The Important Function of Mediator Complex in Controlling the Developmental Transitions in Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of the Mediator Complex in Plants
3. Functions in Vegetative Phase Change in Plants
4. Functions in Floral Transition
5. Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Bucio, J.; Cruz-Ramírez, A.; Herrera-Estrella, L. The role of nutrient availability in regulating root architecture. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, R.D. The molecular basis of eukaryotic transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12955–12961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Roeder, R.G. The metazoan Mediator co-activator complex as an integrative hub for transcriptional regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, S.; Thakur, J.K. Importance of Mediator complex in the regulation and integration of diverse signaling pathways in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, R.J., III; Flanagan, P.M.; Kornberg, R.D. A novel mediator between activator proteins and the RNA polymerase II transcription apparatus. Cell 1990, 61, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckström, S.; Elfving, N.; Nilsson, R.; Wingsle, G.; Björklund, S. Purification of a plant mediator from Arabidopsis thaliana identifies PFT1 as the Med25 subunit. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendía-Monreal, M.; Gillmor, C.S. Mediator: A key regulator of plant development. Dev. Biol. 2016, 419, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Qu, L.J. Plant Mediator complex and its critical functions in transcription regulation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.L.; Yu, X.; Gopalan, S.; Chao, T.C.; Zhang, Y.; Florens, L.; Washburn, M.P.; Murakami, K.; Conaway, R.C.; Conaway, J.W. Mediator structure and rearrangements required for holoenzyme formation. Nature 2017, 544, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, T.M.; Taatjes, D.J. The complex structure and function of Mediator. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 13778–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, K.; Schneider, T.R.; Cramer, P. Core Mediator structure at 3.4 A extends model of transcription initiation complex. Nature 2017, 545, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, S.; Vyas, S.; Kapoor, S.; Tyagi, A.K. The Mediator complex in plants: Structure, phylogeny, and expression profiling of representative genes in a dicot (Arabidopsis) and a monocot (rice) during reproduction and abiotic stress. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1609–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Liang, L.; Xue, Y.; Shi, D.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Arabidopsis CBP1 is a novel regulator of transcription initiation in central cell-mediated pollen tube guidance. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2880–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasrija, R.; Thakur, J.K. Tissue specific expression profile of Mediator genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e23983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Waseem, M.; Dwivedi, N.; Maji, S.; Kumar, A.; Thakur, J.K. KIX domain of AtMed15a, a Mediator subunit of Arabidopsis, is required for its interaction with different proteins. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018, 13, e1428514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, W.L.; Chapple, C. Conservation and divergence of Mediator structure and function: Insights from plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfving, N.; Davoine, C.; Benlloch, R.; Blomberg, J.; Brännström, K.; Müller, D.; Nilsson, A.; Ulfstedt, M.; Ronne, H.; Wingsle, G. The Arabidopsis thaliana Med25 mediator subunit integrates environmental cues to control plant development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8245–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.; Dahiya, P.; Waseem, M.; Dwivedi, N.; Bhat, D.S.; Dar, T.H.; Thakur, J.K. Interaction map of Arabidopsis Mediator complex expounding its topology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3904–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poethig, R.S. Phase change and the regulation of developmental timing in plants. Science 2003, 301, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poethig, R.S. Phase change and the regulation of shoot morphogenesis in plants. Science 1990, 250, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poethig, R.S. The past, present, and future of vegetative phase change. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huijser, P.; Schmid, M. The control of developmental phase transitions in plants. Development 2011, 138, 4117–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Qian, Z.; Zhou, B.; Wu, G. Age-dependent heteroblastic development of leaf hairs in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2019, 224, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.W.; Czech, B.; Weigel, D. miR156-regulated SPL transcription factors define an endogenous flowering pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 2009, 138, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Hwang, I.; Lee, J.S.; Ahn, J.H. Role of SVP in the control of flowering time by ambient temperature in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yoo, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.; Yoo, S.K.; Fitzgerald, H.; Carrington, J.C.; Ahn, J.H. Genetic framework for flowering-time regulation by ambient temperature-responsive miRNAs in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Park, M.Y.; Conway, S.R.; Wang, J.-W.; Weigel, D.; Poethig, R.S. The sequential action of miR156 and miR172 regulates developmental timing in Arabidopsis. Cell 2009, 138, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Poethig, R.S. Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thaliana by miR156 and its target SPL3. Development 2006, 133, 3539–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, Y.; Richter, R.; Vincent, C.; Martinez-Gallegos, R.; Porri, A.; Coupland, G. Multi-layered regulation of SPL15 and cooperation with SOC1 integrate endogenous flowering pathways at the Arabidopsis shoot meristem. Dev. Cell 2016, 37, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukerman, M.J.; Sakai, H. Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a MicroRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2730–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Seo, Y.H.; Seo, P.J.; Reyes, J.L.; Yun, J.; Chua, N.H.; Park, C.M. The GIGANTEA-regulated microRNA172 mediates photoperiodic flowering independent of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2736–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, J.; Yant, L.J.; Murdter, F.; Kuttner, F.; Schmid, M. Repression of flowering by the miR172 target SMZ. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.; Uhlenhaut, N.H.; Godard, F.; Demar, M.; Bressan, R.; Weigel, D.; Lohmann, J.U. Dissection of floral induction pathways using global expression analysis. Development 2003, 130, 6001–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Ye, M.; Sang, M.; Wu, R. A regulatory network for miR156-SPL module in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.M.; Poethig, R.S. Gibberellins promote vegetative phase change and reproductive maturity in maize. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydler, B.; Osadchuk, K.; Cheng, C.; Manak, J.R.; Irish, E.E. The juvenile phase of maize sees upregulation of stress-response genes and is extended by exogenous jasmonic acid. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2648–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Hibara, K.; Isono, M.; Mimura, M.; Sentoku, N.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Kitomi, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Itoh, J.; Nagato, Y. Jasmonate regulates juvenile-to-adult phase transition in rice. Development 2016, 143, 3407–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillmor, C.S.; Silva-Ortega, C.O.; Willmann, M.R.; Buendía-Monreal, M.; Poethig, R.S. The Arabidopsis Mediator CDK8 module genes CCT (MED12) and GCT (MED13) are global regulators of developmental phase transitions. Development 2014, 141, 4580–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendía-Monreal, M.; Gillmor, C.S. Convergent repression of miR156 by sugar and the CDK8 module of Arabidopsis Mediator. Dev. Biol. 2017, 423, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Xu, Y.; Shi, M.; Lai, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Poethig, R.S.; Wu, G. Repression of miR156 by miR159 regulates the timing of the juvenile-to-adult transition in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yoshida, A.; Takahashi, M.; Maekawa, M.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Kyozuka, J. SAD1, an RNA polymerase I subunit A34.5 of rice, interacts with Mediator and controls various aspects of plant development. Plant J. 2015, 81, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Zheng, B.; Yu, Y.; Won, S.Y.; Mo, B.; Chen, X. The role of Mediator in small and long noncoding RNA production in Arabidopsis thaliana. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.; Li, L.; Zhai, Q.; You, Y.; Deng, L.; Wu, F.; Chen, R.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q.; et al. Mediator subunit MED25 links the jasmonate receptor to transcriptionally active chromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8930–E8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Sun, W.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; et al. MED25 connects enhancer–promoter looping and MYC2-dependent activation of jasmonate signalling. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Deng, L.; Zhai, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, C. Mediator subunit MED25 couples alternative splicing of JAZ genes with fine-tuning of jasmonate signaling. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, F.; Mouradov, A.; Soppe, W.; Ravenscroft, D.; Samach, A.; Coupland, G. Photoreceptor regulation of CONSTANS protein in photoperiodic flowering. Science 2004, 303, 1003–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.K.; Chung, K.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, S.M.; Yoo, S.J.; Yoo, S.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Ahn, J.H. Constans activates suppressor of overexpression of constans 1 through Flowering Locus T to promote flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, S.D.; Amasino, R.M. FLOWERING LOCUS C encodes a novel MADS domain protein that acts as a repressor of flowering. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, F.; Porri, A.; Torti, S.; Mateos, J.; Romera-Branchat, M.; García-Martínez, J.L.; Fornara, F.; Gregis, V.; Kater, M.M.; Coupland, G. SHORT VEGETATIVE PHASE reduces gibberellin biosynthesis at the Arabidopsis shoot apex to regulate the floral transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2760–E2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, B.N.; Edgar, C.I.; Kumar, K.K.; Aitken, E.A.; Schenk, P.M.; Manners, J.M.; Kazan, K. The mediator complex subunit PFT1 is a key regulator of jasmonate-dependent defense in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2237–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Guan, H.; Leal, F.; Grey, P.H.; Oppenheimer, D.G. Mediator subunit18 controls flowering time and floral organ identity in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Schluttenhofer, C.M.; Bhide, K.; Shreve, J.; Thimmapuram, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Yun, D.J.; Mengiste, T. MED18 interaction with distinct transcription factors regulates multiple plant functions. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaskolowski, A.; Iñigo, S.; Arellano, S.M.; Arias, L.A.; Fiol, D.F.; Sede, A.R.; Oldra, M.B.; Lorenzi, H.; Muschietti, J.P.; Pagnussat, G.C. The MED30 subunit of mediator complex is essential for early plant development and promotes flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 2019, 146, dev175224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iñigo, S.; Alvarez, M.J.; Strasser, B.; Califano, A.; Cerdán, P.D. PFT1, the MED25 subunit of the plant Mediator complex, promotes flowering through CONSTANS dependent and independent mechanisms in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2012, 69, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, C.; Büche, C.; Fernandez, A.P.; Schäfer, E.; Zwick, E.; Kretsch, T. The mediator complex subunit PFT1 interferes with COP1 and HY5 in the regulation of Arabidopsis light signaling. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rival, P.; Press, M.O.; Bale, J.; Grancharova, T.; Undurraga, S.F.; Queitsch, C. The conserved PFT1 tandem repeat is crucial for proper flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 2014, 198, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Park, B.S.; Mao, H.Z.; Seo, J.S.; Ohama, N.; Li, Y.; Yu, N.; Mustafa, N.F.B.; Huang, C.H.; Chua, N.H. Regulation of flowering time by SPL10/MED25 module in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2019, 224, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñigo, S.; Giraldez, A.N.; Chory, J.; Cerdán, P.D. Proteasome-mediated turnover of Arabidopsis MED25 is coupled to the activation of FLOWERING LOCUS T transcription. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, H.; Thomson, A.J.; McWatters, H.G. Sensitive to freezing6 integrates cellular and environmental inputs to the plant circadian clock. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet, J.V.; Dobón, A.; Tornero, P. Non-recognition-of-BTH4, an Arabidopsis mediator subunit homolog, is necessary for development and response to salicylic acid. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4220–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, W.L.; Chapple, C. Transcriptome analysis of four Arabidopsis thaliana mediator tail mutants reveals overlapping and unique functions in gene regulation. G3-Genes Genom. Genet. 2018, 8, 3093–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imura, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Furutani, M.; Tasaka, M.; Abe, M.; Araki, T. CRYPTIC PRECOCIOUS/MED12 is a novel flowering regulator with multiple target steps in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Kim, J.I.; Wheeler, M.T.; Heintzelman, A.K.; Weake, V.M.; Chapple, C. Mutation of Mediator subunit CDK8 counteracts the stunted growth and salicylic acid hyperaccumulation phenotypes of an Arabidopsis MED5 mutant. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.M.; Vander Schoor, J.K.; Hecht, V.; Weller, J.L. The CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE module of the Mediator complex promotes flowering and reproductive development in pea. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, T.; Karamat, F.; Lehotai, N.; Rentoft, M.; Blomberg, J.; Strand, Å.; Björklund, S. Specific functions for Mediator complex subunits from different modules in the transcriptional response of Arabidopsis thaliana to abiotic stress. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, K.H.; Layla, J.S.; Edina, L.; James, B.; Emily, A.; Swaminathan, D.; Peer, M.S. Suppression of Arabidopsis Mediator subunit-encoding MED18 confers broad resistance against DNA and RNA viruses while MED25 is required for virus defense. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 162. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, N.; Maji, S.; Waseem, M.; Thakur, P.; Kumar, V.; Parida, S.K.; Thakur, J.K. The Mediator subunit OsMED15a is a transcriptional co-regulator of seed size/weight-modulating genes in rice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
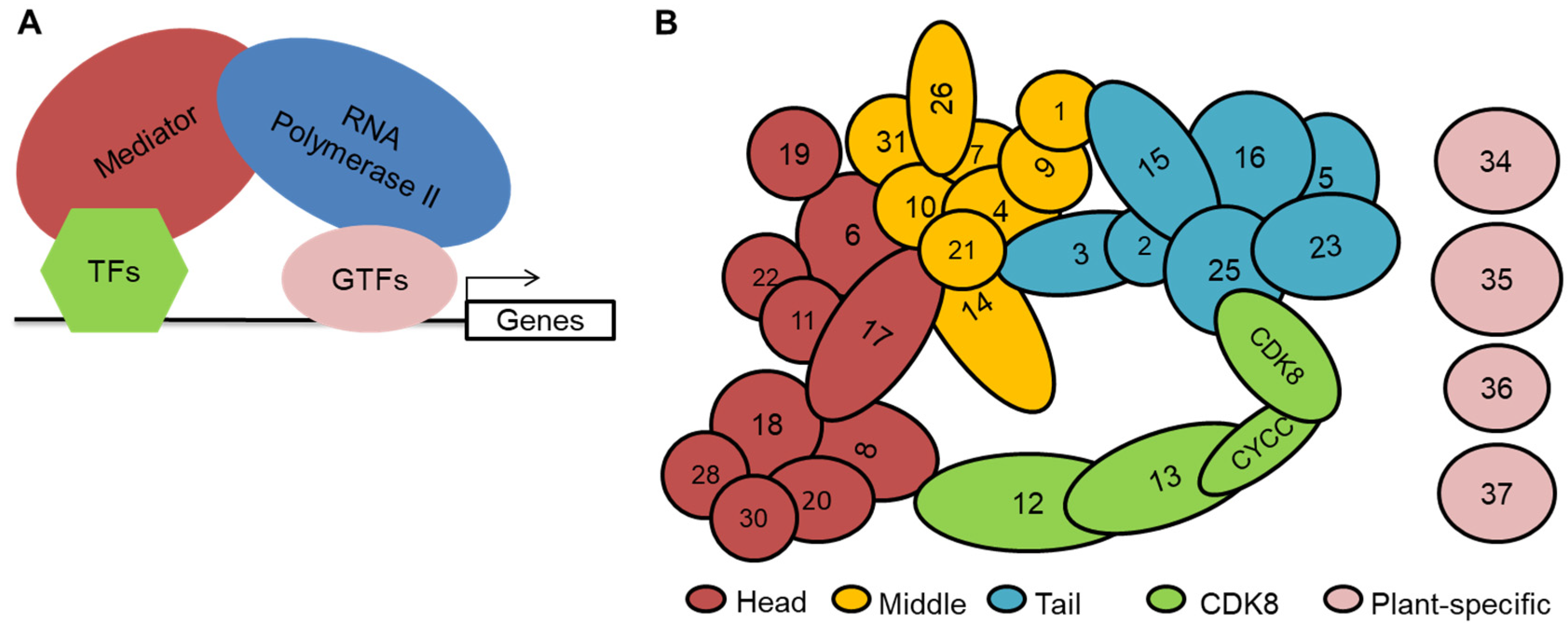
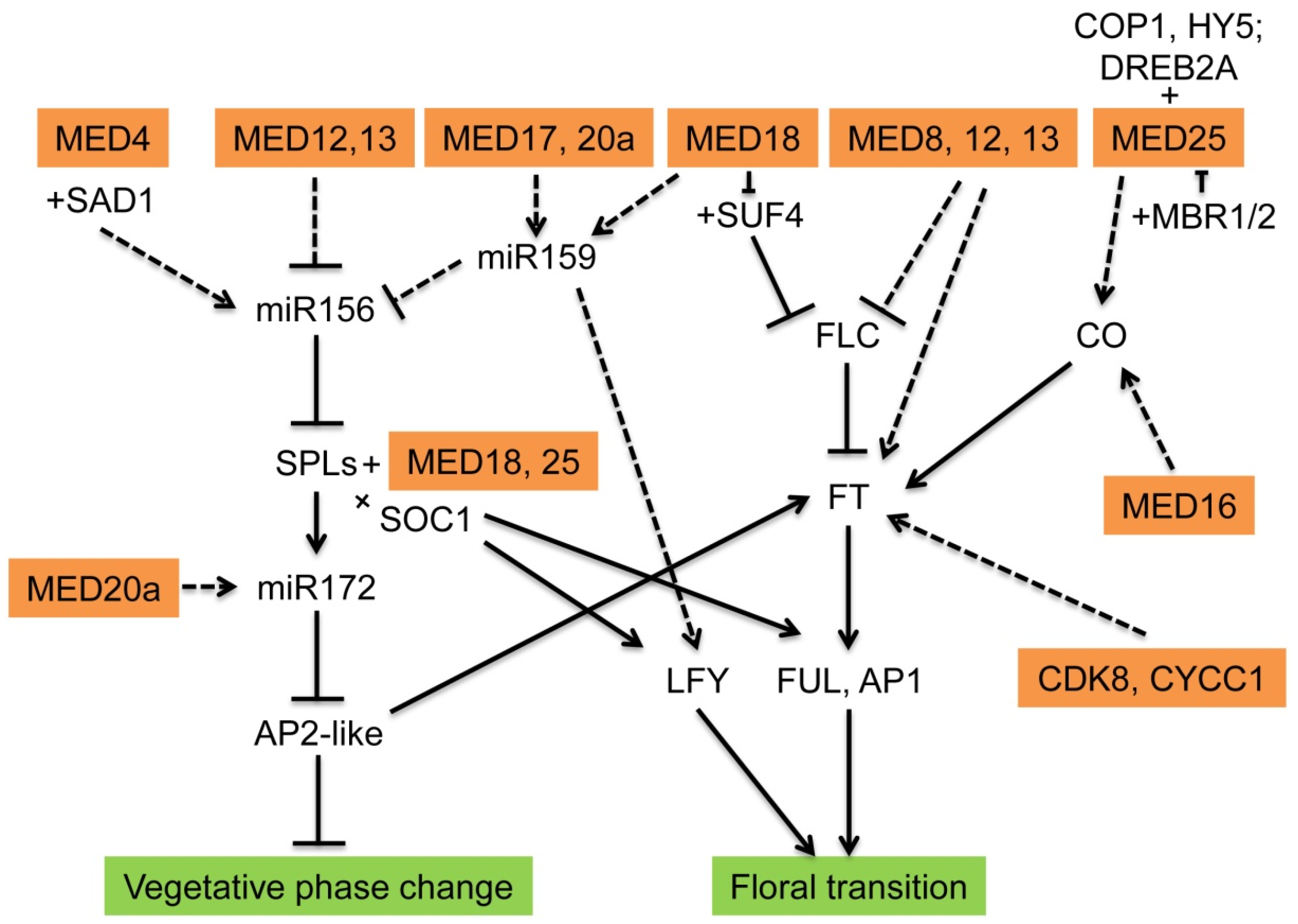
| Mediator Submodule | Subunit | Gene Names | Functions | Interacting Proteins | Regulated Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head | MED8 | AT2G03070, SETH10 | Floral transition | FT, FLC | |
| MED17 | AT5G20170 | Vegetative phase change and floral transition | miR159 | ||
| MED18 | AT2G22370 | Vegetative phase change and floral transition | SUF4, SPL15 | miR159, FLC, FUL, FT | |
| MED20a | AT2G28230 | Floral transition | miR172 | ||
| MED30 | AT5G63480 | Floral transition | SPL3, FT, SOC1, FLC | ||
| Middle | MED4 | AT5G02850 | Vegetative phase change | SAD1 (RPA34.5) | miR156, miR172 (in rice) |
| Tail | MED2 | AT1G11760 | Floral transition | FLC | |
| MED5 | REF4 | Floral transition | JA-pathway | ||
| MED15 | AT1G15780, NRB4 | Floral transition | |||
| MED16 | AT4G04920, SFR6,YID1, IEN1 | Vegetative phase change and floral transition | CCA1, GI, TOC1, CO, FT, FLC | ||
| MED23 | At1g23230 | Floral transition | AG | ||
| MED25 | AT1G25540, PFT1 | Floral transition | COP1, HY5; SPL10; MBR1, MBR2; DREB2A | CO, FT, FLC, FUL | |
| CDK8 | MED12 | AT4G00450, CCT, CRP | Vegetative phase change and floral transition | miR156, miR172, FT, TSF, FLC SOC1, FUL | |
| MED13 | AT1G55325, GCT, MAB2 | Vegetative phase change and floral transition | miR156, miR172, FT, TSF, FLC SOC1, FUL | ||
| CDK8 | At5g63610, HEN3 | Floral transition | FT, TFL1 (in pea) | ||
| CYCC1;1/CYCC1;2 | At5g48640/At5g48630 | Floral transition | FT, TFL1 (in pea) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Guo, C. The Important Function of Mediator Complex in Controlling the Developmental Transitions in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082733
Zhang L, Guo C. The Important Function of Mediator Complex in Controlling the Developmental Transitions in Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(8):2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082733
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lingjie, and Changkui Guo. 2020. "The Important Function of Mediator Complex in Controlling the Developmental Transitions in Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 8: 2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082733
APA StyleZhang, L., & Guo, C. (2020). The Important Function of Mediator Complex in Controlling the Developmental Transitions in Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(8), 2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082733





