Molecular Interactions of Carbapenem Antibiotics with the Multidrug Efflux Transporter AcrB of Escherichia coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Substrates and Inhibitors Co-Crystallized with AcrB
2.2. Carbapenems
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Docking
4.2. MD Simulations and Binding Free-Energy Calculations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP | Access Pocket |
| DP | Distal Pocket |
| EG | Exit Gate |
| HP-Trap | Hydrophobic Trap |
| MD | Molecular Dynamics |
| MDR | Multi Drug Resistance |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MW | Molecular Weight |
| RMSD | Root Mean Square Displacement |
| RND | Resistance Nodulation and cell Division |
| TM | Transmembrane |
References
- Paterson, D.L. Impact of antibiotic resistance in gram-negative bacilli on empirical and definitive antibiotic therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, S14–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H. Multidrug resistance in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 119–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrad, B.; Clark, N.M.; Zhanel, G.G.; Lynch, J.P., 3rd. Antimicrobial resistance in hospital-acquired gram-negative bacterial infections. Chest 2015, 147, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piddock, L.J. Clinically relevant chromosomally encoded multidrug resistance efflux pumps in bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 382–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anes, J.; McCusker, M.P.; Fanning, S.; Martins, M. The ins and outs of RND efflux pumps in Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Plesiat, P.; Nikaido, H. The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 337–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, B.D.; Kaatz, G.W. Multidrug efflux pumps of Gram-positive bacteria. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Wang-Kan, X.; Neuberger, A.; van Veen, H.W.; Pos, K.M.; Piddock, L.J.V.; Luisi, B.F. Multidrug efflux pumps: Structure, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, K. Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, H.A.; Kulah, C.; Ciftci, I.H. The effects of active efflux pumps on antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okusu, H.; Ma, D.; Nikaido, H. AcrAB efflux pump plays a major role in the antibiotic resistance phenotype of Escherichia coli multiple-antibiotic-resistance (Mar) mutants. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmar, J.A.; Su, C.C.; Yu, E.W. Bacterial multidrug efflux transporters. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2014, 43, 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, M.A.; Schiefner, A.; Eicher, T.; Verrey, F.; Diederichs, K.; Pos, K.M. Structural asymmetry of AcrB trimer suggests a peristaltic pump mechanism. Science 2006, 313, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Nakashima, R.; Yamashita, E.; Matsumoto, T.; Yamaguchi, A. Crystal structures of a multidrug transporter reveal a functionally rotating mechanism. Nature 2006, 443, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennhauser, G.; Amstutz, P.; Briand, C.; Storchenegger, O.; Grutter, M.G. Drug export pathway of multidrug exporter AcrB revealed by DARPin inhibitors. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, R.; Sakurai, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Nishino, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Structures of the multidrug exporter AcrB reveal a proximal multisite drug-binding pocket. Nature 2011, 480, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggerone, P.; Murakami, S.; Pos, K.M.; Vargiu, A.V. RND efflux pumps: Structural information translated into function and inhibition mechanisms. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 3079–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang, Z.; James, N.R.; Voss, J.E.; Klimont, E.; Ohene-Agyei, T.; Venter, H.; Chiu, W.; Luisi, B.F. Structure of the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump. Nature 2014, 509, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Nakashima, R.; Sakurai, K. Structural basis of RND-type multidrug exporters. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicher, T.; Seeger, M.A.; Anselmi, C.; Zhou, W.; Brandstatter, L.; Verrey, F.; Diederichs, K.; Faraldo-Gomez, J.D.; Pos, K.M. Coupling of remote alternating-access transport mechanisms for protons and substrates in the multidrug efflux pump AcrB. Elife 2014, 3, e03145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Nakashima, R.; Yamashita, E.; Yamaguchi, A. Crystal structure of bacterial multidrug efflux transporter AcrB. Nature 2002, 419, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.W.; McDermott, G.; Zgurskaya, H.I.; Nikaido, H.; Koshland, D.E., Jr. Structural basis of multiple drug-binding capacity of the AcrB multidrug efflux pump. Science 2003, 300, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pos, K.M.; Schiefner, A.; Seeger, M.A.; Diederichs, K. Crystallographic analysis of AcrB. FEBS Lett. 2004, 564, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.W.; Aires, J.R.; McDermott, G.; Nikaido, H. A periplasmic drug-binding site of the AcrB multidrug efflux pump: A crystallographic and site-directed mutagenesis study. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 6804–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, M.A.; von Ballmoos, C.; Eicher, T.; Brandstatter, L.; Verrey, F.; Diederichs, K.; Pos, K.M. Engineered disulfide bonds support the functional rotation mechanism of multidrug efflux pump AcrB. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswald, C.; Tam, H.K.; Pos, K.M. Transport of lipophilic carboxylates is mediated by transmembrane helix 2 in multidrug transporter AcrB. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.; Vargiu, A.V.; Collu, F.; Kleinekathofer, U.; Ruggerone, P. Functional rotation of the transporter AcrB: Insights into drug extrusion from simulations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1000806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, H.; Oshima, H.; Yasuda, S.; Kinoshita, M. Statistical thermodynamics for functionally rotating mechanism of the multidrug efflux transporter AcrB. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 3423–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, Y.; Yamane, T.; Terada, T.; Moritsugu, K.; Fujisaki, H.; Murakami, S.; Ikeguchi, M.; Kidera, A. Energetics and conformational pathways of functional rotation in the multidrug transporter AcrB. Elife 2018, 7, e31715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargiu, A.V.; Ramaswamy, V.K.; Malvacio, I.; Malloci, G.; Kleinekathofer, U.; Ruggerone, P. Water-mediated interactions enable smooth substrate transport in a bacterial efflux pump. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, T.; Murakami, S.; Ikeguchi, M. Functional rotation induced by alternating protonation states in the multidrug transporter AcrB: All-atom molecular dynamics simulations. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 7648–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eicher, T.; Cha, H.-j.; Seeger, M.A.; Brandstätter, L.; El-Delik, J.; Bohnert, J.A.; Kern, W.V.; Verrey, F.; Grütter, M.G.; Diederichs, K.; et al. Transport of drugs by the multidrug transporter AcrB involves an access and a deep binding pocket that are separated by a switch-loop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5687–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Nakao, K.; Nishino, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Nakashima, R. Crystal structures of multidrug efflux pump MexB bound with high-molecular-mass compounds. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, R.; Sakurai, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Hayashi, K.; Nagata, C.; Hoshino, K.; Onodera, Y.; Nishino, K.; Yamaguchi, A. Structural basis for the inhibition of bacterial multidrug exporters. Nature 2013, 500, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargiu, A.V.; Ruggerone, P.; Opperman, T.J.; Nguyen, S.T.; Nikaido, H. Molecular mechanism of MBX2319 inhibition of Escherichia coli AcrB multidrug efflux pump and comparison with other inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6224–6234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjuts, H.; Vargiu, A.V.; Kwasny, S.M.; Nguyen, S.T.; Kim, H.S.; Ding, X.; Ornik, A.R.; Ruggerone, P.; Bowlin, T.L.; Nikaido, H.; et al. Molecular basis for inhibition of AcrB multidrug efflux pump by novel and powerful pyranopyridine derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3509–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargiu, A.V.; Nikaido, H. Multidrug binding properties of the AcrB efflux pump characterized by molecular dynamics simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20637–20642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinana, A.D.; Vargiu, A.V.; Nikaido, H. Effect of site-directed mutations in multidrug efflux pump AcrB examined by quantitative efflux assays. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 480, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, G.; Hryc, C.F.; Blaza, J.N.; Serysheva, I.I.; Schmid, M.F.; Chiu, W.; Luisi, B.F.; Du, D. An allosteric transport mechanism for the AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux pump. Elife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababou, A. New insights into the structural and functional involvement of the gate loop in AcrB export activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1866, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, N.; Kandt, C. Porter domain opening and closing motions in the multi-drug efflux transporter AcrB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1828, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, V.K.; Vargiu, A.V.; Malloci, G.; Dreier, J.; Ruggerone, P. Molecular Rationale behind the Differential Substrate Specificity of Bacterial RND Multi-Drug Transporters. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wen, P.C.; Moradi, M.; Tajkhorshid, E. Computational characterization of structural dynamics underlying function in active membrane transporters. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 31, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatsuka, Y.; Chen, C.; Nikaido, H. Mechanism of recognition of compounds of diverse structures by the multidrug efflux pump AcrB of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6559–6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobylka, J.; Kuth, M.S.; Muller, R.T.; Geertsma, E.R.; Pos, K.M. AcrB: A mean, keen, drug efflux machine. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2020, 1459, 38–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.Q.; Kimura, N.; Murakami, S.; Takada, S. Drug uptake pathways of multidrug transporter AcrB studied by molecular simulations and site-directed mutagenesis experiments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7474–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Miyashita, N.; Sugita, Y.; Kovalenko, A.; Hirata, F.; Kidera, A. Functionality mapping on internal surfaces of multidrug transporter AcrB based on molecular theory of solvation: Implications for drug efflux pathway. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 8288–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolau, D.P. Carbapenems: A potent class of antibiotics. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2008, 9, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp-Wallace, K.M.; Endimiani, A.; Taracila, M.A.; Bonomo, R.A. Carbapenems: Past, present, and future. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4943–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Gotoh, N.; Nishino, T. Alterations of susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by overproduction of multidrug efflux systems, MexAB-OprM, MexCD-OprJ, and MexXY/OprM to carbapenems: Substrate specificities of the efflux systems. J. Infect. Chemother. 2002, 8, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Ma, D.; Livermore, D.M.; Nikaido, H. Role of efflux pump(s) in intrinsic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Active efflux as a contributing factor to beta-lactam resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1994, 38, 1742–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, T.; Michea-Hamzehpour, M.; Epp, S.F.; Pechere, J.C. Carbapenem activities against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Respective contributions of OprD and efflux systems. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, J.M.; Piddock, L.J. How to Measure Export via Bacterial Multidrug Resistance Efflux Pumps. mBio 2016, 7, e00840–00816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, G.; Wolloscheck, D.; Weeks, J.W.; Croft, C.; Rybenkov, V.V.; Zgurskaya, H.I. Breaking the Permeability Barrier of Escherichia coli by Controlled Hyperporination of the Outer Membrane. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7372–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzori, A.; Malviya, V.N.; Malloci, G.; Dreier, J.; Pos, K.M.; Vargiu, A.V.; Ruggerone, P. Identification and characterization of carbapenem binding sites within the RND-transporter AcrB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, R.; Erwin, A.L. Direct measurement of efflux in Pseudomonas aeruginosa using an environment-sensitive fluorescent dye. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinquin, B.; Maigre, L.; Pinet, E.; Chevalier, J.; Stavenger, R.A.; Mills, S.; Réfrégiers, M.; Pagès, J.-M. Microspectrometric insights on the uptake of antibiotics at the single bacterial cell level. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, K.; Nikaido, H. Kinetic behavior of the major multidrug efflux pump AcrB of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5854–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, A.; Malloci, G.; Prajapati, J.D.; Basciu, A.; Bosin, A.; Kleinekathofer, U.; Dreier, J.; Vargiu, A.V.; Ruggerone, P. Molecular Interactions of Cephalosporins with the Deep Binding Pocket of the RND Transporter AcrB. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 4625–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvacio, I.; Buonfiglio, R.; D’Atanasio, N.; Serra, G.; Bosin, A.; Di Giorgio, F.P.; Ruggerone, P.; Ombrato, R.; Vargiu, A.V. Molecular basis for the different interactions of congeneric substrates with the polyspecific transporter AcrB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collu, F.; Vargiu, A.V.; Dreier, J.; Cascella, M.; Ruggerone, P. Recognition of imipenem and meropenem by the RND-transporter MexB studied by computer simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19146–19158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husain, F.; Nikaido, H. Substrate path in the AcrB multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.P.; Nikaido, H. Kinetic parameters of efflux of penicillins by the multidrug efflux transporter AcrAB-TolC of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinana, A.D.; Vargiu, A.V.; May, T.; Nikaido, H. Aminoacyl beta-naphthylamides as substrates and modulators of AcrB multidrug efflux pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Anjum, M.; Andersson, D.I.; Sandegren, L. Combinations of mutations in envZ, ftsI, mrdA, acrB and acrR can cause high-level carbapenem resistance in Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, J.A.; Schuster, S.; Seeger, M.A.; Fahnrich, E.; Pos, K.M.; Kern, W.V. Site-directed mutagenesis reveals putative substrate binding residues in the Escherichia coli RND efflux pump AcrB. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 8225–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, J.A.; Schuster, S.; Szymaniak-Vits, M.; Kern, W.V. Determination of real-time efflux phenotypes in Escherichia coli AcrB binding pocket phenylalanine mutants using a 1,2′-dinaphthylamine efflux assay. PLoS One 2011, 6, e21196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, K.; Yamada, J.; Hirakawa, H.; Hirata, T.; Yamaguchi, A. Roles of TolC-dependent multidrug transporters of Escherichia coli in resistance to beta-lactams. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3030–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, H.T.; Webber, M.A.; Mushtaq, S.; Woodford, N.; Piddock, L.J. Inactivation or inhibition of AcrAB-TolC increases resistance of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae to carbapenems. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.J.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Wolloscheck, D.; Walker, J.K.; Rybenkov, V.V.; Parks, J.M.; Zgurskaya, H.I. Molecular Properties That Define the Activities of Antibiotics in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, V.K.; Vargiu, A.V.; Malloci, G.; Dreier, J.; Ruggerone, P. Molecular Determinants of the Promiscuity of MexB and MexY Multidrug Transporters of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshidi, S.; Sutton, J.M.; Rahman, K.M. Computational Study Reveals the Molecular Mechanism of the Interaction between the Efflux Inhibitor PAbetaN and the AdeB Transporter from Acinetobacter baumannii. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3002–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargiu, A.V.; Ramaswamy, V.K.; Malloci, G.; Malvacio, I.; Atzori, A.; Ruggerone, P. Computer simulations of the activity of RND efflux pumps. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, E.E.; Legood, S.W.; Alav, I.; Dulyayangkul, P.; Overton, T.W.; Blair, J.M.A. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Efflux by Dye Accumulation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, J.A.; Karamian, B.; Nikaido, H. Optimized Nile Red efflux assay of AcrAB-TolC multidrug efflux system shows competition between substrates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 3770–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergalli, J.; Dumont, E.; Cinquin, B.; Maigre, L.; Pajovic, J.; Bacque, E.; Mourez, M.; Refregiers, M.; Pages, J.M. Fluoroquinolone structure and translocation flux across bacterial membrane. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloci, G.; Vargiu, A.V.; Serra, G.; Bosin, A.; Ruggerone, P.; Ceccarelli, M. A Database of Force-Field Parameters, Dynamics, and Properties of Antimicrobial Compounds. Molecules 2015, 20, 13997–14021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory. Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMBER 18; Case, D.A., Ben-Shalom, I.Y., Brozell, S.R., Cerutti, D.S., Cheatham, T.E., III, Cruzeiro, V.W.D., Darden, T.A., Duke, R.E., Ghoreishi, D., Gilson, M.K., et al., Eds.; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Feenstra, K.A.; Hess, B.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Improving efficiency of large time-scale molecular dynamics simulations of hydrogen-rich systems. J. Comput. Chem. 1999, 20, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollman, P.A.; Massova, I.; Reyes, C.; Kuhn, B.; Huo, S.; Chong, L.; Lee, M.; Lee, T.; Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Calculating structures and free energies of complex molecules: Combining molecular mechanics and continuum models. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrkov, T.V.; Chugunov, A.O.; Krylov, N.A.; Nolde, D.E.; Efremov, R.G. PLATINUM: A web tool for analysis of hydrophobic/hydrophilic organization of biomolecular complexes. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.S.; Bradley, A.R.; Valasatava, Y.; Duarte, J.M.; Prlic, A.; Rose, P.W. NGL viewer: Web-based molecular graphics for large complexes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3755–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
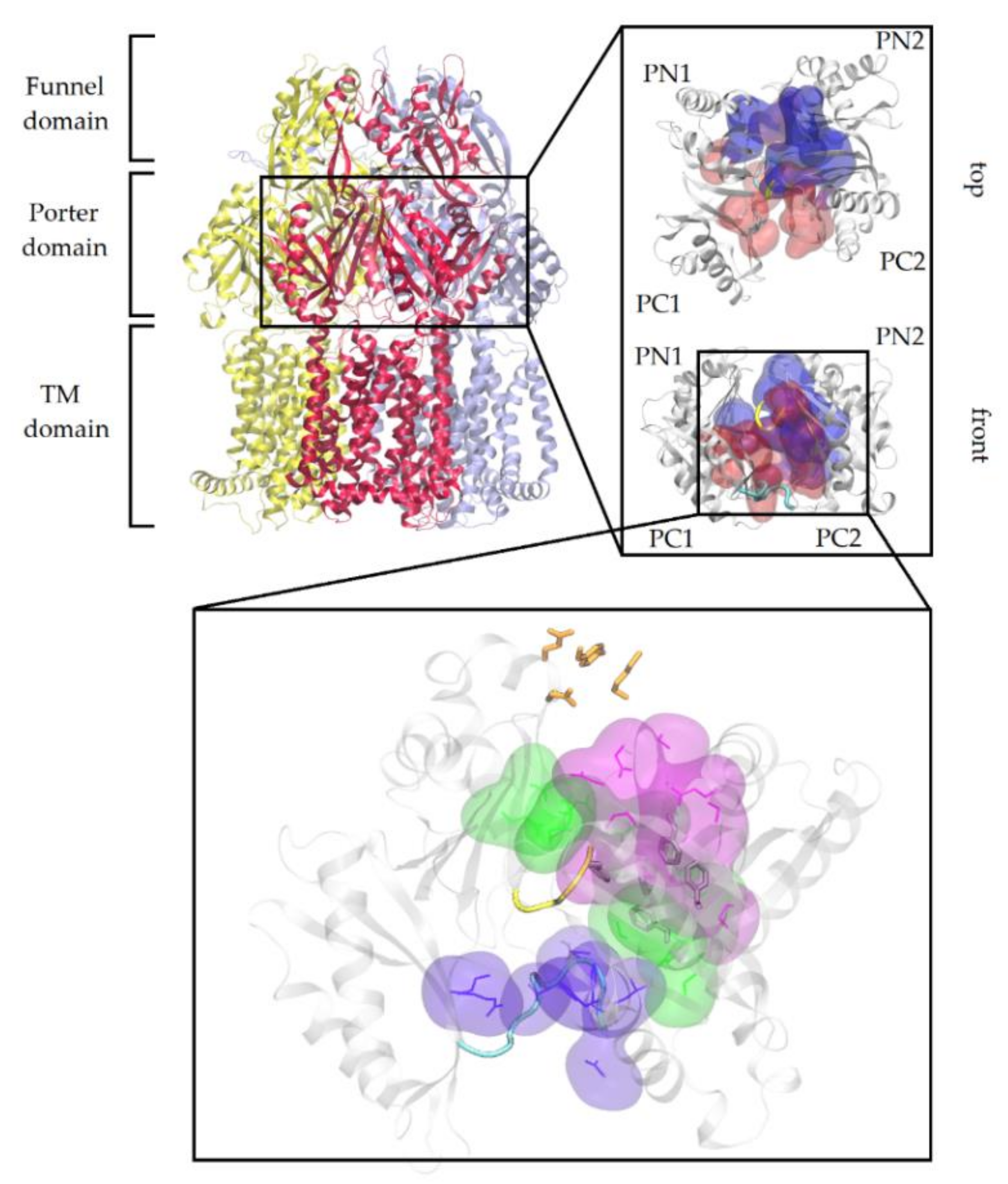
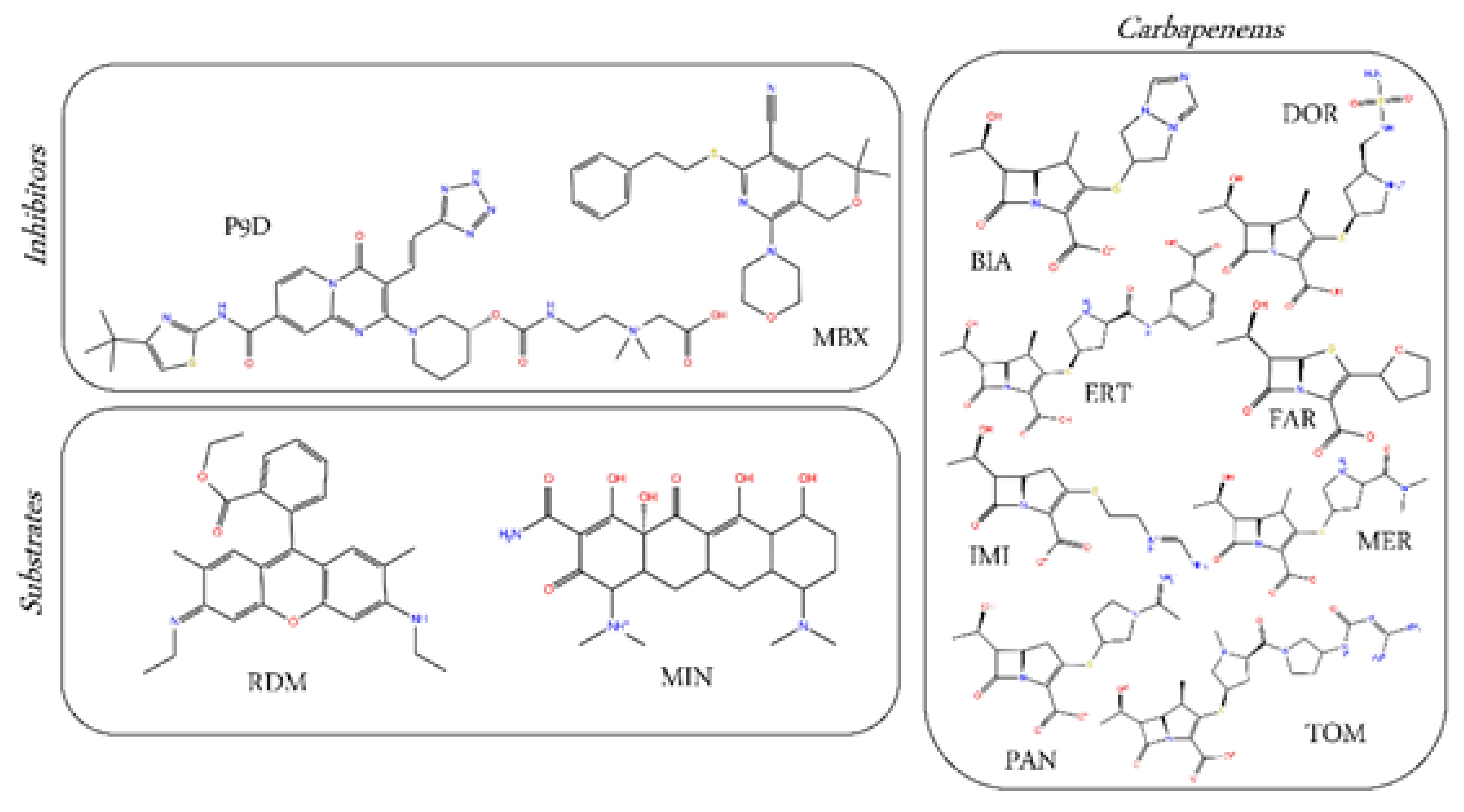

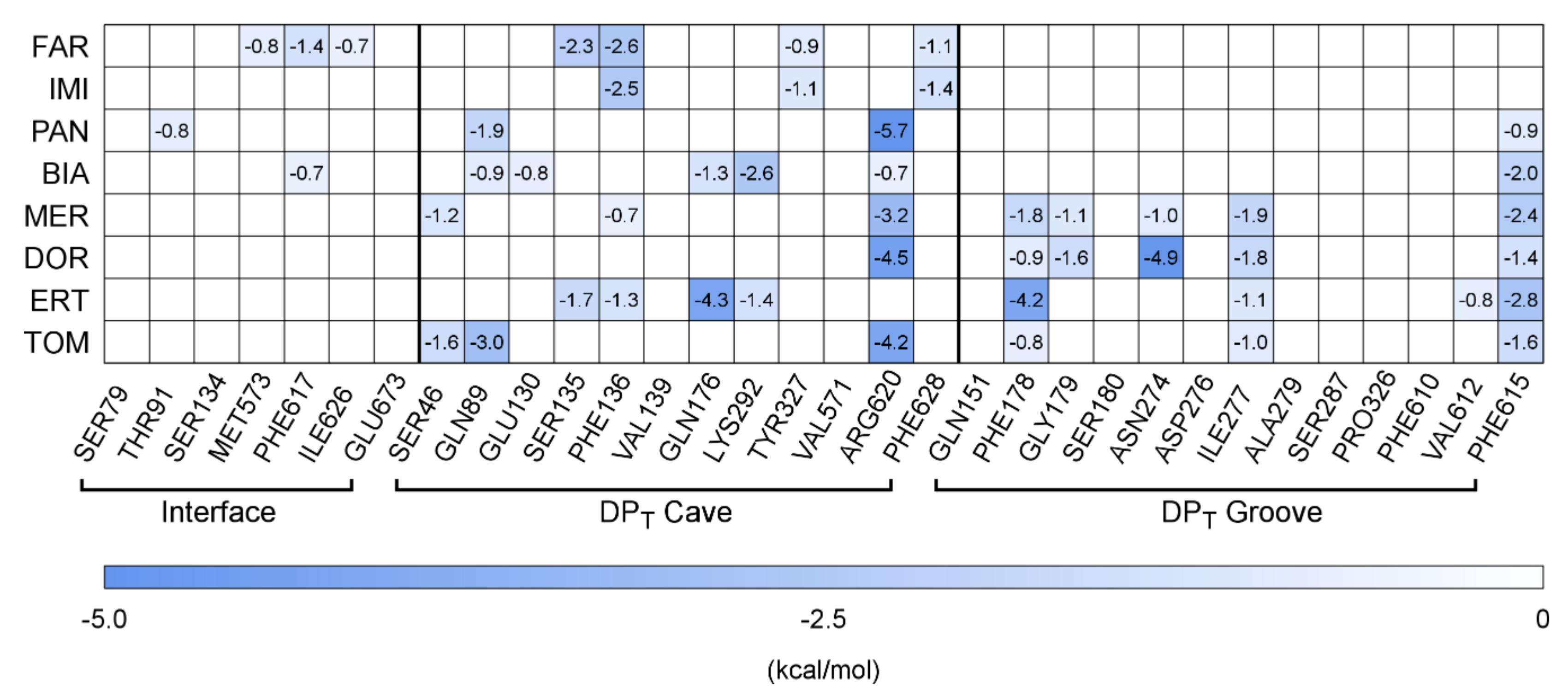
| Co-Crystallized AcrB Compound | ID | MW (Da) | SML | SMH | Hyd (%) | ΔGb (kcal/mol) | Contribution to ΔGb (%) Interface Cave Groove | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhodamine-6G | RDM | 444 | 0.80 | 0.01 | 35 ± 8 | −38.3 ± 3.3 | 2 | 5 | 29 |
| Minocycline | MIN | 458 | 0.80 | 0.70 | 34 ± 8 | −29.3 ± 4.8 | 1 | 5 | 53 |
| MBX3132 | MBX | 495 | 0.87 | 0.63 | 30 ± 8 | −53.6 ± 4.6 | 2 | 18 | 24 |
| D13-9001 | P9D | 693 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 40 ± 7 | −52.3 ± 4.9 | 2 | 22 | 25 |
| Carbapenem Antibiotic | ID | MW (Da) | SML | SMH | Hyd (%) | ΔGb (kcal/mol) | Contribution to ΔGb (%) Interface Cave Groove | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faropenem | FAR | 284 | 0.45 | 0.81 | 27 ± 9 | −25.5 ± 3.5 | 12 | 31 | 5 |
| Imipenem | IMI | 299 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 37 ± 13 | −25.1 ± 4.7 | 6 | 24 | 4 |
| Panipenem | PAN | 339 | 0.01 | 0.80 | 50 ± 11 | −27.6 ± 5.0 | 4 | 23 | 5 |
| Biapenem | BIA | 350 | 0.04 | 0.60 | 45 ± 13 | −30.5 ± 5.5 | 5 | 20 | 7 |
| Meropenem | MER | 383 | 0.29 | 0.73 | 35 ± 8 | −30.8 ± 4.3 | 1 | 15 | 29 |
| Doripenem | DOR | 420 | 0.35 | 0.84 | 47 ± 10 | −33.6 ± 5.5 | 0 | 14 | 33 |
| Ertapenem | ERT | 475 | 0.30 | 0.51 | 42 ± 9 | −33.8 ± 7.8 | 3 | 28 | 31 |
| Tomopenem | TOM | 539 | 0.01 | 0.54 | 50 ± 9 | −32.6 ± 6.7 | 0 | 15 | 12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atzori, A.; Malloci, G.; Cardamone, F.; Bosin, A.; Vargiu, A.V.; Ruggerone, P. Molecular Interactions of Carbapenem Antibiotics with the Multidrug Efflux Transporter AcrB of Escherichia coli. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030860
Atzori A, Malloci G, Cardamone F, Bosin A, Vargiu AV, Ruggerone P. Molecular Interactions of Carbapenem Antibiotics with the Multidrug Efflux Transporter AcrB of Escherichia coli. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030860
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtzori, Alessio, Giuliano Malloci, Francesca Cardamone, Andrea Bosin, Attilio Vittorio Vargiu, and Paolo Ruggerone. 2020. "Molecular Interactions of Carbapenem Antibiotics with the Multidrug Efflux Transporter AcrB of Escherichia coli" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030860
APA StyleAtzori, A., Malloci, G., Cardamone, F., Bosin, A., Vargiu, A. V., & Ruggerone, P. (2020). Molecular Interactions of Carbapenem Antibiotics with the Multidrug Efflux Transporter AcrB of Escherichia coli. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030860







