The Sodium Channel B4-Subunits are Dysregulated in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Drug-Resistant Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
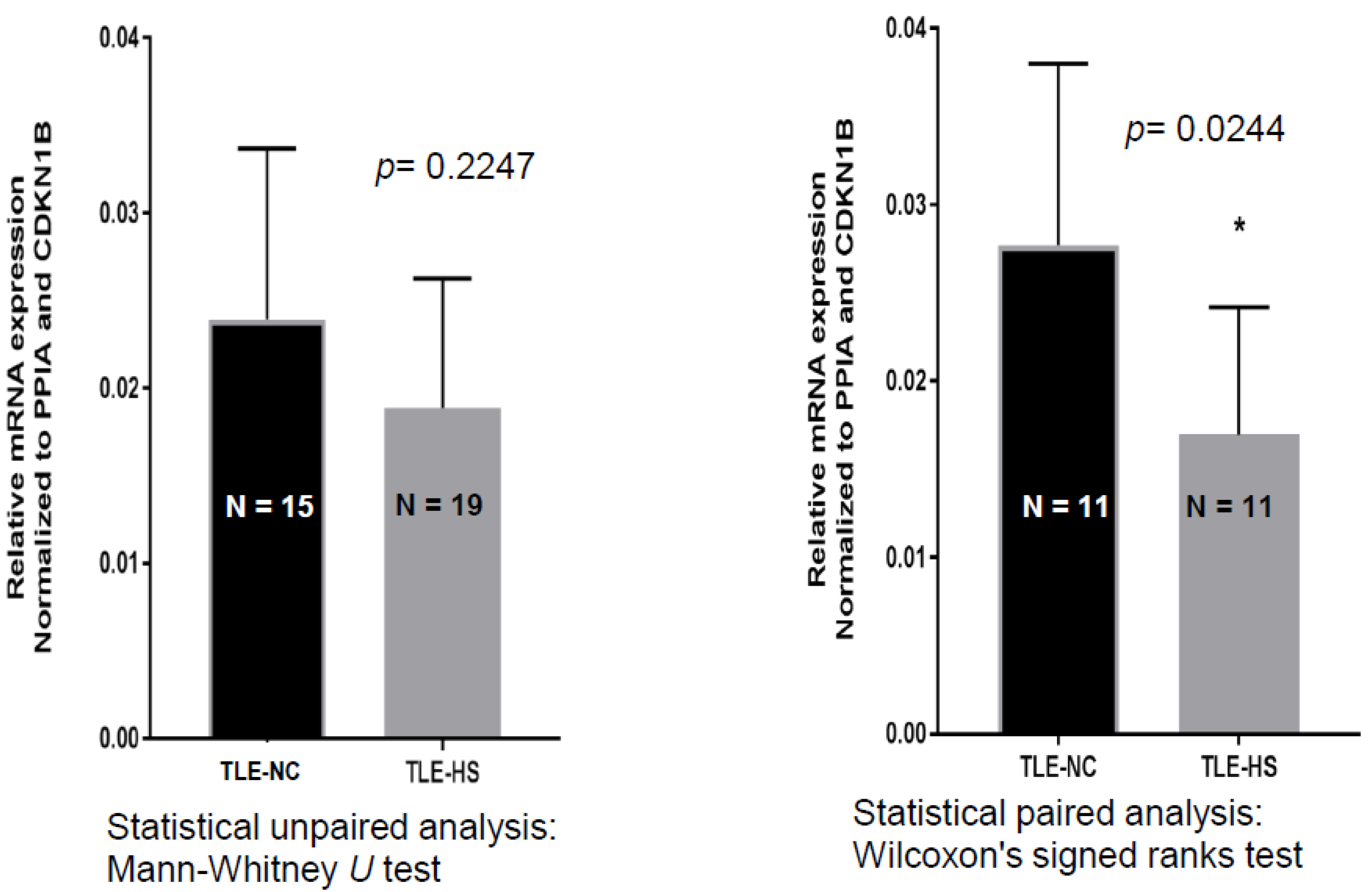
2.1. SCN4B Transcripts Expression in HS and NC Samples
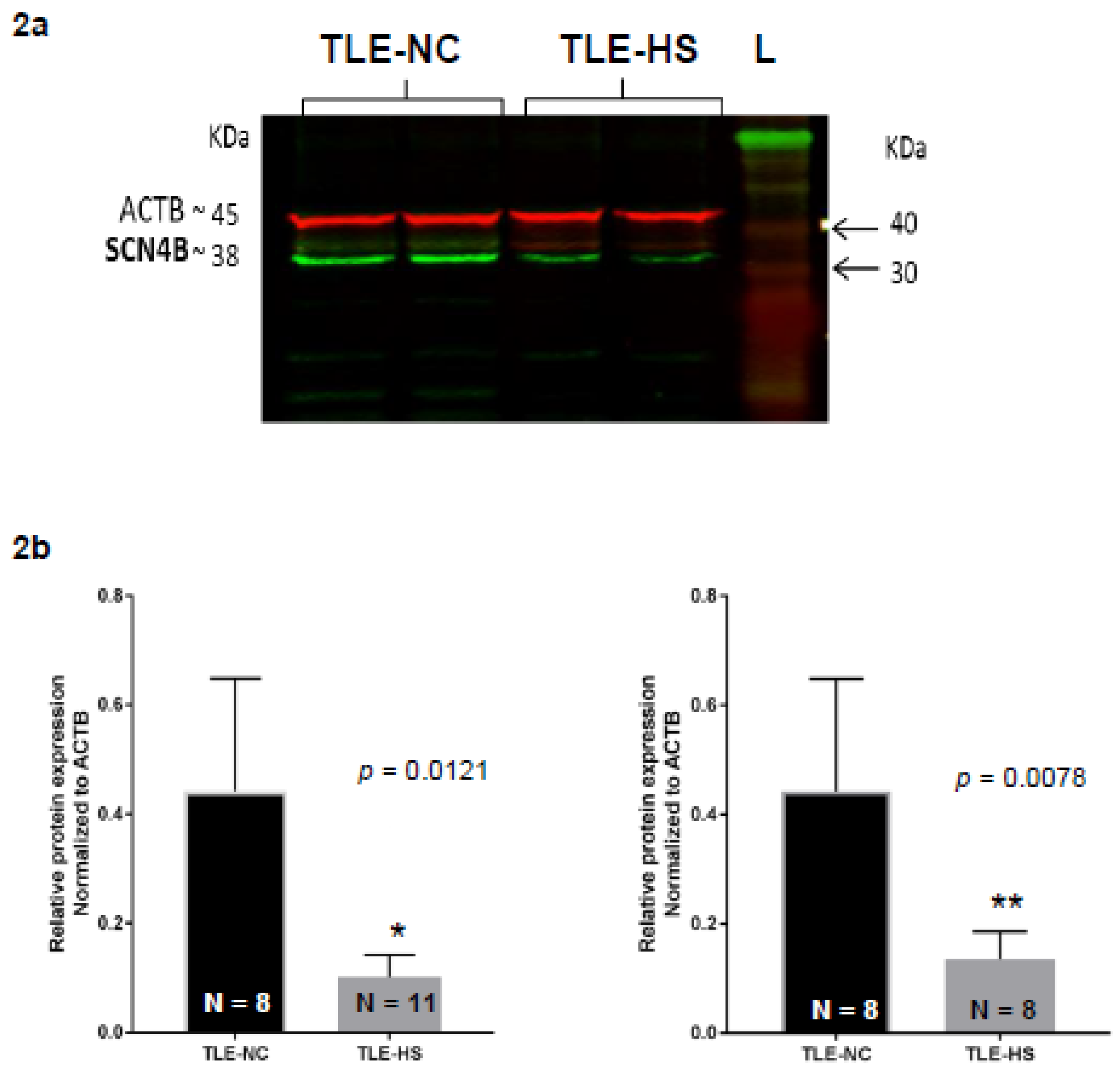
2.2. Western Blot Analysis of Nav β4 in HS and NC Samples
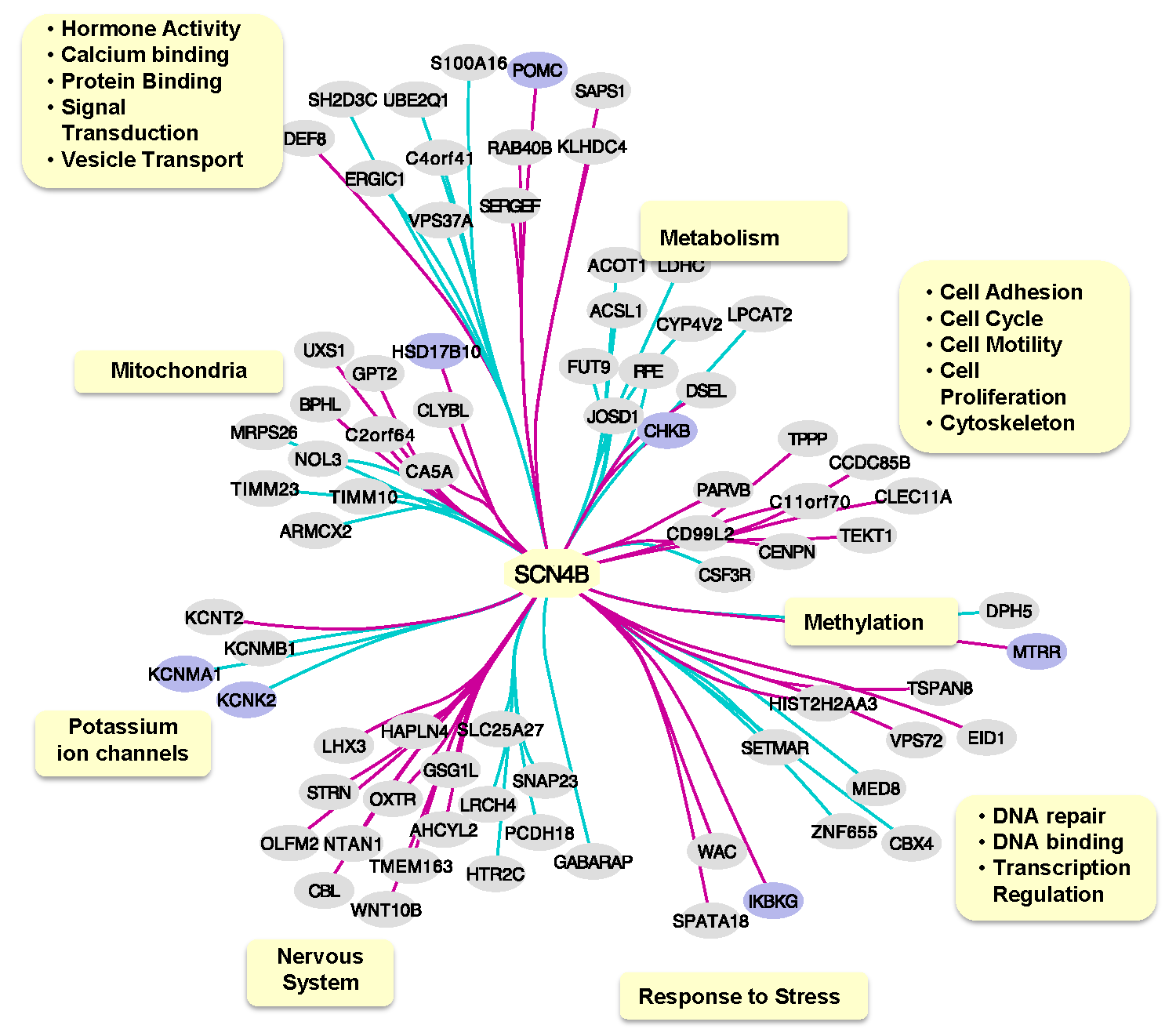
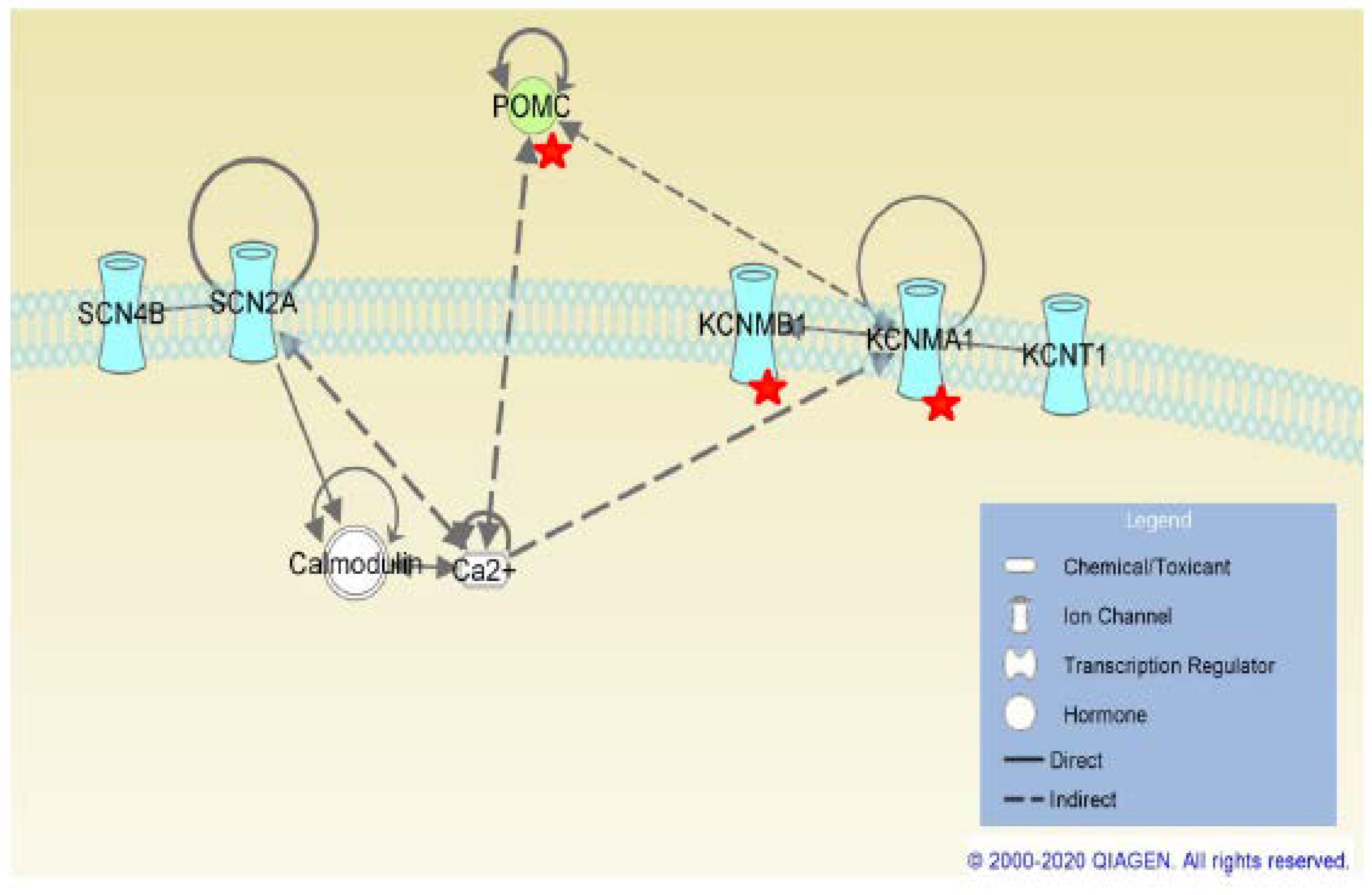
2.3. SCN4B Co-Expression Network Analysis in TLE Patients
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tissue Collection
4.2. qRT-PCR Analysis of SCN4B
4.3. Western Blot Analysis of Nav β4
4.4. Western Blot Band Quantification
4.5. Statistical Analysis of SCN4B Gene Expression and Nav β4 Band Intensities
4.6. SCN4B Co-Expression Network Analysis in TLE Patients
4.7. Functional Analysis of SCN4B Co-Expressed Genes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| AEDs | Antiepileptic drugs |
| ABC | ATP-binding cassete |
| BCA | Bicinchonic acid |
| BACE1 | β-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 |
| DBS | Deep brain stimulation |
| HS | Hippocampal sclerotic |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| TLE | Temporal lobe epilepsy |
| TLE-NC | Temporal lobe epilepsy neocortical |
| TLE-HS | Temporal lobe epilepsy hippocampal sclerotic |
| VGSC | Voltage-gated sodium channel |
| VNS | Vagus brain stimulation |
References
- Thom, M. Hippocampal sclerosis in epilepsy: A neuropathology review. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2014, 40, 520–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harroud, A.; Bouthillier, A.; Weil, A.G.; Nguyen, D.K. Temporal lobe epilepsy surgery failures: A review. Epilepsy Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardi, R.; Irwin, A.; Kayyali, H.; Gupta, A.; Nair, D.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I.M.; Jehi, L.E. Reducing versus stopping antiepileptic medications after temporal lobe surgery. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, E.M.; Wiebe, S.; Fay-McClymont, T.B.; Téllez-Zenteno, J.; Metcalfe, A.; Hernandez-Ronquillo, L.; Jetté, N. Neuropsychological outcomes after epilepsy surgery: Systematic review and pooled estimates. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrodimitris, S.; Sherman, E.M.; Forde, S.; Téllez-Zenteno, J.F.; Metcalfe, A.; Hernández-Ronquillo, L.; Jetté, N. Psychiatric outcomes of epilepsy surgery: A systematic review. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lason, W.; Chlebicka, M.; Rejdak, K. Research advances in basic mechanisms of seizures and antiepileptic drug action. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Signaling complexes of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 486, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, H.A.; Isom, L.L. Sodium channel β subunits: Emerging targets in channelopathies. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, C.F.; Westenbroek, R.E.; Curtis, R.; Catterall, W.A. Sodium channel β1 and β3 subunits associate with neurofascin through their extracellular immunoglobulin-like domain. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.H.; Westenbroek, R.E.; Silos-Santiago, I.; McCormick, K.A.; Lawson, D.; Ge, P.; Ferriera, H.; Lilly, J.; DiStefano, P.S.; Catterall, W.A.; et al. Sodium channel beta4, a new disulfide-linked auxiliary subunit with similarity to beta2. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7577–7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semah, F.; Picot, M.C.; Adam, C.; Broglin, D.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bazin, B.; Cavalcanti, D.; Baulac, M. Is the underlying cause of epilepsy a major prognostic factor for recurrence? Neurology 1998, 51, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, A.; Kerb, R.; Weale, M.E.; Brinkmann, U.; Smith, A.; Goldstein, D.B.; Wood, N.W.; Sisodiya, S.M. Association of multidrug resistance in epilepsy with a polymorphism in the drug-transporter gene ABCB1. Brain 2003, 125, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, C.; Bethmann, K.; Gastens, A.M.; Löscher, W. The multidrug transporter hypothesis of drug resistance in epilepsy: Proof-of-principle in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 24, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournissen, F.G.; Moretti, M.E.; Juurlink, D.; Koren, G.; Walker, M.; Finkelstein, Y. Polymorphisms of MDR1/ABC1B C3435T drug-transporter and resistance in anti-convulsant drugs: A meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Löscher, W. Drug resistance in epilepsy: Putative neurobiologic and clinical mechanisms. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 858–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, S.; Beck, H. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pharmacoresistance in epilepsy. Brain 2006, 129, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, P.; Poon, W.S.; Ng, H.K.; Kang, D.E.; Wong, V.; Ng, P.W.; Lui, C.H.; Sin, N.C.; Wong, K.S.; Baum, L. Multidrug resistance in epilepsy and polymorphisms in the voltage-gated sodium channel genes SCN1A, SCN2A, and SCN3A: Correlation among phenotype, genotype, and mRNA expression. Pharm. Genom. 2008, 18, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhan, R.; Kumari, R.; Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J.; Pradhan, S.; Mittal, B. Differential role of sodium channels SCN1A and SCN2A gene polymorphisms with epilepsy and multiple drug resistance in the north Indian population. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 68, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.S.; Asghari-Roodsari, A.; Tan, H.L. Cardiac sodium channelopathies. Pflug. Arch.-Eur. J. Physiol. 2010, 460, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.L., Jr. Inherited disorders of voltage-gated sodium channels. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1990–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, P.T.; Meadows, L.S.; Nicholls, J.; Ragsdale, D.S. An epilepsy mutation in the beta 1 subunit of the voltage-gated sodium channel results in reduced channel sensitivity to phenytoin. Epilepsy Res. 2005, 64, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; O’Leary, M.E.; Chahine, M. Regulation of Nav1.6 and Nav1.8 peripheral nerve Na+ channels by auxiliary β-subunits. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bean, B.P. The molecular machinery of resurgent sodium current revealed. Neuron 2005, 45, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bant, J.S.; Raman, I.M. Control of transient, resurgent, and persistent current by open-channel block by Na channel beta4 in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12357–12362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, F.; Miyazaki, H.; Sakamoto, N.; Becquet, C.; Machida, Y.; Kaneko, K.; Uchikawa, C.; Suzuki, T.; Kurosawa, M.; Ikeda, T.; et al. Sodium channel β4 subunit: Down-regulation and possible involvement in neuritic degeneration in Huntington’s disease transgenic mice. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros-Domingo, A.; Iturralde-Torres, P.; Ackerman, M.J. Clinical and genetic characteristics of long QT syndrome. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2007, 60, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.G.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.J.; Zhang, M.; Qu, X.K.; Liu, X.; Fang, W.Y.; Yang, Y.Q. Mutations of the SCN4B-encoded sodium channel β4 subunit in familial atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.M.; Sheilabi, M.A.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Kitchen, P.; Conner, A.C.; Bill, R.M.; Woodroofe, M.N.; Conner, M.T.; Princivalle, A.P. Transcriptome analysis suggests a role for the differential expression of cerebral aquaporins and the MAPK signaling pathway in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 46, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, T.K.; Grieco-Calub, T.M.; Chen, C.; Rusconi, R.; Slat, E.A.; Isom, L.L.; Raman, I.M. Regulation of persistent Na current by interactions between beta subunits of voltage-gated Na channels. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2027–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Luo, J.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z. Increased Expression of DNA methyltransferase 1 and 3a in Human Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 46, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, L.; Yin, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X. Increased expression of histone deacetylases 2 in temporal lobe epilepsy: A study of epileptic patients and rat models. Synapse 2012, 66, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, J.C.S.; Robertson, Z.; Reid, V.; Wang, Q.; Hailey, H.; Moore, S.; Rasalam, A.D.; Turnpenny, P.; Lloyd, D.; Shaw, D.; et al. A high frequency of the MTHFR 677C>T polymorphism in Scottish women with epilepsy: Possible role in pathogenesis. Seizures 2008, 17, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wallace, R.H.; Wang, D.W.; Singh, R.; Scheffer, I.E.; George, A.L., Jr.; Phillips, H.A.; Saar, K.; Reis, A.; Johnson, E.W.; Sutherland, G.R.; et al. Febrile seizures and generalized epilepsy associated with a mutation in the Na+-channel beta1 subunit gene SCN1B. Nat. Genet. 1998, 19, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audenaert, D.; Claes, L.; Ceulemans, B.; Lofgren, A.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; De Jonghe, P. A deletion in SCN1B is associated with febrile seizures and early-onset absence epilepsy. Neurology 2003, 61, 854–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, K. Epilepsy and sodium channel gene mutations: Gain or loss of function? Neuroreport 2005, 16, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Harkin, L.A.; Grinton, B.E.; Dibbens, L.M.; Turner, S.J.; Zielinski, M.A.; Xu, R.; Jackson, G.; Adams, J.; Connellan, M.; et al. Temporal lobe epilepsy and GEFS+ phenotypes associated with SCN1B mutations. Brain 2007, 130, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino, G.A.; Brackenbury, W.J.; Bao, Y.; Lopez-Santiago, L.F.; O’Malley, H.A.; Chen, C.; Calhoun, J.D.; Lafrenière, R.G.; Cossette, P.; Rouleau, G.A.; et al. Voltage-gated Na+ channel β1B: A secreted cell adhesion molecule involved in human epilepsy. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 14577–14591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, S.G. Axonal conduction and injury in multiple sclerosis: The role of sodium channels. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshall, D.C. Apoptosis signaling pathways in seizure-induced neuronal death and epilepsy. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 421–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Friedman, A.; Dingledine, R.J. The role of inflammation in epileptogenesis. Neuropharmacology 2013, 69, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, T.; Rittger, A.; Saftig, P. β-Site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) cleaves cerebellar Na+ channel β4-subunit and promotes Purkinje cell firing by slowing the decay of resurgent Na+ current. Pflug. Arch. 2011, 461, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhou, X.; He, W.; Yang, J.; Xiong, W.; Wong, P.; Wilson, C.G.; Yan, R. BACE1 deficiency causes altered neuronal activity and neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8819–8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessler, S.; Zheng, F.; Hartmann, S.; Rittger, A.; Lehnert, S.; Völkel, M.; Nissen, M.; Edelmann, E.; Saftig, P.; Schwake, M.; et al. β-Secretase BACE1 regulates hippocampal and reconstituted M-currents in a β-subunit-like fashion. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 3298–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löscher, W.; Klotz, U.; Zimprich, F.; Schmidt, D. The clinical impact of pharmacogenetics on the treatment of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, P.; Sharma, P. Neurological disorders–epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis. In Clinical Pharmacology, 11th ed.; Peter, N., Bennett, M.J., Brown, P.S., Eds.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2012; Chapter 21; pp. 349–370. ISBN 9780702040849. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, M.J.; Gai, X.; Shigematsu, M.; Vilardo, E.; Takase, R.; McCormick, E.; Christian, T.; Place, E.; Pierce, E.A.; Consugar, M.; et al. A novel HSD17B10 mutation impairing the activities of the mitochondrial RNase P complex causes X-linked intractable epilepsy and neurodevelopmental regression. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, K.; Contreras, G.F.; Pupo, A.; Torres, Y.P.; Gonzáles, C.; Latorre, R.L. Molecular mechanism underlying β1 regulation in voltage- and calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4809–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.R.; Behmoaras, J.; Bottolo, L.; Krishnan, M.L.; Pernhorst, K.; Santoscoy, P.; Rossetti, T.; Speed, D.; Srivastava, P.K.; Chadeau-Hyam, M.; et al. Systems genetics identifies Sestrin 3 as a regulator of a proconvulsant gene network in human epileptic hippocampus. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, J.; Strimmer, K. An empirical Bayes approach to inferring large-scale gene association networks. Bioinformatics (Oxf. Engl.) 2005, 21, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opgen-Rhein, R.; Strimmer, K. From correlation to causation networks: A simple approximate learning algorithm and its application to high-dimensional plant gene expression data. BMC Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Sherman, B.T.; Huang, D.W.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID-WS: A stateful web service to facilitate gene/protein list analysis. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1805–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J., Jr.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D845–D855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbon, S.; Ireland, A.; Mungall, C.J.; Shu, S.; Marshall, B.; Lewis, S.; the AmiGO Hub; the Web Presence Working Group. AmiGO: Online access to ontology and annotation data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 288–289. [Google Scholar]
| Patients | Gender | Age at Surgery (years) | Duration of Epilepsy (years) | Sample Side | Current AED | Previous AEDs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt. 13 | F | 24 | 23 | TLE-HS (Lt) | LCS, LEV | CBZ *, LMT * |
| Pt. 18 | M | 48 | 47 | TLE-HS (Rt) TLE-NC (Rt) | PHT, LEV, LMT, GBP, TPM, PGB, ZNS | PHT *, LEV, LMT *, GBP, TPM *, PGB, ZNS |
| Pt. 21 | M | 32 | 3 | TLE-HS (Rt) TLE-NC (Rt) | LMT, OXC | CBZ *, LEV |
| Pt 24 | F | 54 | 53 | TLE-HS (Lt) TLE-NC (Lt) | LMT, PGB | GBP, VPA *, PHT *, CBZ *, PB, LEV, CNP, LCS |
| Pt 27 | F | 27 | 6 | TLE-HS (Lt) TLE-NC (Lt) | NA | NA |
| Pt. 31 | F | 44 | 10 | TLE-HS (Lt) | LCS, LEV, PHT | OXC *, LMT * |
| Pt. 33 | M | 35 | 14 | TLE-HS (Lt) | LMT, CLB | VPA *, ZNS, CBZ * |
| Pt. 39 | M | 33 | 31 | TLE-HS (Lt) | LEV, LMT* | CBZ*, VPA*, CLB |
| Pt. 41 | F | 39 | 37 | TLE-HS (Rt) | None | GBP *, LEV, LMT * CBZ *, LMT *, VPA * |
| Pt. 46 | M | 48 | 41 | TLE-HS (Rt) | None | PHT *, VGB, CLB, TPM *, TGB |
| Pt. 47 | M | 48 | NA | TLE-HS (Lt) | NA | OXC * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheilabi, M.A.; Takeshita, L.Y.; Sims, E.J.; Falciani, F.; Princivalle, A.P. The Sodium Channel B4-Subunits are Dysregulated in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Drug-Resistant Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082955
Sheilabi MA, Takeshita LY, Sims EJ, Falciani F, Princivalle AP. The Sodium Channel B4-Subunits are Dysregulated in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Drug-Resistant Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(8):2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082955
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheilabi, Mariam A., Louise Y. Takeshita, Edward J. Sims, Francesco Falciani, and Alessandra P. Princivalle. 2020. "The Sodium Channel B4-Subunits are Dysregulated in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Drug-Resistant Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 8: 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082955
APA StyleSheilabi, M. A., Takeshita, L. Y., Sims, E. J., Falciani, F., & Princivalle, A. P. (2020). The Sodium Channel B4-Subunits are Dysregulated in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Drug-Resistant Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(8), 2955. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082955





