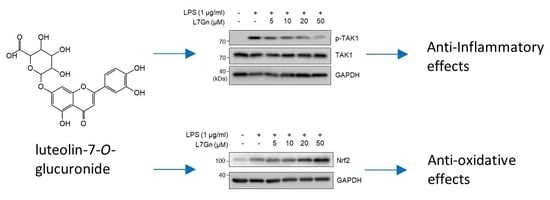
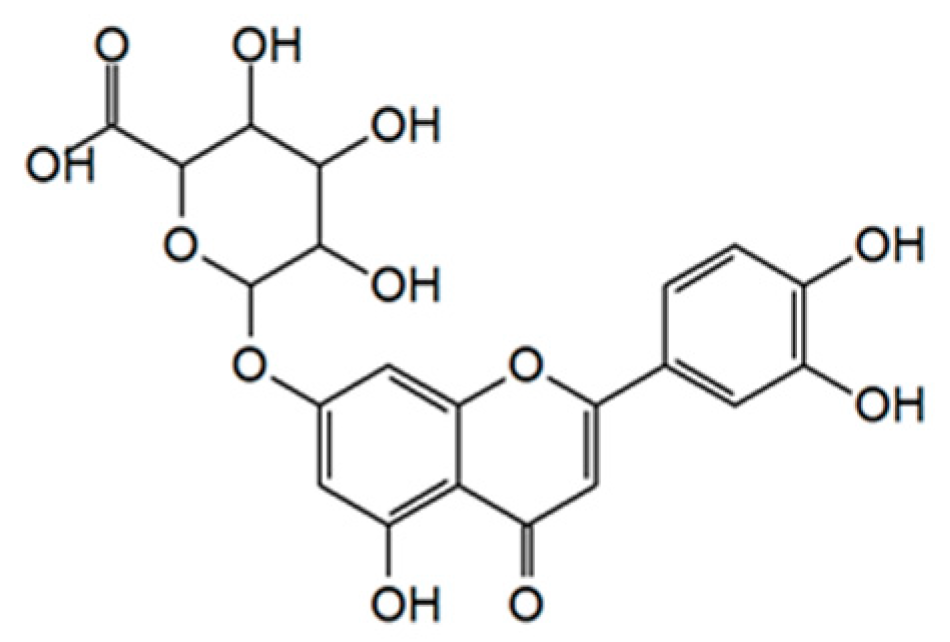
Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of luteolin-7-O-glucuronide in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages through TAK1 Inhibition and Nrf2 Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
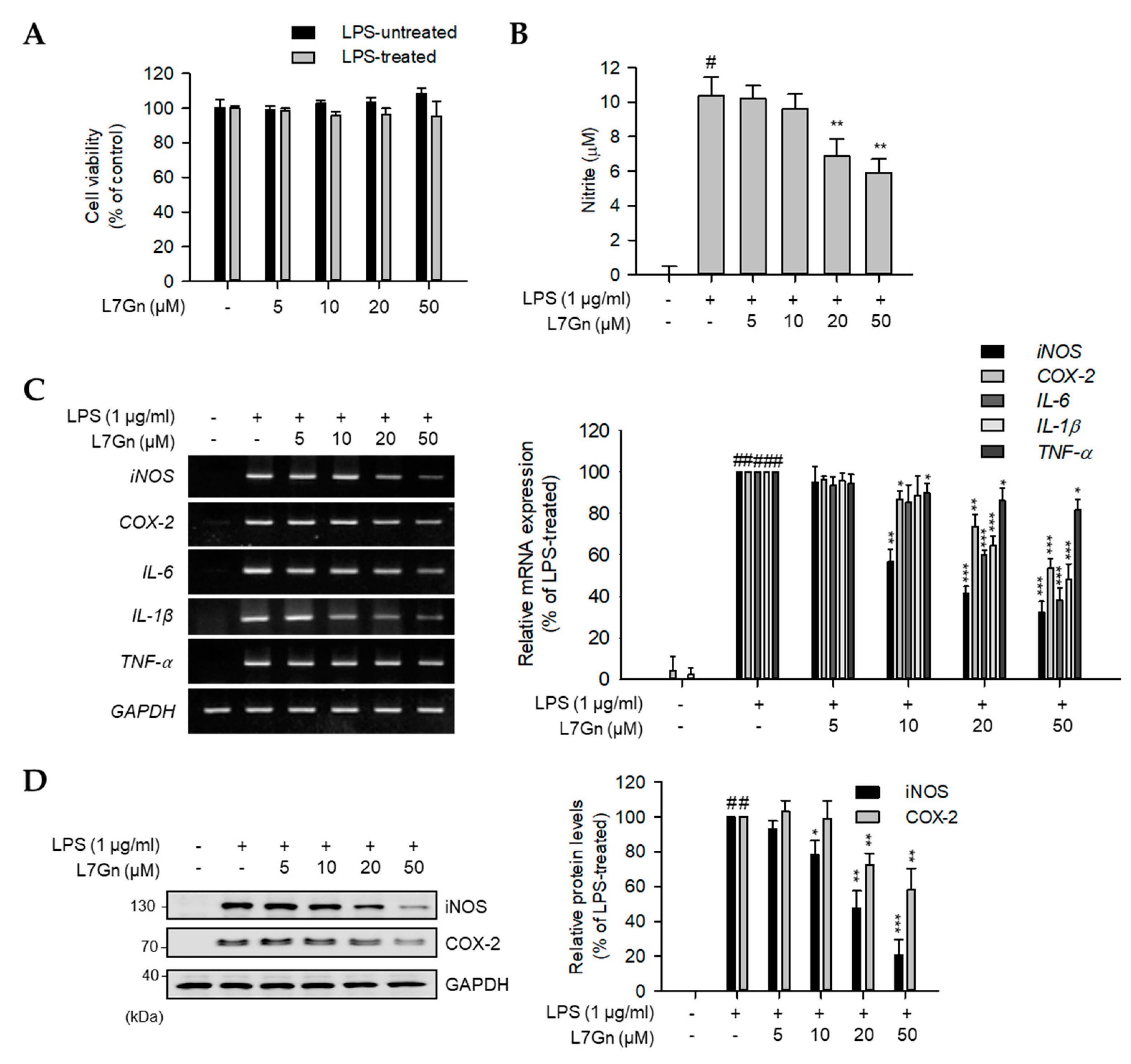
2.1. L7Gn Inhibits the Production of Proinflammatory Mediators in RAW 264.7 Macrophages
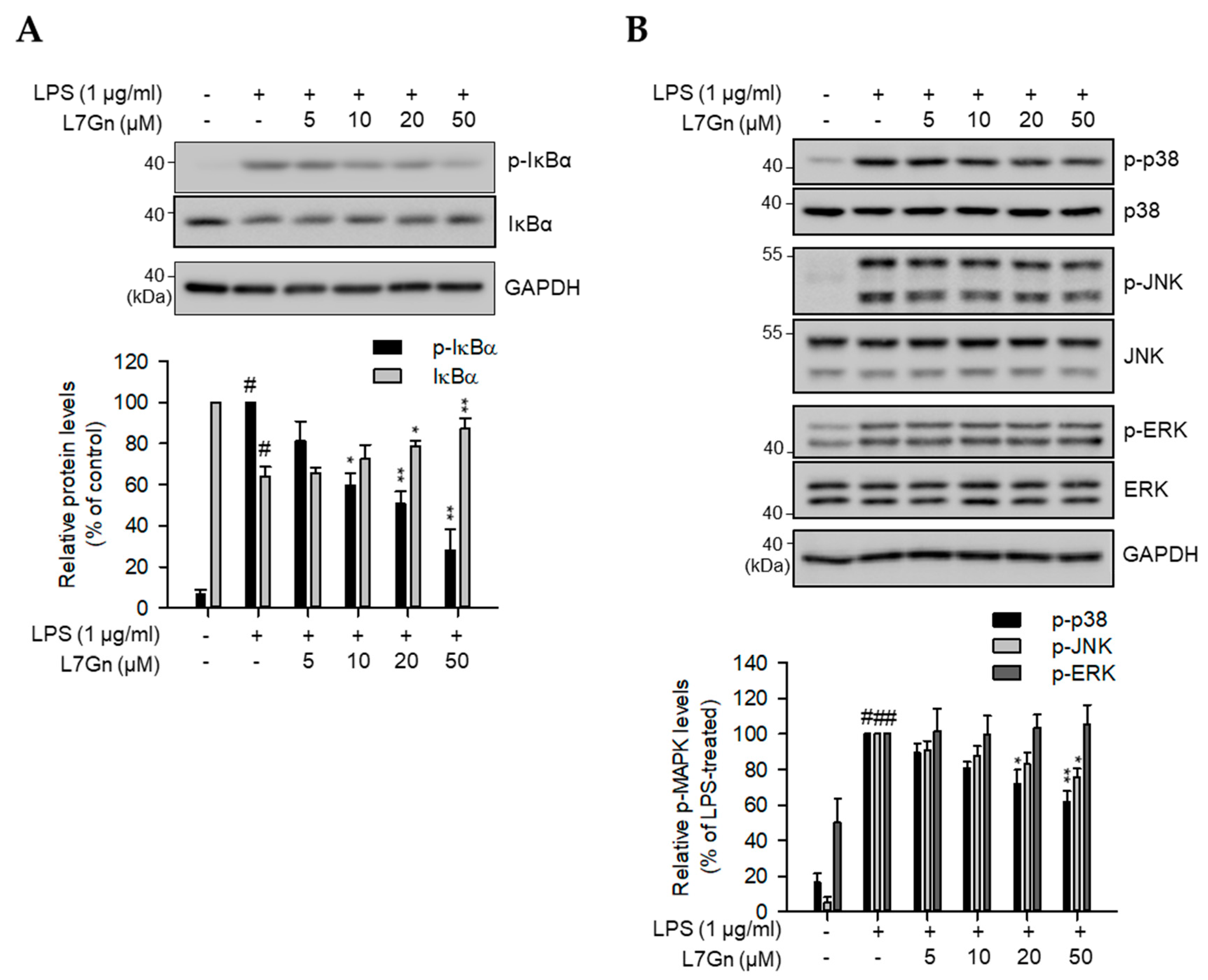
2.2. L7Gn Alleviates NF-κB, p38, and JNK Activation in RAW 264.7 Macrophages
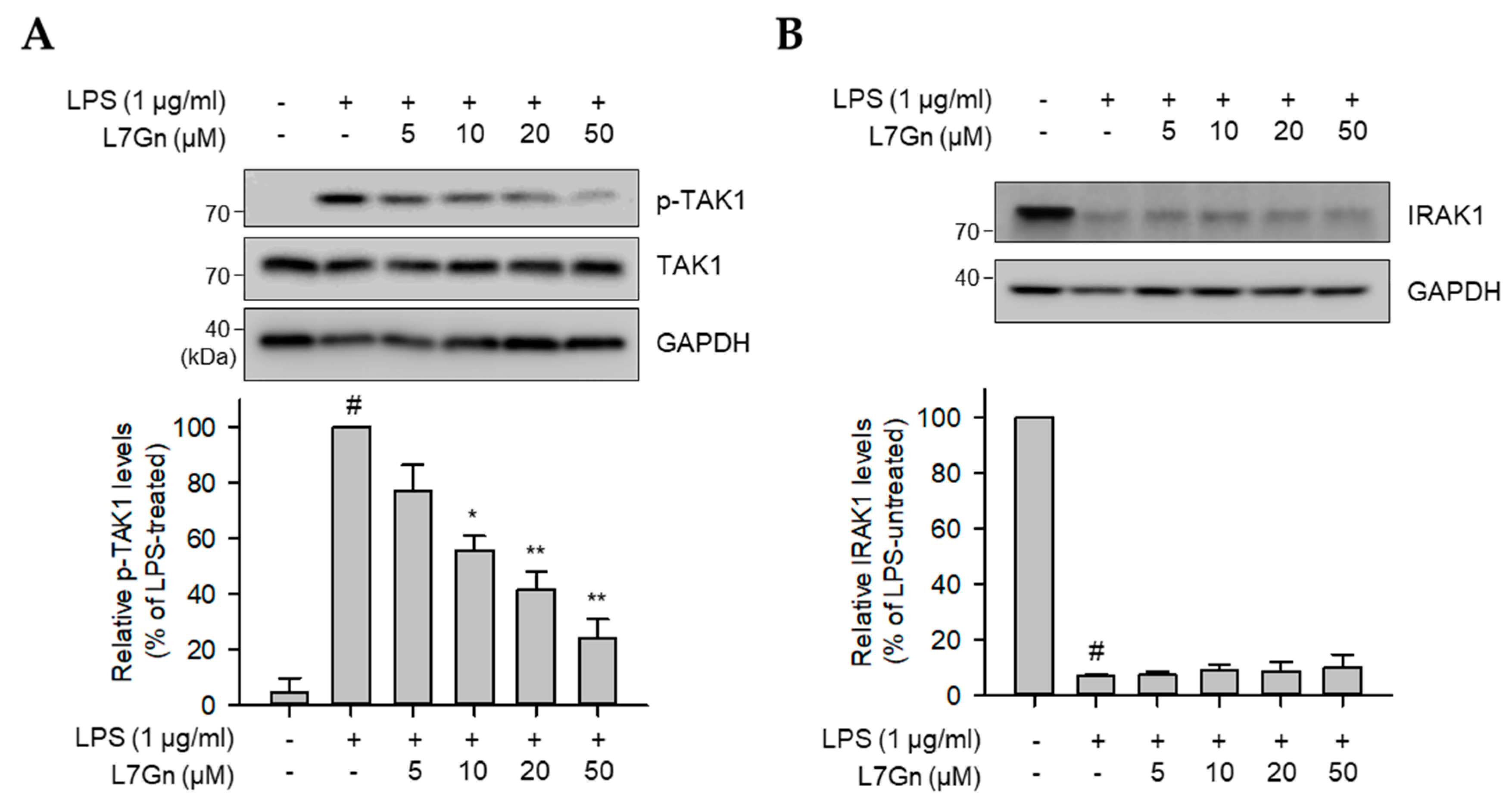
2.3. L7Gn Suppresses TAK1 Phosphorylation, an Upstream Kinase of NF-κB and MAPKs
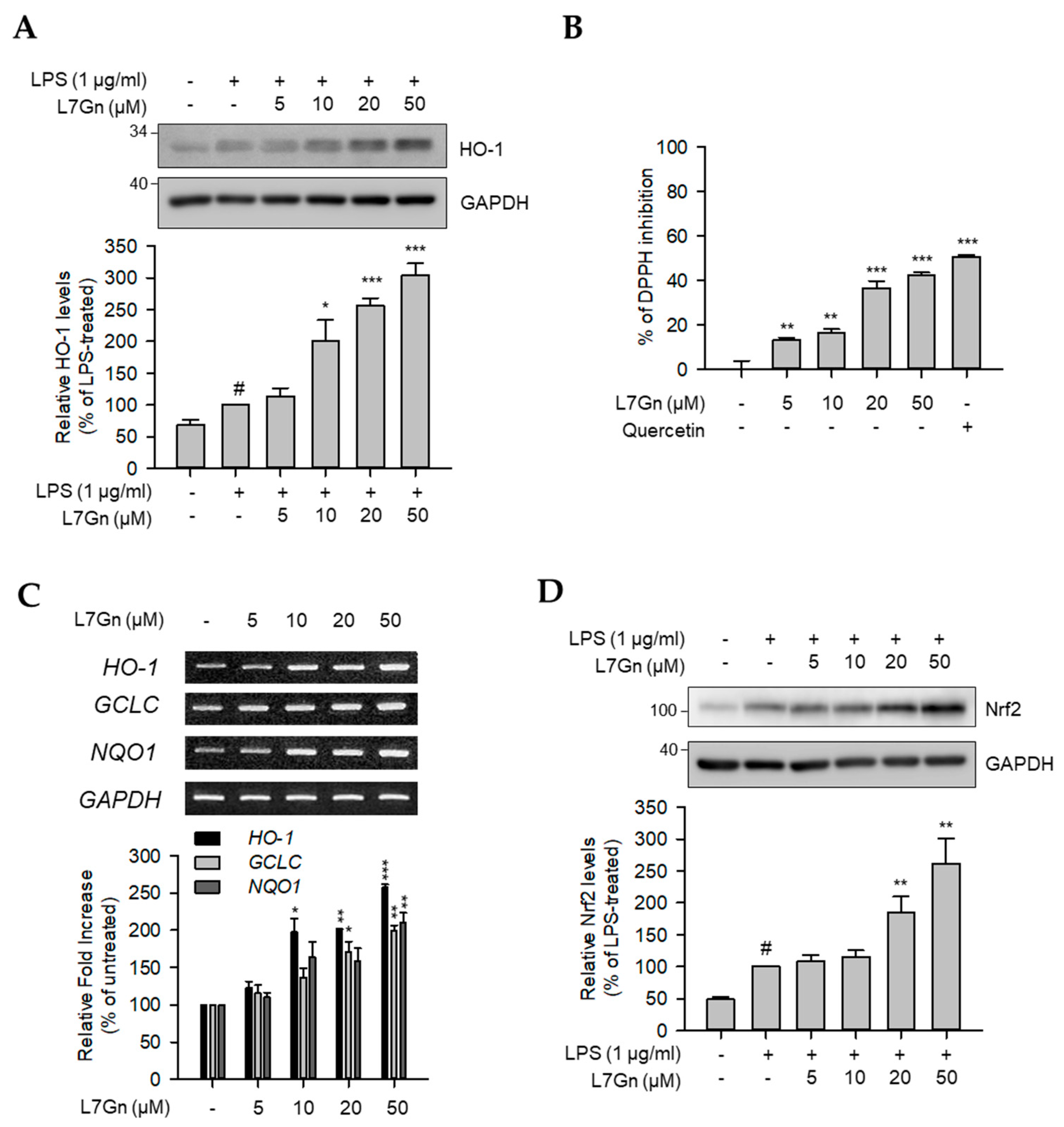
2.4. L7Gn Enhances the Expression of Anti-Oxidative Regulators by Activating Nrf2 Expression
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
3.2. Cell Viability Assay
3.3. NO Assay
3.4. RT-PCR
3.5. Immunoblot Analysis
3.6. Radical Scavenging Assay
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoshino, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Kawai, T.; Sanjo, H.; Ogawa, T.; Takeda, Y.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: Evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 3749–3752. [Google Scholar]
- Poltorak, A.; He, X.; Smirnova, I.; Liu, M.Y.; Van Huffel, C.; Du, X.; Birdwell, D.; Alejos, E.; Silva, M.; Galanos, C.; et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: Mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998, 282, 2085–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderem, A.; Ulevitch, R.J. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 2000, 406, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, C.; Cho, J.H. Inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.N.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S.S. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2007, 15, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedgui, A.; Mallat, Z. Cytokines in atherosclerosis: Pathogenic and regulatory pathways. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 515–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forstermann, U.; Xia, N.; Li, H. Roles of Vascular Oxidative Stress and Nitric Oxide in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, J.N.; Cotter, T.G. ROS signalling in the biology of cancer. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 80, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferret, P.J.; Soum, E.; Negre, O.; Fradelizi, D. Auto-protective redox buffering systems in stimulated macrophages. BMC Immunol. 2002, 3, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, I.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Jeong, S.I.; Kim, S.J.; Jang, S.I. Anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects of luteolin from Perilla (P. frutescens L.) leaves. Molecules 2014, 19, 6941–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, S.; Park, H.J.; Nugroho, A.; Kim, E.J.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Quantification of major compounds from Ixeris dentata, Ixeris dentata Var. albiflora, and Ixeris sonchifolia and their comparative anti-inflammatory activity in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Yoon, K.D.; Lee, W.S.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, S.H.; Sung, N.Y.; Baek, K.S.; Kim, Y.; Htwe, K.M.; Kim, Y.D.; et al. Syk/Src-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of Codariocalyx motorius ethanolic extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabelo, A.S.; Oliveira, I.D.; Guimaraes, A.G.; Quintans, J.S.; Prata, A.P.; Gelain, D.P.; Venceslau, E.M.; Santos, J.P.; Quintans, L.J., Jr.; Bonjardim, L.R.; et al. Antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of aqueous extract from Remirea maritima (Cyperaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Jiang, J.-G.; Zhang, X.-M.; Zhu, W. Identification of luteolin 7-O-β-D-glucuronide from Cirsium japonicum and its anti-inflammatory mechanism. J. Functional Foods 2018, 46, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Lin, H.W.; Yang, D.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Tseng, J.K.; Chang, T.J.; Chang, Y.Y. Luteolin inhibits viral-induced inflammatory response in RAW264.7 cells via suppression of STAT1/3 dependent NF-kappaB and activation of HO-1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 95, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.M.; Song, Y.S. Luteolin and luteolin-7-O-glucoside inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through modulation of NF-kappaB/AP-1/PI3K-Akt signaling cascades in RAW 264.7 cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2013, 7, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuprash, D.V.; Udalova, I.A.; Turetskaya, R.L.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Rice, N.R.; Nedospasov, S.A. Similarities and differences between human and murine TNF promoters in their response to lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 4045–4052. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Lim, H.K.; Sakong, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.R.; Baek, S.H. Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription mediates phosphatidic acid-induced interleukin (IL)-1beta and IL-6 production. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and Function of the MAPKs and Their Substrates, the MAPK-Activated Protein Kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2011, 75, 50–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-κB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Martin, M.; Michalek, S.M.; Katz, J. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-κB in the regulation of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines by porphyromonas gingivalis Hemagglutinin B. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 3990–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finco, T.S.; Beg, A.A.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. Inducible phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha is not sufficient for its dissociation from NF-kappa B and is inhibited by protease inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 11884–11888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, A.; Zehorai, E.; Procaccia, S.; Seger, R. The MAPK cascades: Signaling components, nuclear roles and mechanisms of nuclear translocation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1619–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, C.D.; Ceci, J.D.; Tsatsanis, C.; Kontoyiannis, D.; Stamatakis, K.; Lin, J.H.; Patriotis, C.; Jenkins, N.A.; Copeland, N.G.; Kollias, G.; et al. TNF-alpha induction by LPS is regulated posttranscriptionally via a Tpl2/ERK-dependent pathway. Cell 2000, 103, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Qian, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Li, X. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase-dependent IL-1-induced signaling complexes phosphorylate TAK1 and TAB2 at the plasma membrane and activate TAK1 in the cytosol. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 7158–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordureau, A.; Smith, H.; Windheim, M.; Peggie, M.; Carrick, E.; Morrice, N.; Cohen, P. The IRAK-catalysed activation of the E3 ligase function of Pellino isoforms induces the Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of IRAK1. Biochem. J. 2008, 409, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kure, A.; Nakagawa, K.; Kondo, M.; Kato, S.; Kimura, F.; Watanabe, A.; Shoji, N.; Hatanaka, S.; Tsushida, T.; Miyazawa, T. Metabolic Fate of Luteolin in Rats: Its Relationship to Anti-inflammatory Effect. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4246–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, L.; Li, Q.; Zeng, X.; Lu, L.; Hu, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Metabolic Disposition of Luteolin Is Mediated by the Interplay of UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases and Catechol-O-Methyltransferases in Rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2017, 45, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.R.; Cho, Y.C.; Cho, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of a novel compound, MPQP, through the inhibition of IRAK1 signaling pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.Y.; Park, J.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.; Cho, H.; Park, J.H.; Han, I.O. An alpha-lipoic acid-decursinol hybrid compound attenuates lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation in BV2 and RAW264.7 cells. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.-C.; Park, J.; Cho, S. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of luteolin-7-O-glucuronide in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages through TAK1 Inhibition and Nrf2 Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062007
Cho Y-C, Park J, Cho S. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of luteolin-7-O-glucuronide in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages through TAK1 Inhibition and Nrf2 Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(6):2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062007
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Young-Chang, Jiyoung Park, and Sayeon Cho. 2020. "Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of luteolin-7-O-glucuronide in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages through TAK1 Inhibition and Nrf2 Activation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 6: 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062007
APA StyleCho, Y.-C., Park, J., & Cho, S. (2020). Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of luteolin-7-O-glucuronide in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages through TAK1 Inhibition and Nrf2 Activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(6), 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062007