Jasmonic Acid Signaling and Molecular Crosstalk with Other Phytohormones
Abstract
1. Introduction
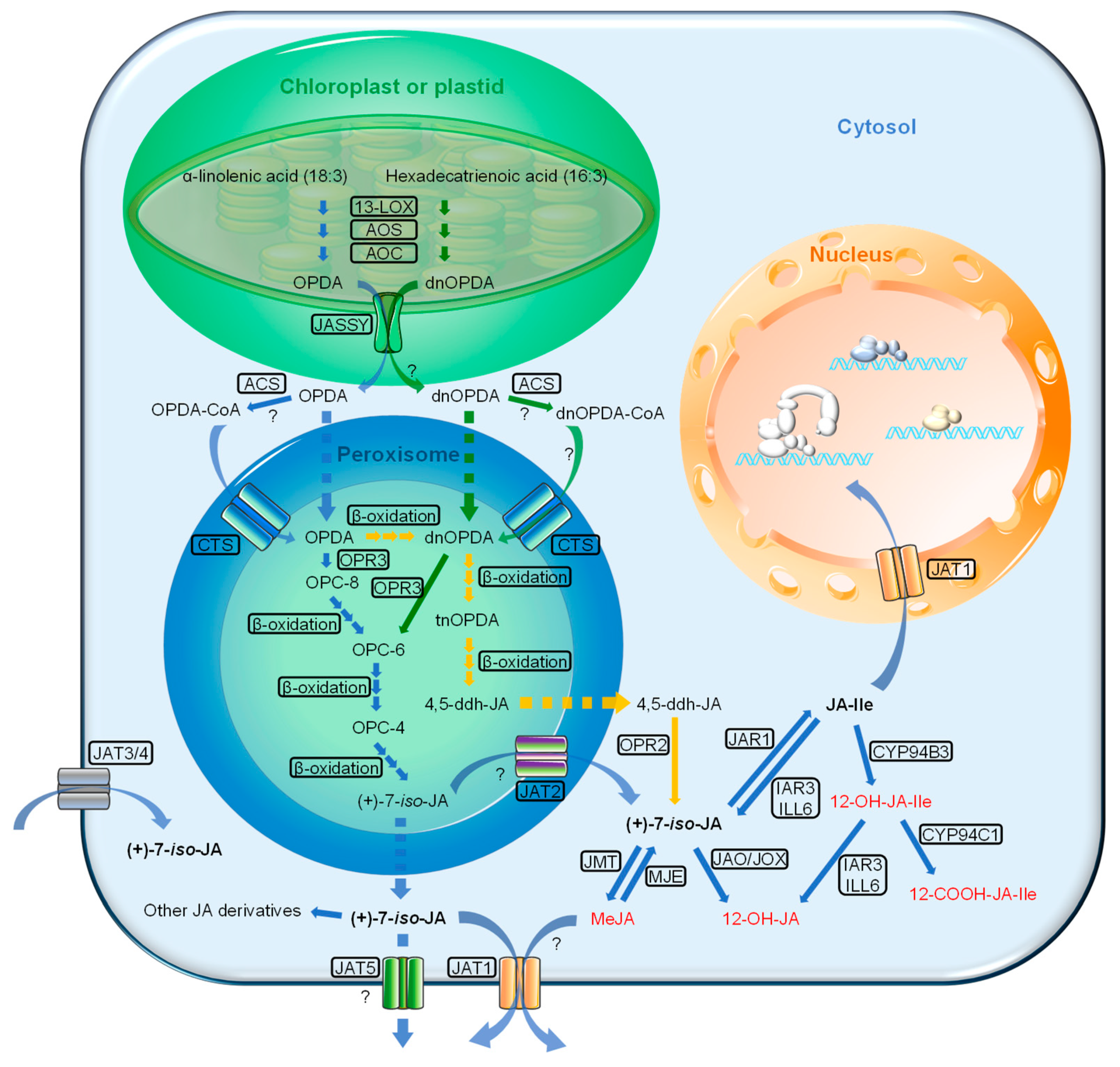
2. JA Biosynthesis
2.1. JA Biosynthesis
2.2. Transporters of JAs and Its Precursors
2.2.1. JASSY
2.2.2. Comatose (CTS)
2.2.3. Jasmonate Transporters (JATs)
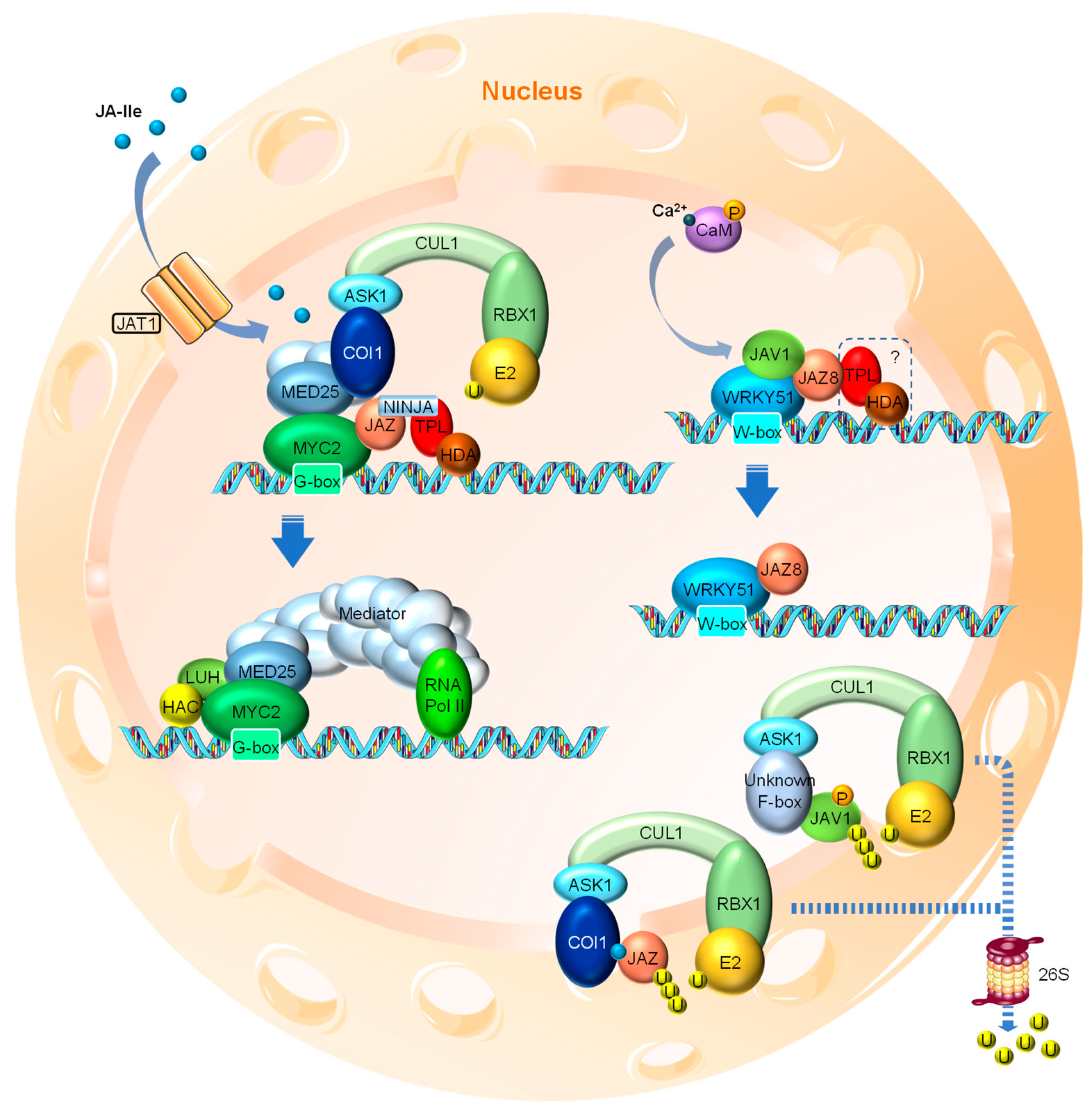
3. JA Signaling
3.1. JA Perception and Signal Transduction
3.2. JA-Regulated Transcription Factors
3.3. Negative Feedbacks and Termination of JA Signal
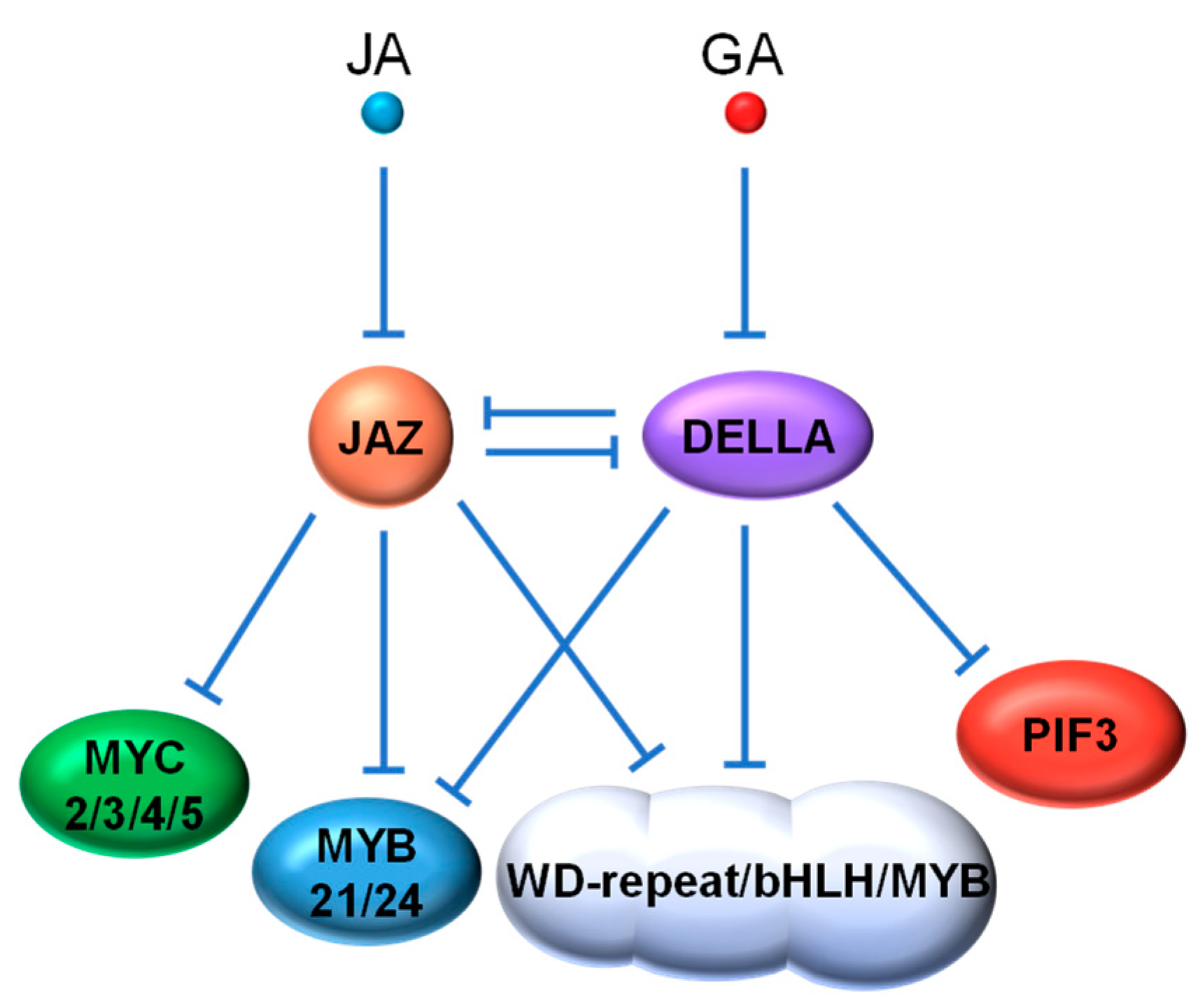
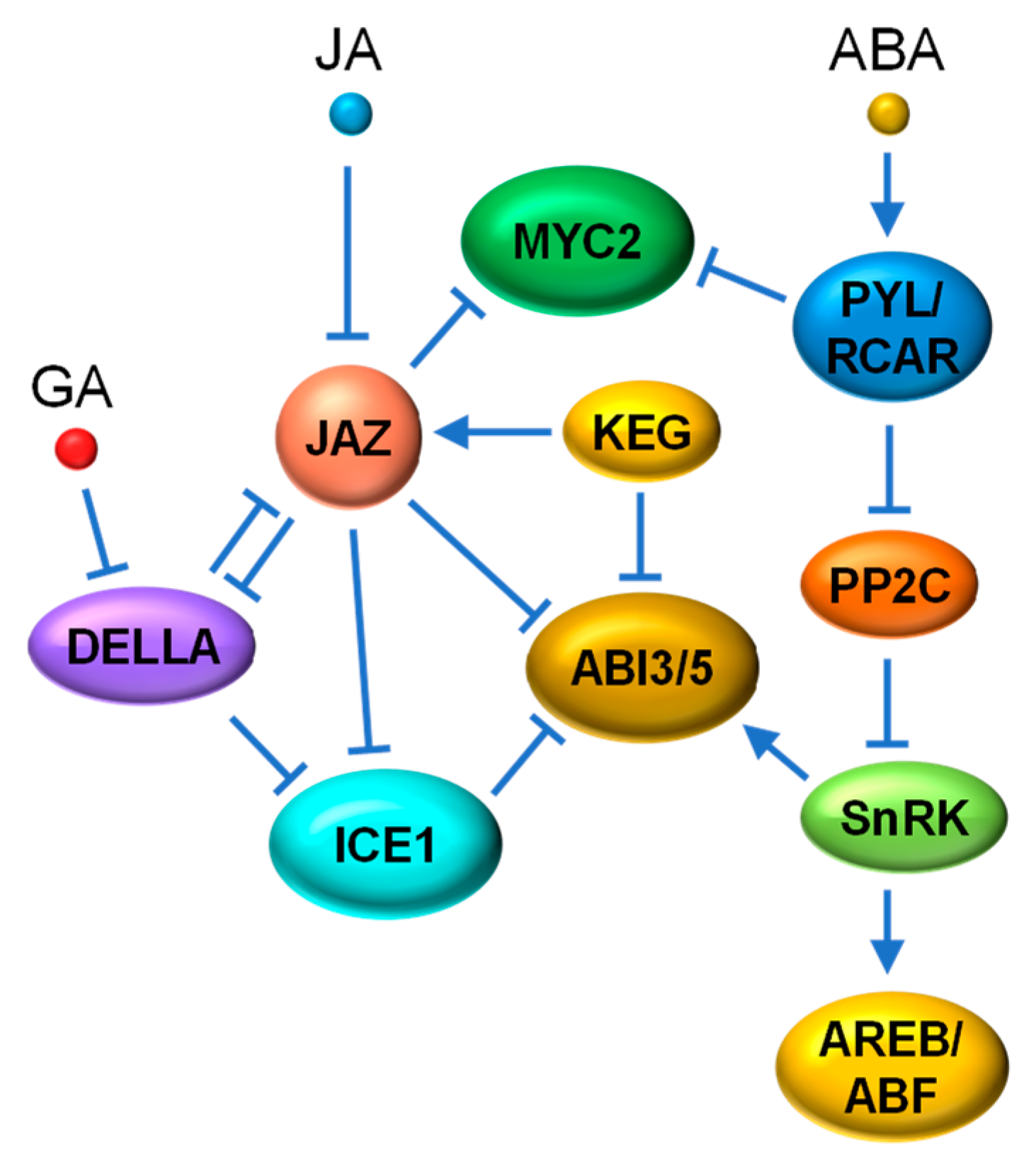
4. Crosstalk Complexity of JA with Other Phytohormones
4.1. JAZ vs. DELLA
4.2. JA vs. Auxin
4.3. JA vs. ET
4.4. JA-ABA
5. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierla, M.; Waszczak, C.; Vahisalu, T.; Kangasjarvi, J. Reactive Oxygen Species in the Regulation of Stomatal Movements. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudla, J.; Becker, D.; Grill, E.; Hedrich, R.; Hippler, M.; Kummer, U.; Parniske, M.; Romeis, T.; Schumacher, K. Advances and current challenges in calcium signaling. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichman, Y.; Mittler, R. Rapid systemic signaling during abiotic and biotic stresses: Is the ROS wave master of all trades? Plant J. 2020, 102, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Qi, T.; Wasternack, C.; Xie, D. Jasmonate signaling and crosstalk with gibberellin and ethylene. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 21, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.H.; Kumar, V.; Shriram, V.; Sah, S.K. Phytohormones and their metabolic engineering for abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Crop J. 2016, 4, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Moore, S.; Chen, C.; Lindsey, K. Crosstalk Complexities between Auxin, Cytokinin, and Ethylene in Arabidopsis Root Development: From Experiments to Systems Modeling, and Back Again. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1480–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, W.; Naseem, S.; Ali, Z. Strigolactones Biosynthesis and Their Role in Abiotic Stress Resilience in Plants: A Critical Review. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Xie, D. Jasmonate action in plant defense against insects. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 3391–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Duan, G.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Han, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C. The Crosstalks Between Jasmonic Acid and Other Plant Hormone Signaling Highlight the Involvement of Jasmonic Acid as a Core Component in Plant Response to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.; Yoon, Y.; Choi, Y.D. Crosstalk with Jasmonic Acid Integrates Multiple Responses in Plant Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Yin, C.C.; Ma, B.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, J.S. Ethylene Biosynthesis, Signaling, and Crosstalk with Other Hormones in Rice. Small Methods 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsir, L.; Chung, H.S.; Koo, A.J.; Howe, G.A. Jasmonate signaling: A conserved mechanism of hormone sensing. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasternack, C.; Hause, B. Jasmonates: Biosynthesis, perception, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development. An update to the 2007 review in Annals of Botany. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 1021–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalhais, L.C.; Schenk, P.M.; Dennis, P.G. Jasmonic acid signalling and the plant holobiont. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 37, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasternack, C.; Song, S. Jasmonates: Biosynthesis, metabolism, and signaling by proteins activating and repressing transcription. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1303–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, I.F.; Przybyl, M. Jasmonate Signaling during Arabidopsis Stamen Maturation. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 2648–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Khurshid, M.; Weng, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, K. Jasmonic Acid Signaling Pathway in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauser, G.; Grata, E.; Dubugnon, L.; Rudaz, S.; Farmer, E.E.; Wolfender, J.L. Spatial and temporal dynamics of jasmonate synthesis and accumulation in Arabidopsis in response to wounding. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16400–16407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, A.J.; Gao, X.; Jones, A.D.; Howe, G.A. A rapid wound signal activates the systemic synthesis of bioactive jasmonates in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009, 59, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, A.; Caldelari, D.; Wolfender, J.L.; Farmer, E.E. Four 13-lipoxygenases contribute to rapid jasmonate synthesis in wounded Arabidopsis thaliana leaves: A role for lipoxygenase 6 in responses to long-distance wound signals. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasternack, C.; Strnad, M. Jasmonates: News on Occurrence, Biosynthesis, Metabolism and Action of an Ancient Group of Signaling Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.S.; Baek, K.H. Jasmonic Acid Signaling Pathway in Response to Abiotic Stresses in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, B.; Liu, L.; Song, S. Jasmonate action in plant growth and development. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasternack, C. How Jasmonates Earned their Laurels: Past and Present. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 34, 761–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druege, U.; Hilo, A.; Perez-Perez, J.M.; Klopotek, Y.; Acosta, M.; Shahinnia, F.; Zerche, S.; Franken, P.; Hajirezaei, M.R. Molecular and physiological control of adventitious rooting in cuttings: Phytohormone action meets resource allocation. Ann. Bot. 2019, 123, 929–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, F.; Chen, L.; Pan, Y.; Sun, L.; Bao, N.; Zhang, T.; Cui, C.X.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Jasmonate-mediated wound signalling promotes plant regeneration. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazan, K. Diverse roles of jasmonates and ethylene in abiotic stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasternack, C.; Strnad, M. Jasmonate signaling in plant stress responses and development-active and inactive compounds. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Bhardwaj, M.; Tran, L.P. Jasmonic Acid at the Crossroads of Plant Immunity and Pseudomonas syringae Virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.; Graham, I.A.; Holdsworth, M.; Smith, S.M.; Theodoulou, F.L. Chewing the fat: Beta-oxidation in signalling and development. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widemann, E.; Smirnova, E.; Aubert, Y.; Miesch, L.; Heitz, T. Dynamics of Jasmonate Metabolism upon Flowering and across Leaf Stress Responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2016, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, S.; Chini, A.; Hamberg, M.; Adie, B.; Porzel, A.; Kramell, R.; Miersch, O.; Wasternack, C.; Solano, R. (+)-7-iso-Jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine is the endogenous bioactive jasmonate. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chini, A.; Fonseca, S.; Fernandez, G.; Adie, B.; Chico, J.M.; Lorenzo, O.; Garcia-Casado, G.; Lopez-Vidriero, I.; Lozano, F.M.; Ponce, M.R.; et al. The JAZ family of repressors is the missing link in jasmonate signalling. Nature 2007, 448, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thines, B.; Katsir, L.; Melotto, M.; Niu, Y.; Mandaokar, A.; Liu, G.; Nomura, K.; He, S.Y.; Howe, G.A.; Browse, J. JAZ repressor proteins are targets of the SCF(COI1) complex during jasmonate signalling. Nature 2007, 448, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheard, L.B.; Tan, X.; Mao, H.; Withers, J.; Ben-Nissan, G.; Hinds, T.R.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hsu, F.F.; Sharon, M.; Browse, J.; et al. Jasmonate perception by inositol-phosphate-potentiated COI1-JAZ co-receptor. Nature 2010, 468, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, L.; Goossens, A. The JAZ proteins: A crucial interface in the jasmonate signaling cascade. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3089–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, A.; Monte, I.; Zamarreno, A.M.; Hamberg, M.; Lassueur, S.; Reymond, P.; Weiss, S.; Stintzi, A.; Schaller, A.; Porzel, A.; et al. An OPR3-independent pathway uses 4,5-didehydrojasmonate for jasmonate synthesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Denkert, N.; Eisa, A.; Lehmann, M.; Sjuts, I.; Weiberg, A.; Soll, J.; Meinecke, M.; Schwenkert, S. JASSY, a chloroplast outer membrane protein required for jasmonate biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10568–10575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoulou, F.L.; Job, K.; Slocombe, S.P.; Footitt, S.; Holdsworth, M.; Baker, A.; Larson, T.R.; Graham, I.A. Jasmonic acid levels are reduced in COMATOSE ATP-binding cassette transporter mutants. Implications for transport of jasmonate precursors into peroxisomes. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyathi, Y.; De Marcos Lousa, C.; van Roermund, C.W.; Wanders, R.J.; Johnson, B.; Baldwin, S.A.; Theodoulou, F.L.; Baker, A. The Arabidopsis peroxisomal ABC transporter, comatose, complements the Saccharomyces cerevisiae pxa1 pxa2Delta mutant for metabolism of long-chain fatty acids and exhibits fatty acyl-CoA-stimulated ATPase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 29892–29902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marcos Lousa, C.; van Roermund, C.W.; Postis, V.L.; Dietrich, D.; Kerr, I.D.; Wanders, R.J.; Baldwin, S.A.; Baker, A.; Theodoulou, F.L. Intrinsic acyl-CoA thioesterase activity of a peroxisomal ATP binding cassette transporter is required for transport and metabolism of fatty acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, Y.; Martinoia, E.; Geisler, M. Plant hormone transporters: What we know and what we would like to know. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.T.; Gonzalez, K.L.; Bartel, B. Peroxisome Function, Biogenesis, and Dynamics in Plants. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Hu, J. Peroxisomes: Versatile organelles with diverse roles in plants. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1410–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Martinoia, E.; Farmer, E.E. Emerging Jasmonate Transporters. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Huang, G.; Skilling, S.J.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Yuan, L.; Liu, P. Transporter-Mediated Nuclear Entry of Jasmonoyl-Isoleucine Is Essential for Jasmonate Signaling. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yu, G.; Liu, P. Transporter-Mediated Subcellular Distribution in the Metabolism and Signaling of Jasmonates. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Yu, G.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Yuan, L.; Liu, P. Importers Drive Leaf-to-Leaf Jasmonic Acid Transmission in Wound-Induced Systemic Immunity. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Chauvin, A.; Pascaud, F.; Kellenberger, S.; Farmer, E.E. GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR-LIKE genes mediate leaf-to-leaf wound signalling. Nature 2013, 500, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Kurenda, A.; Stolz, S.; Chetelat, A.; Farmer, E.E. Identification of cell populations necessary for leaf-to-leaf electrical signaling in a wounded plant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10178–10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyota, M.; Spencer, D.; Sawai-Toyota, S.; Jiaqi, W.; Zhang, T.; Koo, A.J.; Howe, G.A.; Gilroy, S. Glutamate triggers long-distance, calcium-based plant defense signaling. Science 2018, 361, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, J. Systemin-mediated long-distance systemic defense responses. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Miyakawa, S.; Kanno, Y.; Koshiba, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Seo, M. Identification of Arabidopsis thaliana NRT1/PTR FAMILY (NPF) proteins capable of transporting plant hormones. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, H.; Oikawa, T.; Hamamoto, S.; Ishimaru, Y.; Kanamori-Sato, M.; Sasaki-Sekimoto, Y.; Utsumi, T.; Chen, J.; Kanno, Y.; Masuda, S.; et al. The jasmonate-responsive GTR1 transporter is required for gibberellin-mediated stamen development in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Oikawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Takeishi, S.; Matsuura, H.; Takahashi, K.; Hamamoto, S.; Uozumi, N.; Shimizu, T.; Seo, M.; et al. GTR1 is a jasmonic acid and jasmonoyl-l-isoleucine transporter in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.X.; Feys, B.F.; James, S.; Nieto-Rostro, M.; Turner, J.G. COI1: An Arabidopsis gene required for jasmonate-regulated defense and fertility. Science 1998, 280, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Stolz, S.; Chetelat, A.; Reymond, P.; Pagni, M.; Dubugnon, L.; Farmer, E.E. A downstream mediator in the growth repression limb of the jasmonate pathway. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2470–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, C.; Gu, M.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Qi, T.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, W.; Luo, H.; Nan, F.; et al. The Arabidopsis CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1 protein is a jasmonate receptor. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2220–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosblech, A.; Thurow, C.; Gatz, C.; Feussner, I.; Heilmann, I. Jasmonic acid perception by COI1 involves inositol polyphosphates in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2011, 65, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrecht, B.; Xue, G.P.; Sprague, S.J.; Kirkegaard, J.A.; Ross, J.J.; Reid, J.B.; Fitt, G.P.; Sewelam, N.; Schenk, P.M.; Manners, J.M.; et al. MYC2 differentially modulates diverse jasmonate-dependent functions in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2225–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazan, K.; Manners, J.M. MYC2: The master in action. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 686–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamuro, C.; Zhu, J.K.; Yang, Z. Epigenetic Modifications and Plant Hormone Action. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ding, A.B.; Liu, F.; Zhong, X. Linking signaling pathways to histone acetylation dynamics in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 5179–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, C.; Yu, C.W.; Chaikam, V. HDA6 is required for jasmonate response, senescence and flowering in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; An, F.; Feng, Y.; Li, P.; Xue, L.; Mu, A.; Jiang, Z.; Kim, J.M.; To, T.K.; Li, W.; et al. Derepression of ethylene-stabilized transcription factors (EIN3/EIL1) mediates jasmonate and ethylene signaling synergy in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12539–12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyu, C.; Figueroa, P.; Depew, C.L.; Cooke, T.F.; Sheard, L.B.; Moreno, J.E.; Katsir, L.; Zheng, N.; Browse, J.; Howe, G.A. JAZ8 lacks a canonical degron and has an EAR motif that mediates transcriptional repression of jasmonate responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thireault, C.; Shyu, C.; Yoshida, Y.; St Aubin, B.; Campos, M.L.; Howe, G.A. Repression of jasmonate signaling by a non-TIFY JAZ protein in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2015, 82, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, L.; Barbero, G.F.; Geerinck, J.; Tilleman, S.; Grunewald, W.; Perez, A.C.; Chico, J.M.; Bossche, R.V.; Sewell, J.; Gil, E.; et al. NINJA connects the co-repressor TOPLESS to jasmonate signalling. Nature 2010, 464, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Fan, M.; Yang, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Su, Y.; Xiao, L.; Deng, H.; Xie, D. Injury Activates Ca(2+)/Calmodulin-Dependent Phosphorylation of JAV1-JAZ8-WRKY51 Complex for Jasmonate Biosynthesis. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 136–149.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.N.; Li, W.; Chen, B.Q.; Zhu, L.; Fu, Y. Arabidopsis ECAP Is a New Adaptor Protein that Connects JAZ Repressors with the TPR2 Co-repressor to Suppress Jasmonate-Responsive Anthocyanin Accumulation. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, V.; Kidd, B.N.; Zhang, P.; Hill, C.; Kiddle, S.; Denby, K.J.; Holub, E.B.; Cahill, D.M.; Manners, J.M.; Schenk, P.M.; et al. MEDIATOR25 acts as an integrative hub for the regulation of jasmonate-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Jiang, H.; Li, L.; Zhai, Q.; Qi, L.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, W.; Sun, J.; et al. The Arabidopsis mediator subunit MED25 differentially regulates jasmonate and abscisic acid signaling through interacting with the MYC2 and ABI5 transcription factors. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2898–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.; Li, L.; Zhai, Q.; You, Y.; Deng, L.; Wu, F.; Chen, R.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; et al. Mediator subunit MED25 links the jasmonate receptor to transcriptionally active chromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8930–E8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poss, Z.C.; Ebmeier, C.C.; Taatjes, D.J. The Mediator complex and transcription regulation. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 575–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Qu, L.J. Plant Mediator complex and its critical functions in transcription regulation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Q.; Li, C. The plant Mediator complex and its role in jasmonate signaling. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 3415–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yao, J.; Ke, J.; Zhang, L.; Lam, V.Q.; Xin, X.F.; Zhou, X.E.; Chen, J.; Brunzelle, J.; Griffin, P.R.; et al. Structural basis of JAZ repression of MYC transcription factors in jasmonate signalling. Nature 2015, 525, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Zhai, Q.; An, C.; Li, C. LEUNIG_HOMOLOG Mediates MYC2-Dependent Transcriptional Activation in Cooperation with the Coactivators HAC1 and MED25. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 2187–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Deng, L.; Li, C. Mediator subunit MED25: At the nexus of jasmonate signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 57, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Hu, Y.; Vannozzi, A.; Wu, K.C.; Cai, H.Y.; Qin, Y.; Mullis, A.; Lin, Z.G.; Zhang, L.S. The WRKY Transcription Factor Family in Model Plants and Crops. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2017, 36, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z. WRKY transcription factors: Evolution, binding, and action. Phytopathol. Res. 2019, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, Z.; Fan, M.; Wang, L.; Xie, D. JAV1 controls jasmonate-regulated plant defense. Mol. Cell 2013, 50, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Moerkercke, A.; Duncan, O.; Zander, M.; Simura, J.; Broda, M.; Vanden Bossche, R.; Lewsey, M.G.; Lama, S.; Singh, K.B.; Ljung, K.; et al. A MYC2/MYC3/MYC4-dependent transcription factor network regulates water spray-responsive gene expression and jasmonate levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 23345–23356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liang, G.; Yang, S.; Yu, D. Arabidopsis WRKY57 functions as a node of convergence for jasmonic acid- and auxin-mediated signaling in jasmonic acid-induced leaf senescence. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, D. The WRKY57 Transcription Factor Affects the Expression of Jasmonate ZIM-Domain Genes Transcriptionally to Compromise Botrytis cinerea Resistance. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2771–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Calvo, P.; Chini, A.; Fernandez-Barbero, G.; Chico, J.M.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Geerinck, J.; Eeckhout, D.; Schweizer, F.; Godoy, M.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; et al. The Arabidopsis bHLH transcription factors MYC3 and MYC4 are targets of JAZ repressors and act additively with MYC2 in the activation of jasmonate responses. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lei, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, L.; Wu, J. MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 function additively in wounding-induced jasmonic acid biosynthesis and catabolism. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Qi, T.; Huang, H.; Ren, Q.; Wu, D.; Chang, C.; Peng, W.; Liu, Y.; Peng, J.; Xie, D. The Jasmonate-ZIM domain proteins interact with the R2R3-MYB transcription factors MYB21 and MYB24 to affect Jasmonate-regulated stamen development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1000–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Huang, H.; Song, S.; Xie, D. Regulation of Jasmonate-Mediated Stamen Development and Seed Production by a bHLH-MYB Complex in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gao, H.; Liu, B.; Qi, T.; Tong, J.; Xiao, L.; Xie, D.; Song, S. Arabidopsis MYB24 Regulates Jasmonate-Mediated Stamen Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.S.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, B.; Qi, T.C.; Xie, D.X. MYC5 is Involved in Jasmonate-Regulated Plant Growth, Leaf Senescence and Defense Responses. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yao, S.; Zhao, K.; Wang, D.; Qin, Q.; Bian, Z.; Li, Y.; Lan, Y.; et al. Jasmonate Signaling Enhances RNA Silencing and Antiviral Defense in Rice. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 89–103 e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Ye, R.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ji, S.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; et al. Viral-inducible Argonaute18 confers broad-spectrum virus resistance in rice by sequestering a host microRNA. eLife 2015, 4, e05733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yang, S. Cold signal transduction and its interplay with phytohormones during cold acclimation. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, F.; Yu, D. Jasmonate regulates the inducer of cbf expression-C-repeat binding factor/DRE binding factor1 cascade and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2907–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Pan, J.; Yu, D. Jasmonate regulates leaf senescence and tolerance to cold stress: Crosstalk with other phytohormones. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, J.; Fernandez-Calvo, P.; Schweizer, F.; Goossens, A. Jasmonates: Signal transduction components and their roles in environmental stress responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 91, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B.M. Ethylene signaling in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7710–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boter, M.; Golz, J.F.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Fernandez-Barbero, G.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Solano, R. FILAMENTOUS FLOWER Is a Direct Target of JAZ3 and Modulates Responses to Jasmonate. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 3160–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, T.; Song, S.; Ren, Q.; Wu, D.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Fan, M.; Peng, W.; Ren, C.; Xie, D. The Jasmonate-ZIM-domain proteins interact with the WD-Repeat/bHLH/MYB complexes to regulate Jasmonate-mediated anthocyanin accumulation and trichome initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Li, Y.; Qi, T.; Gao, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, M.; Huang, H.; Song, S. The C-terminal domains of Arabidopsis GL3/EGL3/TT8 interact with JAZ proteins and mediate dimeric interactions. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018, 13, e1422460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz, T.; Smirnova, E.; Marquis, V.; Poirier, L. Metabolic Control within the Jasmonate Biochemical Pathway. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 2621–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, A.J.; Thireault, C.; Zemelis, S.; Poudel, A.N.; Zhang, T.; Kitaoka, N.; Brandizzi, F.; Matsuura, H.; Howe, G.A. Endoplasmic reticulum-associated inactivation of the hormone jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine by multiple members of the cytochrome P450 94 family in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 29728–29738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, Y.; Widemann, E.; Miesch, L.; Pinot, F.; Heitz, T. CYP94-mediated jasmonoyl-isoleucine hormone oxidation shapes jasmonate profiles and attenuates defence responses to Botrytis cinerea infection. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3879–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widemann, E.; Miesch, L.; Lugan, R.; Holder, E.; Heinrich, C.; Aubert, Y.; Miesch, M.; Pinot, F.; Heitz, T. The amidohydrolases IAR3 and ILL6 contribute to jasmonoyl-isoleucine hormone turnover and generate 12-hydroxyjasmonic acid upon wounding in Arabidopsis leaves. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31701–31714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, V.; Smirnova, E.; Poirier, L.; Zumsteg, J.; Schweizer, F.; Reymond, P.; Heitz, T. Stress- and pathway-specific impacts of impaired jasmonoyl-isoleucine (JA-Ile) catabolism on defense signalling and biotic stress resistance. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunde, C.; Kimberlin, A.; Leiboff, S.; Koo, A.J.; Hake, S. Tasselseed5 overexpresses a wound-inducible enzyme, ZmCYP94B1, that affects jasmonate catabolism, sex determination, and plant architecture in maize. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, Z.J.; Zhao, Z.W.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, H.F.; Liu, Y.W.; Xu, Q.; Liu, H.T. Tasselseed5 encodes a cytochrome C oxidase that functions in sex determination by affecting jasmonate catabolism in maize. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurotani, K.; Hayashi, K.; Hatanaka, S.; Toda, Y.; Ogawa, D.; Ichikawa, H.; Ishimaru, Y.; Tashita, R.; Suzuki, T.; Ueda, M.; et al. Elevated levels of CYP94 family gene expression alleviate the jasmonate response and enhance salt tolerance in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Xin, Y.; Tan, Y.; Hu, X.; Bai, J.; Liu, Z.Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, L.; Peng, C.; Fan, T.; et al. Natural variation in the HAN1 gene confers chilling tolerance in rice and allowed adaptation to a temperate climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3494–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.S.; Cooke, T.F.; Depew, C.L.; Patel, L.C.; Ogawa, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; Howe, G.A. Alternative splicing expands the repertoire of dominant JAZ repressors of jasmonate signaling. Plant J. 2010, 63, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, J.E.; Shyu, C.; Campos, M.L.; Patel, L.C.; Chung, H.S.; Yao, J.; He, S.Y.; Howe, G.A. Negative feedback control of jasmonate signaling by an alternative splice variant of JAZ10. Plant Physiol. 2013, 162, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ke, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, R.; Sugimoto, K.; Howe, G.A.; Xu, H.E.; Zhou, M.; He, S.Y.; Melcher, K. Structural insights into alternative splicing-mediated desensitization of jasmonate signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Deng, L.; Zhai, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, C. Mediator Subunit MED25 Couples Alternative Splicing of JAZ Genes with Fine-Tuning of Jasmonate Signaling. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki-Sekimoto, Y.; Jikumaru, Y.; Obayashi, T.; Saito, H.; Masuda, S.; Kamiya, Y.; Ohta, H.; Shirasu, K. Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors JASMONATE-ASSOCIATED MYC2-LIKE1 (JAM1), JAM2, and JAM3 are negative regulators of jasmonate responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Qi, T.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Huang, H.; Wu, D.; Guo, H.; Xie, D. The bHLH subgroup IIId factors negatively regulate jasmonate-mediated plant defense and development. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, S.; Fernandez-Calvo, P.; Fernandez, G.M.; Diez-Diaz, M.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Lopez-Vidriero, I.; Godoy, M.; Fernandez-Barbero, G.; Van Leene, J.; De Jaeger, G.; et al. bHLH003, bHLH013 and bHLH017 are new targets of JAZ repressors negatively regulating JA responses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, M.; Deng, L.; Shen, J.; Fang, M.; Chen, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhai, Q. MYC2 Regulates the Termination of Jasmonate Signaling via an Autoregulatory Negative Feedback Loop. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 106–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chico, J.M.; Lechner, E.; Fernandez-Barbero, G.; Canibano, E.; Garcia-Casado, G.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Hammann, P.; Zamarreno, A.M.; Garcia-Mina, J.M.; Rubio, V.; et al. CUL3(BPM) E3 ubiquitin ligases regulate MYC2, MYC3, and MYC4 stability and JA responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6205–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.; Fernandez-Calvo, P.; Colinas, M.; Pauwels, L.; Goossens, A. Jasmonate and auxin perception: How plants keep F-boxes in check. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 3401–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavy, M.; Estelle, M. Mechanisms of auxin signaling. Development 2016, 143, 3226–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyser, O. Auxin Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daviere, J.M.; Achard, P. A Pivotal Role of DELLAs in Regulating Multiple Hormone Signals. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazan, K. The Multitalented MEDIATOR25. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Bano, A.; Ali, S.; Babar, M.A. Crosstalk amongst phytohormones from planta and PGPR under biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 90, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, L.; Gong, X.; Xu, J.; Li, M. Functions of Jasmonic Acid in Plant Regulation and Response to Abiotic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, C.M.; Pierik, R.; Van Wees, S.C. Different shades of JAZ during plant growth and defense. New Phytol. 2014, 204, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caarls, L.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Van Wees, S.C.M. How salicylic acid takes transcriptional control over jasmonic acid signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartweck, L.M. Gibberellin signaling. Planta 2008, 229, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Lee, L.Y.; Xia, K.; Yan, Y.; Yu, H. DELLAs modulate jasmonate signaling via competitive binding to JAZs. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.L.; Yao, J.; Mei, C.S.; Tong, X.H.; Zeng, L.J.; Li, Q.; Xiao, L.T.; Sun, T.P.; Li, J.; Deng, X.W.; et al. Plant hormone jasmonate prioritizes defense over growth by interfering with gibberellin signaling cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, T.Y.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, S.; Chang, S.H.; Chung, P.J.; Oh, K.B.; Kim, J.K.; Jang, G.; Choi, Y.D. Jasmonate Zim-Domain Protein 9 Interacts With Slender Rice 1 to Mediate the Antagonistic Interaction Between Jasmonic and Gibberellic Acid Signals in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Zhao, M.; Leavitt, J.M.; Lloyd, A.M. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant J. 2008, 53, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Morohashi, K.; Hatlestad, G.; Grotewold, E.; Lloyd, A. The TTG1-bHLH-MYB complex controls trichome cell fate and patterning through direct targeting of regulatory loci. Development 2008, 135, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, T.; Huang, H.; Wu, D.; Yan, J.; Qi, Y.; Song, S.; Xie, D. Arabidopsis DELLA and JAZ proteins bind the WD-repeat/bHLH/MYB complex to modulate gibberellin and jasmonate signaling synergy. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Qi, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Ren, C.; Song, S.; Huang, H. Regulation of the WD-repeat/bHLH/MYB complex by gibberellin and jasmonate. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016, 11, e1204061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Gong, Y.; Liu, B.; Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Xie, D.; Song, S. The DELLA proteins interact with MYB21 and MYB24 to regulate filament elongation in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, Y.; Ye, S.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Q.; Liu, F.; Zhou, W.; Chen, R.; Li, X.; Tietz, O.; et al. Arabidopsis ASA1 is important for jasmonate-mediated regulation of auxin biosynthesis and transport during lateral root formation. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1495–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.T.; Xu, P.; Zhao, P.X.; Liu, R.; Yu, L.H.; Xiang, C.B. Arabidopsis ERF109 mediates cross-talk between jasmonic acid and auxin biosynthesis during lateral root formation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhai, Q.; Zhou, W.; Qi, L.; Xu, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, R.; Jiang, H.; Qi, J.; et al. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor MYC2 directly represses PLETHORA expression during jasmonate-mediated modulation of the root stem cell niche in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3335–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, B.; Yu, J.Q.; Chen, Z. Arabidopsis sigma factor binding proteins are activators of the WRKY33 transcription factor in plant defense. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3824–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkenbihl, R.P.; Diezel, C.; Somssich, I.E. Arabidopsis WRKY33 is a key transcriptional regulator of hormonal and metabolic responses toward Botrytis cinerea infection. Plant Physiol. 2012, 159, 266–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, O.; Piqueras, R.; Sanchez-Serrano, J.J.; Solano, R. ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 integrates signals from ethylene and jasmonate pathways in plant defense. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, K.C.; Dombrecht, B.; Manners, J.M.; Schenk, P.M.; Edgar, C.I.; Maclean, D.J.; Scheible, W.R.; Udvardi, M.K.; Kazan, K. Repressor- and activator-type ethylene response factors functioning in jasmonate signaling and disease resistance identified via a genome-wide screen of Arabidopsis transcription factor gene expression. Plant Physiol 2005, 139, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pre, M.; Atallah, M.; Champion, A.; De Vos, M.; Pieterse, C.M.; Memelink, J. The AP2/ERF domain transcription factor ORA59 integrates jasmonic acid and ethylene signals in plant defense. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Meng, Y.; Hu, J.; Ding, M.; Bian, J.; Yan, M.; Han, J.; Zhou, M. Jasmonic acid/ethylene signaling coordinates hydroxycinnamic acid amides biosynthesis through ORA59 transcription factor. Plant J. 2018, 95, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolgikh, V.A.; Pukhovaya, E.M.; Zemlyanskaya, E.V. Shaping Ethylene Response: The Role of EIN3/EIL1 Transcription Factors. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Huang, H.; Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Zhai, Q.; Li, C.; Qi, T.; et al. Interaction between MYC2 and ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3 modulates antagonism between jasmonate and ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; An, F.; Hao, D.; Li, P.; Song, J.; Yi, C.; Guo, H. Jasmonate-activated MYC2 represses ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3 activity to antagonize ethylene-promoted apical hook formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lan, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhu, Z. Diverse contributions of MYC2 and EIN3 in the regulation of Arabidopsis jasmonate-responsive gene expression. Plant Direct 2017, 1, e00015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.; Van der Does, D.; Zamioudis, C.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van Wees, S.C. Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.M.; Melcher, K.; Teh, B.T.; Xu, H.E. Abscisic acid perception and signaling: Structural mechanisms and applications. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, S.R.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Finkelstein, R.R.; Abrams, S.R. Abscisic acid: Emergence of a core signaling network. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 651–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackman, P.; Gonzalez-Guzman, M.; Tilleman, S.; Carqueijeiro, I.; Perez, A.C.; Moses, T.; Seo, M.; Kanno, Y.; Hakkinen, S.T.; Van Montagu, M.C.; et al. Jasmonate signaling involves the abscisic acid receptor PYL4 to regulate metabolic reprogramming in Arabidopsis and tobacco. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5891–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleman, F.; Yazaki, J.; Lee, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Kim, A.Y.; Li, Z.; Kinoshita, T.; Ecker, J.R.; Schroeder, J.I. An ABA-increased interaction of the PYL6 ABA receptor with MYC2 Transcription Factor: A putative link of ABA and JA signaling. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Guo, Q.; Froehlich, J.E.; Hersh, H.L.; Zienkiewicz, A.; Howe, G.A.; Benning, C. Two Abscisic Acid-Responsive Plastid Lipase Genes Involved in Jasmonic Acid Biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 1006–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Qiu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Tang, L.; Tong, X.; Zhang, J. Abscisic acid promotes jasmonic acid biosynthesis via a ‘SAPK10-bZIP72-AOC’ pathway to synergistically inhibit seed germination in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1336–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, L.; Ritter, A.; Goossens, J.; Durand, A.N.; Liu, H.; Gu, Y.; Geerinck, J.; Boter, M.; Vanden Bossche, R.; De Clercq, R.; et al. The RING E3 Ligase KEEP ON GOING Modulates JASMONATE ZIM-DOMAIN12 Stability. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Jing, Y.; Shi, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Yan, J.; Chu, J.; Chen, K.M.; Sun, J. JAZ proteins modulate seed germination through interaction with ABI5 in bread wheat and Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Howe, G.A.; Yu, D. Molecular Mechanism Underlying the Synergetic Effect of Jasmonate on Abscisic Acid Signaling during Seed Germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 3846–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Han, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M.; Pan, J.; Yu, D. The Transcription Factor Inducer of CBF expression1 Interacts with Abscisic Acid Insensitive5 and Della Proteins to Fine-Tune Abscisic Acid Signaling during Seed Germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 1520–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sun, J.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, C. The bHLH-type transcription factor AtAIB positively regulates ABA response in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, M.; Mitsuda, N.; Herde, M.; Koo, A.J.; Moreno, J.E.; Suzuki, K.; Howe, G.A.; Ohme-Takagi, M. A bHLH-type transcription factor, Aba-Inducible Bhlh-Type Transcription Factor/JA-Associated MYC2-LIKE1, acts as a repressor to negatively regulate jasmonate signaling in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1641–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Hsieh, E.J.; Cheng, M.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lin, T.P. ORA47 (octadecanoid-responsive AP2/ERF-domain transcription factor 47) regulates jasmonic acid and abscisic acid biosynthesis and signaling through binding to a novel cis-element. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avramova, Z. The jasmonic acid-signalling and abscisic acid-signalling pathways cross talk during one, but not repeated, dehydration stress: A non-specific ‘panicky’ or a meaningful response? Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Hong, G.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, X.; MacFarlane, S.; Yan, F.; Chen, J. Jasmonic acid-mediated defense suppresses brassinosteroid-mediated susceptibility to Rice black streaked dwarf virus infection in rice. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, K.; Peng, Y.J.; Yuan, L.B.; Dai, Y.S.; Chen, Q.F.; Yu, L.J.; Bai, M.Y.; Zhang, W.Q.; Xie, L.J.; Xiao, S. Brassinosteroids Antagonize Jasmonate-Activated Plant Defense Responses through BRI1-EMS-SUPPRESSOR1 (BES1). Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1066–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Wen, P.; You, X.; Zhang, X.; Pan, G.; Li, Q.; et al. Rice stripe virus suppresses jasmonic acid-mediated resistance by hijacking brassinosteroid signaling pathway in rice. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, F.K.; Devireddy, A.R.; Azad, R.K.; Shulaev, V.; Mittler, R. Local and Systemic Metabolic Responses during Light-Induced Rapid Systemic Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandalinas, S.I.; Fichman, Y.; Devireddy, A.R.; Sengupta, S.; Azad, R.K.; Mittler, R. Systemic signaling during abiotic stress combination in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13810–13820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperini, D.; Chauvin, A.; Acosta, I.F.; Kurenda, A.; Stolz, S.; Chetelat, A.; Wolfender, J.L.; Farmer, E.E. Axial and Radial Oxylipin Transport. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2244–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, A.; Zimmer, M.; Mielke, S.; Stellmach, H.; Melnyk, C.W.; Hause, B.; Gasperini, D. Wound-Induced Shoot-to-Root Relocation of JA-Ile Precursors Coordinates Arabidopsis Growth. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Timko, M.P. Jasmonic Acid Signaling and Molecular Crosstalk with Other Phytohormones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062914
Liu H, Timko MP. Jasmonic Acid Signaling and Molecular Crosstalk with Other Phytohormones. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):2914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062914
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hai, and Michael P. Timko. 2021. "Jasmonic Acid Signaling and Molecular Crosstalk with Other Phytohormones" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 2914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062914
APA StyleLiu, H., & Timko, M. P. (2021). Jasmonic Acid Signaling and Molecular Crosstalk with Other Phytohormones. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 2914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062914






