Rag1 and Rag2 Gene Expressions Identify Lymphopoietic Tissues in Larvae of Rice-Field Eel (Monopterus albus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
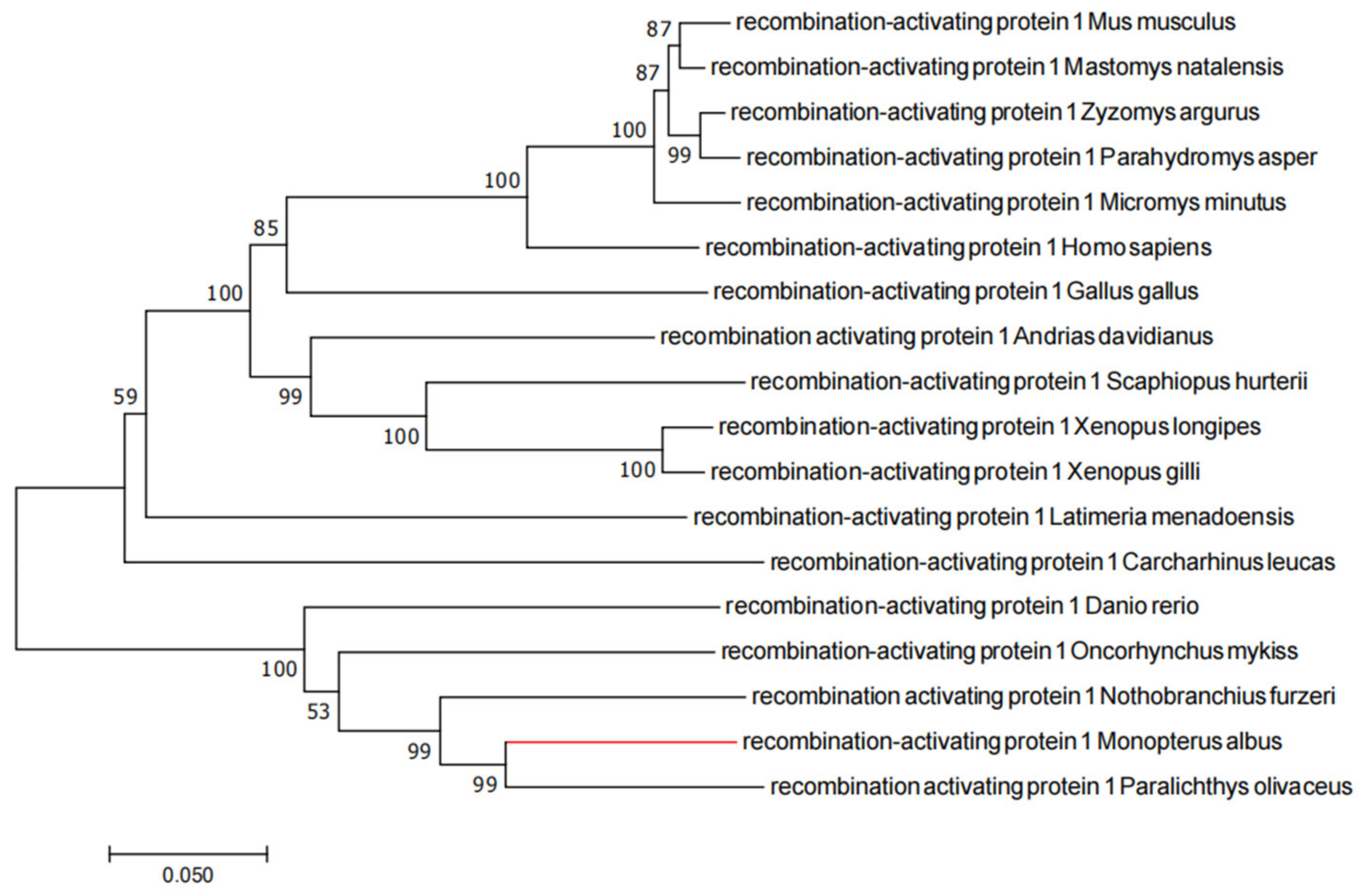
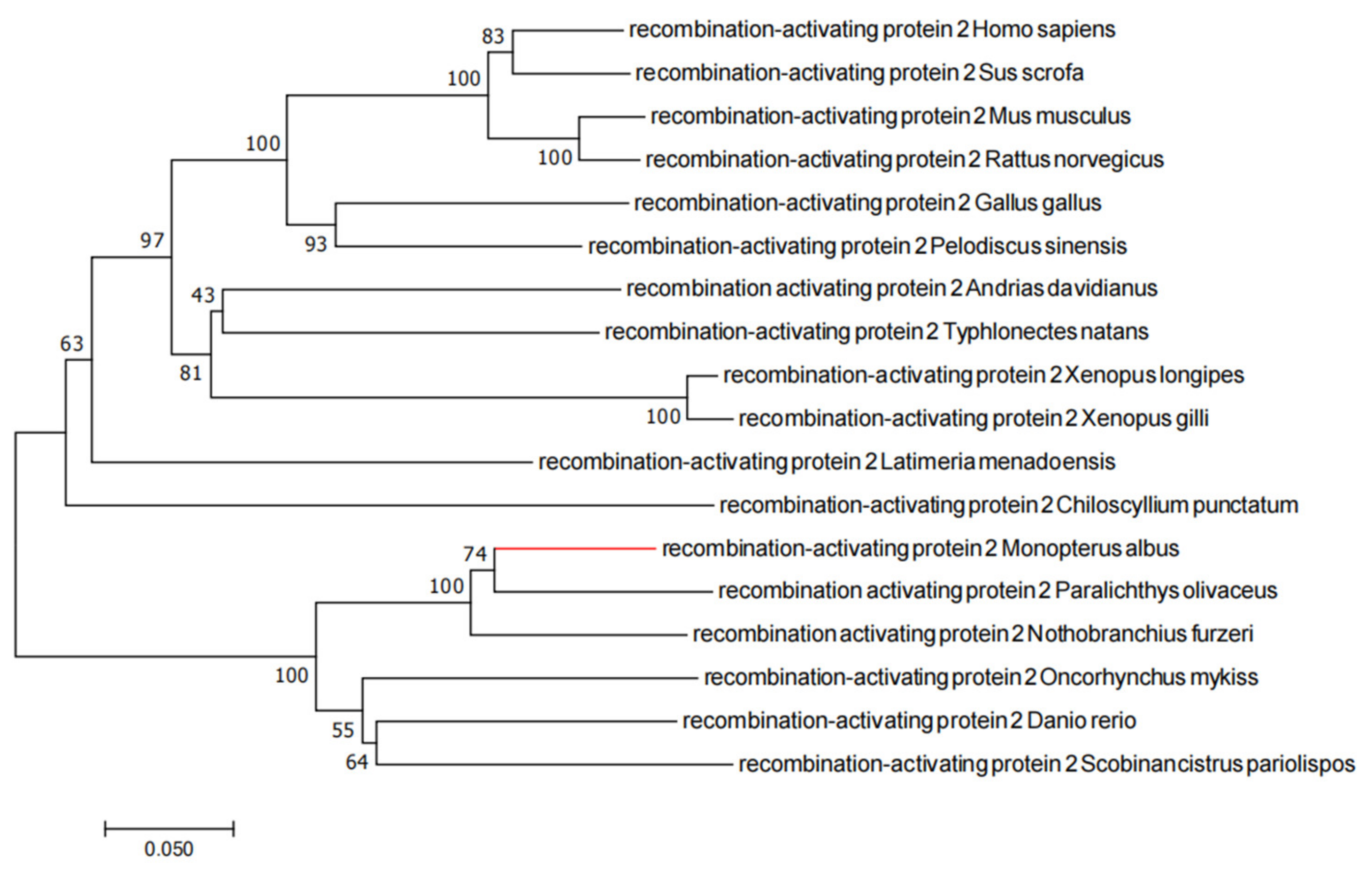
2.1. Evolutionary Tree Analysis
2.2. Rag1 and Rag2 mRNA Expressions
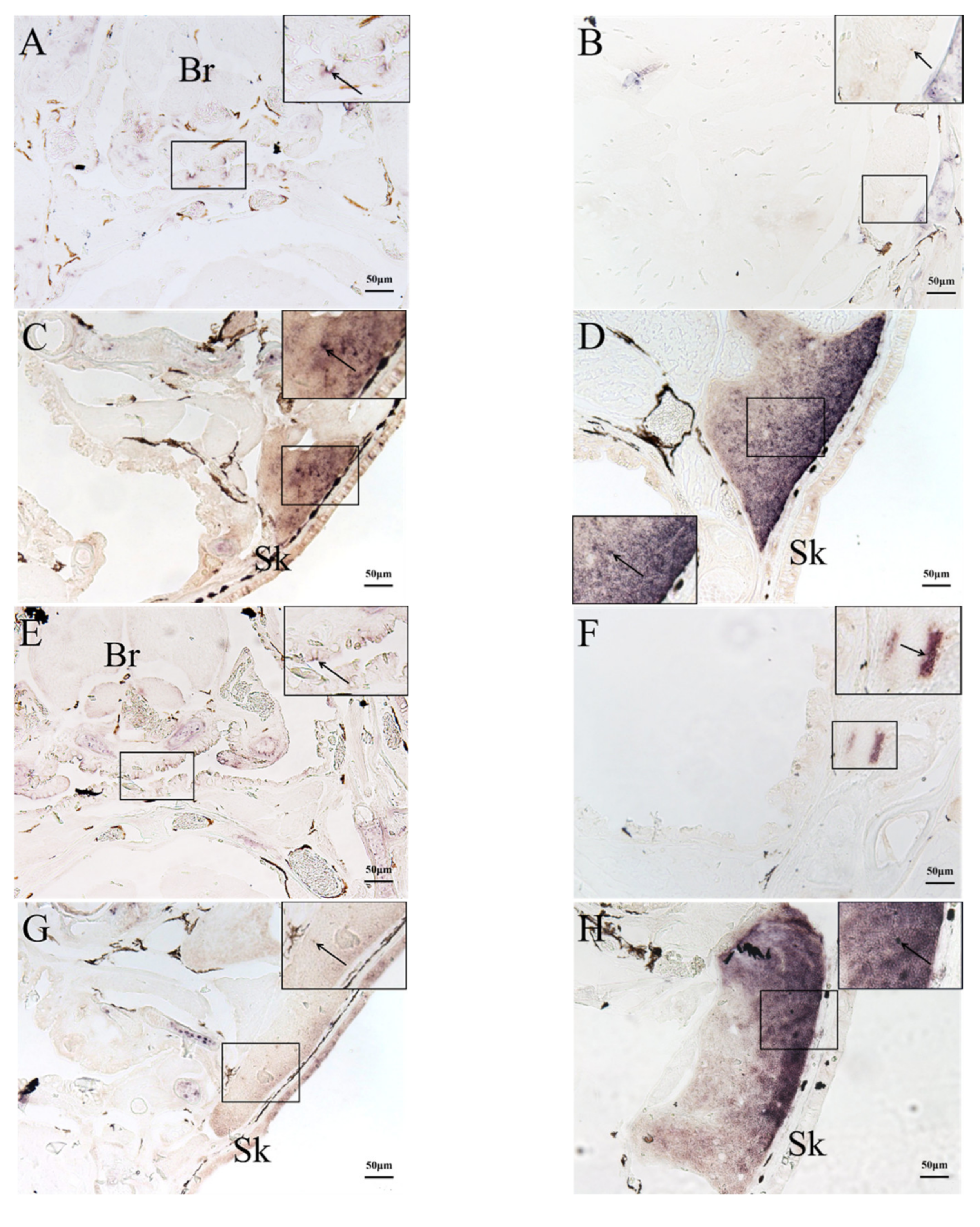
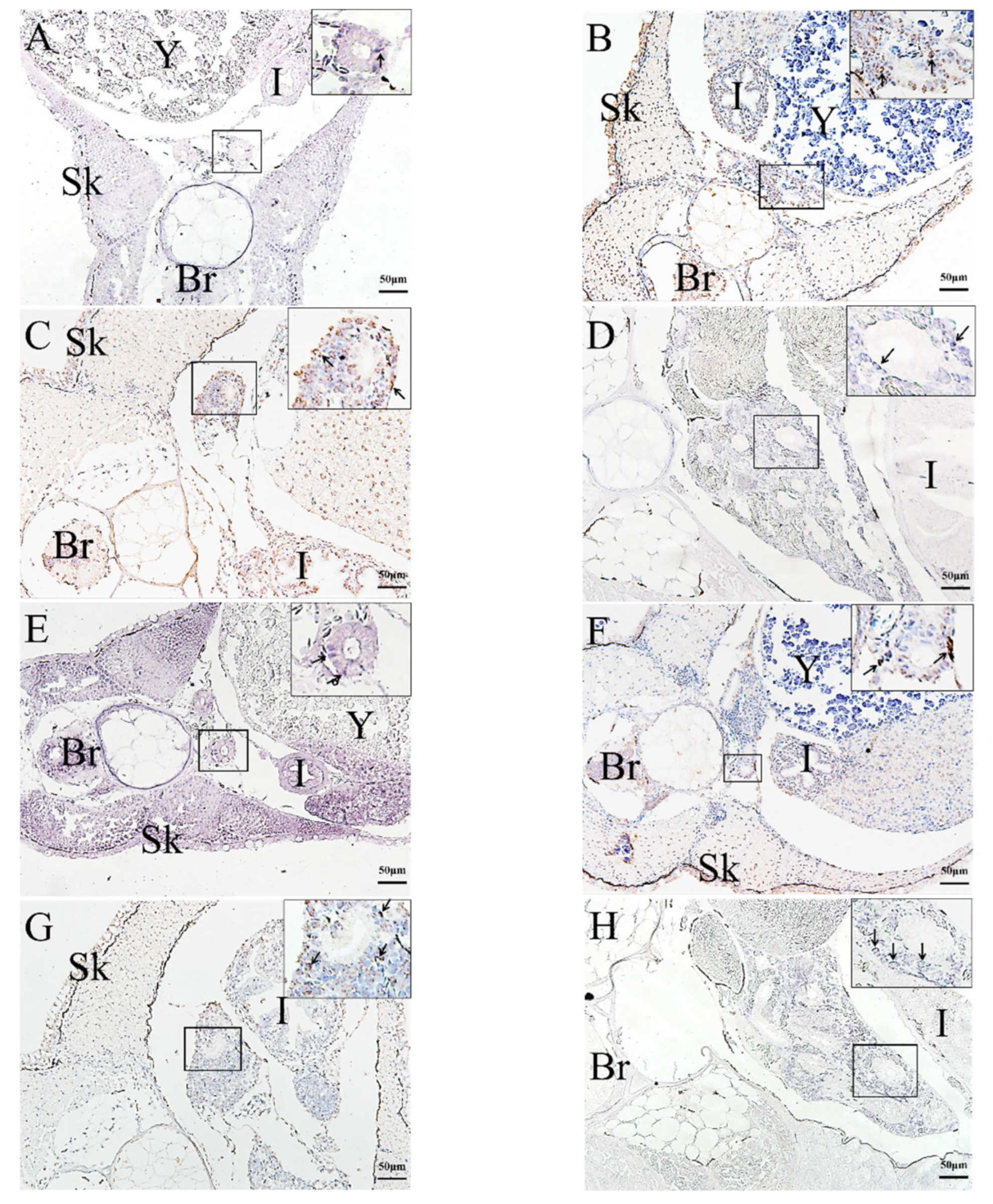
2.3. In Situ Hybridization (ISH) Detection of Rag1 and Rag2 Transcriptions
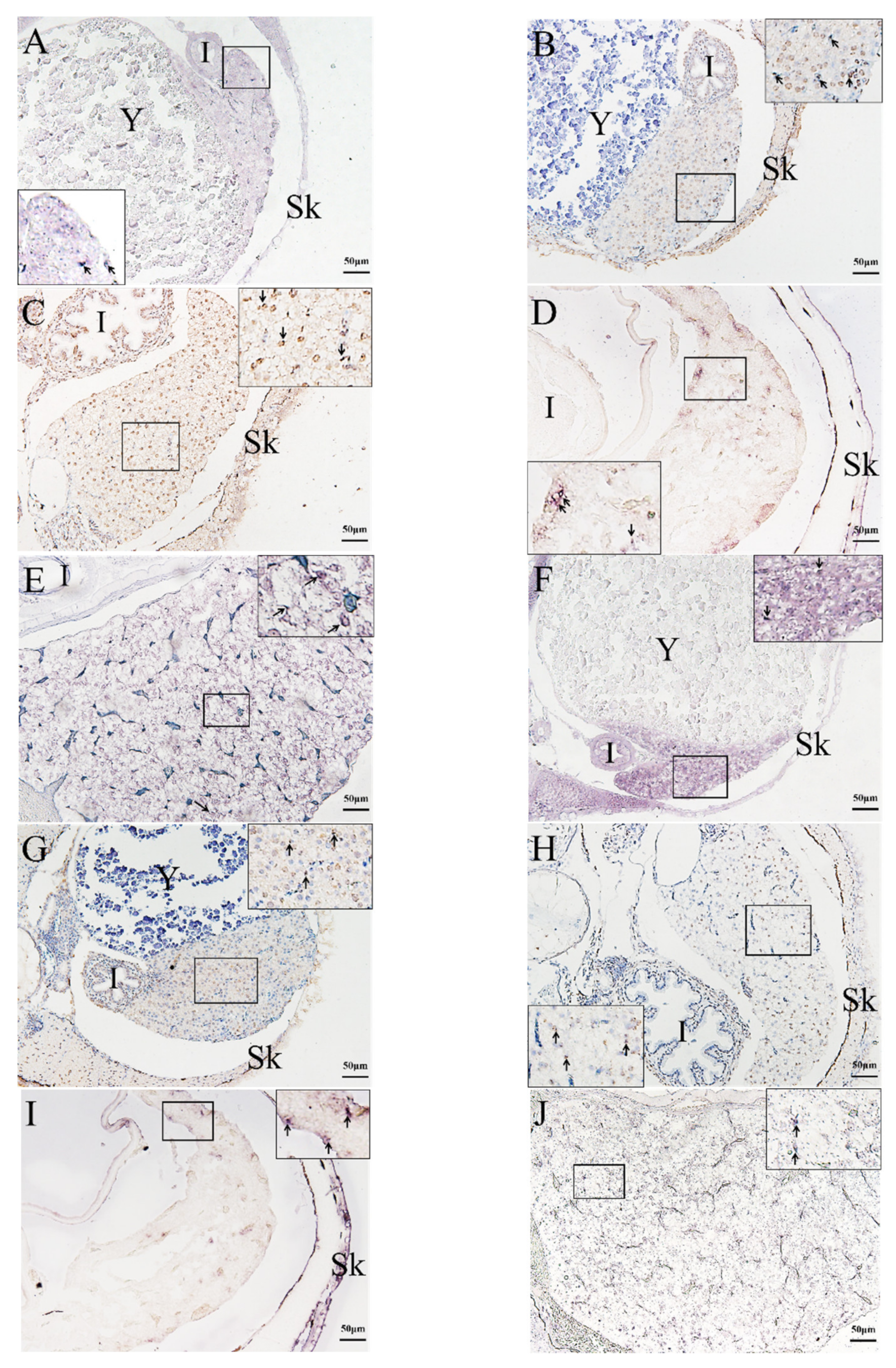
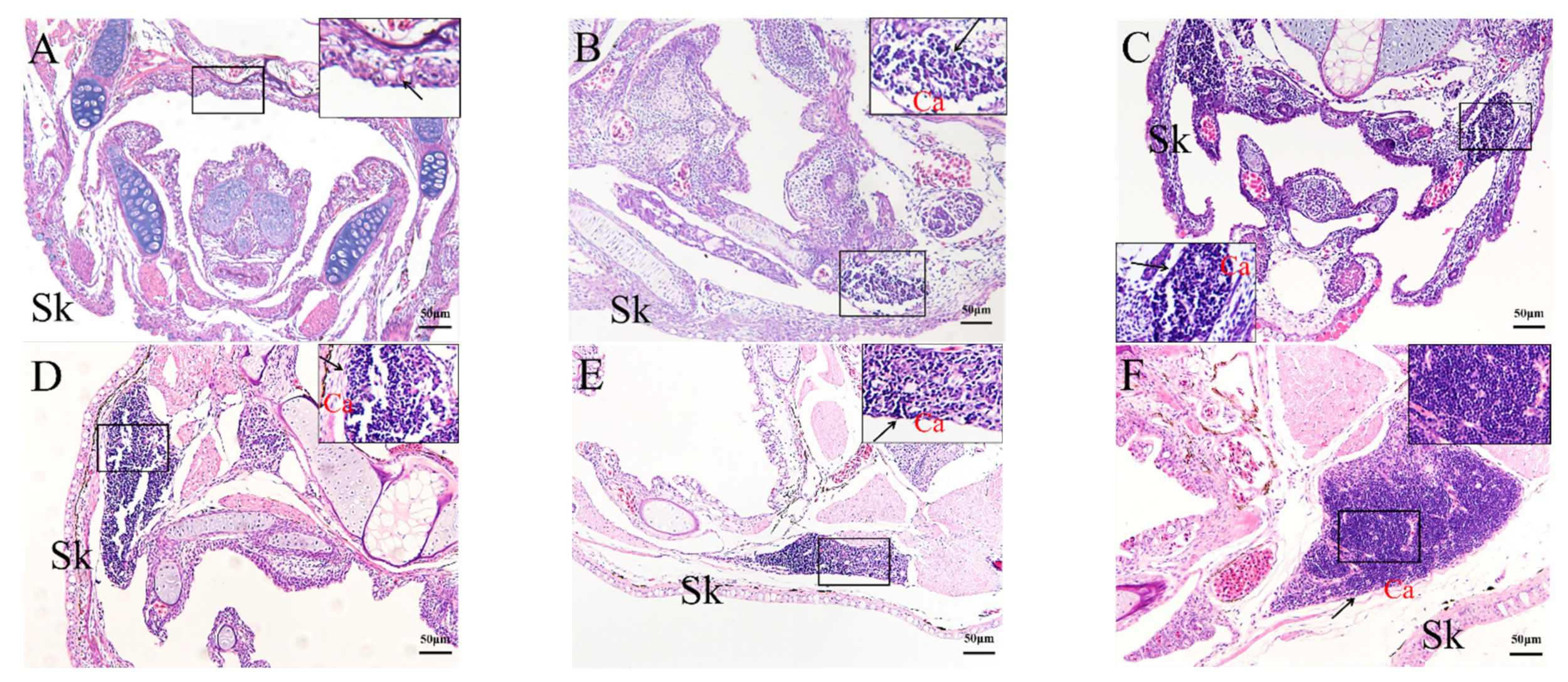
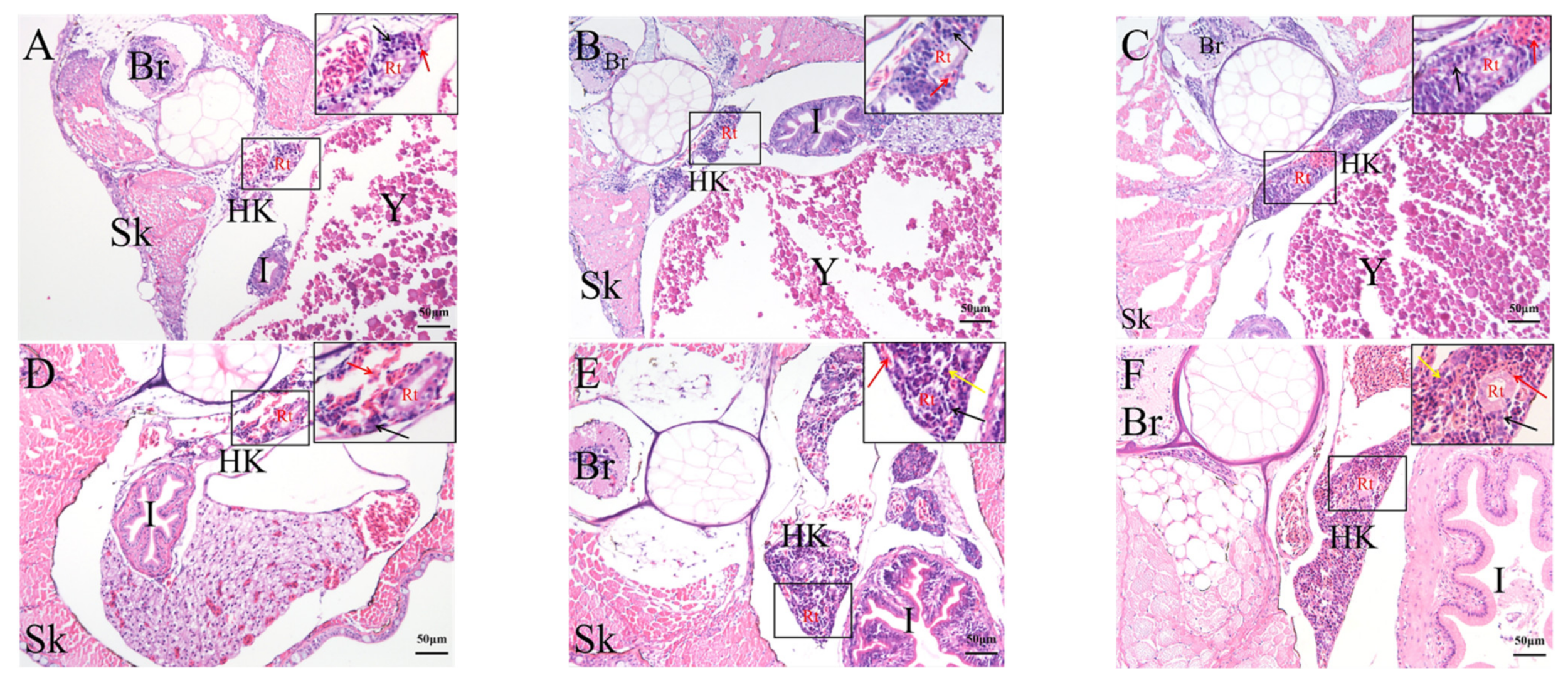
2.4. Histological Analysis of the Genesis of Lymphopoiesis Tissues
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Extraction of RNA and Synthesis of cDNA
4.3. Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
4.4. qRT-PCR Analysis
4.5. In Situ Hybridization
4.6. HE Staining and Histology
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Q.B.; Wu, H.D.; Wu, H.X.; Yang, F.Q. The embryonic and postembryonic development of Monopterus albus. J. Fish. China 2003, 27, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.Y. Analysis on Key Technologies of Monopterus albus breeding. New Agric. 2021, 6, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.Q.; He, L. Risk analysis on quality and safety of rice-field eel, Monopterus albus products. Chin. Fish. Qual. Stand. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.F. Advances in biology of Monopterus albus. Chin. J. Fish. 2001, 14, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.Q.; Chen, F.; Li, D.X.; Liu, B. The Embryonic Development and Fingerling Culture of Eel, Monopterus albus. J. Hubei Agric. Coll. 1999, 19, 149–153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.X.; Dong, Y.K. Studies on gonad development and differentiation of rice-field eel (Monopterus albus). Reserv. Fish. 1994, 5, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Z.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, D.Y.; Xie, D.Q.; Tian, X.L.; Wan, Q.F. Pathogenic Biology and Immunology; Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.A.; Sun, B.J.; Nie, P. Immune tissues and cells of fish: A review. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2000, 24, 648–654. [Google Scholar]
- Dalmo, R.A.; Ngebrigtsen, K.; Bøgwald, J. Non-specific defence mechanisms in fish, with particular reference to the reticuloendothelial system (RES). J. Fish Dis. 1997, 20, 241–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Li, X.; Ji, G.D. On the Ontogeny of the Fish Immune System. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2007, 37, 557–562. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.Z.; He, T.; Li, J.; Gao, T. Ontogeny of the immune system in rock bream Oplegnathus fasciatus. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrøder, M.B.; Villena, A.J.; Jørgensen, T.Ø. Ontogeny of lymphoid organs and immunoglobulin producing cells in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1998, 22, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Aquatic Animal Histology and Embryology; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Market, E.; Papavasiliou, F.N. V(D)J recombination and the evolution of the adaptive immune system. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patricia, G.; Lisa, A.S. Recombination activating gene1 (Rag1) in zebrafish and shark. Immunogenetic 1995, 41, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.D.; Kaattari, S.L. The recombination activating gene 2 (RAG2) of the rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Immunogenetic 1996, 44, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wen, S.H.; Mao, M.G.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Jiang, J.L. Rag1 and IgM detection in Pacificcod (Gadus microcephalus) using real-time PCR. J. Fish. China 2015, 39, 475–484. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, M.G.; Lei, J.L.; Jiang, Z.Q. Functional mechanisms of RAGs and its research progress in fish development. J. Fish. Sci. China 2013, 20, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.J.; Qin, X.Y. The role of RAG proteins in V (D) J recombination. Lett. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, C.E.; Cherry, J.J.; Steiner, L.A. Characterization and expression of the recombination activating genes (rag1 and rag2) of zebrafish. Immunogenetic 1997, 45, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, P.; Olesen, C.E.; Steiner, L.A. Characterization and expression of recombination activating genes (rag-1 and rag-2) in Xenopus laevis. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 3100–3110. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, C.; Charlemagne, J.; Fellah, J.S. Rag expression is restricted to the first year of life in the Mexican axolotl. Immunogenetic 2000, 51, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.D.; Kaattari, S.L. The recombination activation gene 1 (rag1) of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Cloning, expression, and phylogenetic analysis. Immunogenetic 1995, 42, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttenhuis, H.B.; Huising, M.O.; Van Der Meulen, T.; Van Oosterhoud, C.N.; Sánchez, N.A.; Taverne-Thiele, A.J.; Stroband, H.W.; Rombout, J.H. Rag expression identifies B and T cell lymphopoietic tissues during the development of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2005, 29, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.D.; Zapata, A.G. Lymphocyte development in fish and amphibians. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 166, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trede, N.S.; Zon, L.I. Development of T-cell during fish embryogenesis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1998, 22, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, C.E.; Cortes, A.; Zuasti, A.; Zapata, A.G. Early hematopoiesis and developing lymphoid organs in the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1999, 214, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, A.G. Lympho-Hematopoietic Microenvironments and Fish Immune System. Biology 2022, 11, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W. Study on Organic and Cellular Organizations of Immune System and Some Effector Cells of Paralichthys olivaceus. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, J.; Ohta, Y. Comparative and developmental study of the immune system in Xenopus. Dev. Dyn. 2009, 238, 1249–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, N.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Robert, J.; Zeng, L. Rag1 and rag2 gene expressions identify lymphopoietic tissues in juvenile and adult Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 87, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, A.G.; Thomas, J.K. Immunology, 5th ed.; W. H. Freeman and Co., Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2003; p. 250. [Google Scholar]
- Josefsson, S.; Tatner, M.F. Histogenesis of the lymphoid organs in sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1993, 3, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.X.; Nie, P. Fish thym us research: A review. J. Fish. China 2003, 27, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, C.E.; Zapata, A.G.; Hopkins, N.; Steiner, L.A. Expression of zebrafish rag genes during early development identifies the thymus. Dev. Biol. 1997, 182, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botham, J.W.; Manning, M.J. The histogenesis of the lymphoid organs in the carp Cyprinus carpio L. and the ontogenetic development of allograft reactivity. J. Fish Biol. 1981, 19, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyuth, C.; Tadahisa, S.; Masaru, T. Comparative study of the ontogeny of the lymphoid organs in three species of marine fish. Aquaculture 1991, 99, 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Study on the Structure, Development and Infected Pathological Reactions of the Immune System in Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gradil, A.M.; Wright, G.M.; Wadowska, D.W.; Fast, M.D. Ontogeny of the immune system in Acipenserid juveniles. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 44, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klosterhoff, M.C.; Pereira Junior, J.; Rodrigues, R.V.; GUSMãO, E.P.; Sampaio, L.A.; Tesser, M.B.; Romano, L.A. Ontogenic development of kidney, thymus and spleen and phenotypic expression of CD3 and CD4 receptors on the lymphocytes of cobia (Rachycentroncanadum). An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2015, 87, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.Y.; Lin, H.R. Ontogeny of lymphoid organs in the orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Acta Zool. Sin. 2003, 49, 819–828. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.F.; Di, J.; Tian, B.; Du, H.; Leng, X.Q.; Zhang, S.H.; Wei, Q.W. Ontogeny of immune organs during early developmental stages of Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis). J. Fish. Sci. China 2019, 26, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Williams, A.; Hong, C.-S.; You, Y.; Senoo, M.; Saint-Jeannet, J.-P. Early development of the thymus in Xenopus laevis. Dev. Dyn. 2013, 242, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, X.B. Microstructure and Immune Cells’ Distribution of Early Development Immune Organs in Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.W. Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Danilova, N.; Hohman, V.S.; Sacher, F.; Ota, T.; Willett, C.E.; Steiner, L.A. T cells and the thymus in developing zebrafish. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2004, 28, 670–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Meng, Y.; Xie, C.; Zeng, L. Characterization of Chinese giant salamander iridovirus tissue tropism and in-flammatory response after infection. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 114, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.J.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y.J.; Su, Y.Q. Post-embryonic histological development in digestive system of large yellow croaker Pseudosciaend crocea. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2010, 25, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, M.C.; Huang, Z. Ontogeny of lymphoid organs in catfish (Silurus asotusl). J. Fish. China 1995, 19, 258–262. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.-C.; Jiang, G.; Yang, N.; Lian, J.; Yang, Y. The development of the lymphoid organs of flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, from hatching to 13 months. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2004, 16, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.L.; Liu, S.G.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, C.S.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, Q.B. Microstructure and ultrastructure of liver in Monopterus albus. Freshw. Fish. 2015, 45, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.Y.; Lin, H.R. Histological studieson post-embryonic developmentof thedigestive system of Epinephelus coioides. J. Fish. China 2003, 27, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Zhao, X.; Bu, H.; Sun, S. Ontogenetic Histological Development of Digestive Organ in Post-embryonic loach. Fish. Sci. 2015, 34, 702–707. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, H.L.; Wang, Z.J. Micro-and Untra-structure of Culter alburnus Liver. J. Southwest Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2011, 33, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Liu, Y.; Mou, Z.; Li, Y. Ontogeny of immune organs during early developmental stages of Brachymystax lenok. J. Fish. Sci. China 2013, 19, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudhir, K.; Glen, S.; Koichiro, T. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C.; Wu, S.W.; Jiang, N.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zhong, Q.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y. Characterization of reference genes for qRT-PCR normalization in rice-field eel (Monopterus albus) to assess differences in embryonic developmental stages, the early development of immune organs, and cells infected with rhabdovirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Symbol | Primer Pairs Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Size (bp) | Accession Nos. |
|---|---|---|---|
| rag1 (Real-time PCR) | F: TGCAGCTGATACCATCGGTC | 128 | XM020615225 |
| R: CTGAGGTGCAAGCACTGTCT | |||
| rag2 (Real-time PCR) | F: CTCATGCCCGACAGGAGTTT | 114 | XM020615222 |
| R: ACAGCAGGACAACGTAGTGG | |||
| ef1α (Real-time PCR) | F: ATCCGTCGTGGATATGTGGC | 125 | XM020588923 |
| R: AGCACTGGGGCATAACCTTC | |||
| rag1-H (Probe synthesis) | F: AAAGCCAAACTCAGAACTATCC | 516 | XM020615225 |
| R: TACACCTCGCCAATCTCATCT | |||
| rag2-H (Probe synthesis) | F: CTTTACTTCGGTCGTGAGCCT | 413 | XM020615222 |
| R: GGGGACATCTTGATTGTTGGAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, M.; Zhong, Q.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y. Rag1 and Rag2 Gene Expressions Identify Lymphopoietic Tissues in Larvae of Rice-Field Eel (Monopterus albus). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147546
Liu Y, Jiang N, Liu W, Zhou Y, Xue M, Zhong Q, Li Z, Fan Y. Rag1 and Rag2 Gene Expressions Identify Lymphopoietic Tissues in Larvae of Rice-Field Eel (Monopterus albus). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(14):7546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147546
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuchen, Nan Jiang, Wenzhi Liu, Yong Zhou, Mingyang Xue, Qiwang Zhong, Zhong Li, and Yuding Fan. 2022. "Rag1 and Rag2 Gene Expressions Identify Lymphopoietic Tissues in Larvae of Rice-Field Eel (Monopterus albus)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 14: 7546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147546
APA StyleLiu, Y., Jiang, N., Liu, W., Zhou, Y., Xue, M., Zhong, Q., Li, Z., & Fan, Y. (2022). Rag1 and Rag2 Gene Expressions Identify Lymphopoietic Tissues in Larvae of Rice-Field Eel (Monopterus albus). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(14), 7546. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23147546







