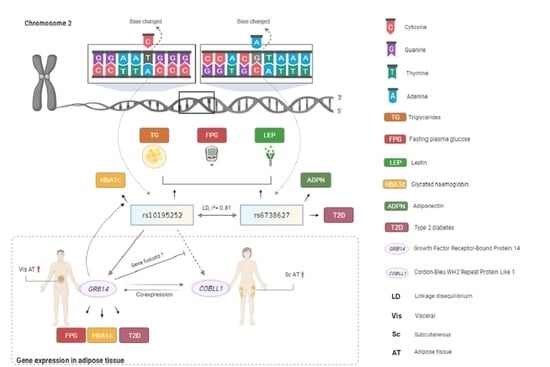
Metabolic Effects of the Waist-To-Hip Ratio Associated Locus GRB14/COBLL1 Are Related to GRB14 Expression in Adipose Tissue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
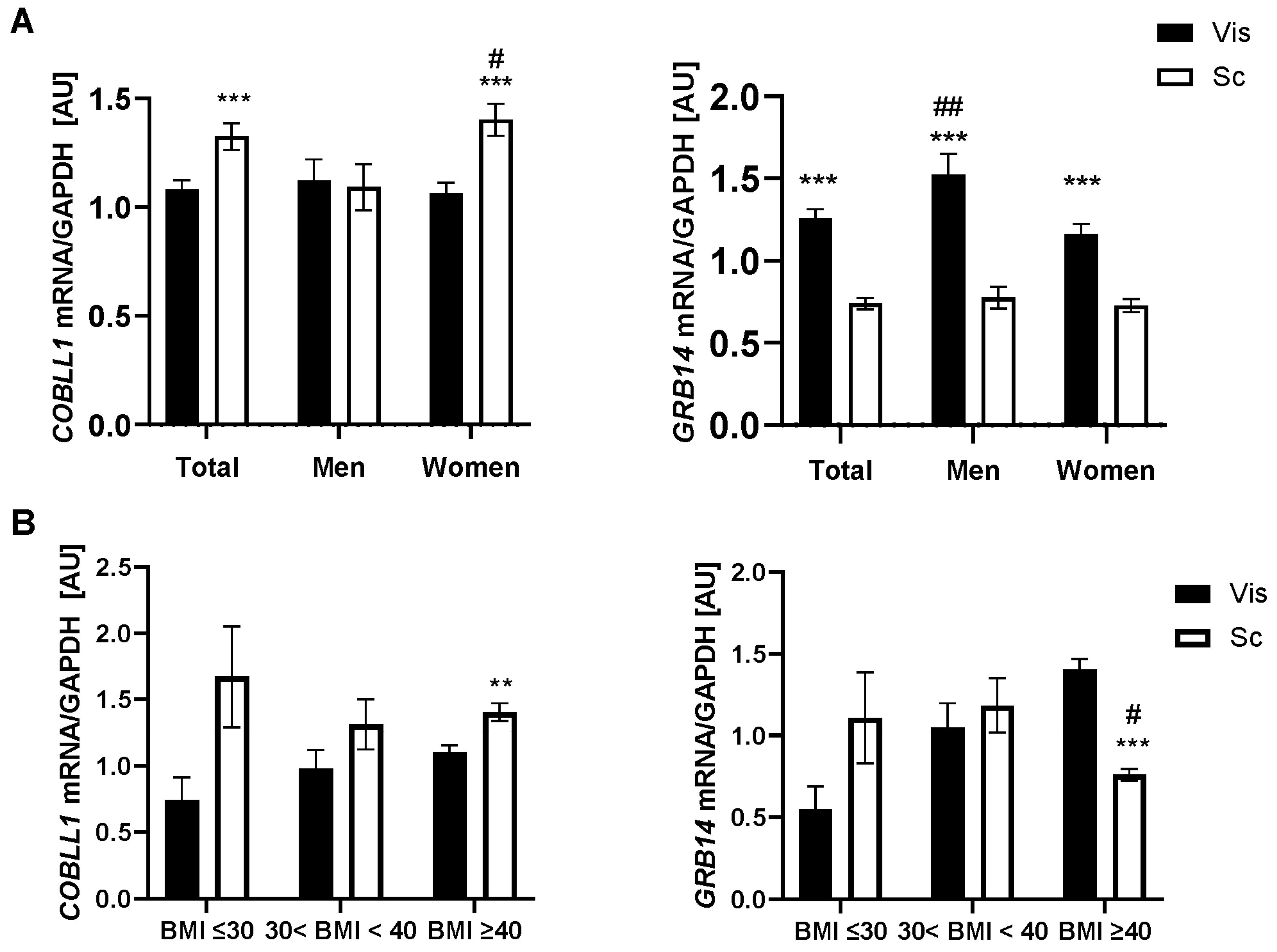
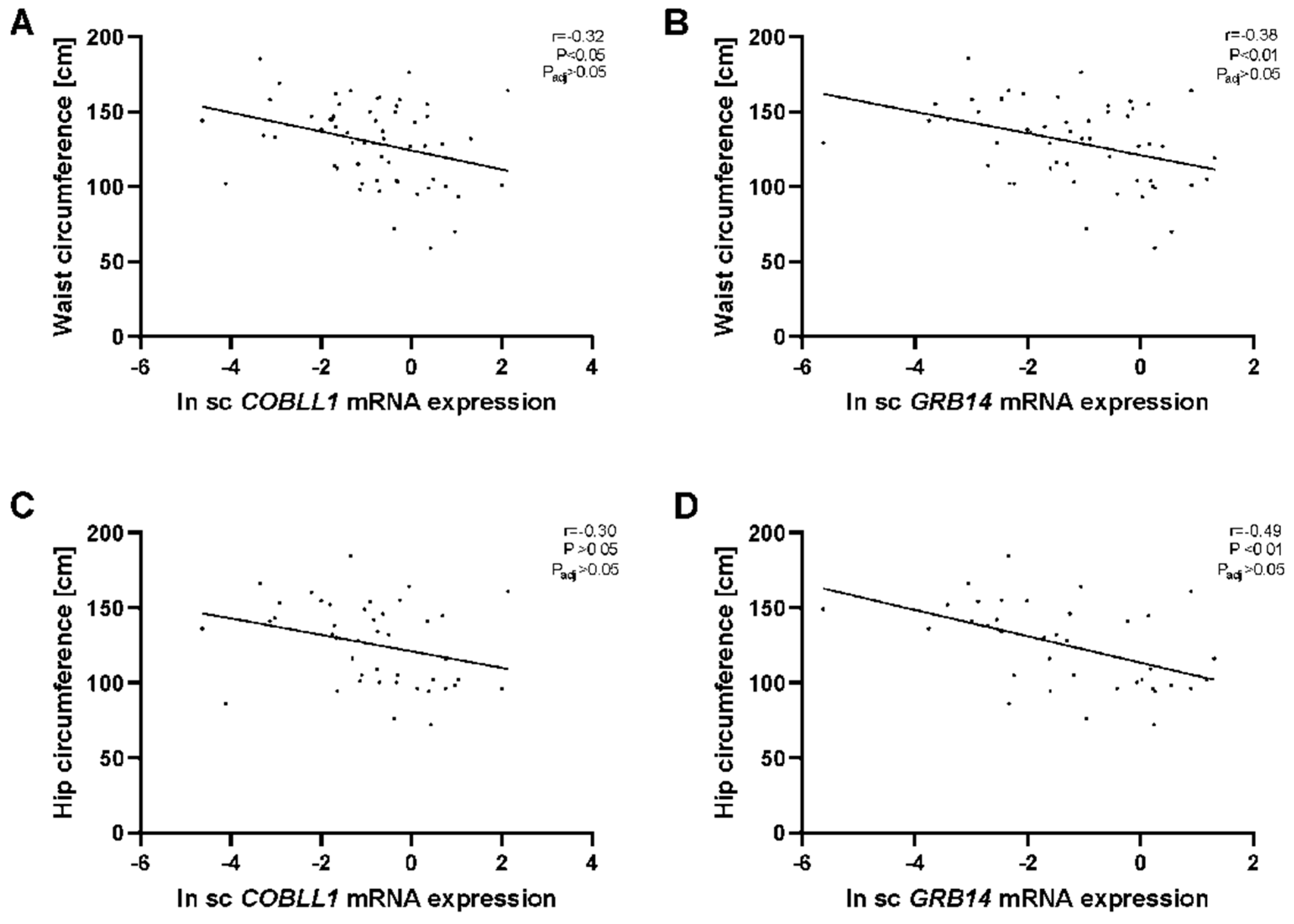
2.1. GRB14 and COBLL1 mRNA Expression in AT Correlates with Parameters of Obesity and Body Fat Distribution
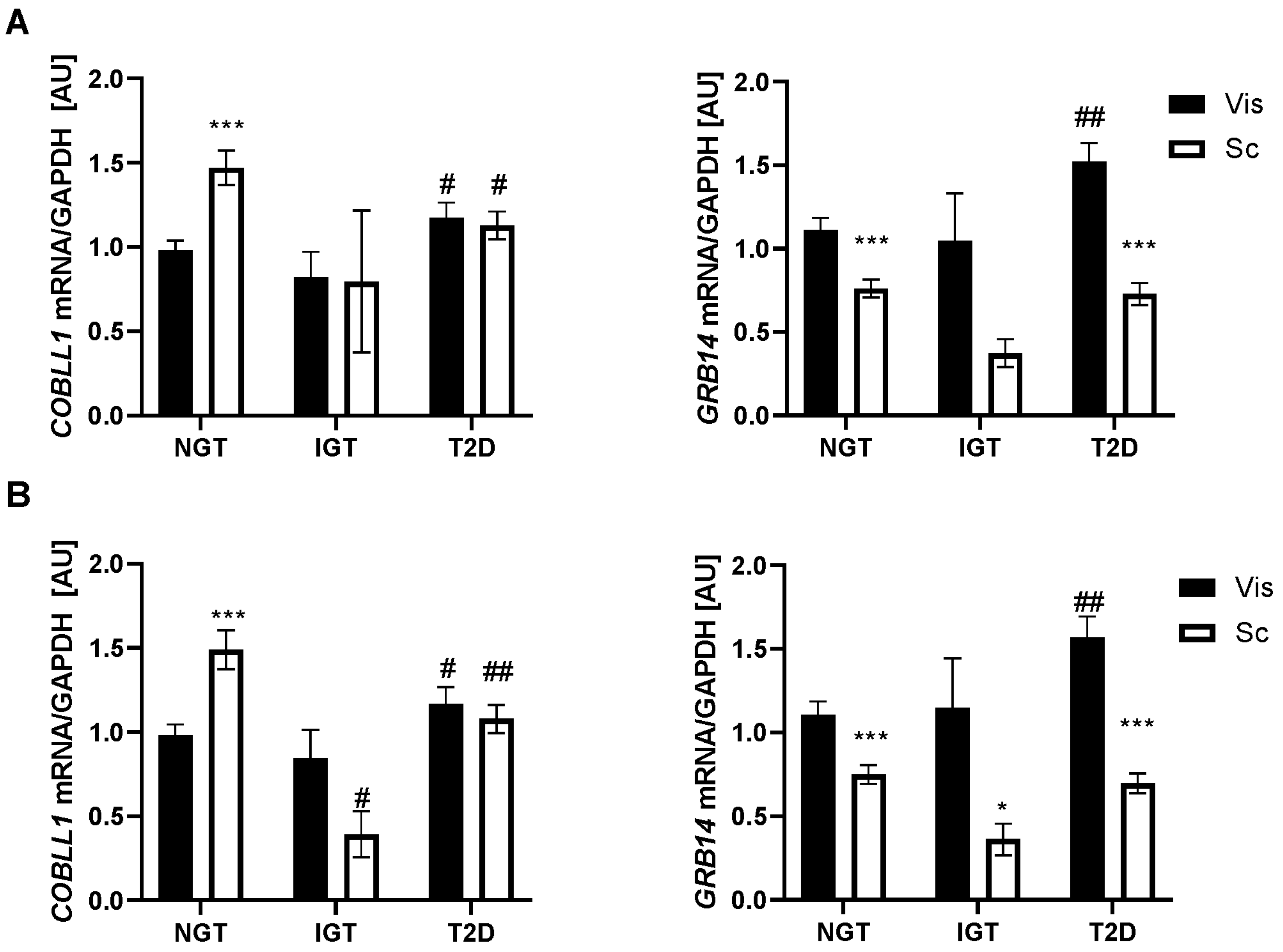
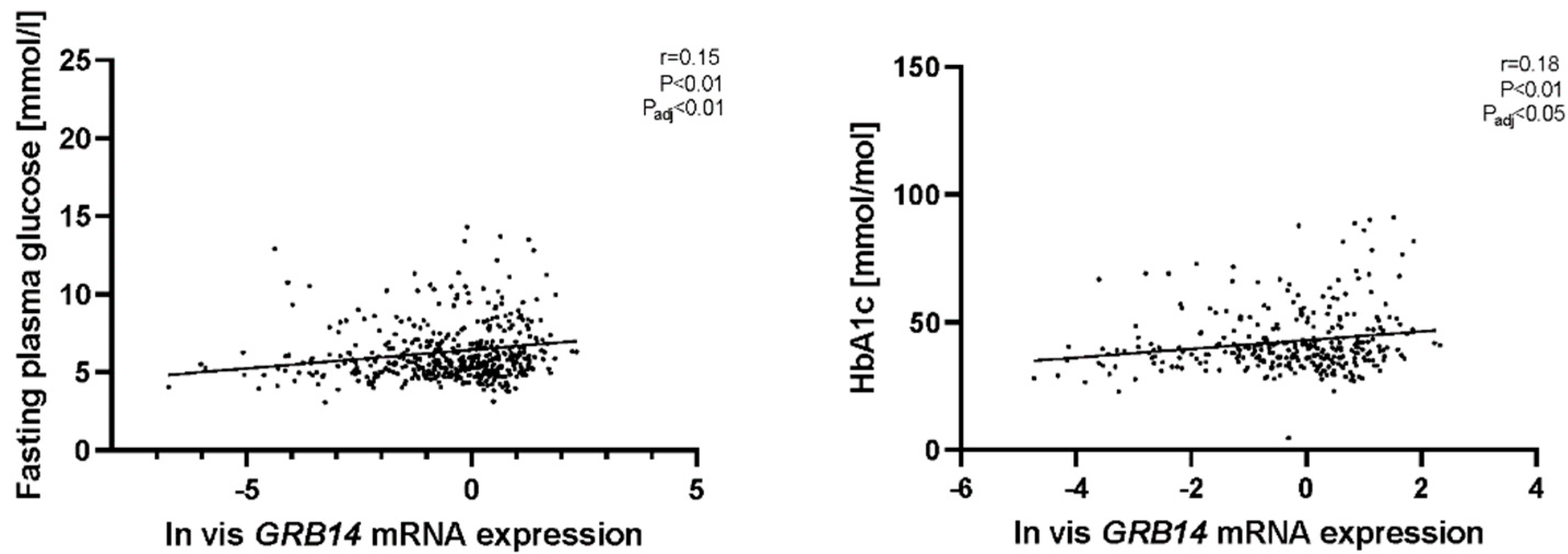
2.2. GRB14 and COBLL1 mRNA Expression in AT Correlates with Diabetes and Parameters of Glucose
2.3. Both rs10195252 and rs6738627 Are Associated with Glucose and Lipid Metabolism, as well as Circulating Adipokines
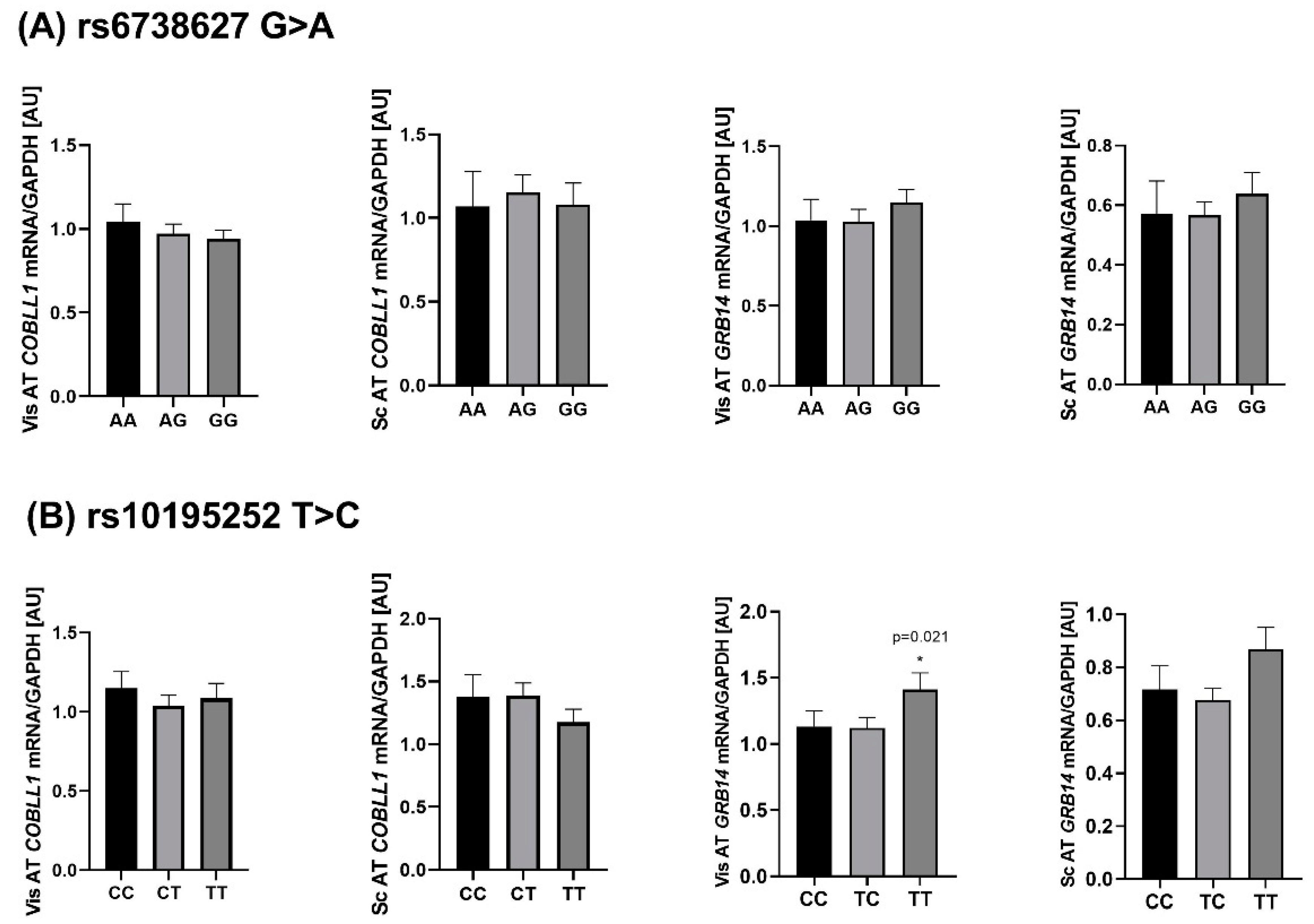
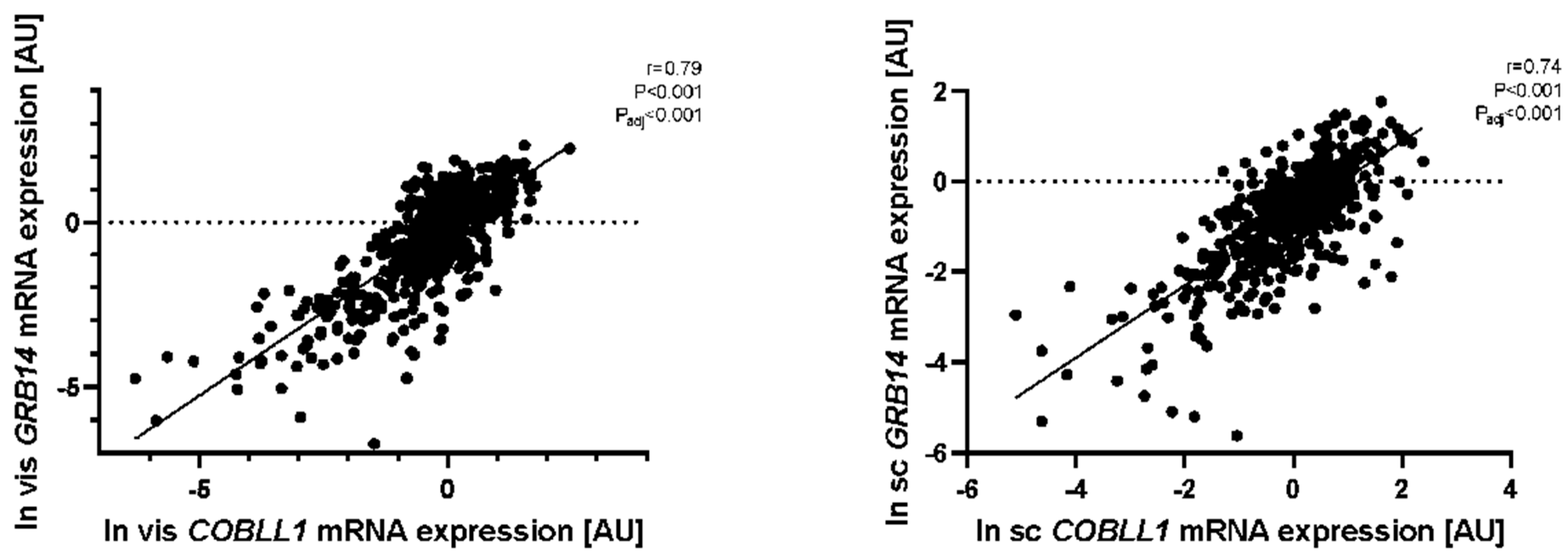
2.4. Genotype-Specific mRNA Expression at Loci Associated with WHR and Body Fat
2.5. Mediation Analyses
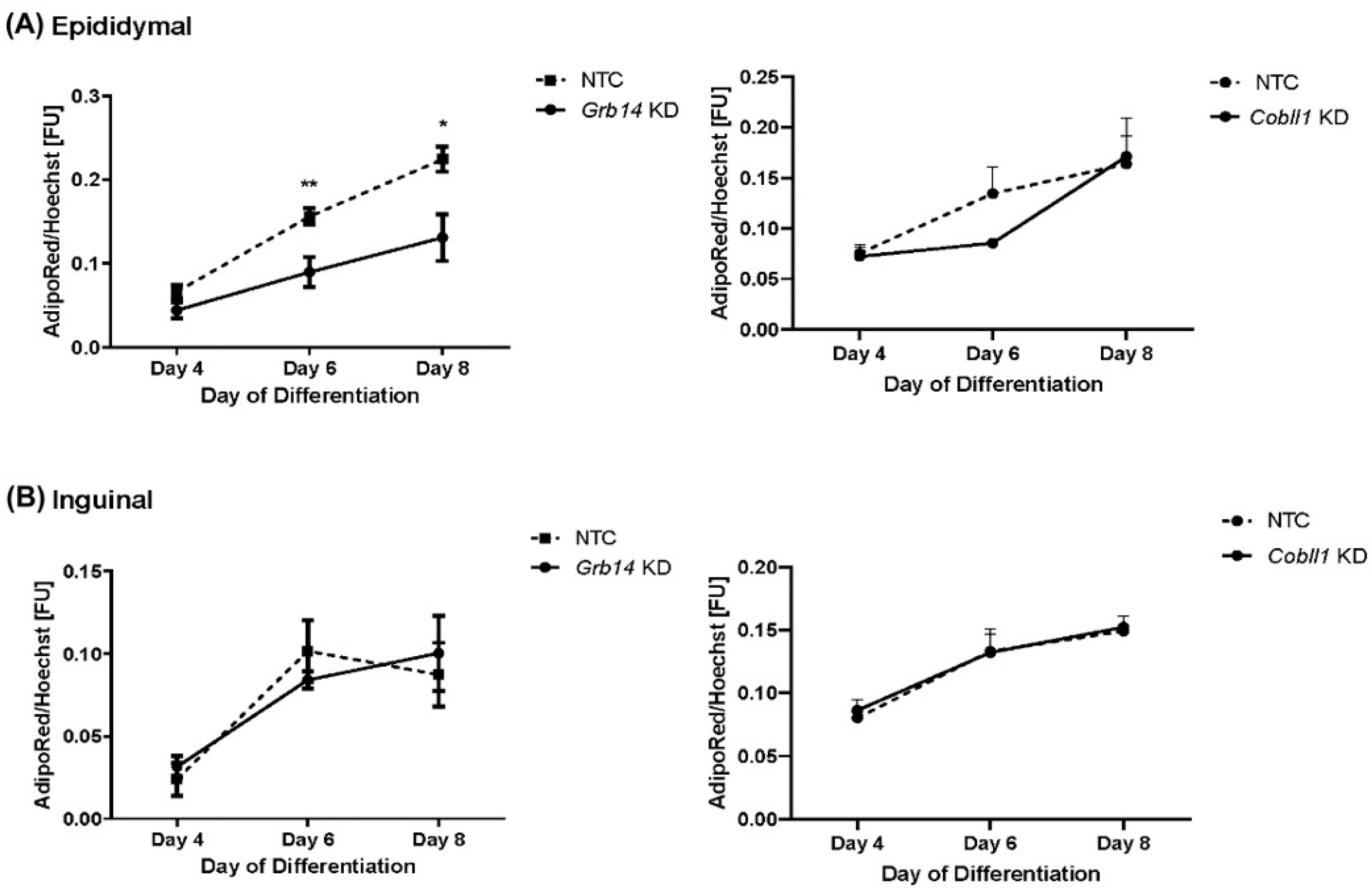
2.6. Decreased Lipid Accumulation in Grb14 Knockdown in Epididymal Cell Line
3. Discussion
3.1. GRB14 and COBLL1 Expression Is Fat-Depot-Specific and Related to Obesity and T2D
3.2. Genetic Association of WHR-Related SNPs with Clinical Variables
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. COBLL1 and GRB14 mRNA Expression Analyses in AT
4.3. Genotyping
4.4. Mediation Analysis
4.5. In Vitro Grb14 and Cobll1 Knockdown in Murine Epididymal and Inguinal Cell Lines
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Wadden, T.A. Mechanisms, Pathophysiology, and Management of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, A.V.; Chaffin, M.; Wade, K.H.; Zahid, S.; Brancale, J.; Xia, R.; Distefano, M.; Senol-Cosar, O.; Haas, M.E.; Bick, A.; et al. Polygenic Prediction of Weight and Obesity Trajectories from Birth to Adulthood. Cell 2019, 177, 587–596.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khera, A.V.; Chaffin, M.; Aragam, K.G.; Haas, M.E.; Roselli, C.; Choi, S.H.; Natarajan, P.; Lander, E.S.; Lubitz, S.A.; Ellinor, P.T.; et al. Genome-wide polygenic scores for common diseases identify individuals with risk equivalent to monogenic mutations. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Kovacs, P.; Guiu-Jurado, E. Genetics of Obesity in East Asians. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 575049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Kovacs, P.; Guiu-Jurado, E. Genetics of Body Fat Distribution: Comparative Analyses in Populations with European, Asian and African Ancestries. Genes 2021, 12, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heid, I.M.; Jackson, A.U.; Randall, J.C.; Winkler, T.W.; Qi, L.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Thorleifsson, G.; Zillikens, M.C.; Speliotes, E.K.; Mägi, R.; et al. Meta-analysis identifies 13 new loci associated with waist-hip ratio and reveals sexual dimorphism in the genetic basis of fat distribution. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Paré, G.; Parker, A.N.; Zee, R.Y.; Miletich, J.P.; Chasman, D.I. Polymorphism in the CETP Gene Region, HDL Cholesterol, and Risk of Future Myocardial Infarction. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shungin, D.; Winkler, T.W.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; Ferreira, T.; Locke, A.E.; Mägi, R.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Pers, T.H.; Fischer, K.; Justice, A.E.; et al. New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution. Nature 2015, 518, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Day, F.R.; Gustafsson, S.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Na, J.; Bataille, V.; Cousminer, D.L.; Dastani, Z.; Drong, A.W.; Esko, T.; et al. New loci for body fat percentage reveal link between adiposity and cardiometabolic disease risk. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, A.K.; Hivert, M.-F.; Scott, R.A.; Grimsby, J.L.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Chen, H.; Rybin, D.; Liu, C.-T.; Bielak, L.F.; Pro-kopenko, I.; et al. A genome-wide approach accounting for body mass index identifies genetic variants influencing fasting glycemic traits and insulin resistance. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depetris, R.S.; Hu, J.; Gimpelevich, I.; Holt, L.; Daly, R.; Hubbard, S.R. Structural Basis for Inhibition of the Insulin Receptor by the Adaptor Protein Grb14. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béréziat, V.; Kasus-Jacobi, A.; Perdereau, D.; Cariou, B.; Girard, J.; Burnol, A.-F. Inhibition of Insulin Receptor Catalytic Activity by the Molecular Adapter Grb14. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4845–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popineau, L.; Morzyglod, L.; Carré, N.; Caüzac, M.; Bossard, P.; Prip-Buus, C.; Lenoir, V.; Ragazzon, B.; Fauveau, V.; Robert, L.; et al. Novel Grb14-Mediated Cross Talk between Insulin and p62/Nrf2 Pathways Regulates Liver Lipogenesis and Selective Insulin Resistance. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 2168–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, N.; Caüzac, M.; Girard, J.; Burnol, A.-F. Dual Effect of the Adapter Growth Factor Receptor-Bound Protein 14 (Grb14) on Insulin Action in Primary Hepatocytes. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Carroll, E.A.; Gerrelli, D.; Gasca, S.; Berg, E.; Beier, D.R.; Copp, A.; Klingensmith, J. Cordon-bleu is a conserved gene involved in neural tube formation. Dev. Biol. 2003, 262, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, Y.; Choi, S.-Y.; Park, G.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, A.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.-M.; et al. Cobll1 is linked to drug resistance and blastic transformation in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plešingerová, H.; Janovská, P.; Mishra, A.; Smyčková, L.; Poppová, L.; Libra, A.; Plevová, K.; Ovesná, P.; Radová, L.; Doubek, M.; et al. Expression of COBLL1 encoding novel ROR1 binding partner is robust predictor of survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2017, 103, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Shi, X.; Warren, C.R.; Lotta, L.A.; Friesen, M.; Meissner, T.B.; Langenberg, C.; Wabitsch, M.; Wareham, N.; et al. Functional Screening of Candidate Causal Genes for Insulin Resistance in Human Preadipocytes and Adipocytes. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 330–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleinitz, D.; Klöting, N.; Lindgren, C.; Breitfeld, J.; Dietrich, A.; Schön, M.R.; Lohmann, T.; Dreßler, M.; Stumvoll, M.; McCarthy, M.; et al. Fat depot-specific mRNA expression of novel loci associated with waist-hip ratio. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 38, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.D. Role of Body Fat Distribution and the Metabolic Complications of Obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, s57–s63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischon, T.; Boeing, H.; Hoffmann, K.; Bergmann, M.; Schulze, M.B.; Overvad, K.; Van Der Schouw, Y.T.; Spencer, E.; Moons, K.G.M.; Tjønneland, A.; et al. General and Abdominal Adiposity and Risk of Death in Europe. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, S.; Hawken, S.; Ôunpuu, S.; Bautista, L.; Franzosi, M.G.; Commerford, P.; Lang, C.C.; Rumboldt, Z.; Onen, C.L.; Lisheng, L.; et al. Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27 000 participants from 52 countries: A case-control study. Lancet 2005, 366, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Comparison of abdominal adiposity and overall obesity in predicting risk of type 2 diabetes among men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, M.; Bredella, M.A.; Tsai, P.; Mendes, N.; Miller, K.K.; Klibanski, A. Lower growth hormone and higher cortisol are associated with greater visceral adiposity, intramyocellular lipids, and insulin resistance in overweight girls. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2008, 295, E385–E392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karastergiou, K.; Fried, S.K. Multiple Adipose Depots Increase Cardiovascular Risk via Local and Systemic Effects. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2013, 15, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, G.J.; Lyons, R.J.; Crew, A.J.; Jensen, T.E.; Molero, J.C.; Mitchell, C.J.; Biden, T.J.; Ormandy, C.J.; James, D.E.; Daly, R.J. Improved glucose homeostasis and enhanced insulin signalling in Grb14-deficient mice. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, L.J.; Lyons, R.J.; Ryan, A.S.; Beale, S.M.; Ward, A.; Cooney, G.J.; Daly, R.J. Dual Ablation of Grb10 and Grb14 in Mice Reveals Their Combined Role in Regulation of Insulin Signaling and Glucose Homeostasis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 1406–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-J.; Berggren, J.R.; Hulver, M.W.; Houmard, J.A.; Hoffman, E.P. GRB14, GPD1, and GDF8 as potential network collaborators in weight loss-induced improvements in insulin action in human skeletal muscle. Physiol. Genom. 2006, 27, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpeläinen, T.O.; Carli, J.F.M.; Skowronski, A.A.; Sun, Q.; Kriebel, J.; Feitosa, M.F.; Hedman, Å.K.; Drong, A.W.; Hayes, J.E.; Zhao, J.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis uncovers novel loci influencing circulating leptin levels. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teslovich, T.M.; Musunuru, K.; Smith, A.V.; Edmondson, A.C.; Stylianou, I.M.; Koseki, M.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Ripatti, S.; Chasman, D.I.; Willer, C.J.; et al. Biological, clinical and population relevance of 95 loci for blood lipids. Nature 2010, 466, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagou, V.; Mägi, R.; Hottenga, J.-J.; Grallert, H.; Perry, J.R.B.; Bouatia-Naji, N.; Marullo, L.; Rybin, D.; Jansen, R.; Min, J.L.; et al. Sex-dimorphic genetic effects and novel loci for fasting glucose and insulin variability. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.; Taliun, D.; Thurner, M.; Robertson, N.R.; Torres, J.M.; Rayner, N.W.; Payne, A.J.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Scott, R.A.; Grarup, N.; et al. Fine-mapping type 2 diabetes loci to single-variant resolution using high-density imputation and islet-specific epigenome maps. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- STRING CONSORTIUM. 2021. Available online: https://string-db.org/cgi/network?taskId=bgS30COMyNqT&sessionId=bkY8toNhfF54 (accessed on 16 September 2021).
- Klöting, N.; Fasshauer, M.; Dietrich, A.; Kovacs, P.; Schön, M.R.; Kern, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M. Insulin-sensitive obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocr. Metab. 2010, 299, E506–E515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M.; Unger, R.; Rassoul, F.; Richter, V.; Paschke, R. Relation between glycaemic control, hyperinsulinaemia and plasma concentrations of soluble adhesion molecules in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or Type II diabetes. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37 (Suppl. S1), S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardinoglu, A.; Heiker, J.T.; Gärtner, D.; Björnson, E.; Schön, M.R.; Flehmig, G.; Klöting, N.; Krohn, K.; Fasshauer, M.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Extensive weight loss reveals distinct gene expression changes in human subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesta, S.; Blüher, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Norris, A.W.; Berndt, J.; Kralisch, S.; Boucher, J.; Lewis, C.; Kahn, C.R. Evidence for a role of developmental genes in the origin of obesity and body fat distribution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6676–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Fasshauer, M.; Ito, M.; Lowell, B.B.; Benito, M.; Kahn, C.R. β3-Adrenergic Stimulation Differentially Inhibits Insulin Signaling and Decreases Insulin-induced Glucose Uptake in Brown Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 34795–34802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovsan, J.; Osnis, A.; Maissel, A.; Mazor, L.; Tarnovscki, T.; Hollander, L.; Ovadia, S.; Meier, B.; Klein, J.; Bashan, N.; et al. Depot-specific adipocyte cell lines reveal differential drug-induced responses of white adipocytes—Relevance for partial lipodystrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2009, 296, E315–E322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genetic Variants | NGT | T2D | MAF NGT/T2D | p-Value (Add Model) adj. for Age, Sex, BMI (OR [95% CI]) | (a) p-Value (Add Model) adj. for Age, Sex, BMI (OR [95% CI]) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs6738627 (G/A) | |||||
| GG | 215 (36.7%) | 176 (38.1%) | 0.4/0.36 | 0.018(1.269 [1.041–1.547]) | 0.005 (1.85 [1.21–2.83]) |
| AG | 270 (46.1%) | 235 (50.9%) | 0.006 (1.78 [1.18–2.68]) | ||
| AA | 101 (17.2%) | 51 (11%) | |||
| rs10195252 (T/C) | |||||
| CC | 132 (19%) | 94 (17%) | 0.43/0.42 | 0.339 (1.09 [0.914–1.3]) | |
| TC | 334 (47.8%) | 285 (52%) | |||
| TT | 233 (33.2) | 174 (31%) | |||
| BMI < 30 kg/m2 | BMI 30~40 kg/m2 | BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 256) | (N = 354) | (N = 2250) | |
| Age (years) | 61 ± 15 | 50 ± 13 | 46 ± 12 |
| Women/Men (n) | 134/122 | 248/106 | 1585/665 |
| T2D (n) | 36 | 118 | 880 |
| Body weight (kg) | 72 ± 11.6 | 104.4 ±14.7 | 146.7 ± 27.4 |
| Height (m) | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.0 ± 2.8 | 36.2 ± 2.8 | 50.6 ± 7.8 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 89.7 ± 17.9 | 116.6 ± 14.8 | 142.5 ± 17.4 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 94.6 ± 12 | 118.3 ± 12.9 | 148.8 ± 17 |
| WHR | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1 ± 0.1 | 1 ± 0.1 |
| Body fat (%) | 23.5 ± 5.3 | 38 ± 8.8 | 48.1 ± 8.4 |
| FPG (mmol/L) | 5.7 ± 1.2 | 6.2 ± 2.6 | 6.6 ± 2.7 |
| FPI (pmol/L) | 56.3 ± 74.8 | 109.3 ± 143 | 153 ± 136.5 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.6 ± 0.6 | 5.9 ± 0.9 | 6.2 ± 1.3 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 29.4 ± 2.4 | 40.1 ± 11.8 | 43.3 ± 15.2 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.2 ± 1 | 5.1 ± 1.2 | 4.9 ± 1.1 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.5 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 3.1 ± 0.9 | 3.3 ± 1 | 3.1 ± 0.9 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 1.7 ± 1.1 | 1.9 ± 1.4 |
| AT COBLL1 mRNA expression n (%) | 19 (3) | 38 (7) | 467 (90) |
| AT GRB14 mRNA expression n (%) | 18 (3) | 44 (8) | 498 (89) |
| rs10195252 (T > C) carrier n (%) | 131 (10) | 146 (11) | 1106 (79) |
| rs6738627 (G > A) carrier n (%) | 133 (13) | 123 (12) | 870 (75) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Förster, F.; Gutsmann, B.; Moulla, Y.; Stroh, C.; Dietrich, A.; Schön, M.R.; Gärtner, D.; Lohmann, T.; Dressler, M.; et al. Metabolic Effects of the Waist-To-Hip Ratio Associated Locus GRB14/COBLL1 Are Related to GRB14 Expression in Adipose Tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158558
Sun C, Förster F, Gutsmann B, Moulla Y, Stroh C, Dietrich A, Schön MR, Gärtner D, Lohmann T, Dressler M, et al. Metabolic Effects of the Waist-To-Hip Ratio Associated Locus GRB14/COBLL1 Are Related to GRB14 Expression in Adipose Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158558
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Chang, Franz Förster, Beate Gutsmann, Yusef Moulla, Christine Stroh, Arne Dietrich, Michael R. Schön, Daniel Gärtner, Tobias Lohmann, Miriam Dressler, and et al. 2022. "Metabolic Effects of the Waist-To-Hip Ratio Associated Locus GRB14/COBLL1 Are Related to GRB14 Expression in Adipose Tissue" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158558
APA StyleSun, C., Förster, F., Gutsmann, B., Moulla, Y., Stroh, C., Dietrich, A., Schön, M. R., Gärtner, D., Lohmann, T., Dressler, M., Stumvoll, M., Blüher, M., Kovacs, P., Breitfeld, J., & Guiu-Jurado, E. (2022). Metabolic Effects of the Waist-To-Hip Ratio Associated Locus GRB14/COBLL1 Are Related to GRB14 Expression in Adipose Tissue. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158558