibenluft, E.; M’Bailara, K.; Houenou, J.; Leboyer, M. Emotional dysfunction as a marker of bipolar disorders. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 2622–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strakowski, S.M.; Adler, C.M.; Almeida, J.; Altshuler, L.L.; Blumberg, H.; Chang, K.D.; DelBello, M.P.; Frangou, S.; McIntosh, A.; Phillips, M.L.; et al. The functional neuroanatomy of bipolar disorder: A consensus model. Bipolar Disord. 2012, 14, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, A.; De Peri, L.; Sacchetti, E. Gray matter, white matter, brain, and intracranial volumes in first-episode bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging studies. Bipolar Disord. 2009, 11, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompili, M.; Innamorati, M.; Mann, J.J.; Oquendo, M.A.; Lester, D.; Del Casale, A.; Serafini, G.; Rigucci, S.; Romano, A.; Tamburello, A.; et al. Periventricular white matter hyperintensities as predictors of suicide attempts in bipolar disorders and unipolar depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, K.; Burdick, K.E.; Szeszko, P.R. A role for white matter abnormalities in the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 533–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favre, P.; Pauling, M.; Stout, J.; Hozer, F.; Sarrazin, S.; Abé, C.; Alda, M.; Alloza, C.; Alonso-Lana, S.; Andreassen, O.A.; et al. Widespread white matter microstructural abnormalities in bipolar disorder: Evidence from mega- and meta-analyses across 3033 individuals. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison-Wright, I.; Bullmore, E. Anatomy of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Schizophr. Res. 2010, 117, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, E.; Fornito, A.; Yücel, M.; Pantelis, C. Voxelwise meta-analysis of gray matter abnormalities in bipolar disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.; Walder, K.; McGee, S.L.; Dean, O.M.; Tye, S.J.; Maes, M.; Berk, M. A model of the mitochondrial basis of bipolar disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T. Neurobiological basis of bipolar disorder: Mitochondrial dysfunction hypothesis and beyond. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 187, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffett, J.R.; Arun, P.; Ariyannur, P.S.; Namboodiri, A.M.A. N-Acetylaspartate reductions in brain injury: Impact on post-injury neuroenergetics, lipid synthesis, and protein acetylation. Front. Neuroenergetics 2013, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffett, J.R.; Ross, B.; Arun, P.; Madhavarao, C.N.; Namboodiri, A.M.A. N-Acetylaspartate in the CNS: From neurodiagnostics to neurobiology. Prog. Neurobiol. 2007, 81, 89–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E. N-acetylaspartate and N-acetylaspartylglutamate: Neurobiology and clinical significance. Neurology 2008, 70, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraguljac, N.V.; Reid, M.; White, D.; Jones, R.; Hollander, J.D.; Lowman, D.; Lahti, A.C. Neurometabolites in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 203, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz-Yesiloglu, A.; Ankerst, D.P. Review of 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy findings in major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2006, 147, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, J.T.; Brosnan, M.E. Glutamate: A truly functional amino acid. Amino Acids. 2013, 45, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.F.; Doepke, A.; Filosa, J.A.; Wardle, R.L.; Lu, A.; Meeker, T.; Pyne-Geithman, G.J. N-acetylaspartate as a reservoir for glutamate. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 67, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Gray, N.A.; Falke, C.A.; Chen, W.; Yuan, P.; Szabo, S.T.; Einat, H.; Manji, H.K. Modulation of synaptic plasticity by antimanic agents: The role of AMPA glutamate receptor subunit 1 synaptic expression. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6578–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Frye, M.A.; Tsai, G.E.; Huggins, T.; Coyle, J.T.; Post, R.M. Low cerebrospinal fluid glutamate and glycine in refractory affective disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacker, C.J.; Lewis, C.P.; Frye, M.A.; Veldic, M. Metabotropic glutamate receptors as emerging research targets in bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 257, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.X.D.; Lau, I.Y.; Graham, S.; Sim, K. Neurobiological evidence for thalamic, hippocampal and related glutamatergic abnormalities in bipolar disorder: A review and synthesis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2009, 33, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, S.; Takamiya, A.; Noda, Y.; Horita, N.; Wada, M.; Tsugawa, S.; Plitman, E.; Sano, Y.; Tarumi, R.; ElSalhy, M.; et al. Glutamatergic neurometabolite levels in major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-Analysis in Clinical Trials Revisited. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, C. Mean Difference, Standardized Mean Difference (SMD), and Their Use in Meta-Analysis: As Simple as It Gets. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2020, 81, 20f13681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, J.A.D.M.S.; Tamada, R.S.; Issler, C.K.; Caetano, S.C.; Cerri, G.G.; de Castro, C.C.; Lafer, B. A 1HMRS study of the anterior cingulate gyrus in euthymic bipolar patients. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 21, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, M.; Yildirim, H. Altered neurochemical ingredient of hippocampus in patients with bipolar depression. Depress Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 485249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brady, R.O.; Cooper, A.; Jensen, J.E.; Tandon, N.; Cohen, B.; Renshaw, P.; Keshavan, M.; Öngür, D. A longitudinal pilot proton MRS investigation of the manic and euthymic states of bipolar disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, M.; Schubert, F.; Bubner, M.; Heidenreich, J.O.; Bajbouj, M.; Seifert, F.; Luborzewski, A.; Heuser, I.; Kronenberg, G. Glutamate as a spectroscopic marker of hippocampal structural plasticity is elevated in long-term euthymic bipolar patients on chronic lithium therapy and correlates inversely with diurnal cortisol. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 647, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, M.; Hawkins, E.L.; O’Hora, D.; Whalley, H.C.; Hall, J.; Lawrie, S.M.; Dauvermann, M.R. Are working memory and glutamate concentrations involved in early-life stress and severity of psychosis? Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croarkin, P.E.; Thomas, M.A.; Port, J.D.; Baruth, J.M.; Choi, D.-S.; Abulseoud, O.A.; Frye, M.A. N-acetylaspartate normalization in bipolar depression after lamotrigine treatment. Bipolar Disord. 2015, 17, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumurcu, B.E.; Karlidag, R.; Sarac, K.; Unal, S.; Ozcan, C.; Erkorkmaz UCerebral, M.R. spectroscopy evaluation of the neuroprotective effects of lithium and olanzapine in bipolar affective disorder patients. Neurol. Psychiatry Brain Res. 2008, 15, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Deicken, R.F.; Pegues, M.P.; Anzalone, S.; Feiwell, R.; Soher, B. Lower concentration of hippocampal N-acetylaspartate in familial bipolar I disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, A.; Schubert, F.; Pehrs, C.; Gallinat, J. Alterations of cerebral glutamate in the euthymic state of patients with bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 233, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarman, B.C.M.B.; Burger, H.; Doorduin, J.; Renken, R.J.; Sibeijn-Kuiper, A.J.; Marsman, J.-B.C.; de Vries, E.F.; de Groot, J.C.; Drexhage, H.A.; Mendes, R.; et al. Volume, metabolites and neuroinflammation of the hippocampus in bipolar disorder—A combined magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 56, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosifescu, D.V.; Moore, C.M.; Deckersbach, T.; Tilley, C.A.; Ostacher, M.; Sachs, G.S.; Nierenberg, A.A. Galantamine-ER for cognitive dysfunction in bipolar disorder and correlation with hippocampal neuronal viability: A proof-of-concept study. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2009, 15, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaycı, D.; Ozdel, O.; Sözeri-Varma, G.; Kıroğlu, Y.; Tümkaya, S. A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study in schizoaffective disorder: Comparison of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 37, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, H.; Nakataki, M.; Sumitani, S.; Iga, J.-I.; Numata, S.; Kameoka, N.; Watanabe, S.-Y.; Umehara, H.; Kinoshita, M.; Inoshita, M.; et al. 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of glutamate-related abnormality in bipolar disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 208, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Zhong, S.; Shan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Luo, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Huang, H.; et al. Altered biochemical metabolism and its lateralization in the cortico-striato-cerebellar circuit of unmedicated bipolar II depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 259, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Shen, Z.; Xiao, B.; Liang, C.; Chen, K.; et al. Differential neurometabolite alterations in brains of medication-free individuals with bipolar disorder and those with unipolar depression: A two-dimensional proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Bipolar Disord. 2016, 18, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, S.; Wang, B.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Jia, Y. A comparison of neurometabolites between remitted bipolar disorder and depressed bipolar disorder: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 211, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, G.S.; Ivanovski, B.; Wen, W.; Lagopoulos, J.; Moss, K.; Sachdev, P. Measuring mania metabolites: A longitudinal proton spectroscopy study of hypomania. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2007, 434, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellen, E.J.; Harper, D.G.; Ravichandran, C.; Jensen, E.; Silveri, M.; Forester, B.P. Lamotrigine Therapy and Biomarkers of Cerebral Energy Metabolism in Older Age Bipolar Depression. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2019, 27, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, N.; Erfurth, A.; Pfleiderer, B. Elevated metabolites within dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in rapid cycling bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 172, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, V.; Sánchez, J.; Sanz, J.; Reig, S.; Benito, C.; Leal, I.; Sarramea, F.; Rebolledo, R.; Palomo, T.; Desco, M. Dorsolateral prefrontal N-acetyl-aspartate concentration in male patients with chronic schizophrenia and with chronic bipolar disorder. Eur. Psychiatry 2007, 22, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.V.; Nery-Fernandes, F.; Guimaraes, J.L.; Quarantini, L.D.C.; De Oliveira, I.R.; Ladeia-Rocha, G.G.; Jackowski, A.P.; Neto, C.D.A.; Miranda-Scippa, A. Normal Metabolic Levels in Prefrontal Cortex in Euthymic Bipolar I Patients with and without Suicide Attempts. Neural Plast. 2015, 2015, 165180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherk, H.; Backens, M.; Schneider-Axmann, T.; Kemmer, C.; Usher, J.; Reith, W.; Falkai, P.; Gruber, O. Neurochemical pathology in hippocampus in euthymic patients with bipolar I disorder. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2008, 117, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherk, H.; Backens, M.; Schneider-Axmann, T.; Usher, J.; Kemmer, C.; Reith, W.; Falkai, P.; Gruber, O. Cortical neurochemistry in euthymic patients with bipolar I disorder. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 10, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senaratne, R.; Milne, A.M.; MacQueen, G.M.; Hall, G.B.C. Increased choline-containing compounds in the orbitofrontal cortex and hippocampus in euthymic patients with bipolar disorder: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 172, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaragdi, A.; Chavez, S.; Lobaugh, N.J.; Meyer, J.H.; Kolla, N.J. Differential levels of prefrontal cortex glutamate+glutamine in adults with antisocial personality disorder and bipolar disorder: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 93, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeiro-De-Souza, M.G.; Henning, A.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Moreno, R.A.; Pastorello, B.F.; Leite, C.D.C.; Vallada, H.; Otaduy, M.C.G. Anterior cingulate Glutamate-Glutamine cycle metabolites are altered in euthymic bipolar I disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeiro-De-Souza, M.G.; Otaduy, M.C.G.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Moreno, R.A.; Nery, F.G.; Leite, C.; Lafer, B. Anterior Cingulate Cortex Glutamatergic Metabolites and Mood Stabilizers in Euthymic Bipolar I Disorder Patients: A Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2018, 3, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeiro-De-Souza, M.G.; Otaduy, M.C.G.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Moreno, R.A.; Nery, F.G.; Leite, C.; Lafer, B. Lithium-associated anterior cingulate neurometabolic profile in euthymic Bipolar I disorder: A 1H-MRS study. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 241, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winsberg, M.E.; Sachs, N.; Tate, D.L.; Adalsteinsson, E.; Spielman, D.; Ketter, T.A. Decreased dorsolateral prefrontal N-acetyl aspartate in bipolar disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 47, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.V.; Otaduy, M.C.; de Sousa, R.T.; Gattaz, W.F.; Busatto, G.F.; Leite, C.C.; Machado-Vieira, R. Bimodal effect of lithium plasma levels on hippocampal glutamate concentrations in bipolar II depression: A pilot study. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 18, pyu058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Wang, Y.; Lai, S.; Liu, T.; Liao, X.; Chen, G.; Jia, Y. Associations between executive function impairment and biochemical abnormalities in bipolar disorder with suicidal ideation. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 241, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Xiang, Q.; Ling, X.; Liu, S.; Huang, L.; Jia, Y. Similarities of biochemical abnormalities between major depressive disorder and bipolar depression: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 168, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeiro-De-Souza, M.; Scotti-Muzzi, E.; Fernandes, F.; De Sousa, R.; Leite, C.; Otaduy, M.; Machado-Vieira, R. Anterior cingulate cortex neuro-metabolic changes underlying lithium-induced euthymia in bipolar depression: A longitudinal 1H-MRS study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 49, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signoretti, S.; Marmarou, A.; Tavazzi, B.; Dunbar, J.; Amorini, A.M.; Lazzarino, G.; Vagnozzi, R. The protective effect of cyclosporin A upon N-acetylaspartate and mitochondrial dysfunction following experimental diffuse traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2004, 21, 1154–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, T.B.; Clark, J.B. Synthesis of N-acetyl-L-aspartate by rat brain mitochondria and its involvement in mitochondrial/cytosolic carbon transport. Biochem. J. 1979, 184, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, T.E.; Strangward, M.; Keelan, J.; Davey, G.P.; Munro, P.M.; Clark, J.B. Inhibition of N-acetylaspartate production: Implications for 1H MRS studies in vivo. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padamsey, Z.; Foster, W.J.; Emptage, N.J. Intracellular Ca2+ Release and Synaptic Plasticity: A Tale of Many Stores. Neuroscientist 2019, 25, 208–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.M.; Gallo, G. The Role of Mitochondria in Axon Development and Regeneration. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloesser, R.J.; Huang, J.; Klein, P.S.; Manji, H.K. Cellular plasticity cascades in the pathophysiology and treatment of bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 110–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houenou, J.; Frommberger, J.; Carde, S.; Glasbrenner, M.; Diener, C.; Leboyer, M.; Wessa, M. Neuroimaging-based markers of bipolar disorder: Evidence from two meta-analyses. J. Affect. Disord. 2011, 132, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zeng, W.-Z.; Yuan, P.-X.; Huang, L.-D.; Jiang, Y.-M.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Manji, H.K. The mood-stabilizing agents lithium and valproate robustly increase the levels of the neuroprotective protein bcl-2 in the CNS. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.J.F.; Low, I.C.C.; Pervaiz, S. Mitochondrial ROS and involvement of Bcl-2 as a mitochondrial ROS regulator. Mitochondrion 2014, 19, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.J.; Bebchuk, J.M.; Hasanat, K.; Chen, G.; Seraji-Bozorgzad, N.; Wilds, I.B.; Faulk, M.W.; Koch, S.; Glitz, D.A.; Jolkovsky, L.; et al. Lithium increases N-acetyl-aspartate in the human brain: In vivo evidence in support of bcl-2’s neurotrophic effects? Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauch, R.A.; Adnan El-Masri, M.; Parker, J.C.; El-Mallakh, R.S. Glial cell number and neuron/glial cell ratios in postmortem brains of bipolar individuals. J. Affect. Disord. 2006, 91, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Schulz, S.C.; Lee, S.; Reutiman, T.J.; Fatemi, S.H. Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell size is reduced in bipolar disorder. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2007, 27, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konradi, C.; Eaton, M.; MacDonald, M.L.; Walsh, J.; Benes, F.M.; Heckers, S. Molecular Evidence for Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Bipolar Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, K.O.; Föcking, M.; Cotter, D.R. Proteomic pathway analysis of the hippocampus in schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder implicates 14-3-3 signaling, aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling, and glucose metabolism: Potential roles in GABAergic interneuron pathology. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 167, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowy, M.T.; Gault, L.; Yamamoto, B.K. Adrenalectomy attenuates stress-induced elevations in extracellular glutamate concentrations in the hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 1993, 61, 1957–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti-Muzzi, E.; Umla-Runge, K.; Soeiro-de-Souza, M.G. Anterior cingulate cortex neurometabolites in bipolar disorder are influenced by mood state and medication: A meta-analysis of 1H-MRS studies. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 47, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J. Could glutamate spectroscopy differentiate bipolar depression from unipolar? J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 167, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, B. Cingulate Neurobiology and Disease; OUP: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Matelli, M.; Luppino, G.; Rizzolatti, G. Architecture of superior and mesial area 6 and the adjacent cingulate cortex in the macaque monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 1991, 311, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstone, P.H.; Wu, R.H.; O’Donnell, T.; Ulrich, M.; Asghar, S.J.; Hanstock, C.C. Chronic treatment with both lithium and sodium valproate may normalize phosphoinositol cycle activity in bipolar patients. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2002, 17, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.H.; O’Donnell, T.; Ulrich, M.; Asghar, S.J.; Hanstock, C.C.; Silverstone, P.H. Brain choline concentrations may not be altered in euthymic bipolar disorder patients chronically treated with either lithium or sodium valproate. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dager, S.R.; Friedman, S.D.; Parow, A.; Demopulos, C.; Stoll, A.L.; Lyoo, I.K.; Dunner, D.L.; Renshaw, P.F. Brain metabolic alterations in medication-free patients with bipolar disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.D.; Dager, S.R.; Parow, A.; Hirashima, F.; Demopulos, C.; Stoll, A.L.; Lyoo, I.K.; Dunner, D.L.; Renshaw, P.F. Lithium and valproic acid treatment effects on brain chemistry in bipolar disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 56, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, P.; Stanley, J.A.; Nicoletti, M.A.; Sassi, R.B.; Mallinger, A.G.; Frank, E.; Kupfer, D.; Keshavan, M.S.; Soares, J.C. 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy investigation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in bipolar disorder patients. J. Affect Disord. 2005, 86, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, J.D.; Unal, S.S.; Mrazek, D.A.; Marcus, S.M. Metabolic alterations in medication-free patients with bipolar disorder: A 3T CSF-corrected magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2008, 162, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, R.E.; Ostacher, M.J.; Marks, E.H.; Simon, N.M.; Sachs, G.S.; Jensen, J.E.; Renshaw, P.F.; Pollack, M.H. Brain GABA levels in patients with bipolar disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, F.G.; Stanley, J.A.; Chen, H.H.; Hatch, J.P.; Nicoletti, M.A.; Monkul, E.S.; Lafer, B.; Soares, J.C. Bipolar Disorder Comorbid With Alcoholism: A 1h Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2010, 44, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öngür, D.; Prescot, A.P.; Jensen, J.E.; Rouse, E.D.; Cohen, B.M.; Renshaw, P.F.; Olson, D.P. T2 relaxation time abnormalities in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Magn. Reason. Med. 2010, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, B.N.; Walss-Bass, C.; Stanley, J.A.; Nery, F.G.; Matsuo, K.; Nicoletti, M.A.; Hatch, J.P.; Bowden, C.L.; Escamilla, M.A.; Soares, J.C. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor val66met polymorphism affects prefrontal energy metabolism in bipolar disorder. NeuroReport 2007, 18, 1567–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, B.N.; Stanley, J.A.; Nery, F.G.; Serap Monkul, E.; Nicoletti, M.A.; Chen, H.H.; Hatch, J.P.; Caetano, S.C.; Ortiz, O.; Kapczinski, F.; et al. Abnormal cellular energy and phospholipid metabolism in the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of medication-free individuals with bipolar disorder: An in vivo 1H MRS study. Bipolar Disord. 2007, 9, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, B.N.; Stanley, J.A.; Nicoletti, M.A.; Hatch, J.P.; Soares, J.C. Corrected values of brain metabolites for the article: ‘Abnormal cellular energy and phospholipid metabolism in the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of medication-free individuals with bipolar disorder: An in vivo 1H MRS study’. Bipolar Disord. 2008, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagopoulos, J.; Hermens, D.F.; Tobias-Webb, J.; Duffy, S.; Naismith, S.L.; White, D.; Scott, E.; Hickie, I.B. In vivo glutathione levels in young persons with bipolar disorder: A magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitty, K.M.; Lagopoulos, J.; Hickie, I.B.; Hermens, D.F. Investigating the role of glutathione in mismatch negativity: An insight into NMDA receptor disturbances in bipolar disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atagün, M.I.; Şıkoğlu, E.M.; Soykan, Ç.; Süleyman, C.S.; Ulusoy-Kaymak, S.; Çayköylü, A.; Algın, O.; Phillips, M.L.; Öngür, D.; Moore, C.M. Perisylvian GABA levels in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 637, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Vieira, R.; Zanetti, M.V.; Otaduy, M.C.; De Sousa, R.T.; Soeiro-de-Souza, M.G.; Costa, A.C.; Carvalho, A.F.; Leite, C.C.; Busatto, G.F.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; et al. Increased Brain Lactate During Depressive Episodes and Reversal Effects by Lithium Monotherapy in Drug-Naive Bipolar Disorder: A 3-T 1H-MRS Study. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 37, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdel, O.; Kalayci, D.; Sözeri-Varma, G.; Kiroğlu, Y.; Tümkaya, S.; Toker-Uğurlu, T. Neurochemical metabolites in the medial prefrontal cortex in bipolar disorder: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Neural. Regen. Res. 2012, 7, 2929–2936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silveira, L.E.; Bond, D.J.; MacMillan, E.L.; Kozicky, J.M.; Muralidharan, K.; Bücker, J.; Rosa, A.R.; Kapczinski, F.; Yatham, L.N. Hippocampal neurochemical markers in bipolar disorder patients following the first-manic episode: A prospective 12-month proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2017, 51, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Stanley, J.A.; Selvaraj, S.; Mwangi, B.; Passos, I.C.; Zunta-Soares, G.B.; Soares, J.C. Evidence of altered membrane phospholipid metabolism in the anterior cingulate cortex and striatum of patients with bipolar disorder I: A multi-voxel 1H MRS study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 81, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, B.; Yurt, A.; Gökmen, N.; Renshaw, P.; Olson, D.; Yildiz, A. Trait-related alterations of N-acetyl-aspartate in euthymic bipolar patients: A longitudinal proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 206, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galińska-Skok, B.; Konarzewska, B.; Kubas, B.; Tarasów, E.; Szulc, A. Neurochemical alterations in anterior cingulate cortex in bipolar disorder: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study (1H-MRS). Psychiatr. Polska 2016, 50, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; A Stanley, J.; Passos, I.C.; Mwangi, B.; Selvaraj, S.; Zunta-Soares, G.B.; Soares, J.C. Elevated Choline-Containing Compound Levels in Rapid Cycling Bipolar Disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 2252–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.J.; E Silveira, L.; Macmillan, E.L.; Torres, I.J.; Lang, D.J.; Su, W.; Honer, W.G.; Lam, R.W.; Yatham, L.N. Diagnosis and body mass index effects on hippocampal volumes and neurochemistry in bipolar disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisciandaro, J.J.; Tolliver, B.K.; Prescot, A.P.; Brenner, H.M.; Renshaw, P.F.; Brown, T.R.; Anton, R.F. Unique prefrontal GABA and glutamate disturbances in co-occurring bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Kaufman, M.J.; Cohen, B.M.; Jensen, J.E.; Coyle, J.T.; Du, F.; Öngür, D. In Vivo Brain Glycine and Glutamate Concentrations in Patients With First-Episode Psychosis Measured by Echo Time–Averaged Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy at 4T. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galińska-Skok, B.; Małus, A.; Konarzewska, B.; Rogowska-Zach, A.; Milewski, R.; Tarasów, E.; Szulc, A.; Waszkiewicz, N. Choline Compounds of the Frontal Lobe and Temporal Glutamatergic System in Bipolar and Schizophrenia Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermens, D.F.; Hatton, S.N.; Lee, R.S.C.; Naismith, S.L.; Duffy, S.L.; Amminger, G.P.; Kaur, M.; Scott, E.M.; Lagopoulos, J.; Hickie, I.B. In vivo imaging of oxidative stress and fronto-limbic white matter integrity in young adults with mood disorders. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 268, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, T.; Calkin, C.; Blagdon, R.; Slaney, C.; Alda, M. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A potentially modifiable risk factor for neuro-chemical brain changes in bipolar disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 77, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.; Jelen, L.A.; Horne, C.M.; Cleare, A.; Pariante, C.M.; Young, A.H.; Stone, J.M. Inflammation, Glutamate, and Cognition in Bipolar Disorder Type II: A Proof of Concept Study. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo, J.R.; Jones, T.; Qualls, C.; Chavez, L.; Lin, D.; Lenroot, R.K.; Gasparovic, C. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of gray and white matter in bipolar-I and schizophrenia. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 246, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Venkatasubramanian, P.N.; Bárány, M.; Davis, J.M. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain in schizophrenic and affective patients. Schizophr. Res. 1992, 8, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, A.L.; Renshaw, P.F.; Sachs, G.S.; Guimaraes, A.R.; Miller, C.; Cohen, B.M.; Lafer, B.; Gonzalez, R.G. The human brain resonance of choline-containing compounds is similar in patients receiving lithium treatment and controls: An in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Biol. Psychiatry 1992, 32, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.M.; Breeze, J.L.; A Gruber, S.; Babb, S.M.; Frederick, B.D.; A Villafuerte, R.; Stoll, A.L.; Hennen, J.; A Yurgelun-Todd, D.; Cohen, B.M.; et al. Choline, myoinositol and mood in bipolar disorder: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study of the anterior cingulate cortex. Bipolar Disord. 2000, 2, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolino, A.; Frye, M.; Callicott, J.; Mattay, V.S.; Rakow, R.; Shelton-Repella, J.; Post, R.; Weinberger, D.R. Neuronal pathology in the hippocampal area of patients with bipolar disorder: A study with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 53, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstone, P.H.; Wu, R.H.; O’Donnell, T.; Ulrich, M.; Asghar, S.J.; Hanstock, C.C. Chronic treatment with lithium, but not sodium valproate, increases cortical N-acetyl-aspartate concentrations in euthymic bipolar patients. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2003, 18, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstone, P.H.; Asghar, S.J.; O’Donnell, T.; Ulrich, M.; Hanstock, C.C. Lithium and valproate protect against dextro-amphetamine induced brain choline concentration changes in bipolar disorder patients. World J. Biol. Psychiatry Off. J. World Fed. Soc. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 5, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, G.; Bertolino, A.; Brudaglio, F.; Sciota, D.; Altamura, M.; Antonucci, N.; Scarabino, T.; Weinberger, D.R.; Nardini, M. Hippocampal neurochemical pathology in patients at first episode of affective psychosis: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study. Psychiatry Res. 2004, 131, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.W.; Sailasuta, N.; Chandler, R.A.; Ketter, T.A. Magnetic resonance spectroscopic measurement of cerebral gamma-aminobutyric acid concentrations in patients with bipolar disorders. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2006, 18, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherk, H.; Backens, M.; Schneider-Axmann, T.; Kraft, S.; Kemmer, C.; Usher, J.; Reith, W.; Falkai, P.; Meyer, J.; Gruber, O. Dopamine transporter genotype influences N-acetyl-aspartate in the left putamen. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 10, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwagar, Z.; Wylezinska, M.; Jezzard, P.; Evans, J.; Ashworth, F.; Sule, A.; Matthews, P.M.; Cowen, P.J. Reduction in occipital cortex gamma-aminobutyric acid concentrations in medication-free recovered unipolar depressed and bipolar subjects. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, R.O., Jr.; McCarthy, J.M.; Prescot, A.P.; Jensen, J.E.; Cooper, A.J.; Cohen, B.M.; Renshaw, P.F.; Öngür, D. Brain gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) abnormalities in bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2013, 15, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewska, B.R.; Yip, S.W.; Near, J.; Goodwin, G.M.; Cowen, P.J. Cortical glutathione levels in young people with bipolar disorder: A pilot study using magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Psychopharmacology 2013, 231, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermens, D.F.; Naismith, S.L.; Chitty, K.M.; Lee, R.S.; Tickell, A.; Duffy, S.L.; Paquola, C.; White, D.; Hickie, I.B.; Lagopoulos, J. Cluster analysis reveals abnormal hippocampal neurometabolic profiles in young people with mood disorders. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Nery, F.G.; Tallman, M.J.; Patino, L.R.; Adler, C.M.; Strawn, J.R.; Fleck, D.E.; Barzman, D.H.; Sweeney, J.A.; Strakowski, S.M.; et al. Individual prediction of symptomatic converters in youth offspring of bipolar parents using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2020, 30, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelen, L.A.; King, S.; Horne, C.M.; Lythgoe, D.J.; Young, A.H.; Stone, J.M. Functional magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar affective disorder: Glutamate dynamics in the anterior cingulate cortex during a working memory task. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 29, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmaca, M.; Yildirim, H.; Ozdemir, H.; Ogur, E.; Tezcan, E. Hippocampal 1H MRS in patients with bipolar disorder taking valproate versus valproate plus quetiapine. Psychol. Med. 2006, 37, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherk, H.; Backens, M.; Zill, P.; Schneider-Axmann, T.; Wobrock, T.; Usher, J.; Reith, W.; Falkai, P.; Möller, H.-J.; Bondy, B.; et al. SNAP-25 genotype influences NAA/Cho in left hippocampus. J. Neural Transm. 2008, 115, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, O.; Hasan, A.; Scherk, H.; Wobrock, T.; Schneider-Axmann, T.; Ekawardhani, S.; Schmitt, A.; Backens, M.; Reith, W.; Meyer, J.; et al. Association of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor val66met polymorphism with magnetic resonance spectroscopic markers in the human hippocampus: In vivo evidence for effects on the glutamate system. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 262, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahana, N.; DelBello, M.; Chu, W.-J.; Jarvis, K.; Fleck, D.; Welge, J.; Strakowski, S.; Adler, C. Neurochemical alteration in the caudate: Implications for the pathophysiology of bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2011, 193, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howells, F.M.; Ives-Deliperi, V.L.; Horn, N.R.; Stein, D.J. Increased thalamic phospholipid concentration evident in bipolar I disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 41, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.-J.; DelBello, M.P.; Jarvis, K.B.; Norris, M.M.; Kim, M.-J.; Weber, W.; Lee, J.-H.; Strakowski, S.M.; Adler, C.M. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging of lactate in patients with bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2013, 213, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitty, K.M.; Lagopoulos, J.; Hickie, I.B.; Hermens, D.F. Hippocampal glutamatergic/NMDA receptor functioning in bipolar disorder: A study combining mismatch negativity and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 233, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeiro-De-Souza, M.G.; Pastorello, B.F.; Leite, C.D.C.; Henning, A.; Moreno, R.A.; Otaduy, M.C.G. Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Lactate and Glutathione Levels in Euthymic Bipolar I Disorder:1H-MRS Study. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, pyw032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotti-Muzzi, E.; Chile, T.; Moreno, R.; Pastorello, B.F.; Leite, C.D.C.; Henning, A.; Otaduy, M.C.G.; Vallada, H.; Soeiro-De-Souza, M.G. ACC Glu/GABA ratio is decreased in euthymic bipolar disorder I patients: Possible in vivo neurometabolite explanation for mood stabilization. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 271, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, C.M.; DelBello, M.P.; Weber, W.A.; Jarvis, K.B.; Welge, J.; Chu, W.J.; Rummelhoff, E.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, J.H.; Strakowski, S.M. Neurochemical effects of quetiapine in patients with bipolar mania: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 33, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, A.D.; Lafer, B.; Yatham, L.N. 1H-MRS of hippocampus in patients after first manic episode. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 15, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soeiro-de-Souza, M.G.; Salvadore, G.; Moreno, R.A.; Otaduy, M.C.; Chaim, K.T.; Gattaz, W.F.; Zarate, C.A.; Machado-Vieira, R. Bcl-2 rs956572 Polymorphism is Associated with Increased Anterior Cingulate Cortical Glutamate in Euthymic Bipolar I Disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 38, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atagün, M.; Şıkoğlu, E.; Can, S.; Karakaş-Uğurlu, G.; Ulusoy-Kaymak, S.; Çayköylü, A.; Algın, O.; Phillips, M.; Moore, C.; Öngür, D. Investigation of Heschl’s gyrus and planum temporale in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 161, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atagün, M.I.; Şıkoğlu, E.M.; Can, S.S.; Uğurlu, G.K.; Kaymak, S.U.; Çayköylü, A.; Algın, O.; Phillips, M.L.; Moore, C.M.; Öngür, D. Neurochemical differences between bipolar disorder type I and II in superior temporal cortices: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 235, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deicken, R.F.; Eliaz, Y.; Feiwell, R.; Schuff, N. Increased thalamic N-acetyl-aspartate in male patients with familial bipolar I disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2001, 106, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldic, M.; Millischer, V.; Port, J.D.; Ho, A.M.; Jia, Y.F.; Geske, J.R.; Biernacka, J.M.; Backlund, L.; McElroy, S.L.; Bond, D.J.; et al. Genetic variant in SLC1A2 is associated with elevated anterior cingulate cortex glutamate and lifetime history of rapid cycling. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajek, T.; Bauer, M.; Pfennig, A.; Cullis, J.; Ploch, J.; O’Donovan, C.; Bohner, G.; Klingebiel, R.; Young, L.; MacQueen, G.; et al. Large positive effect of lithium on prefrontal cortex N-acetyl-aspartate in patients with bipolar disorder: 2-centre study. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012, 37, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Frye, M.; Watzl, J.; Banakar, S.; O’Neill, J.; Mintz, J.; Davanzo, P.; Fischer, J.; Chirichigno, J.W.; Ventura, J.; Elman, S.; et al. Increased Anterior Cingulate/Medial Prefrontal Cortical Glutamate and Creatine in Bipolar Depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 2490–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Dydak, U.; Harezlak, J.; Nixon, J.; Dzemidzic, M.; Gunn, A.D.; Karne, H.S.; Anand, A. Neurochemical abnormalities in unmedicated bipolar depression and mania: A 2D 1H MRS investigation. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2013, 213, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarramea Crespo, F.; Luque, R.; Prieto, D.; Sau, P.; Albert, C.; Leal, I.; De Luxan, A.; Osuna, M.I.; Ruiz, M.; Galán, R.; et al. Biochemical changes in the cingulum in patients with schizophrenia and chronic bipolar disorder. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 258, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Vieira, R.; Gattaz, W.F.; Zanetti, M.V.; De Sousa, R.T.; Carvalho, A.F.; Soeiro-De-Souza, M.G.; Leite, C.C.; Otaduy, M.C. A Longitudinal (6-week) 3T 1H-MRS Study on the Effects of Lithium Treatment on Anterior Cingulate Cortex Metabolites in Bipolar Depression. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015, 25, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chen, G.; Chen, F.; Shen, S.; Huang, H.; Jia, Y. Association of altered thyroid hormones and neurometabolism to cognitive dysfunction in unmedicated bipolar II depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 105, 110027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bio, D.S.; Moreno, R.A.; Garcia-Otaduy, M.C.; Nery, F.; Lafer, B.; Soeiro-De-Souza, M.G. Altered brain creatine cycle metabolites in bipolar I disorder with childhood abuse: A 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 109, 110233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Hamakawa, H.; Shioiri, T.; Murashita, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Inubushi, T. Choline-containing compounds detected by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the basal ganglia in bipolar disorder. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 1996, 21, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Hamakawa, H.; Kato, T.; Murashita, J.; Kato, N. Quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the basal ganglia in patients with affective disorders. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1998, 248, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, K.; Isoda, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Takehara, Y.; Ochiai, M.; Takeda, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Ohara, K. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the lenticular nuclei in bipolar I affective disorder. Psychiatry Res. 1998, 84, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Zhong, S.; Liao, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, H.; Jia, Y. Biochemical abnormalities in basal ganglia and executive dysfunction in acute- and euthymic-episode patients with bipolar disorder: A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 225, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Lai, S.; Yue, J.; Wang, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liao, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, G.; Chen, F.; et al. The characteristic of cognitive impairments in patients with bipolar II depression and its association with N-acetyl-aspartate of the prefrontal white matter. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletti, S.; Mazza, M.G.; Vai, B.; Lorenzi, C.; Colombo, C.; Benedetti, F. Proinflammatory Cytokines Predict Brain Metabolite Concentrations in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex of Patients With Bipolar Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 590095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamakawa, H.; Kato, T.; Shioiri, T.; Inubushi, T.; Kato, N. Quantitative proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the bilateral frontal lobes in patients with bipolar disorder. Psychol. Med. 1999, 29, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.J.; Silveira, L.E.; Torres, I.J.; Lam, R.W.; Yatham, L.N. Weight gain as a risk factor for progressive neurochemical abnormalities in first episode mania patients: A longitudinal magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Psychol. Med. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo, J.R.; Mayer, E.G.; Upston, J.; Jones, T.; Garcia, C.; Sheriff, S.; Maudsley, A.; Tohen, M.; Gasparovic, C.; Lenroot, R. Increased Glutamate Plus Glutamine in the Right Middle Cingulate in Early Schizophrenia but Not in Bipolar Psychosis: A Whole Brain 1H-MRS Study. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 660850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari-Zadeh, F.; Cao, B.; Stanley, J.A.; Liu, Y.; Wu, M.-J.; Tannous, J.; Lopez, M.; Sanches, M.; Mwangi, B.; Zunta-Soares, G.B.; et al. Evidence of altered metabolism of cellular membranes in bipolar disorder comorbid with post-traumatic stress disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 289, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximo, J.O.; Briend, F.; Armstrong, W.P.; Kraguljac, N.V.; Lahti, A.C. Salience network glutamate and brain connectivity in medication-naïve first episode patients—A multimodal magnetic resonance spectroscopy and resting state functional connectivity MRI study. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 32, 102845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, A.E.; Kumar, P.; Treadway, M.T.; Rutherford, A.V.; Ironside, M.L.; Foti, D.; Fitzmaurice, G.; Du, F.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Mapping Disease Course Across the Mood Disorder Spectrum Through a Research Domain Criteria Framework. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).