AG1478 Elicits a Novel Anti-Influenza Function via an EGFR-Independent, GBF1-Dependent Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
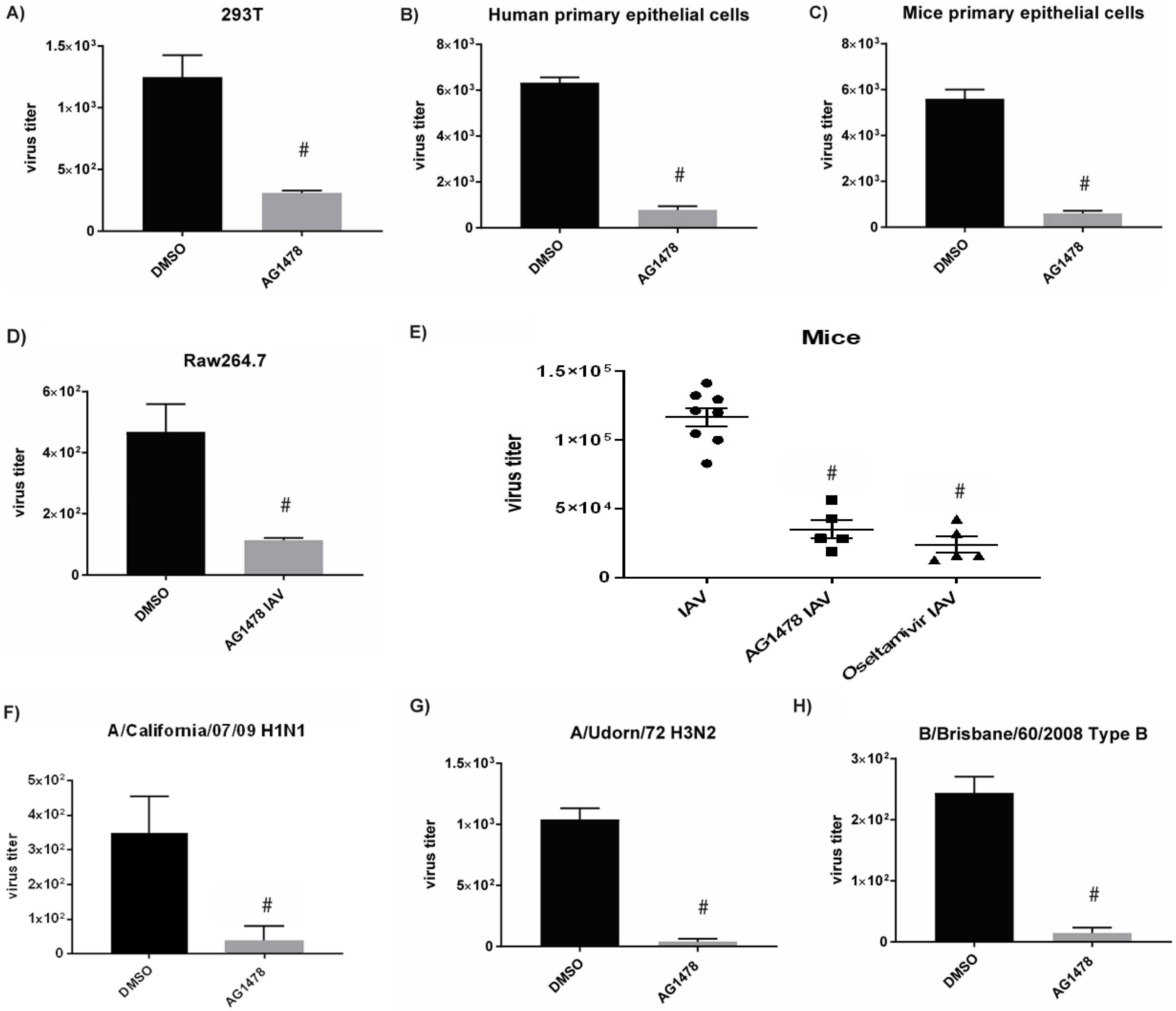
2.1. A Small-Molecule EGFR Inhibitor, AG1478, Inhibited IAV Production Independent of EGFR Blockade
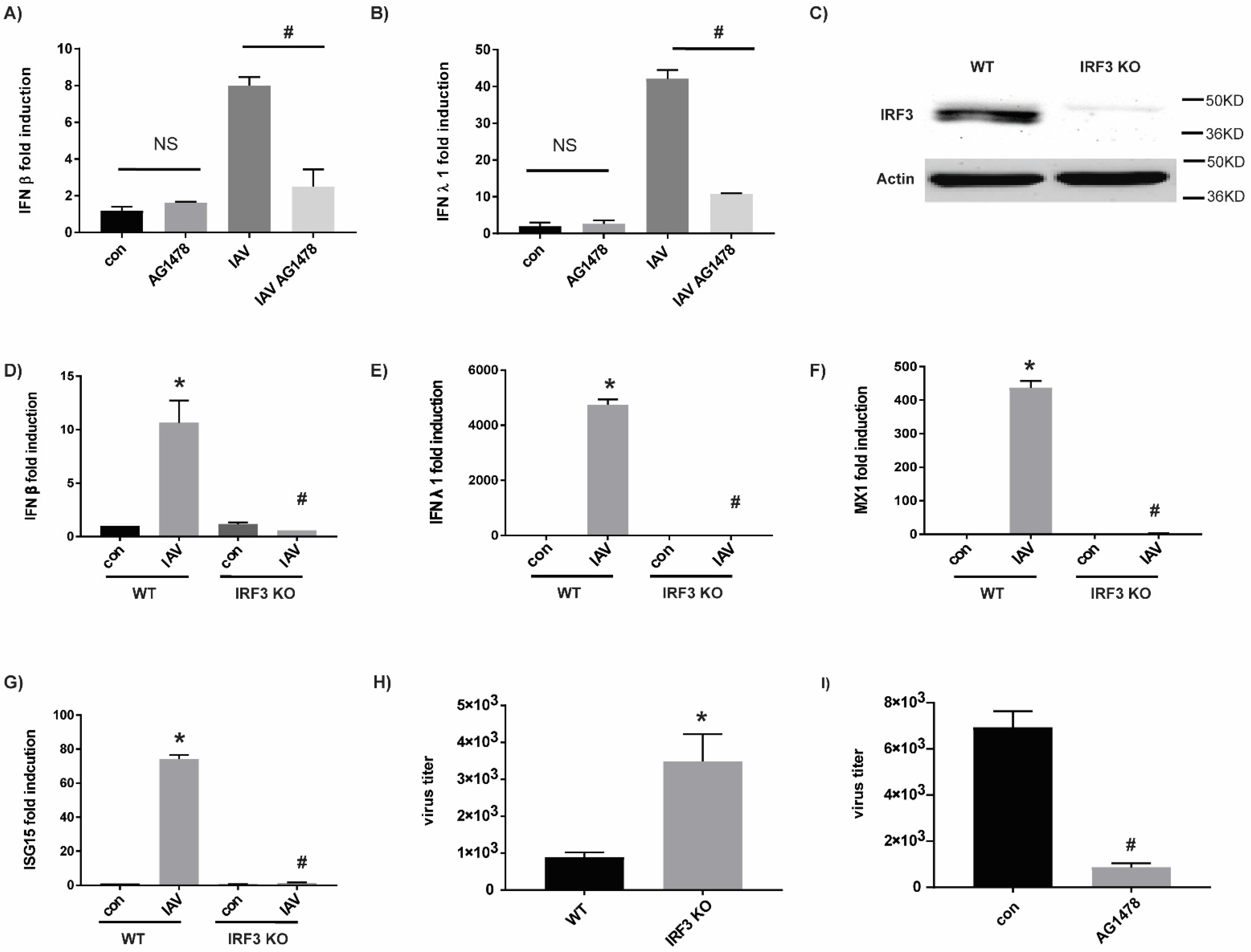
2.2. AG1478 Had a Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity across Different Cell Models Independent of IFN
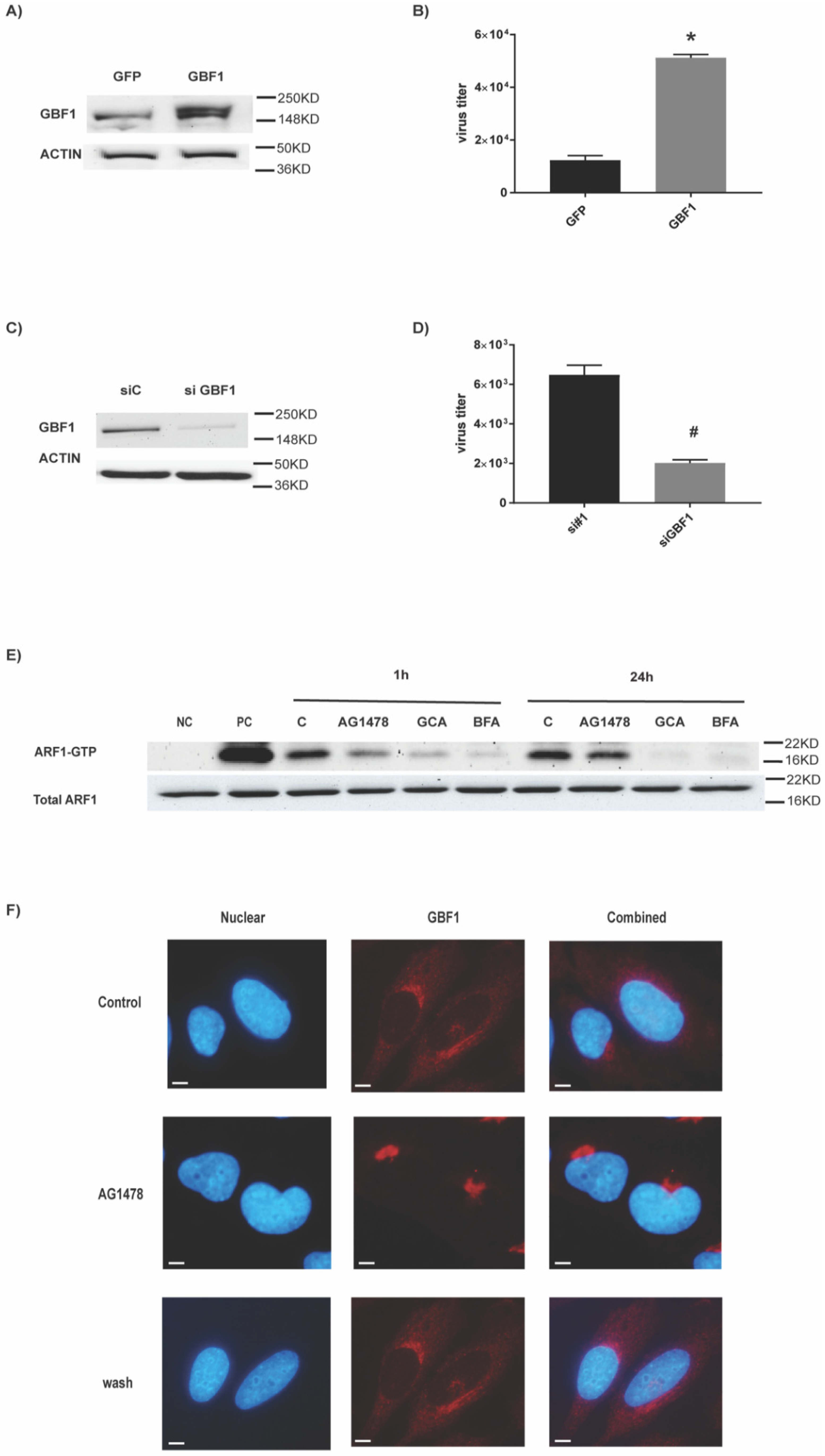
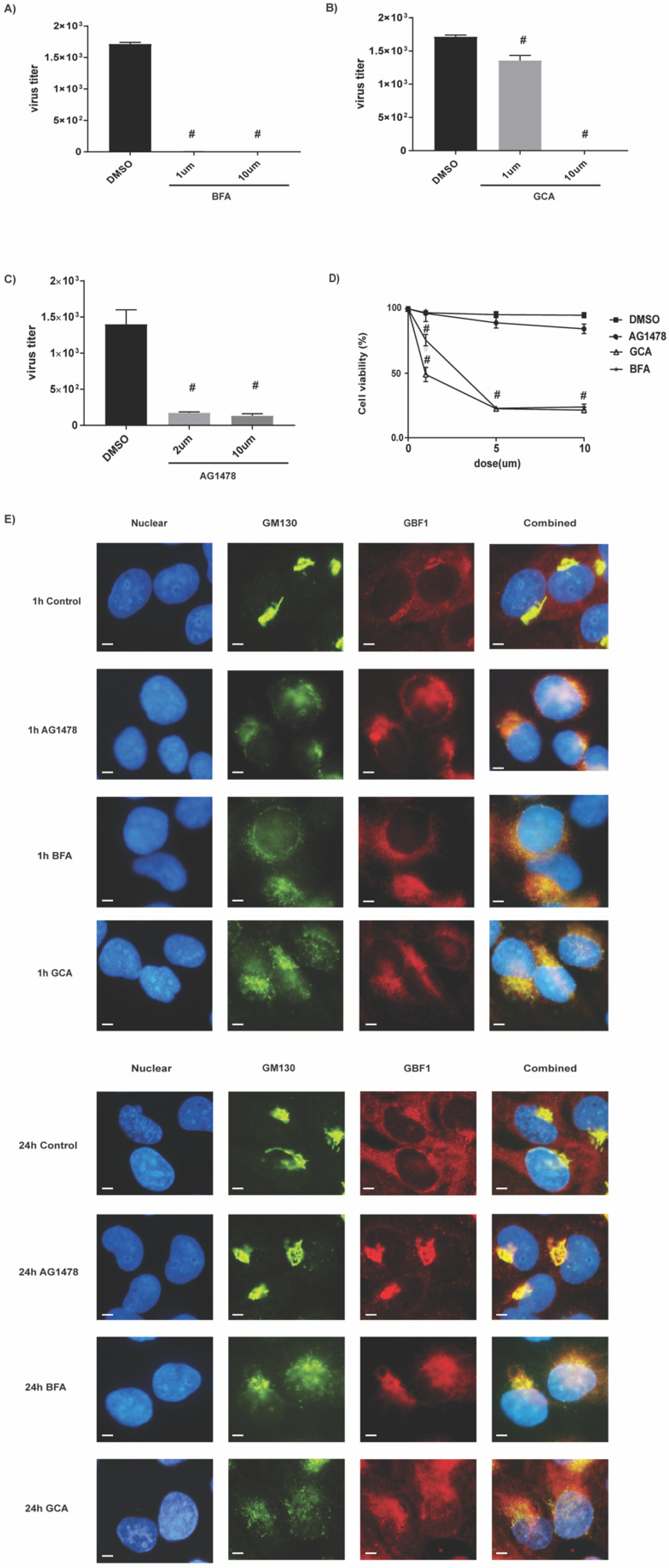
2.3. The Target of AG1478 Is GBF1
2.4. AG1478 Had a Superior Safety Profile as Compared to GCA and BFA
2.5. GBF1 Interacted with Selected Viral Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Virus
4.2. Plaque Assay
4.3. A Mouse Model of Influenza Infection
4.4. Inhibitors and Treatments
4.5. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.6. Antibodies and Western Blot
4.7. Gene Knockout Using Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)
4.8. Immunofluorescence
4.9. Transfection
4.10. Cell Viability Assay
4.11. Immunoprecipitation and ARF1 Activity Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krammer, F.; Palese, P. Advances in the development of influenza virus vaccines. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Influenza Antiviral Medications: Summary for Clinicians. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/professionals/antivirals/summary-clinicians.htm (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Gasparini, R.; Amicizia, D.; Lai, P.L.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Panatto, D. Compounds with anti-influenza activity: Present and future of strategies for the optimal treatment and management of influenza. Part I: Influenza life-cycle and currently available drugs. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2014, 55, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bloom, J.D.; Gong, L.I.; Baltimore, D. Permissive secondary mutations enable the evolution of influenza oseltamivir resistance. Science 2010, 328, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, B.N.; Knipe, D.M.; Howley, P.M. Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lofgren, E.; Fefferman, N.H.; Naumov, Y.N.; Gorski, J.; Naumova, E.N. Influenza seasonality: Underlying causes and modeling theories. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5429–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Aramini, J.M.; Ma, L.C.; Krug, R.M.; Arnold, E. Structures of influenza A proteins and insights into antiviral drug targets. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Martin, S.R.; Haire, L.F.; Wharton, S.A.; Daniels, R.S.; Bennett, M.S.; McCauley, J.W.; Collins, P.J.; Walker, P.A.; Skehel, J.J.; et al. Receptor binding by an H7N9 influenza virus from humans. Nature 2013, 499, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, M.; Fouchier, R.A. Role of receptor binding specificity in influenza A virus transmission and pathogenesis. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 823–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upham, J.P.; Pickett, D.; Irimura, T.; Anders, E.M.; Reading, P.C. Macrophage receptors for influenza A virus: Role of the macrophage galactose-type lectin and mannose receptor in viral entry. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3730–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, C.J.; Doherty, P.C.; Thomas, P.G. Respiratory epithelial cells in innate immunity to influenza virus infection. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 343, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eierhoff, T.; Hrincius, E.R.; Rescher, U.; Ludwig, S.; Ehrhardt, C. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) promotes uptake of influenza A viruses (IAV) into host cells. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, I.F.; Min-Oo, G.; Kalinowski, A.; Ballon-Landa, E.; Lanier, L.L.; Nadel, J.A.; Koff, J.L. Respiratory virus-induced EGFR activation suppresses IRF1-dependent interferon lambda and antiviral defense in airway epithelium. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoguchi, K.; Yoneyama, M.; Takemura, A.; Akira, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Namiki, H.; Fujita, T. Viral infections activate types I and III interferon genes through a common mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7576–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iversen, M.B.; Paludan, S.R. Mechanisms of type III interferon expression. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010, 30, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Carpenter, A.; Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Ma, D.; Yuan, J. A novel small molecule regulator of guanine nucleotide exchange activity of the ADP-ribosylation factor and golgi membrane trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31087–31096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, M.R.; Morrison, K.C.; Jacques, S.J.; Leadbeater, W.E.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Berry, M.; Logan, A.; Ahmed, Z. Off-target effects of epidermal growth factor receptor antagonists mediate retinal ganglion cell disinhibited axon growth. Brain 2009, 132, 3102–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorobantu, C.M.; Harak, C.; Klein, R.; van der Linden, L.; Strating, J.R.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Lohmann, V.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. Tyrphostin AG1478 Inhibits Encephalomyocarditis Virus and Hepatitis C Virus by Targeting Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase IIIalpha. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6402–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Kawakami, E.; Shoemaker, J.E.; Lopes, T.J.; Matsuoka, Y.; Tomita, Y.; Kozuka-Hata, H.; Gorai, T.; Kuwahara, T.; Takeda, E.; et al. Influenza virus-host interactome screen as a platform for antiviral drug development. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lasell, T.K.; Melancon, P. Localization of large ADP-ribosylation factor-guanine nucleotide exchange factors to different Golgi compartments: Evidence for distinct functions in protein traffic. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilty, D.; Gray, F.; Summerfeldt, N.; Cassel, D.; Melancon, P. Arf activation at the Golgi is modulated by feed-forward stimulation of the exchange factor GBF1. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T.K.; Pfeifer, A.C.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Jackson, C.L. Dynamics of GBF1, a Brefeldin A-sensitive Arf1 exchange factor at the Golgi. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, L.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Lanke, K.H.; Neyts, J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. Differential effects of the putative GBF1 inhibitors Golgicide A and AG1478 on enterovirus replication. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7535–7542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhat, R.; Ankavay, M.; Lebsir, N.; Gouttenoire, J.; Jackson, C.L.; Wychowski, C.; Moradpour, D.; Dubuisson, J.; Rouille, Y.; Cocquerel, L. Identification of GBF1 as a cellular factor required for hepatitis E virus RNA replication. Cell Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlin, J.; Farhat, R.; Belouzard, S.; Cocquerel, L.; Bertin, A.; Hober, D.; Dubuisson, J.; Rouille, Y. Investigation of the role of GBF1 in the replication of positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, D.; Bartenschlager, R. Architecture and biogenesis of plus-strand RNA virus replication factories. World J. Virol. 2013, 2, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheije, M.H.; Raaben, M.; Mari, M.; Te Lintelo, E.G.; Reggiori, F.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Rottier, P.J.; de Haan, C.A. Mouse hepatitis coronavirus RNA replication depends on GBF1-mediated ARF1 activation. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, A.H.; Wannee, K.F.; Scholte, F.E.; Goeman, J.J.; Ten Dijke, P.; Snijder, E.J.; Kikkert, M.; van Hemert, M.J. A Kinome-Wide Small Interfering RNA Screen Identifies Proviral and Antiviral Host Factors in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication, Including Double-Stranded RNA-Activated Protein Kinase and Early Secretory Pathway Proteins. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8318–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpp, L.N.; Rogers, R.S.; Moritz, R.L.; Aitchison, J.D. Quantitative proteomic analysis of host-virus interactions reveals a role for Golgi brefeldin A resistance factor 1 (GBF1) in dengue infection. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2014, 13, 2836–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goueslain, L.; Alsaleh, K.; Horellou, P.; Roingeard, P.; Descamps, V.; Duverlie, G.; Ciczora, Y.; Wychowski, C.; Dubuisson, J.; Rouille, Y. Identification of GBF1 as a cellular factor required for hepatitis C virus RNA replication. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 773–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zheng, M.; Bao, C.; Zhang, Y. CSFV proliferation is associated with GBF1 and Rab2. J. Biosci. 2017, 42, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonderstein, K.; Nilsson, E.; Hubel, P.; Nygard Skalman, L.; Upadhyay, A.; Pasto, J.; Pichlmair, A.; Lundmark, R.; Overby, A.K. Viperin targets flavivirus virulence by inducing assembly of non-infectious capsid particles. J. Virol. 2017, 92, e01751-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, G.A.; Feng, Q.; Nikovics, K.; Jackson, C.L.; Ehrenfeld, E. A critical role of a cellular membrane traffic protein in poliovirus RNA replication. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanke, K.H.; van der Schaar, H.M.; Belov, G.A.; Feng, Q.; Duijsings, D.; Jackson, C.L.; Ehrenfeld, E.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. GBF1, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Arf, is crucial for coxsackievirus B3 RNA replication. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 11940–11949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Si, X.; Wu, H.; Zhai, X.; Wang, Y.; Tong, L.; Pan, B.; et al. Curcumin inhibits the replication of enterovirus 71 in vitro. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Du, J.; Jin, Q. Class I ADP-ribosylation factors are involved in enterovirus 71 replication. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Aponte-Diaz, D.; Yeager, C.; Sharma, S.D.; Ning, G.; Oh, H.S.; Han, Q.; Umeda, M.; Hara, Y.; Wang, R.Y.L.; et al. Hijacking of multiple phospholipid biosynthetic pathways and induction of membrane biogenesis by a picornaviral 3CD protein. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, L. Key components of COPI and COPII machineries are required for chikungunya virus replication. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Das, A.; Dinh, P.X.; Subramaniam, S.; Nayak, D.; Barrows, N.J.; Pearson, J.L.; Thompson, J.; Kelly, D.L.; Ladunga, I.; et al. RNAi screening reveals requirement for host cell secretory pathway in infection by diverse families of negative-strand RNA viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19036–19041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, E.; Duijsings, D.; Lanke, K.H.; van Dooren, S.H.; Jackson, C.L.; Melchers, W.J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. Effects of picornavirus 3A Proteins on Protein Transport and GBF1-dependent COP-I recruitment. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11852–11860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wessels, E.; Duijsings, D.; Lanke, K.H.; Melchers, W.J.; Jackson, C.L.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. Molecular determinants of the interaction between coxsackievirus protein 3A and guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5238–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hsu, N.Y.; Ilnytska, O.; Belov, G.; Santiana, M.; Chen, Y.H.; Takvorian, P.M.; Pau, C.; van der Schaar, H.; Kaushik-Basu, N.; Balla, T.; et al. Viral reorganization of the secretory pathway generates distinct organelles for RNA replication. Cell 2010, 141, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolokoltsov, A.A.; Adhikary, S.; Garver, J.; Johnson, L.; Davey, R.A.; Vela, E.M. Inhibition of Lassa virus and Ebola virus infection in host cells treated with the kinase inhibitors genistein and tyrphostin. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viktorova, E.G.; Nchoutmboube, J.; Ford-Siltz, L.A.; Belov, G.A. Cell-specific establishment of poliovirus resistance to an inhibitor targeting a cellular protein. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4372–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Hamati, E.; Lee, P.K.; Lee, W.M.; Wachi, S.; Schnurr, D.; Yagi, S.; Dolganov, G.; Boushey, H.; Avila, P.; et al. Rhinovirus induces airway epithelial gene expression through double-stranded RNA and IFN-dependent pathways. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 34, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oslund, K.L.; Zhou, X.; Lee, B.; Zhu, L.; Duong, T.; Shih, R.; Baumgarth, N.; Hung, L.Y.; Wu, R.; Chen, Y. Synergistic up-regulation of CXCL10 by virus and IFN gamma in human airway epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, S.; Sakai-Tagawa, Y.; Kiso, M.; Goto, H.; Kawakami, C.; Mitamura, K.; Sugaya, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Kawaoka, Y. Enhanced expression of an alpha2,6-linked sialic acid on MDCK cells improves isolation of human influenza viruses and evaluation of their sensitivity to a neuraminidase inhibitor. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4139–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, F.; Musharrafieh, R.G.; Wang, J. Discovery of cyclosporine A and its analogs as broad-spectrum anti-influenza drugs with a high in vitro genetic barrier of drug resistance. Antivir. Res. 2016, 133, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjana, N.E.; Shalem, O.; Zhang, F. Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalem, O.; Sanjana, N.E.; Hartenian, E.; Shi, X.; Scott, D.A.; Mikkelson, T.; Heckl, D.; Ebert, B.L.; Root, D.E.; Doench, J.G.; et al. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science 2014, 343, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szul, T.; Grabski, R.; Lyons, S.; Morohashi, Y.; Shestopal, S.; Lowe, M.; Sztul, E. Dissecting the role of the ARF guanine nucleotide exchange factor GBF1 in Golgi biogenesis and protein trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 3929–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.H.; Kunz, A.; Simon, V.A.; Palese, P.; Shaw, M.L. Broad-spectrum antiviral that interferes with de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5777–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Primer |
|---|---|
| β-Actin | Forward ACTGGAACGGTGAAGGTGACA |
| Reverse ATGGCAAGGGACTTCCTGTAAC | |
| IFNβ | Forward ATTGCCTCAAGGACAGGATG |
| Reverse GCTGCAGCTGCTTAATCTCC | |
| IFNλ1 | Forward GGACGCCTTGGAAGAGTCACT |
| Reverse AGAAGCCTCAGGTCCCAATTC | |
| IFNλ2/3 | Forward CTGCCACATAGCCCAGTTCA |
| Reverse AGAAGCGACTCTTCTAAGGCATCTT | |
| MX1 | Forward AGAGAAGGTGAGAAGCTGATCC |
| Reverse TTCTTCCAGCTCCTTCTCTCTG | |
| ISG15 | Forward GGACCTGACGGTGAAGATGCT |
| Reverse ACGCCAATCTTCTGGGTGATCT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Zhu, L.; Bondy, C.; Wang, J.; Luo, Q.; Chen, Y. AG1478 Elicits a Novel Anti-Influenza Function via an EGFR-Independent, GBF1-Dependent Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105557
Zhou X, Zhu L, Bondy C, Wang J, Luo Q, Chen Y. AG1478 Elicits a Novel Anti-Influenza Function via an EGFR-Independent, GBF1-Dependent Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(10):5557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105557
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xu, Lingxiang Zhu, Cheryl Bondy, Jun Wang, Qianwen Luo, and Yin Chen. 2022. "AG1478 Elicits a Novel Anti-Influenza Function via an EGFR-Independent, GBF1-Dependent Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 10: 5557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105557
APA StyleZhou, X., Zhu, L., Bondy, C., Wang, J., Luo, Q., & Chen, Y. (2022). AG1478 Elicits a Novel Anti-Influenza Function via an EGFR-Independent, GBF1-Dependent Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(10), 5557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23105557






