Hypertension in Patients with Insulin Resistance: Etiopathogenesis and Management in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
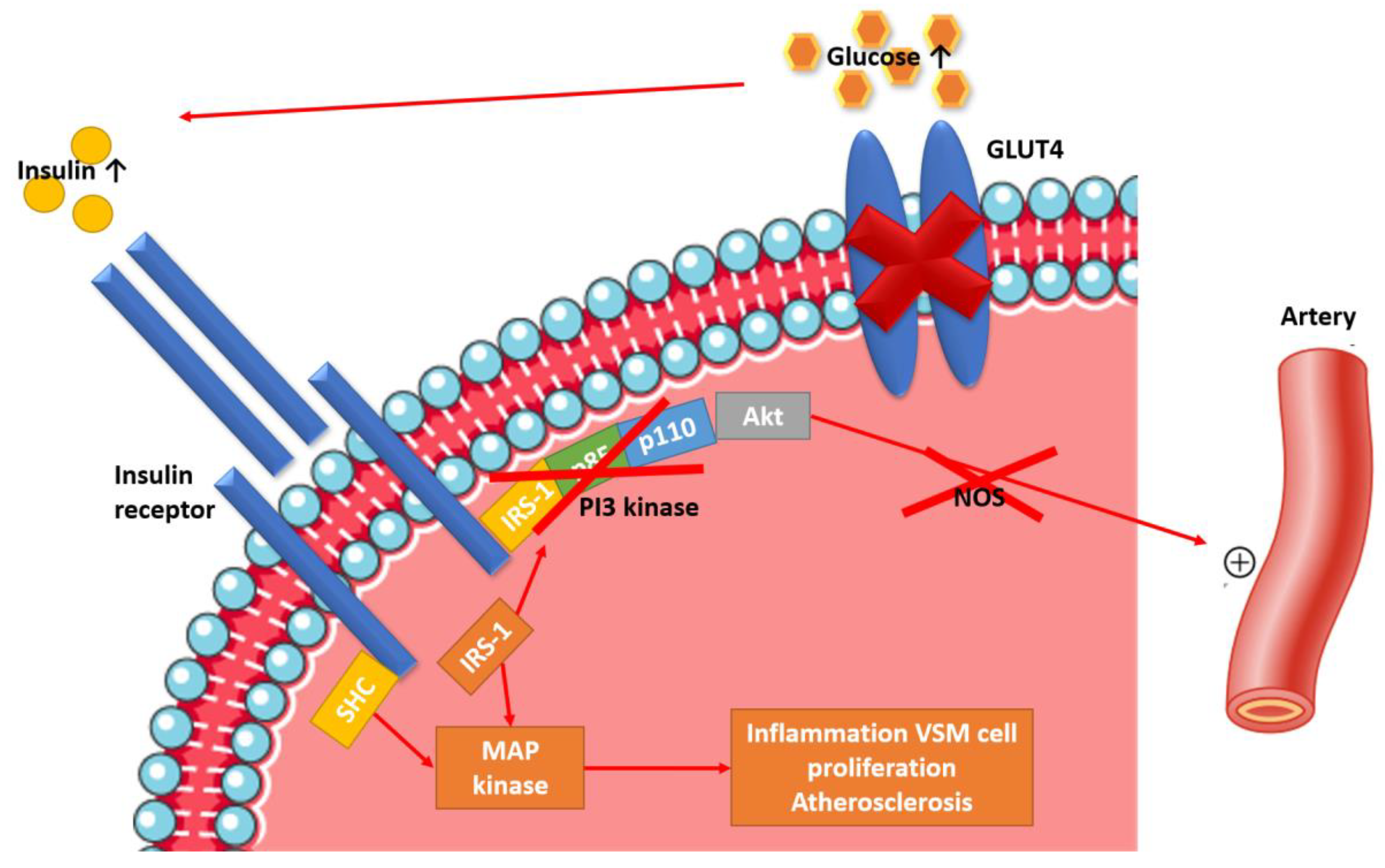
2. Etiopathogenesis
3. Management of HS in Children with DM
3.1. Definition
3.2. Prevention
3.3. Lifestyle Intervention
3.4. First-Line Pharmacologic Treatment
3.5. Second Agent Treatment
3.6. BP Goal
3.7. Heart Failure
3.8. Metabolic Syndrome
3.9. Glucose Lowering Therapies
3.10. Follow-Up
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mancusi, C.; Izzo, R.; di Gioia, G.; Losi, M.A.; Barbato, E.; Morisco, C. Insulin Resistance the Hinge Between hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2020, 27, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, H.O.; Chaker, H.; Leaming, R.; Johnson, A.; Brechtel, G.; Baron, A.D. Obesity/Insulin resistance is associated with endothelial dysfunction. Implications for the syndrome of insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2601–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, N.; Satoh, C.; Hu, W.Y.; Nakayama, M.; Kishioka, H.; Kanmatsuse, K. Endogenous AngII suppresses insulin signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells from spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lembo, G.; Napoli, R.; Capaldo, B.; Rendina, V.; Iaccarino, G.; Volpe, M.; Trimarco, B.; Sacca, L. Abnormal sympathetic overactivity evoked by insulin in the skeletal muscle of patients with essential hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowers, J.R. hypertension, AngII, and oxidative stress. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1999–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabit, C.E.; Chung, W.B.; Hamburg, N.M.; Vita, J.A. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2010, 11, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabit, C.E.; Shenouda, S.M.; Holbrook, M.; Fetterman, J.L.; Kiani, S.; Frame, A.A.; Kluge, M.A.; Held, A.; Dohadwala, M.M.; Gokce, N.; et al. Protein kinase C-β contributes to impainsulin resistanceed endothelial insulin signaling in humans with diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2013, 127, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TODAY Study, Group; Shah, R.D.; Braffett, B.H.; Tryggestad, J.B.; Hughan, K.S.; Dhaliwal, R.; Nadeau, K.J.; Levitt Katz, L.E.; Gidding, S.S. Cardiovascular risk factor progression in adolescents and young adults with youth-onset type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2022, 36, 108123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbaje, A.O.; Barker, A.R.; Mitchell, G.F.; Tuomainen, T.P. Effect of Arterial Stiffness and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Progression on the Risk of Dysglycemia, Insulin Resistance, and Dyslipidemia: A Temporal Causal Longitudinal Study. Hypertension 2022, 79, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarella, P.; Kiseleva, T.A.; Valeeva, F.V.; Gosmanov, A.R. Hypertension Management in DIABETES: 2018 Update. Diabetes Spectr. 2018, 31, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report website. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html. (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Adler, A.I.; Stratton, I.M.; Neil, H.A.W.; Yudkin, J.S.; Matthews, D.R.; Cull, C.A.; Wright, A.D.; Turner, R.C.; Holman, R.R. Association of systolic blood pressure with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 36): Prospective observational study. BMJ 2000, 321, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosmanov, A.R.; Lu, J.L.; Sumida, K.; Potukuchi, P.K.; Rhee, C.M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Molnar, M.Z.; Kovesdy, C.P. Synergistic association of combined glycemic and blood pressure level with risk of complications in US veterans with diabetes. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamler, J.; Vaccaro, O.; Neaton, J.D.; Wentworth, D. Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurbe, E.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dominiczak, A.; Erdine, S.; Hinsulin, A.; Invitti, C.; Litwin, M.; Mancia, G.; Pall, D.; et al. 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1887–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.T.; Kaelber, D.C.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Blowey, D.; Carroll, A.E.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dionne, J.M.; Falkner, B.; Flinn, S.K.; et al. Subcommittee on Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children. Clinical Practice Guideline for Screening and Management of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pino, A.; DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis: Implications for Insulin-Sensitizing Agents. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1447–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.C.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2133–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, M.; Defronzo, R.A. Metabolic and molecular basis of insulin resistance. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 2003, 10, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rask-Madsen, C.; Li, Q.; Freund, B.; Feather, D.; Abramov, R.; Wu, I.H.; Chen, K.; Yamamoto-Hinsulin, J.; Goldenbogen, J.; Sotinsulin, K.B.; et al. Loss of insulin signaling in vascular endothelial cells accelerates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E null mice. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.W.; Clemont, A.; Feener, E.P.; Hein, K.D.; Igarashi, M.; Yamauchi, T.; White, M.F.; King, G.L. Characterization of selective resistance to insulin signaling in th.he vasculature of obese Zucker (fa/fa) rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K.; Maezono, K.; Osman, A.; Pendergrass, M.; Patti, M.E.; Pratipanawatr, T.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Kahn, C.R.; Mandarino, L.J. Insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase- and MAP kinase-mediated signaling in human muscle. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaoka, T.; Rose, D.W.; Jhun, B.H.; Saltiel, A.R.; Draznin, B.; Olefsky, J.M. Evidence for a functional role of Shc proteins in mitogenic signaling induced by insulin, insulin-like growth factor-1, and epidermal growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 13689–13694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hypertensionueh, W.A.; Law, R.E. Insulin signaling in the arterial wall. Am. J. Cardiol. 1999, 84, 21J–24J. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.C.; Goalstone, M.L.; Draznin, B. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance that impact cardiovascular biology. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draznin, B. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance: Serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 and increased expression of p85a: The two sides of a coin. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2392–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.L.; Park, K.; Li, Q. Selective insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular diseases in diabetes: The 2015 Edwin Bierman Award Lecture. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A. From the triumvinsulin resistanceate to the ominous octet: A new paradigm for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2009, 58, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis: The missing links. The Claude Bernard Lecture 2009. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1270–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaven, G.M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaoka, T.; Ishiki, M.; Sawa, T.; Ishihara, H.; Takata, Y.; Imamura, T.; Usui, I.; Olefsky, J.M.; Kobayashi, M. Comparison of the insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 mitogenic intracellular signaling pathways. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 4427–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifle, B.; Ditschuneit, H. Effect of insulin on growth of cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells. Diabetologia 1981, 20, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, J.W.; Kline, T.; Carel, K.; Goalstone, M.; Draznin, B. Hyperinsulinemia potentiates activation of p21Ras by growth factors. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 2211–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E.; Natali, A.; Muscelli, E.; Nilsson, P.M.; Golay, A.; Laasko, M.; Beck-Mielsen, H.; Mari, H. RISC Investigators. Natural history and physiological determinants.of changes in glucose tolerance in a non-diabetic population: The RISC study. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E. Insulin Resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NID diabetes, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 1991, 14, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Balkau, B.; Coppack, S.W.; Dekker, J.M.; Mari, A.; Nolan, J.; Walker, M.; Natali, A.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; RISC Investigators. Insulin resistance, insulin response, and obesity as indicators of metabolic risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2885–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Pilch, P.F. The insulin receptor: Structure, function, and signaling. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, C319–C334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.N.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; McGibbon, M.A.; Taylor, S.I.; Quon, M.J. Physiological role of akt in insulin-stimulated translocation of glut4 in transfected rat adipose cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegenga, M.E.; van der Crabben, S.N.; Levi, M.; de Vos, A.F.; Tanck, M.W.; Sauerwein, H.P.; van der Poll, T. Hyperglycemia stimulates coagulation, whereas hyperinsulinemia impainsulin resistances fibrinolysis in healthy humans. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, E.J.; Philippou, H.; Ariens, R.A.; Grant, P.J. Molecular mechanisms involved in the resistance of fibrin to clot lysis by plasmin in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Thorne, K.I.; Farmer, A.J.; Davies, M.J.; Keenan, J.F.; Paul, S.; Levy, J.C. Addition of biphasic, prandial, or basal insulin to oral therapy in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1716–1730.75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnell, J.Q.; Dev, R.K.; Steffes, M.W.; Cleary, P.A.; Palmer, J.P.; Hinsulin, I.B.; Hokanson, J.E.; Brunzell, J.D. Relationship of family history of type 2 diabetes, hypoglycemia, and autoantibodies to weight gain and lipids with intensive and conventional therapy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, U. Abdominal obesity: A marker of ectopic fat accumulation. J Clin Investig. 2015, 125, 1790–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, M.; Baig, R.; Suraamornkul, S.; Hardies, L.J.; Coletta, D.K.; Cline, G.W.; Monroy, A.; Koul, S.; Sriwijitkamol, A.; Musi, N.; et al. Effects of pioglitazone on intramyocellular fat metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bays, H.; Mandarino, L.; DeFronzo, R.A. Role o.of the adipocyte, free fatty acids, and ectopic fat in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor agonists provide a rational therapeutic approach. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, M.; Suraamornkul, S.; Romanelli, A.; Cline, G.W.; Mandarino, L.J.; Shulman, G.I.; DeFronzo, R.A. Effect of a sustained reduction in plasma free fatty acid concentration on intramuscular long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs and insulin action in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3148–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoguchi, T.; Li, P.; Umeda, F.; Yu, H.Y.; Kakimoto, M.; Imamura, M.; Aoki, T.; Etoh, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Naruse, M.; et al. High glucose level and free fatty acid stimulate reactive oxygen species production through protein kinase C—Dependent activation of NAD(P)H oxidase in cultured vascular cells. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.; Tay, E.; Cusi, K. Elevated plasma free fatty acids increase cardiovascular risk by inducing plasma biomarkers of endothelial activation, myeloperoxidase and PAI-1 in healthy subjects. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2010, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wende, A.R.; Symons, J.D.; Abel, E.D. Mechanisms of lipotoxicity in the cardiovascular system. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2012, 14, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.K.; Kashyap, S.; Bajaj, M.; Cusi, K.; Mandarino, S.J.; Finlayson, J.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Jenkinson, C.P.; Mandarino, L.J. Lipid infusion decreases the expression of nuclear encoded mitochondrial genes and increases the expression of extracellular matrix genes in human skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10290–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresner, A.; Laurent, D.; Marcucci, M.; Grifffin, M.E.; Dufour, S.; Cline, G.W.; Slezak, L.A.; Andersen, D.K.; Hundal, R.S.; Rothman, D.L.; et al. Effects of free fatty acids on glucose transport and insulin resistance-1-associated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfort, R.; Mandarino, L.; Kashyap, S.; Winsulin, K.; Pratipanawatr, T.; Berria, R.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Cusi, K. Dose-response effect of elevated plasma free fatty acid on insulin signaling. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Fillmore, J.J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, C.; Moore, I.K.; Pypaert, M.; Lutz, E.P.; Kako, Y.; Velez-Carrasco, W.; Goldberg, I.J.; et al. Tissue-specific overexpression of lipoprotein lipase causes tissue-specific insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7522–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, B.L.; Dabelea, D.; Liese, A.D.; Fujimoto, W.; Waitzfelder, B.; Liu, L.; Bell, R.; Talton, J.; Snively, B.M.; Kershnar, A.; et al. SEARCH Study Group. Prevalence and correlates of elevated blood pressure in youth with diabetes mellitus: The SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. J. Pediatr. 2010, 157, 245–251.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambam, B.; DuBose, S.N.; Nathan, B.M.; Beck, R.W.; Maahypertension, D.M.; Wadwa, R.P.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Foster, N.C.; Miller, K.M.; Haller, M.J.; et al. T1D Exchange Clinic Network. Therapeutic inertia: Underdiagnosed and undertreated hypertension in children participating in the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry. Pediatr. Diabetes 2016, 17, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, W.J.; Meyer, P.M. Incident diabetes in clinical trials of antihypertensive drugs: A network meta-analysis. Lancet 2007, 369, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, A.L.; Liese, A.D.; Bell, R.A.; Dabelea, D.; Lawrence, J.M.; Rodriguez, B.L.; Standiford, D.A.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. Association between the dietary approaches to hypertension diet and hypertension in youth with diabetes mellitus. Hypertension 2009, 53, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, S.C.; Saelens, B.E.; Levin, L.; Dart, K.; Falciglia, G.; Daniels, S.R. The efficacy of a clinic-based behavioral nutrition intervention emphasizing a DASH-type diet for adolescents with elevated blood pressure. J. Pediatr. 2008, 152, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, T.L.; Crandell, J.L.; Bell, R.A.; Mayer Davis, E.J.; Dabelea, D.; Liese, A.D. Change in DASH diet score and cardiovascular risk factors in youth with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study. Nutr. Diabetes 2013, 3, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wühl, E.; Hadtstein, C.; Mehls, O.; Schaefer, F. Escape Trial Group. Home, clinic, and ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 55, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, V.; Izzo, R.; Manzi, M.V.; De Luca, M.R.; Barbato, E.; Morisco, C. Modulation of insulin resistance by renin angiotensin system inhibitors: Implications for cardiovascular prevention. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2021, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdös, E.G. Angiotensin I convertingenzyme. Circ. Res. 1975, 36, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryer, L.G.; Hajduch, E.; Rencurel, F.; Salt, I.P.; Hundal, H.S.; Hardie, D.G.; Carling, D. Activation of glucose transport by AMP-activated protein kinase via stimulation of nitric oxide synthase. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Henriksen, E.J.; Jacob, S.; Kinnick, T.R.; Youngblood, E.B.; Schmit, M.B.; Dietze, G.J. ACE inhibition and glucose transport in insulinresistant muscle: Roles of bradykinin and nitric oxide. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, R332–R336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, Y.; Gadient, A.; Keller, U.; Vadas, L.; Golay, A. Insulin sensitivity in obese hypertensive dyslipidemic patients treated with enalapril or atenolol. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1995, 26, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollare, T.; Lithell, H.; Berne, C. A comparison of the effects of hydrochlorothiazide and captopril on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 321, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.M.; Janke, J.; Gorzelniak, K.; Engeli, S.; Luft, F.C. Angiotensin blockade prevents type 2 diabetes by formation of fat cells. Hypertension 2002, 40, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, P.O.; Berne, C.; Jansson, L. AngII and the endocrine pancreas: Effects on islet blood flow and insulin secretion in rats. Diabetologia 1998, 41, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, P.A.; Oparil, S.; Carter, B.L.; Cushman, W.C.; Dennison-Himmelfarb, C.; Handler, J.; Lackland, D.T.; LeFevre, M.L.; MacKenzie, T.D.; Ogedegbe, O.; et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: Report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014, 311, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; De Backer, G.; Dominiczak, A.; Cifkova, R.; Fagard, R.; Germano, G.; Grassi, G.; Heagerty, A.M.; Kjeldsen, S.E.; Laurent, S.; et al. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 2159–2219. [Google Scholar]
- Woroniecki, R.P.; Flynn, J.T. How are hypertensive children evaluated and managed? A survey of North American pediatric nephrologists. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2005, 20, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council, E.S.; Redon, J.; Narkiewicz, K.; Nilsson, P.M.; Burnier, M.; Viigimaa, M.; Ambrosioni, E.; Caufield, M.; Coca, A.; Hecht, M.; et al. Task Force Members. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1281–1357. [Google Scholar]
- de Boer, I.H.; Rue, T.C.; Cleary, P.A.; Lachin, J.M.; Molitch, M.E.; Steffes, M.W.; Sun, W.; Zinman, B.; Brunzell, Z.D. DIABETES Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Study Research Group. Long-term renal outcomes of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: An analysis of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications cohort. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents: Summary report. Pediatrics 2011, 128, S213–S256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensimhon, H.F.; Cavender, M.A. Hypertension Treatment in Diabetes: Focus on Heart Failure Prevention. Heart Fail. Clin. 2019, 15, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbina, E.M.; Khoury, P.R.; McCoy, C.; Daniels, S.R.; Kimball, T.R.; Dolan, L.M. Cardiac and vascular consequences of prehypertension in youth. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2011, 13, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasso, F.C.; Pafundi, P.C.; Simeon, V.; De Nicola, L.; Chiodini, P.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Nevola, R.; Salvatore, T.; Sardu, C.; et al. Efficacy and durability of multifactorial intervention on mortality and MACEs: A randomized clinical trial in type-2 diabetic kidney disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabouli, S.; Kotsis, V.; Rizos, Z.; Toumanidis, S.; Karagianni, C.; Constantopoulos, A.; Zakopoulos, N. Left ventricular mass in normotensive, prehypertensive and hypertensive children and adolescents. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 24, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, L.; Pafundi, P.C.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Morone, M.V.; Silvestri, C.F.; Giordano, M.; Salvatore, T.; Sasso, F.C. Mechanisms of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in the Metabolic Syndrome. A Narrative Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkner, B.; DeLoach, S.; Keith, S.W.; Gidding, S.S. High risk blood pressure and obesity increase the risk for left ventricular hypertrophy in African-American adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Urakami, T. New insights into the pharmacological treatment of pediatric patients with type 2 DIABETES. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2018, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Hu, S.; Fu, M.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, Y.; Dong, R.; Yang, Y.; Tu, L.; et al. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase alleviates insulin resistance and hypertension via downregulation of SGLT2 in the mouse kidney. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sherbeni, A.A.; El-Kadi, A.O.S. The role of epoxide hydrolases in health and disease. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 2013–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkel, M.J.; Liu, L.; Cao, Z.; Packwood, W.; Young, J.; Alkayed, N.J.; van Winkle, D.M. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase preserves cardiomyocytes: Role of STAT3 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2010, 298, H679–H687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y.; Hammock, B.D.; Kong, W.; Zhu, Y. Homocysteine upregulates soluble epoxide hydrolase in vascular endothelium in vitro and in vivo. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-H.; Duan, J.-X.; Liu, S.-K.; Xiong, J.-B.; Guan, X.-X.; Zhong, W.-J.; Sun, C.-C.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Luo, X.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-F.; et al. A COX-2/sEH dual inhibitor PTUPB alleviates lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4749–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.K.; Ye, C.; Campbell, S.; Retnakaran, R. Comparison of new glucose-lowering drugs on risk of heart failure in type 2 diabetes. JACC Heart Fail. 2018, 6, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Swedberg, K.; Carlsson, J.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Michelson, E.L.; Olofsson, B.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Yusuf, S. The hemoglobin A1c level as a progressive risk factor for cardiovascular death, hospitalization for heart failure, or death in patients with chronic heart failure. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, D.; Bozkurt, B.; Ramasubbu, K.; Deswal, A. Relationship of hemoglobin A1C and mortality in heart failure patients with diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9742976 (accessed on 6 January 2019). [CrossRef]
- Boussageon, R.; Bejan-Angoulvant, T.; Saadatian-Elahi, M.; Lafont, S.; Bergeonneau, C.; Kassai, B.; Erpeldinger, S.; Wright, J.M.; Gueyffier, F.; Cornu, C. Effect of intensive glucose lowering treatment on all cause mortality, cardiovascular death, and microvascular events in type 2 diabetes: Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavender, M.A.; Norhammar, A.; Binsulin, K.I.; Jørgensen, M.E.; Wilding, J.P.; Khunti, K.; Fu, A.Z.; Bodegård, J.; Blak, B.T.; Wittbrodt, E.; et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors and cardiovascular risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, C.; Bakris, G.L. Blood pressure reduction: An added benefit of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, D.Z.; Perkins, B.A.; Soleymanlou, N.; Har, R.; Fagan, N.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.-J.; Von Eynatten, M.; Broedl, U.C. The effect of empagliflozin on arterial stiffness and heart rate variability in subjects with uncomplicated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitchett, D.; Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Hantel, S.; Salsali, A.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Inzucchi, S.E. Heart failure outcomes with empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk: Results of the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maahs, D.M.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dichek, H.L.; Flynn, J.; Goldstein, B.I.; Kelly, A.S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Martyn-Nemeth, P.; Osganian, S.K.; et al. American Heart Association Atherosclerosis, Hypertension and Obesity in Youth Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, Council on Clinical Cardiology, Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, Council for High Blood Pressure Research, and Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health. Cardiovascular disease risk factors in youth with diabetes mellitus: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2014, 130, 1532–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, J.T.; Tullus, K. Severe Hypertension in children and adolescents: Pathophysiology and treatment. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 24, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, E.M.; Assadi, F. Management of Hypertension in children with cardiovascular disease and heart failure. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Matteucci, M.C.; Chinali, M.; Rinelli, G.; Wühl, E.; Zurowska, A.; Charbit, M.; Pongiglione, G.; ESCAPE Trial Group. Change in cardiac geometry and function in CKD children during strict BP control: A randomized study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupferman, J.C.; Friedman, L.A.; Cox, C.; Flynn, J.; Furth, S.; Warady, B.; Mitsnefes, M. CKiD Study Group. BP control and left ventricular hypertrophy regression in children with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ESH | AAP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | 0–15 years SBP and/or DBP (percentile values) | ≥16 years SBP and/or DBP (mmHg) | 1–12 years (percentile values) | ≥13 years (mmHg) |
| Normal | <90th | <130/85 | <90th | <120/<80 |
| High-normal/Elevated BP | ≥90th to <95th | 130 to 139/85 to 89 | ≥90th to <95th | 120/<80 to 129/<80 |
| Stage 1 HS | 95th to 99th +5 mmHg | 140 to 159/90 to 99 | 95th to 95th +12 mmHg | 130/80 to 139/89 |
| Stage 2 HS | >99th + 5 mmHg | 160 to 179/100 to 109 | ≥95th + 5 mmHg | ≥140/90 |
| Drug | Age | Initial Dose (mg/kg per Dose) | Maximal Dose (mg/kg per Dose) | Dosing Interval | Contraindications and Adverse Drug Reactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE inhibitors | Contraindications: pregnancy, angioedema. Common ADR: cough, headache, dizziness, asthenia. Severe ADR: hyperkaliemia, acute kidney injury, angioedema, fetal toxicity | ||||
| Benazepril | ≥6 y | 0.2 (up to 10 mg/d) | 0.6 (up to 40 mg/d) | 1/day | |
| Captopril | Infants | 0.05 | 6 | 1–4/day | |
| Children | 0.5 | 6 | 3/day | ||
| Enalapril | ≥1 mo | 0.08 (up to 10 mg/d) | 0.6 (up to 40 mg/d) | 1–2/day | |
| Fosinopril | ≥6 y | 0.1 (up to 5 mg/d) | 40 mg/d | 1/day | |
| ˂50 kg | |||||
| ≥50 kg | 5 mg/d | 40 mg per d | |||
| Lisinopril | ≥6 y | 0.07 (up to 10 mg/d) | 0.6 (up to 40 mg/d) | 1/day | |
| Ramipril | - | 1.6 mg/m2/d | 6 mg/m2/d | 1/day | |
| Quinapril | - | 5 mg/d | 80 mg/d | 1/day | |
| ARB | Contraindications: pregnancy. Common ADR: headache, dizziness. Severe ADR: hyperkaliemia, acute kidney injury, fetal toxicity | ||||
| Candesartan | 1–5 y | 0.02 (up to 4 mg/d) | 0.4 (up to 16 mg/d) | 1–2/day | |
| ≥6 y | |||||
| ˂50 kg | 4 mg/d | 16 mg/d | |||
| ≥50 kg | 8 mg/d | 32 mg/d | |||
| Irbesartan | 6–12 y | 75 mg/d | 150 mg/d | 1/day | |
| ≥13 y | 150 mg/d | 300 mg/d | |||
| Losartan | ≥6 y | 0.7 (up to 50 mg/d) | 1.4 (up to 50 mg/d) | 1/day | |
| Olmesartan | ≥6 y | 1/day | |||
| ˂35 kg | 10 mg | 20 mg | |||
| ≥35 kg | 20 mg | 40 mg | |||
| Valsartan | ≥6 y | 1.3 (up to 40 mg/d) | 2.7 (up to 160 mg/d) | 1/day | |
| Thiazide diuretics | Contraindications: anuria. Common ADR: hypokalemia, dizziness. Severe ADR: dysrhythmias, cholestatic jaundice, new-onset DM, pancreatitis. | ||||
| Chlorthalidone | Child | 0.3 | 2 (up to 50 mg/d) | 1/day | |
| Chlorothiazide | Child | 10 | 20 (up to 375 mg/d) | 1–2/day | |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | Child | 1 | 2 (up to 37.5 mg/d) | 1–2/day | |
| Calcium channel blockers | Contraindications: hypersensitivity to CCB. Common ADR: flushing, peripheral edema, dizziness. Severe ADR: angioedema. | ||||
| Amlodipine | 1–5 y | 0.1 | 0.6 (up to 5 mg/d) | 1/day | |
| ≥6 y | 2.5 mg | 10 mg | |||
| Felodipine | ≥6 y | 2.5 mg | 10 mg | 1/day | |
| Isradipine | Child | 0.05–0.1 | 0.6 (up to 10 mg/d) | Capsule: 2–3/day Extended-release tablet: 1/day | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tagi, V.M.; Mainieri, F.; Chiarelli, F. Hypertension in Patients with Insulin Resistance: Etiopathogenesis and Management in Children. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105814
Tagi VM, Mainieri F, Chiarelli F. Hypertension in Patients with Insulin Resistance: Etiopathogenesis and Management in Children. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105814
Chicago/Turabian StyleTagi, Veronica Maria, Francesca Mainieri, and Francesco Chiarelli. 2022. "Hypertension in Patients with Insulin Resistance: Etiopathogenesis and Management in Children" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105814
APA StyleTagi, V. M., Mainieri, F., & Chiarelli, F. (2022). Hypertension in Patients with Insulin Resistance: Etiopathogenesis and Management in Children. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5814. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105814






