Evaluating a Targeted Cancer Therapy Approach Mediated by RNA trans-Splicing In Vitro and in a Xenograft Model for Epidermolysis Bullosa-Associated Skin Cancer
Abstract
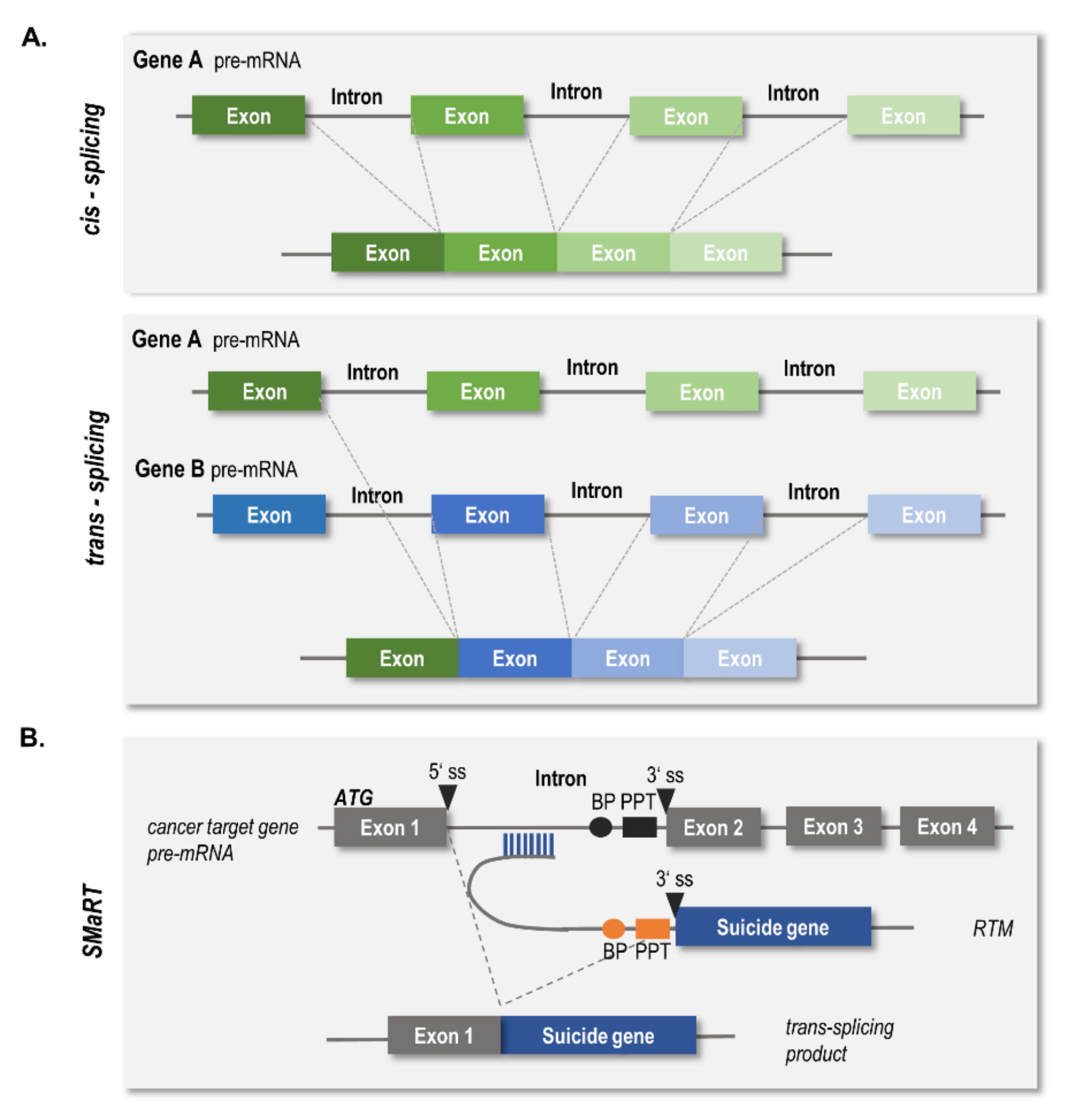
:1. Introduction
2. Results
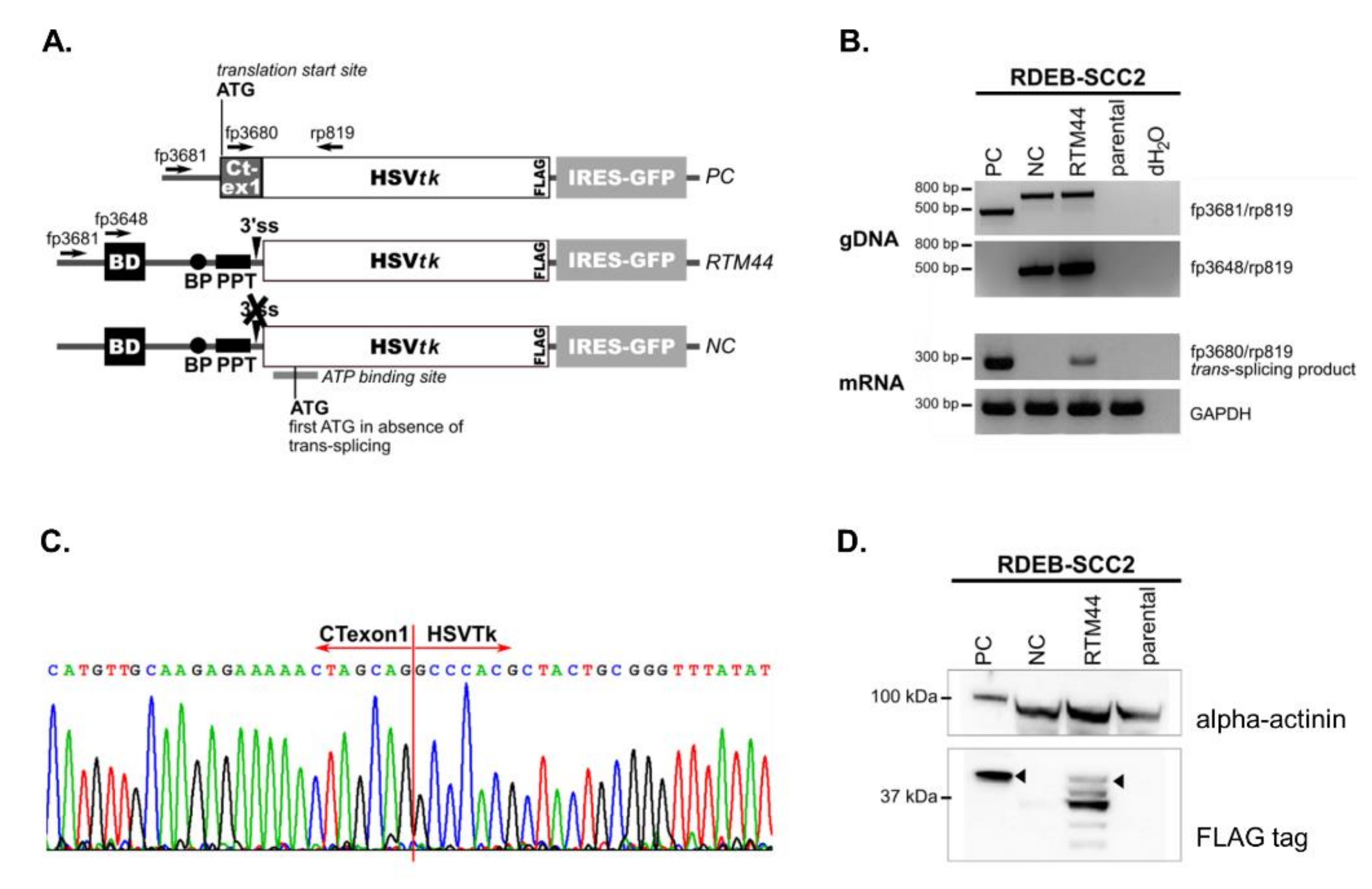
2.1. RTM44 Facilitates the Trans-Splicing Reaction in RDEB-SCC Cells
2.2. RTM44 Renders RDEB-SCC Sensitive to Ganciclovir Treatment In Vitro
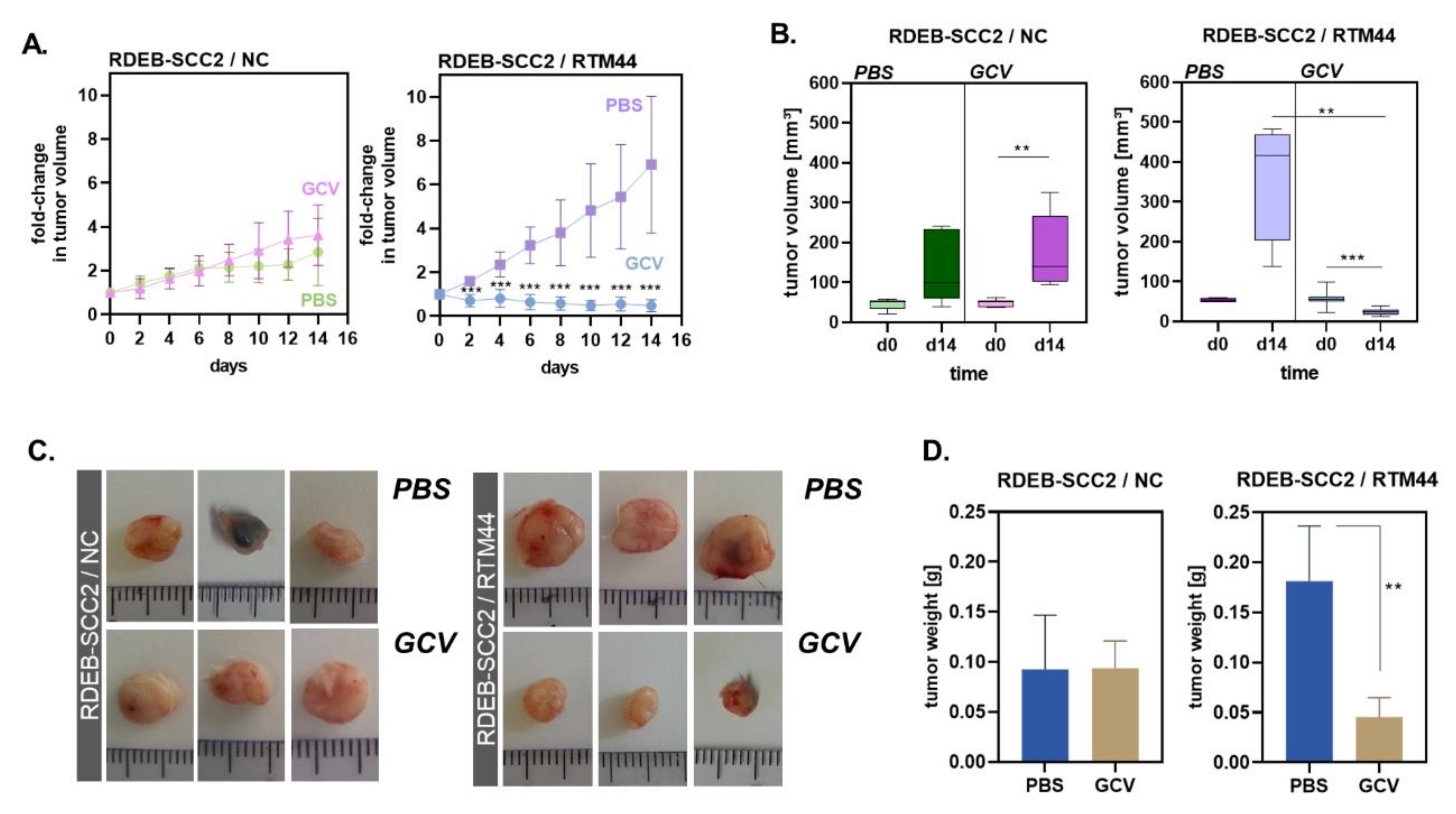
2.3. RTM44 Shows Efficacy in a Xenograft Mouse Model for RDEB-SCC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. RTM44
4.3. Transient Transfection
4.4. PCR Analysis
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. TUNEL Staining
4.7. MTT Assay and Confluency Measurement
4.8. Animal Model
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, Q.; Li, C.; Zuo, Z.; Huang, C.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, R. Evolutionary Insights into RNA trans-Splicing in Vertebrates. Genome. Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 562–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, H. Intergenically Spliced Chimeric RNAs in Cancer. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kannan, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Ittmann, M.M.; Li, W.; Yen, L. Recurrent chimeric RNAs enriched in human prostate cancer identified by deep sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9172–9177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Qin, F.; Li, H. Chimeric RNAs and their implications in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 48, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttaraju, M.; Jamison, S.F.; Mansfield, S.G.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A.; Mitchell, L.G. Spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing as a tool for gene therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peking, P.; Breitenbach, J.S.; Ablinger, M.; Muss, W.H.; Poetschke, F.J.; Kocher, T.; Koller, U.; Hainzl, S.; Kitzmueller, S.; Bauer, J.W.; et al. An ex vivo RNA trans-splicing strategy to correct human generalized severe epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wally, V.; Klausegger, A.; Koller, U.; Lochmuller, H.; Krause, S.; Wiche, G.; Mitchell, L.G.; Hintner, H.; Bauer, J.W. 5′ trans-splicing repair of the PLEC1 gene. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murauer, E.M.; Gache, Y.; Gratz, I.K.; Klausegger, A.; Muss, W.; Gruber, C.; Meneguzzi, G.; Hintner, H.; Bauer, J.W. Functional correction of type VII collagen expression in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peking, P.; Koller, U.; Duarte, B.; Murillas, R.; Wolf, S.; Maetzig, T.; Rothe, M.; Kocher, T.; Garcia, M.; Brachtl, G.; et al. An RNA-targeted therapy for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 10259–10269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tockner, B.; Kocher, T.; Hainzl, S.; Reichelt, J.; Bauer, J.W.; Koller, U.; Murauer, E.M. Construction and validation of an RNA trans-splicing molecule suitable to repair a large number of COL7A1 mutations. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huttner, C.; Murauer, E.M.; Hainzl, S.; Kocher, T.; Neumayer, A.; Reichelt, J.; Bauer, J.W.; Koller, U. Designing Efficient Double RNA trans-Splicing Molecules for Targeted RNA Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, U.; Wally, V.; Mitchell, L.G.; Klausegger, A.; Murauer, E.M.; Mayr, E.; Gruber, C.; Hainzl, S.; Hintner, H.; Bauer, J.W. A novel screening system improves genetic correction by internal exon replacement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.M.; Ingemarsdotter, C.K.; Lever, A.M.L. Therapeutic applications of trans-splicing. Br. Med. Bull. 2020, 136, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, C.; Koller, U.; Murauer, E.M.; Hainzl, S.; Huttner, C.; Kocher, T.; South, A.P.; Hintner, H.; Bauer, J.W. The design and optimization of RNA trans-splicing molecules for skin cancer therapy. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingemarsdotter, C.K.; Poddar, S.; Mercier, S.; Patzel, V.; Lever, A.M.L. Expression of Herpes Simplex Virus Thymidine Kinase/Ganciclovir by RNA Trans-Splicing Induces Selective Killing of HIV-Producing Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 7, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poddar, S.; Loh, P.S.; Ooi, Z.H.; Osman, F.; Eul, J.; Patzel, V. RNA Structure Design Improves Activity and Specificity of trans-Splicing-Triggered Cell Death in a Suicide Gene Therapy Approach. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Pinon Hofbauer, J.; Harada, M.; Woss, K.; Koller, U.; Morio, H.; Stierschneider, A.; Kitamura, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Chiba, K.; et al. Cancer-type organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 is a target for cancer suicide gene therapy using RNA trans-splicing technology. Cancer Lett. 2018, 433, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillat, C.; Carrio, M.; Cascante, A.; Sangro, B. Suicide gene therapy mediated by the Herpes Simplex virus thymidine kinase gene/Ganciclovir system: Fifteen years of application. Curr. Gene Ther. 2003, 3, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, C.; Gratz, I.K.; Murauer, E.M.; Mayr, E.; Koller, U.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Meneguzzi, G.; Hintner, H.; Bauer, J.W. Spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing facilitates targeted delivery of suicide genes to cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, K.; Farasyn, T.; Ding, K.; Yue, W. Characterization of Liver- and Cancer-type-Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide (OATP) 1B3 Messenger RNA Expression in Normal and Cancerous Human Tissues. Drug Metab. Lett. 2018, 12, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Furihata, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Ishii, S.; Motohashi, S.; Yoshino, I.; Ugajin, M.; Miyajima, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Chiba, K. Identification of a new organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 mRNA isoform primarily expressed in human cancerous tissues and cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, N.; Kim, K.; Jang, E.R.; Han, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.; Merchant, N.; Lockhart, A.C.; Lee, W. A cancer-specific variant of the SLCO1B3 gene encodes a novel human organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 (OATP1B3) localized mainly in the cytoplasm of colon and pancreatic cancer cells. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Woess, K.; Kienzl, M.; Leb-Reichl, V.M.; Feinle, A.; Wimmer, M.; Zauner, R.; Wally, V.; Luetz-Meindl, U.; Mellerio, J.E.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers for the Detection of a Tumor Marker Gene in Epidermolysis Bullosa-Associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1197–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bardhan, A.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Fine, J.D.; Harper, N.; Has, C.; Magin, T.M.; Marinkovich, M.P.; Marshall, J.F.; McGrath, J.A.; et al. Epidermolysis bullosa. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, J.D.; Johnson, L.B.; Weiner, M.; Li, K.P.; Suchindran, C. Epidermolysis bullosa and the risk of life-threatening cancers: The National EB Registry experience, 1986–2006. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 60, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, J.D. Epidemiology of Inherited Epidermolysis Bullosa Based on Incidence and Prevalence Estimates From the National Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Li, M.; Intong-Wheeler, L.R.A.; Tran, K.; Marucci, D.; Murrell, D.F. Epidemiology and Outcome of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Epidermolysis Bullosa in Australia and New Zealand. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2018, 98, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, R.J.; Alexandrov, L.B.; den Breems, N.Y.; Atanasova, V.S.; Farshchian, M.; Purdom, E.; Nguyen, T.N.; Coarfa, C.; Rajapakshe, K.; Prisco, M.; et al. APOBEC mutation drives early-onset squamous cell carcinomas in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Summers, W.C. Site-directed mutagenesis of a nucleotide-binding domain in HSV-1 thymidine kinase: Effects on catalytic activity. Virology 1988, 163, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Murrell, D.F. Update on the pathogenesis of squamous cell carcinoma development in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2015, 25 (Suppl. S1), 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.; Mansfield, S.G.; Bartel, R.C.; Hiriyanna, S.; Mitchell, L.G.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A.; Walsh, C.E. Phenotype correction of hemophilia A mice by spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, S.J.; McDougald, D.S.; Fisher, K.J.; Bennicelli, J.L.; Mitchell, L.G.; Bennett, J. Spliceosome-Mediated Pre-mRNA trans-Splicing Can Repair CEP290 mRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 12, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Mansfield, S.G.; Puttaraju, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Cohn, J.A.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A.; Mitchell, L.G.; Engelhardt, J.F. Partial correction of endogenous DeltaF508 CFTR in human cystic fibrosis airway epithelia by spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindt, H.; Tom, C.M.; Lorson, C.L.; Mattis, V.B. Optimization of trans-Splicing for Huntington’s Disease RNA Therapy. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahara, M.; Pergolizzi, R.G.; Kobayashi, H.; Krause, A.; Luettich, K.; Lesser, M.L.; Crystal, R.G. Trans-splicing repair of CD40 ligand deficiency results in naturally regulated correction of a mouse model of hyper-IgM X-linked immunodeficiency. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochet, D.; Prudhon, B.; Jollet, A.; Lorain, S.; Bitoun, M. Reprogramming the Dynamin 2 mRNA by Spliceosome-mediated RNA Trans-splicing. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaizumi, M.; Mekada, E.; Uchida, T.; Okada, Y. One molecule of diphtheria toxin fragment A introduced into a cell can kill the cell. Cell 1978, 15, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaner, C. Prodrug cancer gene therapy. Cancer Lett. 2008, 270, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, I.M.; Somia, N. Gene therapy—Promises, problems and prospects. Nature 1997, 389, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raper, S.E.; Chirmule, N.; Lee, F.S.; Wivel, N.A.; Bagg, A.; Gao, G.P.; Wilson, J.M.; Batshaw, M.L. Fatal systemic inflammatory response syndrome in a ornithine transcarbamylase deficient patient following adenoviral gene transfer. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2003, 80, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.Y.; He, C.Y.; Ehrhardt, A.; Kay, M.A. Minicircle DNA vectors devoid of bacterial DNA result in persistent and high-level transgene expression in vivo. Mol. Ther. 2003, 8, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, D.; Sigen, A.; Alshehri, F.; Lara-Saez, I.; Zheng, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, W. Highly branched poly(beta-amino ester)s for gene delivery in hereditary skin diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, D.V.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated microneedles for gene and drug delivery. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 2, 289–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peking, P.; Koller, U.; Hainzl, S.; Kitzmueller, S.; Kocher, T.; Mayr, E.; Nystrom, A.; Lener, T.; Reichelt, J.; Bauer, J.W.; et al. A Gene Gun-mediated Nonviral RNA trans-splicing Strategy for Col7a1 Repair. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rinaldi, L.; Folliero, V.; Palomba, L.; Zannella, C.; Isticato, R.; Di Francia, R.; Berretta, M.; de Sio, I.; Adinolfi, L.E.; Morelli, G.; et al. Sonoporation by microbubbles as gene therapy approach against liver cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 32182–32190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woess, K.; Sun, Y.; Morio, H.; Stierschneider, A.; Kaufmann, A.; Hainzl, S.; Trattner, L.; Kocher, T.; Tockner, B.; Leb-Reichl, V.; et al. Evaluating a Targeted Cancer Therapy Approach Mediated by RNA trans-Splicing In Vitro and in a Xenograft Model for Epidermolysis Bullosa-Associated Skin Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010575
Woess K, Sun Y, Morio H, Stierschneider A, Kaufmann A, Hainzl S, Trattner L, Kocher T, Tockner B, Leb-Reichl V, et al. Evaluating a Targeted Cancer Therapy Approach Mediated by RNA trans-Splicing In Vitro and in a Xenograft Model for Epidermolysis Bullosa-Associated Skin Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(1):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010575
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoess, Katharina, Yuchen Sun, Hanae Morio, Anna Stierschneider, Anna Kaufmann, Stefan Hainzl, Lisa Trattner, Thomas Kocher, Birgit Tockner, Victoria Leb-Reichl, and et al. 2022. "Evaluating a Targeted Cancer Therapy Approach Mediated by RNA trans-Splicing In Vitro and in a Xenograft Model for Epidermolysis Bullosa-Associated Skin Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 1: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010575
APA StyleWoess, K., Sun, Y., Morio, H., Stierschneider, A., Kaufmann, A., Hainzl, S., Trattner, L., Kocher, T., Tockner, B., Leb-Reichl, V., Steiner, M., Brachtl, G., South, A. P., Bauer, J. W., Reichelt, J., Furihata, T., Wally, V., Koller, U., Piñón Hofbauer, J., & Guttmann-Gruber, C. (2022). Evaluating a Targeted Cancer Therapy Approach Mediated by RNA trans-Splicing In Vitro and in a Xenograft Model for Epidermolysis Bullosa-Associated Skin Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(1), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010575





