Tissue Distribution of the Readthrough Isoform of AQP4 Reveals a Dual Role of AQP4ex Limited to CNS
Abstract
1. Introduction
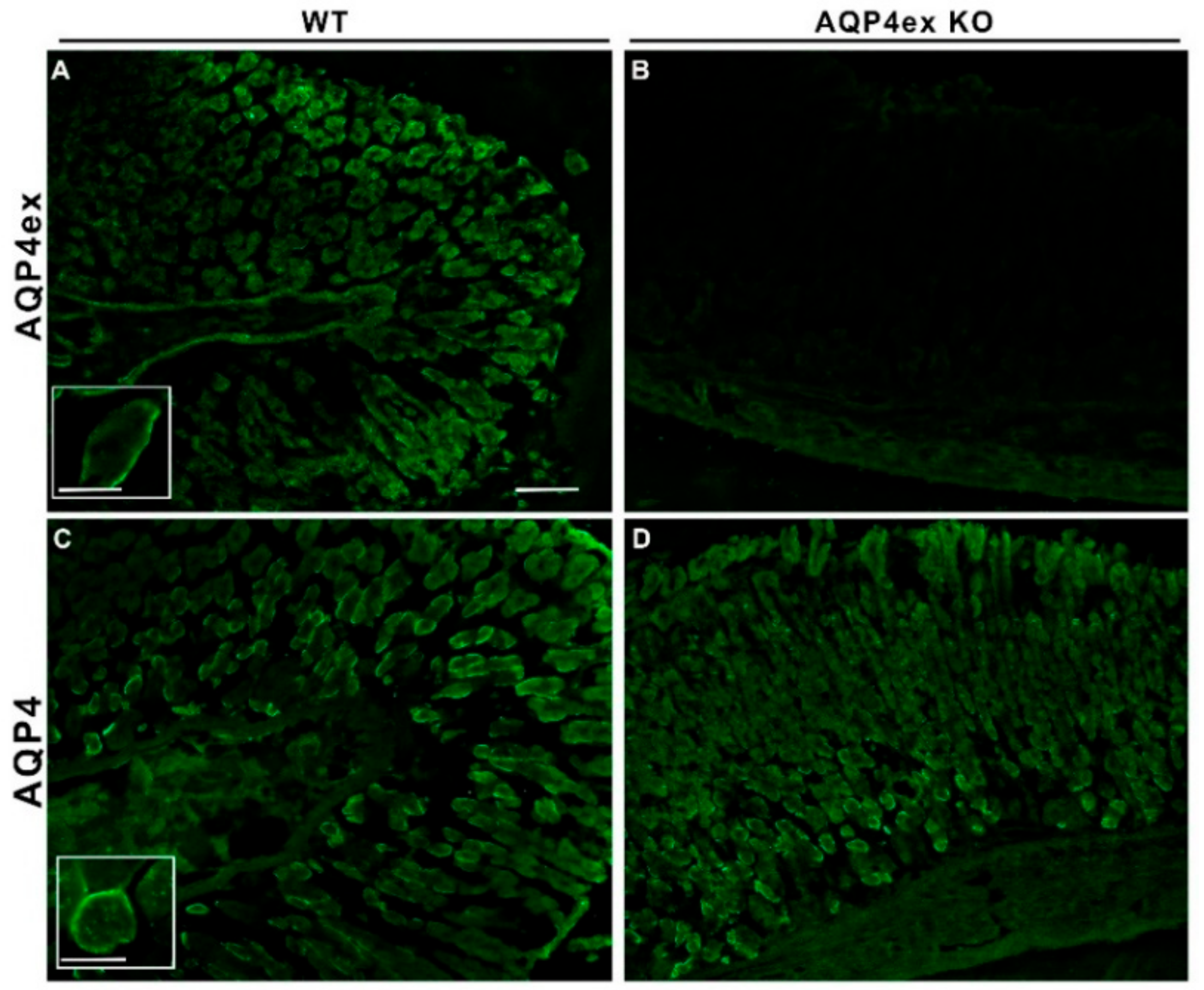
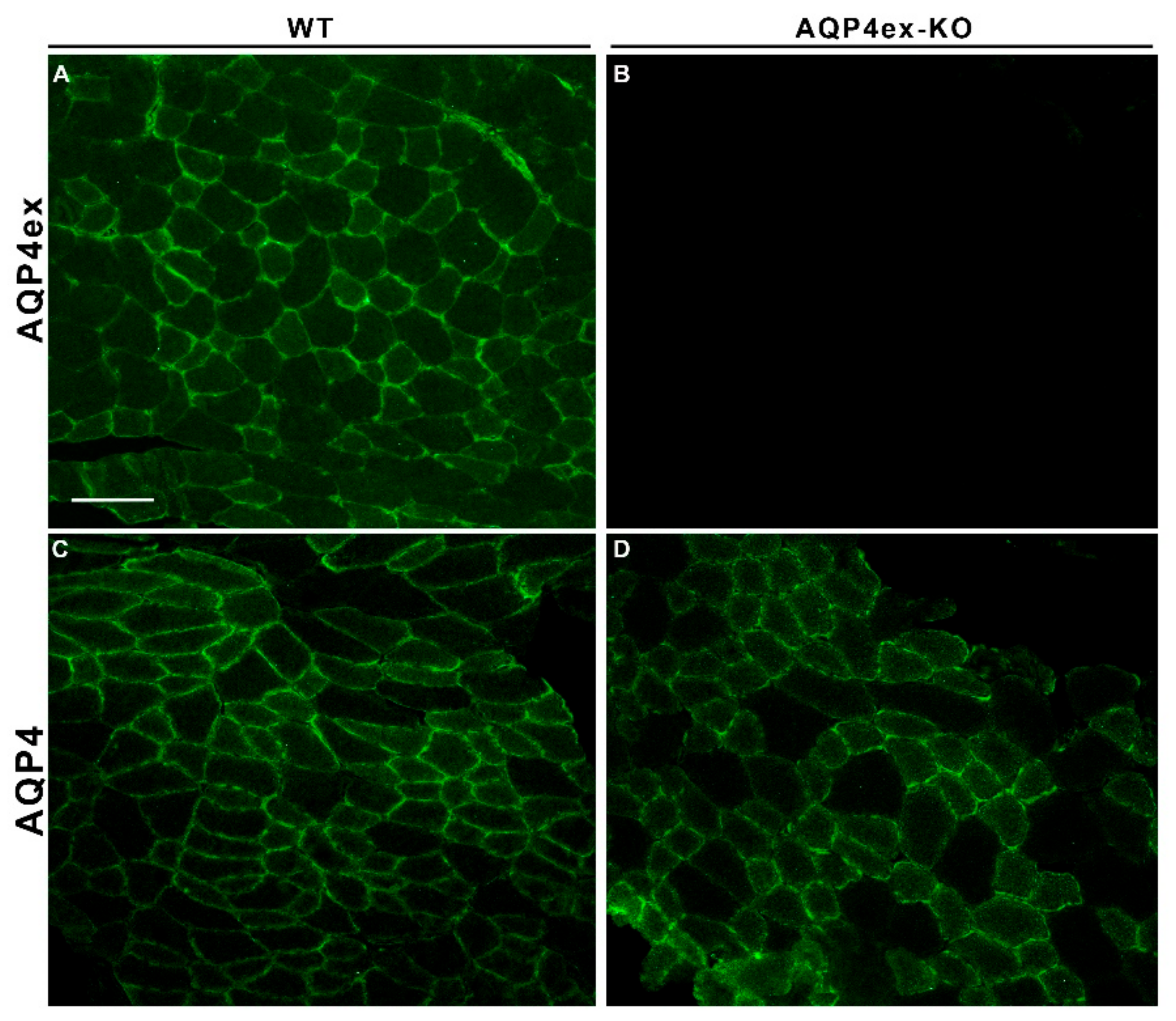
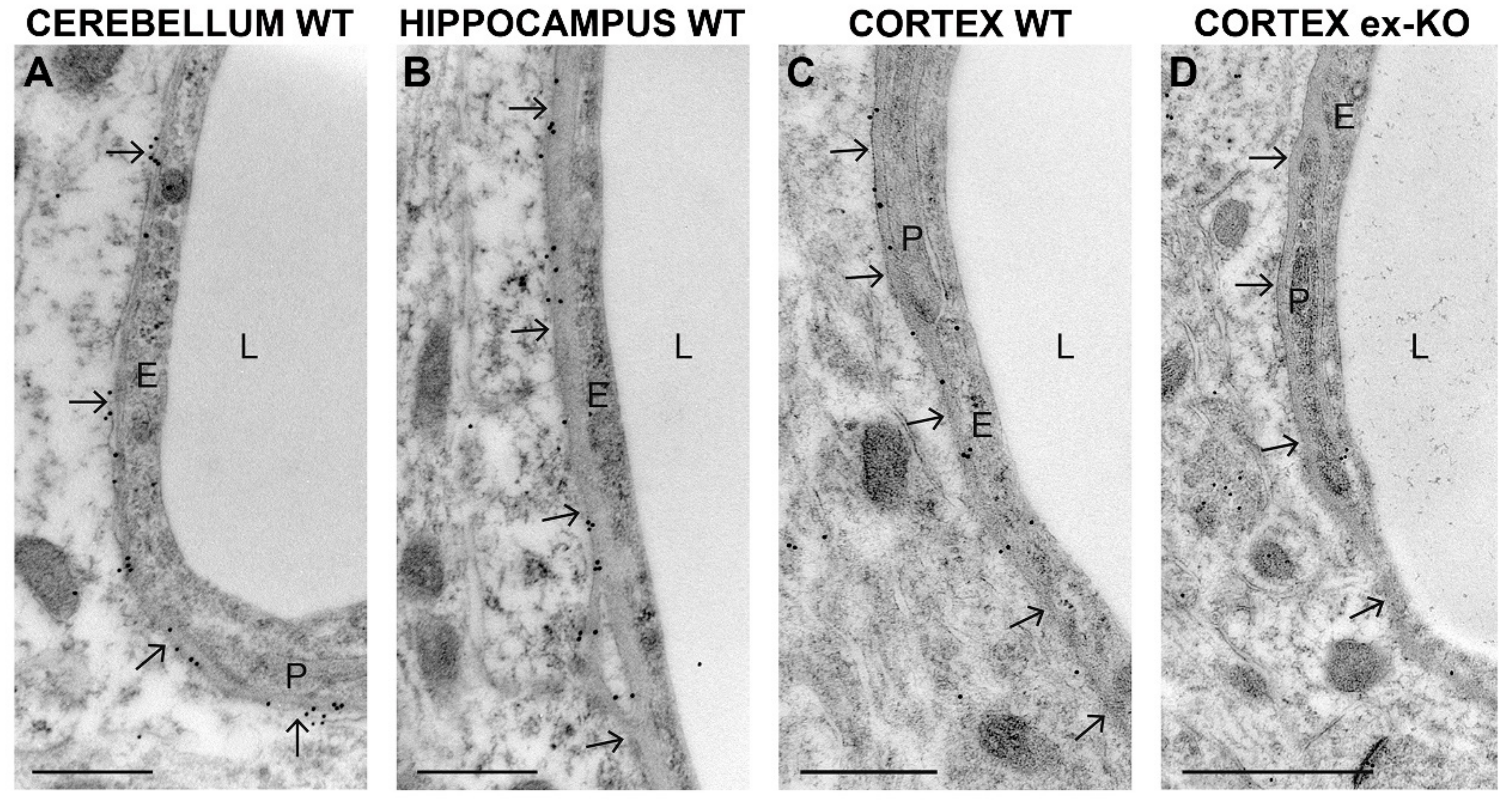
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Antibodies
4.3. Immunofluorescence on Tissue Sections
4.4. Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE
4.5. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Perfusion and Tissue Preparation for Electron Microscopy
4.7. Postembedding Immunogold Electron Microscopy
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verkman, A.S.; Anderson, M.O.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Aquaporins: Important but elusive drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigeri, A.; Gropper, M.A.; Umenishi, F.; Kawashima, M.; Brown, D.; Verkman, A.S. Localization of MIWC and GLIP water channel homologs in neuromuscular, epithelial and glandular tissues. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Bourque, C.; Agre, P.; Ottersen, O.P. Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: High-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.S.; Bhat, R.V.; Preston, G.M.; Guggino, W.B.; Baraban, J.M.; Agre, P. Molecular characterization of an aquaporin cDNA from brain: Candidate osmoreceptor and regulator of water balance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 13052–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Ma, T.; Skach, W.; Matthay, M.A.; Verkman, A.S. Molecular cloning of a mercurial-insensitive water channel expressed in selected water-transporting tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 5497–5500. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.J.; Rossi, A.; Verkman, A.S. Model of aquaporin-4 supramolecular assembly in orthogonal arrays based on heterotetrameric association of M1-M23 isoforms. Biophys. J. 2011, 100, 2936–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, C.S.; Gorelick-Feldman, D.A.; Davidson, K.G.; Yasumura, T.; Neely, J.D.; Agre, P.; Rash, J.E. Aquaporin-4 square array assembly: Opposing actions of M1 and M23 isoforms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13609–13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Rossi, A.; Mola, M.G.; Pisani, F.; Stigliano, C.; Basco, D.; Mastrototaro, M.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. Higher order structure of aquaporin-4. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosito, S.; Nicchia, G.P.; Palazzo, C.; Lia, A.; Buccoliero, C.; Pisani, F.; Svelto, M.; Trojano, M.; Frigeri, A. Supramolecular aggregation of aquaporin-4 is different in muscle and brain: Correlation with tissue susceptibility in neuromyelitis optica. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wax, M.B.; Patil, R.V. Regulation of aquaporin-4 water channels by phorbol ester-dependent protein phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 6001–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, E.S.; Haas, B.R.; Sontheimer, H. Water permeability through aquaporin-4 is regulated by protein kinase C and becomes rate-limiting for glioma invasion. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, F.; Rossi, A.; Nicchia, G.P.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. Translational regulation mechanisms of aquaporin-4 supramolecular organization in astrocytes. Glia 2011, 59, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bellis, M.; Pisani, F.; Mola, M.G.; Basco, D.; Catalano, F.; Nicchia, G.P.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. A novel human aquaporin-4 splice variant exhibits a dominant-negative activity: A new mechanism to regulate water permeability. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bellis, M.; Pisani, F.; Mola, M.G.; Rosito, S.; Simone, L.; Buccoliero, C.; Trojano, M.; Nicchia, G.P.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. Translational readthrough generates new astrocyte AQP4 isoforms that modulate supramolecular clustering, glial endfeet localization, and water transport. Glia 2017, 65, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughran, G.; Chou, M.Y.; Ivanov, I.P.; Jungreis, I.; Kellis, M.; Kiran, A.M.; Baranov, P.V.; Atkins, J.F. Evidence of efficient stop codon readthrough in four mammalian genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8928–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, C.; Buccoliero, C.; Mola, M.G.; Abbrescia, P.; Nicchia, G.P.; Trojano, M.; Frigeri, A. AQP4ex is crucial for the anchoring of AQP4 at the astrocyte end-feet and for neuromyelitis optica antibody binding. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigeri, A.; Gropper, M.A.; Turck, C.W.; Verkman, A.S. Immunolocalization of the mercurial-insensitive water channel and glycerol intrinsic protein in epithelial cell plasma membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4328–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigeri, A.; Nicchia, G.P.; Verbavatz, J.M.; Valenti, G.; Svelto, M. Expression of aquaporin-4 in fast-twitch fibers of mammalian skeletal muscle. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 102, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasheri, A.; Marples, D.; Young, I.S.; Floyd, R.V.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Frigeri, A. Distribution of the AQP4 water channel in normal human tissues: Protein and tissue microarrays reveal expression in several new anatomical locations, including the prostate gland and seminal vesicles. Channels (Austin) 2007, 1, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.E.; Kitchen, P.; Owen, D.S.; Bland, C.; Marshall, L.; Conner, A.C.; Bill, R.M.; Conner, M.T. Human aquaporins: Regulators of transcellular water flow. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1492–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Patil, R.V.; Verkman, A.S. Mildly abnormal retinal function in transgenic mice without Müller cell aquaporin-4 water channels. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.; Agre, P. The aquaporin family of water channels in kidney. Kidney Int. 1995, 48, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, A.; Horio, Y.; Nielsen, S.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Hata, F.; Ottersen, O.P.; Kurachi, Y. High-resolution immunogold cytochemistry indicates that AQP4 is concentrated along the basal membrane of parietal cell in rat stomach. FEBS Lett. 1999, 459, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tola, V.B.; Fang, P.; Soybel, D.I.; Van Hoek, A.N. Partitioning of aquaporin-4 water channel mRNA and protein in gastric glands. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2003, 48, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigeri, A.; Nicchia, G.P.; Desaphy, J.F.; Pierno, S.; De Luca, A.; Camerino, D.C.; Svelto, M. Muscle loading modulates aquaporin-4 expression in skeletal muscle. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 1282–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, D.; Lake, A.M.; Yang, W.; Yang, C.; Wesseling, H.; Guise, A.; Uncu, C.; Dalal, J.S.; Kraft, A.W.; Lee, J.M.; et al. Cell-Type-Specific Profiling of Alternative Translation Identifies Regulated Protein Isoform Variation in the Mouse Brain. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 594–607.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersch, K.; Lobos Matthei, I.; Thoms, S. Multiple Localization by Functional Translational Readthrough. Subcell Biochem. 2018, 89, 201–219. [Google Scholar]
- Stiebler, A.C.; Freitag, J.; Schink, K.O.; Stehlik, T.; Tillmann, B.A.; Ast, J.; Bölker, M. Ribosomal readthrough at a short UGA stop codon context triggers dual localization of metabolic enzymes in Fungi and animals. Plos Genet. 2014, 10, e1004685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueren, F.; Lingner, T.; George, R.; Hofhuis, J.; Dickel, C.; Gärtner, J.; Thoms, S. Peroxisomal lactate dehydrogenase is generated by translational readthrough in mammals. Elife 2014, 3, e03640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, R.; Le Maout, S.; Barrault, M.B.; Janvier, K.; Benichou, S.; Mérot, J. Polarized trafficking and surface expression of the AQP4 water channel are coordinated by serial and regulated interactions with different clathrin-adaptor complexes. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 7008–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, J.D.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Froehner, S.C.; Agre, P.; Adams, M.E. Syntrophin-dependent expression and localization of Aquaporin-4 water channel protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14108–14113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Otsuka, T.; Hurn, P.D.; Traystman, R.J.; Haug, F.M.; Froehner, S.C.; Adams, M.E.; Neely, J.D.; Agre, P.; Ottersen, O.P.; et al. An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2106–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragg, A.D.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Adams, M.E.; Froehner, S.C. Assembly of a perivascular astrocyte protein scaffold at the mammalian blood-brain barrier is dependent on alpha-syntrophin. Glia 2006, 53, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Srinivas, M.; Li, W.; Brosnan, C.F.; Frigeri, A.; Spray, D.C. New possible roles for aquaporin-4 in astrocytes: Cell cytoskeleton and functional relationship with connexin43. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Cogotzi, L.; Rossi, A.; Basco, D.; Brancaccio, A.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. Expression of multiple AQP4 pools in the plasma membrane and their association with the dystrophin complex. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 2156–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Rossi, A.; Nudel, U.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. Dystrophin-dependent and -independent AQP4 pools are expressed in the mouse brain. Glia 2008, 56, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Mastrototaro, M.; Rossi, A.; Pisani, F.; Tortorella, C.; Ruggieri, M.; Lia, A.; Trojano, M.; Frigeri, A.; Svelto, M. Aquaporin-4 orthogonal arrays of particles are the target for neuromyelitis optica autoantibodies. Glia 2009, 57, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Rossi, A.; Mola, M.G.; Procino, G.; Frigeri, A.; Svelto, M. Actin cytoskeleton remodeling governs aquaporin-4 localization in astrocytes. Glia 2008, 56, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunde, L.K.; Camassa, L.M.; Hoddevik, E.H.; Khan, F.H.; Ottersen, O.P.; Boldt, H.B.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M. Postnatal development of the molecular complex underlying astrocyte polarization. Brain Struct Funct. 2015, 220, 2087–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoddevik, E.H.; Khan, F.H.; Rahmani, S.; Ottersen, O.P.; Boldt, H.B.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M. Factors determining the density of AQP4 water channel molecules at the brain-blood interface. Brain Struct Funct. 2017, 222, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palazzo, C.; Abbrescia, P.; Valente, O.; Nicchia, G.P.; Banitalebi, S.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Trojano, M.; Frigeri, A. Tissue Distribution of the Readthrough Isoform of AQP4 Reveals a Dual Role of AQP4ex Limited to CNS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041531
Palazzo C, Abbrescia P, Valente O, Nicchia GP, Banitalebi S, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Trojano M, Frigeri A. Tissue Distribution of the Readthrough Isoform of AQP4 Reveals a Dual Role of AQP4ex Limited to CNS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(4):1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041531
Chicago/Turabian StylePalazzo, Claudia, Pasqua Abbrescia, Onofrio Valente, Grazia Paola Nicchia, Shervin Banitalebi, Mahmood Amiry-Moghaddam, Maria Trojano, and Antonio Frigeri. 2020. "Tissue Distribution of the Readthrough Isoform of AQP4 Reveals a Dual Role of AQP4ex Limited to CNS" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 4: 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041531
APA StylePalazzo, C., Abbrescia, P., Valente, O., Nicchia, G. P., Banitalebi, S., Amiry-Moghaddam, M., Trojano, M., & Frigeri, A. (2020). Tissue Distribution of the Readthrough Isoform of AQP4 Reveals a Dual Role of AQP4ex Limited to CNS. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(4), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041531





