Enhancing Anti-Tumoral Potential of CD-NHF by Modulating PI3K/Akt Axis in U87 Ex Vivo Glioma Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
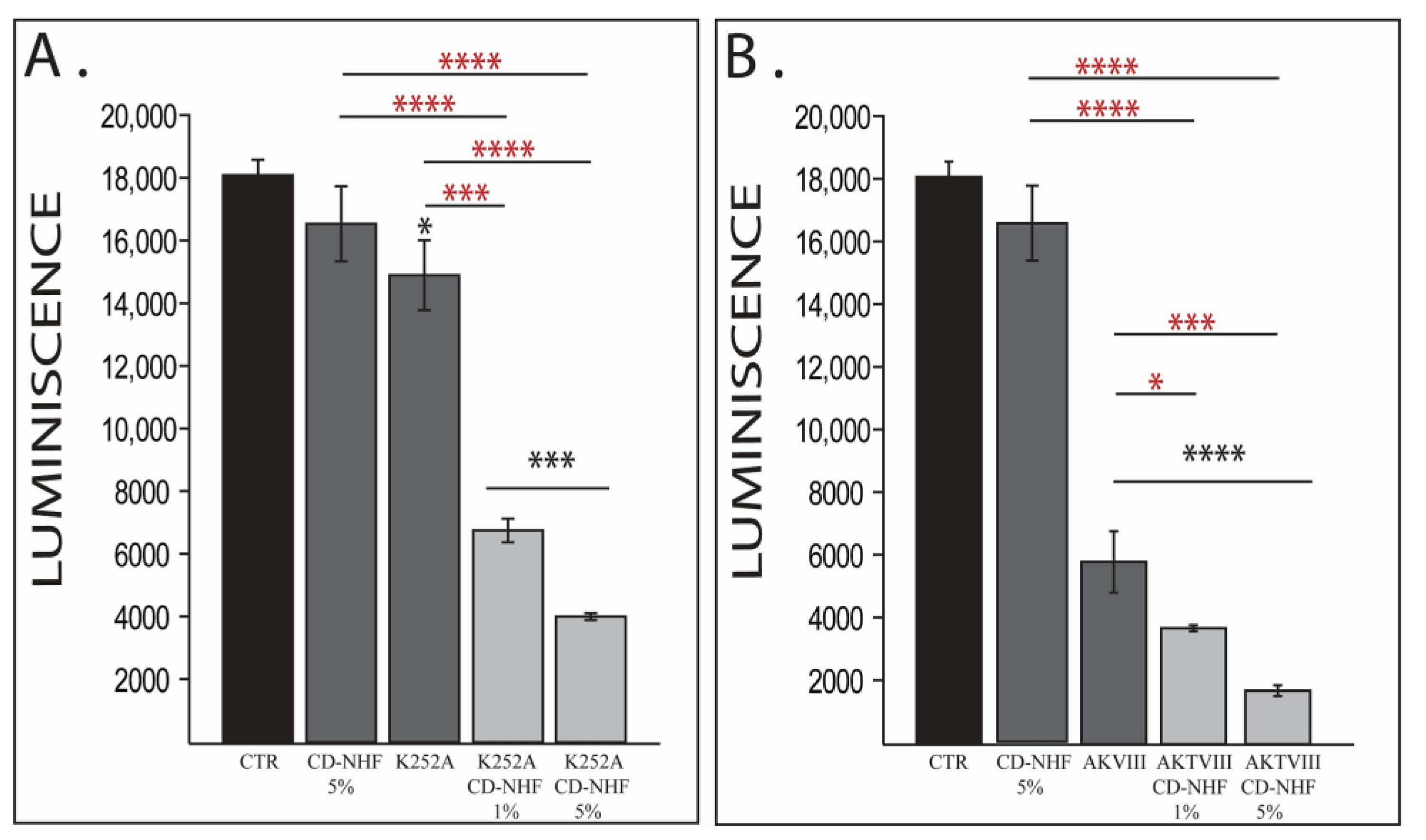
2.1. The Effects of Combination Therapy on U87 2D Cell Viability
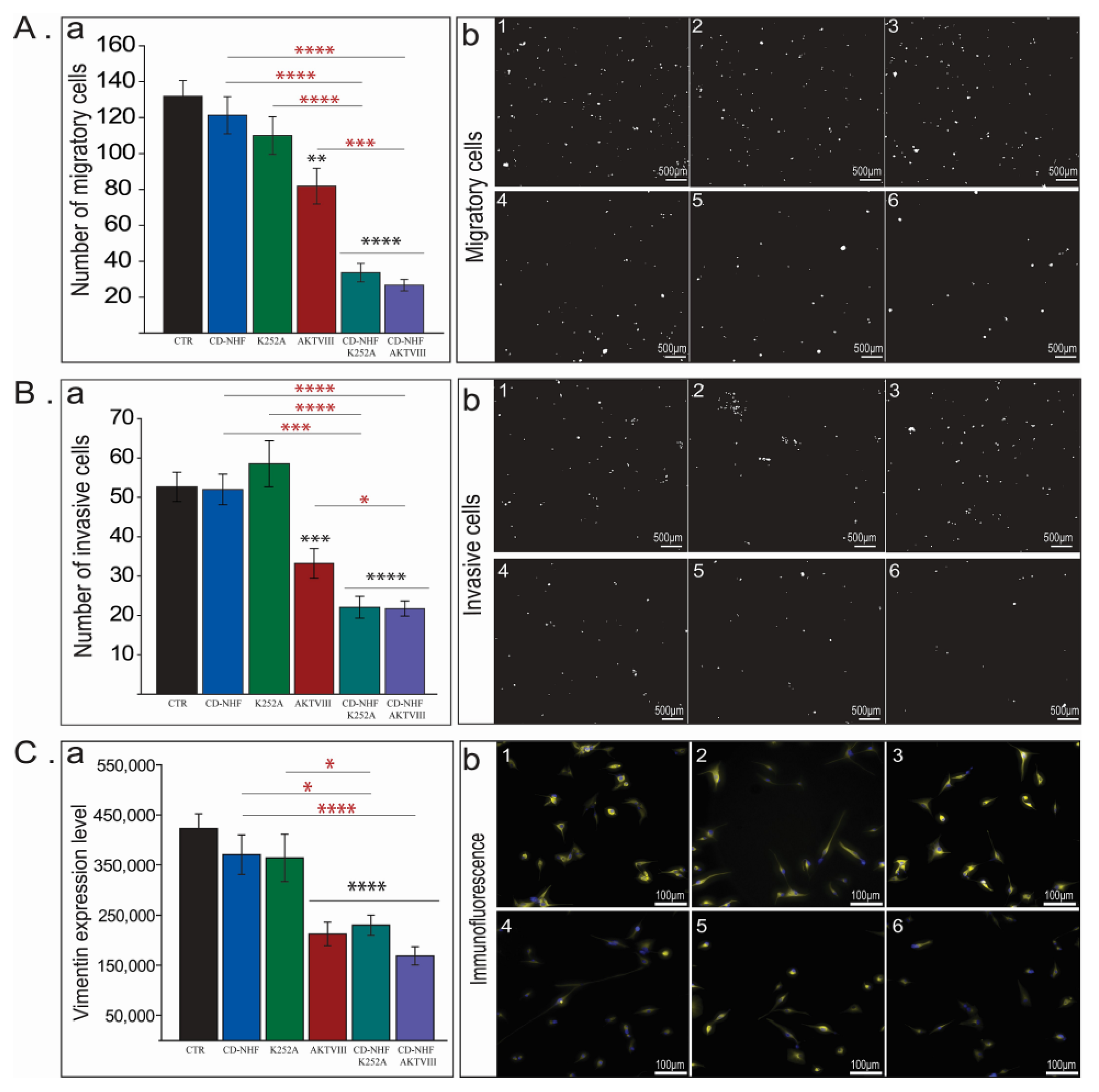
2.2. The Effects of Combination Therapy on U87 Cell Migration and Invasion
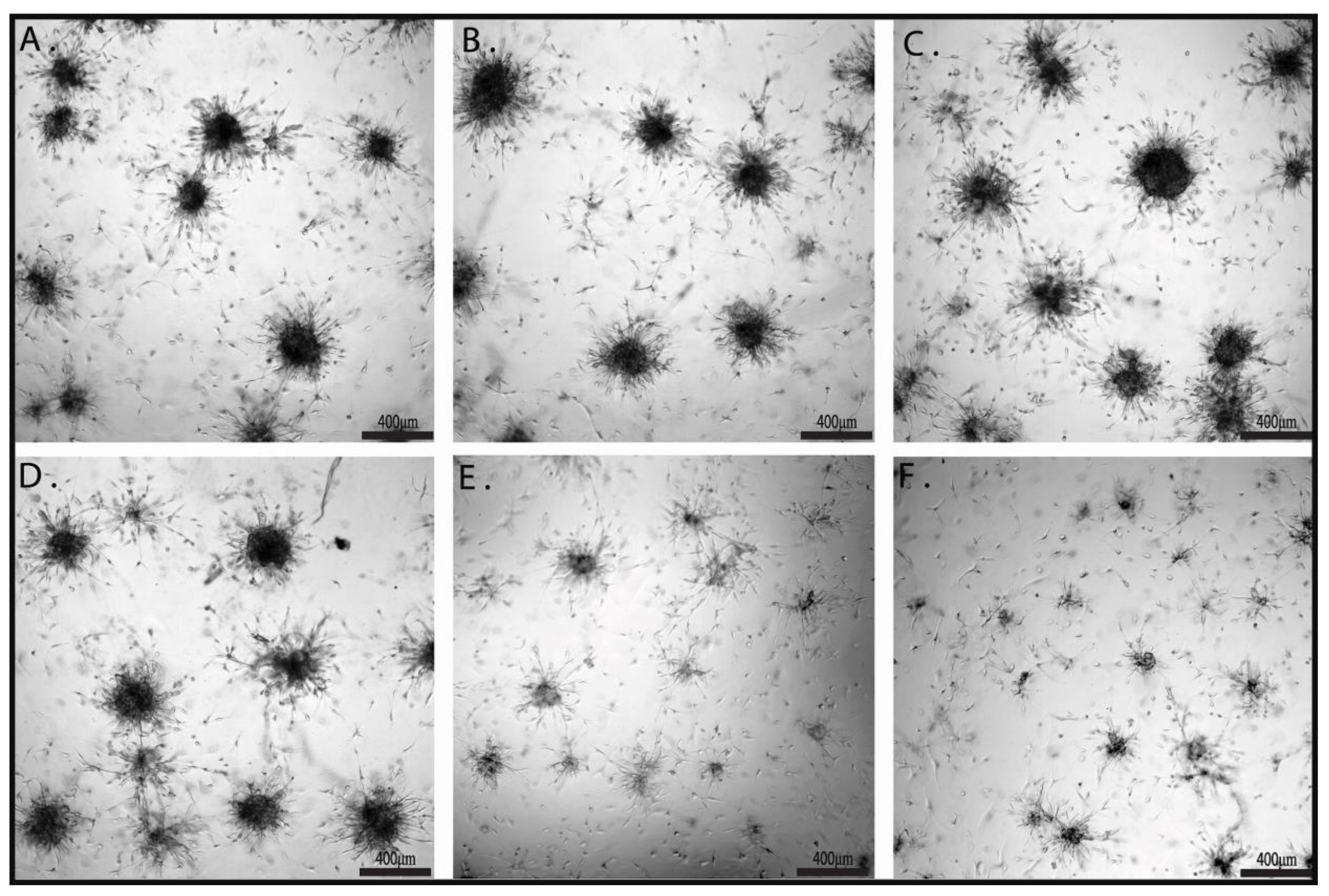
2.3. The Effects of Combination Therapy on U87 3D Matrigel Assay
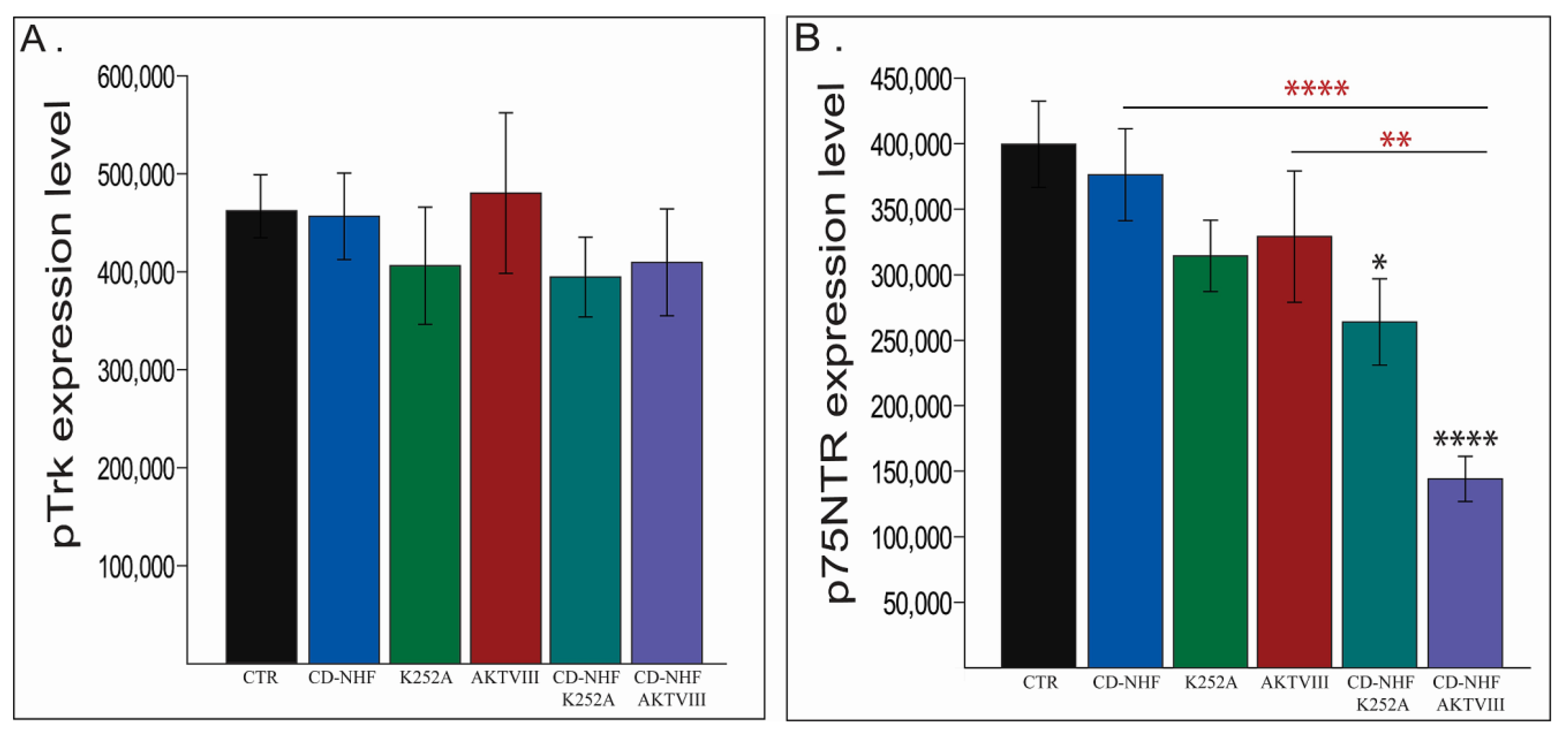
2.4. The Effects of Combination Therapy on TrkB and P75NTR Receptors
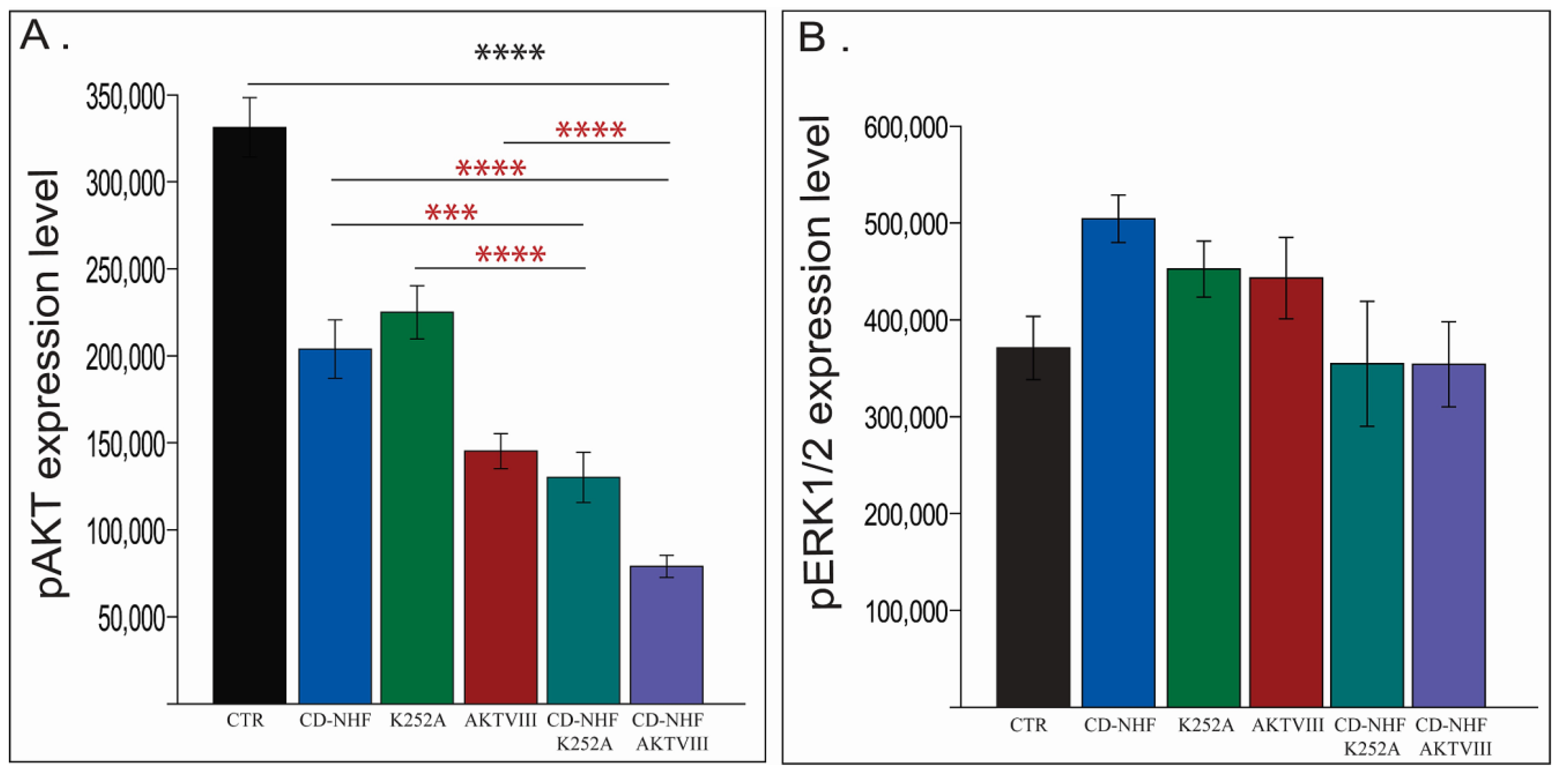
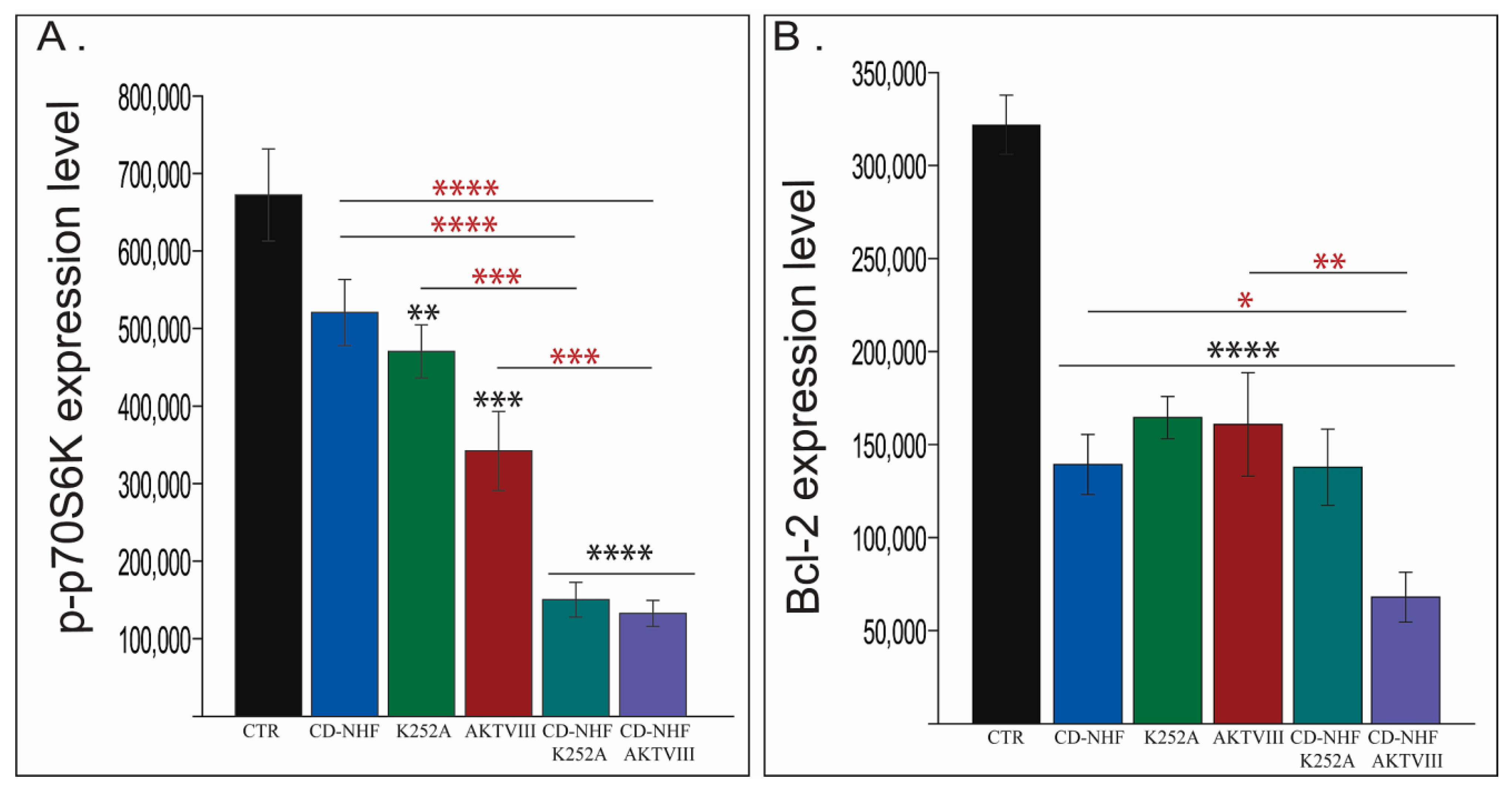
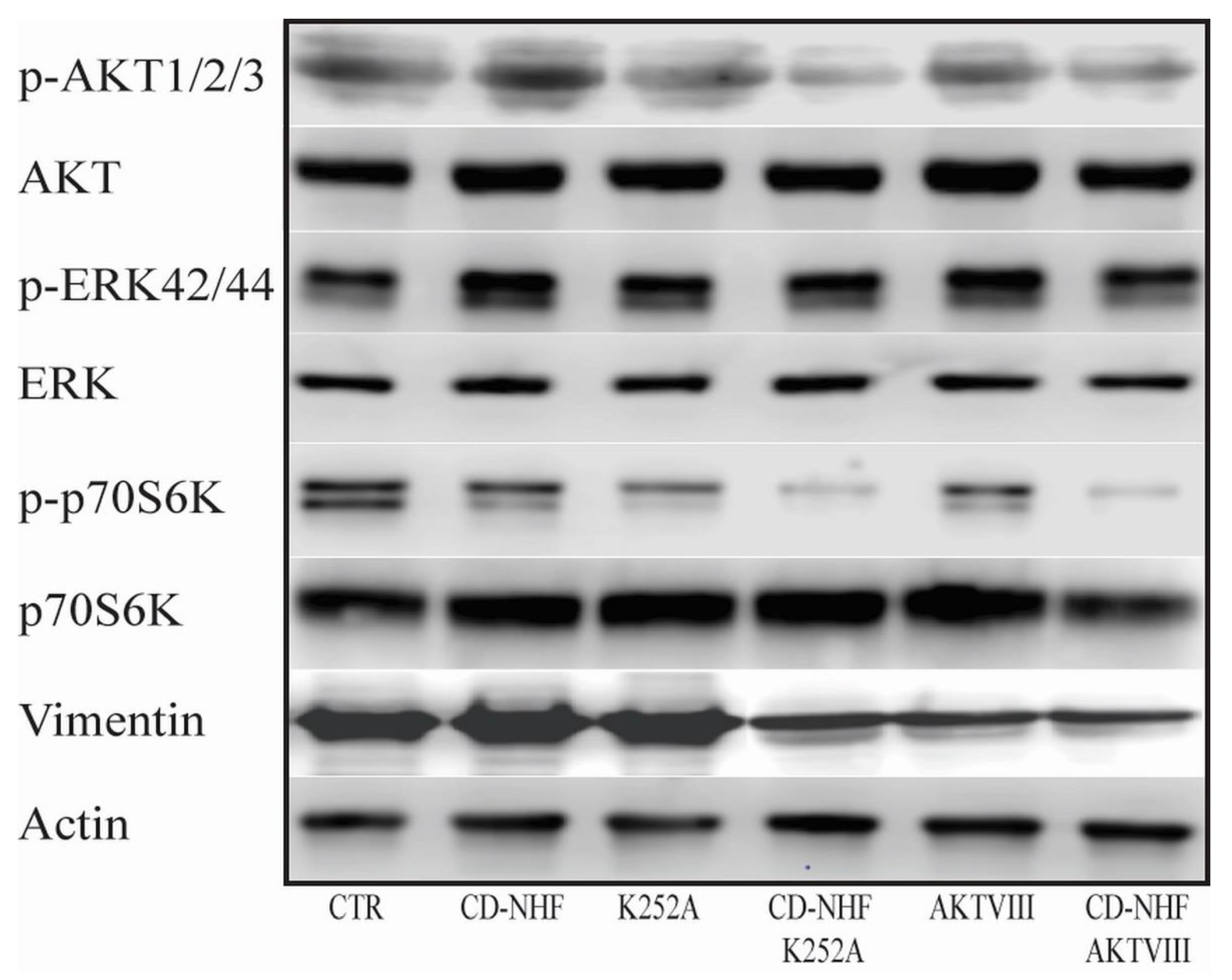
2.5. The Effects of Combination Therapy on Downstream Trk Signalling Pathways
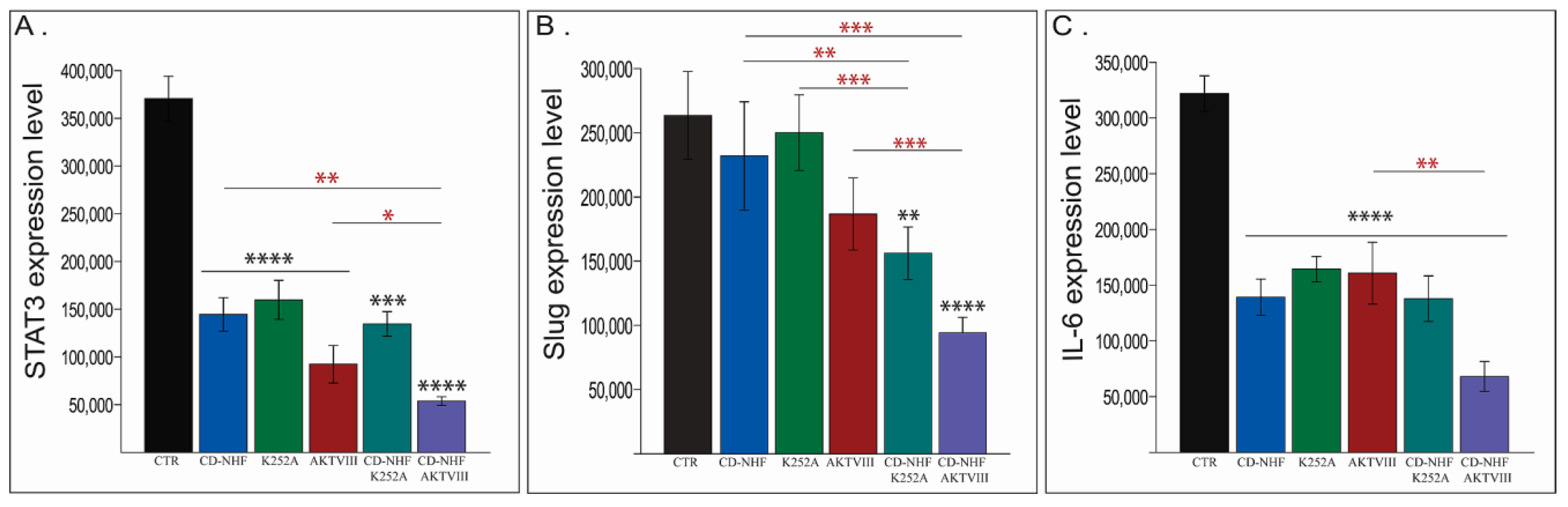
2.6. Other PI3K/Akt Downstream Targets
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Cultures
3.2. Cell Viability
3.3. Migration and Invasion Assay
3.4. D Matrigel Assays
3.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
3.6. Western Blot
3.7. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamson, C.; Kanu, O.O.; Mehta, A.I.; Di, C.; Lin, N.; Mattox, A.K.; Bigner, D.D. Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Review of Where We Have Been and Where We Are Going. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 1061–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowery, F.J.; Yu, D. Brain Metastasis: Unique Challenges and Open Opportunities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2017, 1867, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Wick, W.; Aldape, K.; Brada, M.; Berger, M.; Pfister, S.M.; Nishikawa, R.; Rosenthal, M.; Wen, P.Y.; Stupp, R.; et al. Glioma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; Van Den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 10, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qazi, M.A.; Vora, P.; Venugopal, C.; Sidhu, S.S.; Moffat, J.; Swanton, C.; Singh, S.K. Intratumoral Heterogeneity: Pathways to Treatment Resistance and Relapse in Human Glioblastoma. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies Clinically Relevant Subtypes of Glioblastoma Characterized by Abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segerman, A.; Niklasson, M.; Haglund, C.; Bergström, T.; Jarvius, M.; Xie, Y.; Westermark, A.; Sönmez, D.; Hermansson, A.; Kastemar, M.; et al. Clonal Variation in Drug and Radiation Response among Glioma-Initiating Cells Is Linked to Proneural-Mesenchymal Transition. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 2994–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Tilló, E.; Liu, Y.; de Barrios, O.; Siles, L.; Fanlo, L.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Darling, D.S.; Dean, D.C.; Castells, A.; Postigo, A. EMT-activating transcription factors in cancer: Beyond EMT and tumor invasiveness. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3429–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K.R.; Durrans, A.; Lee, S.; Sheng, J.; Li, F.; Wong, S.T.; Choi, H.; El Rayes, T.; Ryu, S.; Troeger, J.; et al. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Is Not Required for Lung Metastasis but Contributes to Chemoresistance. Nature 2015, 527, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.P.; Kim, J.H.; Han, M.E.; Sim, H.E.; Kim, K.S.; Yoon, S.; Baek, S.Y.; Kim, B.S.; Oh, S.O. SNAI1 Is Involved in the Proliferation and Migration of Glioblastoma Cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikheeva, S.A.; Mikheev, A.M.; Petit, A.; Beyer, R.; Oxford, R.G.; Khorasani, L.; Maxwell, J.P.; Glackin, C.A.; Wakimoto, H.; González-Herrero, I.; et al. TWIST1 Promotes Invasion through Mesenchymal Change in Human Glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.W.; Menon, L.G.; Black, P.M.; Carroll, R.S.; Johnson, M.D. SNAI2/Slug promotes growth and invasion in human gliomas. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, A.L.; Lun, X.; Rahn, J.J.; Liacini, A.; Wang, L.; Hamilton, M.G.; Parney, I.F.; Hempstead, B.L.; Robbins, S.M.; Forsyth, P.A.; et al. The P75 Neurotrophin Receptor Is a Central Regulator of Glioma Invasion. Edited by Christopher Kemp. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, M.V. Neurotrophins and Their Receptors: A Convergence Point for Many Signalling Pathways. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boltaev, U.; Meyer, Y.; Tolibzoda, F.; Jacques, T.; Gassaway, M.; Xu, Q.; Wagner, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Palmer, M.; Holson, E.; et al. Multiplex Quantitative Assays Indicate a Need for Re-Evaluating Reported Small-Molecule TrkB Agonists. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, H.S.; Kharbanda, S.; Chen, R.; Forrest, W.F.; Soriano, R.H.; Wu, T.D.; Misra, A.; Nigro, J.M.; Colman, H.; Soroceanu, L.; et al. Molecular Subclasses of High-Grade Glioma Predict Prognosis, Delineate a Pattern of Disease Progression, and Resemble Stages in Neurogenesis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, D.; Witt, H.; Hovestadt, V.; Khuong-Quang, D.A.; Jones, D.T.; Konermann, C.; Pfaff, E.; Tönjes, M.; Sill, M.; Bender, S.; et al. Hotspot mutations in H3F3A and IDH1 define distinct epigenetic and biological subgroups of glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiadeh, A.N.; Karaman, R. Strategies for Enhancing the Permeation of CNS-Active Drugs through the Blood-Brain Barrier: A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, Z.; Seven, E.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier with Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2017, 270, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Miyanji, E.H.; Zhou, Y.; Pardo, J.; Hettiarachchi, S.D.; Li, S.; Blackwelder, P.L.; Skromne, I.; Leblanc, R.M. Carbon Dots: Promising Biomaterials for Bone-Specific Imaging and Drug Delivery. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 17533–17543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamarov, S.; Näkki, W.X.; Lehto, V.P. Approaches to improve biocompatibility and systemic circulation of inorganic porous nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3632–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, D.; Khuroo, T.; Talegaonkar, S.; Iqbal, Z. Nanopotentiated Combination Cancer Therapy: Chemotherapeutic and Chemosensitizer (2C Approach). Med. Hypotheses 2015, 84, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaelzer, M.M.; Coelho, B.P. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/AKT Pathway Inhibition by Doxazosin Promotes Glioblastoma Cells Death, Upregulation of P53 and Triggers Low Neurotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Fan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X. Curcumin Potentiates the Antitumor Effects of 5-FU in Treatment of Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma Cells through Downregulating the Activation of NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Vitro and in Vivo. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2012, 44, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Asada, M.; Imaizumi, A.; Suzuki, C.; Matsumoto, S.; Nishimura, T.; Mori, Y.; Masui, T.; Kawaguchi, Y.; et al. A Phase I/II Study of Gemcitabine-Based Chemotherapy plus Curcumin for Patients with Gemcitabine-Resistant Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 68, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wu, R.A.; Zhao, L.; Wu, M.; Yang, L.; Zou, H. P-Glycoprotein Antibody Functionalized Carbon Nanotube Overcomes the Multidrug Resistance of Human Leukemia Cells. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milane, L.; Duan, Z.; Amiji, M. Development of EGFR-Targeted Polymer Blend Nanocarriers for Combination Paclitaxel/Lonidamine Delivery to Treat Multi-Drug Resistance in Human Breast and Ovarian Tumor Cells. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettiarachchi, S.D.; Graham, R.M.; Mintz, K.J.; Zhou, Y.; Vanni, S.; Peng, Z.; Leblanc, R.M. Triple Conjugated Carbon Dots as a Nano-Drug Delivery Model for Glioblastoma Brain Tumors. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6192–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Jing, Z.; Wu, W.; Zou, B.; Peng, Z.; Ren, P.; Wikramanayake, A.; Lu, Z.; Leblanc, R.M. Biocompatible and Blood–Brain Barrier Permeable Carbon Dots for Inhibition of Aβ Fibrillation and Toxicity, and BACE1 Activity. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12862–12866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, C.L.; Tiron, C.; Carasevici, E.; Stan, C.S.; Ibanescu, S.A.; Simionescu, B.C.; Peptu, C.A. Entrapment of N-Hydroxyphthalimide Carbon Dots in Different Topical Gel Formulations: New Composites with Anticancer Activity. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiron, C.E.; Luta, G.; Butura, M.; Zugun-Eloae, F.; Stan, C.S.; Coroaba, A.; Ursu, E.L.; Stanciu, G.D.; Tiron, A. NHF-derived carbon dots: Prevalidation approach in breast cancer treatment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiron, C.E.; Zugun-Eloae, F.; Peptu, C.A.; Tiron, A.; Stan, C.S. Imide Derived Carbon Dots Exhibit Promising Antitumoral Properties on Multiple In Vitro Experimental Designs. Nano Sci. Nano Technol. Indian J. 2019, 13, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.C.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Siu, I.M.; Gallia, G.L.; et al. An Integrated Genomic Analysis of Human Glioblastoma Multiforme. Science 2008, 321, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive Genomic Characterization Defines Human Glioblastoma Genes and Core Pathways. Nature 2008, 455, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilot, D.; Giudicelli, F.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D.; Fardel, O. Akti-1/2, an Allosteric Inhibitor of Akt 1 and 2, Efficiently Inhibits CaMKIα Activity and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, S.; Gandhi, S.; Joy, A.A.; Edwards, S.; Gorr, M.; Hopkins, S.; Kondejewski, J.; Ayoub, J.P.; Califaretti, N.; Rayson, D.; et al. Novel Agents and Associated Toxicities of Inhibitors of the Pi3k/Akt/Mtor Pathway for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2015, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Setyawati, M.I.; Tee, J.K.; Ding, X.; Wang, J.; Nga, M.E.; Ho, H.K.; Leong, D.T. Nanoparticles Promote in Vivo Breast Cancer Cell Intravasation and Extravasation by Inducing Endothelial Leakiness. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Okumura, T.; Hirano, K.; Watanabe, T.; Nagata, T.; Shimada, Y.; Tsukada, K. p75 neu-rotrophin receptor expression is a characteristic of the mitotically quiescent cancer stem cell population present in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berchtold, M.W.; Vilallobo, A. The Many Faces of Calmodulin in Cell Proliferation, Programmed Cell Death, Autophagy, and Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1843, 398–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolcher, A.; Goldman, J.; Patnaik, A.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Westwood, P.; Kelly, C.S.; Bumgardner, W.; Sams, L.; Geeganage, S.; Wang, T. A phase I trial of LY2584702 tosylate, a p70 S6 kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in Cancer Inflammation and Immunity: A Leading Role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.; Tsai, J.T.; Chao, T.Y.; Ma, H.I.; Liu, W.H. The STAT3/Slug Axis Enhances Radiation-Induced Tumor Invasion and Cancer Stem-like Properties in Radioresistant Glioblastoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lathia, J.D.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Heddleston, J.M.; Eyler, C.E.; Elderbroom, J.; Gallagher, J.; Schuschu, J.; et al. Targeting Interleukin 6 Signaling Suppresses Glioma Stem Cell Survival and Tumor Growth. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Liu, B.; Ji, R.; Jiang, X.; Yan, X.; Xin, Y. Targeting the BDNF/TrkB Pathway for the Treatment of Tumors (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, M.M.; France, T.J.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, P. Interleukin-6 Role in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 2, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegeye, M.M.; Lindkvist, M.; Fälker, K.; Kumawat, A.K.; Paramel, G.; Grenegård, M.; Sirsjö, A.; Ljungberg, L.U. Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT Pathways Are Crucial for IL-6 Trans-Signaling-Mediated pro-Inflammatory Response in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luta, G.; Butura, M.; Tiron, A.; Tiron, C.E. Enhancing Anti-Tumoral Potential of CD-NHF by Modulating PI3K/Akt Axis in U87 Ex Vivo Glioma Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083873
Luta G, Butura M, Tiron A, Tiron CE. Enhancing Anti-Tumoral Potential of CD-NHF by Modulating PI3K/Akt Axis in U87 Ex Vivo Glioma Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(8):3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083873
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuta, Gabriel, Mihail Butura, Adrian Tiron, and Crina E. Tiron. 2021. "Enhancing Anti-Tumoral Potential of CD-NHF by Modulating PI3K/Akt Axis in U87 Ex Vivo Glioma Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 8: 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083873
APA StyleLuta, G., Butura, M., Tiron, A., & Tiron, C. E. (2021). Enhancing Anti-Tumoral Potential of CD-NHF by Modulating PI3K/Akt Axis in U87 Ex Vivo Glioma Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(8), 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22083873





