Control of Maternal-to-Zygotic Transition in Human Embryos and Other Animal Species (Especially Mouse): Similarities and Differences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
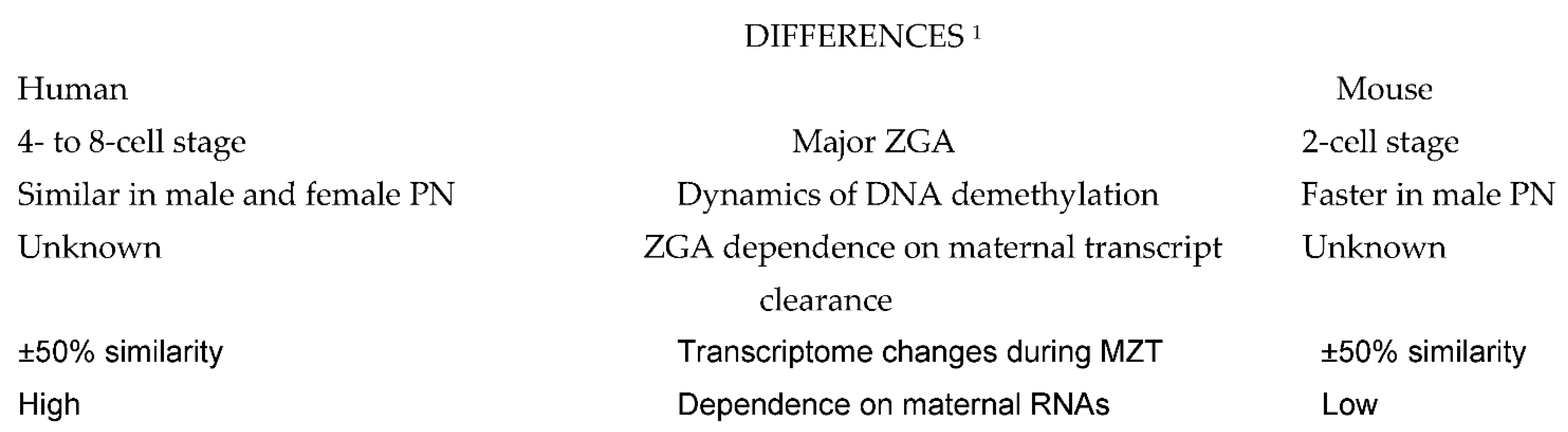
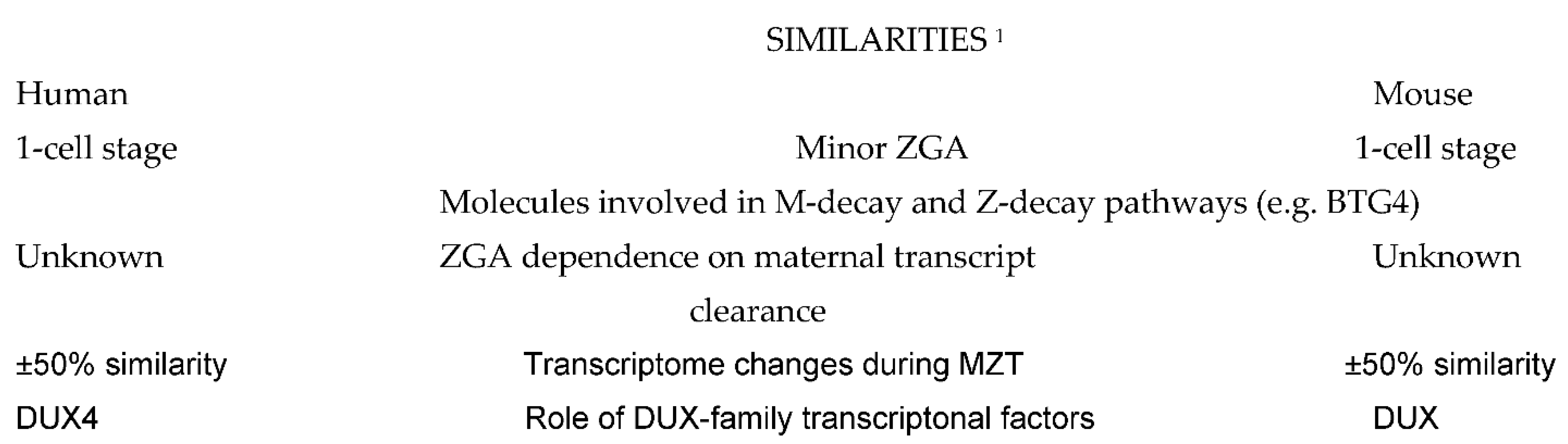
2. Similarities and Particularities of MZT in Human Preimplantation Embryos as Related to Other Animal Species
3. Implications in Research and Clinical Issues Related to Human ART
4. Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tadros, W.; Lipshitz, H.D. The maternal-to-zygotic transition: A play in two acts. Development 2009, 136, 3033–304242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sha, Q.Q.; Zhang, J.; Fan, H.Y. A story of birth and death: mRNA translation and clearance at the onset of maternal-to-zygotic transition in mammals. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 101, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jukam, D.; Shariati, S.A.M.; Skotheim, J.M. Zygotic Genome Activation in Vertebrates. Dev. Cell 2017, 42, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paonessa, M.; Borini, A.; Coticchio, G. Genetic causes of preimplantation embryo developmental failure. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2021, 88, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesarik, J. Toward molecular medicine in female infertility management: Editorial to the Special Issue “Molecular Mechanisms of Human Oogenesis and Early Embryogenesis”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosby, I.M.; Gandolfi, F.; Moor, R.M. Control of protein synthesis during early cleavage of sheep embryos. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1988, 82, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frei, R.E.; Schultz, G.A.; Church, R.B. Qualitative and quantitative changes in protein synthesis occur at the 8–16-cell stage of embryogenesis in the cow. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1989, 86, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christians, E.; Rao, V.H.; Renard, J.P. Sequential acquisition of transcriptional control during early embryonic development in the rabbit. Dev. Biol. 1994, 164, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, R.D.; Bavister, B.D. Onset of nucleolar and extranucleolar transcription and expression of fibrillarin in macaque embryos developing in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 60, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, S.; Han, J.; Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W.; Pei, Y.; Ruan, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. Specific gene-regulation networks during the pre-implantation development of the pig embryo as revealed by deep sequencing. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesarik, J.; Kopecny, V.; Plachot, M.; Mandelbaum, J. Activation of nucleolar and extranucleolar RNA synthesis and changes in the ribosomal content of human embryos developing in vitro. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1986, 78, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braude, P.; Bolton, V.; Moore, S. Human gene expression first occurs between the four- and eight-cell stages of preimplantation development. Nature 1988, 332, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesarik, J.; Kopecny, V.; Plachot, M.; Mandelbaum, J. Early morphological signs of embryonic genome expression in human preimplantation development as revealed by quantitative electron microscopy. Dev. Biol. 1988, 128, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.I.; Funaya, S.; Tsukioka, D.; Kawamura, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, M.G.; Schultz, R.M.; Aoki, F. Minor zygotic gene activation is essential for mouse preimplantation development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6780–E6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tesarik, J.; Kopecny, V. Assembly of the nucleolar precursor bodies in human male pronuclei is correlated with an early RNA synthetic activity. Exp. Cell Res. 1990, 191, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, M.; Lam, B.Y.H.; Ma, M.K.; Rainbow, K.; Braun, S.; VerMilyea, M.D.; Yeo, G.S.H.; Perry, A.C.F. Human embryonic genome activation initiates at the one-cell stage. Cell Stem Cell 2022, 29, 209–216.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Cai, M.; Du, K.; Bai, X.; Tang, L.; Jia, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Lai, S. Dynamics of known long non-coding RNAs during the maternal-to-zygotic transition in rabbit. Animals 2021, 11, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, L.R.F.M.; de Assis, E.I.T.; Azevedo, V.A.N.; Silva, B.R.; da Cunha, E.V.; Silva, J.R.V. Why is it so difficult to have competent oocytes from in vitro cultured preantral follicles? Reprod. Sci. 2022. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winata, C.L.; Korzh, V. The translational regulation of maternal mRNAs in time and space. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 3007–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shav-Tal, Y.; Singer, R.H. RNA localization. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4077–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, P.; Kedersha, N. RNA granules: Post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberfarb, M.E.; Chu, T.; Wreden, C.; Theurkauf, W.; Gergen, J.P.; Strickland, S. Mutations that perturb poly(A)-dependent maternal mRNA activation block the initiation of development. Development 1996, 122, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, F.; Hara, K.T.; Schultz, R.M. Acquisition of transcriptional competence in the 1-cell mouse embryo: Requirement for recruitment of maternal mRNAs. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2003, 64, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Q.Q.; Zheng, W.; Wu, Y.W.; Li, S.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S.; Lin, G.; Ou, X.H.; Fan, H.Y. Dynamics and clinical relevance of maternal mRNA clearance during the oocyte-to-embryo transition in humans. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, P.; Wong-Deyrup, S.W.; McCarthy, A.; Breznak, S.; Hurton, M.D.; Upadhyay, M.; Bennink, B.; Camacho, J.; Lee, M.T.; Rangan, P. RNA degradation is required for the germ-cell to maternal transition in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 2984–2994.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashirullah, A.; Halsell, S.R.; Cooperstock, R.L.; Kloc, M.; Karaiskakis, A.; Fisher, W.W.; Fu, W.; Hamilton, J.K.; Etkin, L.D.; Lipshitz, H.D. Joint action of two RNA degradation pathways controls the timing of maternal transcript elimination at the midblastula transition in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2610–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, Z.; Kageyama, S.; Aoki, F. Degradation of maternal mRNA in mouse embryos: Selective degradation of specific mRNAs after fertilization. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2005, 72, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhou, Z.; Sha, Q.; Niu, X.; Sun, X.; Shi, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Dai, J.; Cai, S.; et al. Homozygous mutations in BTG4 cause zygotic cleavage failure and female infertility. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 107, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yang, M.; Guo, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Liu, P.; Lian, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yan, J.; et al. Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human preimplantation embryos and embryonic stem cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontis, J.; Planet, E.; Offner, S.; Turelli, P.; Duc, J.; Coudray, A.; Theunissen, T.W.; Jaenisch, R.; Trono, D. Hominoid-Specific Transposable Elements and KZFPs Facilitate Human Embryonic Genome Activation and Control Transcription in Naive Human ESCs. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 724–735.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Zhu, P.; Yan, L.; Li, R.; Hu, B.; Lian, Y.; Yan, J.; Ren, X.; Lin, S.; Li, J.; et al. The DNA methylation landscape of human early embryos. Nature 2014, 511, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Qin, Q.; Nisenblat, V.; Chang, H.M.; Yu, Y.; Wang, T.; Lu, C.; Yang, M.; Yang, S.; et al. Transcriptome landscape of human folliculogenesis reveals oocyte and granulosa cell interactions. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 1021–1034.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyer, L.A.; Lee, T.I.; Cole, M.F.; Johnstone, S.E.; Levine, S.S.; Zucker, J.P.; Guenther, M.G.; Kumar, R.M.; Murray, H.L.; Jenner, R.G.; et al. Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic stem cells. Cell 2005, 122, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tesarík, J. Involvement of oocyte-coded message in cell differentiation control of early human embryos. Development 1989, 105, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Bonneau, A.R.; Giraldez, A.J. Zygotic genome activation during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 581–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiddon, J.L.; Langford, A.T.; Wong, C.J.; Zhong, J.W.; Tapscott, S.J. Conservation and innovation in the DUX4-family gene network. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Iaco, A.; Planet, E.; Coluccio, A.; Verp, S.; Duc, J.; Trono, D. DUX-family transcription factors regulate zygotic genome activation in placental mammals. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, P.G.; Doráis, J.A.; Grow, E.J.; Whiddon, J.L.; Lim, J.W.; Wike, C.L.; Weaver, B.D.; Pflueger, C.; Emery, B.R.; Wilcox, A.L.; et al. Conserved roles of mouse DUX and human DUX4 in activating cleavage-stage genes and MERVL/HERVL retrotransposons. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuoristo, S.; Bhagat, S.; Hydén-Granskog, C.; Yoshihara, M.; Gawriyski, L.; Jouhilahti, E.M.; Ranga, V.; Tamirat, M.; Huhtala, M.; Kirjanov, I.; et al. DUX4 is a multifunctional factor priming human embryonic genome activation. iScience 2022, 25, 104137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steptoe, P.C.; Edwards, R.G. Birth after the reimplantation of a human embryo. Lancet 1978, 2, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesarik, J. Forty years of in vitro fertilization: A history of continuous expansion. In 40 Years After In Vitro Fertilisation; Tesarik, J., Ed.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gleicher, N.; Kushnir, V.A.; Barad, D.H. Worldwide decline of IVF birth rates and its probable causes. Hum. Reprod. Open 2019, 2019, hoz017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Yu, Y. Precise personalized medicine in gynecology cancer and infertility. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 7, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesarik, J.; Kopecny, V.; Plachot, M.; Mandelbaum, J. Ultrastructural and autoradiographic observations on multinucleated blastomeres of human cleaving embryos obtained by in-vitro fertilization. Hum. Reprod. 1987, 2, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seikkula, J.; Oksjoki, S.; Hurme, S.; Mankonen, H.; Polo-Kantola, P.; Jokimaa, V. Pregnancy and perinatal outcomes after transfer of binucleated or multinucleated frozen-thawed embryos: A case-control study. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2018, 36, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesarik, J. Is blastomere multinucleation a safeguard against embryo aneuploidy? Back to the future. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2018, 37, 506–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleicher, N.; Barad, D.H.; Patrizio, P.; Orvieto, R. We have reached a dead end for preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy. Hum. Reprod. 2022, deac052, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleicher, N.; Patrizio, P.; Brivanlou, A. Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy—A castle built on sand. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, E.; Minasi, M.G.; Fiorentino, F. Healthy babies after intrauterine transfer of mosaic aneuploid blastocysts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2089–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Chen, J.J.; Nabu, S.; Yeung, Q.S.Y.; Li, Y.; Tan, J.H.; Suksalak, W.; Chanchamroen, S.; Quangkananurug, W.; Wong, P.S.; et al. The pregnancy outcome of mosaic embryo transfer: A prospective multicenter study and meta-analysis. Genes 2020, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tesarik, J. Control of Maternal-to-Zygotic Transition in Human Embryos and Other Animal Species (Especially Mouse): Similarities and Differences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158562
Tesarik J. Control of Maternal-to-Zygotic Transition in Human Embryos and Other Animal Species (Especially Mouse): Similarities and Differences. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158562
Chicago/Turabian StyleTesarik, Jan. 2022. "Control of Maternal-to-Zygotic Transition in Human Embryos and Other Animal Species (Especially Mouse): Similarities and Differences" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158562
APA StyleTesarik, J. (2022). Control of Maternal-to-Zygotic Transition in Human Embryos and Other Animal Species (Especially Mouse): Similarities and Differences. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8562. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158562





