Rearrangement in the Hypervariable Region of JC Polyomavirus Genomes Isolated from Patient Samples and Impact on Transcription Factor-Binding Sites and Disease Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Curation of 989 JCPyV NCCR Sequences from Patient Samples
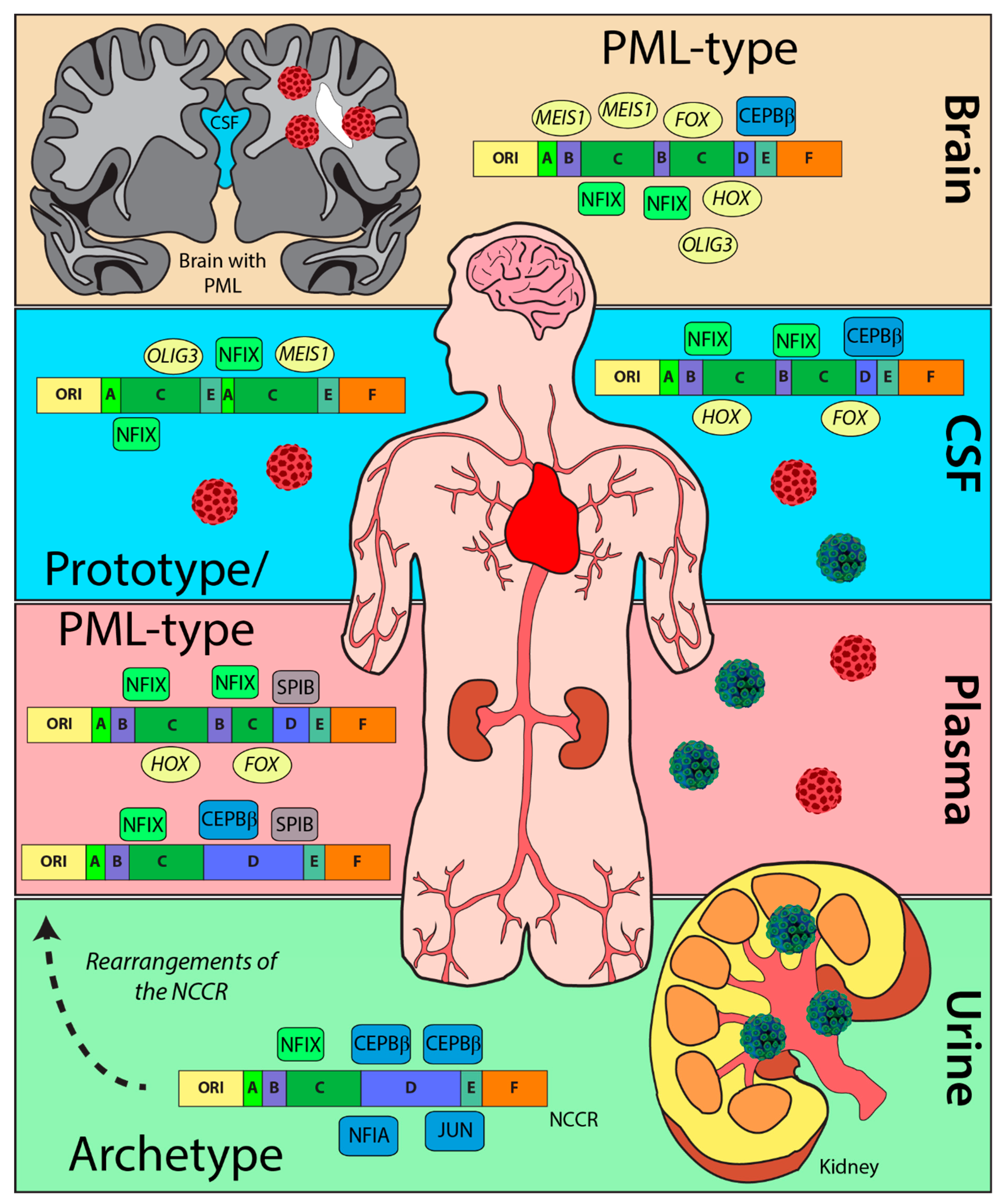
2.2. NCCR Sequences from PML Patients Derived from Urine Samples Were Distinct from Those from CSF, Brain, and Plasma Samples
2.3. The Heterogenicity of NCCR Blocks across Sample Isolation Sites
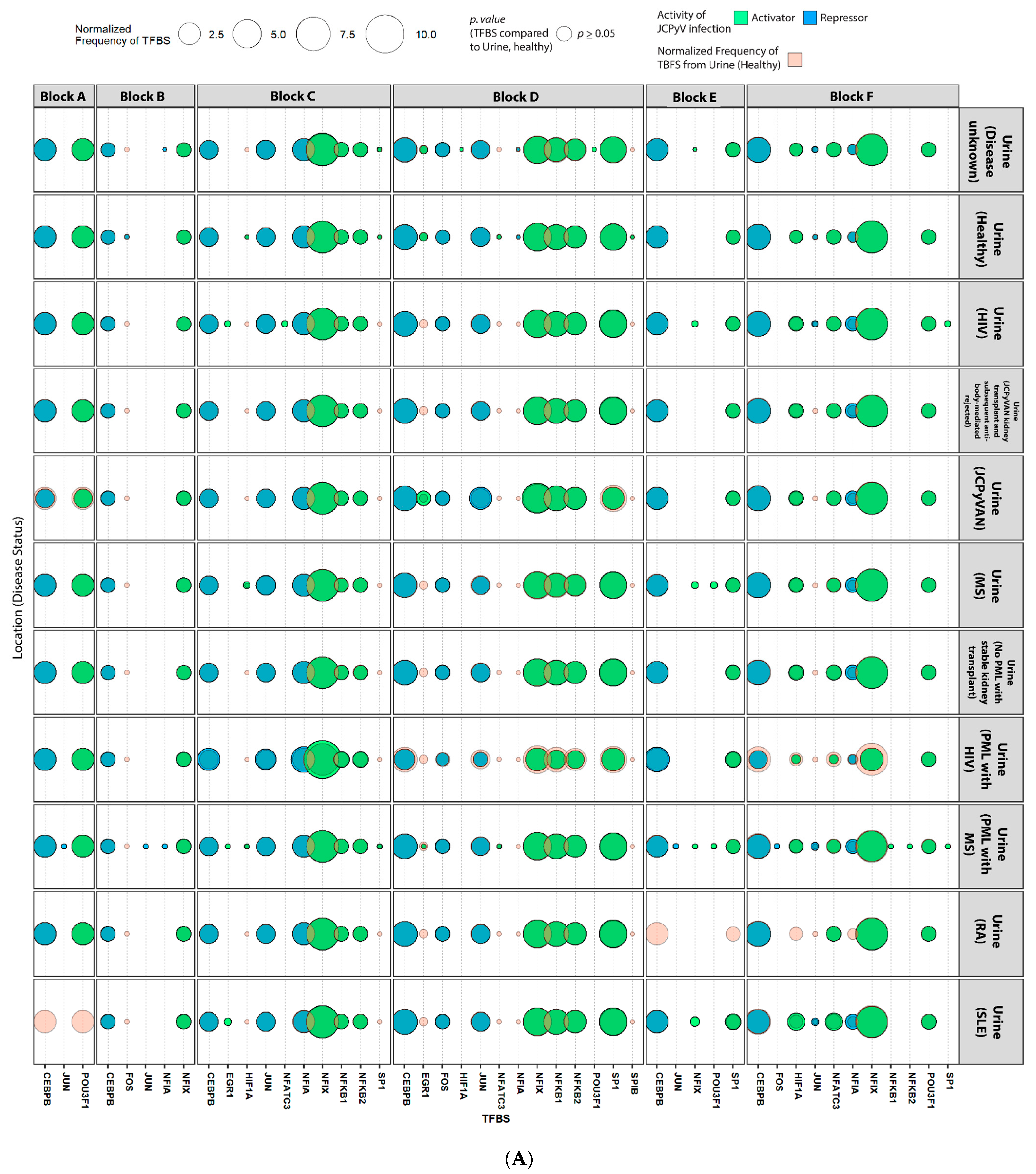
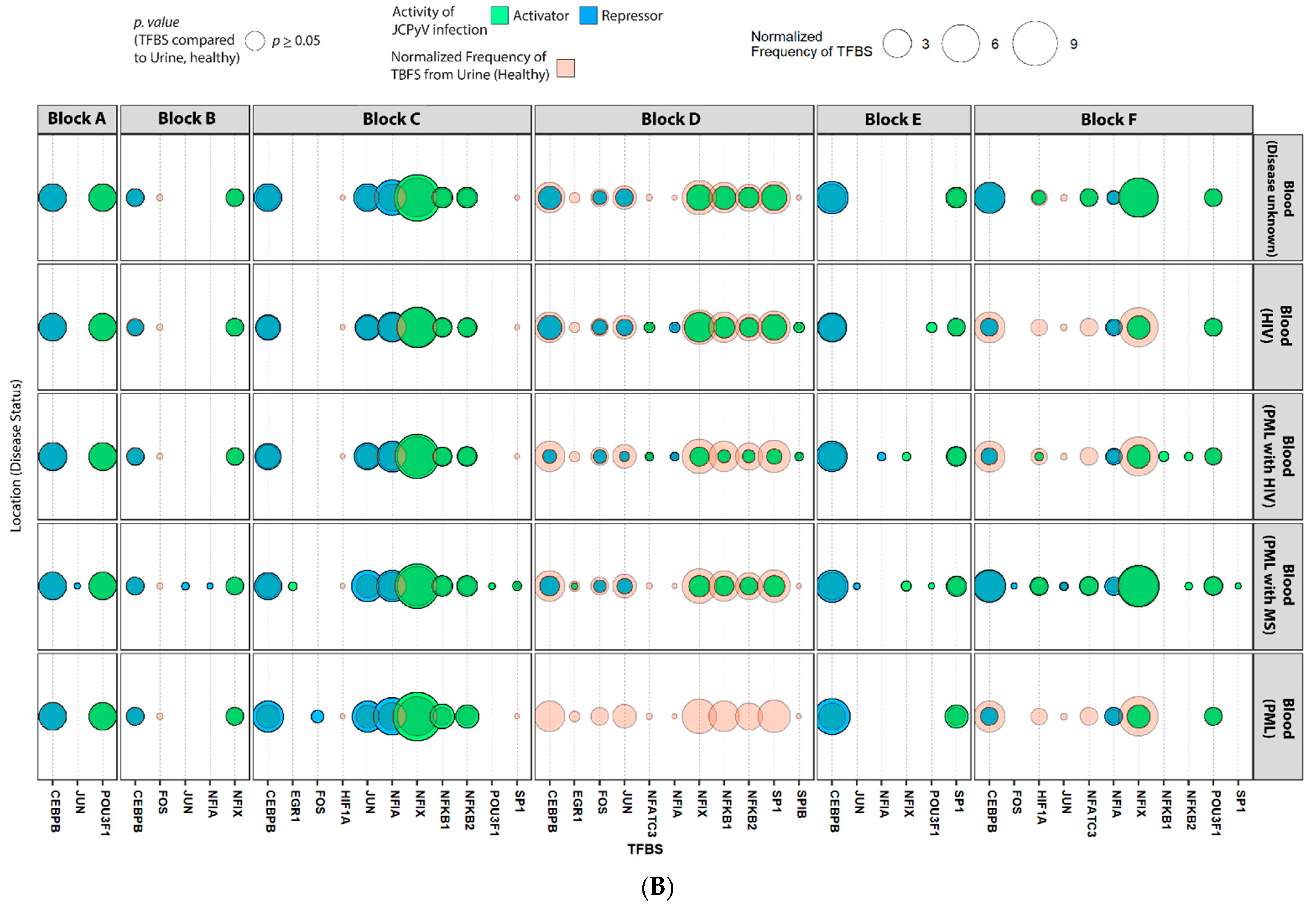
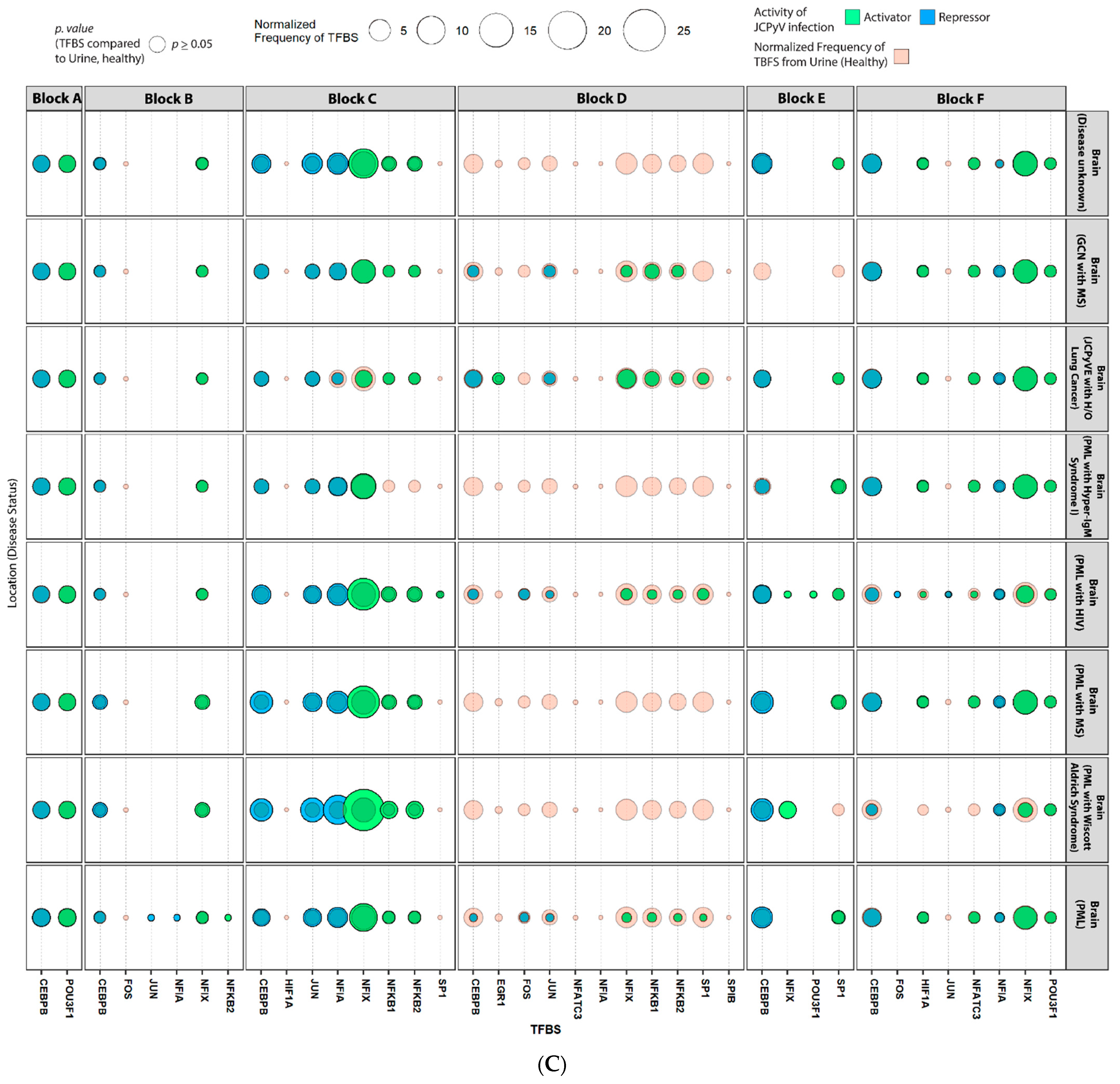
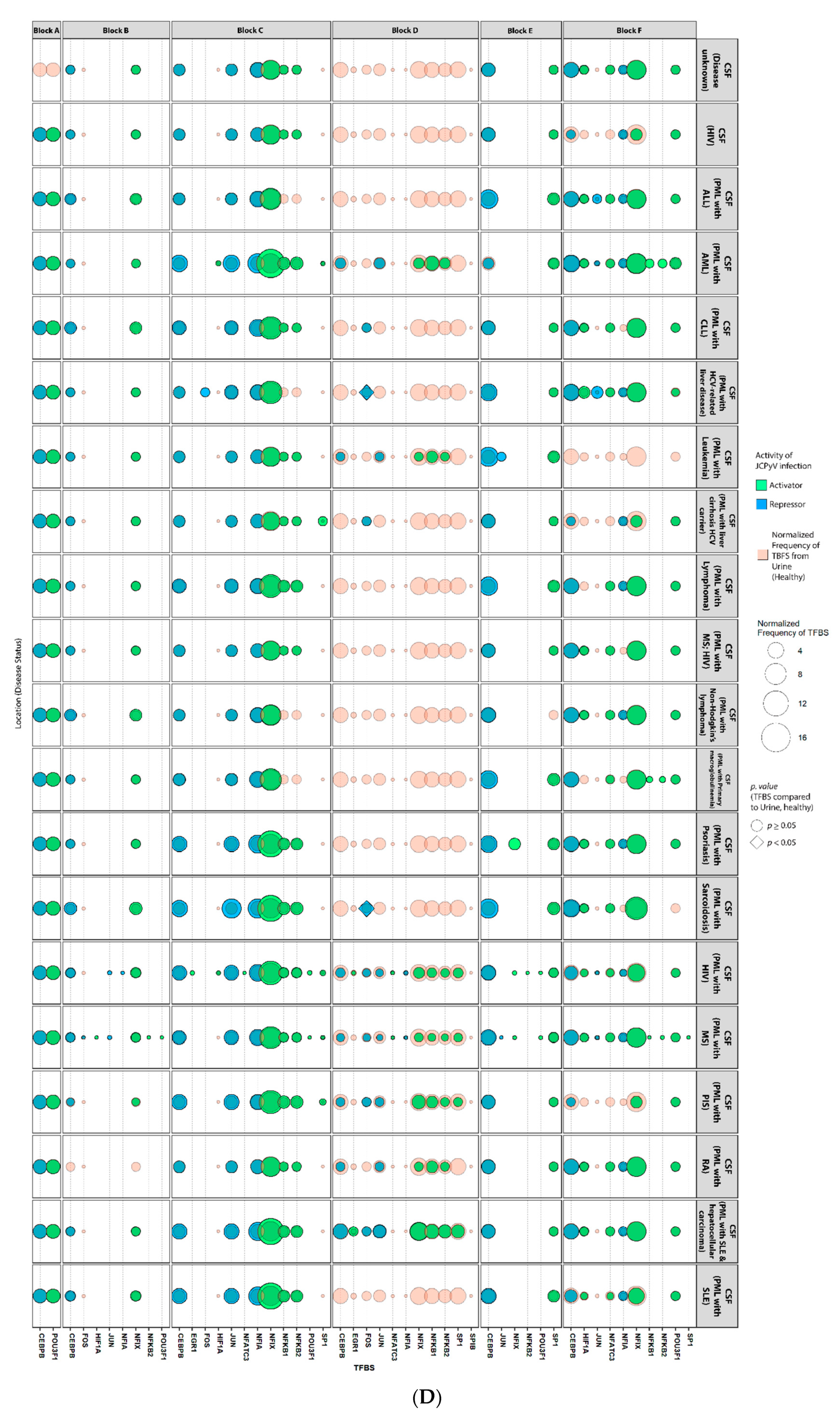
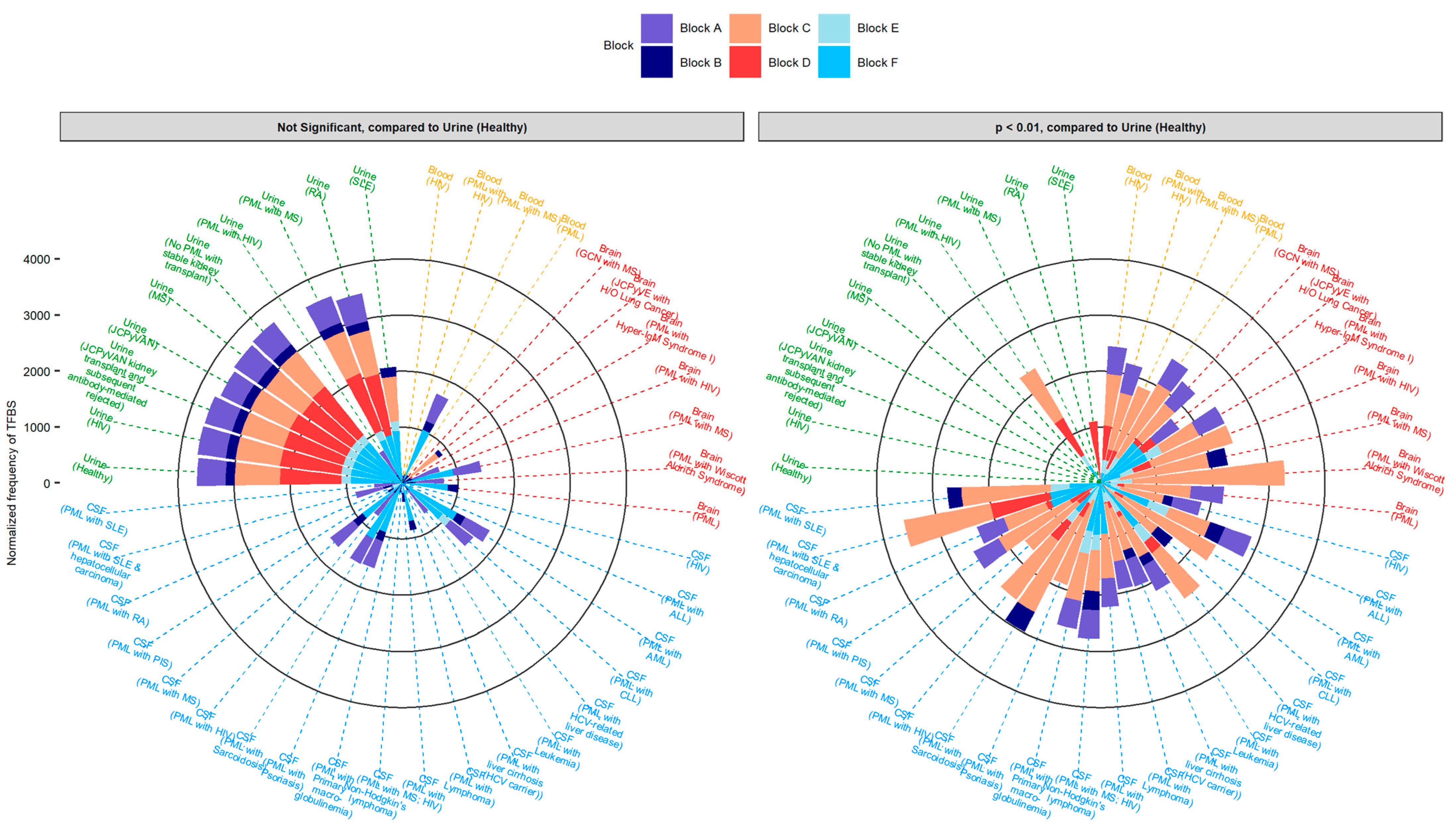
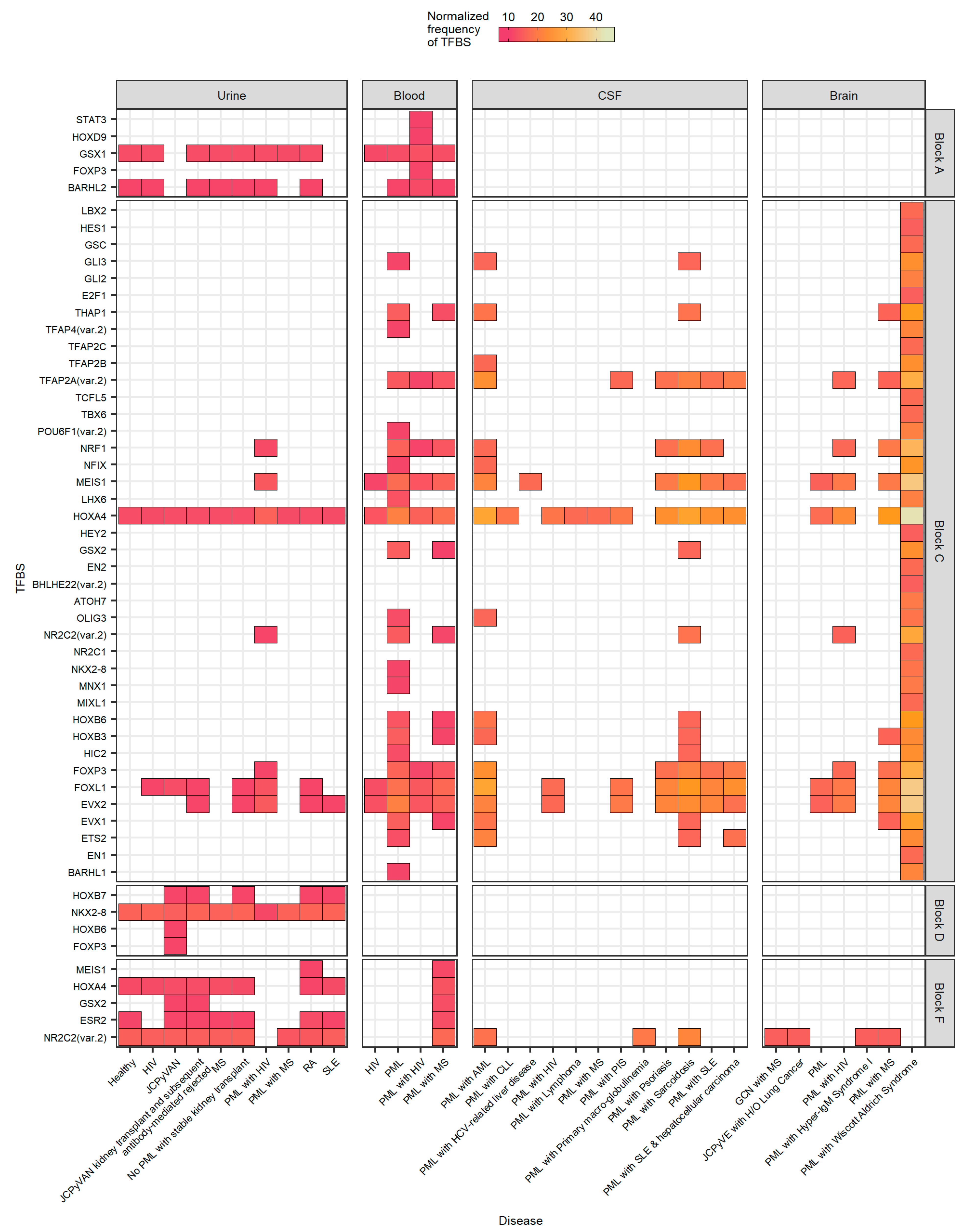
2.4. Sequences Isolated from Urine Samples Had a Higher Frequency of TFBS That Repress JCPyV Infection, While TFBS That Facilitate JCPyV Infection Were More Frequent in Sequences from Other Tissues
2.5. Highly Variable Number of TFBS in NCCR Viral Isolates from the Brain, Plasma, and CSF, Specifically in Blocks “c” and “d”
2.6. The Number of Forkhead and Homeobox TFBS Were Increased in the “c” Block of Patients with PML
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Determining and Visualizing the Blocks of Each NCCR Viral Isolate
4.2. Comprehensive Search for JCPyV NCCR Sequences
4.3. Analysis of Blocks among 989 NCCR Sequences
4.4. Validating the Perl Script to Determine the Accuracy and Precision of Capturing the NCCR and the Individual Blocks
4.5. Cladogram
4.6. Mapping TFBS for Each NCCR Sequence Using the JASPAR Database
4.7. Statistical Analysis of TFBS
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kean, J.M.; Rao, S.; Wang, M.; Garcea, R.L. Seroepidemiology of Human Polyomaviruses. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egli, A.; Infanti, L.; Dumoulin, A.; Buser, A.; Samaridis, J.; Stebler, C.; Gosert, R.; Hirsch, H.H. Prevalence of Polyomavirus BK and JC Infection and Replication in 400 Healthy Blood Donors. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, H.H.; Kardas, P.; Kranz, D.; Leboeuf, C. The Human JC Polyomavirus (JCPyV): Virological Background and Clinical Implications. APMIS 2013, 121, 685–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padgett, B.L.; Walker, D.L.; ZuRhein, G.M.; Eckroade, R.J.; Dessel, B.H. Cultivation of Papova-like Virus from Human Brain with Progressive Multifocal Leucoencephalopathy. Lancet 1971, 1, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, M.C.; Atwood, W.J.; Gravell, M.; Tornatore, C.S.; Major, E.O. JC Virus Infection of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells, Primary B Lymphocytes, and Tonsillar Stromal Cells: Implications for Viral Latency. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7004–7012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, V.; Dutronc, H.; Lafon, M.E.; Poinsot, V.; Pellegrin, J.L.; Ragnaud, J.M.; Ferrer, A.M.; Fleury, H.J. Latency and Reactivation of JC Virus in Peripheral Blood of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1-Infected Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2288–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapagain, M.L.; Nerurkar, V.R. Human Polyomavirus JC (JCV) Infection of Human B Lymphocytes: A Possible Mechanism for JCV Transmigration across the Blood-Brain Barrier. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.K.; Khalili, K. Pathogenesis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy—Revisited. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, D.; Patera, A.C.; Nyberg, F.; Gerber, M.; Liu, M.; Progressive Multifocal Leukeoncephalopathy Consortium. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy: Current Treatment Options and Future Perspectives. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2015, 8, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.L.; Koralnik, I.J.; Rumbaugh, J.A.; Burger, P.C.; King-Rennie, A.; McArthur, J.C. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in a Patient without Immunodeficiency. Neurology 2011, 77, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, H.; Hoffmann, C.; Degen, O.; Stoehr, A.; Plettenberg, A.; Mertenskötter, T.; Eggers, C.; Stellbrink, H.-J. Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy Significantly Improves the Prognosis of Patients with HIV-Associated Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Aids 1998, 12, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engsig, F.N.; Hansen, A.-B.E.; Omland, L.H.; Kronborg, G.; Gerstoft, J.; Laursen, A.L.; Pedersen, C.; Mogensen, C.B.; Nielsen, L.; Obel, N. Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Outcome of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in HIV-Infected Patients during the Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy Era: A Nationwide Cohort Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortese, I.; Reich, D.S.; Nath, A. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy and the Spectrum of JC Virus-Related Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, K.R.; Evens, A.M.; Richey, E.A.; Habermann, T.M.; Focosi, D.; Seymour, J.F.; Laubach, J.; Bawn, S.D.; Gordon, L.I.; Winter, J.N.; et al. Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy after Rituximab Therapy in HIV-Negative Patients: A Report of 57 Cases from the Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports Project. Blood 2009, 113, 4834–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomgren, G.; Richman, S.; Hotermans, C.; Subramanyam, M.; Goelz, S.; Natarajan, A.; Lee, S.; Plavina, T.; Scanlon, J.V.; Sandrock, A.; et al. Risk of Natalizumab-Associated Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermersch, P.; Kappos, L.; Gold, R.; Foley, J.F.; Olsson, T.; Cadavid, D.; Bozic, C.; Richman, S. Clinical Outcomes of Natalizumab-Associated Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (Podcast). Neurology 2011, 76, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosperini, L.; de Rossi, N.; Scarpazza, C.; Moiola, L.; Cosottini, M.; Gerevini, S.; Capra, R.; on behalf of the Italian PML study group. Natalizumab-Related Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy in Multiple Sclerosis: Findings from an Italian Independent Registry. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balduzzi, A.; Lucchini, G.; Hirsch, H.H.; Basso, S.; Cioni, M.; Rovelli, A.; Zincone, A.; Grimaldi, M.; Corti, P.; Bonanomi, S.; et al. Polyomavirus JC-Targeted T-Cell Therapy for Progressive Multiple Leukoencephalopathy in a Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Recipient. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2011, 46, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muftuoglu, M.; Olson, A.; Marin, D.; Ahmed, S.; Mulanovich, V.; Tummala, S.; Chi, T.L.; Ferrajoli, A.; Kaur, I.; Li, L.; et al. Allogeneic BK Virus–Specific T Cells for Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, I.; Muranski, P.; Enose-Akahata, Y.; Ha, S.-K.; Smith, B.; Monaco, M.; Ryschkewitsch, C.; Major, E.O.; Ohayon, J.; Schindler, M.K.; et al. Pembrolizumab Treatment for Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assetta, B.; Atwood, W.J. The Biology of JC Polyomavirus. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddington, R.C.; Yan, Y.; Moulai, J.; Sahli, R.; Benjamin, T.L.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of Simian Virus 40 at 3.8-A Resolution. Nature 1991, 354, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisque, R.J.; Bream, G.L.; Cannella, M.T. Human Polyomavirus JC Virus Genome. J. Virol. 1984, 51, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenczy, M.W.; Marshall, L.J.; Nelson, C.D.; Atwood, W.J.; Nath, A.; Khalili, K.; Major, E.O. Molecular Biology, Epidemiology, and Pathogenesis of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy, the JC Virus-Induced Demyelinating Disease of the Human Brain. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 471–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A.J. Surfing the P53 Network. Nature 2000, 408, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, N.; Bernards, R.; Friend, S.H.; Gooding, L.R.; Hassell, J.A.; Major, E.O.; Pipas, J.M.; Vandyke, T.; Harlow, E. Large T Antigens of Many Polyomaviruses Are Able to Form Complexes with the Retinoblastoma Protein. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1353–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, L.D.; Gordon, J.; Assimakopoulou, M.; Enam, S.; Geddes, J.F.; Varakis, J.N.; Katsetos, C.D.; Croul, S.; Khalili, K. Detection of JC Virus DNA Sequences and Expression of the Viral Regulatory Protein T-Antigen in Tumors of the Central Nervous System. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4287–4293. [Google Scholar]
- Dickmanns, A.; Zeitvogel, A.; Simmersbach, F.; Weber, R.; Arthur, A.K.; Dehde, S.; Wildeman, A.G.; Fanning, E. The Kinetics of Simian Virus 40-Induced Progression of Quiescent Cells into S Phase Depend on Four Independent Functions of Large T Antigen. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5496–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, K.; Sariyer, I.K.; Safak, M. Small Tumor Antigen of Polyomaviruses: Role in Viral Life Cycle and Cell Transformation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2008, 215, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollag, B.; Kilpatrick, L.H.; Tyagarajan, S.K.; Tevethia, M.J.; Frisque, R.J. JC Virus T’135, T’136 and T’165 Proteins Interact with Cellular P107 and P130 in Vivo and Influence Viral Transformation Potential. J. Neurovirol. 2006, 12, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.S.; Stehle, T.; Harrison, S.C. Interaction of Polyomavirus Internal Protein VP2 with the Major Capsid Protein VP1 and Implications for Participation of VP2 in Viral Entry. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3233–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safak, M.; Barrucco, R.; Darbinyan, A.; Okada, Y.; Nagashima, K.; Khalili, K. Interaction of JC Virus Agno Protein with T Antigen Modulates Transcription and Replication of the Viral Genome in Glial Cells. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Orba, Y.; Okada, Y.; Sunden, Y.; Kimura, T.; Tanaka, S.; Nagashima, K.; Hall, W.W.; Sawa, H. The Human Polyoma JC Virus Agnoprotein Acts as a Viroporin. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, C.E.; Li, H.; Sur, G.; Carmillo, P.; Bushnell, S.; Tizard, R.; McAuliffe, M.; Tonkin, C.; Simon, K.; Goelz, S.; et al. Sequencing and Analysis of JC Virus DNA from Natalizumab-Treated PML Patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, H.T.; Ryschkewitsch, C.F.; Singer, E.J.; Stoner, G.L. JC Virus Regulatory Region Rearrangements and Genotypes in Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy: Two Independent Aspects of Virus Variation. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.K.; Safak, M.; Khalili, K. Regulation of Gene Expression in Primate Polyomaviruses. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10846–10856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabath, B.F.; Major, E.O. Traffic of JC Virus from Sites of Initial Infection to the Brain: The Path to Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186 (Suppl. 2), S180–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L.J.; Major, E.O. Molecular Regulation of JC Virus Tropism: Insights into Potential Therapeutic Targets for Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Off. J. Soc. NeuroImmune Pharmacol. 2010, 5, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogo, Y.; Kitamura, T.; Sugimoto, C.; Ueki, T.; Aso, Y.; Hara, K.; Taguchi, F. Isolation of a Possible Archetypal JC Virus DNA Sequence from Nonimmunocompromised Individuals. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3139–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ault, G.S.; Stoner, G.L. Human Polyomavirus JC Promoter/Enhancer Rearrangement Patterns from Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy Brain Are Unique Derivatives of a Single Archetypal Structure. J. Gen. Virol. 1993, 74, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.N.; Major, E.O. A Classification Scheme for Human Polyomavirus JCV Variants Based on the Nucleotide Sequence of the Noncoding Regulatory Region. J. Neurovirology 2001, 7, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, T.V.; Thys, K.; Ryschkewitsch, C.; Lagatie, O.; Monaco, M.C.; Major, E.O.; Tritsmans, L.; Stuyver, L.J. JC Virus Quasispecies Analysis Reveals a Complex Viral Population Underlying Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy and Supports Viral Dissemination via the Hematogenous Route. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardi, M.R.; Zingaropoli, M.A.; Iannetta, M.; Prezioso, C.; Perri, V.; Pasculli, P.; Lichtner, M.; d’Ettorre, G.; Altieri, M.; Conte, A.; et al. JCPyV NCCR Analysis in PML Patients with Different Risk Factors: Exploring Common Rearrangements as Essential Changes for Neuropathogenesis. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.D.; King, D.M.; Slauch, J.M.; Frisque, R.J. Differences in Regulatory Sequences of Naturally Occurring JC Virus Variants. J. Virol. 1985, 53, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.D.; Foster, G.C. Multiple JC Virus Genomes from One Patient. J. Gen. Virol. 1984, 65, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisque, R.J. Nucleotide Sequence of the Region Encompassing the JC Virus Origin of DNA Replication. J. Virol. 1983, 46, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.M.; Swenson, J.J.; Mayreddy, R.P.R.; Khalili, K.; Frisque, R.J. Sequences within the Early and Late Promoters of Archetype JC Virus Restrict Viral DNA Replication and Infectivity. Virology 1996, 216, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronostajski, R.M. Roles of the NFI/CTF Gene Family in Transcription and Development. Gene 2000, 249, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemiya, K.; Traub, R.; Durham, L.; Major, E.O. Adjacent Nuclear Factor-1 and Activator Protein Binding Sites in the Enhancer of the Neurotropic JC Virus. A Common Characteristic of Many Brain-Specific Genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 14204–14211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, C.; Shinohara, T.; Durham, L.; Traub, R.; Major, E.O.; Amemiya, K. Expression of Multiple Classes of the Nuclear Factor-1 Family in the Developing Human Brain: Differential Expression of Two Classes of NF-1 Genes. J. Neurovirol. 1996, 2, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, L.J.; Dunham, L.; Major, E.O. Transcription Factor Spi-B Binds Unique Sequences Present in the Tandem Repeat Promoter/Enhancer of JC Virus and Supports Viral Activity. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 3042–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manley, K.; O’hara, B.A.; Gee, G.V.; Simkevich, C.P.; Sedivy, J.M.; Atwood, W.J. NFAT4 Is Required for JC Virus Infection of Glial Cells. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12079–12085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, L.J.; Ferenczy, M.W.; Daley, E.L.; Jensen, P.N.; Ryschkewitsch, C.F.; Major, E.O. Lymphocyte Gene Expression and JC Virus Noncoding Control Region Sequences Are Linked with the Risk of Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5177–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohman, E.M.; Monaco, M.C.; Remington, G.; Ryschkewitsch, C.; Jensen, P.N.; Johnson, K.; Perkins, M.; Liebner, J.; Greenberg, B.; Monson, N.; et al. JC Virus in CD34+ and CD19+ Cells in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Treated with Natalizumab. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, K.; Shimokawa, T. Database and Statistical Analyses of Transcription Factor Binding Sites in the Non-Coding Control Region of JC Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornes, O.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; Khan, A.; van der Lee, R.; Zhang, X.; Richmond, P.A.; Modi, B.P.; Correard, S.; Gheorghe, M.; Baranašić, D.; et al. JASPAR 2020: Update of the Open-Access Database of Transcription Factor Binding Profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D87–D92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, L.-A.; Letvin, N.L.; Koralnik, I.J. JC Virus Regulatory Region Tandem Repeats in Plasma and Central Nervous System Isolates Correlate with Poor Clinical Outcome in Patients with Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5672–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X Version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Le, S.; Li, Y.; Hu, F. SeqKit: A Cross-Platform and Ultrafast Toolkit for FASTA/Q File Manipulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME Suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.E.; Bailey, T.L.; Noble, W.S. FIMO: Scanning for Occurrences of a given Motif. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1017–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpulla, R.C. Nuclear Control of Respiratory Chain Expression by Nuclear Respiratory Factors and PGC-1-Related Coactivator. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1147, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhar, S.S.; Wong-Riley, M.T.T. Coupling of Energy Metabolism and Synaptic Transmission at the Transcriptional Level: Role of Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 in Regulating Both Cytochrome c Oxidase and NMDA Glutamate Receptor Subunit Genes. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boldorini, R.; Omodeo-Zorini, E.; Nebuloni, M.; Benigni, E.; Vago, L.; Ferri, A.; Monga, G. Lytic JC Virus Infection in the Kidneys of AIDS Subjects. Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Inaga, T.T.; Yogo, Y.; Kitamura, T.; Aso, Y. Persistence of Archetypal JC Virus DNA in Normal Renal Tissue Derived from Tumor-Bearing Patients. Virology 1992, 186, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, H.T.; Ryschkewitsch, C.F.; Stoner, G.L. Rearrangements of Archetypal Regulatory Regions in JC Virus Genomes from Urine. Res. Virol. 1998, 149, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, T.; Nagashima, K.; Major, E.O. Propagation of the Human Polyomavirus, JCV, in Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines. Virology 1997, 228, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Romagnoli, L.; Wollebo, H.S.; Deshmane, S.L.; Mukerjee, R.; Valle, L.D.; Safak, M.; Khalili, K.; White, M.K. Modulation of JC Virus Transcription by C/EBPbeta. Virus Res. 2009, 146, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, V.; Sabath, B.F.; Jensen, P.N.; Houff, S.A.; Major, E.O. Interactions between C-Jun, Nuclear Factor 1, and JC Virus Promoter Sequences: Implications for Viral Tropism. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 10506–10513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Honneur, A.-S.S.; Leh, H.; Laurent-Tchenio, F.; Hazan, U.; Rozenberg, F.; Bury-Moné, S. Exploring the Role of NCCR Variation on JC Polyomavirus Expression from Dual Reporter Minicircles. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, Q.; Wei, G.-H. The Role of HOX Transcription Factors in Cancer Predisposition and Progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, M.; Kang, L.; Li, Y.; Dai, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Tan, Y.; Wu, G. HHEX: A Crosstalker between HCMV Infection and Proliferation of VSMCs. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, H.; Mochizuki, K.; Tanaka, T.; Yamashita, A.; Matsuura, Y.; Moriishi, K. Induction of HOX Genes by Hepatitis C Virus Infection via Impairment of Histone H2A Monoubiquitination. J. Virol. 2020, 95, e01784-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Q.-L.; Liu, C.-Y.; Bai, Y.-Q. Effect of ATRA on the Expression of HOXA5 Gene in K562 Cells and Its Relationship with Cell Cycle and Apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 4221–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczek, M.P.; DuShane, J.K.; Armstrong, F.J.; Maginnis, M.S. JC Polyomavirus Infection Reveals Delayed Progression of the Infectious Cycle in Normal Human Astrocytes. J. Virol. 2019, 94, e01331-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golson, M.L.; Kaestner, K.H. Fox Transcription Factors: From Development to Disease. Development 2016, 143, 4558–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, A.; Nikravesh, H.; Faghihloo, E. The Roles of FOX Proteins in Virus-associated Cancers. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3347–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Yao, Y.; Jie, W.; Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, J.; Song, Y. Up-Regulation of Foxp3 Participates in Progression of Cervical Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitildzans, A.; Isajevs, S.; Rezeberga, D. P33 Up-Regulation of FOXP3 T Regulatory Lymphocytes in Patients with High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions Correlated with HPV Infection. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2019, 29, A70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuShane, J.K.; Wilczek, M.P.; Mayberry, C.L.; Maginnis, M.S. ERK Is a Critical Regulator of JC Polyomavirus Infection. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01529-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, Y.D.; Seger, R. The MEK/ERK Cascade: From Signaling Specificity to Diverse Functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell. Res. 2007, 1773, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querbes, W.; Benmerah, A.; Tosoni, D.; Fiore, P.P.D.; Atwood, W.J. A JC Virus-Induced Signal Is Required for Infection of Glial Cells by a Clathrin- and Eps15-Dependent Pathway. J. Virol. 2003, 78, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczek, M.P.; Armstrong, F.J.; Geohegan, R.P.; Mayberry, C.L.; DuShane, J.K.; King, B.L.; Maginnis, M.S. The MAPK/ERK Pathway and the Role of DUSP1 in JCPyV Infection of Primary Astrocytes. Viruses 2021, 13, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, J.N.; Lin, B.; Shin, J.; Phelan, P.J.; Tsichlis, P.; Schwob, J.E.; Bullock, P.A. The Replication of JCV DNA in the G144 Oligodendrocyte Cell Line Is Dependent Upon Akt. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00735-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczek, M.P.; Armstrong, F.J.; Mayberry, C.L.; King, B.L.; Maginnis, M.S. PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Pathway Is Required for JCPyV Infection in Primary Astrocytes. Cells 2021, 10, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, E.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Orton, R.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Smith, D.B. Virus Taxonomy: The Database of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, gkx932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, U.; Prezioso, C.; Pietropaolo, V. Genetic Diversity of the Noncoding Control Region of the Novel Human Polyomaviruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, R.B.; Dynan, W.S. Binding of Cellular Proteins to the Regulatory Region of BK Virus DNA. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 3388–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, U.; Johansen, T.; Johnsen, J.I.; Seternes, O.M.; Traavik, T. Noncoding Control Region of Naturally Occurring BK Virus Variants: Sequence Comparison and Functional Analysis. Virus Genes 1995, 10, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.; Andresen, P.A.; Hilmarsen, H.T.; Bjørang, O.; Scott, H.; Midtvedt, K.; Rinaldo, C.H. Genetic Variability in BK Virus Regulatory Regions in Urine and Kidney Biopsies from Renal-transplant Patients. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethge, T.; Ajuh, E.; Hirsch, H.H. Imperfect Symmetry of Sp1 and Core Promoter Sequences Regulates Early and Late Virus Gene Expression of the Bidirectional BK Polyomavirus Noncoding Control Region. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 10083–10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosert, R.; Rinaldo, C.H.; Funk, G.A.; Egli, A.; Ramos, E.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Hirsch, H.H. Polyomavirus BK with Rearranged Noncoding Control Region Emerge in Vivo in Renal Transplant Patients and Increase Viral Replication and Cytopathology. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, P.; Zygmunt, D.; Shapiro, R.; Vats, A.; Weck, K.; Swalsky, P.; Finkelstein, S. Viral Regulatory Region Sequence Variations in Kidney Tissue Obtained from Patients with BK Virus Nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethge, T.; Hachemi, H.A.; Manzetti, J.; Gosert, R.; Schaffner, W.; Hirsch, H.H. Sp1 Sites in the Noncoding Control Region of BK Polyomavirus Are Key Regulators of Bidirectional Viral Early and Late Gene Expression. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3396–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Tikhanovich, I.; Nasheuer, H.P.; Folk, W.R. Stimulation of BK Virus DNA Replication by NFI Family Transcription Factors. J. Virol. 2011, 86, 3264–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Carreras, J.; Mineeva-Sangwo, O.; Topalis, D.; Snoeck, R.; Andrei, G.; Maes, P. BKTyper: Free Online Tool for Polyoma BK Virus VP1 and NCCR Typing. Viruses 2020, 12, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajuh, E.T.; Wu, Z.; Kraus, E.; Weissbach, F.H.; Bethge, T.; Gosert, R.; Fischer, N.; Hirsch, H.H. Novel Human Polyomavirus Noncoding Control Regions Differ in Bidirectional Gene Expression According to Host Cell, Large T-Antigen Expression, and Clinically Occurring Rearrangements. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02231-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The Neighbor-Joining Method: A New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailund, T.; Brodal, G.S.; Fagerberg, R.; Pedersen, C.N.; Phillips, D. Recrafting the Neighbor-Joining Method. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Tissue Source | Primary Disease State | Total | Secondary Disease | Number of Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain (n = 32) | PML | 26 (81%) | HIV | 11 (34%) |
| MS a | 1 (3%) | |||
| WAS 1 | 1 (3%) | |||
| HIGM 2 | 1 (3%) | |||
| N/A | 12 (38%) | |||
| JCPyVE 3 | 1 (3%) | H/O Lung Cancer | 1 (3%) | |
| GCN b | 1 (3%) | MS | 1 (3%) | |
| N/A | 4 (13%) | N/A | 4 (13%) | |
| Plasma/serum/PBMC (i.e., blood) (n = 111) | PML | 91 (82%) | HIV | 7 (6%) |
| MS | 81 (73%) | |||
| N/A | 3 (3%) | |||
| Consistent with PML | 7 (6%) | HIV | 7 (6%) | |
| N/A | 13 (12%) | HIV | 5 (5%) | |
| N/A | 8 (7%) | |||
| CSF (n = 217) | PML | 195 (90%) | HIV | 46 (21%) |
| HIV/MS | 2 (1%) | |||
| RA 4 | 1 (1%) | |||
| SLE c | 9 (4%) | |||
| MS | 80 (37%) | |||
| AML d | 15 (7%) | |||
| ALL e | 7 (3%) | |||
| CLL f | 4 (2%) | |||
| NHL | 4 (2%) | |||
| WM 5 | 8 (4%) | |||
| Other # | 14 (6%) | |||
| N/A | 5 (2%) | |||
| Consistent with PML | 6 (3%) | HIV | 6 (3%) | |
| Suspected of PML | 14 (6%) | HIV | 2 (1%) | |
| MS | 1 (1%) | |||
| N/A | 11 (5%) | |||
| N/A | 2 (1%) | HIV | 1 (1%) | |
| N/A | 1 (1%) | |||
| Kidney (n = 2) | JCPyVAN 6 | 2 (100%) | N/A | 2 (100%) |
| Kidney; Urine (n = 3) | JCPyVAN 6 | 3 (100%) | N/A | 3 (100%) |
| Brain; Kidney (n = 6) | N/A | 6 (100%) | N/A | 6 (100%) |
| CSF; Plasma (n = 2) | Consistent with PML | 2 (100%) | HIV | 2 (100%) |
| Urine (n = 565) | PML | 78 (14%) | HIV | 4 (1%) |
| MS | 74 (13%) | |||
| JCPyVAN 6 | 1 (0%) | N/A | 1 (0%) | |
| 4 (1%) | kidney transplant and subsequent antibody-mediated rejection | 4 (1%) | ||
| Healthy | 179 (15%) | N/A | 179 (32%) | |
| No PML | 25 (%) | Stable Kidney Transplant | 25 (4%) | |
| N/A | 279 (65%) | HIV | 21 (4%) | |
| SLE | 8 (1%) | |||
| MS | 12 (2%) | |||
| RA | 1 (0%) | |||
| N/A | 236 (42%) | |||
| No tissue reported (n = 50)% | PML | 47 (94%) | HIV | 3 (6%) |
| MS | 44 (88%) | |||
| N/A | 3 (6%) | N/A | 3 (6%) |
| NCCR Block Code | Total # | Number of PML Patient Samples (Total Samples) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSF | Urine | Blood | Brain | Other | Not Specified | ||
| AB----CD-----------------EF | 592 | 35 (36) | 75 (490) | 35 (44) | 1 (2) | 0 (6) | 13 (14) |
| AB----C—-E-------------C-EF | 74 | 20 (23) | 1 (1) | 36 (38) | 2 (4) | 0 (1) | 7 (7) |
| AB----CD---------------CDEF | 64 | 13 (13) | 2 (50) | 0 (1) | |||
| AB----C—-E--B----------C-EF | 28 | 19 (22) | 0 (1) | 2 (3) | 2 (2) | ||
| AB----C------------------EF | 22 | 9 (14) | 5 (6) | 2 (2) | |||
| AB----C—-E------------FC-EF | 21 | 9 (9) | 10 (10) | 1 (2) | |||
| AB----CD-E—-B----------CDEF | 17 | 9 (10) | 0 (1) | 2 (2) | 4 (4) | ||
| A-----CD-----------------EF | 13 | 2 (2) | 0 (10) | 0 (1) | |||
| AB----CD-E-------------CDEF | 11 | 6 (7) | 0 (1) | 2 (2) | 0 (1) | ||
| AB----CD-----CD------EFCDEF | 10 | 10 (10) | |||||
| AB----C-------------------F | 10 | 7 (7) | 3 (3) | ||||
| AB----CD-EF-B----------CDEF | 10 | 5 (5) | 5 (5) | ||||
| AB----C-B--------------C-EF | 10 | 2 (2) | 0 (1) | 0 (2) | 5 (5) | ||
| A-----C—-E-A-----------C-EF | 9 | 2 (4) | 2 (2) | 2 (2) | 0 (1) | ||
| -B----CD-----------------EF | 8 | 0 (8) | |||||
| AB----CD-------------EFCDEF | 7 | 5 (5) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | |||
| AB----C-B--------------CDEF | 5 | 4 (5) | |||||
| AB----CD-----------------E- | 4 | 3 (3) | 0 (1) | ||||
| A-----CD---------------CDEF | 4 | 2 (2) | 0 (2) | ||||
| AB----CD------------------F | 4 | 1 (2) | 0 (1) | 0 (1) | |||
| A-----C------------------EF | 4 | 1 (1) | 0 (2) | 0 (1) | |||
| AB----C-B----C-E-------C-EF | 4 | 4 (4) | |||||
| AB----C-B----CD--------CDEF | 3 | 3 (3) | |||||
| AB----CDB--------------CDEF | 3 | 3 (3) | |||||
| AB----CD—------------EF-DEF | 3 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | |||
| A-----C—-E-------------C-EF | 3 | 2 (2) | 0 (1) | ||||
| AB----CD---------------CDE- | 3 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | |||
| AB----C--E--BC-E-B-----C-EF | 2 | 2 (2) | |||||
| AB----C--EF-BC-E-B-----C-EF | 2 | 2 (2) | |||||
| AB----C-B----C---B-----C-EF | 2 | 1 (1) | 0 (1) | ||||
| AB----CD-------------EFC--F | 2 | 2 (2) | |||||
| AB----C------------------E- | 2 | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | ||||
| AB----CD-----CDEFB-----CDEF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD-----CDEF--CDEFCDEF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD-E--B----------CDE- | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD-EF-BCDEFB-----CDEF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD-EF--CDEF--CDEFCD-- | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--E-A-----B-----C-EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--E---C---B-----C-EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--E---C-E-B-----C-EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--E---C-E---C-E-C-EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--E---C-------EFC-EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB-E--C--E---C-------E-C-EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB---FCD-----------------EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| A----FCD-----------------EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| -B----CD-------------E-CDEF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--E-------------C--F | 1 | 0 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--EF-B----------C-EF | 1 | 0 (1) | |||||
| A----FCD---------------CDEF | 1 | 0 (1) | |||||
| -BC----------------------EF | 1 | 0 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD----B----------C--F | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD---------------CD-F | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD-E--BC-E-B-----CDEF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD-EF--------CDEFCDEF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--E---C---B-C-E-C-EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--E---------C-E-C-EF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| A-----CD---------------CD-F | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| ABC-B-CD----BCD--B-----C--- | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| A-----C------------------E- | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD-----------CD-F--E- | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| AB----CD-------------EF--EF | 1 | 0 (1) | |||||
| AB-----D-----------------EF | 1 | 0 (1) | |||||
| AB----C--E-A-----------C-EF | 1 | 0 (1) | |||||
| A-----CD----B----------CDEF | 1 | 1 (1) | |||||
| A-----C--E-A-C-E--A----C-EF | 1 | 0 (1) | |||||
| Total | 989 | 195 (217) | 78 (566) | 91 (111) | 26 (32) | 0 (14) | 47 (49) |
| Block Letter | Nucleotide Sequence | Maximum Mismatch Value |
|---|---|---|
| Block “a” | CCTGTATATATAAAAAAAAGGGAAGG | 9 |
| Block “b” | AGGGAGGAGCTGGCTAAAACTG | 8 |
| Block “c” | GATGGCTGCCAGCCAAGCATGAGCTCATACCTAGGGAGCCAACCAGCTGACAGCC | 27 |
| Block “d” | AGAGGGAGCCCTGGCTGCATGCCACTGGCAGTTATAGTGAAACCCCTCCCATAGTCCTTAATCACA | 31 |
| Block “e” | AGTAAACAAAGCACAAGG | 1 |
| Block “f” | GGAAGTGGAAAGCAGCCAAGGGAACATGTTTTGCGAGCCAGAGCTGTTTTGGCTTGTCACCAGCTGGCCAGT | 31 |
| Description of Error | Frequency of Error (%) | Mean (SD) (Block Code or Base Pairs) | % of Error out of the Average Length of the NCCR with Error (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Block code less than 85% accurate | 13% | 77.7% (±4.2%) | N/A |
| Block code greater than 100% (larger blocks from the initial analysis were interpreted as smaller and different block codes) | 6% | 123.5% (±26%) | N/A |
| Autogenerated block annotation had nucleotides counted in two sequential blocks, occurring when the start of a block occurs before the end of the previous | 63% | 2.93 (±1.88) | 0.998% (±0.0807%) |
| Predicted block lacks at least one base pair that was counted in the manual annotation | 93% | 8.84 (±9.12) | 3.07% (±3.29%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilczek, M.P.; Pike, A.M.C.; Craig, S.E.; Maginnis, M.S.; King, B.L. Rearrangement in the Hypervariable Region of JC Polyomavirus Genomes Isolated from Patient Samples and Impact on Transcription Factor-Binding Sites and Disease Outcomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105699
Wilczek MP, Pike AMC, Craig SE, Maginnis MS, King BL. Rearrangement in the Hypervariable Region of JC Polyomavirus Genomes Isolated from Patient Samples and Impact on Transcription Factor-Binding Sites and Disease Outcomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105699
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilczek, Michael P., Aiden M. C. Pike, Sophie E. Craig, Melissa S. Maginnis, and Benjamin L. King. 2022. "Rearrangement in the Hypervariable Region of JC Polyomavirus Genomes Isolated from Patient Samples and Impact on Transcription Factor-Binding Sites and Disease Outcomes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105699
APA StyleWilczek, M. P., Pike, A. M. C., Craig, S. E., Maginnis, M. S., & King, B. L. (2022). Rearrangement in the Hypervariable Region of JC Polyomavirus Genomes Isolated from Patient Samples and Impact on Transcription Factor-Binding Sites and Disease Outcomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105699







