The Effect of Neddylation Inhibition on Inflammation-Induced MMP9 Gene Expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
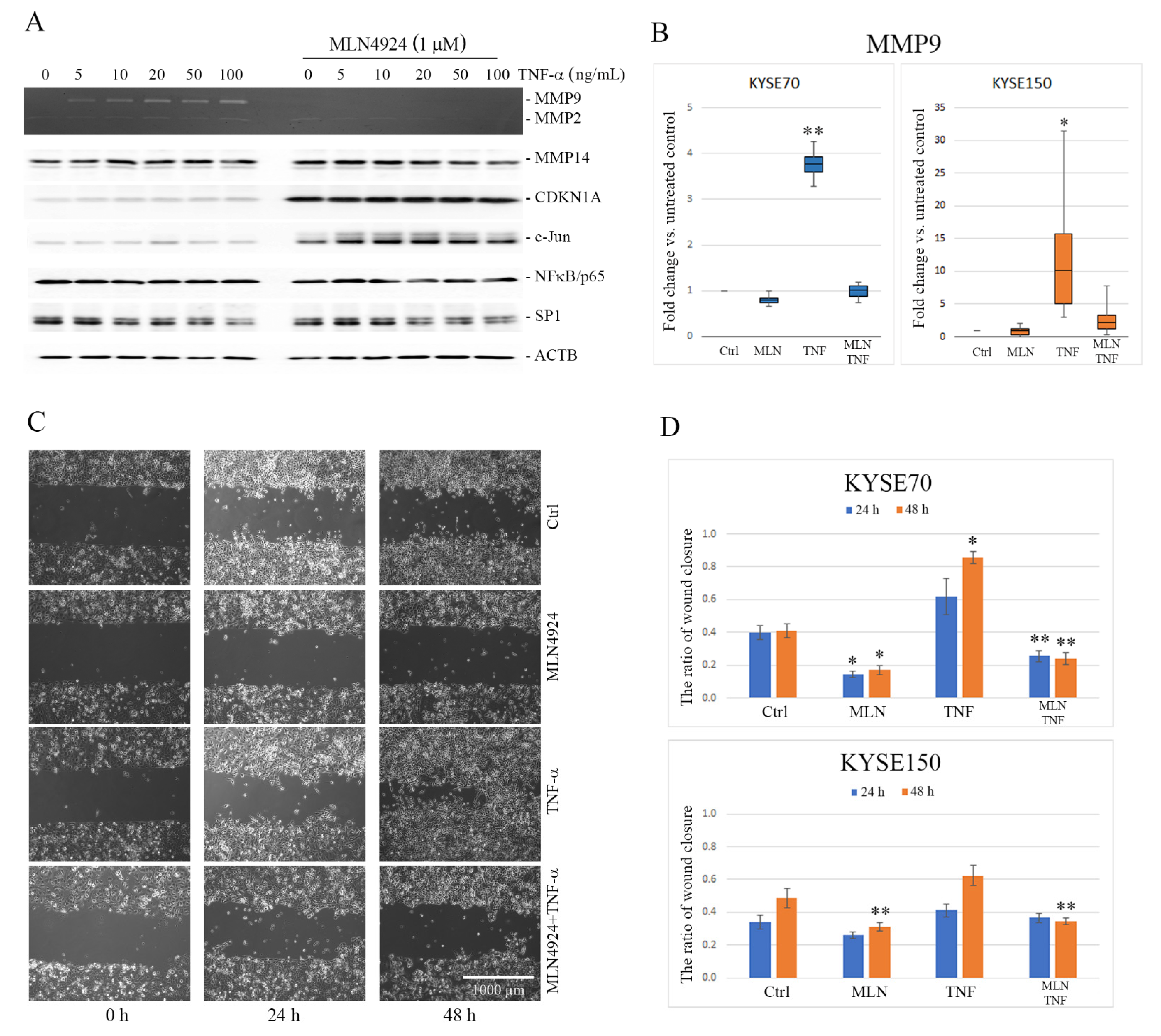
2.1. MLN4924 Downregulates TNF-α-Induced MMP9 Expression in ESCC Cells
2.2. MLN4924 Inhibits Migration of ESCC Cells In Vitro
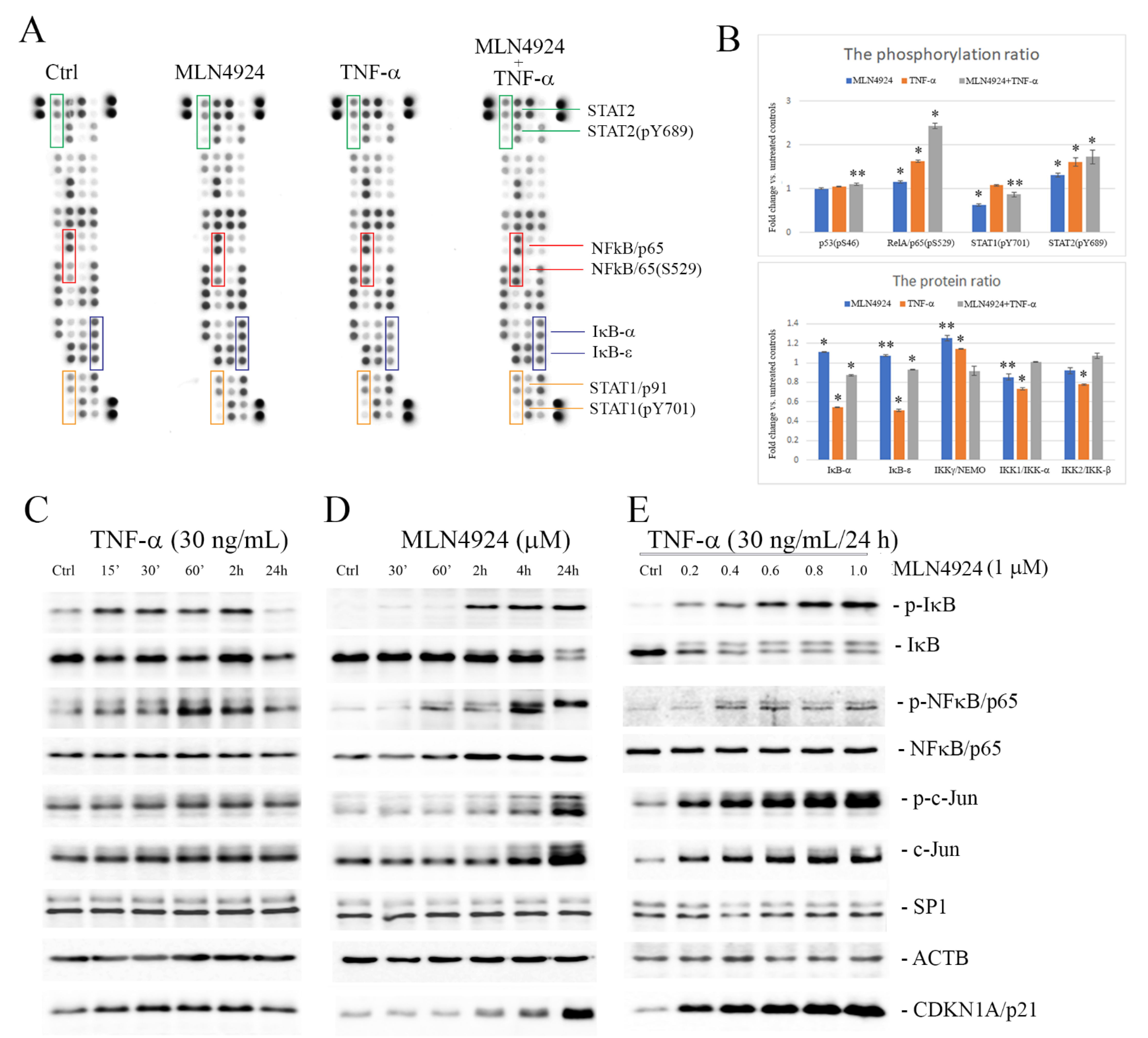
2.3. MLN4924 Upregulates Phosphorylation of IκB-α and NFκB/p65
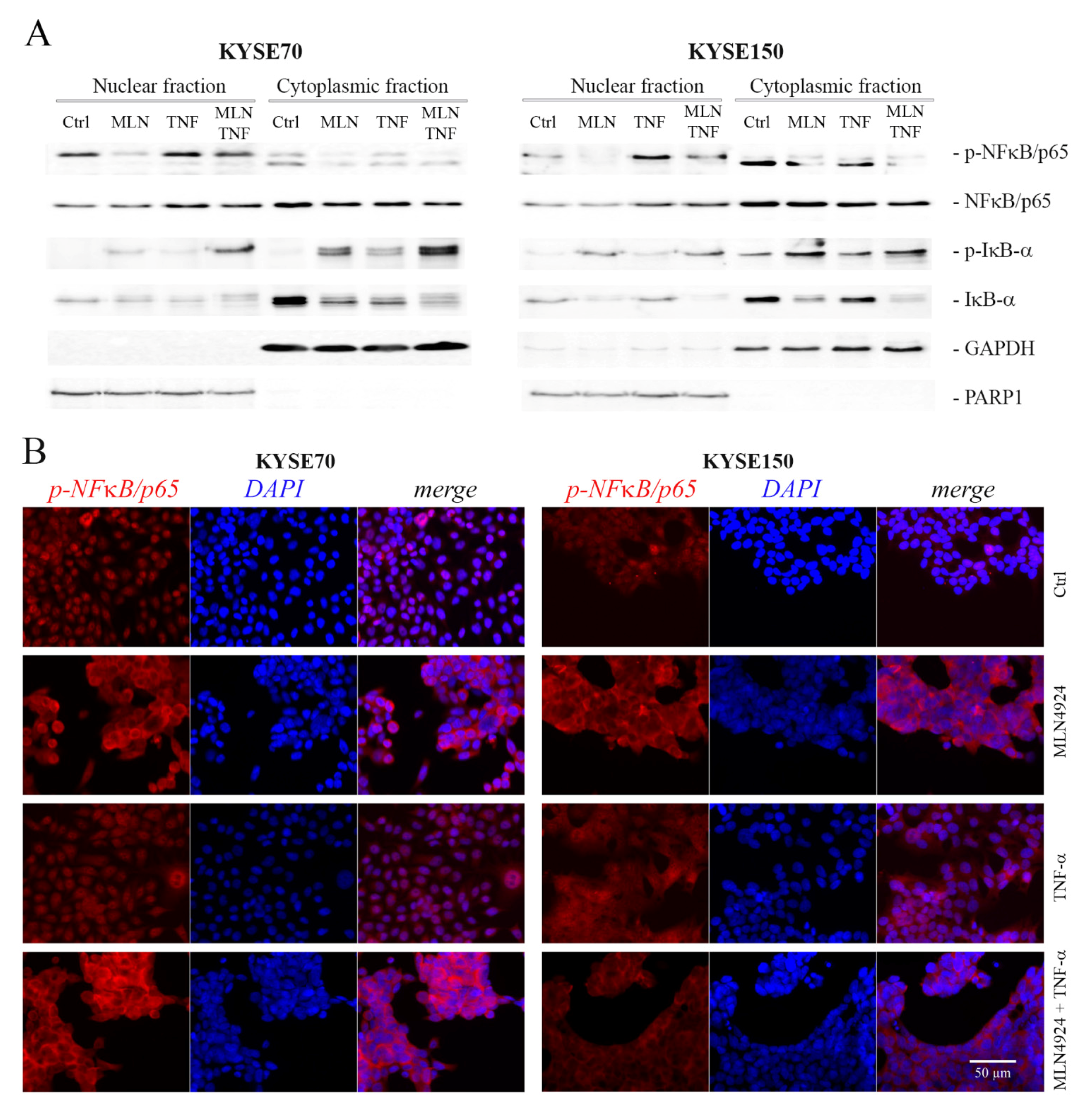
2.4. MLN4924 Dysregulates Subcellular Localization of Phospho-NFκB/p65 and Phospho-IκB-α
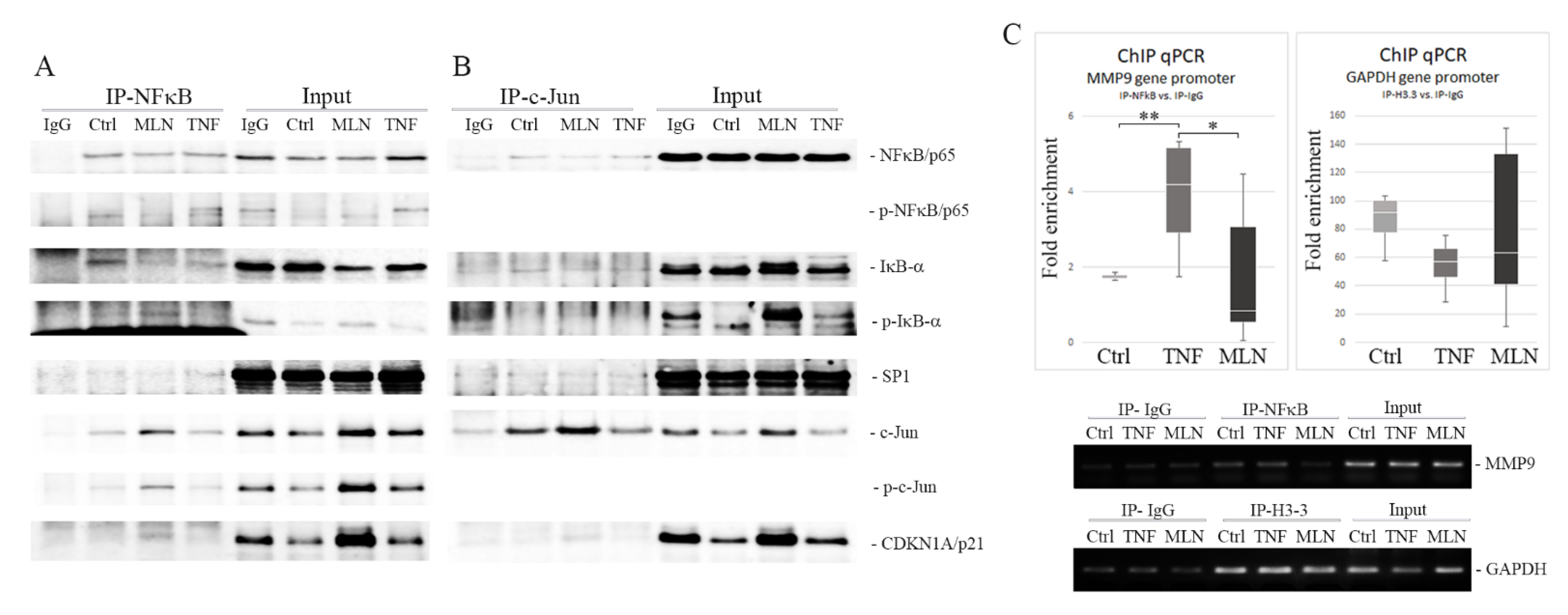
2.5. MLN4924 Generates Nuclear NFκB/p65-IκB-α Complexes Rich in Phospho-IκB-α (Ser32) and c-Jun/phospho-c-Jun (Ser73)
2.6. MLN4924 Blocks NFκB/p65–DNA Binding
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2. Gelatin Zymography
4.3. Cell Fractionation
4.4. Coimmunoprecipitation and Western Blotting
4.5. Profiling NFκB Signaling Pathway Proteins
4.6. Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
4.7. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
4.8. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.9. Wound Healing Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abnet, C.C.; Arnold, M.; Wei, W. Epidemiology of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2017, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, USA. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/ (accessed on 28 January 2021).
- Chung, S.Y.; Xiaoxin, C.; Shuiping, T. Etiology and Prevention of Esophageal Cancer. Gastrointest. Tumors 2016, 3, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Smyth, E.C.; Lagergren, J.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Lordick, F.; Shah, M.A.; Lagergren, P.; Cunningham, D. Oesophageal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multhoff, G.; Molls, M.; Radons, J. Chronic Inflammation in Cancer Development. Front. Immunol. 2012, 2, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korniluk, A.; Koper, O.; Kemona, H.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V. From inflammation to cancer. Ir. J. Med Sci. 2017, 186, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.W.; Karakasheva, T.A.; Hicks, P.D.; Bass, A.J.; Rustgi, A.K. The tumor microenvironment in esophageal cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5337–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parameswaran, N.; Patial, S. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Signaling in Macrophages. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Express 2010, 20, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.R. Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, J.P.; Pober, J.S.; Bradley, J.R. Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. J. Pathol. 2013, 230, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, W.N.; Liang, K.C.; Luo, S.F.; Wu, C.B.; Wang, S.W.; Yang, C.M. TNF-α induces MMP-9 expression via activation of Src/EGFR, PDGFR/PI3K/Akt cascade and promotion of NFkappaB/p300 binding in human tracheal smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell Mol. Physiol. 2007, 292, L799–L812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandooren, J.; Van den Steen, P.E.; Opdenakker, G. Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metallo-proteinase-9 (MMP-9): The next decade. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 222–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, A.R.; Mackay, A.R. Gelatinase B/MMP-9 in Tumour Pathogenesis and Progression. Cancers 2014, 6, 240–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Hart, E.; Shchurin, A.; Hoover-Plow, J. Inflammatory macrophage migration requires MMP-9 activation by plas-minogen in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3012–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Guo, Q.; Duan, F.; Tang, F.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, G. Overexpression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2009, 22, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augoff, K.; Hryniewicz-Jankowska, A.; Tabola, R.; Czapla, L.; Szelachowski, P.; Wierzbicki, J.; Grabowski, K.; Sikorski, A.F. Upregu-lated expression and activation of membrane associated proteases in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2820–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaremba-Czogalla, M.; Hryniewicz-Jankowska, A.; Tabola, R.; Nienartowicz, M.; Stach, K.; Wierzbicki, J.; Cirocchi, R.; Ziölkowski, P.; Tabaczar, S.; Augoff, K. A novel regulatory function of CDKN1A/p21 in TNFα-induced matrix metalloproteinase 9-dependent migration and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2018, 47, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, M.; Chase, A.J.; Baker, A.H.; Newby, A.C. Inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappaB reduces matrix metallopro-teinase-1, -3 and -9 production by vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 50, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wullaert, A.; Heyninck, K.; Beyaert, R. Mechanisms of crosstalk between TNF-induced NF-kappaB and JNK activation in hepatocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Tseng, H.W.; Hsieh, H.L.; Lee, C.W.; Wu, C.Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Yang, C.M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces MMP-9 expression via p42/p44 MAPK, JNK, and nuclear factor-kappaB in A549 cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 229, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y. Cullin-RING Ligases as attractive anti-cancer targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 3215–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, D.M.; Borg, L.A.; Scott, D.C.; Hunt, H.W.; Hammel, M.; Schulman, B.A. Structural insights into NEDD8 activation of cul-lin-RING ligases: Conformational control of conjugation. Cell 2008, 134, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Zhang, J. Diverse and pivotal roles of neddylation in metabolism and immunity. FEBS J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soucy, T.A.; Smith, P.G.; Milhollen, M.A.; Berger, A.J.; Gavin, J.M.; Adhikari, S.; Brownell, J.E.; Burke, K.E.; Cardin, D.P.; Critchley, S.; et al. An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a new approach to treat cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 458, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Pavlick, A.C.; Boasberg, P.; Thompson, J.A.; Mulligan, G.; Pickard, M.D.; Faessel, H.; Dezube, B.J.; Hamid, O. A phase I study of the investigational NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor pevonedistat (TAK-924/MLN4924) in patients with metastatic melanoma. Investig. New Drugs 2016, 34, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.J.; Jakubowiak, A.J.; O’Connor, O.A.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Harvey, R.D.; Smith, M.R.; Lebovic, D.; Diefenbach, C.; Kelly, K.; Hua, Z.; et al. Phase I Study of the Novel Investiga-tional NEDD8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor Pevonedistat (MLN4924) in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma or Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantopoulos, J.; Shapiro, G.I.; Cohen, R.B.; Clark, J.W.; Kauh, J.S.; Weiss, G.J.; Cleary, J.M.; Mahalingam, D.; Pickard, M.D.; Faessel, H.M.; et al. Phase I Study of the Investigational NEDD8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor Pevonedistat (TAK-924/MLN4924) in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Wyckoff, J.; Condeelis, J. Cell migration in tumors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, T.; Singh, R.; Sabharwal, L.; Bando, H.; Meng, J.; Arima, Y.; Yamada, M.; Harada, M.; Jiang, J.J.; Kamimura, D.; et al. Inflammation amplifier, a new paradigm in cancer biology. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, B.P. Inflammation: A driving force speeds cancer metastasis. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3267–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, B.P. TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, J.; Hagemann, T. Cancer-Related Inflammation. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Ma, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Yang, D. High expression of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 in tissue is associated with progression and prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 80, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolczyk, D.; Zaremba-Czogalla, M.; Hryniewicz-Jankowska, A.; Tabola, R.; Grabowski, K.; Sikorski, A.F.; Augoff, K. TNF-α promotes breast cancer cell migration and enhances the concentration of membrane-associated proteases in lipid rafts. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 39, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolli, M.; Fransvea, E.; Pilch, J.; Saven, A.; Felding-Habermann, B. Activated integrin alphavbeta3 cooperates with metallo-proteinase MMP-9 in regulating migration of metastatic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9482–9487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, H.; Tang, Z.; Jin, H.; Sun, Y. Neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 suppresses growth and migration of human gastric cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolenski, F.; Fisher, C.D.; Sano, T.; Wyllie, S.D.; Cicia, L.A.; Gallacher, M.J.; Baker, R.A.; Kirby, P.J.; Senn, J.J. The NAE inhibitor pevonedistat (MLN4924) synergizes with TNF-α to activate apoptosis. Cell Death Discov. 2015, 1, 15034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuele, M.J.; Elia, A.E.; Xu, Q.; Thoma, C.R.; Izhar, L.; Leng, Y.; Guo, A.; Chen, Y.-N.; Rush, J.; Hsu, P.W.-C.; et al. Global Identification of Modular Cullin-RING Ligase Substrates. Cell 2011, 147, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Hagler, J.; Palombella, V.J.; Melandri, F.; Scherer, D.; Ballard, D.; Maniatis, T. Signal-induced site-specific phos-phorylation targets I kappa B alpha to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkalay, I.; Yaron, A.; Hatzubai, A.; Orian, A.; Ciechanover, A.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Stimulation-dependent I kappa B alpha phosphorylation marks the NF-kappa B inhibitor for degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10599–10603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Okumura, F.; Takahashi, N.; Kataoka, A.; Kamiyama, T.; Todo, S.; Hatakeyama, S. TRIM40 promotes neddylation of IKKγ and is downregulated in gastrointestinal cancers. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Cheng, J.; Shi, T.; Yeh, E.T. Neddylation of a breast cancer-associated protein recruits a class III histone deacetylase that represses NFkappaB-dependent transcription. Nat Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridharan, S.M.; Srinivasan, M. Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradère, P.P.; Hernandez, C.; Koppe, C.; Friedman, R.A.; Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. Negative regulation of NF-κB p65 activity by serine 536 phosphorylation. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Voll, R.E.; Ghosh, S. Phosphorylation of NF-kappa B p65 by PKA stimulates transcriptional activity by promoting a novel bivalent interaction with the coactivator CBP/p300. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, F.; Smith, E.L.; Carmody, R.J. The Regulation of NF-κB Subunits by Phosphorylation. Cells 2016, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Westerheide, S.D.; Hanson, J.L.; Baldwin, A.S. Tumor Necrosis Factor α-induced Phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on Ser529 Is Controlled by Casein Kinase II. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32592–32597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mikecz, A. The nuclear ubiquitin-proteasome system. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warfel, N.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. p21WAF1 and tumourigenesis: 20 years after. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Chang, L.-S. NFκB- and AP-1-mediated DNA looping regulates matrix metalloproteinase-9 transcription in TNF-α-treated human leukemia U937 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.; Davis, R.J.; McLaren, A.; Cohen, P. A reinvestigation of the multisite phosphorylation of the transcription factor c-Jun. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3876–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgunova, E.; Taipale, J. Structural perspective of cooperative transcription factor binding. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmsdorf, H.J. Jun: Transcription factor and oncoprotein. J. Mol. Med. 1996, 74, 725–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Ndoja, A. Regulation of gene expression by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.A.; Iakova, P.; Maneix, L.; Shih, F.-Y.; Cho, H.E.; Sahin, E.; Catic, A. The ubiquitin ligase Cullin-1 associates with chromatin and regulates transcription of specific c-MYC target genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yue, P.; Lonial, S.; Khuri, F.R.; Sun, S.-Y. The NEDD8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor, MLN4924, Cooperates with TRAIL to Augment Apoptosis through Facilitating c-FLIP Degradation in Head and Neck Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2415–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, Y. MLN4924: Additional activities beyond neddylation inhibition. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2019, 6, e1618174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hryniewicz-Jankowska, A.; Wierzbicki, J.; Tabola, R.; Stach, K.; Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Augoff, K. The Effect of Neddylation Inhibition on Inflammation-Induced MMP9 Gene Expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041716
Hryniewicz-Jankowska A, Wierzbicki J, Tabola R, Stach K, Sossey-Alaoui K, Augoff K. The Effect of Neddylation Inhibition on Inflammation-Induced MMP9 Gene Expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(4):1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041716
Chicago/Turabian StyleHryniewicz-Jankowska, Anita, Jaroslaw Wierzbicki, Renata Tabola, Kamilla Stach, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui, and Katarzyna Augoff. 2021. "The Effect of Neddylation Inhibition on Inflammation-Induced MMP9 Gene Expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 4: 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041716
APA StyleHryniewicz-Jankowska, A., Wierzbicki, J., Tabola, R., Stach, K., Sossey-Alaoui, K., & Augoff, K. (2021). The Effect of Neddylation Inhibition on Inflammation-Induced MMP9 Gene Expression in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(4), 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22041716





