Inhibition of Ubiquitin-Specific Protease-13 Improves Behavioral Performance in Alpha-Synuclein Expressing Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
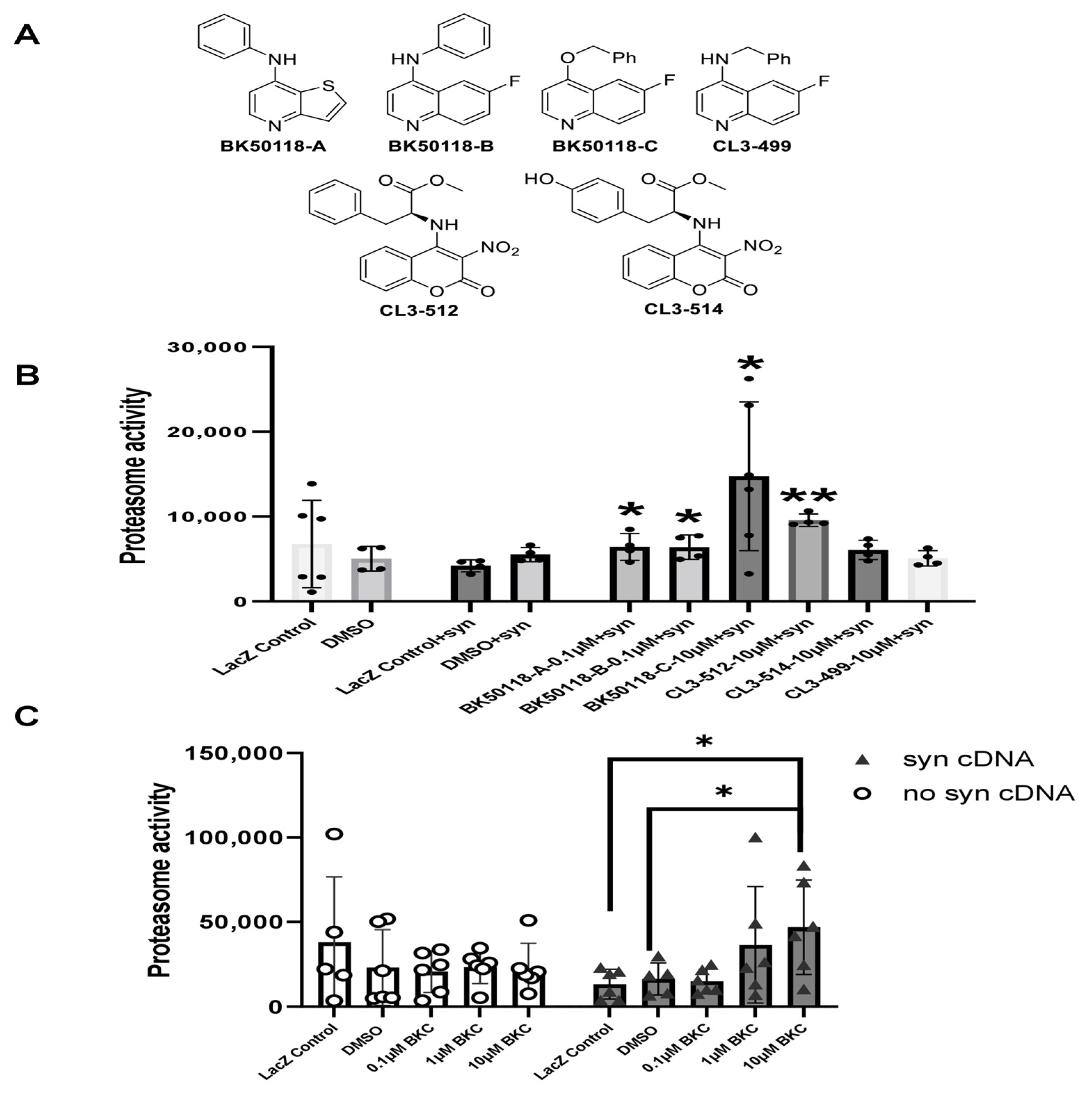
2.1. BK50118-C Increases Proteasome Activity and Reduces Alpha-Synculein
2.2. Determination of a Maximal Tolerated Dose and Tissue Toxicity
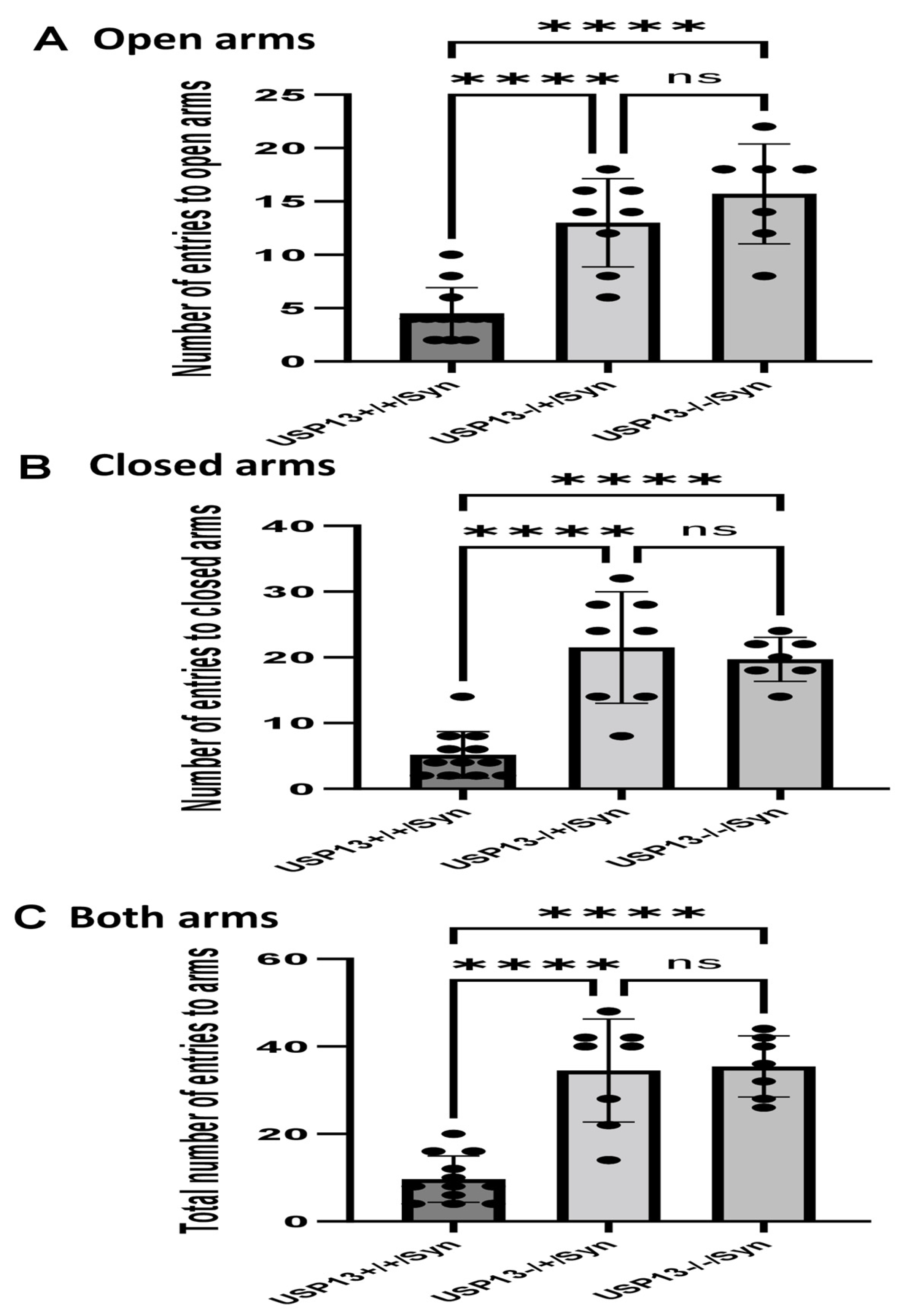
2.3. Lentiviral Expression of Human Alpha-Synuclein Induces Motor and Behavioral Symptoms in USP13+/+ but Not in USP13+/− or USP13−/− Mice
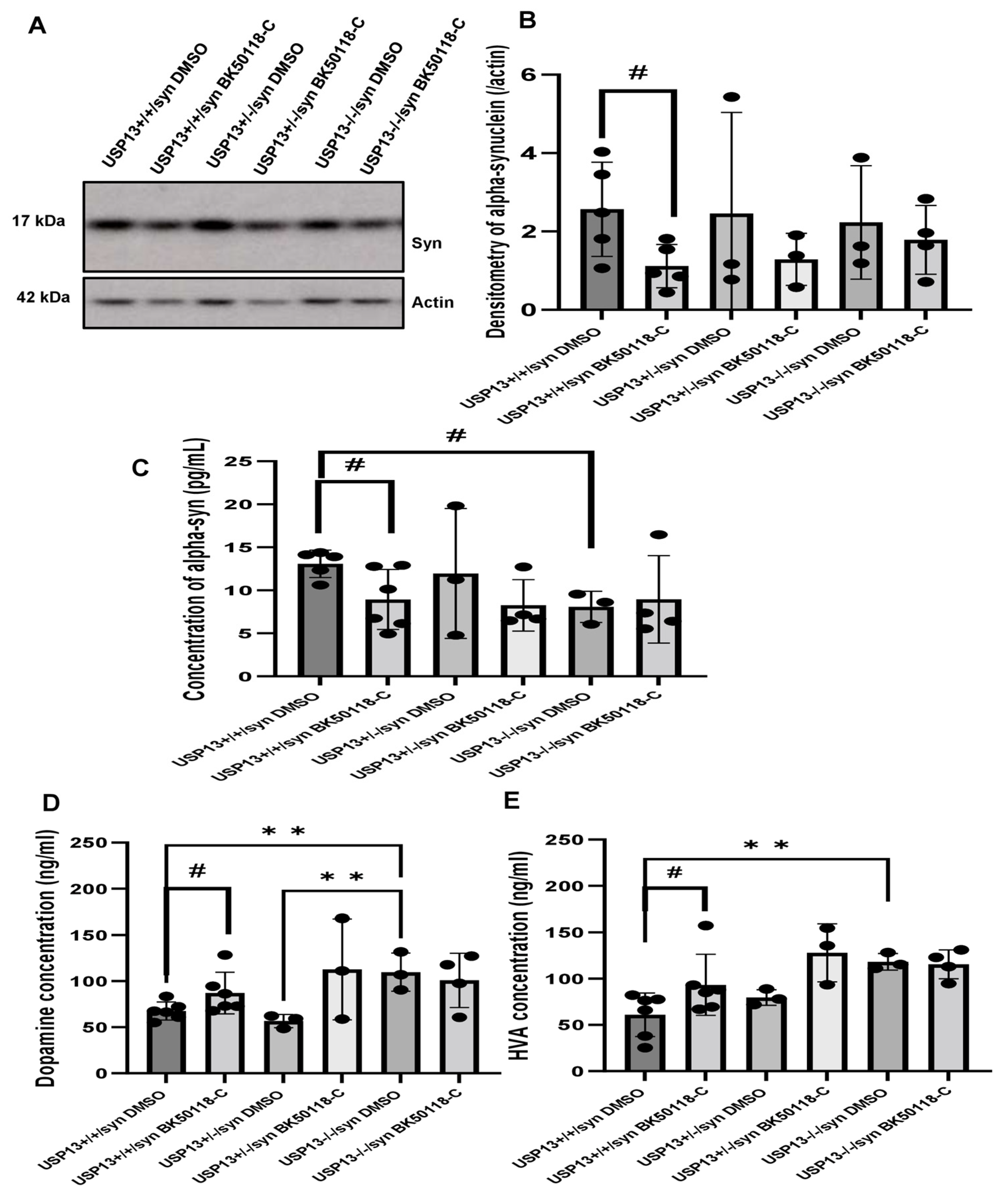
2.4. BK50118-C Lowers Alpha-Synuclein in USP13+/+ but Not in USP13+/− or USP13−/− Mice
2.5. BK50118-C Protects against Dopamine Loss in USP13+/+ but Not in USP13+/− or USP13−/− Mice
2.6. BK50118-C Lowers the Level of Ubiquitinited Alpha-Synuclein and Increases Autophagy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Structures and Synthesis of USP13 Inhibitors
4.2. Cell Lines, Transfection, and Treatment
4.3. Proteasome Assay
4.4. Caspase-3 Activity Assay
4.5. Determination of Maximal Tolerated Dose and Tissue Toxicity
4.6. Transgenic Mice, Surgery and Treatment
4.7. Behavior Tests
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.10. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.11. Dopamine and Homovanillic Acid (HVA) Measurement
4.12. Statistical and Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Hebron, M.; Shi, W.; Lonskaya, I.; Moussa, C.E. Ubiquitin specific protease-13 independently regulates parkin ubiquitination and alpha-synuclein clearance in alpha-synucleinopathies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Balaraman, K.; Lynch, C.C.; Hebron, M.; Wolf, C.; Moussa, C. Novel Ubiquitin Specific Protease-13 Inhibitors Alleviate Neurodegenerative Pathology. Metabolites 2021, 11, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.E.; Hallett, P.J.; Moens, T.; Smith, G.; Mangano, E.; Kim, H.T.; Goldberg, A.L.; Liu, J.L.; Isacson, O.; Tofaris, G.K. Enhanced ubiquitin-dependent degradation by Nedd4 protects against alpha-synuclein accumulation and toxicity in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 64, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Gutierrez, G.J.; Ronai, Z.A. Ubiquitin-recognition protein Ufd1 couples the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response to cell cycle control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9119–9124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Hebron, M.L.; Mulki, S.; Wang, C.; Lekah, E.; Ferrante, D.; Shi, W.; Kurd-Misto, B.; Moussa, C. Ubiquitin Specific Protease 13 Regulates Tau Accumulation and Clearance in Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 72, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Jin, S.; Wu, Y.; Xian, H.; Tian, S.; Liu, D.A.; Guo, Z.; Cui, J. Auto-ubiquitination of NEDD4-1 Recruits USP13 to Facilitate Autophagy through Deubiquitinating VPS34. Cell Rep 2020, 30, 2807–2819 e2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, W.; Jin, S.; Cui, J. The NEDD4-USP13 axis facilitates autophagy via deubiquitinating PIK3C3. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1150–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, S.S. Deubiquitinating enzymes--the importance of driving in reverse along the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 590–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clague, M.J.; Urbe, S.; Komander, D. Breaking the chains: Deubiquitylating enzyme specificity begets function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Moussa, C. Regulatory Role of Ubiquitin Specific Protease-13 (USP13) in Misfolded Protein Clearance in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neuroscience 2021, 460, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visanji, N.P.; Brotchie, J.M.; Kalia, L.V.; Koprich, J.B.; Tandon, A.; Watts, J.C.; Lang, A.E. alpha-Synuclein-Based Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease: Challenges and Opportunities in a New Era. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson-Lewis, V.; Blesa, J.; Przedborski, S. Animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18 (Suppl. S1), S183–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, P.J.; Moussa, C.E. The Relationship between Parkin and Protein Aggregation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Psychiatry 2010, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K. Neuropathological Staging of Brain Pathology in Sporadic Parkinson’s disease: Separating the Wheat from the Chaff. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 7, S73–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hebron, M.L.; Lonskaya, I.; Moussa, C.E. Tyrosine kinase inhibition facilitates autophagic SNCA/alpha-synuclein clearance. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1249–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Q.J.; Han, Y.X.; Shi, Y.J.; Huang, H.Q.; Fang, Z.G.; Hu, Y.H. Universal stress proteins contribute Edwardsiella piscicida adversity resistance and pathogenicity and promote blocking host immune response. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 95, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, C.J.; Zhou, Z.R.; Song, A.X.; Hu, H.Y. Domain analysis reveals that a deubiquitinating enzyme USP13 performs non-activating catalysis for Lys63-linked polyubiquitin. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muzny, D.M.; Scherer, S.E.; Kaul, R.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Sudbrak, R.; Buhay, C.J.; Chen, R.; Cree, A.; Ding, Y. The DNA sequence, annotation and analysis of human chromosome 3. Nature 2006, 440, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegrzynowicz, M.; Bar-On, D.; Calo, L.; Anichtchik, O.; Iovino, M.; Xia, J.; Ryazanov, S.; Leonov, A.; Giese, A.; Dalley, J.W.; et al. Depopulation of dense alpha-synuclein aggregates is associated with rescue of dopamine neuron dysfunction and death in a new Parkinson’s disease model. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 575–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hebron, M.L.; Lonskaya, I.; Moussa, C.E. Nilotinib reverses loss of dopamine neurons and improves motor behavior via autophagic degradation of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease models. Hum. Mol. Genet 2013, 22, 3315–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timms, K.M.; Ansari-Lari, M.A.; Morris, W.; Brown, S.N.; Gibbs, R.A. The genomic organization of Isopeptidase T-3 (ISOT-3), a new member of the ubiquitin specific protease family (UBP). Gene 1998, 217, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Qi, S.; Mi, Y.; Liu, D.; Tian, Q. Identification of candidate substrates of ubiquitin-specific protease 13 using 2D-DIGE. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fraile, J.M.; Quesada, V.; Rodriguez, D.; Freije, J.M.; Lopez-Otin, C. Deubiquitinases in cancer: New functions and therapeutic options. Oncogene 2012, 31, 2373–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexopoulou, Z.; Lang, J.; Perrett, R.M.; Elschami, M.; Hurry, M.E.; Kim, H.T.; Mazaraki, D.; Szabo, A.; Kessler, B.M.; Goldberg, A.L.; et al. Deubiquitinase Usp8 regulates alpha-synuclein clearance and modifies its toxicity in Lewy body disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4688–E4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todi, S.V.; Scaglione, K.M.; Blount, J.R.; Basrur, V.; Conlon, K.P.; Pastore, A.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.; Paulson, H.L. Activity and cellular functions of the deubiquitinating enzyme and polyglutamine disease protein ataxin-3 are regulated by ubiquitination at lysine 117. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 39303–39313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kristensen, L.V.; Oppermann, F.S.; Rauen, M.J.; Fog, K.; Schmidt, T.; Schmidt, J.; Harmuth, T.; Hartmann-Petersen, R.; Thirstrup, K. Mass spectrometry analyses of normal and polyglutamine expanded ataxin-3 reveal novel interaction partners involved in mitochondrial function. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 112, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.T.; Zheng, X.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Gao, Y.G.; Song, A.X.; van der Goot, F.G.; Hu, H.Y. Cytoplasmic Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 19 (USP19) Modulates Aggregation of Polyglutamine-Expanded Ataxin-3 and Huntingtin through the HSP90 Chaperone. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.; Fang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, Q.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Balajee, A.S.; Zhao, Y. USP33 deubiquitinates PRKN/parkin and antagonizes its role in mitophagy. Autophagy 2020, 16, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyano, F.; Okatsu, K.; Kosako, H.; Tamura, Y.; Go, E.; Kimura, M.; Kimura, Y.; Tsuchiya, H.; Yoshihara, H.; Hirokawa, T.; et al. Ubiquitin is phosphorylated by PINK1 to activate parkin. Nature 2014, 510, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, C.; Ruiz-Hincapie, P.; Ruiz, L.M. The Interplay among PINK1/PARKIN/Dj-1 Network during Mitochondrial Quality Control in Cancer Biology: Protein Interaction Analysis. Cells 2018, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Choo, Y.S.; Ma, H.; Tang, C.; Xia, K.; Jiang, W.; Ronai, Z.; Zhuang, X.; et al. Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1 form a ubiquitin E3 ligase complex promoting unfolded protein degradation. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Xia, H.; Kim, M.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Norberg, H.V.; Zhang, T.; Furuya, T.; et al. Beclin1 controls the levels of p53 by regulating the deubiquitination activity of USP10 and USP13. Cell 2011, 147, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lonskaya, I.; Hebron, M.L.; Desforges, N.M.; Schachter, J.B.; Moussa, C.E. Nilotinib-induced autophagic changes increase endogenous parkin level and ubiquitination, leading to amyloid clearance. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebron, M.L.; Lonskaya, I.; Sharpe, K.; Weerasinghe, P.P.; Algarzae, N.K.; Shekoyan, A.R.; Moussa, C.E. Parkin ubiquitinates Tar-DNA binding protein-43 (TDP-43) and promotes its cytosolic accumulation via interaction with histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 4103–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacomin, A.C.; Taillebourg, E.; Fauvarque, M.O. Deubiquitinating Enzymes Related to Autophagy: New Therapeutic Opportunities? Cells 2018, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Balaraman, K.; Lynch, C.C.; Hebron, M.; Shah, P.K.; Hu, S.; Stevenson, M.; Wolf, C.; Moussa, C. Inhibition of Ubiquitin-Specific Protease-13 Improves Behavioral Performance in Alpha-Synuclein Expressing Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158131
Liu X, Balaraman K, Lynch CC, Hebron M, Shah PK, Hu S, Stevenson M, Wolf C, Moussa C. Inhibition of Ubiquitin-Specific Protease-13 Improves Behavioral Performance in Alpha-Synuclein Expressing Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(15):8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158131
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoguang, Kaluvu Balaraman, Ciarán C. Lynch, Michaeline Hebron, Priya Ketankumar Shah, Shicheng Hu, Max Stevenson, Christian Wolf, and Charbel Moussa. 2022. "Inhibition of Ubiquitin-Specific Protease-13 Improves Behavioral Performance in Alpha-Synuclein Expressing Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 15: 8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158131
APA StyleLiu, X., Balaraman, K., Lynch, C. C., Hebron, M., Shah, P. K., Hu, S., Stevenson, M., Wolf, C., & Moussa, C. (2022). Inhibition of Ubiquitin-Specific Protease-13 Improves Behavioral Performance in Alpha-Synuclein Expressing Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15), 8131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158131





