Molecular Physiology of Anaerobic Phototrophic Purple and Green Sulfur Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Characteristics of the Chromatiaceae and Chlorobiaceae Families
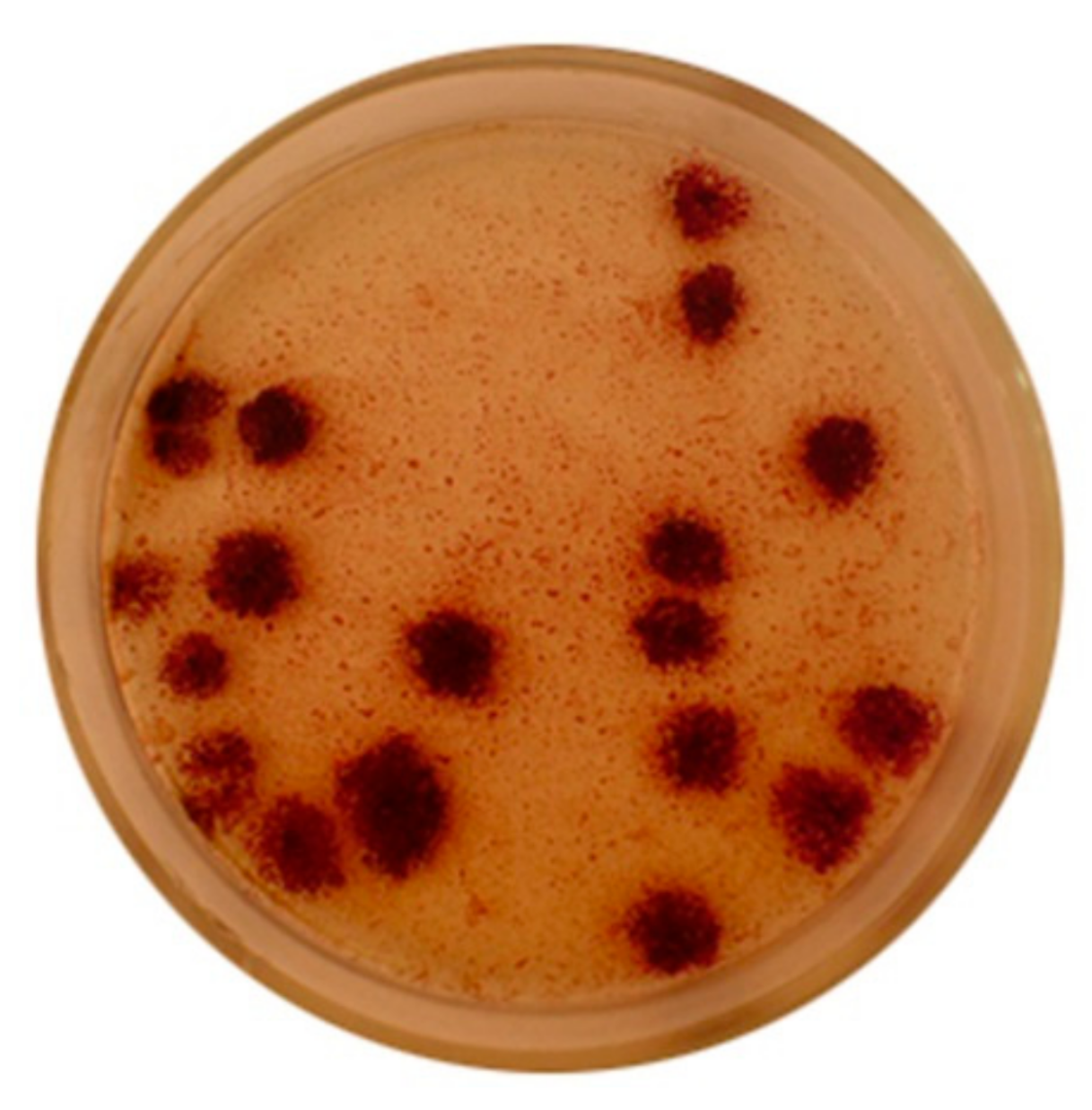
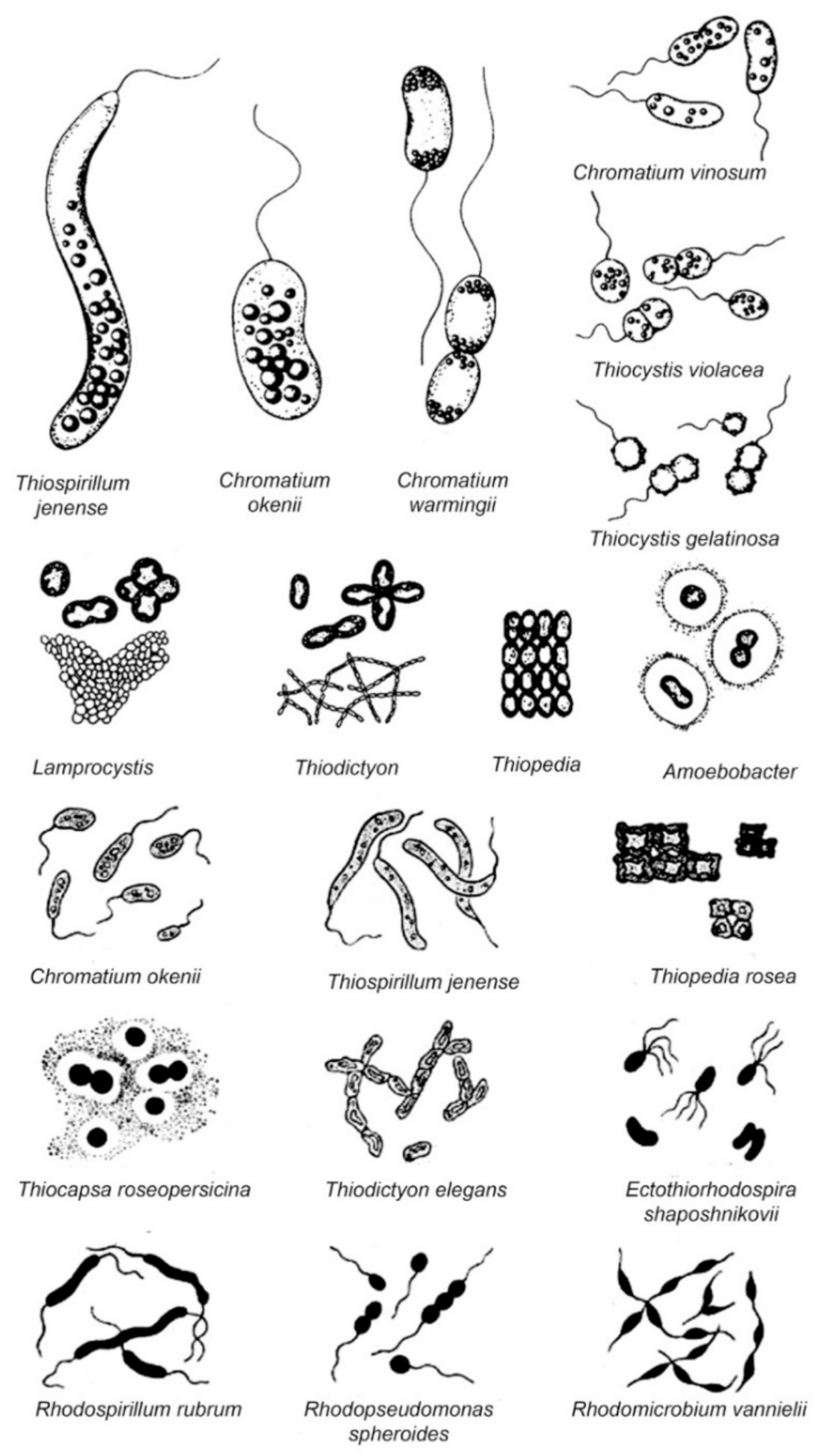
2.1. Chromatiaceae
- sources of wastewater [21] or
2.2. Chlorobiaceae
3. Phylogenetic and Taxonomy
3.1. Chromatiaceae
3.2. Chlorobiaceae
- the composition of carotenoids and bacteriochlorophyll, for the division of species into green and brown,
4. Molecular Mechanisms of Sulfur Metabolism in Phototrophic Bacteria
4.1. Oxidation of Sulfide to Elemental Sulfur
4.1.1. Flavocytochrome c
4.1.2. Sulfide: Quinone Oxidoreductase
4.1.3. The Sox Enzyme System and Reverse Operating Sulfite Reductase
4.2. Oxidation of Polysulfides
4.3. Intake and Oxidation of Elemental Sulfur from the Environment
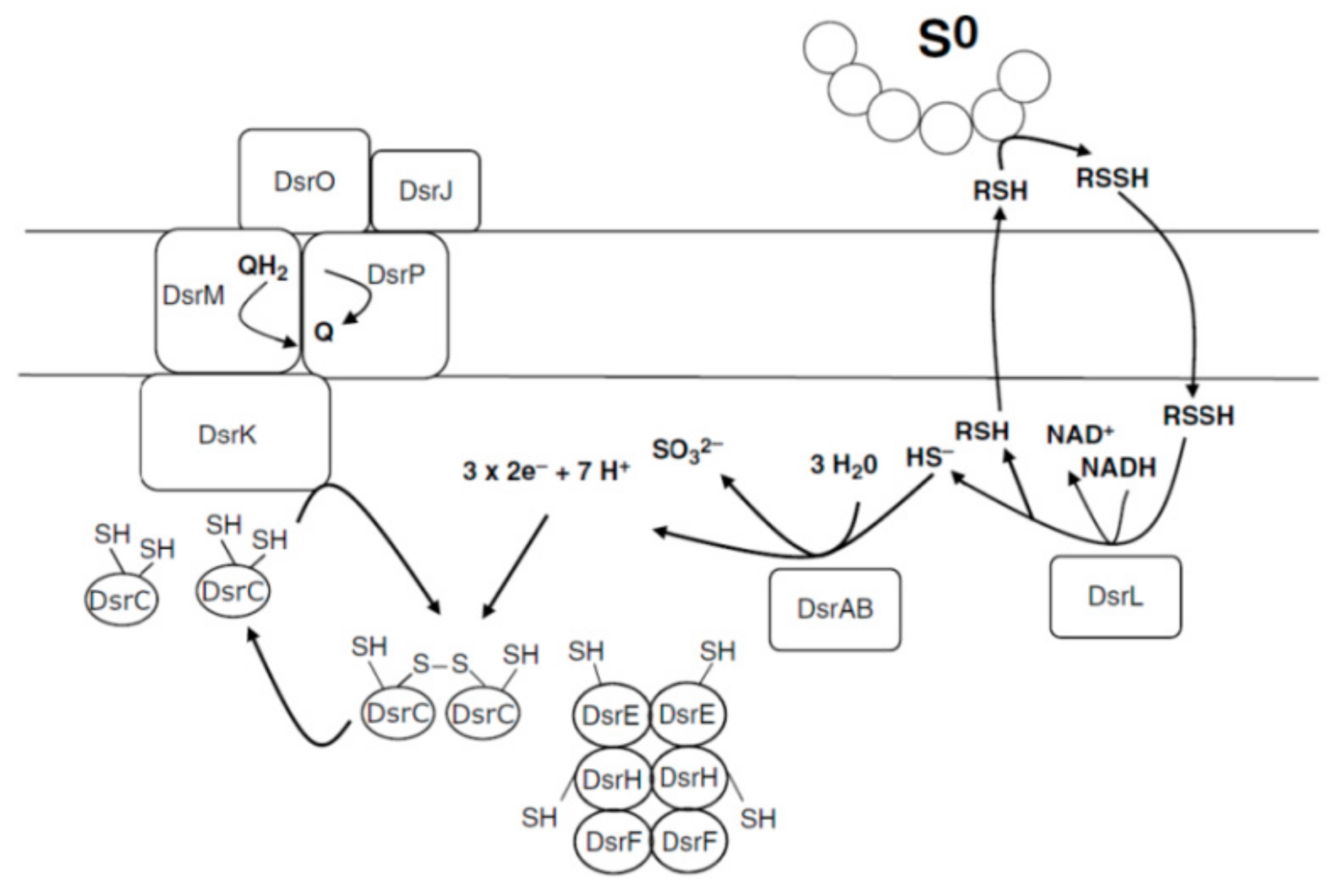
4.4. Oxidation of Accumulated Sulfur to Sulfites
4.5. Oxidation of Sulfites to Sulfate
4.5.1. Direct Oxidation by Sulfite Dehydrogenase
4.5.2. Indirect AMP Dependent Oxidation
4.6. Oxidation of Thiosulfates
4.6.1. Oxidation of Thiosulfates to Tetrathionate
4.6.2. Oxidation of Thiosulfates to Sulfates
5. Photosynthetic Apparatus
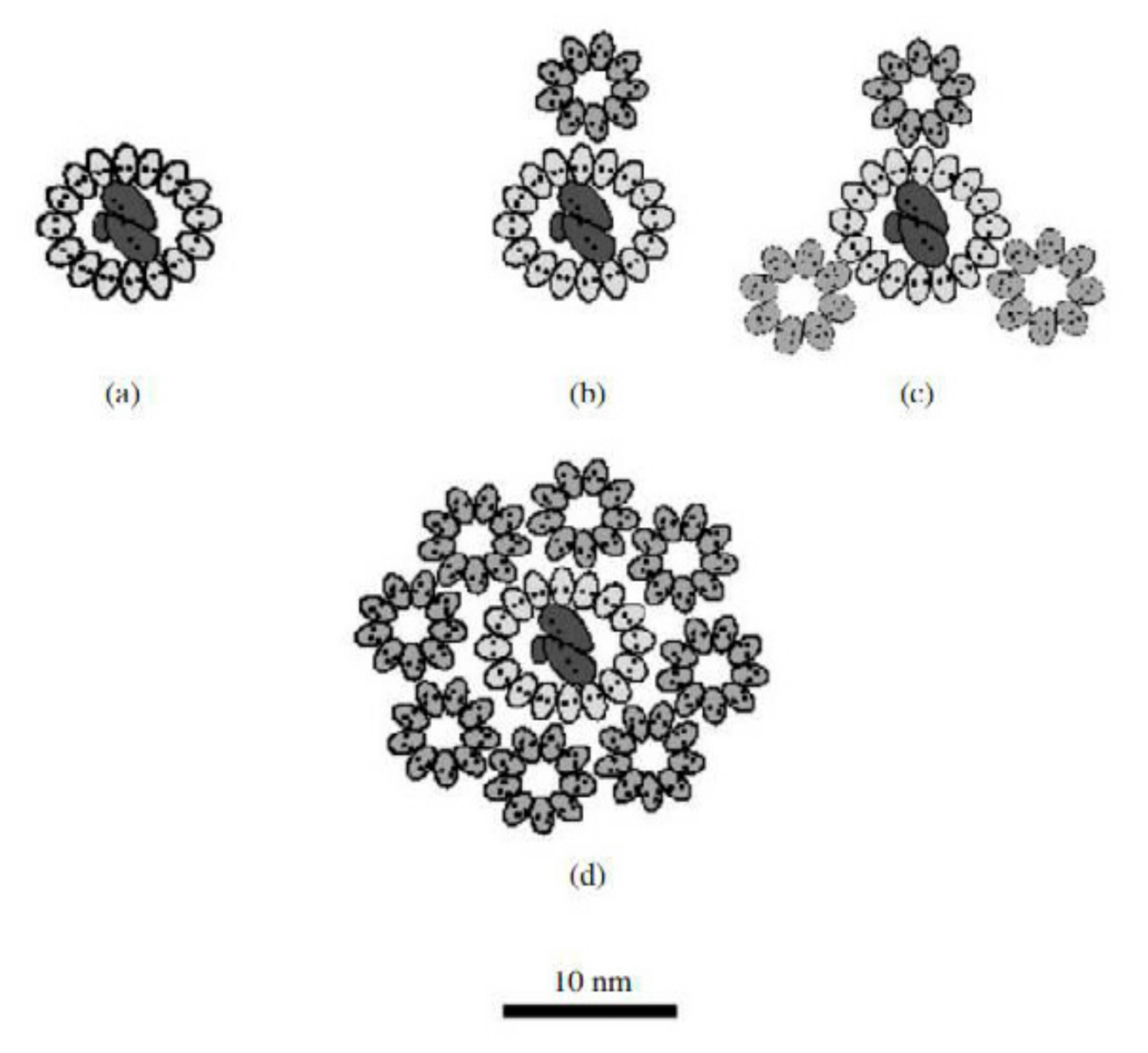
5.1. Light-Harvesting Complexes of the Chromatiaceae
5.2. Reaction Centers of the Chromatiaceae
5.3. Structure of Chlorosomes
5.4. The Reaction Center of the Chlorobiaceae Family
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Overmann, J.; van Gemerden, H. Microbial Interactions Involving Sulfur Bacteria: Implications for the Ecology and Evolution of Bacterial Communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overmann, J. The Family Chlorobiaceae. In The Prokaryotes; Dworkin, M., Falkow, S., Rosenberg, E., Schleifer, K.-H., Stackebrandt, E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 359–378. ISBN 978-0-387-25497-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig, N. Green sulfur bacteria: Archaeobacteria, Cyanobacteria, and Remaining Gram-Negative Bacteria. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Staley, J.T., Bryant, M.P., Pfennig, N., Holt, J.C., Eds.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1989; pp. 1682–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Imhoff, J.F. Taxonomy and Physiology of Phototrophic Purple Bacteria and Green Sulfur Bacteria. In Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria; Blankenship, R.E., Madigan, M.T., Bauer, C.E., Eds.; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-0-7923-3681-5. [Google Scholar]
- Overmann, J.; Tuschak, C. Phylogeny and Molecular Fingerprinting of Green Sulfur Bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 1997, 167, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, C.; Engels, S.; Pott-Sperling, A.S.; Schulte, A.; Sander, J.; Lübbe, Y.; Deuster, O.; Brune, D.C. Novel Genes of the Dsr Gene Cluster and Evidence for Close Interaction of Dsr Proteins during Sulfur Oxidation in the Phototrophic Sulfur Bacterium Allochromatium vinosum. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molisch, H.; Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh. Die Purpurbakterien: Nach Neuen Untersuchungen; Eine Mikrobiologische Studie; Fischer: Jena, Germany, 1907. [Google Scholar]
- Imhoff, J.F. Reassignment of the Genus Ectothiorhodospira Pelsh 1936 to a New Family, Ectothiorhodospiraceae Fam. Nov., and Emended Description of the Chromatiaceae Bavendamm 1924. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1984, 34, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdács, M.; Spengler, G.; Urbán, E. Identification and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Anaerobic Bacteria: Rubik’s Cube of Clinical Microbiology? Antibiotics 2017, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhoff, J.F. The Family Chromatiaceae. In The Prokaryotes; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 151–178. ISBN 978-3-642-38921-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kushkevych, I.V.; Hnatush, S.O. The Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Purple Bacteria. Biol. Stud. 2010, 4, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, A.; Bounedjoum, N.; Vincze, G.E.; Erdeiné Kis, Á.; Laczi, K.; Bende, G.; Szilágyi, Á.; Kovács, T.; Perei, K.; Rákhely, G. Challenges of Unculturable Bacteria: Environmental Perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Kováč, J.; Vítězová, M.; Vítěz, T.; Bartoš, M. The Diversity of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in the Seven Bioreactors. Arch. Microbiol. 2018, 200, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushkevych, I.; Dordević, D.; Kollar, P.; Vítězová, M.; Drago, L. Hydrogen Sulfide as a Toxic Product in the Small–Large Intestine Axis and Its Role in IBD Development. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushkevych, I.; Cejnar, J.; Treml, J.; Dordević, D.; Kollar, P.; Vítězová, M. Recent Advances in Metabolic Pathways of Sulfate Reduction in Intestinal Bacteria. Cells 2020, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushkevych, I.; Fafula, R.; Parák, T.; Bartoš, M. Activity of Na+/K+-Activated Mg2+-Dependent ATP-Hydrolase in the Cell-Free Extracts of the Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria Desulfovibrio Piger Vib-7 and Desulfomicrobium Sp. Rod-9. Acta Vet. Brno 2015, 84, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberg, C.G. Die Infusionsthierchen Als Vollkommene Organismen: Ein Blick in das Tiefere Organische Leben der Natur; L. Voss: Leipzig, Germany, 1838. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, F. Untersuchungen Über Bakterien. Beitr. Biol. Pflanz. 1875, 1, 147–207. [Google Scholar]
- Winogradsky, S. Beiträge zur Morphologie und Physiologie der Bakterien: Heft 1, zur Morphologie und Physiologie der Schwefelbakterien; Arthur Felix: Leipzig, Germany, 1888; pp. 1–120. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, M. Studien Über Die Schwefelrasenbildung Und Die Schwefelbakterien Der Thermen von Yumoto Bei Nikko. Zent. Bakteriol. Parasitenkd. Infekt. 1897, 3, 526–527. [Google Scholar]
- Holm, H.W.; Vennes, J.W. Occurrence of Purple Sulfur Bacteria in a Sewage Treatment Lagoon. Appl. Microbiol. 1970, 19, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caumette, P. Distribution and Characterization of Phototrophic Bacteria Isolated from the Water of Bietri Bay (Ebrie Lagoon, Ivory Coast). Can. J. Microbiol. 1984, 30, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.A.M.; Stolz, J.F.; Pierson, B.K. Structure of a Microbiol Mat at Great Sippewissett Marsh, Cape Cod, Massachusetts. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1987, 45, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.T. Chromatium tepidum Sp. Nov., a Thermophilic Photosynthetic Bacterium of the Family Chromatiaceae. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1986, 36, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Genetic Analysis of Sea-Ice Bacterial Communities of the Western Baltic Sea Using an Improved Double Gradient Method. Polar Biol. 2001, 24, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlund, T.M.; Woese, C.R.; Castenholz, R.W.; Madigan, M.T. A Thermophilic Green Sulfur Bacterium from New Zealand Hot Springs, Chlorobium tepidum Sp. Nov. Arch. Microbiol. 1991, 156, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhuis, M.J.W.; Gemerden, H. Competition between Purple and Brown Phototrophic Bacteria in Stratified Lakes: Sulfide, Acetate, and Light as Limiting Factors. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1986, 38, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gemerden, H.; Mas, J. Ecology of Phototrophic Sulfur Bacteria. In Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Blankenship, R.E., Madigan, M.T., Bauer, C.E., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 49–85. ISBN 978-0-7923-3681-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bavendamm, W. Die Farblosen und Roten Schwefelbakterien des Süß-Und Salzwassers; G. Fischer: Schaffhausen, Switzerland, 1924. [Google Scholar]
- Guyoneaud, R.; Suling, J.; Petri, R.; Matheron, R.; Caumette, P.; Pfennig, N.; Imhoff, J.F. Taxonomic Rearrangements of the Genera Thiocapsa and Amoebobacter on the Basis of 16S RDNA Sequence Analyses, and Description of Thiolamprovum Gen. Nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F.; Kushner, D.J.; Kushwaha, S.C.; Kates, M. Polar Lipids in Phototrophic Bacteria of the Rhodospirillaceae and Chromatiaceae Families. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 150, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F. Polar Lipids and Fatty Acids in the Genus Rhodobacter. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1991, 14, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F.; Bias-lmhoff, U. Lipids, Quinones and Fatty Acids of Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria. In Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Blankenship, R.E., Madigan, M.T., Bauer, C.E., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 179–205. ISBN 978-0-7923-3681-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, J.; Stackebrandt, E.; Zablen, L.B.; Gupta, R.; Woese, C.R. A Phylogenetic Analysis of the Purple Photosynthetic Bacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 1979, 3, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, V.J.; Pfennig, N.; Schubert, W.; Stackebrandt, E. Towards a Phylogeny of Phototrophic Purple Sulfur Bacteria?16S RRNA Oligonucleotide Cataloguing of 11 Species of Chromatiaceae. Arch. Microbiol. 1984, 139, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F.; Caumette, P. Recommended Standards for the Description of New Species of Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tank, M.; Thiel, V. Phylogenetic Relationship of Phototrophic Purple Sulfur Bacteria According to PufL and PufM Genes. Int. Microbiol. 2009, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F. Taxonomy, Phylogeny, and General Ecology of Anoxygenic Phototrophic Bacteria. In Photosynthetic Prokaryotes; Mann, N.H., Carr, N.G., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 53–92. ISBN 978-1-4757-1334-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig, N.; Overmann, J.; Genus, I. Chlorobium. The Archaea and the deeply branching and phototrophic Bacteria. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Boone, D.R., Castenholz, R.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 605–610. [Google Scholar]
- Figueras, J.B.; Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Abella, C.A. Phylogeny of the Genus Chlorobium Based on 16S RDNA Sequence. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 152, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gibson, J.; Ludwig, W.; Stackebrandt, E.; Woese, C.R. The Phylogeny of the Green Photosynthetic Bacteria: Absence of a Close Relationship Between Chlorobium and Chloroflexus. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1985, 6, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woese, C.R.; Stackebrandt, E.; Macke, T.J.; Fox, G.E. A Phylogenetic Definition of the Major Eubacterial Taxa. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1985, 6, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.; Andersen, J.; Cox, R.; Imhoff, J. Phylogeny of Green Sulfur Bacteria on the Basis of Gene Sequences of 16S RRNA and of the Fenna-Matthews-Olson Protein. Arch. Microbiol. 2002, 178, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, J.F. Phylogenetic Taxonomy of the Family Chlorobiaceae on the Basis of 16S RRNA and Fmo (Fenna-Matthews-Olson Protein) Gene Sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppen, O.I.; Tourova, T.P.; Ivanovsky, R.N.; Lebedeva, N.V.; Baslerov, R.V.; Berg, I.A. Phylogenetic Position of Three Strains of Green Sulfur Bacteria. Microbiology 2008, 77, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigaard, N.-U.; Dahl, C. Sulfur Metabolism in Phototrophic Sulfur Bacteria. In Advances in Microbial Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 54, pp. 103–200. ISBN 978-0-12-374323-7. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, M.W.; Gray, G.O.; Knaff, D.B. Interaction of Chromatium vinosum Flavocytochrome c-552 with Cytochromes c Studied by Affinity Chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1985, 187, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, D.C. Sulfur Compounds as Photosynthetic Electron Donors. In Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Blankenship, R.E., Madigan, M.T., Bauer, C.E., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 847–870. ISBN 978-0-7923-3681-5. [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz, M.A.; Fischer, U. Cytochromes of the Green Sulfur Bacterium Chlorobium vibrioforme f. thiosulfatophilum. Purification, Characterization and Sulfur Metabolism. Arch. Microbiol. 1982, 131, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesbeck, C.; Hauska, G.; Schütz, M. Biological Sulfide-Oxidation: Sulfide-Quinone Reductase (SQR), the Primary Reaction. Recent Res. Dev. Microbiol. 2000, 4, 179–203. [Google Scholar]
- Theissen, U. Single Eubacterial Origin of Eukaryotic Sulfide: Quinone Oxidoreductase, a Mitochondrial Enzyme Conserved from the Early Evolution of Eukaryotes during Anoxic and Sulfidic Times. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 1564–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahak, Y.; Arieli, B.; Padan, E.; Hauska, G. Sulfide Quinone Reductase (SQR) Activity in Chlorobium. FEBS Lett. 1992, 299, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinartz, M.; Tschäpe, J.; Brüser, T.; Trüper, H.G.; Dahl, C. Sulfide Oxidation in the Phototrophic Sulfur Bacterium Chromatium vinosum. Arch. Microbiol. 1998, 170, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesbeck, C.; Schütz, M.; Schödl, T.; Bathe, S.; Nausch, L.; Mederer, N.; Vielreicher, M.; Hauska, G. Mechanism of Sulfide-Quinone Reductase Investigated Using Site-Directed Mutagenesis and Sulfur Analysis †,‡. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 11552–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudel, R. Mechanism for the Formation of Elemental Sulfur from Aqueous Sulfide in Chemical and Microbiological Desulfurization Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1996, 35, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedel, M.; Vanselow, M.; Trüper, H.G. Siroheme Sulfite Reductase Isolated from Chromatium vinosum. Purification and Investigation of Some of Its Molecular and Catalytic Properties. Arch. Microbiol. 1979, 121, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, A.S.; Dahl, C. Sirohaem Sulfite Reductase and Other Proteins Encoded by Genes at the Dsr Locus of Chromatium vinosum Are Involved in the Oxidation of Intracellular Sulfur. Microbiology 1998, 144, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gemerden, H. Competition between purple sulfur bacteria and green sulfur bacteria: Role of sulfide, sulfur and polysulfides. In Ecology of Photosynthetic Prokaryotes with Special Reference to Meromictic Lakes and Coastal Lagoons, Proceedings of the International Seminar, Tvärminne Zoological Station, Helsinki, Finland, 17–20 October 1985; Acta Academiae Aboensis, Åbo Academy Press: Åbo, Finland, 1987; pp. 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Steudel, R.; Holdt, G.; Visscher, P.T.; van Gemerden, H. Search for Polythionates in Cultures of Chromatium vinosum after Sulfide Incubation. Arch. Microbiol. 1990, 153, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, P.T.; Nijburg, J.W.; van Gemerden, H. Polysulfide Utilization by Thiocapsa roseopersicina. Arch. Microbiol. 1990, 155, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, A.; Arzberger, I.; Engemann, C.; Modrow, H.; Schumann, O.; Trüper, H.G.; Steudel, R.; Dahl, C.; Hormes, J. In Situ Analysis of Sulfur in the Sulfur Globules of Phototrophic Sulfur Bacteria by X-Ray Absorption near Edge Spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 1999, 1428, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, A.; Chauvistré, R.; Modrow, H.; Hormes, J.; Trüper, H.G.; Dahl, C. Quantitative Speciation of Sulfur in Bacterial Sulfur Globules: X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Reveals at Least Three Different Species of Sulfur. Microbiology 2002, 148, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudel, R.; Eckert, B. Solid Sulfur Allotropes Sulfur Allotropes. In Elemental Sulfur and Sulfur-Rich Compounds I; Topics in Current Chemistry; Steudel, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 230, pp. 1–80. ISBN 978-3-540-40191-9. [Google Scholar]
- Steudel, R. On the nature of the “elemental sulfur” (S0) produced by sulfur-oxidizing bacteria—A model for S0 globules. In Autotrophic Bacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 289–303. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, J.M.; Myers, C.R. Role for Outer Membrane Cytochromes OmcA and OmcB of Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1 in Reduction of Manganese Dioxide. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, C. Inorganic Sulfur Compounds as Electron Donors in Purple Sulfur Bacteria. In Sulfur Metabolism in Phototrophic Organisms; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Hell, R., Dahl, C., Knaff, D., Leustek, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 27, pp. 289–317. ISBN 978-1-4020-6862-1. [Google Scholar]
- Gehrke, T.; Telegdi, J.; Thierry, D.; Sand, W. Importance of Extracellular Polymeric Substances from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for Bioleaching. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2743–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, B.; Lichtenberg, H.; Hormes, J.; Modrow, H.; Dahl, C.; Prange, A. Utilization of Solid ‘Elemental’ Sulfur by the Phototrophic Purple Sulfur Bacterium Allochromatium vinosum: A Sulfur K-Edge X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Study. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pibernat, I.V.; Abella, C.A. Sulfide Pulsing as the Controlling Factor of Spinae Production in Chlorobium limicola Strain UdG 6038. Arch. Microbiol. 1996, 165, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohwerder, T.; Sand, W. The Sulfane Sulfur of Persulfides Is the Actual Substrate of the Sulfur-Oxidizing Enzymes from Acidithiobacillus and Acidiphilium Spp. Microbiology 2003, 149, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, T.E.; Tabita, F.R. A Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase (RubisCO)-like Protein from Chlorobium tepidum That Is Involved with Sulfur Metabolism and the Response to Oxidative Stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4397–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, Y.; Shigi, N.; Kato, J.; Nishimura, A.; Suzuki, T. Mechanistic Insights into Sulfur Relay by Multiple Sulfur Mediators Involved in Thiouridine Biosynthesis at TRNA Wobble Positions. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, T.; Fukai, S.; Ikeuchi, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Nureki, O. Structural Basis for Sulfur Relay to RNA Mediated by Heterohexameric TusBCD Complex. Structure 2006, 14, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedderich, R.; Hamann, N.; Bennati, M. Heterodisulfide Reductase from Methanogenic Archaea: A New Catalytic Role for an Iron-Sulfur Cluster. Biol. Chem. 2005, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, C.; Rákhely, G.; Pott-Sperling, A.S.; Fodor, B.; Takács, M.; Tóth, A.; Kraeling, M.; Győrfi, K.; Kovács, Á.; Tusz, J.; et al. Genes Involved in Hydrogen and Sulfur Metabolism in Phototrophic Sulfur Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 180, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kappler, U.; Dahl, C. Enzymology and Molecular Biology of Prokaryotic Sulfite Oxidation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 203, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truper, H.G.; Fischer, U. Anaerobic Oxidation of Sulphur Compounds as Electron Donors for Bacterial Photosynthesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1982, 298, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.D.; Kelly, D.J. A Sulphite Respiration System in the Chemoheterotrophic Human Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni. Microbiology 2005, 151, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüser, T.; Selmer, T.; Dahl, C. “ADP Sulfurylase” from Thiobacillus denitrificans Is an Adenylylsulfate: Phosphate Adenylyltransferase and Belongs to a New Family of Nucleotidyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigaard, N.-U.; Bryant, D.A. Genomic Insights into the Sulfur Metabolism of Phototrophic Green Sulfur Bacteria. In Sulfur Metabolism in Phototrophic Organisms; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Hell, R., Dahl, C., Knaff, D., Leustek, T., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 27, pp. 337–355. ISBN 978-1-4020-6862-1. [Google Scholar]
- Frigaard, N.-U.; Bryant, D.A. Genomic and Evolutionary Perspectives on Sulfur Metabolism in Green Sulfur Bacteria. In Microbial Sulfur Metabolism; Dahl, C., Friedrich, C.G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 60–76. ISBN 978-3-540-72679-1. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.J.; Lascelles, J. Thiosulphate Metabolism and Rhodanese in Chromatium Sp. Strain D. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1966, 42, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumori, Y.; Yamanaka, T. A High-Potential Nonheme Iron Protein (HiPIP)-Linked, Thiosulfate-Oxidizing Enzyme Derived From Chromatium vinosum. Curr. Microbiol. 1979, 3, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensen, D.; Sperling, D.; Trüper, H.G.; Brune, D.C.; Dahl, C. Thiosulphate Oxidation in the Phototrophic Sulphur Bacterium Allochromatium vinosum. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 794–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, C.; Franz, B.; Hensen, D.; Kesselheim, A.; Zigann, R. Sulfite oxidation in the purple sulfur bacterium Allochromatium vinosum: Identification of SoeABC as a major player and relevance of SoxYZ in the process. Microbiology 2013, 159, 2626–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solov’ev, A.A.; Erokhin, Y.E. Distribution of Bacteriochlorophyll between the Pigment-Protein Complexes of the Sulfur Photosynthetic Bacterium Allochromatium minutissimum Depending on Light Intensity at Different Temperatures. Microbiology 2008, 77, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdaong, N.M.; LaFountain, A.M.; Hacking, K.; Niedzwiedzki, D.M.; Gibson, G.N.; Cogdell, R.J.; Frank, H.A. Spectral Heterogeneity and Carotenoid-to-Bacteriochlorophyll Energy Transfer in LH2 Light-Harvesting Complexes from Allochromatium vinosum. Photosynth. Res. 2016, 127, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, G.; Golecki, J.R. Structure, Molecular Organization, and Biosynthesis of Membranes of Purple Bacteria. In Anoxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria; Advances in Photosynthesis and Respiration; Blankenship, R.E., Madigan, M.T., Bauer, C.E., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 231–257. ISBN 978-0-7923-3681-5. [Google Scholar]
- Feher, G. Three Decades of Research in Bacterial Photosynthesis and the Road Leading to It: A Personal Account. Photosynth. Res. 1998, 55, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenship, R.E. Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis, 2nd ed.; Wiley/Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dostál, J. Photosynthetic Apparatus of Green Sulfur Bacteria Studied by Coherent Twodimensional Electronic Spectroscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, Matematicko-Fyzikální Fakulta, Univerzita Karlova, Prague, Czech Republic, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hauska, G.; Schoedl, T.; Remigy, H.; Tsiotis, G. The Reaction Center of Green Sulfur Bacteria1Dedicated to the Memory of Jan Amesz.1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Bioenerg. 2001, 1507, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kushkevych, I.; Procházka, J.; Gajdács, M.; Rittmann, S.K.-M.R.; Vítězová, M. Molecular Physiology of Anaerobic Phototrophic Purple and Green Sulfur Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126398
Kushkevych I, Procházka J, Gajdács M, Rittmann SK-MR, Vítězová M. Molecular Physiology of Anaerobic Phototrophic Purple and Green Sulfur Bacteria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(12):6398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126398
Chicago/Turabian StyleKushkevych, Ivan, Jiří Procházka, Márió Gajdács, Simon K.-M. R. Rittmann, and Monika Vítězová. 2021. "Molecular Physiology of Anaerobic Phototrophic Purple and Green Sulfur Bacteria" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 12: 6398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126398
APA StyleKushkevych, I., Procházka, J., Gajdács, M., Rittmann, S. K.-M. R., & Vítězová, M. (2021). Molecular Physiology of Anaerobic Phototrophic Purple and Green Sulfur Bacteria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(12), 6398. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126398







