Development of Phosphodiesterase–Protein-Kinase Complexes as Novel Targets for Discovery of Inhibitors with Enhanced Specificity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
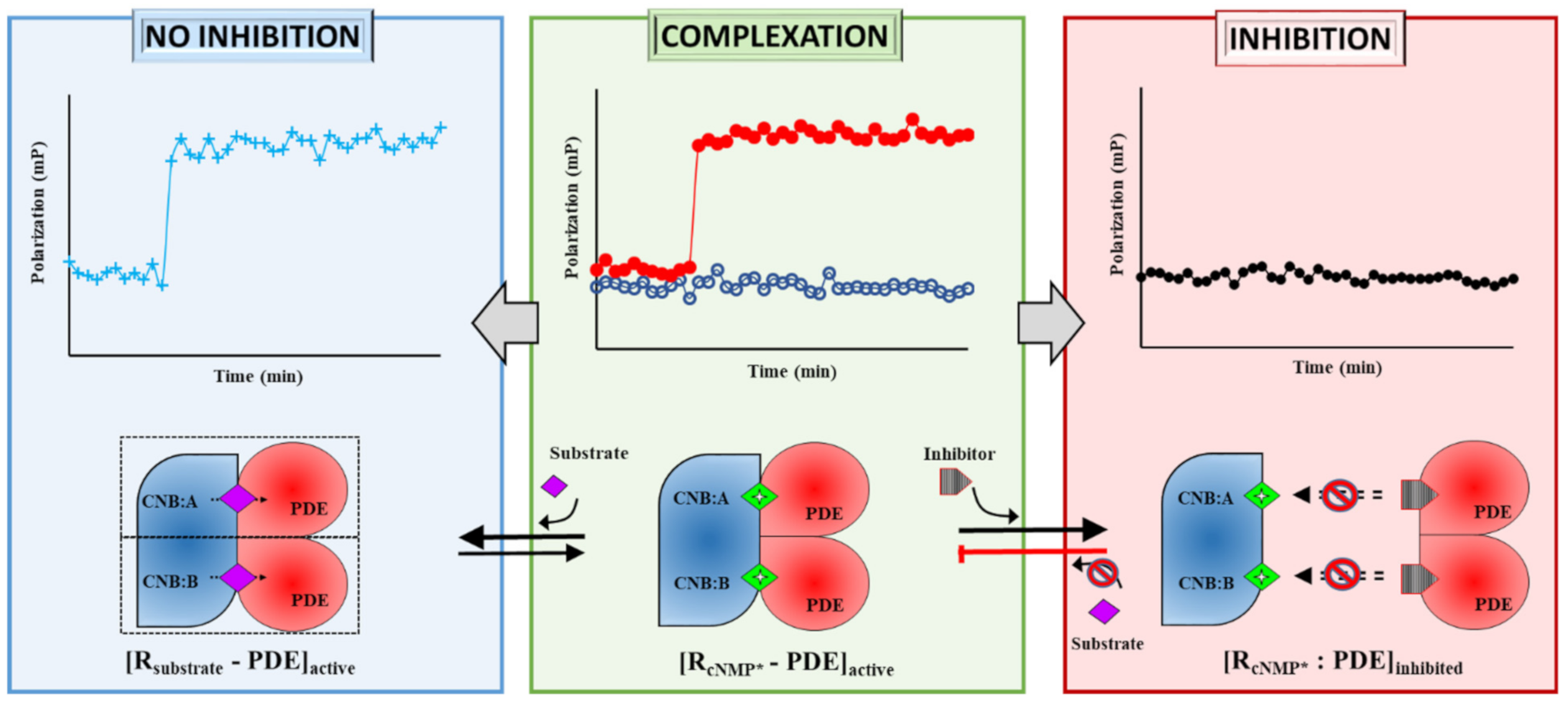
2.1. Designing Competitive cNMP-Dependent Displacement Assay for PDE Inhibitors
2.1.1. Designing a cAMP-Specific Assay Using PDE8–PKAR Complex
2.1.2. Designing Assay for cGMP-Specificity Using PDE5–PKG Complex
2.1.3. Designing a Dual cAMP/cGMP Assay Using a Broader Specificity RegA–RD Complex
2.2. Screening Novel Inhibitors in Plant Extracts Using Competitive Displacement Assay
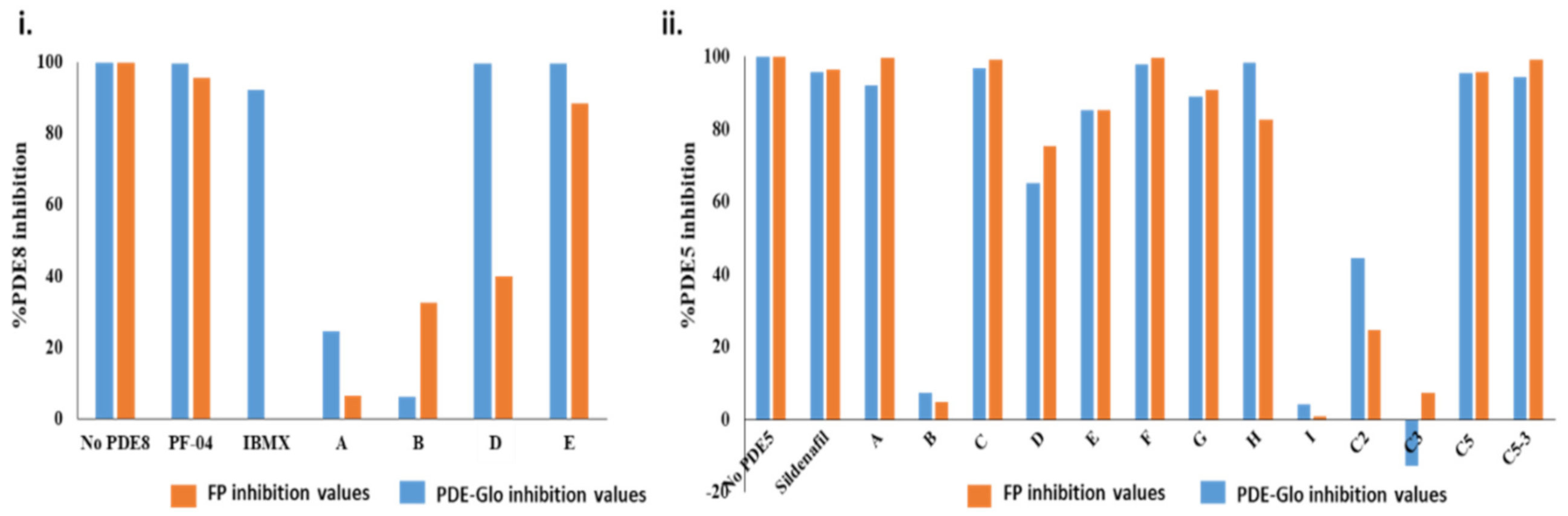
2.2.1. Screening cAMP-Specific Inhibitors Using PDE8–PKAR Complex
2.2.2. Screening Plant Extracts for Dual cAMP/cGMP PDE Inhibition of the RegA–RD Complex
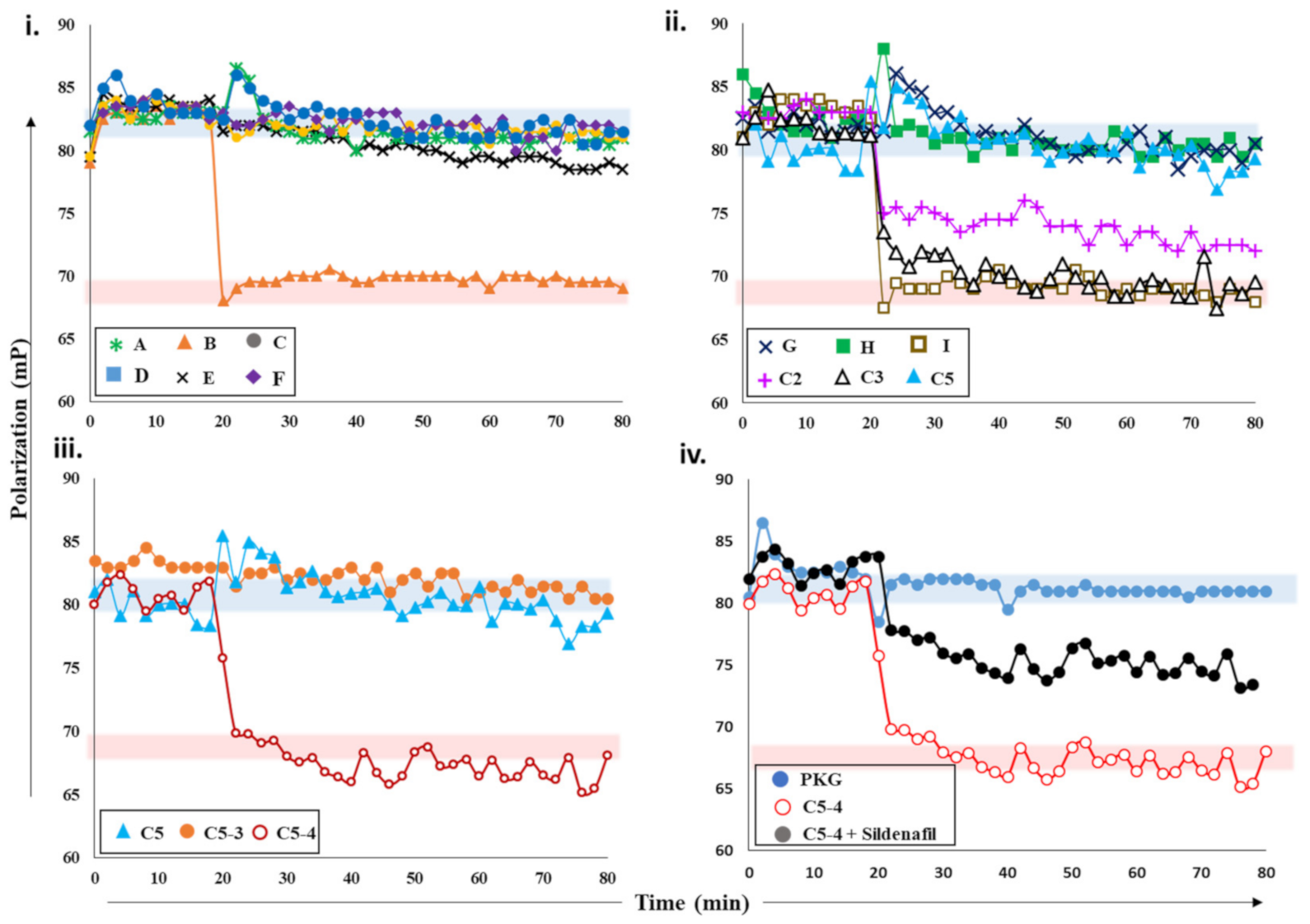
2.2.3. Screening cGMP-Specific Inhibitors by Targeting PKG–PDE5 Complexes
2.3. Ranking Inhibitors Targeting the Specific PDE–PK Complexes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Expression and Purification of Proteins
4.2.2. Preparation of Plant Extracts
4.2.3. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
4.2.4. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
4.2.5. Fluorescence Polarization
Designing the PDE–PK Complex as Target
- Free PDE8c (1 µM) and PDE8c saturated with cAMP (250 µM), IBMX (500 µM), or PF-04 (10 µM) were added separately to 2fc-PKAR at t = 20 min.
- To 2fg-PKG, cGMP (100 µM) and PDE5 (0.2 µM) with or without sildenafil (1 µM) and cGMP were added independently, and their FP values were measured for additional 60 min.
- FP values of 2fc-RD (1 µM) and 2fc-RD with RegA (2 µM) were recorded for 20 min, followed by addition of cAMP (250 µM), cGMP (250 µM), or IBMX (500 µM) to preformed 2fc-RD–RegA complex, and FP was measured for total time of 100 min.
Testing PDE–PK Complex with Known Inhibitors
Targeting PDE–PK Complexes with Plant Extracts
4.2.6. PDE-Glo™ Phosphodiesterase Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Conti, M.; Beavo, J. Biochemistry and physiology of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: Essential components in cyclic nucleotide signaling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.L.; Lan, L.; Zoudilova, M.; Conti, M. Specific role of phosphodiesterase 4B in lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling in mouse macrophages. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.C.; Beavo, J.A. Regulation of adrenal steroidogenesis by the high-affinity phosphodiesterase 8 family. Horm. Metab. Res. 2012, 44, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavo, J.A. Multiple isozymes of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Adv. Second Messenger Phosphoprot. Res. 1988, 22, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Dodge, K.L.; Khouangsathiene, S.; Kapiloff, M.S.; Mouton, R.; Hill, E.V.; Houslay, M.D.; Langeberg, L.K.; Scott, J.D. mAKAP assembles a protein kinase A/PDE4 phosphodiesterase cAMP signaling module. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Moorthy, B.S.; Xin Xiang, L.; Shan, L.X.; Bharatham, K.; Tulsian, N.K.; Mihalek, I.; Anand, G.S. Active site coupling in PDE:PKA complexes promotes resetting of mammalian cAMP signaling. Biophys. J. 2014, 107, 1426–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, D.R.; Wilson, L.S.; Carter, R.L.; Maurice, D.H. Numerous distinct PKA-, or EPAC-based, signalling complexes allow selective phosphodiesterase 3 and phosphodiesterase 4 coordination of cell adhesion. Cell Signal. 2007, 19, 2507–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillie, G.S.; Scott, J.D.; Houslay, M.D. Compartmentalisation of phosphodiesterases and protein kinase A: Opposites attract. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 3264–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderling, S.H.; Beavo, J.A. Regulation of cAMP and cGMP signaling: New phosphodiesterases and new functions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.G.; Gonen, T.; Scott, J.D. Local cAMP signaling in disease at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126 Pt 20, 4537–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.; Scott, J.D. AKAP signalling complexes: Focal points in space and time. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Mika, D.; Richter, W. Cyclic AMP compartments and signaling specificity: Role of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 143, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, K.; Baillie, G.S. Compartmentalisation of second messenger signalling pathways. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2014, 27, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulsian, N.K.; Ghode, A.; Anand, G.S. Adenylate control in cAMP signaling: Implications for adaptation in signalosomes. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 2981–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Quesada, O.; Mayrhofer, J.E.; Stefan, E. The many faces of compartmentalized PKA signalosomes. Cell Signal. 2017, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulsian, N.K.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Anand, G.S. Channeling of cAMP in PDE-PKA Complexes Promotes Signal Adaptation. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 2552–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, D.G.; Toler, S.M.; Swanson, W.H.; Fish, G.E.; Laties, A.M. A double-blind placebo-controlled evaluation of the acute effects of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on visual function in subjects with early-stage age-related macular degeneration. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 133, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laties, A.; Zrenner, E. Viagra (sildenafil citrate) and ophthalmology. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2002, 21, 485–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Tulsian, N.K.; Chandramohan, A.; Anand, G.S. Parallel Allostery by cAMP and PDE Coordinates Activation and Termination Phases in cAMP Signaling. Biophys. J. 2015, 109, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogreid, D.; Ekanger, R.; Suva, R.H.; Miller, J.P.; Doskeland, S.O. Comparison of the two classes of binding sites (A and B) of type I and type II cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinases by using cyclic nucleotide analogs. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 181, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Casteel, D.E.; Huang, G.; Kwon, T.H.; Ren, R.K.; Zwart, P.; Headd, J.J.; Brown, N.G.; Chow, D.C.; Palzkill, T.; et al. Co-crystal structures of PKG Ibeta (92-227) with cGMP and cAMP reveal the molecular details of cyclic-nucleotide binding. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18413. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.Y.; Kim, J.J.; Reger, A.S.; Lorenz, R.; Moon, E.W.; Zhao, C.; Casteel, D.E.; Bertinetti, D.; Vanschouwen, B.; Selvaratnam, R.; et al. Structural basis for cyclic-nucleotide selectivity and cGMP-selective activation of PKG I. Structure 2014, 22, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.S.; Elbatarny, H.S.; Crawley, S.W.; Bennett, B.M.; Maurice, D.H. Compartmentation and compartment-specific regulation of PDE5 by protein kinase G allows selective cGMP-mediated regulation of platelet functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13650–13655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.C.; Shimizu-Albergine, M.; Beavo, J.A. The high-affinity cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase 8B controls steroidogenesis in the mouse adrenal gland. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vang, A.G.; Basole, C.; Dong, H.; Nguyen, R.K.; Housley, W.; Guernsey, L.; Adami, A.J.; Thrall, R.S.; Clark, R.B.; Epstein, P.M.; et al. Differential Expression and Function of PDE8 and PDE4 in Effector T cells: Implications for PDE8 as a Drug Target in Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderling, S.H.; Bayuga, S.J.; Beavo, J.A. Cloning and characterization of a cAMP-specific cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 8991–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, Z.; Yang, S.; Cai, J.; Robinson, H.; Ke, H. Kinetic and structural studies of phosphodiesterase-8A and implication on the inhibitor selectivity. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 12760–12768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, B.S.; Gao, Y.; Anand, G.S. Phosphodiesterases catalyze hydrolysis of cAMP-bound to regulatory subunit of protein kinase A and mediate signal termination. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2011, 10, M110002295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaulsky, G.; Fuller, D.; Loomis, W.F. A cAMP-phosphodiesterase controls PKA-dependent differentiation. Development 1998, 125, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusnina, A.; Lugnier, C. Therapeutic potentials of natural compounds acting on cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase families. Cell Signal. 2017, 39, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, V.; Singh, V.P.; Kaundal, M.; Gupta, M.K.; Bariwal, J.; Deshmukh, R. Herbs to curb cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and their potential role in Alzheimer’s disease. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2015, 149, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, E. Potency, selectivity, and consequences of nonselectivity of PDE inhibition. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2004, 16 (Suppl. 1), S11–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.; Ghiasi, S.; Azimi, H.; Fakhari, S.; Abdollahi, M. A review of the herbal phosphodiesterase inhibitors; future perspective of new drugs. Cytokine 2010, 49, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, G. Natural products in drug discovery: Present status and perspectives. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 655, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sin, V.J.; Anand, G.S.; Koh, H.L. Botanical Medicine and Natural Products Used for Erectile Dysfunction. Sex. Med. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sportsman, J.R. A fluorescence polarization assay for cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. J. Biomol. Screen 2002, 7, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Agli, M.; Galli, G.V.; Dal Cero, E.; Belluti, F.; Matera, R.; Zironi, E.; Pagliuca, G.; Bosisio, E. Potent inhibition of human phosphodiesterase-5 by icariin derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1513–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temkitthawon, P.; Hinds, T.R.; Beavo, J.A.; Viyoch, J.; Suwanborirux, K.; Pongamornkul, W.; Sawasdee, P.; Ingkaninan, K. Kaempferia parviflora, a plant used in traditional medicine to enhance sexual performance contains large amounts of low affinity PDE5 inhibitors. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.C.; Shih, C.M.; Lai, Y.H.; Chen, J.H.; Huang, H.L. Inhibitory effects of flavonoids on phosphodiesterase isozymes from guinea pig and their structure-activity relationships. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titus, S.A.; Li, X.; Southall, N.; Lu, J.; Inglese, J.; Brasch, M.; Austin, C.P.; Zheng, W. A cell-based PDE4 assay in 1536-well plate format for high-throughput screening. J. Biomol. Screen 2008, 13, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, M.; Yu, T.; Moleschi, K.; Van, K.; Anand, G.S.; Melacini, G. An NMR based phosphodiesterase assay. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2020, 56, 8091–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurice, D.H.; Ke, H.; Ahmad, F.; Wang, Y.; Chung, J.; Manganiello, V.C. Advances in targeting cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 290–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzi, L.; Rastelli, G. Molecular Docking: Shifting Paradigms in Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubina, V.; Niinivehmas, S.; Pentikainen, O.T. Reliability of Virtual Screening Methods in Prediction of PDE4B-inhibitor Activity. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2015, 12, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, Y.Y.; Zareisedehizadeh, S.; Seetoh, W.G.; Neo, S.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Koh, H.L. Ethnobotanical survey of usage of fresh medicinal plants in Singapore. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1450–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, V.J.-E. Medicinal plants and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitory activity. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Singapore, Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Koutalos, Y.; Brown, R.L.; Karpen, J.W.; Yau, K.W. Diffusion coefficient of the cyclic GMP analog 8-(fluoresceinyl)thioguanosine 3′,5′ cyclic monophosphate in the salamander rod outer segment. Biophys. J. 1995, 69, 2163–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, P.H.; Parton, A.; Gandhi, A.K.; Capone, L.; Adams, M.; Wu, L.; Bartlett, J.B.; Loveland, M.A.; Gilhar, A.; Cheung, Y.F.; et al. Apremilast, a cAMP phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, demonstrates anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in a model of psoriasis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| % Inhibition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extract | PDE8–PKAR | PDE5–PKG | RegA–RD | Characteristics |
| A | 6.5% | 99.8% | 61.1% | Potent inhibition of cGMP-selective PDEs |
| B | 32.6% | 4.9% | 75.0% | Partial inhibition of cAMP-specific PDEs |
| D | 40.1% | 75.5% | 48.6% | Partial inhibition of general PDEs |
| E | 88.6% | 85.3% | 99.5% | Potent inhibition of general PDEs |
| F | 30% | 98% | 50% | Inhibition of cGMP-selective PDE sites |
| Sildenafil | - * | 96.5% | n.d * | Known PDE5-specific inhibitor |
| PF-04957325 | 95.6% | - * | n.d * | Known PDE8-specific inhibitor |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tulsian, N.K.; Sin, V.J.-E.; Koh, H.-L.; Anand, G.S. Development of Phosphodiesterase–Protein-Kinase Complexes as Novel Targets for Discovery of Inhibitors with Enhanced Specificity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105242
Tulsian NK, Sin VJ-E, Koh H-L, Anand GS. Development of Phosphodiesterase–Protein-Kinase Complexes as Novel Targets for Discovery of Inhibitors with Enhanced Specificity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(10):5242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105242
Chicago/Turabian StyleTulsian, Nikhil K., Valerie Jia-En Sin, Hwee-Ling Koh, and Ganesh S. Anand. 2021. "Development of Phosphodiesterase–Protein-Kinase Complexes as Novel Targets for Discovery of Inhibitors with Enhanced Specificity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 10: 5242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105242
APA StyleTulsian, N. K., Sin, V. J.-E., Koh, H.-L., & Anand, G. S. (2021). Development of Phosphodiesterase–Protein-Kinase Complexes as Novel Targets for Discovery of Inhibitors with Enhanced Specificity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(10), 5242. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105242






