The Rice Basic Helix–Loop–Helix 79 (OsbHLH079) Determines Leaf Angle and Grain Shape
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
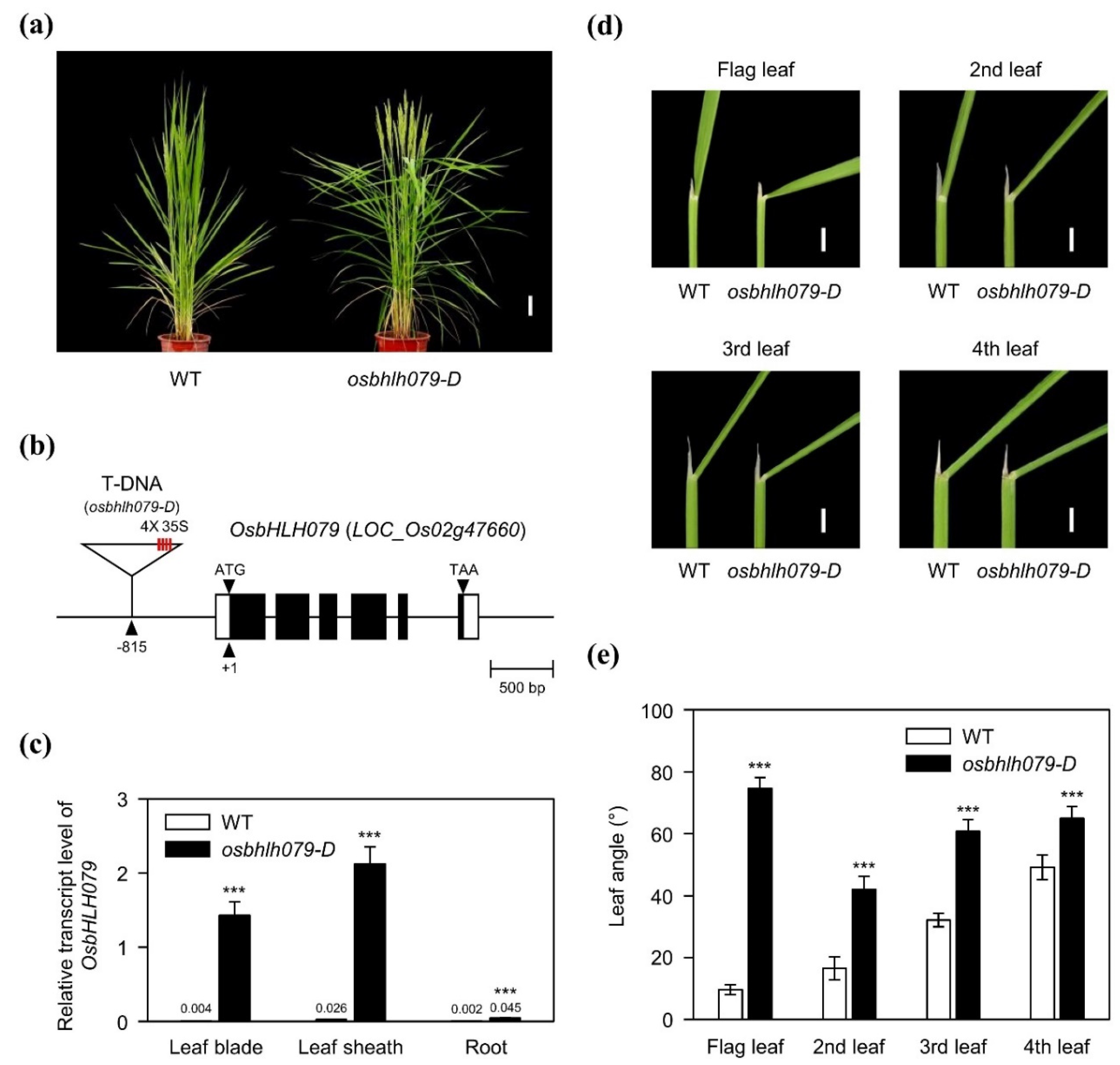
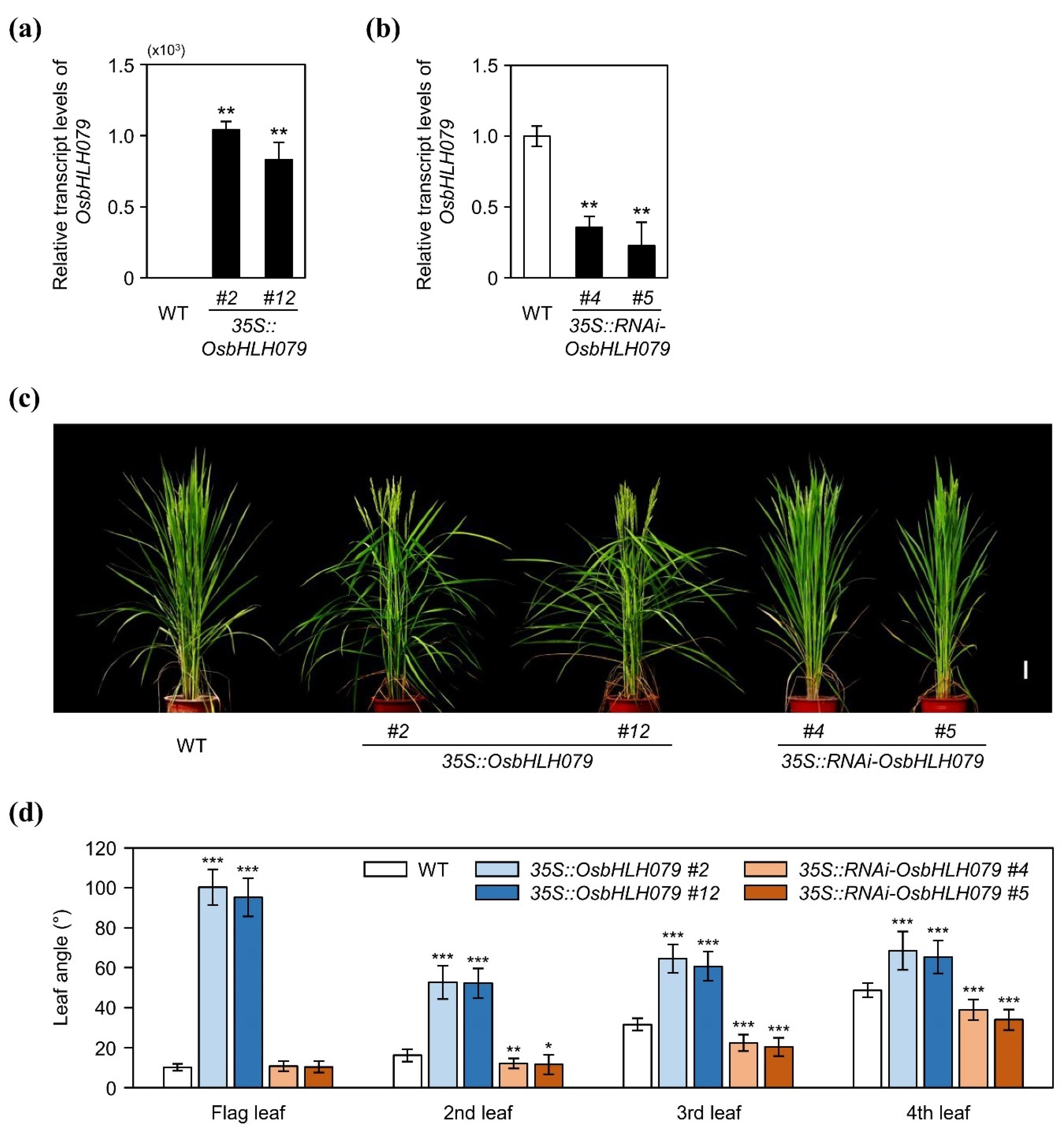
2.1. OsbHLH079 Increases Leaf Angle in Rice
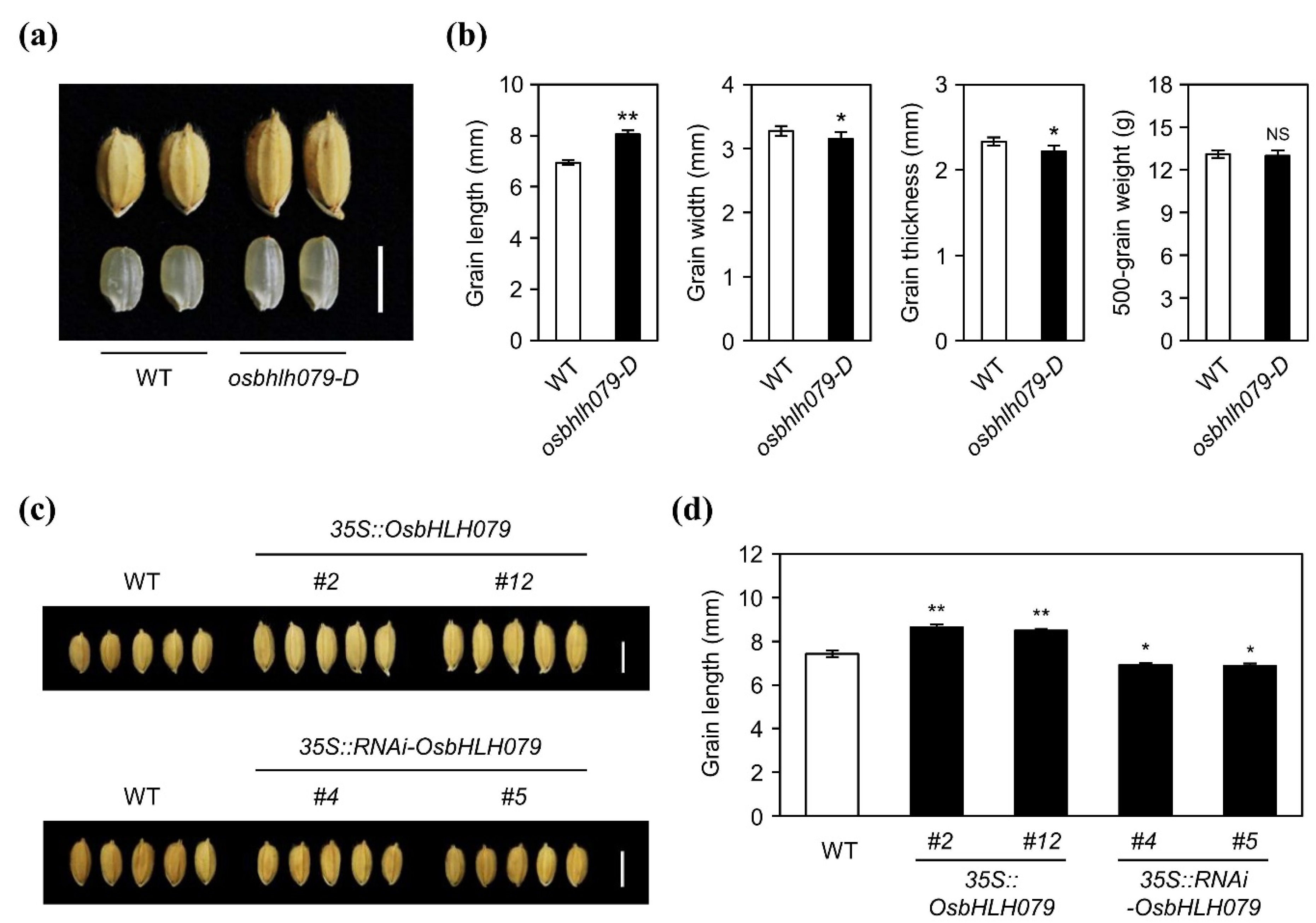
2.2. OsbHLH079 Increases Grain Length in Rice
2.3. OsbHLH079 is a Transcription Factor of the Basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) Family in Rice
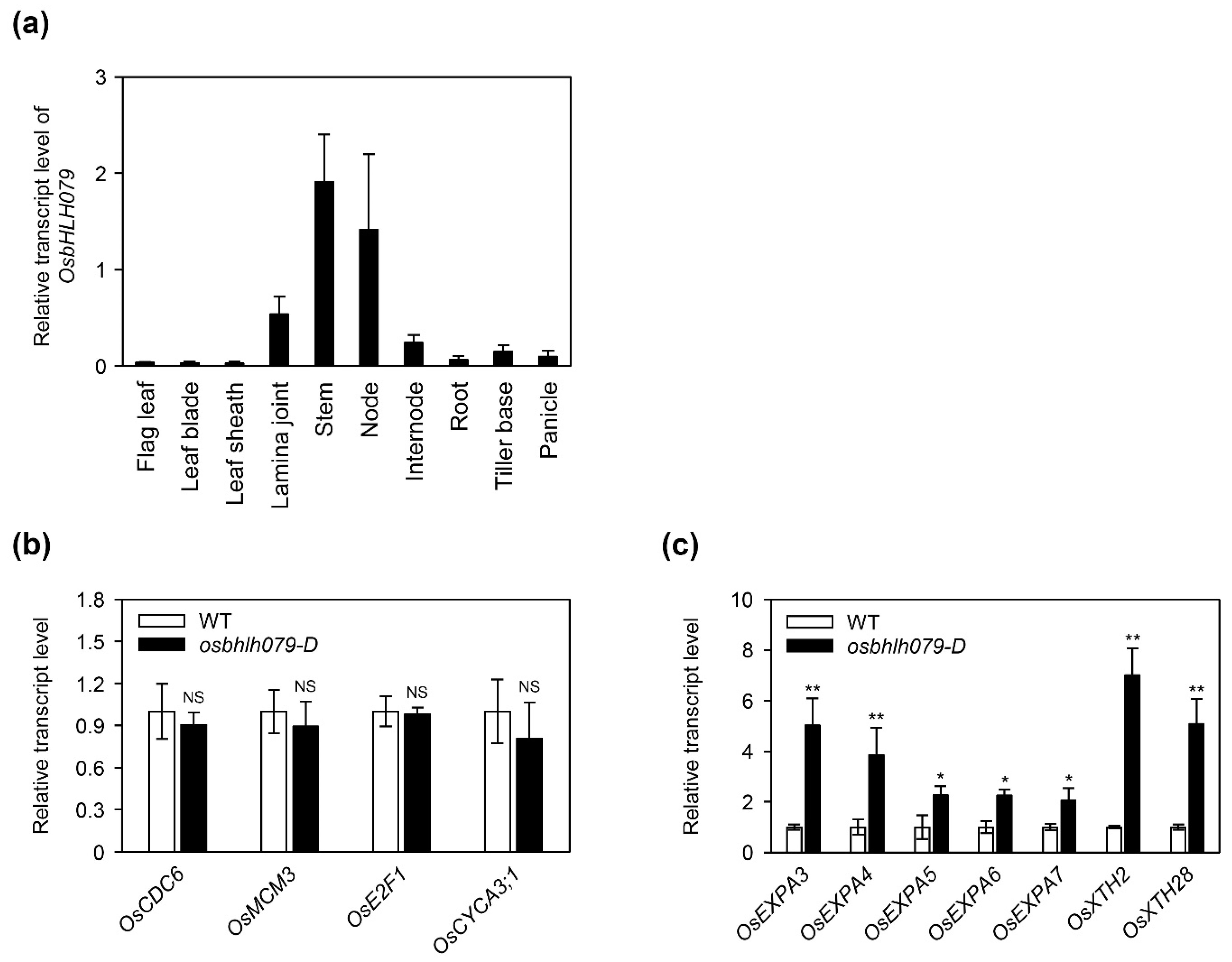
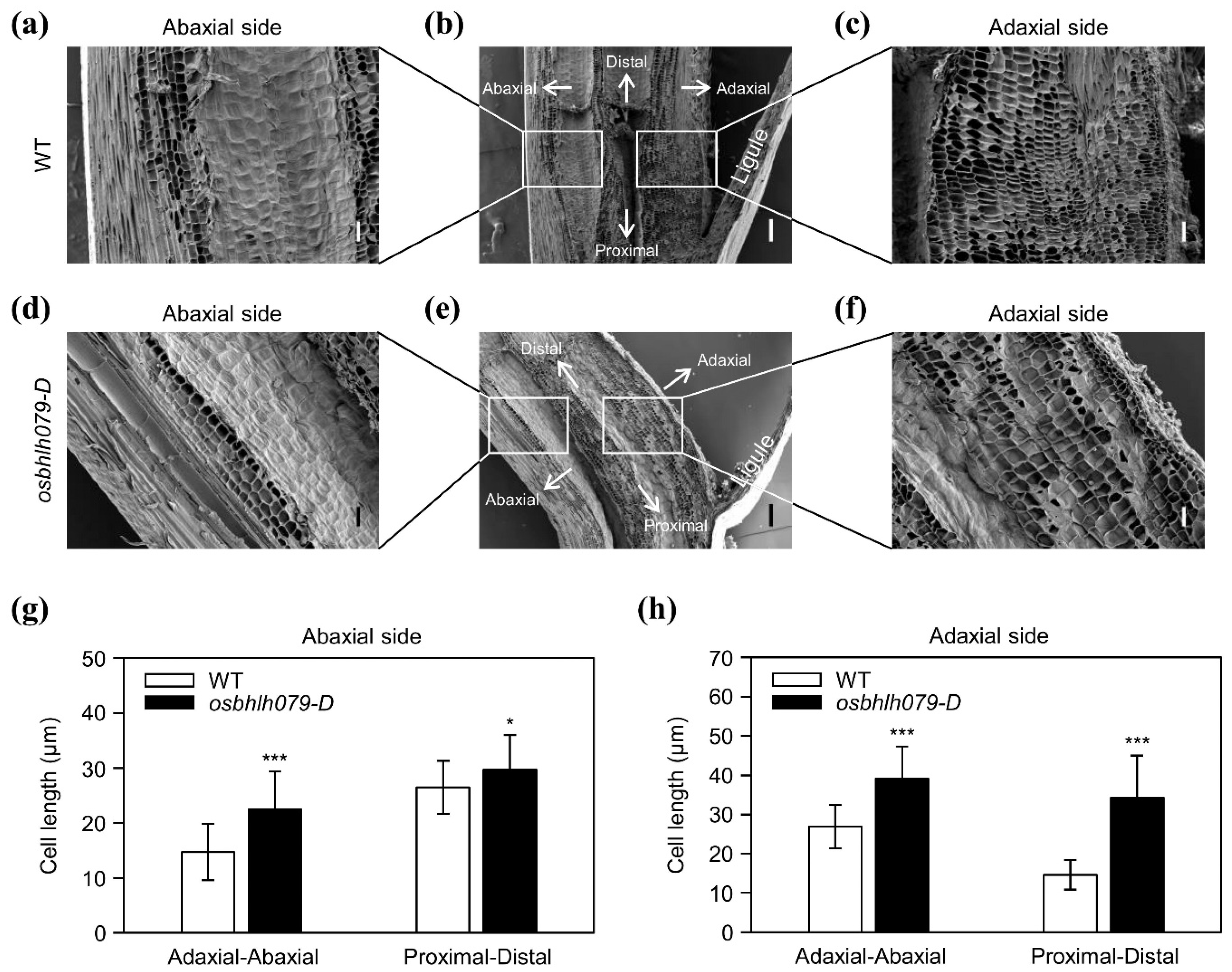
2.4. OsbHLH079 Enlarges Cell Size in the Adaxial Side of Leaf Lamina Joints by Upregulating Cell Expansion-Related Genes
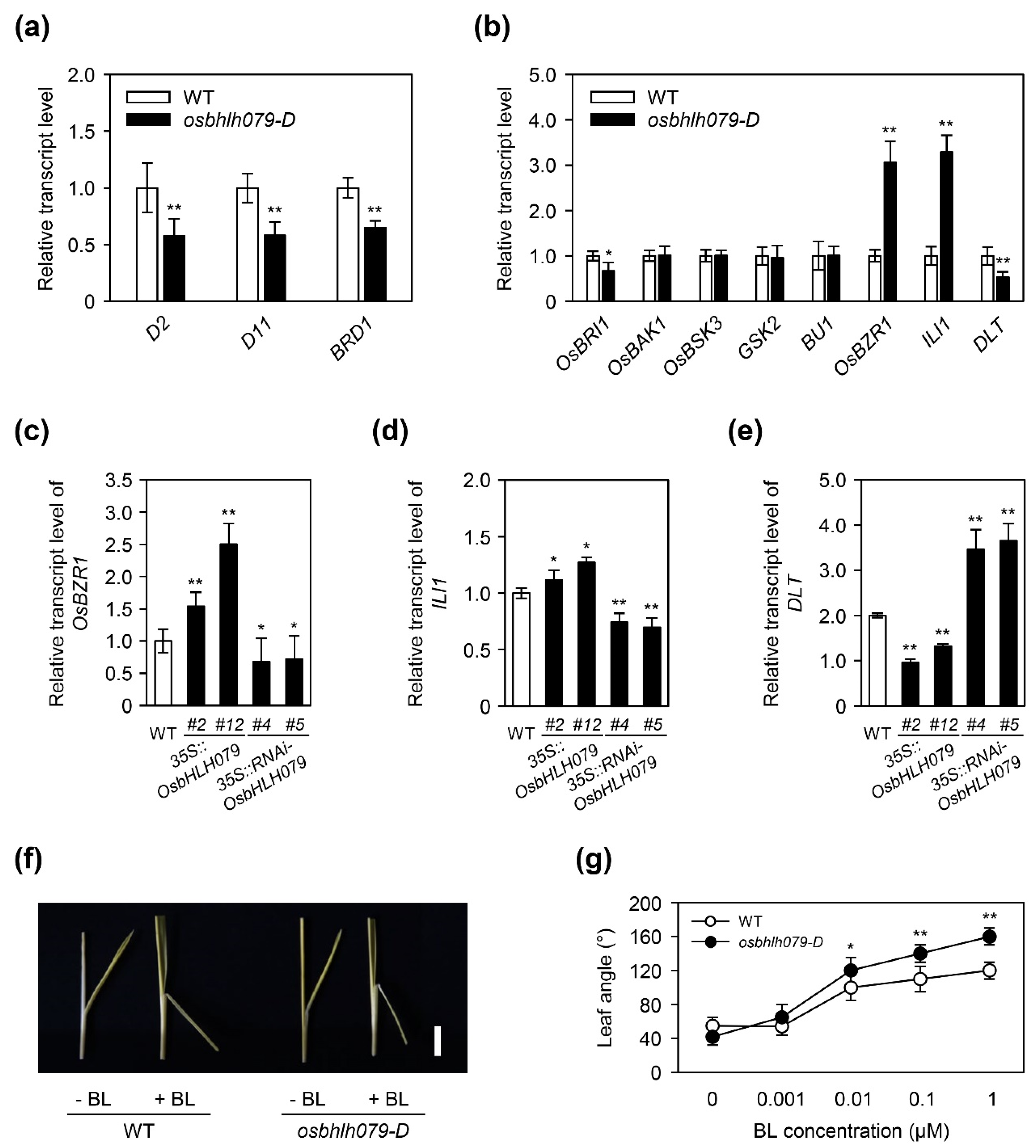
2.5. OsbHLH079 Regulates the Expression of BR Signaling-Related Genes
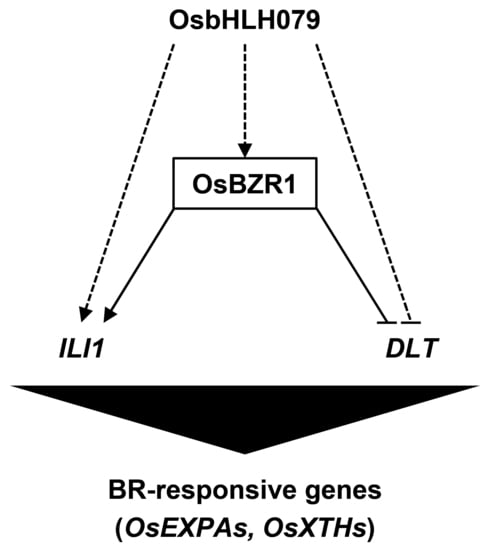
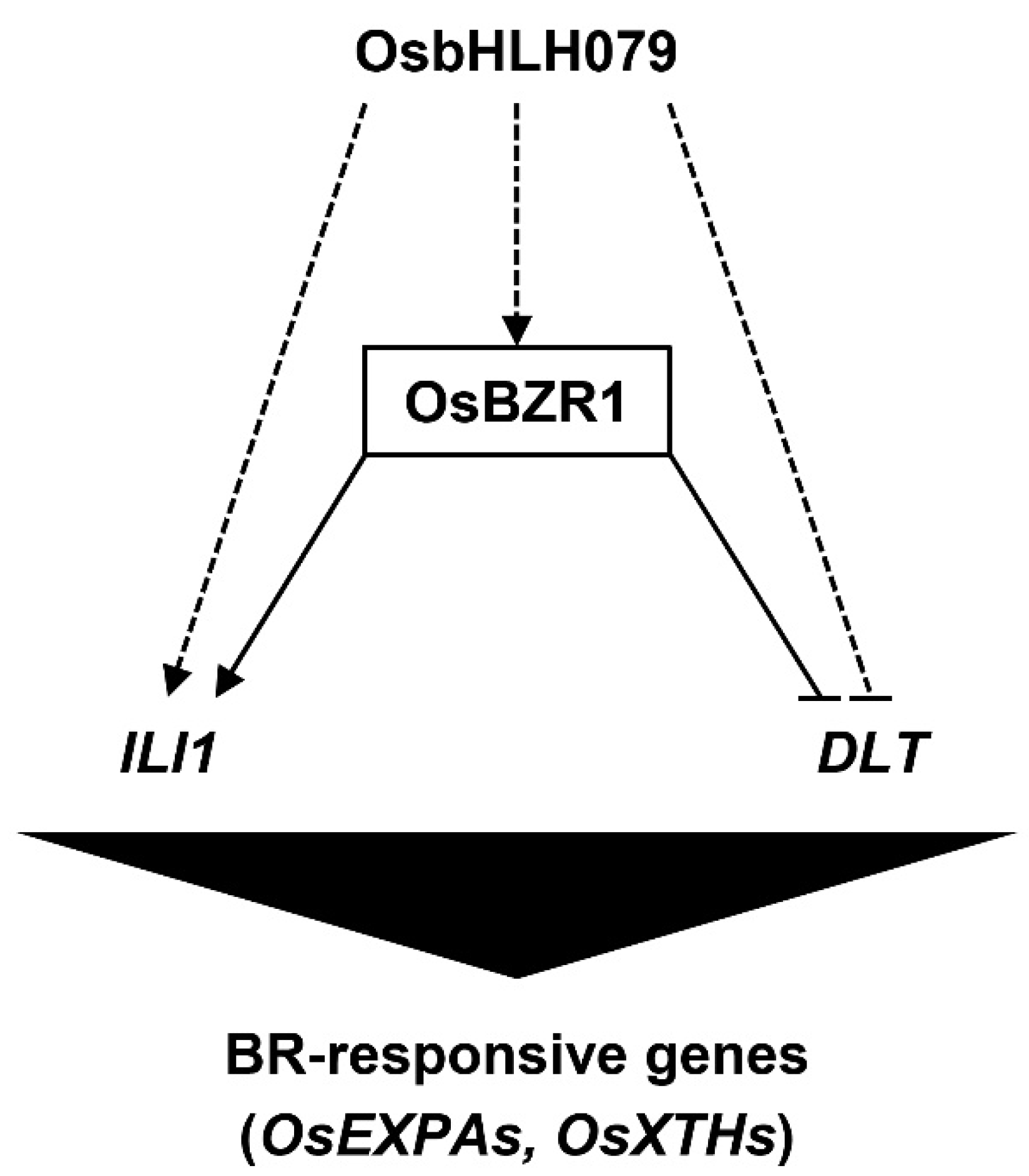
2.6. OsbHLH079 Might Indirectly Regulate Expressions of OsBZR1, and ILI1
2.7. OsbHLH079 Might Directly Regulate the Cell Expansion-Associated Genes
2.8. OsbHLH079 Increases Grain Length by Altering TGW6 Expression
2.9. OsbHLH079 is an Ortholog of Arabidopsis CRYPTOCHROME-INTERACTING bHLH 1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
3.2. Vector Construction and Rice Transformation
3.3. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription-Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) Analysis
3.4. Subcellular Localization of OsbHLH079
3.5. Transactivation Activity Assay
3.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.7. BR-Induced Lamina Joint Inclination Assay
3.8. Gene Information
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| bHLH | basic Helix-Loop-Helix |
| BL | 24-epibrassinolide |
| BR | Brassinosteroid |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| GL | Grain length |
| GS | Grain size |
| GW | Grain width |
| LD | Long day |
| NLD | Natural long day |
| QTL | Quantitative trait loci |
| SD | Short day |
| WT | Wild-type |
References
- Sakamoto, T.; Morinaka, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Sunohara, H.; Fujioka, S.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Mizutani, M.; Sakata, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Cho, L.H.; Lee, S.; Pasriga, R.; Tun, W.; Yang, J.; Yoon, H.; Jeong, H.J.; Jeon, J.S.; An, G. Chromatin interacting factor OsVIL2 is required for outgrowth of axillary buds in rice. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 858–868. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, T.R.; Sheehy, J.E. Erect leaves and photosynthesis in rice. Science 1999, 283, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Tsujimoto, M.; Kitano, H.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Nakano, T. Involvement of C-22-hydroxylated brassinosteroids in auxin-induced lamina joint bending in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, K.; Marumo, S.; Ikekawa, N.; Morisaki, M.; Mori, K. Brassinolide and homobrassinolide promotion of lamina inclination of rice seedling. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981, 22, 323–325. [Google Scholar]
- Bajguz, A. Brassinosteroids—Occurrence and chemical structures in plants. In Brassinosteroids: A Class of Plant Hormone; Hayat, S., Ahmad, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Szekeres, M.; Nemeth, K.; Koncz-Kalman, Z.; Mathur, J.; Kauschmann, A.; Altmann, T.; Redei, G.P.; Nagy, F.; Schell, J.; Koncz, C. Brassinosteroids rescue the deficiency of CYP90, a cytochrome P450, controlling cell elongation and de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Cell 1996, 85, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clouse, S.D.; Sasse, J.M. Brassinosteroids: Essential regulators of plant growth and development. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, S.; Yokota, T. Biosynthesis and metabolism of brassinosteroids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashita, H.; Yasuda, M.; Nitta, T.; Asami, T.; Fujioka, S.; Arai, Y.; Sekimata, K.; Takatsuto, S.; Yamaguchi, I.; Yoshida, S. Brassinosteroid functions in a broad range of disease resistance in tobacco and rice. Plant J. 2003, 33, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Trieu, A.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Kwok, S.F.; Harris, S.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Wan, J.; Zhai, H.; Takatsuto, S.; et al. Brassinosteroids regulate grain filling in rice. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2130–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudesblat, G.E.; Russinova, E. Plants grow on brassinosteroids. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Moon, J.; Roh, J.; Kim, S.K. Castasterone can be biosynthesized from 28-homodolichosterone in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Biol. 2018, 61, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamuro, C.; Ihara, Y.; Wu, X.; Noguchi, T.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Umemura, K.; Uozu, S.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Ashikari, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. A rice brassinosteroid-deficient mutant, ebisu dwarf (d2), is caused by a loss of function of a new member of cytochrome P450. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2900–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S.; Ashikari, M.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yoshida, S.; Yano, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Fujisawa, Y.; et al. A novel cytochrome P450 is implicated in brassinosteroid biosynthesis via the characterization of a rice dwarf mutant, dwarf11, with reduced seed length. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 776–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.K.; Paterson, A.H.; Pinson, S.R.M.; Khush, G.S. A major gene, Ta1 and QTLs affecting tiller and leaf anlgles in rice. Rice Genet. Newsl. 1998, 15, 154–156. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Paterson, A.H.; Pinson, S.R.M.; Stansel, J.W. RFLP facilitated analysis of tiller and leaf angles in rice. Euphytica 1999, 109, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Q.; Hu, J.; Guo, L.B.; Qian, Q.; Xue, H.W. Rice leaf inclination2, a VIN3-like protein, regulates leaf angle through modulating cell division of the collar. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 935–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, L. Increased leaf angle1, a Raf-like MAPKKK that interacts with a nuclear protein family, regulates mechanical tissue formation in the Lamina joint of rice. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 4334–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Roh, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Hu, J.; et al. SLG controls grain size and leaf angle by modulating brassinosteroid homeostasis in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 4241–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinaka, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Inukai, Y.; Agetsuma, M.; Kitano, H.; Ashikari, M.; Matsuoka, M. Morphological alteration caused by brassinosteroid insensitivity increases the biomass and grain production of rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Bai, M.Y.; Chong, K. Brassinosteroid-mediated regulation of agronomic traits in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Nam, K.H. Regulation of brassinosteroid signaling by a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase. Science 2002, 295, 1299–1301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, T.; Cano-Delgado, A.; Seto, H.; Hiranuma, S.; Fujioka, S.; Yoshida, S.; Chory, J. Binding of brassinosteroids to the extracellular domain of plant receptor kinase BRI1. Nature 2005, 433, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.X.; Gendron, J.M.; Sun, Y.; Gampala, S.S.; Gendron, N.; Sun, C.Q.; Wang, Z.Y. BZR1 is a transcriptional repressor with dual roles in brassinosteroid homeostasis and growth responses. Science 2005, 307, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Vafeados, D.; Tao, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; Chory, J. A new class of transcription factors mediates brassinosteroid-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. Cell 2005, 120, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fan, X.Y.; Cao, D.M.; Tang, W.; He, K.; Zhu, J.Y.; He, J.X.; Bai, M.Y.; Zhu, S.; Oh, E.; et al. Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Powell, R.A.; Xu, Z.H.; Chong, K. Transgenic rice plants ectopically expressing AtBAK1 are semi-dwarfed and hypersensitive to 24-epibrassinolide. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 164, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.Y.; Luo, W.; Liu, Y.J.; Xu, Z.H.; Li, J.; Chong, K. Engineering OsBAK1 gene as a molecular tool to improve rice architecture for high yield. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2009, 7, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.J.; Xu, T. Mechanisms of size control. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto-Shirasu, K.; Roberts, K. “Big it up”: Endoreduplication and cell-size control in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2003, 6, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.J.; Huang, W.; Shi, M.; Zhu, M.Z.; Lin, H.X. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.; Gu, S.; Wan, X.; Gao, H.; Guo, T.; Su, N.; Lei, C.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, X.; et al. Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Sang, Y.; Li, Q.H.; Yang, H.Q. A role for Arabidopsis cryptochromes and COP1 in the regulation of stomatal opening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12270–12275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Xing, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, L.; Sun, L.; Shao, D.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; et al. Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Lan, H.; Wang, C.; Yin, C.; Wu, Y.; Tang, H.; Qian, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21534–21539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, K.; Hirotsu, N.; Madoka, Y.; Murakami, N.; Hara, N.; Onodera, H.; Kashiwagi, T.; Ujiie, K.; Shimizu, B.; Onishi, A.; et al. Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tong, H.; Xiao, Y.; Che, R.; Xu, F.; Hu, B.; Liang, C.; Chu, J.; Li, J.; Chu, C. Activation of Big Grain1 significantly improves grain size by regulating auxin transport in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11102–11107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, G.; Hu, J.; Jiang, L.; Yu, H.; Xu, J.; Fang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Xu, E.; Xu, J.; et al. Copy number variation at the GL7 locus contributes to grain size diversity in rice. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Yu, C.; Shen, C.; Qian, Q.; Geisler, M.; de Jiang, A.; Qi, Y. The auxin response factor, OsARF19, controls rice leaf angles through positively regulating OsGH3-5 and OsBRI1. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 638–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heang, D.; Sassa, H. Antagonistic actions of HLH/bHLH proteins are involved in grain length and weight in rice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, P.; Ni, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y. Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Plants 2015, 2, 15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledent, V.; Vervoort, M. The basic helix-loop-helix protein family: Comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 754–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Duan, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, L.; Yin, J.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massari, M.E.; Murre, C. Helix-loop-helix proteins: Regulators of transcription in eucaryotic organisms. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Bai, M.Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Antagonistic HLH/bHLH transcription factors mediate brassinosteroid regulation of cell elongation and plant development in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3767–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Nakagawa, H.; Tomita, C.; Shimatani, Z.; Ohtake, M.; Nomura, T.; Jiang, C.J.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Kikuchi, S.; Sekimoto, H.; et al. BRASSINOSTEROID UPREGULATED1, encoding a helix-loop-helix protein, is a novel gene involved in brassinosteroid signaling and controls bending of the lamina joint in rice. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; An, G.; Li, H.Y. Rice leaf angle and grain size are affected by the OsBUL1 transcriptional activator complex. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ren, Y.; Cai, Y.; Niu, M.; Feng, Z.; Jing, R.; Mou, C.; Liu, X.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Overexpression of OsbHLH107, a member of the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family, enhances grain size in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 2018, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice Functional Genomic Express Database. Available online: http://signal.salk.edu/cgi-bin/RiceGE (accessed on 21 July 2017).
- NCBI-BLASTP Program. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastp&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&LINK_LOC=blasthome (accessed on 20 June 2018).
- Cao, H.; Chen, S. Brassinosteroid-induced rice lamina joint inclination and its relation to indole-3-acetic acid and ethylene. Plant Growth Regul. 1995, 16, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Q.; Xiang, J.J.; Xue, H.W. Studies on the rice LEAF INCLINATION1 (LC1), an IAA-amido synthetase, reveal the effects of auxin in leaf inclination control. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Qiao, S.; Shi, C.; Li, C.; Shen, H.; Wang, X. Brassinosteroid signaling regulates leaf erectness in Oryza sativa via the control of a specific U-type cyclin and cell proliferation. Dev. Cell 2015, 34, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.J.; Xiao, L.T.; Xue, H.W. Dynamic cytology and transcriptional regulation of rice lamina joint development. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 1728–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Chong, K.; Xu, Y. OsmiR396d affects gibberellin and brassinosteroid signaling to regulate plant architecture in rice. Plant Physiol. 2018, 17, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, G.; Zhao, J.; Chu, H.; Lin, W.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Liang, W. DWARF TILLER1, a WUSCHEL-related homeobox transcription factor, is required for tiller growth in rice. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, R.; Rose, J.K.; Nishitani, K. A surprising diversity and abundance of xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolases in rice. Classification and expression analysis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 1088–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.; Cho, H.T.; Lee, Y. Expansins: Expanding importance in plant growth and development. Physiol. Plant 2006, 126, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Shimizu-Sato, S.; Inukai, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Shimada, Y.; Takatsuto, S.; Agetsuma, M.; Yoshida, S.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. Loss-of-function of a rice brassinosteroid biosynthetic enzyme, C-6 oxidase, prevents the organized arrangement and polar elongation of cells in the leaves and stem. Plant J. 2002, 32, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Matsuoka, M. Characterization of CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENESIS AND DWARFISM homologs in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2006, 25, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.Y.; Zhang, L.Y.; Gampala, S.S.; Zhu, S.W.; Song, W.Y.; Chong, K.; Wang, Z.Y. Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13839–13844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, D.M.; Clouse, S.D. Molecular cloning and characterization of a brassinosteroid-regulated gene from elongating soybean (Glycine max L.) epicotyls. Plant Physiol. 1994, 104, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uozu, S.; Tanaka-Ueguchi, M.; Kitano, H.; Hattori, K.; Matsuoka, M. Characterization of XET-related genes of rice. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Gao, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, A. The α-and β-expansin and xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase gene families of wheat: Molecular cloning, gene expression, and EST data mining. Genomics 2007, 90, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, V.; Fornalé, S.; Fry, S.C.; Ruel, K.; Ferrer, P.; Encina, A.; Sonbol, F.M.; Bosch, J.; Puigdomenech, P.; Rigau, J. ZmXTH1, a new xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase in maize, affects cell wall structure and composition in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozuka, T.; Kobayashi, J.; Horiguchi, G.; Demura, T.; Sakakibara, H.; Tsukaya, H.; Nagatani, A. Involvement of auxin and brassinosteroid in the regulation of petiole elongation under the shade. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuqamar, S.; Ajeb, S.; Sham, A.; Enan, M.R.; Iratni, R. A mutation in the expansin-like A2 gene enhances resistance to necrotrophic fungi and hypersensitivity to abiotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Dixon, R.A. Brassinosteroid mediated cell wall remodeling in grasses under abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Liu, L.; Jin, Y.; Du, L.; Yin, Y.; Qian, Q.; Zhu, L.; Chu, C. DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING acts as a direct downstream target of a GSK3/SHAGGY-Like Kinase to medate brassinosteroid responses in rice. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2562–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Jin, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, F.; Fang, J.; Yin, Y.; Qian, Q.; Zhu, L.; Chu, C. DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING, a new member of the GRAS family, plays positive roles in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Plant J. 2009, 58, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.Y.; Shang, J.X.; Oh, E.; Fan, M.; Bai, Y.; Zentella, R.; Sun, T.P.; Wang, Z.Y. Brassinosteroid, gibberellin and phytochrome impinge on a common transcription module in Arabidopsis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Sae-Seaw, J.; Wang, Z.Y. Brassinosteroid signalling. Development 2013, 140, 1615–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, R.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; et al. OsBRI1 activates BR signaling by preventing binding between the TPR and kinase domains of OsBSK3 via phosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Nakano, T.; Gendron, J.; He, J.; Chen, M.; Vafeados, D.; Yang, Y.; Fujika, S.; Yoshida, S.; Asami, T.; et al. Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates brassinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaka, D.; Nakashima, K.; Maruyama, K.; Kidokoro, S.; Osakabe, Y.; Ito, Y.; Matsukura, S.; Fujita, Y.; Yoshiwara, K.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; et al. Rice phytochrome-interacting factor-like protein OsPIL1 functions as a key regulator of internode elongation and induces a morphological response to drought stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15947–15952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Din El-Assal, S.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Peeters, A.J.; Raz, V.; Koornneef, M. A QTL for flowering time in Arabidopsis reveals a novel allele of CRY2. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Grancher, N.; Heil, M.; Black, R.C.; Giovani, B.; Galland, P.; Lardemer, D. Action spectrum for cryptochrome-dependent hypocotyl growth inhibition in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgishi, M.; Saji, K.; Okada, K.; Sakai, T. Functional analysis of each blue light receptor, cry1, cry2, phot1, and phot2, by using combinatorial multiple mutants in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usami, T.; Mochizuki, N.; Kondo, M.; Nishimura, M.; Nagatani, A. Cryptochromes and phytochromes synergistically regulate Arabidopsis root greening under blue light. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1798–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danon, A.; Coll, N.S.; Apel, K. Cryptochrome-1-dependent execution of programmed cell death induced by singlet oxygen in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17036–17041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Li, K.; Klejnot, J.; Yang, H.; Lisiero, D.; Lin, C. Photoexcited CRY2 interacts with CIB1 to regulate transcription and floral initiation in Arabidopsis. Science 2008, 322, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.J.; Hughes, R.M.; Peteya, L.A.; Schwartz, J.W.; Ehlers, M.D.; Tucker, C.L. Rapid blue-light-mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idevall-Hagren, O.; Dickson, E.J.; Hille, B.; Toomre, D.K.; De Camilli, P. Optogenetic control of phosphoinositide metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2316–E2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B.; Lin, C. Blue light-dependent interaction between cryptochrome2 and CIB1 regulates transcription and leaf senescence in soybean. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 4405–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, M.D.; Grossniklaus, U. A gateway cloning vector set for high-throughput functional analysis of genes in planta. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, D.; Shimamoto, K. Simple RNAi vectors for stable and transient suppression of gene function in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.S.; Lee, S.; Jung, K.H.; Jun, S.H.; Jeong, D.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.; Jang, S.; Yang, K.; Nam, J.; et al. T-DNA insertional mutagenesis for functional genomics in rice. Plant J. 2000, 22, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Nijhawan, A.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Validation of housekeeping genes as internal control for studying gene expression in rice by quantitative real-time PCR. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 345, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Huang, K.; Chen, M.; Chen, C.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Ma, Z.; et al. Identification and characterization of EDT1 conferring drought tolerance in rice. J. Plant Biol. 2019, 62, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Zhang, D.; Jeon, J.S. The role of rice vacuolar invertase2 in seed size control. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 711–720. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhu, J.; Huan, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Luo, G.; Wang, X.; Chong, K. Dynamics of brassinosteroid response modulated by negative regulator LIC in rice. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ImageJ Software. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 18 May 2019).

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, H.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, B.-D.; Lim, J.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; An, G.; Paek, N.-C. The Rice Basic Helix–Loop–Helix 79 (OsbHLH079) Determines Leaf Angle and Grain Shape. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062090
Seo H, Kim S-H, Lee B-D, Lim J-H, Lee S-J, An G, Paek N-C. The Rice Basic Helix–Loop–Helix 79 (OsbHLH079) Determines Leaf Angle and Grain Shape. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(6):2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062090
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Hyoseob, Suk-Hwan Kim, Byoung-Doo Lee, Jung-Hyun Lim, Sang-Ji Lee, Gynheung An, and Nam-Chon Paek. 2020. "The Rice Basic Helix–Loop–Helix 79 (OsbHLH079) Determines Leaf Angle and Grain Shape" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 6: 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062090
APA StyleSeo, H., Kim, S.-H., Lee, B.-D., Lim, J.-H., Lee, S.-J., An, G., & Paek, N.-C. (2020). The Rice Basic Helix–Loop–Helix 79 (OsbHLH079) Determines Leaf Angle and Grain Shape. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(6), 2090. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062090