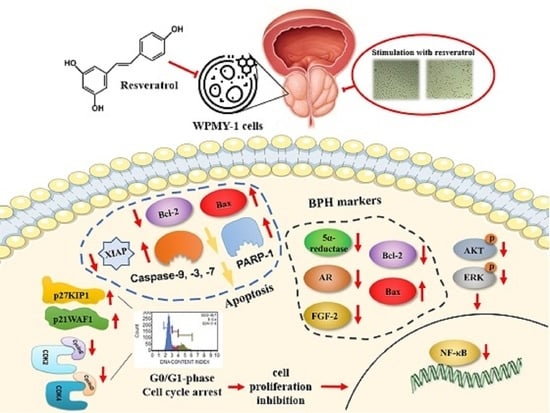
Resveratrol Attenuates the Proliferation of Prostatic Stromal Cells in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Regulating Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis, Signaling Pathways, BPH Markers, and NF-κB Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
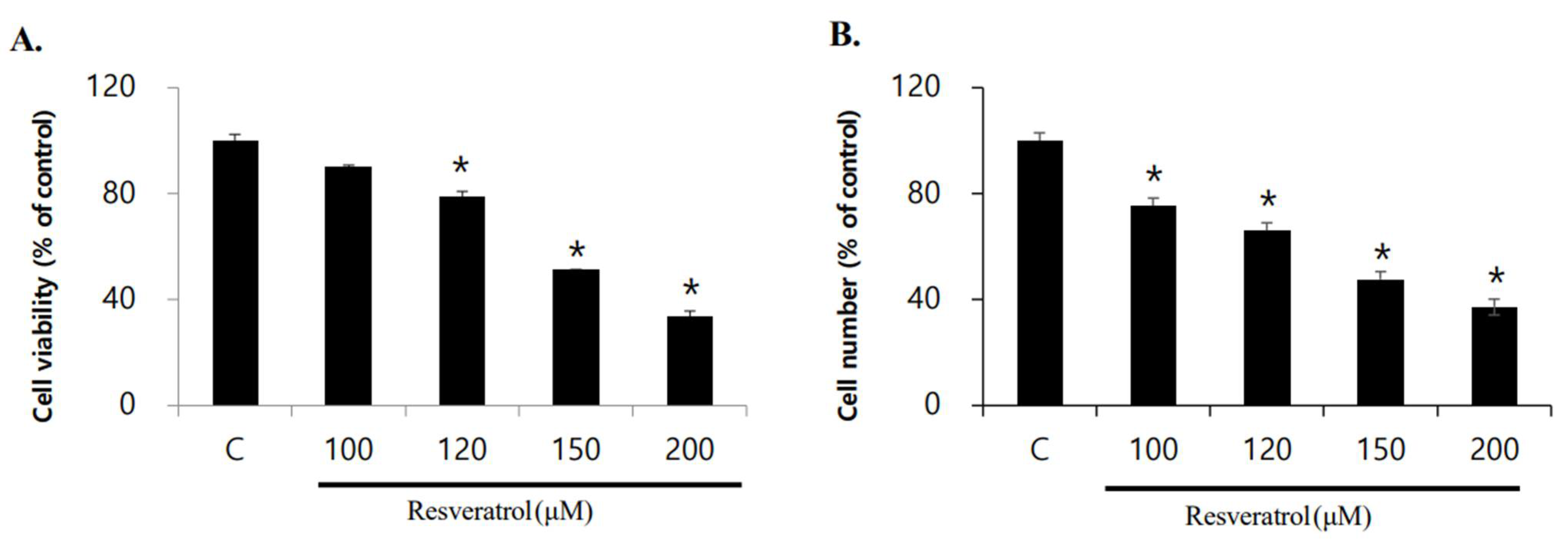
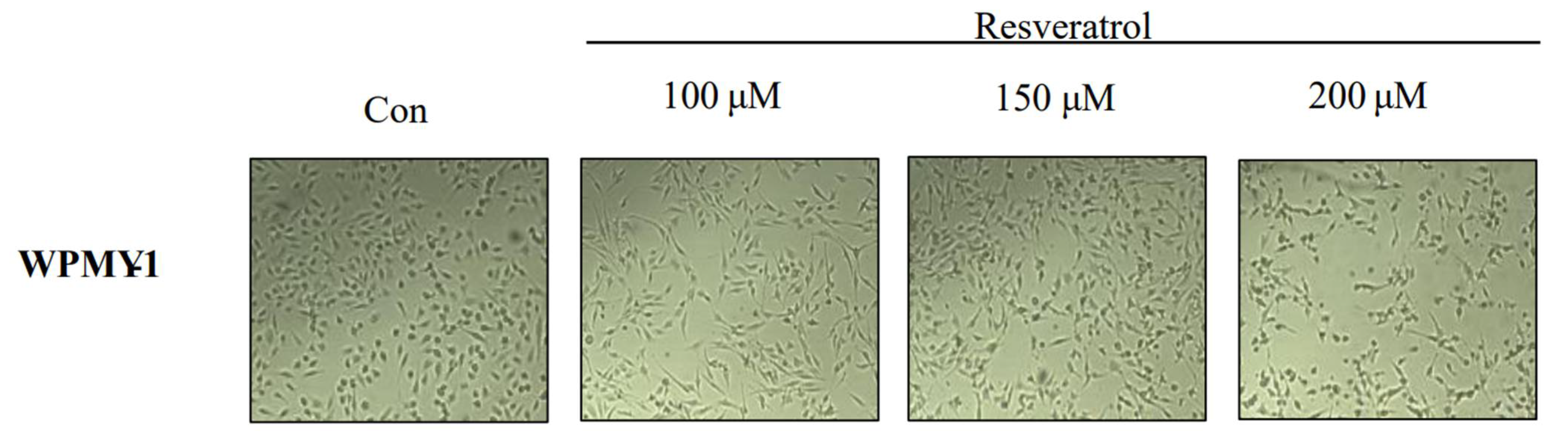
2.1. Effects of Resveratrol on Inhibition of WPMY-1 Cell Proliferation
2.2. Effects of Resveratrol on G0/G1-Phase Cell Cycle Arrest in WPMY-1 Cells
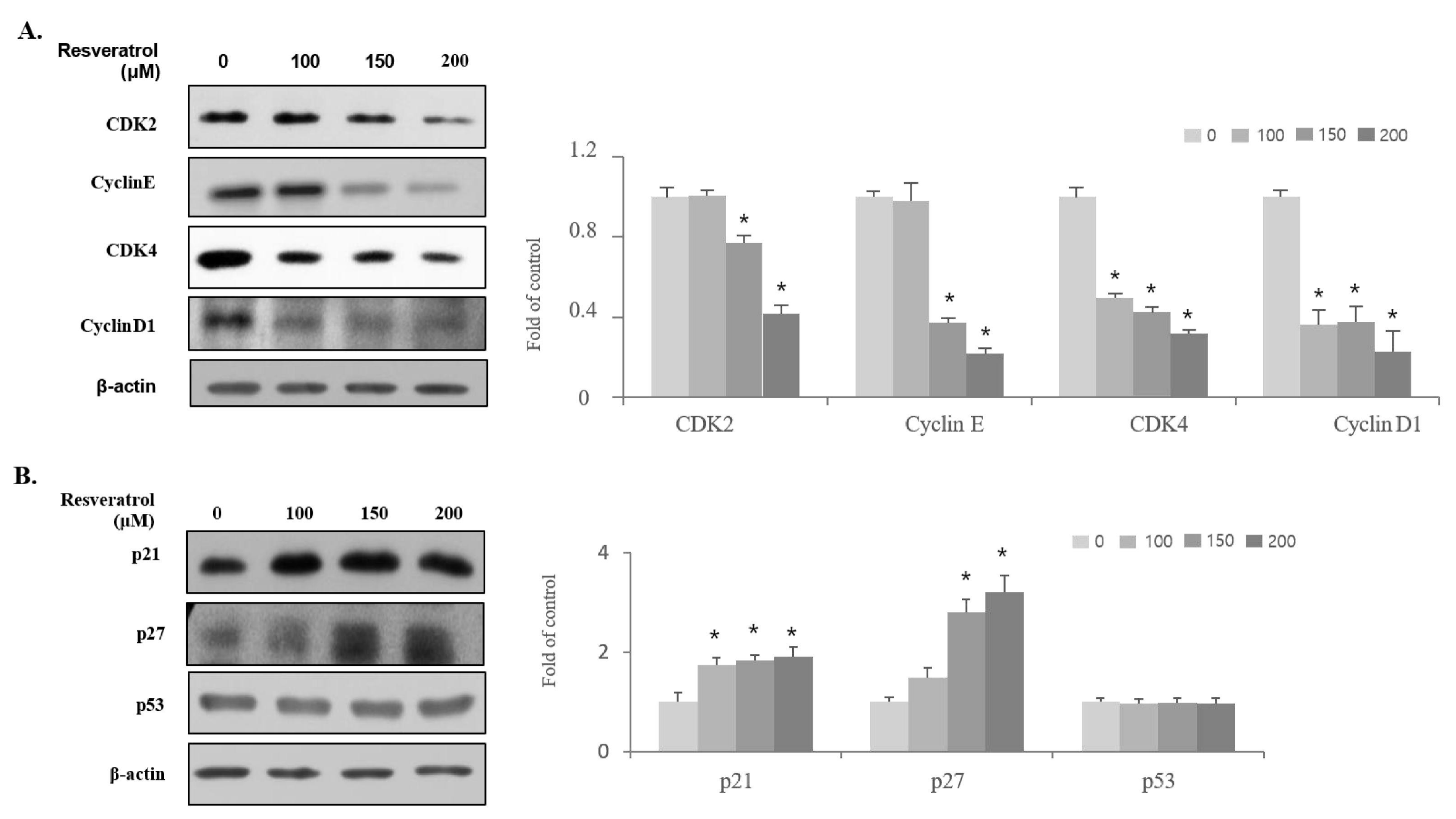
2.3. Effects of Resveratrol on the Regulation of Cell Cycle-Related Protein Expression in WPMY-1 Cells
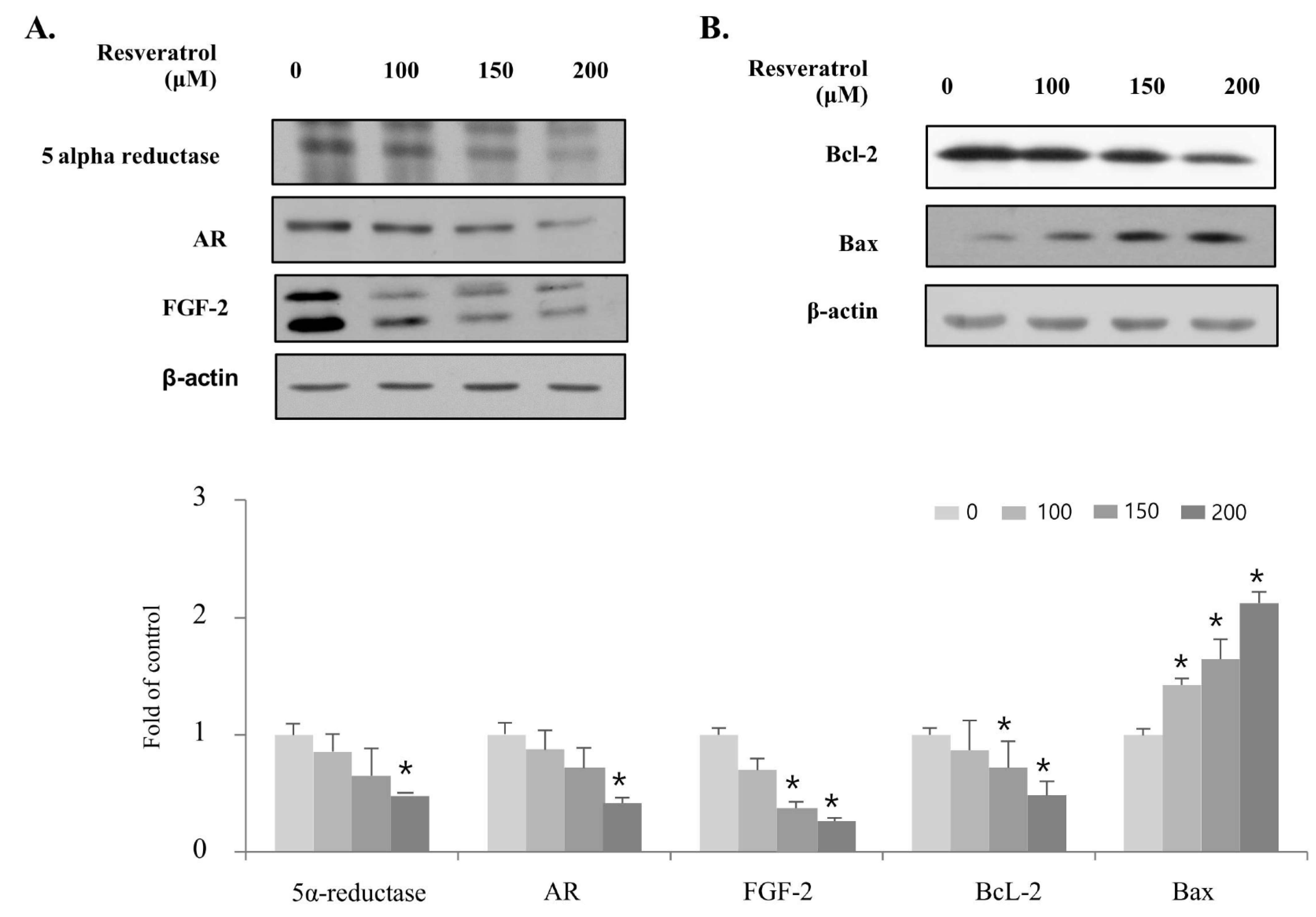
2.4. Effects of Resveratrol on Regulation of BPH Markers in WPMY-1 Cells
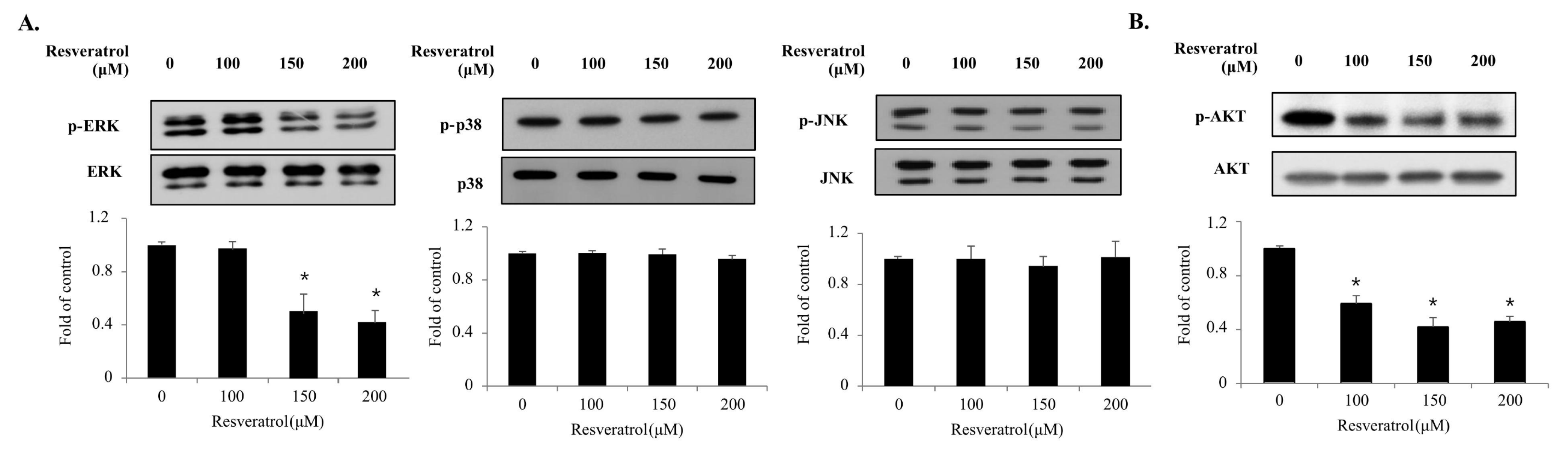
2.5. Effects of Resveratrol on the Phosphorylation of the MAPKs and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway Components in WPMY-1 Cells
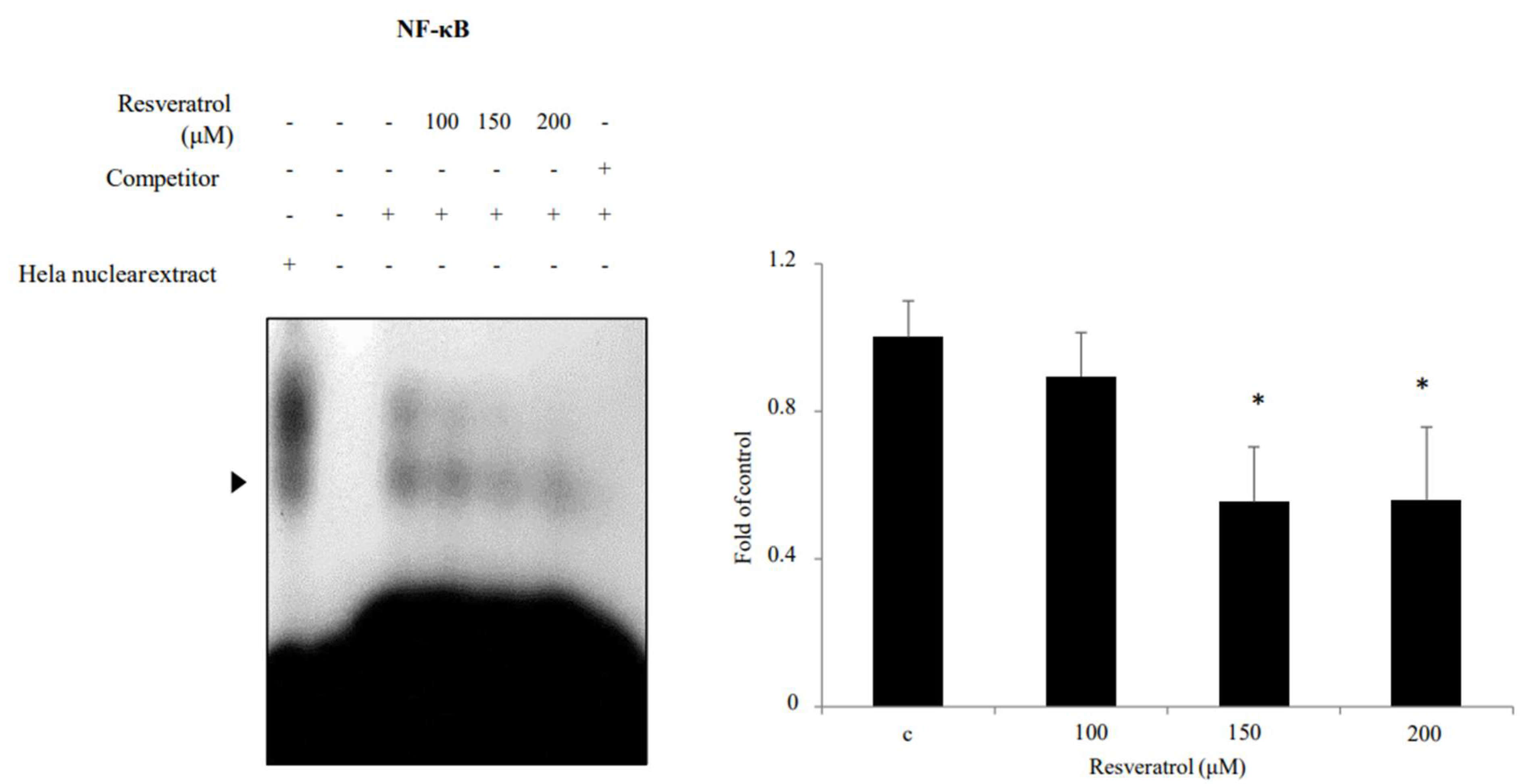
2.6. Effects of Resveratrol on Inhibition of NF-κB Binding Activity in WPMY-1 Cells
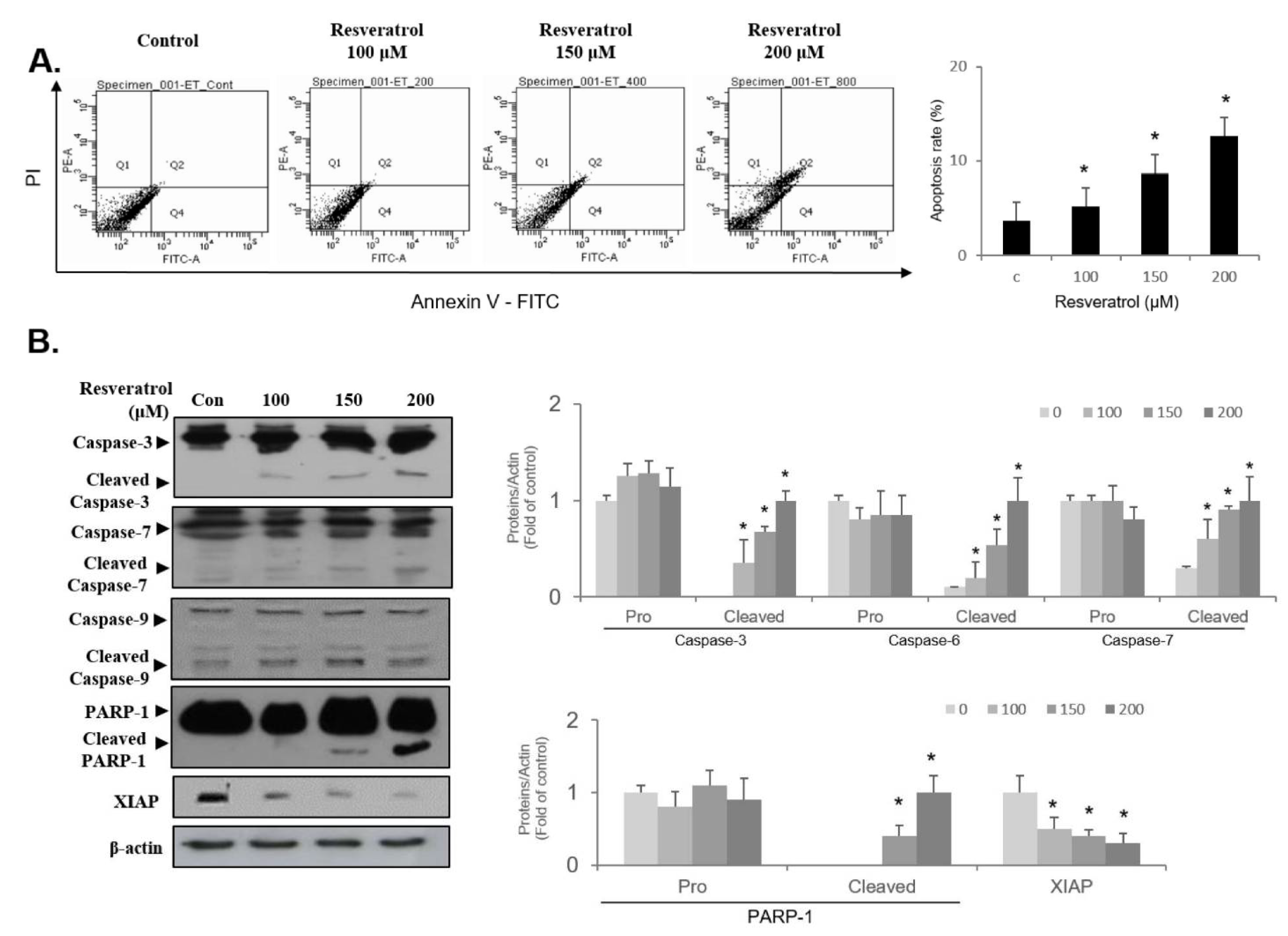
2.7. Resveratrol Stimulates Apoptosis through Regulating Intrinsic Pathway in WPMY-1 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Cell Counting
4.5. Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.6. Immunoblotting
4.7. EMSA (Nuclear Extracts and Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay)
4.8. Apoptosis Analysis by Flow Cytometry
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | Alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| EMSA | Electrophoretic mobility shift assay |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| P38 MAPK | p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PI3K/AKT | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT |
| XIAP | X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein |
| PARP-1 | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 |
References
- Khusbu, F.Y.; Zhou, X.; Roy, M.; Chen, F.; Cao, Q.; Chen, H. Resveratrol Induces Depletion of TRAF6 and Suppresses Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 118, 105644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, V.S.; Cole, R.J. Trans-Resveratrol Content in Commercial Peanuts and Peanut Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, A.R.; Silva, G.D.B.D.; Jornada, D.H.; Chiba, D.E.; Fernandes, G.F.D.S.; Man Chin, C.; Dos Santos, J.L. Unraveling the Anticancer Effect of Curcumin and Resveratrol. Nutrients 2016, 8, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, S.J.; Coffey, D.S.; Walsh, P.C.; Ewing, L.L. The Development of Human Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with Age. J. Urol. 1984, 132, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, D.; Misso, M. Lycopene for the Prevention and Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review. Maturitas 2012, 72, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.; Lee, M.; Seo, C.; Jeon, W.; Shin, H. Yongdamsagan-Tang, a Traditional Herbal Formula, Inhibits Cell Growth through the Suppression of Proliferation and Inflammation in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Epithelial-1 Cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 209, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trachtenberg, J.; Hicks, L.L.; Walsh, P.C. Androgen-and Estrogen-Receptor Content in Spontaneous and Experimentally Induced Canine Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 65, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrack, E.R.; Berry, S.J. DNA Synthesis in the Canine Prostate: Effects of Androgen and Estrogen Treatment. Prostate 1987, 10, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez, G. Zonal Variation of Apoptosis and Proliferation in the Normal Prostate and in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Br. J. Urol. 1998, 82, 380–385. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Miao, L.; Yu, X.; Orgah, J.O.; Barnabas, O.; Chang, Y.; Liu, E.; Fan, G.; Gao, X. Cynomorium Songaricum Rupr Demonstrates Phytoestrogenic Or Phytoandrogenic Like Activities that Attenuates Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Via Regulating Steroid 5-A-Reductase. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, L.; So, A.; Fleshner, N.; Rendon, R.; Drachenberg, D.; Elhilali, M. The Role of 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors in Prostate Pathophysiology: Is there an Additional Advantage to Inhibition of Type 1 Isoenzyme? CUAJ 2009, 3, S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.L.; Peehl, D.M. Molecular and Cellular Pathogenesis of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 1784–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyprianou, N.; Tu, H.; Jacobs, S.C. Apoptotic Versus Proliferative Activities in Human Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Hum. Pathol. 1996, 27, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Maneix, L.; Insunza, J.; Nalvarte, I.; Antonson, P.; Kere, J.; Yu, N.Y.; Tohonen, V.; Katayama, S.; Einarsdottir, E. Estrogen Receptor Β, a Regulator of Androgen Receptor Signaling in the Mouse Ventral Prostate. Proc. Acad. Natl. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3816–E3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.H.; Hwang, B.; Chung, H.J.; Moon, B.; Kim, J.W.; Ko, K.; Kim, B.W.; Kim, W.R.; Kim, W.J.; Myung, S.C.; et al. Peanut Sprout Extracts Cultivated with Fermented Sawdust Medium Inhibits Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Vitro and in Vivo. World J. Mens. Health. 2020, 38, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Lin, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, W.; Hong, Z. Anti-Proliferative Effects of Qianliening Capsules on Prostatic Hyperplasia in Vitro and in vivo. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hartwell, L.H.; Weinert, T.A. Checkpoints: Controls that Ensure the Order of Cell Cycle Events. Science 1989, 246, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Hannon, G.J.; Zhang, H.; Casso, D.; Kobayashi, R.; Beach, D. P21 is a Universal Inhibitor of Cyclin Kinases. Nature 1993, 366, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, H.; Hunter, T. p27, a Novel Inhibitor of G1 Cyclin-Cdk Protein Kinase Activity, is Related to p21. Cell 1994, 78, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, A.R.; Potemkin, N.; Ward, R.D. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Signalling Corresponds with Distinct Behavioural Profiles in a Rat Model of Maternal Immune Activation. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 396, 112876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivanco, I.; Sawyers, C.L. The Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–AKT Pathway in Human Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.W. Function and Activation of NF-Kappa B in Immune System. Korean J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 48, 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Brantley, D.M.; Chen, C.; Muraoka, R.S.; Bushdid, P.B.; Bradberry, J.L.; Kittrell, F.; Medina, D.; Matrisian, L.M.; Kerr, L.D.; Yull, F.E. Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) Regulates Proliferation and Branching in Mouse Mammary Epithelium. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldani, C.; Scovassi, A.I. Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 Cleavage during Apoptosis: An Update. Apoptosis 2002, 7, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almagro, M.C.; Vucic, D. The Inhibitor of Apoptosis (IAP) Proteins are Critical Regulators of Signaling Pathways and Targets for Anti-Cancer Therapy. Exp. Oncol. 2012, 34, 200–211. [Google Scholar]
- Fremont, L. Biological Effects of Resveratrol. Life Sci. 2000, 66, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Wu, J.M. Resveratrol suppresses prostate cancer epithelial cell scatter/invasion by targeting inhibition of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) secretion by prostate stromal cells and upregulation of E-cadherin by prostate cancer epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, K.R.; Tindall, D.J. Minireview: Alternative Activation Pathways for the Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 25, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Duan, L.; Du, X.; Ma, H.; Park, I.; Lee, C.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J. The Proliferative Effect of Estradiol on Human Prostate Stromal Cells is Mediated through Activation of ERK. Prostate 2008, 68, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, J.; Lu, M.; Shi, Z.; Na, N.; Di, J. Carvacrol Alleviates Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion through Regulation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Botchway, B.O.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X. Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling Pathway by Resveratrol Improves Spinal Cord Injury. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
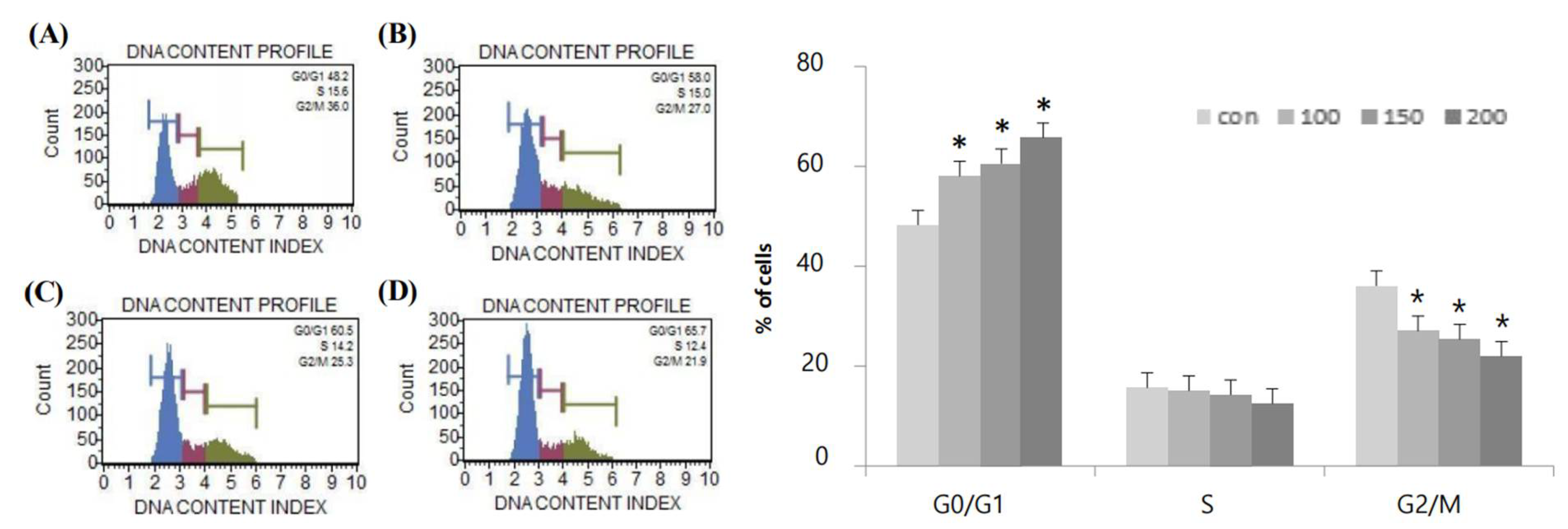
| Resveratrol Concentration (μM) | G0/G1 | S | G2/M |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 48.2% | 15.6% | 36.0% |
| 100 | 58.0% | 15.0% | 27.0% |
| 150 | 60.5% | 14.2% | 25.3% |
| 200 | 65.7% | 12.4% | 21.9% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, J.; Song, J.; Lee, J.; Moon, S.-K.; Moon, B. Resveratrol Attenuates the Proliferation of Prostatic Stromal Cells in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Regulating Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis, Signaling Pathways, BPH Markers, and NF-κB Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115969
Jang J, Song J, Lee J, Moon S-K, Moon B. Resveratrol Attenuates the Proliferation of Prostatic Stromal Cells in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Regulating Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis, Signaling Pathways, BPH Markers, and NF-κB Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(11):5969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115969
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Jowon, Junhui Song, Jiyun Lee, Sung-Kwon Moon, and Bokyung Moon. 2021. "Resveratrol Attenuates the Proliferation of Prostatic Stromal Cells in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Regulating Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis, Signaling Pathways, BPH Markers, and NF-κB Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 11: 5969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115969
APA StyleJang, J., Song, J., Lee, J., Moon, S.-K., & Moon, B. (2021). Resveratrol Attenuates the Proliferation of Prostatic Stromal Cells in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Regulating Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis, Signaling Pathways, BPH Markers, and NF-κB Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(11), 5969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115969