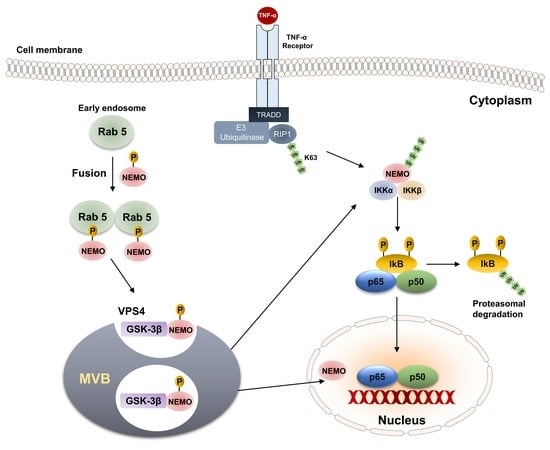
IKKγ/NEMO Localization into Multivesicular Bodies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
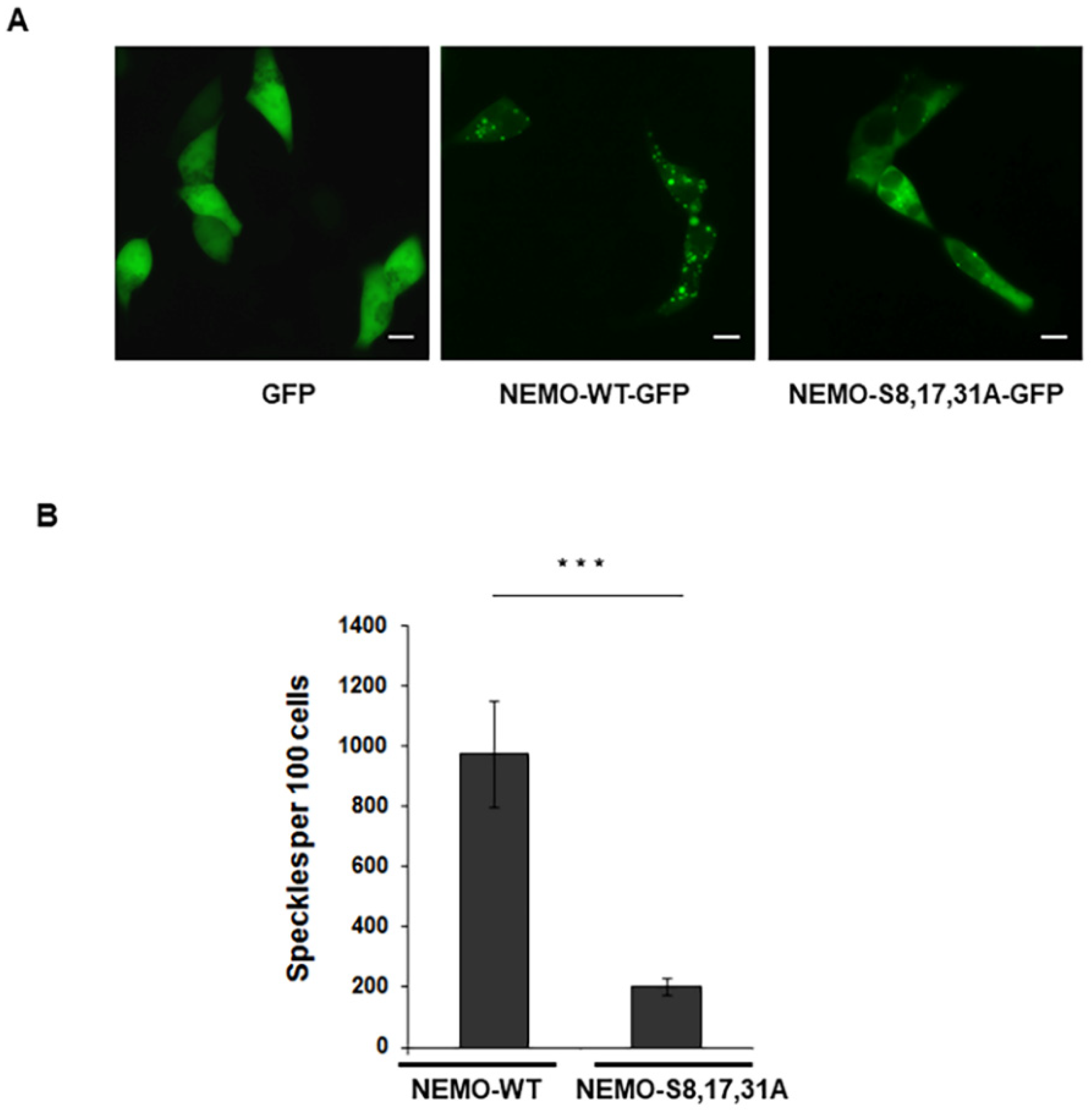
2.1. IKKγ/NEMO Localization into So-Called “Speckles”
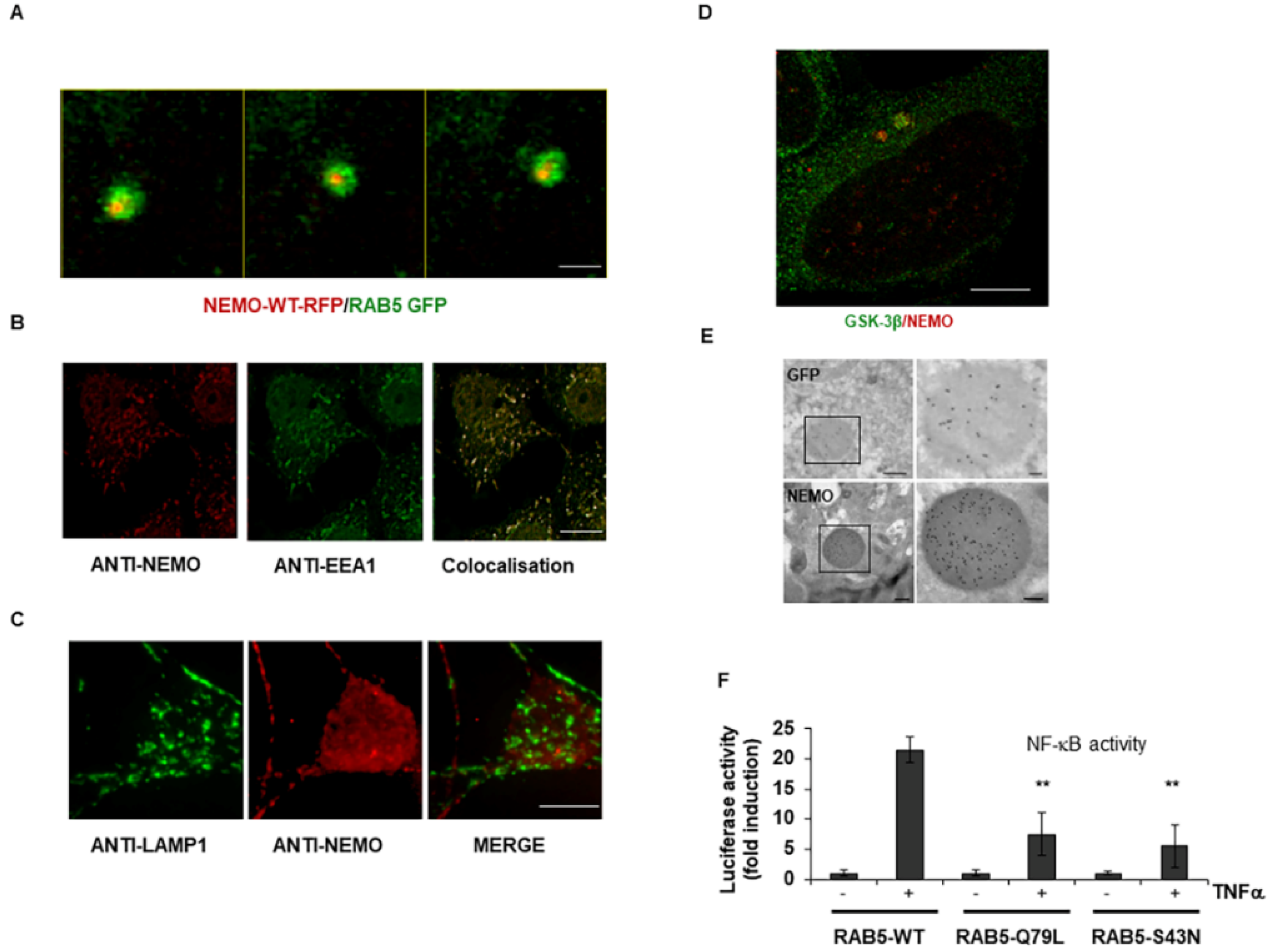
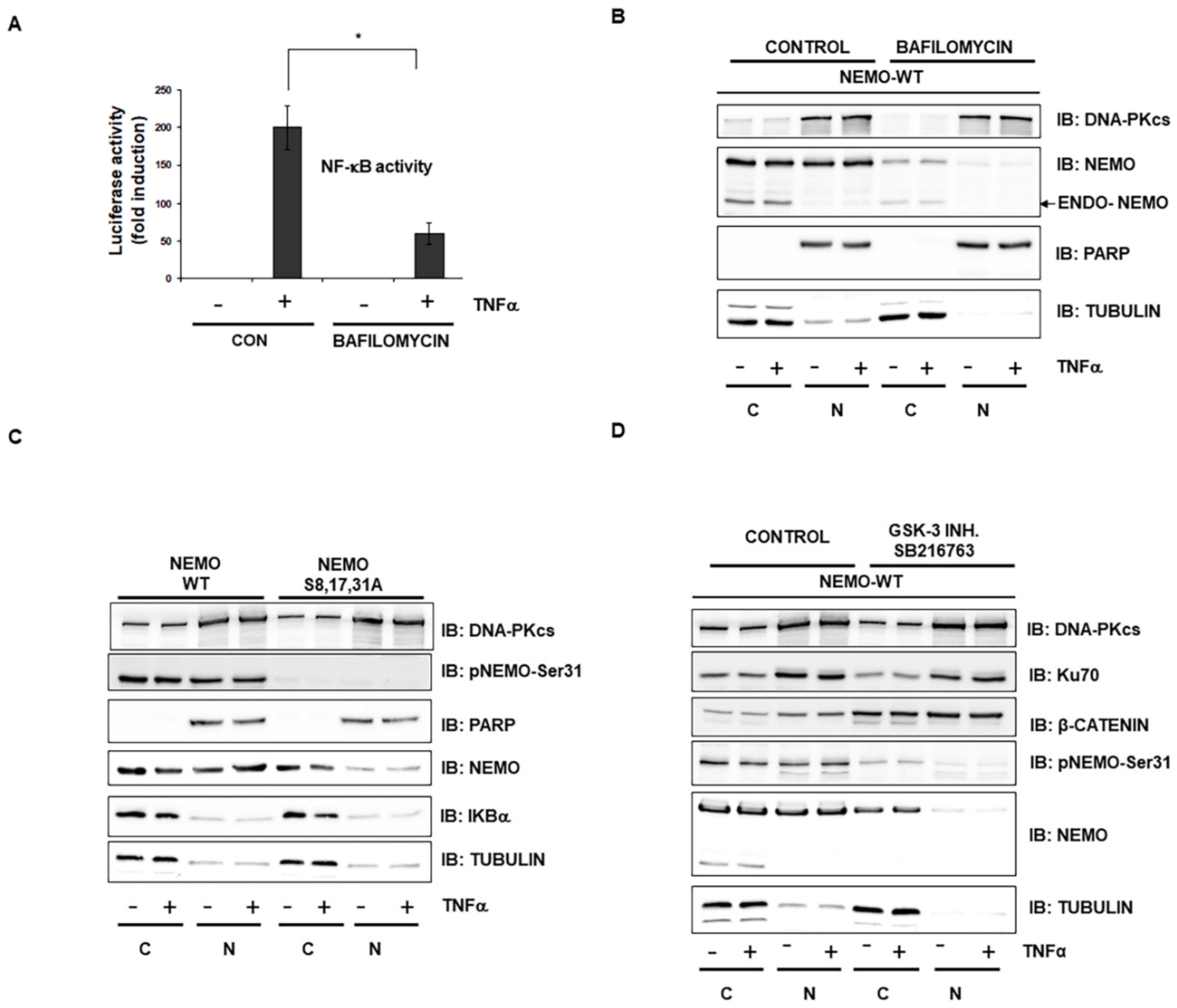
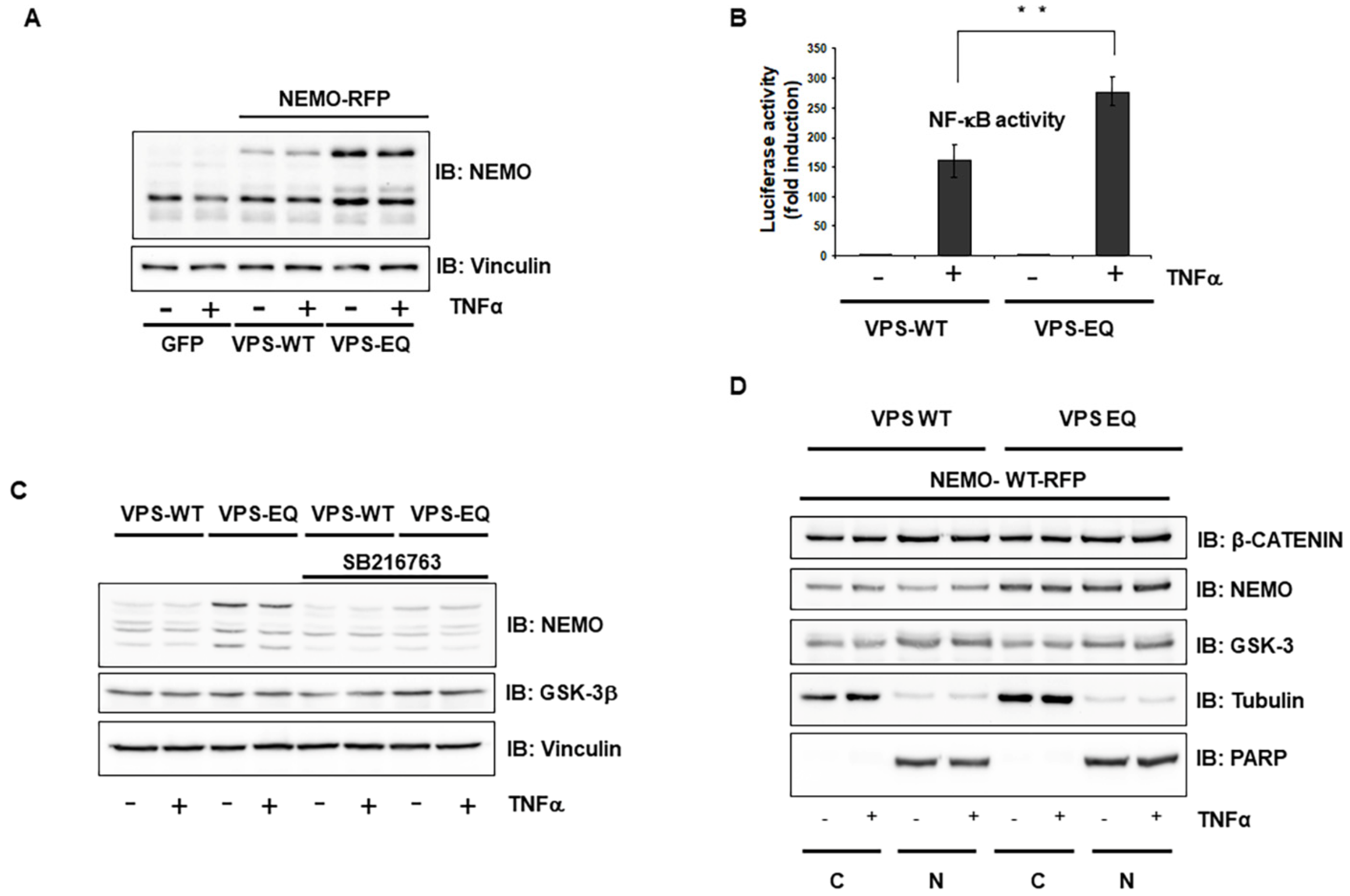
2.2. GSK-3-Mediated Phosphorylation Induces the Localization of NEMO into Multivesicular Bodies
2.3. Selective Inhibitor of V-ATPase Bafilomycin Blocks NF-κB Activity
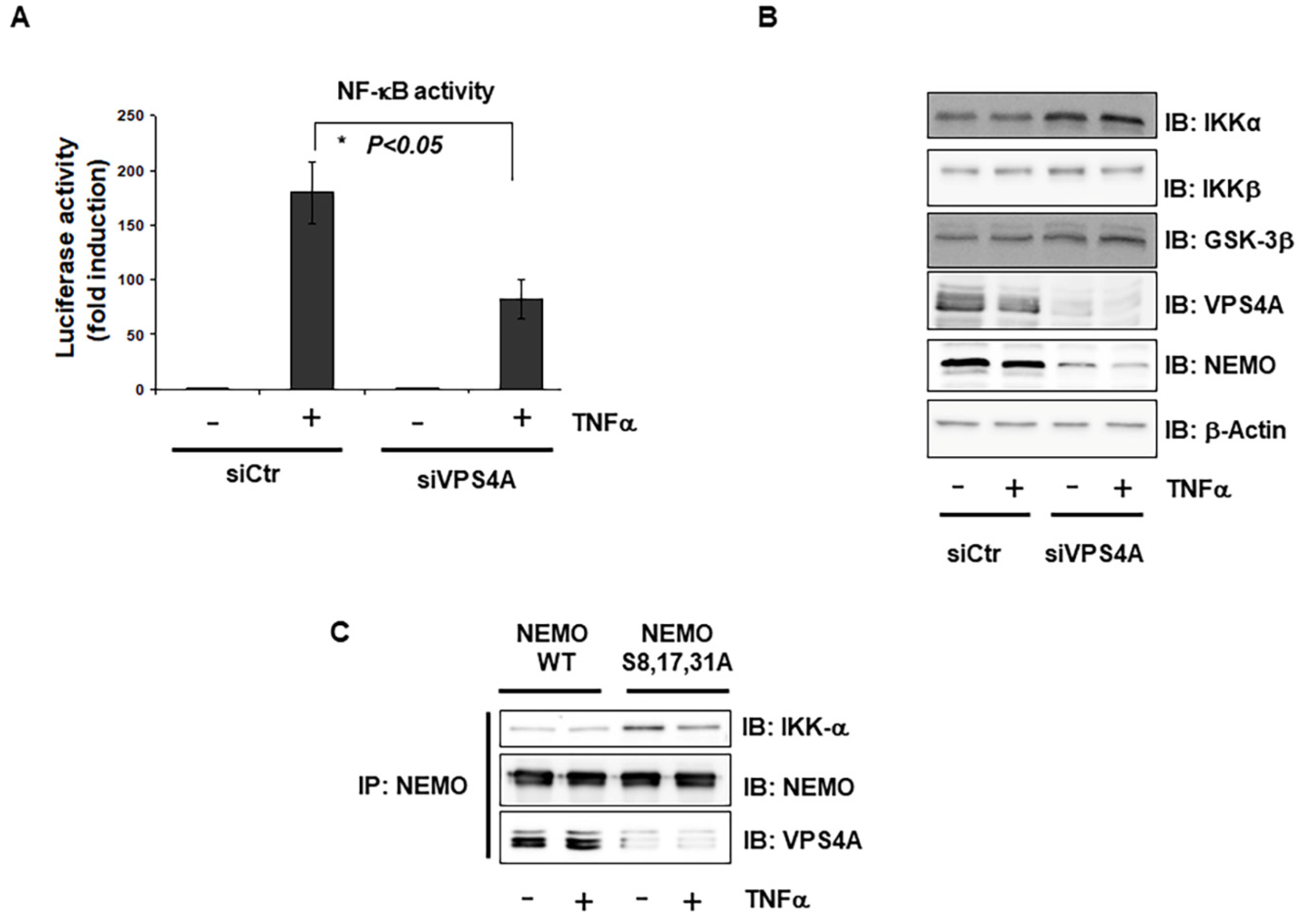
2.4. Interaction of Vps4A with IKKγ/NEMO
2.5. Vps4A Is a Key Enzyme That Modulates NEMO Expression and Function
3. Discussion
4. Material & Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Luciferase Assay
4.4. Immunoprecipitation
4.5. Gene Silencing with Small Interfering RNAs
4.6. Plasmids
4.7. Preparation of Nuclear Extracts
4.8. Staining of Cell Cultures for STED Microscopy
4.9. Image Acquisition of Stained Cell Cultures by STED Microscopy
4.10. Image Processing
4.11. Immunoelectron Microscopy
4.12. Widefield FLIM Setup
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shih, V.F.; Tsui, R.; Caldwell, A.; Hoffmann, A. A single NFκB system for both canonical and non-canonical signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellweg, C.E. The Nuclear Factor κB pathway: A link to the immune system in the radiation response. Cancer Lett. 2015, 368, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Lin, A. NF-κB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwarf, D.M.; Zandi, E.; Natoli, G.; Karin, M. IKK-gamma is an essential regulatory subunit of the IκB kinase complex. Nature 1998, 395, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israël, A. The IKK complex, a central regulator of NF-κB activation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozes, A.R.; Miller, D.F.; Ozes, O.N.; Fang, F.; Liu, Y.; Matei, D.; Huang, T.; Nephew, K.P. NF-κB-HOTAIR axis links DNA damage response, chemoresistance and cellular senescence in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5350–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brach, M.A.; Gruss, H.J.; Kaisho, T.; Asano, Y.; Hirano, T.; Herrmann, F. Ionizing radiation induces expression of interleukin 6 by human fibroblasts involving activation of nuclear factor-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8466–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Gonzalez, J.; Auclair, S.; Luan, S.; Thomas, L.; Atkins, K.M.; Aslan, J.E.; Thomas, L.L.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Thomas, G. PACS-2 mediates the ATM and NF-κB-dependent induction of anti-apoptotic Bcl-xL in response to DNA damage. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-H.; Shi, Y.; Tibbetts, R.S.; Miyamoto, S. Molecular linkage between the kinase ATM and NF-κB signaling in response to genotoxic stimuli. Science 2006, 311, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.T.; Wuerzberger-Davis, S.M.; Wu, Z.-H.; Miyamoto, S. Sequential modification of NEMO/IKKgamma by SUMO-1 and ubiquitin mediates NF-κB activation by genotoxic stress. Cell 2003, 115, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.I.; Pescatore, A.; Paciolla, M.; Esposito, E.; Miano, M.G.; Lioi, M.B.; McAleer, M.A.; Giardino, G.; Pignata, C.; Irvine, A.D.; et al. Insight into IKBKG/NEMO locus: Report of new mutations and complex genomic rearrangements leading to incontinentia pigmenti disease. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, F.; Pescatore, A.; Conte, M.I.; Mirabelli, P.; Paciolla, M.; Esposito, E.; Lioi, M.B.; Ursini, M.V. EDA-ID and IP, two faces of the same coin: How the same IKBKG/NEMO mutation affecting the NF-κB pathway can cause immunodeficiency and/or inflammation. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 34, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, D.; Yeh, W.C.; Wakeham, A.; Rudolph, B.; Nallainathan, D.; Potter, J.; Elia, A.J.; Mak, T.W. Severe liver degeneration and lack of NF-κB activation in NEMO/IKKgamma-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jope, R.S.; Johnson, G.V.W. The glamour and gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeflich, K.P.; Luo, J.; Rubie, E.A.; Tsao, M.S.; Jin, O.; Woodgett, J.R. Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-κB activation. Nature 2000, 406, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iha, H.; Kibler, K.V.; Yedavalli, V.R.K.; Peloponese, J.-M.; Haller, K.; Miyazato, A.; Kasai, T.; Jeang, K.-T. Segregation of NF-κB activation through NEMO/IKKgamma by Tax and TNFalpha: Implications for stimulus-specific interruption of oncogenic signaling. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8912–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taelman, V.F.; Dobrowolski, R.; Plouhinec, J.-L.; Fuentealba, L.C.; Vorwald, P.P.; Gumper, I.; Sabatini, D.D.; De Robertis, E.M. Wnt signaling requires sequestration of glycogen synthase kinase 3 inside multivesicular endosomes. Cell 2010, 143, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, E.M.; Almers, W.; Soldati, T. Morphology and dynamics of the endocytic pathway in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 1390–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Leahy, H.; Zhou, J.; Morin, P.J. The vacuolar-ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin and mutant VPS35 inhibit canonical Wnt signaling. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 26, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babst, M.; Katzmann, D.J.; Estepa-Sabal, E.J.; Meerloo, T.; Emr, S.D. Escrt-III: An endosome-associated heterooligomeric protein complex required for mvb sorting. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janvier, K.; Pelchen-Matthews, A.; Renaud, J.-B.; Caillet, M.; Marsh, M.; Berlioz-Torrent, C. The ESCRT-0 component HRS is required for HIV-1 Vpu-mediated BST-2/tetherin down-regulation. PLoS. Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babst, M.; Katzmann, D.J.; Snyder, W.B.; Wendland, B.; Emr, S.D. Endosome-associated complex, ESCRT-II, recruits transport machinery for protein sorting at the multivesicular body. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babst, M.; Wendland, B.; Estepa, E.J.; Emr, S.D. The Vps4p AAA ATPase regulates membrane association of a Vps protein complex required for normal endosome function. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2982–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felder, S.; Miller, K.; Moehren, G.; Ullrich, A.; Schlessinger, J.; Hopkins, C.R. Kinase activity controls the sorting of the epidermal growth factor receptor within the multivesicular body. Cell 1990, 61, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.; Schwamborn, K.; Alcover, A.; Bessia, C.; Di Bartolo, V.; Israël, A. Induction of the NF-κB cascade by recruitment of the scaffold molecule NEMO to the T cell receptor. Immunity 2003, 18, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tokunaga, F.; Sakata, S.-i.; Saeki, Y.; Satomi, Y.; Kirisako, T.; Kamei, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Kato, M.; Murata, S.; Yamaoka, S.; et al. Involvement of linear polyubiquitylation of NEMO in NF-κB activation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastori, V.; Sangalli, E.; Coccetti, P.; Pozzi, C.; Nonnis, S.; Tedeschi, G.; Fusi, P. CK2 and GSK3 phosphorylation on S29 controls wild-type ATXN3 nuclear uptake. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuderland, D.; Konson, A.; Seger, R. Identification and characterization of a general nuclear translocation signal in signaling proteins. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medunjanin, S.; Hermani, A.; Servi, B.d.; Grisouard, J.; Rincke, G.; Mayer, D. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 interacts with and phosphorylates estrogen receptor alpha and is involved in the regulation of receptor activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33006–33014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, M.; Kawano, Y.; Zhu, H.; Waxman, J.; Kypta, R.M. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 represses androgen receptor activity and prostate cancer cell growth. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7882–7892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuyasu, K.T. A technique for ultracryotomy of cell suspensions and tissues. J. Cell Biol. 1973, 57, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G.; Simons, K.; Warren, G.; Tokuyasu, K.T. Immunoelectron microscopy using thin, frozen sections: Application to studies of the intracellular transport of Semliki Forest virus spike glycoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983, 96, 466–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slot, J.W.; Geuze, H.J. Cryosectioning and immunolabeling. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2480–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, M.; Picazo, F.; Prokazov, Y.; Duci, A.; Turbin, E.; Götze, C.; Llopis, J.; Hartig, R.; Visser, A.J.W.G.; Zuschratter, W. Wide-Field Multi-Parameter FLIM: Long-term minimal invasive observation of proteins in living cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, N.; Woodman, P. ATPase-defective mammalian VPS4 localizes to aberrant endosomes and impairs cholesterol trafficking. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wackernagel, L.-M.; Abdi Sarabi, M.; Weinert, S.; Zuschratter, W.; Richter, K.; Fischer, K.D.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Medunjanin, S. IKKγ/NEMO Localization into Multivesicular Bodies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126778
Wackernagel L-M, Abdi Sarabi M, Weinert S, Zuschratter W, Richter K, Fischer KD, Braun-Dullaeus RC, Medunjanin S. IKKγ/NEMO Localization into Multivesicular Bodies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(12):6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126778
Chicago/Turabian StyleWackernagel, Lisa-Marie, Mohsen Abdi Sarabi, Sönke Weinert, Werner Zuschratter, Karin Richter, Klaus Dieter Fischer, Ruediger C. Braun-Dullaeus, and Senad Medunjanin. 2022. "IKKγ/NEMO Localization into Multivesicular Bodies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 12: 6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126778
APA StyleWackernagel, L.-M., Abdi Sarabi, M., Weinert, S., Zuschratter, W., Richter, K., Fischer, K. D., Braun-Dullaeus, R. C., & Medunjanin, S. (2022). IKKγ/NEMO Localization into Multivesicular Bodies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(12), 6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126778